1. Introduction
1.1. Life History
The Asian clam is a small bivalve mollusc with a shell length less than 50 mm. Its shell has concentric sulcations, with serrated anterior and posterior lateral teeth [
1]. The shell coloration appears to be latitude dependent, with lighter morphs found in the northeast United States and darker morphs found in the southwestern United States. Asian clams have high physiological plasticity but prefer areas of slower water flow and environmental factors such as temperature, food availability, and dissolved oxygen can affect individual growth rates and reproductive capacity [
2,
3,
4]. The Asian clam is also a self-fertilizing hermaphroditic species that can produce up to 570 larvae per day, resulting in more than 68,000 larvae produced per an individual per year [
5]. This combined with their rapid growth and early sexual maturity enables a single individual to initiate rapid reproduction in isolation [
6]. In addition to their high fecundity, their extensive dispersal capacities due to their association with human activities makes the Asian clam a successful and highly invasive species that is difficult to control and manage [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11].
Although native to Eastern Asia and Africa, Asian clams have invaded aquatic ecosystems in Europe, North America, and South America. Asian clams are thought to have originally been introduced to the West Coast of North America in 1938 through transoceanic ballast water exchange and Chinese immigrant importation for use as a food source [
9,
12,
13]. By the 1960s, the Asian clam had spread throughout the United States’ waterways to reach the Atlantic coast [
7]. Since then, Asian clams have established themselves above the 40° latitude line, previously thought to be the threshold of their low temperature tolerance [
14].
1.2. Asian Clams Dispersal in Massachusetts, USA
Previous studies reported that the Asian clam was first sighted in Massachusetts in the Charles River in 2001. This is fitting as the state’s likely origin of infestation as the Charles River is a central figure in the Eastern Massachusetts landscape and is a hotspot for boating year-round [
14]. However, newly discovered historical data reveal that Asian clams were first detected in Massachusetts farther South in Long, Pond at Lakeville as early as 1999 [
15]. Long Pond is frequently used for recreational boating, fishing, and swimming, all of which are common vehicles for aquatic invasive species introduction and contamination. Before 2017, Asian clams were found in 36 waterbodies, mostly in the south and southeast of the state with an abundance of up to 6,124 clams/m² recorded in an infested unnamed tributary in Forest Park, Springfield, Massachusetts [
16]. Since their introduction in 1999, Asian clams have been found in 45 waterbodies, including 8 rivers and 37 ponds and lakes in Massachusetts [
14]. In the past 5 years, Asian clams have expanded into waterbodies farther northwest within Massachusetts (Figure. 1), where minimum water temperatures are usually lower. This northern expansion of range is consistent with other research as the species’ presence has recently been detected in other New England states, such as Lake Bomoseen in the State of Vermont [
14,
17] and in the lower Merrimack River and in several ponds in the State of New Hampshire [
14,
18,
19].
Figure 1.
Distribution map depicting Corbicula fluminea in Massachusetts. Sightings were grouped by first reported sight years and color coded to demonstrate the northwestern expansion of their range over 24 years (See supplementary material Table S1 for site descriptions).
Figure 1.
Distribution map depicting Corbicula fluminea in Massachusetts. Sightings were grouped by first reported sight years and color coded to demonstrate the northwestern expansion of their range over 24 years (See supplementary material Table S1 for site descriptions).
1.3. Impacts of Invasion
As climate change causes temperatures to continue to increase, Asian clams are likely to continue to expand their range farther north and represent an emerging issue for the Northeast United States. Not only are Asian clams the most widely distributed aquatic nuisance species in the contiguous United States, but they are also one of the most ecologically and economically impactful aquatic invasive species globally [
7,
9]. As suspension feeders, Asian clams can drastically change the ecosystems through selective feeding, consuming large quantities of microscopic plants and animal species, greatly altering the macroinvertebrate communities. This also leads to outcompeting natural prey species for benthic microbes and causing up to 70% reduction in phytoplankton [
20,
21]. They also sequester a large amount of available carbon in the water and may displace native unionid mussels [
22,
23].
In addition to their ecological impacts, Asian clams also have a significant economic impact due to the loss of ecosystem services and direct economic damages. As Asian clams are introduced to new waterways by human activity, they can damage or occlude equipment such as water intake pipes in electrical power plant cooling systems and sewage treatment plants [
14,
22,
24]. Although difficult to quantify, the costs to control Asian clam populations across the United States are estimated to be over
$1 billion annually since 1980 [
25]. As Asian clams continue to expand their range and infest new waterways, their ecological and economic impact is expected to increase [
14].
1.4. Management Strategies
While prevention of aquatic invasive species infestations is the ideal management strategy, an integrated approach is necessary to best treat waterways once Asian clams have been detected to prevent further spread. Wong [
14] lists that this integrated strategy should contain 4 steps:
- 2.
-
Create a plan to stop or slow the spread.
- 3.
Analyze the ecological and economic impact of infestations on new water bodies.
- 4.
Create an emergency response plan to proactively limit the species’ invasiveness.
The emergency response plan will contain components of all 4 steps outlined above, but it will focus primarily on the active treatment. These methods can be both reactive, once a population of Asian clams has been detected, and proactive, targeting Asian clams in the larval stage before they have been established. Proactive treatments tend to be more effective, versatile, and cost-effective than reactive measures. However, due to limited resources, they are often not employed until after infestations have been detected [
14,
26]. Treatments options include physical, biological, genetic, and chemical options, as depicted in
Table 1. While each treatment type can be employed individually, there is potential to combine techniques to enhance their efficacy.
Table 1.
Evaluation characteristics of each option available for treating Asian clams.
Table 1.
Evaluation characteristics of each option available for treating Asian clams.
1.5. Treatment Options
1.5.1. Physical Treatments
Physical treatments alter the Asian clam’s habitat to make it less suitable for their survival and include altering the temperature or dissolved oxygen content of the water. Gas impermeable benthic barriers have been proven effective at depleting dissolved oxygen and culling Asian clam populations. However, they are only a short-term control strategy and are often detrimental to non-target benthic species [
14,
26,
27]. Thermal shock, either through dry ice or open flame, have also been effective at treating Asian clams but are not always feasible under natural conditions. Physical removal, either through suction dredging or hand removal, remain the most effective forms of physical control but are costly and only target adult life stages [
14].
1.5.2. Biological Treatments
Biological treatment options are more limited because although Asian clams are small in size, their shells are proportionately quite strong and few predators are able to consume them. Parasites or disease vectors may be more effective at controlling Asian clam populations, but few options are currently available on the market [
14]. As a biological treatment, Zequanox® induces mortality by damaging the epithelial cells in the intestinal lining following ingestion [
35].
1.5.3. Genetic Treatments
A newer technology has been introduced to prevent invasive species from reproducing by either manipulating genes to reduce fecundity or by using x-rays to prevent development of the zygote. While it may be a promise tool for other bivalves that this could be used both as proactive and reactive management, it is expensive and laboratory testing was not able to achieve 100% success on preventing further spread [
34] and it may not work on the Asian clam due to its unique reproduction strategy. Further research is needed to determine whether or not radiation such as x-rays can work on treating Asian clams and how to increase efficacy and perform this technique at scale in a cost-effective manner.
1.5.4. Chemical Treatments
The use of chemicals to treat a waterbody remains one of the only forms of proactive treatment and most efficacious and cost-effective manors of Asian clam eradication, suppression, and control. However, it also has the greatest potential to negatively impact non-target species and the surrounding environment [
14].
This analysis will focus on studies on Asian clam chemical treatments currently available for applications. It will also evaluate treatments and toxicities that have been tested only in a laboratory setting or on other invasive bivalves that have potential for success in Asian clam control.
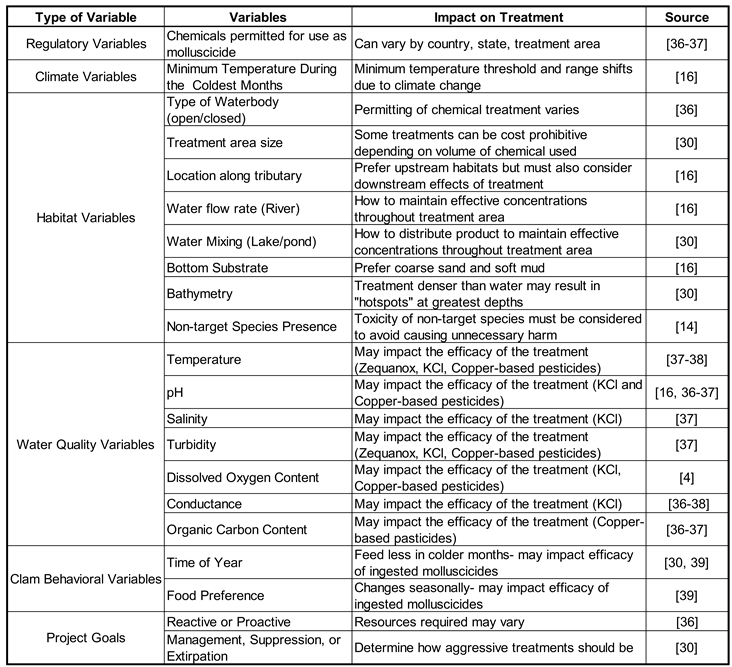
1.6. Treatment Selection
Chemical treatments have the largest range of options available that allows for site specific Asian clam control plans. A variety of factors must be considered when determining which chemical treatment to use to achieve the goals of the project. A summary of the most crucial factors to consider when choosing a chemical treatment are listed below in
Table 2. However, special attention is needed to determine whether a water system is considered open or closed. Closed systems include water intake pipes, wastewater treatment facilities, and electric powerplants cooling systems [
16]. Treatment is aimed at eradicating existing or preventing biofouling clams from accumulating on these commercial structures. Due to their great potential economic impact, many treatments have been specifically designed to be used in in these industrial settings [
26]. Non-target species are of minimal concern in this setting so more aggressive control strategies can be employed. In these closed systems, usually oxidative chemicals such as chlorine or bromide are used to eradicate the invasive bivalves quickly and effectively. However, chlorine and bromide produce carcinogenic byproducts and halogens that are toxic to non-target species [
35,
36]. To prevent environmental contamination, chemical treatments used to prevent or treat biofouling clams in closed systems are not suitable chemical treatments for open water systems [
27].
It is more difficult to stop the spread of Asian clams in open water systems, where treatment methods are more restricted due to their potential to negatively impact water quality, including drinking water contamination, and non-target species [
14]. Additional consideration and extensive testing protocols must be employed to ensure that the chemical treatment used to eradicate invasive Asian clams does not have deleterious environmental consequences. For the purposes of this review, only treatments that have been used or have the potential to be used in open water systems have been included in the analysis. One of the most common active ingredients used in molluscicides for Asian clam chemical treatment is copper-based compounds. The copper-based treatments induce mortality in Asian clams through binding to receptors on the bivalves’ gills, thus inhibiting gas exchange across the cellular membrane [
14,
37].
Table 2.
Variables to consider when selecting a control strategy for Asian clams.
Table 2.
Variables to consider when selecting a control strategy for Asian clams.
1.7. Regulations
The chemical treatment selected must be approved by the regulatory body in the country or state of use. The European Union Regulation number 1143/2014 adheres to hierarchical measures of prevention, early detection and rapid eradication, and management to combat invasive species [
40]. In the United States, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) sets the standard for molluscicide use either by regulating specific products or granting special permits for emergency circumstances. This review will focus on chemical treatments used in the United States, but specific consideration for more local regulations on approved molluscicides and the regulations regarding the potential water quality and environmental impacts must be strictly adhered to.
The Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA) is the primary EPA regulation for chemical treatments used as molluscicides. Currently brand-named Natrix® and EarthTec QZ® are copper-based products registered with the EPA as molluscicides, although Cutrine® Ultra has been registered with the EPA as an algaecide, herbicide and cyanobactericide. KCl, or unrefined potash, is not registered with the EPA as a molluscicide but can instead be approved for use through site-specific regulatory exemption processes [
37]. Section 24(c) allows states to register a pesticide for a special local need, defined as “an existing or imminent pest problem for which there is no federally registered pesticide available” [
37,
40]. In addition, Section 18 “allows unregistered use of pesticides to address emergency conditions” [
37,
40]. Examples of use in projects for rapid response zebra mussel eradication include Lake Irene and Rose Lake in Minnesota in 2011 and for use in population suppression in Lake Ossawinamakee in Minnesota in 2004 and 2005 [
37].
In addition to specific molluscicide regulations, regulations involving the discharge of chemicals into water bodies must also be adhered to. The Clean Water Act regulates all molluscicides and biocides discharged into US waters. Chemical treatments must be registered with the United States EPA and handled and applied according to label instructions [
36]. Chemical treatments may also be subject to different regulations in different countries or states/provinces. For example, if chemicals are applied to bodies of water in Massachusetts, USA, for the control of aquatic nuisance species, a WM04 Chemical Application License needs to be granted by the Massachusetts Department of Environmental Protection, per Massachusetts General Laws c. 111, s. 5E. More detailed information can be found from the book titled “Invasive Animals and Plants in Massachusetts Lakes and Rivers: Lessons for International Aquatic Management” [
14].
2. Methods
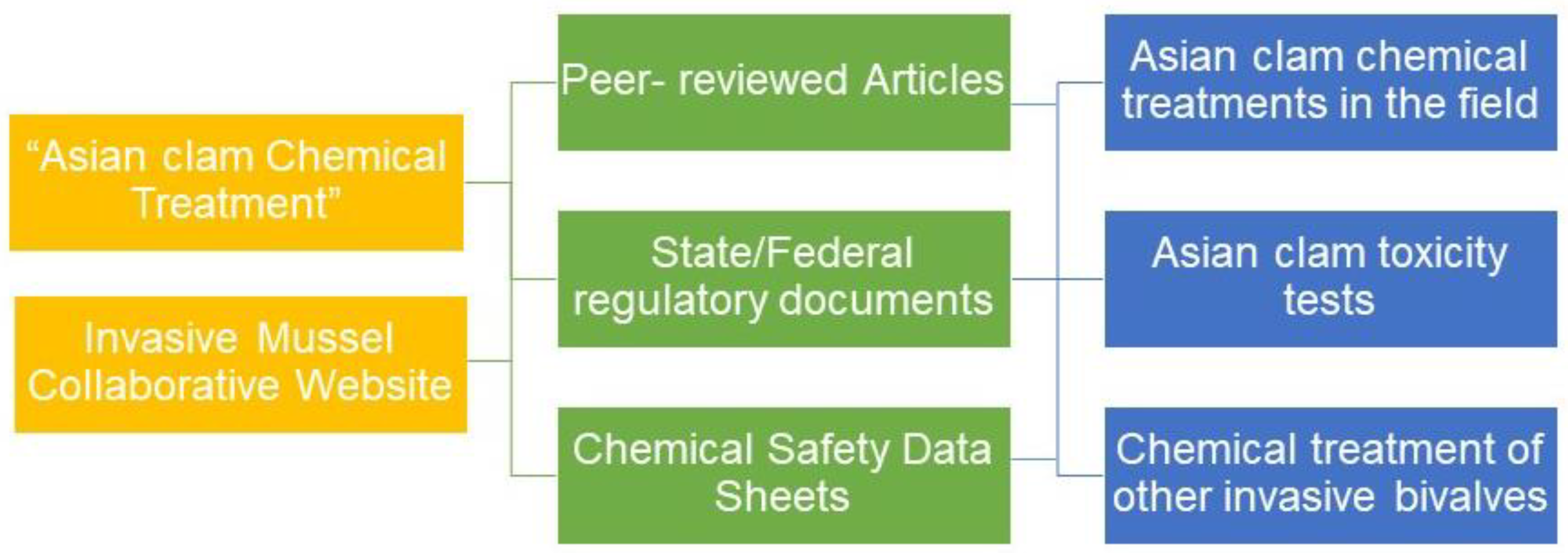
2.1. Systematic Review
A variety of Asian clam control methods have been developed for practitioners that include physical, biological, and chemical control. This review will focus primarily on chemical control as this strategy requires natural resource managers to use the least resources while achieving the greatest impact. A systemic review was conducted on Google Scholar using the key words “Asian clam Chemical Treatment” to identify peer-reviewed articles, state and federal regulatory documents, and chemical product safety data sheets through March 2024. In addition to these documents, the Invasive Mussel Collaborative website was used to identify primary, peer-reviewed sources. The sources were then categorized by subject matter, determined by whether reported studies were conducted on Asian clams in the field, Asian clam toxicity studies in a laboratory setting, or if the study focused on the treatment of other species of invasive bivalves of which the treatment could potentially be applied to Asian clams in future studies. The following results are categorized as such.
Figure 2.
Workflow of systematic review categorization process.
Figure 2.
Workflow of systematic review categorization process.
3. Results
3.1. Applied Chemical Treatments
Despite their market availability, chemical treatments have not been widely applied to Asian clam infestations in natural waterbodies. This is most likely due to the lack of public and resources manager education and awareness regarding the impacts of this invasive species. In addition, as Asian clams inhabit the substrate at the bottom of a waterbody, they usually do not impact popular recreational activities, such as swimming and boating. Invasive plants, such as Eurasian milfoil or curly-leaf pondweed, are more exposed and therefore garner more public attention and response from resource managers as these species can impair the general public’s recreation. Asian clams that infiltrate industrial equipment or intakes, known as biofouling, cause the greatest economic impact and as such, chemical treatments have focused on Asian clam eradication in this setting [
4]. Oxidative treatments, such as chlorination and bromination, are the most common treatments used to treat Asian clams. Chlorine treatments have had success inducing mortality of biofouling Asian clams in industrial, closed water systems, such as hydroelectric dams and water treatment facilities. However, oxidizing treatments are not suitable for use in natural, open water systems due to their lethal effects on non-target species in low concentrations [
28]. As such, they will be omitted from this review.
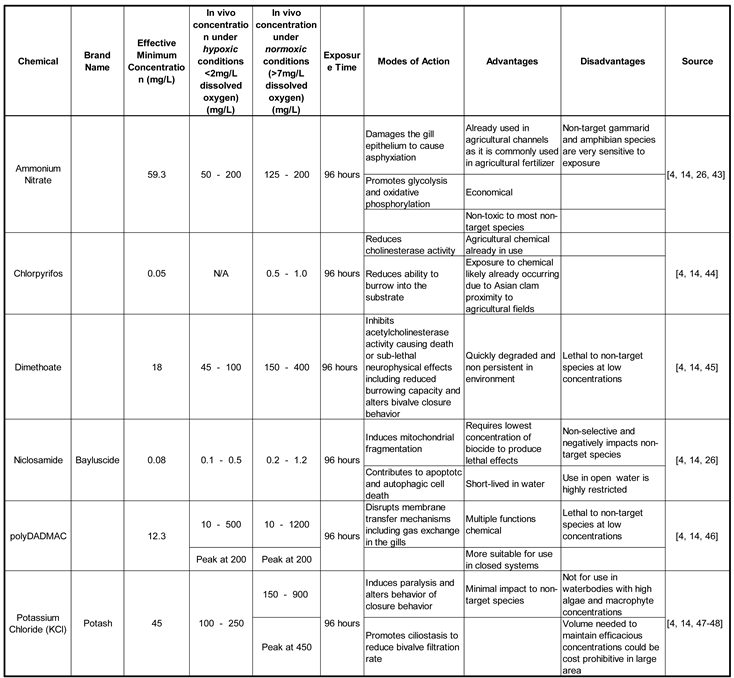
3.2. Toxicity Studies
Apart from existing chemical applications, there are numerous toxicity studies on Asian clams and some of these treatments may have potential to be applied as new methods in the future. These molluscicides and their concentrations under various dissolved oxygen concentrations are listed in
Table 3 and the original studies are described below.
Table 3.
Toxicity of common active ingredients in molluscicides on Asian clams..
Table 3.
Toxicity of common active ingredients in molluscicides on Asian clams..
3.2.1. Asian Clam Sensitivity in Laboratory Testing
Wild-caught adult Asian clams were acclimated to municipal water maintained at 20 ± 2 °C with a 16hr
L and 8hr
D photoperiod cycle with continuous aeration. Mortality tests were then conducted under a geometric range of concentrations for each of the six chemicals. Each treatment was conducted under both normoxic conditions (>7mg/L dissolved oxygen) and under hypoxic conditions where nitrogen gas was infused into the water to decrease the dissolved oxygen content to less than 2 mg/L. While Asian clams display great physiological plasticity and are able to acclimate to various environmental conditions, they are largely intolerant to low oxygen levels. The results of this study demonstrate that the hypoxic conditions increased the susceptibility of clams to the chemical treatment by up to 400% relative to the same treatments performed under normoxic conditions [
4]. The concentrations for the minimum effective concentration as well as the most effective concentrations of each chemical treatment under both hypoxic and normoxic conditions are summarized in
Table 3.
The results of this study have important implications for managing invasive Asian clam populations. This toxicity study provides target concentrations for a variety of chemical treatments options. However, it also highlights how natural resource managers can combine treatment options to optimize results. Combining physical and chemical management of invasive species could increase the effects of chemical treatment while decreasing the concentration of chemicals used, thereby minimizing the deleterious effects on non-target species and the surrounding environment. Use of curtain barriers reduces dissolved oxygen content and increases Asian clam oxidative stress as well as boosts the efficacy of chemical treatments. Similarly, the use of benthic barriers over treatment areas could help to induce hypoxic conditions to increase treatment efficacy and clam mortality [
30].
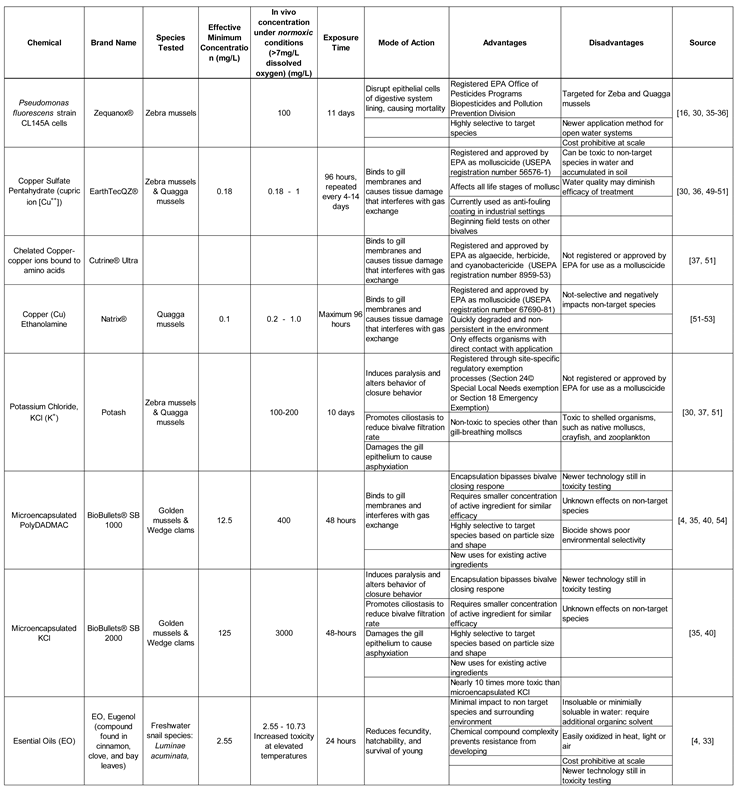
3.3. Chemical Treatments on Other Bivalves
Numerous molluscicides have already been developed to induce mortality in other invasive bivalves, such as zebra, quagga, and golden mussels. There is potential to expand the targeted species to include Asian clams following laboratory toxicity and field testing. As such,
Table 4 represents an inexhaustive list of chemical treatments currently used to treat other invasive bivalves that should be the subject of further study for use in Asian clam chemical treatment studies.
Table 4.
Chemical Treatments of other Invasive Bivalves with potential applications for Asian clam management.
Table 4.
Chemical Treatments of other Invasive Bivalves with potential applications for Asian clam management.
3.3.1. Potassium Chloride and Formalin
In a study by Layhee et al. [
48], a laboratory toxicity study was performed to determine if the molluscicide of 750 mg/L KCl and 25 mg/L Formalin (37% formaldehyde) used to treat zebra mussel veligers in hatcheries had similar success in Asian clams. Using this process, commonly referred to as the Edward’s protocol [
38], the study determined that there was 100% mortality of Asian clam veligers after 3- and 5-hour exposure times [
48]. While further testing is needed to determine how this treatment effects different life stages as well as its potential for use in open-water systems, this initial study is promising that chemical treatments used in management of other invasive bivalves can successfully be used to treat Asian clams.
3.3.2. Zequanox®
Another potential treatment for Asian clams is a biopesticide under the brand name Zequanox® that contains
Pseudomonas fluorescens strain CL145A cells in a spent fermentation media. This bacterium naturally occurs in soil and water and is ingested by filter feeders, subsequently destroying their digestive lining and selectively killing dreissenid mussels [
36,
55]. While current studies discuss the effectiveness of Zequanox® to control zebra and quagga mussels, evidence suggests it could be applied to treat Asian clams as well. Bolam et al. [
39] investigated the feeding rates and prey selection of Asian clams and determined that they prefer diatoms in warmer months but switch their diet to preferentially feed on flagellates in the fall [
39]. The bacterium
Pseudomonas fluorescens in Zequanox® is a flagellate bacterium, and thus this product has potential to be an effective treatment for invasive Asian clams specifically during the fall months. Further testing is required to determine if Asian clams will preferentially filter out Zequanox® bacterium to ingest, what life stages it will treat, and what concentrations are required for the population density and feeding rates of a detected population during different seasons.
3.3.3. Combination of Zequanox®, EarthTec QZ®, potash (KCl)
Treatments can be combined to facilitate a rapid response to early detection of invasive bivalves. Such was the case in Christmas Lake, Minnesota when in 2014, a localized population of zebra mussels was detected near the public boat landing. A combination of Zequanox®, EarthTec QZ®, and potash were used in successional treatments, with Zequanox® used first in September 2014, only 23 days after initial infestation detection. This instance also represents the first time Zequanox® had been employed as a treatment for Zebra mussels in the field. In October and November of the same year, a series of EarthTec QZ® treatments were used in the initial detection area and in the area immediately surrounding it, although no curtain barrier was installed until the second treatment. Finally, in December 2014 and in April and ay of the following year, potash was used to maintain a concentration of 73.5 and 110 ppm K
+ within the treatment area for 10 days. Although these treatments resulted in no detected surviving Zebra mussels, individuals were found a year later in untreated parts of the lake. While this study represents an immediate response with early success, it also highlights the need for post-treatment monitoring and the limitations of treatments in only a portion of a water body [
30]. The use of chemical treatment combinations and the lessons learned from this field study should be applied to treatments of all invasive bivalves, including Asian clams as field studies continue to increase in frequency.
3.3.4. Microencapsulation
Microencapsulation represents a promising technology that could be applied to a variety of active ingredients already approved and used in molluscicides to treat invasive bivalves [
35]. Microencapsulation technology encases the control agent in an edible coating to bypass a bivalve’s shell-closing response. Instead of sensing a harsh chemical such as chlorine and closing its shell for 2-3 weeks at a time, the encapsulated active ingredient is ingested quickly during filter feeding and thus is taken up more rapidly than harsh chemicals [
32]. As the active ingredient is selectively absorbed by the target species, microencapsulation requires lower concentrations of active ingredients while increasing its toxicity. This allows for more effective treatment while also reducing the residual environmental contamination [
35].
BioBullets® are a manufactured lipid walled microparticle that encases various control agents. In a report by Tang and Aldridge [
40], two new formulations of BioBullets® with the smallest particle size most similar to filter feeder’s prey were tested on
Rangia cuneata or Wedge clams. The SB 1000 model had a particle size of 9.5 ± 0.5µm with a smooth surface and the SB 2000 model had a particle size of 24.6 ± 1.3µm with a crystallized surface. Asian clams have a prey particle size preference of <20-25µm, so both models are likely to be ingested by Asian clams. Despite their small size, SB 2000 had an extended-release rate over 20 hours. A single dose of 2-6mg/L of the active ingredients resulted in 90% mortality within 30 days [
40]. While the study does not specify what the active ingredients are in the tested BioBullets®, it does refer to SB 1000 as having a cationic polymer that acts as a surfactant, which is most likely poly-diallyldimethyl ammonium chloride (polyDADMAC) used in previously reported studies [
4] while the SB 2000 BioBullets® used an anionic salt, most likely KCl. While both active ingredients are toxic to bivalves, Calazans et al. [
35] reported that encapsulated polyDADMAC was 9.3 times more toxic than encapsulated KCl in golden mussels [
35]. As the prey particle size is within the preferred range and the various models with differing surface texture could be used according to their seasonal diet preferences, BioBullets® have great potential for use as Asian clam chemical treatments [
40].
3.3.5. Essential Oils
There is rising interest in essential oils and their constituents as a safer alternative to pesticides used to treat aquatic gastropods. To determine the immersion lethal toxicity value of various essential oils, researchers immersed adults and egg clusters of freshwater
Pomacea canaliculata snails in essential oils for 24 hours followed by a recovery period in dechlorinated tap water. After a 12-hour exposure, 100% mortality was achieved at 156.25µg/ml . However, this review also showed that essential oil constituents were more deadly to aquatic gastropods when ingested through baiting as opposed to diffuse essential oils released into the water column. Specifically, feeding on baits that contained sublethal concentrations of eugenol, a compound found in cinnamon, clove, and bay leaves, the 24- hour lethal concentration of 50% of the sample size (24 h-LC50) ranged between 2.55 and 10.73µg/ml, with the highest toxicity occurring in conjunction with elevated temperatures. Eugenol also reduced fecundity, hatchability, and survival of young
Lymnaea acuminata [
33]. Although Asian clams are different from gastropods, there is potential to combine essential oil baiting techniques with microencapsulation technology to enable invasive bivalves to filter out and consume the toxic essential oils constituents and maximize their efficacy.
Although the mechanism of toxic action remains unknown, it has been proposed that the various constituents of essential oils interfere with metabolic, physiological, and behavioral functions [
33]. Further research is needed to identify the mode of action to determine the most effective formulation and delivery system to reach the target species. Site-specific toxicity testing is also needed to determine the impacts of essential oils on non-target species.
4. Future Directions
To date, there are no known control methods that have achieved complete eradication of Asian clams in open waterbodies. Only opportunistic studies have occurred as invasive bivalves are detected, and paid responses have been deployed [
30]. However, infestations in industrial settings have been extirpated and there is increasing research on invasive bivalve population responses to molluscicides that have pr omising results [
28].
The tables presented in this review outline the potential for future studies. Toxicity studies (
Table 3) should be tested in the field to determine if they could be candidates for permittable Asian clam treatments. The compounds in
Table 4 represent chemical treatments that have proven successful in treating other invasive bivalves such as zebra and quagga mussels and have potential to effectively treat Asian clams as well. Further testing is needed to first determine the toxicity concentrations that induce mortality in Asian clams in a laboratory setting, followed by field testing to determine the environmental impacts of releasing molluscicides into infested waterbodies. Pre- and post-treatment monitoring is required to determine the impacts of chemical treatments on all life stages of Asian clams, non-target species, and water quality data as well as efficacy-related data that will help to inform safe and effective adaptive management [
37].
Finally, future research should investigate how best to combine chemical treatments with other physical or biological treatments to maximize efficacy. As shown in the study by Rosa et al. [
4], inducing hypoxic conditions with the use of benthic barriers increased the Asian clam mortality using lower concentrations of each chemical treatment [
4]. Combining treatment methods to manage invasive species could help to increase the effects of chemical treatment while decreasing the concentration of chemicals used, thereby decreasing the potential impacts on the surrounding environment and non-target species.
5. Conclusions
Asian clam’s high fecundity and physiologic plasticity have allowed them to become a highly successful invasive species in the North America. As Asian clams expand their range to infest waterbodies extending farther into the Northeast United States, effective control strategies are needed to help manage these invasive populations to prevent ecological and economic harm. While physical, biological, and genetic control strategies present opportunities for effective invasive bivalve control, chemical treatments are one of the only preventative control strategies currently available at scale. They are also the most cost-effective management option and effectively treat all life stages of this species, although careful consideration of variables such as habitat and water quality of the proposed treatment area is needed to determine the most suitable molluscicide. Despite multiple molluscicides available on the market, their use to eradicate Asian clam infestations in natural waterbodies are quite limited, most likely due to lack of awareness regarding their ecological and economic impacts. Chemical treatments have undergone lab testing to determine the minimum concentrations to initiate Asian clam mortality, as well as the concentrations that cause 100% mortality under hypoxic and normoxic conditions [
4]. Finally, chemical treatments used to eradicate other invasive bivalves, including zebra and quagga mussels, have been identified. Both the laboratory toxicity testing, and the treatments of other invasive bivalves require further research to determine their efficacy in treating Asian clams both individually and in tandem with other forms of management. This review summarizes the current available research on the chemical treatment of Asian clams to direct future research efforts and to guide resource managers and practitioners on invasive Asian clam management.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org, Table S1: Geo-referenced records of Corbicula fluminea in Massachusetts, 1999-2023.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.H.W.; methodology, W.H.W.; validation, K.D.G. and W.H.W.; formal analysis, K.D.G. and W.H.W.; investigation K.D.G. and W.H.W.; resources, W.H.W.; data curation, K.D.G. and W.H.W.; writing—original draft preparation, K.D.G.; writing—review and editing, K.D.G. and W.H.W.; visualization, K.D.G.; supervision, W.H.W; project administration, W.H.W.; funding acquisition, W.H.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Nandor Dinka from MDPI for inviting our contribution to this special issue of Animals. We thank Juliet Swigor at MassDEP for providing valuable assistance with ArcGIS Pro. We thank Dr. Francisco Sylvester and Dr. Esteban M. Paolucci for their efforts in editing this special issue. We also thank Northeastern University’s Co-Op Program and the MassDEP’s Michelle Waters-Ekanem Internship Program for their support in completing this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Benson, A.; Foster, A. M.; Fuller, P.; Constant, S.; Raikow, D.; Larson, J.; Fusaro, A.; Bartos, A. Corbicula fluminea (O. F. Müller, 1774). NOAA Great Lakes Aquatic Nonindigenous Species Information System. https://nas.er.usgs.gov/queries/greatlakes/FactSheet.aspx?Species_ID=92.
- Cataldo, D.; Boltovskoy, D. Population Dynamics of Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia) in the Paraná River Delta (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 1998, 380 (1/3), 153–163. [CrossRef]
- Viergutz, C.; Linn, C.; Weitere, M. Intra- and Interannual Variability Surpasses Direct Temperature Effects on the Clearance Rates of the Invasive Clam Corbicula fluminea. Mar. Biol. 2012, 159 (11), 2379–2387. [CrossRef]
- Rosa, I. C.; Garrido, R.; Ré, A.; Gomes, J.; Pereira, J. L.; Gonçalves, F.; Costa, R. Sensitivity of the Invasive Bivalve Corbicula fluminea to Candidate Control Chemicals: The Role of Dissolved Oxygen Conditions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2015, 536, 825–830. [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R. F. Invasive Characteristics of the Freshwater Bivalve Corbicula fluminea. In Nonindigenous Freshwater Organisms: Vectors, Biology, and Impacts; Claudi, R., Leach, J. H., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000; pp. 315–343.
- Gomes, C.; Sousa, R.; Mendes, T.; Borges, R.; Vilares, P.; Vasconcelos, V.; Guilhermino, L.; Antunes, A. Low Genetic Diversity and High Invasion Success of Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia, Corbiculidae) (Müller, 1774) in Portugal. PLoS ONE 2016, 11 (7), e0158108. [CrossRef]
- McMahon, R. F.; Bogan, A. E. Mollusca: Bivalvia. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates; Thorpe, J. H., Covich, A. P., Eds.; Academic Press, 2001; pp. 331–429. [CrossRef]
- Karatayev, A. Y.; Burlakova, L. E.; Padilla, D. K. Contrasting Distribution and Impacts of Two Freshwater Exotic Suspension Feeders, Dreissena polymorpha and Corbicula fluminea. In The Comparative Roles of Suspension-Feeders in Ecosystems; Dame, R. F., Olenin, S., Eds.; NATO Science Series IV, 2005; Vol. 47, pp. 239–262. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Antunes, C.; Guilhermino, L. Ecology of the Invasive Asian Clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller, 1774) in Aquatic Ecosystems: An Overview. Annales de Limnologie – Int. J. Limnol. 2008, 44 (2), 85–94. [CrossRef]
- Lucy, F.; Karatayev, A.; Burlakova, L. Predictions for the Spread, Population Density, and Impacts of Corbicula fluminea in Ireland. Aquat. Invasions 2012, 7 (4), 465–474. [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, N.; Walsh, D. A.; Caffrey, J. M.; Davis, E.; Lucy, F. E.; Cuthbert, R. N.; Dick, J. T. A. Cold as Ice: A Novel Eradication and Control Method for Invasive Asian Clam, Corbicula fluminea, Using Pelleted Dry Ice. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2018, 9 (4), 463–474. [CrossRef]
- Counts, C. L. Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Sphaeriacea) in British Columbia. Nautilus 1981, 95 (1), 12–13.
- Counts, C. L. The Zoogeography and History of the Invasion of the United States by Corbicula fluminea (Bivalvia: Corbiculidae). Am. Malacol. Bull. 1986, Special Edition 2, 7–39.
- Wong, W. H. Asian Clam (Corbicula fluminea). In Invasive Animals and Plants in Massachusetts Lakes and Rivers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; pp. 35–50.
- Reed, B. Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation (DCR) Asian Clam Detection, 1999.
- Colwell, H.; Ryder, J.; Nuzzo, R.; Reardon, M.; Holland, R.; Wong, W. H. Invasive Asian Clams (Corbicula fluminea) Recorded from 2001 to 2016 in Massachusetts, USA. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2017, 8 (4), 507–515. [CrossRef]
- Bove, A. (Vermont Department of Environmental Conservation, Montpelier, Vermont, USA). Personal Communication, 2016.
- Smagula, A. P.; Nelson, E.; Snook, H. Asian Clam Habitat, Population Density and Size Range in Select New Hampshire Waterbodies; New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services, 2018. https://www.des.nh.gov/sites/g/files/ehbemt341/files/documents/2020-01/r-wd-18-18.pdf.
- New Hampshire Department of Environmental Services. Environmental Fact Sheet: Asian Clams; 2019. https://www.des.nh.gov/sites/g/files/ehbemt341/files/documents/2020-01/bb-62.pdf (archived 29 March 2024).
- Hakenkamp, C. C.; Ribblett, S. G.; Palmer, M. A.; Swan, C. M.; Reid, J. W.; Goodison, M. R. The Impact of an Introduced Bivalve (Corbicula fluminea) on the Benthos of a Sandy Stream. Freshw. Biol. 2001, 46 (4), 491–501. [CrossRef]
- Pigneur, L.-M.; Falisse, E.; Roland, K.; Everbecq, E.; Deliège, J.-F.; Smitz, J. S.; Van Doninck, K.; Descy, J.-P. Impact of Invasive Asian Clams, Corbicula Spp., on a Large River Ecosystem. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 59 (3), 573–583. [CrossRef]
- Müller, O.; Baur, B. Survival of the Invasive Clam Corbicula fluminea (Müller) in Response to Winter Water Temperature. Malacologia 2011, 53 (2), 367–371. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M. Asian Clam: An Exotic Aquatic Species. mass.gov. https://www.mass.gov/files/documents/2017/09/06/asian-clam.pdf.
- McMahon, R. F. Evolutionary and Physiological Adaptations of Aquatic Invasive Animals: R Selection versus Resistance. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59 (7), 1235–1244. [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, D.; Zuniga, R.; Morrison, D. Update on the Environmental and Economic Costs Associated with Alien-Invasive Species in the United States. Ecol. Econ. 2005, 52 (3), 273–288. [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.; Novais, A.; Costa, R.; Strayer, D. L. Invasive Bivalves in Fresh Waters: Impacts from Individuals to Ecosystems and Possible Control Strategies. Hydrobiologia 2013, 735 (1), 233–251. [CrossRef]
- Wittmann, M. E.; Chandra, S.; Reuter, J. E.; Schladow, S. G.; Allen, B. C.; Webb, K. J. The Control of an Invasive Bivalve, Corbicula Fluminea, Using Gas Impermeable Benthic Barriers in a Large Natural Lake. Environ. Manage. 2012, 49 (6), 1163–1173. [CrossRef]
- Modesto, V.; Ilarri, M. I.; Anna Maria Labecka; Noé Ferreira-Rodríguez; Coughlan, N. E.; Liu, X.; Sousa, R. What We Know and Do Not Know about the Invasive Asian Clam Corbicula fluminea. Hydrobiologia 2023. [CrossRef]
- Coughlan, N.; Walsh, D. A.; Caffrey, J. M.; Davis, E.; Lucy, F. E.; Cuthbert, R. N.; Dick, J. T. A. Cold as Ice: A Novel Eradication and Control Method for Invasive Asian Clam, Corbicula Fluminea, Using Pelleted Dry Ice. Management of Biological Invasions 2018, 9 (4), 463–474. [CrossRef]
- Lund, K.; Cattoor, K. B.; Fieldseth, E.; Sweet, J.; McCartney, M. A. Zebra Mussel (Dreissena polymorpha) Eradication Efforts in Christmas Lake, Minnesota. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2017, 34 (1), 7–20. [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J. L.; Pinho, S.; Ré, A.; Costa, P. A.; Costa, R.; Gonçalves, F.; Castro, B. B. Biological Control of the Invasive Asian Clam, Corbicula fluminea: Can Predators Tame the Beast? Hydrobiologia 2016, 779 (1), 209–226. [CrossRef]
- Aldridge, D. C.; Elliott, P.; Moggridge, G. D. Microencapsulated BioBullets for the Control of Biofouling Zebra Mussels. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40 (3), 975–979. [CrossRef]
- Radwan, M. A.; Gad, A. F. Essential Oils and Their Components as Promising Approach for Gastropod Mollusc Control: A Review. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2021, 128 (4), 923–949. [CrossRef]
- Misamore, M.; Wong, W. H.; Gerstenberger, S.; Madsen, S. Effects of X-Ray Irradiation on Fertilization and Early Development in Quagga Mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis). Manag. Biol. Invasions 2024, in press.
- Calazans, S. H. C.; Americo, J. A.; Fernandes, F. da C.; Aldridge, D. C.; Rebelo, M. de F. Assessment of Toxicity of Dissolved and Microencapsulated Biocides for Control of the Golden Mussel Limnoperna fortunei. Mar. Environ. Res. 2013, 91, 104–108. [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of the Interior Bureau of Reclamation. Available Methods for Invasive Mussel Control: Quagga and Zebra Mussels; 2015. https://www.usbr.gov/mussels/control/docs/musselcontrol.pdf.
- Dahlberg, A. D.; Waller, D. L.; Hammond, D.; Lund, K.; Phelps, N. B. D. Open Water Dreissenid Mussel Control Projects: Lessons Learned from a Retrospective Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13 (1), 10410. [CrossRef]
- Stockton-Fiti, K.; Moffitt, C. Investigation of the Edwards Protocol’s Effectiveness on Dreissenid Mussel Veligers; 2017. http://www.mrbp.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/04/Edwards-protocol-Dreissenid-veligers-Report-Final_PCC.2019.pdf.
- Bolam, B. A.; Rollwagen-Bollens, G.; Bollens, S. M. Feeding Rates and Prey Selection of the Invasive Asian Clam, Corbicula fluminea, on Microplankton in the Columbia River, USA. Hydrobiologia 2019, 833 (1), 107–123. [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Aldridge, D. C. Microcapsulated Biocides for the Targeted Control of Invasive Bivalves. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9 (1). [CrossRef]
-
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA); 2008; Vol. Section 24(c). https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/documents/fifra.pdf.
-
Federal Insecticide, Fungicide, and Rodenticide Act (FIFRA); 2008; Vol. Section 18. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/documents/fifra.pdf.
- Rehman, S. U.; Ahmed, R.; Ma, K.; Xu, S.; Aslam, M. A.; Bi, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, J. Ammonium Nitrate is a Risk for Environment: A Case Study of Beirut (Lebanon) Chemical Explosion and the Effects on Environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 210, 111834. [CrossRef]
- Cooper, N. L.; Bidwell, J. R. Cholinesterase Inhibition and Impacts on Behavior of the Asian Clam, Corbicula fluminea, after Exposure to an Organophosphate Insecticide. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 76 (3-4), 258–267. [CrossRef]
- Van Scoy, A.; Pennell, A.; Zhang, X. Environmental Fate and Toxicology of Dimethoate. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 53–70. [CrossRef]
- Santos, Ltd. Qualitative Tier 2 Assessment (PolyDADMAC); 2021. https://www.santos.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/PolyDADMAC_Tier2_March2021.pdf.
- Densmore, C. L.; Iwanowicz, L. R.; Henderson, A. P.; Blazer, V. S.; Reed-Grimmett, B. M.; Sanders, L. R. An Evaluation of the Toxicity of Potassium Chloride, Active Compound in the Molluscicide Potash, on Salmonid Fish and Their Forage Base. USGS Sci. Chang. World 2018, 1–46. [CrossRef]
- Layhee, M.; Yoshioka, M.; Farokhkish, B.; Gross, J. A.; Sepulveda, A. J. Toxicity of a Traditional Molluscicide to Asian Clam Veligers. J. Fish Wildl. Manag. 2013, 5 (1), 141–145. [CrossRef]
- Watters, A. Effectiveness of EarthTec ® on Killing Invasive Quagga Mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugenis) and Preventing Their Colonization in the Western U.S. UNLV Theses, Dissertations, Professional Papers, and Capstones, 908, University of Nevada Las Vegas, 2011. [CrossRef]
- Offutt Air Force Base. Final Summary Report: Zebra Mussel Eradication Project, Lake Offutt Nebraska; 55CES/CEV: Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, 2009. https://invasivemusselcollaborative.net/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/OAFB-ZM-Final-Summary-Report-2.pdf.
- Invasive Mussel Collaborative. Control Methods. Invasive Mussel Collaborative. https://invasivemusselcollaborative.net/management-control/control-methods/ (accessed 2024-04-16).
- SePro Corporation. Natrix Safety Data Sheet, August 28, 2018. https://www.sepro.com/Documents/Natrix_SDS.pdf.
- Idaho State Department of Agriculture. Snake River Quagga Mussel . https://agri.idaho.gov/main/plants/snake-river-quagga-mussel-veligers/.
- Gomes, J.; Pereira, J. L.; Rosa, I. C.; Saraiva, P. M.; Goncalves, F.; Costa, R. Evaluation of Candidate Biocides to Control the Biofouling Asian Clam in the Drinking Water Treatment Industry: An Environmentally Friendly Approach. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40 (2), 421–428. [CrossRef]
- Whitledge, G. W.; Weber, M. M.; DeMartini, J.; Oldenburg, J.; Roberts, D.; Link, C.; Rackl, S. M.; Rude, N. P.; Yung, A. J.; Bock, L. R.; Oliver, D. C. An Evaluation Zequanox® Efficacy and Application Strategies for Targeted Control of Zebra Mussels in Shallow-Water Habitats in Lakes. Manag. Biol. Invasions 2015, 6 (1), 71–82. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).