Submitted:
01 May 2024
Posted:
02 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- S(t) = the survival function.
- -
- T = the most likely time at which symptoms develop in each genotype.
- -
- P(t) = the conditional probability function that describes the instantaneous risk for the symptom to develop at time t, from day 10 DAI to day 60 DAI.
3. Results
3.1. Incidence of Rust under Field Conditions
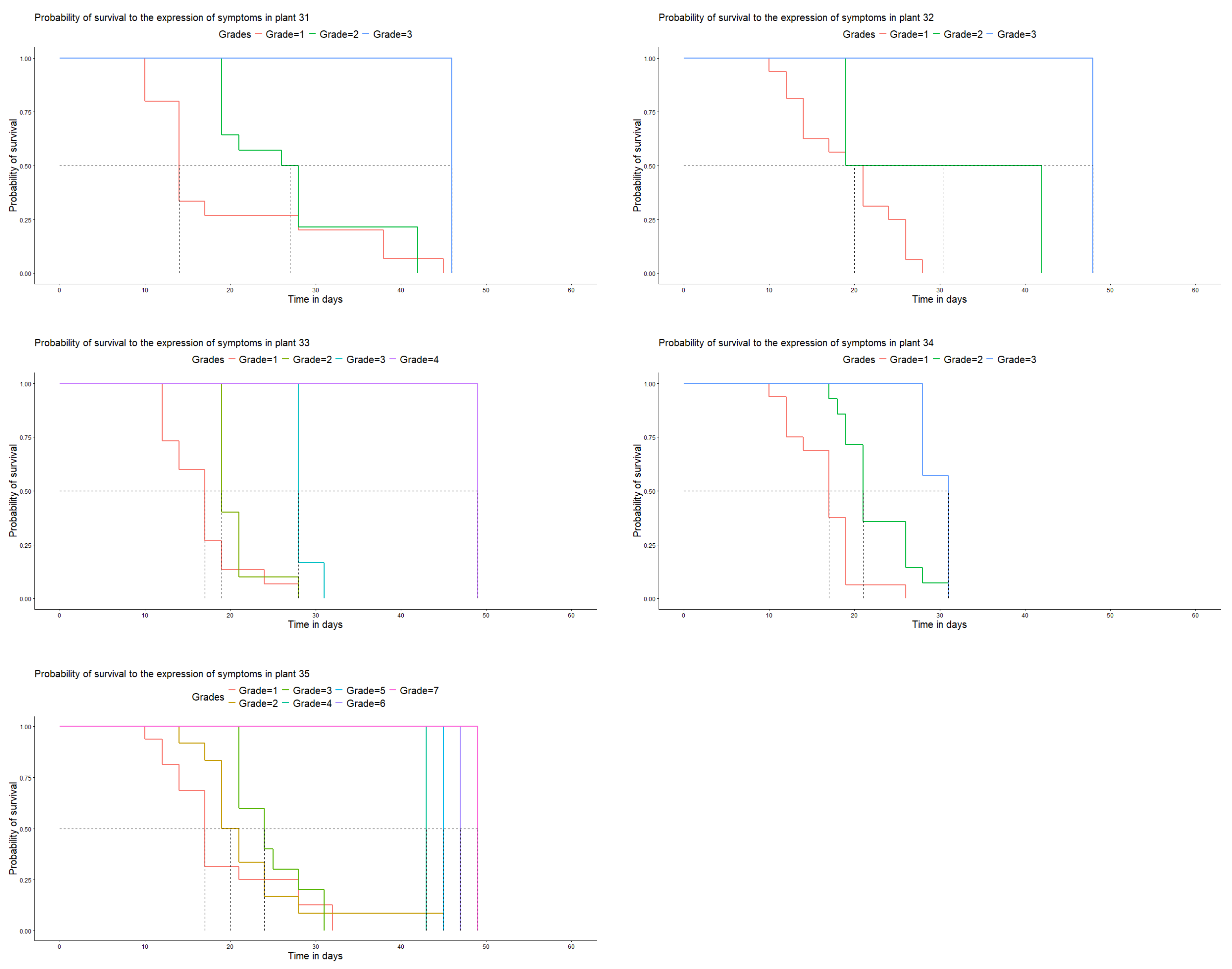
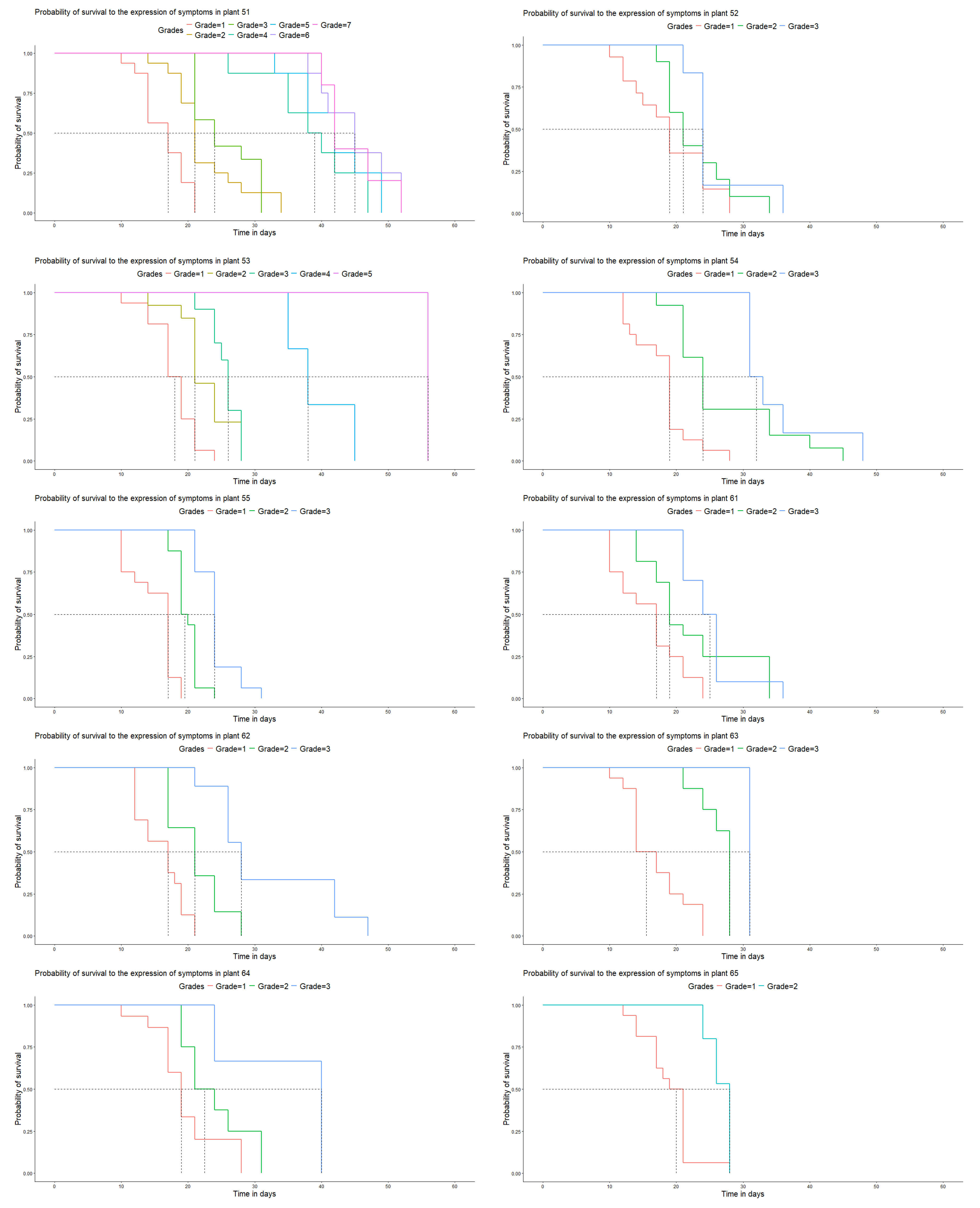
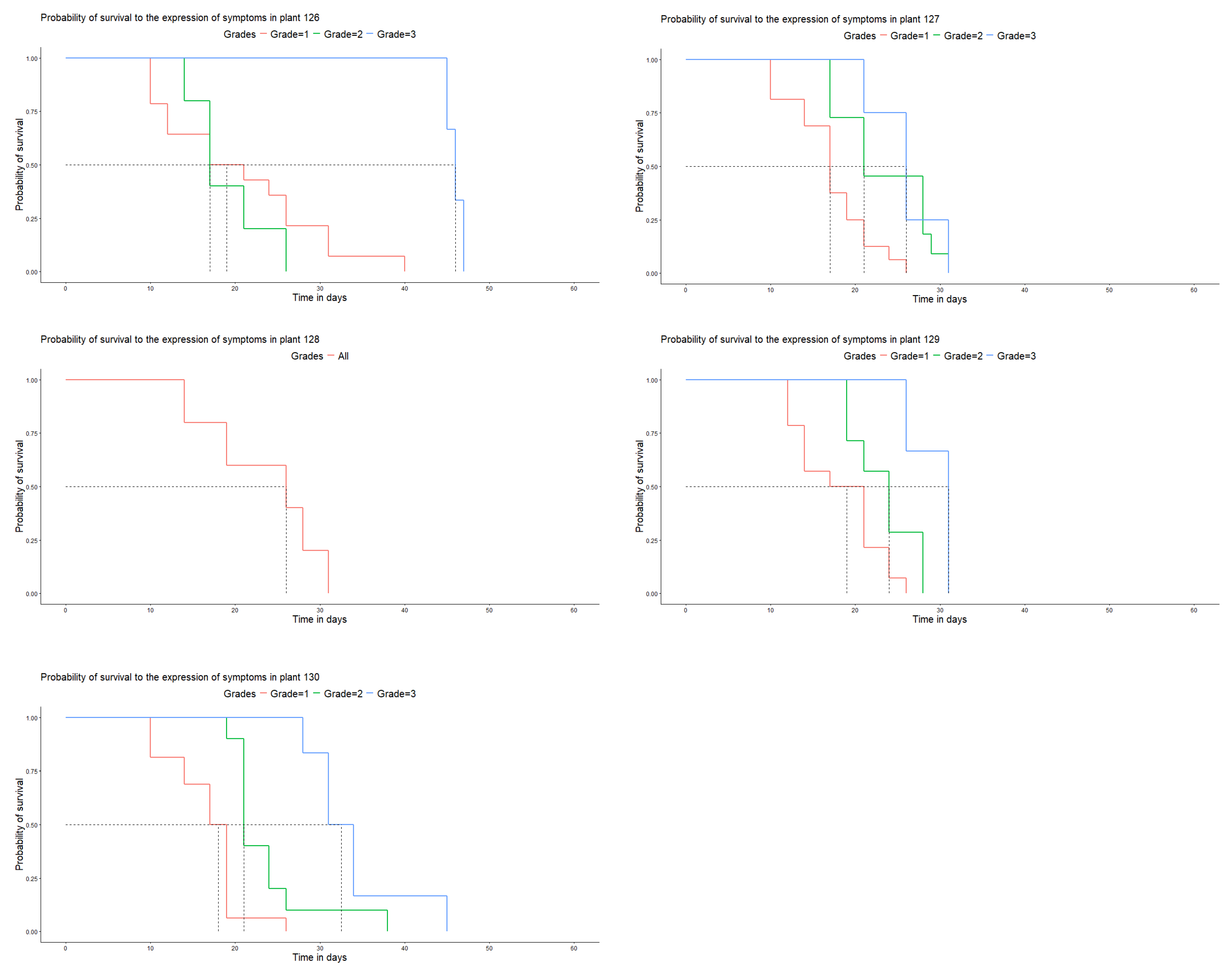
3.2. Probable Times of Symptom Onset under Controlled Conditions
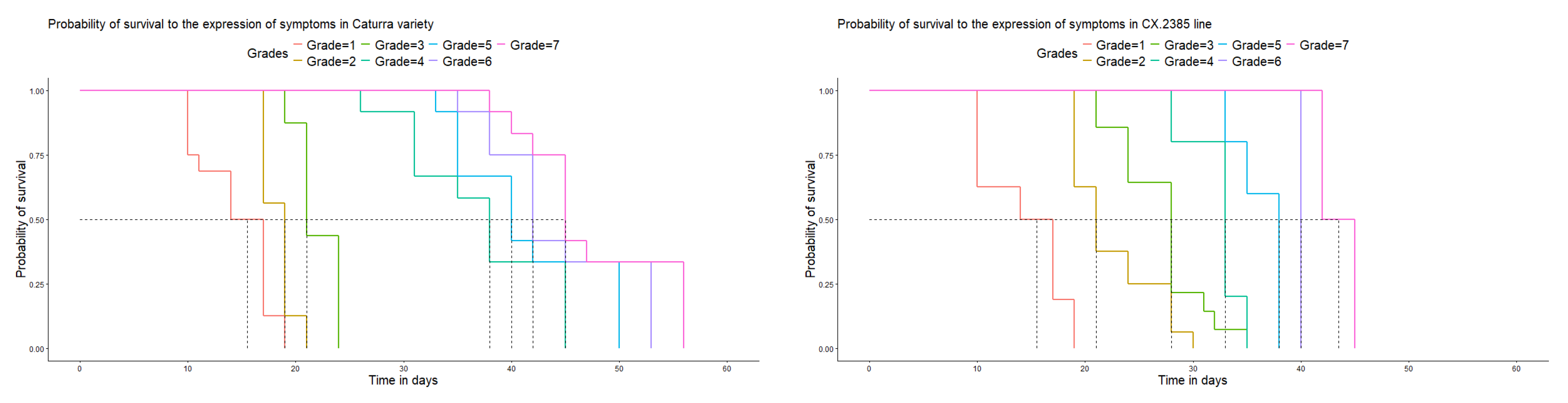
3.3. Probability of Survival to the Expression of Symptoms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noronha Wagner, M., & Bettencourt, A. J. (1967). Genetic study of the resistance of Coffea spp. to leaf rust - Identification and behavior of four factors conditioning disease reaction in Coffea arabica to twelve physiologic races of Hemileia vastatrix. Canadian Journal of Botany, 45(11), 2021-2031. [CrossRef]
- Flor, H. H. (1942). Inheritance of pathogenicity in Melampsora lini. Phytopathology, 32(8), 653-669.
- do Céu Silva, M., Rijo, L., Rodrigues Jr, C. J., & Vasconselos, M. I. (1992). Histological study of the heterozigosity effect of coffee resistance genes SH1 and SH4, SH5 towards Hemileia vastatrix. Broteria Genética, XIII(LXXX), 169-184.
- Eskes, A. B., & Carvalho, A. (1983). Variation for incomplete resistance to Hemileia vastatrix in Coffea arabica. Euphytica, 32, 625–637. [CrossRef]
- Leguizamón Caicedo, J. (1985). Contribution a la connaissnace de la resistance incomplete du cafier arabica (Coffea arabica L.) a la rouille orangee (Hemileia vastatrix Berk. et Br.). Montpellier: IRCC.
- Castillo Zapata, J., & Leguizamón Caicedo, J. (1992). Viruelencia de Hemileia vastatrix determinada por medio de plantas diferenciales de café en Colombia. Cenicafé, 43(4), 114-124.
- Rios, J. A., & Debona, D. (2018). Efeito epidemiológico da resistência de hospedeiro. En J. L. Dallagnol, Resistência genética de plantas a patógenos (pág. 437). Pelotas, RS - Brasil: UFPel.
- Ficke, A., Cowger, C., Bergstrom, G., & Brodal, G. (2018). Understanding Yield Loss and Pathogen Biology to Improve Disease Management: Septoria Nodorum Blotch - A Case Study in Wheat. Plant Diseases, 102(4), 696-707. [CrossRef]
- Toniutti, L., Breitler, J. C., Etienne, H., Campa, C., Doulbeau, S., Urban, et al., (2017). Influence of Environmental Conditions and Genetic Background of Arabica Coffee (C. arabica L) on Leaf Rust (Hemileia vastatrix) Pathogenesis. Frontiers in Plant Science, 8, 2025. [CrossRef]
- Pérez, C. P., Pozza, E. A., Pozza, A. A., de Freitas, A. S., Silva, M. G., & Gomes Guimarães, D. d. (2019). Impact of nitrogen and potassium on coffee rust. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 155, 219–229. [CrossRef]
- Ghufron Rosyady, M., Anom Wijaya, K., Wulanjari, D., & Wafa, A. (2020). Role of Mineral Elements to Induce the Resistance of Arabica Coffee Against Rust Disease at Lowland Area. E3S Web of Conferences, 142(03003), 03. [CrossRef]
- Eskes, A. B., & Toma-Braghini, M. (1982). The effect of leaf age on incomplete resistance of coffee to Hemileia vastatrix. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology, 88, 219–230. [CrossRef]
- Marla, S. R., Chu, K., Chintamanani, S., Multani, D. S., Klempien, A., De Leon., et al., (2018). Adult plant resistance in maize to northern leaf spot is a feature of partial loss-of-function alleles of Hm1. PLoS Pathogens, 14(10), e1007356. [CrossRef]
- Ning, Y., Liu, W., & Wang, G. L. (2017). Balancing Immunity and Yield in Crop Plants. Trends in Plant Science, 22(12), 1069-1079. [CrossRef]
- Li, W., Chern, M., Yin, J., Wang, J., & Chen, X. (2019). Recent advances in broad-spectrum resistance to the rice blast disease. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 50, 114-120. [CrossRef]
- Countinho, T. A., Rijkenberg, F. J., & van Asch, M. (1994). The effect of leaf age on infection of Coffea genotypes by Hemileia vastatrix. Plant Pathology, 43(1), 97-103. [CrossRef]
- Alvarado Alvarado, G. (2011). El café y la roya: Estrategias de resistencia incompleta. Chinchiná: FNC - Cenicafé.
- DaMatta, F. M. (2004). Ecophysiological constraints on the production of shaded and unshaded coffee: a review. Field Crops Research, 86(2-3), 99-114. [CrossRef]
- Romero Guerrero, G., Herrera Pinilla, J. C., Ligarreto Moreno, G. A., & Alvarado Alvarado, G. (2008). Análisis genético de la resistencia incompleta a Hemileia vastatrix en progenies de Caturra x Híbrido de Timor. Cenicafé, 59(2), 103-119.
- Liebig, T., Ribeyre, F., Läderach, P., Poehling, H.-M., Asten, P. v., & Avelino, J. (2019). Interactive effects of altitude, microclimate and shading system on coffee leaf rust. Journal of Plant Interactions, 14(1), 407-415. [CrossRef]
- Belachew, K., Senbeta, G. A., Garedew, W., Barreto, R. W., & Del Ponte, E. M. (2020). Altitude is the main driver of coffee leaf rust epidemics: a large-scale survey in Ethiopia. Tropical Plant Pathology, 45, 511–521. [CrossRef]
- Merle, I., Pico, J., Granados, E., Boudrot, A., Tixier, P., Virginio Filho., et al., (2020). Unraveling the Complexity of Coffee Leaf Rust Behavior and Development in Different Coffea arabica Agroecosystems. Phytopathology, 110, 418-427. [CrossRef]
- Vasco, G. B., Pozza, E. A., Silva, M. G., Pozza, A. A., & Chaves, E. (2018). Interaction of K and B in the intensity of coffee rust in nutrient solution. Coffee Science, 13(2), 238-244. [CrossRef]
- Eskes, A. B., & Da Costa, W. M. (1983). Characterization of incomplete resistance to Hemileia vastatrix in the icatu coffee population. Euphytica, 32, 649–657. [CrossRef]
- Romero Guerrero, G., Alvarado Alvarado, G., Cortina Guerrero, H., Ligarreto Moreno, G., Galeano, N. F., & Herrera Pinilla, J. C. (2010). Partial resistance to leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix) in coffee (Coffea arabica L.): genetic analysis and molecular characterization of putative candidate genes. Molecular Breeding, 25, 685–697. [CrossRef]
- Castillo Zapata, J., Moreno Ruíz, G., & López Duque, S. (1976). Uso de resistencia genética a Hemileia vastatrix Berk. y Br. existente en germoplasma de café en Colombia. Cenicafé, 27(1), 3-25.
- Karki, H. S., & Halterman, D. A. (2021). Phytophthora infestans (Late blight) Infection Assay in a Detached Leaf of Potato. 11(4), e3926. [CrossRef]
- Parlevliet, J. E. (1979). Components of Resistance that Reduce the Rate of Epidemic Development. Annual Review of Phytopathology (17), 203-222. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira de Mendonça, R., Cintra de Jesus Junior, W., Gava Ferrão, M., Bucker Moraes, W., Magno Busato, L., Gava Ferrão, R., et al., (2019). Genótipos de café conilon e sua reação à ferrugem alaranjada. Summa Phytopathologica, 45(3), 279-284. [CrossRef]
- Scherm, H., & Ojiambo, P. S. (2004). Applications of Survival Analysis in Botanical Epidemiology. Phytopathology, 94(9), 1022-1026. [CrossRef]
- Amalraj, A., Taylor, J., & Sutton, T. (2019). A hydroponics based high throughput screening system for Phytophthora root rot resistance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Plant Methods, 15, 82. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, E. L., & Meier, P. (1958). Nonparametric Estimation from Incomplete Observation. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 53(282), 45-481. [CrossRef]
- Romano, A., & Stevanato, P. (2020). Germination Data Analysis by Time-to-Event Approaches. Plants, 9(5), 617. [CrossRef]
- Madden, L. V., & Nault, L. R. (1983). Differential Pathogenicity of Corn Stunting Mollicutes to Leafhopper Vectors in Dalbulus and Baldulus species. Phytopathology, 73, 1608-1614. [CrossRef]
- Westra G, A. A., Arneson, C. P., & Slack, S. A. (1994). Effect of Interaction of Inoculum Dose, Cultivar, and Geographic Location on the Development of Foliar Symptoms of Bacterial Ring of Potato. Ecology and Epidemiology, 84(4), 410-415.
- Jules, E. S., Kauffman, M. J., Ritts, W. D., & Carroll, A. L. (2002). Spread of an Invasive Pathogen over a Variable Landscape: A Nonnative Root Rot on Port Orford Cedar. Ecology, 83(11), 3167-3181. [CrossRef]
- Neher, D. A., Wilkinson, H. T., & Augspurger, C. K. (1992). Progression of damping-off epidemics in Glycine populations of even-age and mixed-age structure. Canadian Journal of Botany, 70(5), 1032-1038. [CrossRef]
- Stalpers, L. J., & Kaplan, E. L. (2018). Edward L. Kaplan and the Kaplan-Meier Survival Curve. Journal of the British Society for the History of Mathematics, 33(2), 109-135. [CrossRef]
- Eskes, A. B., & Toma Braghini, M. (1981). Assessment methods for resistance to coffee leaf rust (Hemileia vastatrix Berk. and Br.). FAO-Plant-Protection-Bulletin, 29(3/4), 56-66.
- do Céu Silva, M., Nicole, M., Guerra Guimaraes, L., & Rodrigues Jr., C. J. (2002). Hypersensitive cell death and post-haustorial defence responses arrest the orange rust (Hemileia vastatrix) growth in resistant coffee leaves. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology, 60(4), 169-183. [CrossRef]
- Andersen, E. J., Ali, S., Byamukama, E., Yen, Y., & Nepal, M. P. (2018). Disease Resistance Mechanisms in Plants. Genes, 9(1), 339. [CrossRef]
- Albert, M., Axtell, M. J., & Timko, M. P. (2021). Mechanisms of resistance and virulence in parasitic plant–host interactions. Plant Physiology, 185(4), 1282–1291. [CrossRef]
- do Céu Silva, M., Guerra-Guimarães, L., Diniz, I., Loureiro, A., Gil Azinheira, H., Carmo Pereira, A. P., et al., (2022). An Overview of the Mechanisms Involved in Coffee-Hemileia vastatrix Interactions: Plant and Pathogen Perspectives. Agronomy, 12(2), 326. [CrossRef]
- Simardeep, K., Kumar Samota, M., Choudhary, M., Choudhary, M., Pandey, A. K., Sharma, A., & Thakur, J. (2022). How do plants defend themselves against pathogens-Biochemical mechanisms and genetic interventions. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 28, 485–504. [CrossRef]
- Gill, U. S., Lee, S., & Mysore, K. S. (2015). Host Versus Nonhost Resistance: Distinct Wars with Similar Arsenals. Phytopathology, 105(5), 580-587. [CrossRef]
- Eskes, A. B. (1989). Resistance. En A. C. Kushalappa, & A. B. Eskes, Coffee Rust: Epidemiology, Resistance and Management (pág. 345). Boca Ratón, Florida: CRC Press. Inc.
- Zambolim, L., & Teixeira Caixeta, E. (2021). An Overview Of Physiological Specialization Of Coffee Leaf Rust – New Designation Of Pathotypes. International Journal of Current Research, 13(1), 15564 - 15575.
- Eskes, A. B. (1982). The effect of light intensity on incomplete resistance of coffee to Hemileia vastatrix. Netherlands Journal of Plant Pathology, 88, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Capucho, A. S., Caixeta, E. T., Zambolim, E. M., & Zambolim, L. (2009). Herança da resistência do Híbrido de Timor UFV 443-03 à ferrugem-do-cafeeiro. Pesquisa Agropecuária Brasileira, 44(3), 276-282. [CrossRef]
- Parvatha Reddy, P. (2013). Variety Mixtures/Cultivar Mixtures/Multilines. En P. Parvatha Reddy, Recent advances in crop protection (págs. 201-221). India: Springer. [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y., Pardey, P. G., & Silverstein, K. T. (2022). Scientific selection: A century of increasing crop varietal diversity in US wheat. PNAS, 119(51), e2210773119. [CrossRef]
- Goulart Castro, D., Mendes de Moura, A., Botega Alves, N., Moretti Tomé, L., Silva Botelho, F., Rosário Neto, A., & Correa de Souza, D. (2022). Multiline aiming at phenotypic stability and rice blast resistance. Bioscience Journal, 38, e38100. [CrossRef]
- Flórez Ramos, C. P., Arias Suárez, J. C., Maldonado L, C. E., Cortina G, H. A., Moncada B, M. d., Quiroga Cardona, J., ... Duque O, H. (2018). Variedades Castillo® Zonales resistencia a la roya con mayor productividad. AVT489. Manizales, Caldas, Colombia.

| Population | Rust incidence in field | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | Total Plants |
|
| 1.[(Caturra × CCC.32) × (Caturra × CCC.66)] × CX.2385 | 5 | 5 | |||||||||
| 2.CX.2385 × [(Caturra × CCC.32) × (Caturra × CCC.66)] | 1 | 9 | 10 | ||||||||
| 3.[Catuaí × (Caturra × CCC.66)] × CX.2385 | 1 | 4 | 5 | ||||||||
| Total Plants | 0 | 1 | 1 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
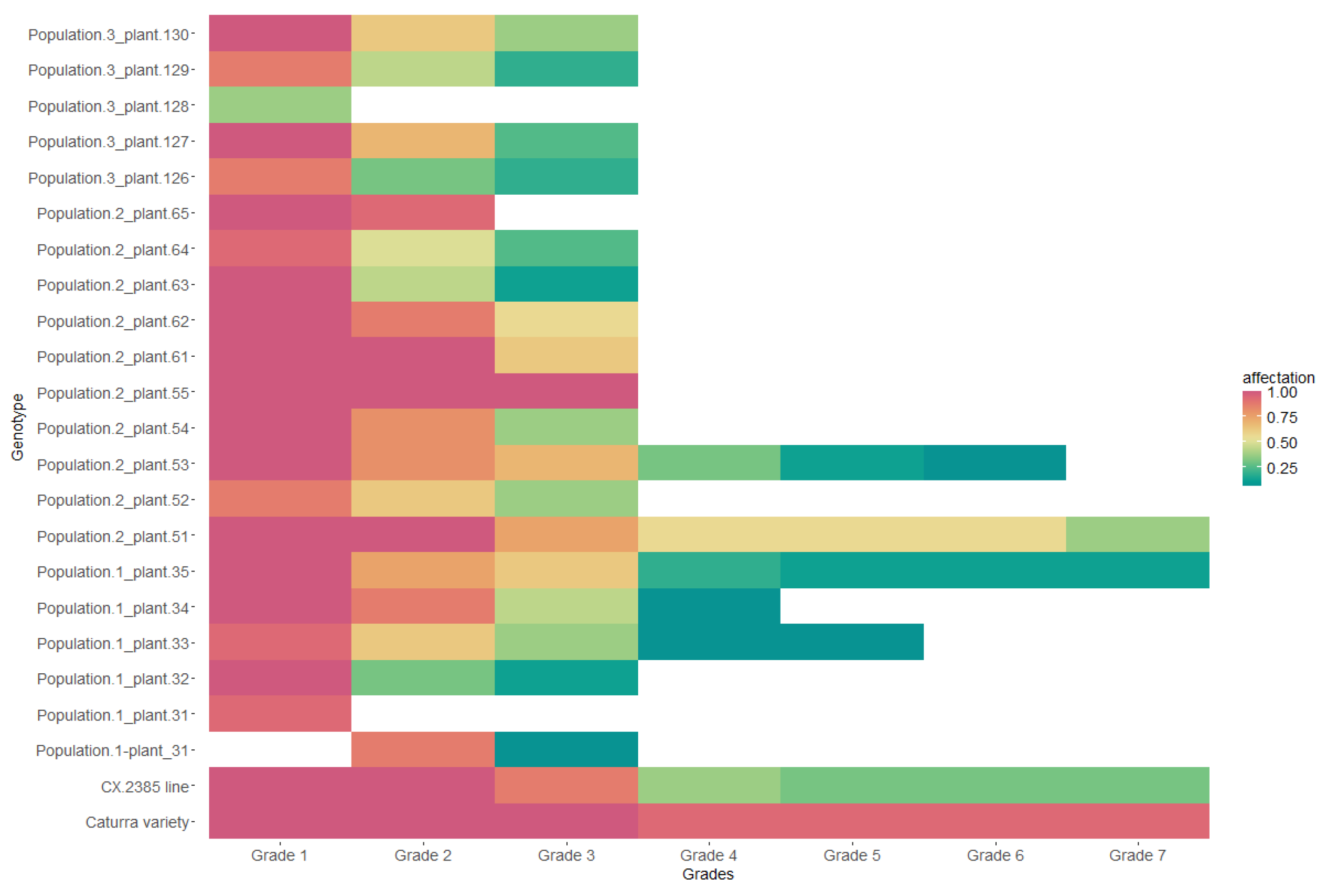
| Population | Plant | Percentages of involvement in the scale of increasing injuries | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | Grade 4 | Grade 5 | Grade 6 | Grade 7 | ||
| 1 | 31 | 93.80 | 87.50 | 6.30 | ||||
| 32 | 100.00 | 27.30 | 9.40 | |||||
| 33 | 93.80 | 62.50 | 37.50 | 3.90 | 0.80 | |||
| 34 | 100.00 | 87.50 | 43.80 | 0.80 | ||||
| 35 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 62.50 | 6.30 | 5.50 | 5.50 | 5.50 | |
| 2 | 51 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 75.00 | 46.10 | 44.50 | 40.60 | 29.70 |
| 52 | 87,50 | 62.50 | 37.50 | |||||
| 53 | 100.00 | 81.30 | 63.30 | 18.00 | 6.30 | 0.80 | ||
| 54 | 100.00 | 81.30 | 37.50 | |||||
| 55 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | |||||
| 61 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 62.50 | |||||
| 62 | 100.00 | 87.50 | 56.30 | |||||
| 63 | 100.00 | 43.80 | 12.50 | |||||
| 64 | 93.80 | 50.00 | 21.90 | |||||
| 65 | 100.00 | 93.80 | ||||||
| 3 | 126 | 87.50 | 31.30 | 18.80 | ||||
| 127 | 100.00 | 68.80 | 25.00 | |||||
| 128 | 32.80 | |||||||
| 129 | 87.50 | 43.80 | 18.80 | |||||
| 130 | 100.00 | 62.50 | 37.50 | |||||
| Caturra variety | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 78.10 | 78.10 | 78.10 | 77.30 | |
| CX.2385 line | 100.00 | 100.00 | 87.50 | 26.60 | 25.80 | 24.20 | 24.20 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




