Submitted:
06 May 2024
Posted:
07 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- RQ1. What types of household waste management processes are supported by smart waste management?
- RQ2. What dimensions support smart waste management for managing household waste?
- RQ3. What are the information technology subdimensions that support smart waste management for managing household waste?
- RQ4. What is a framework for a smart and integrated household waste management system?
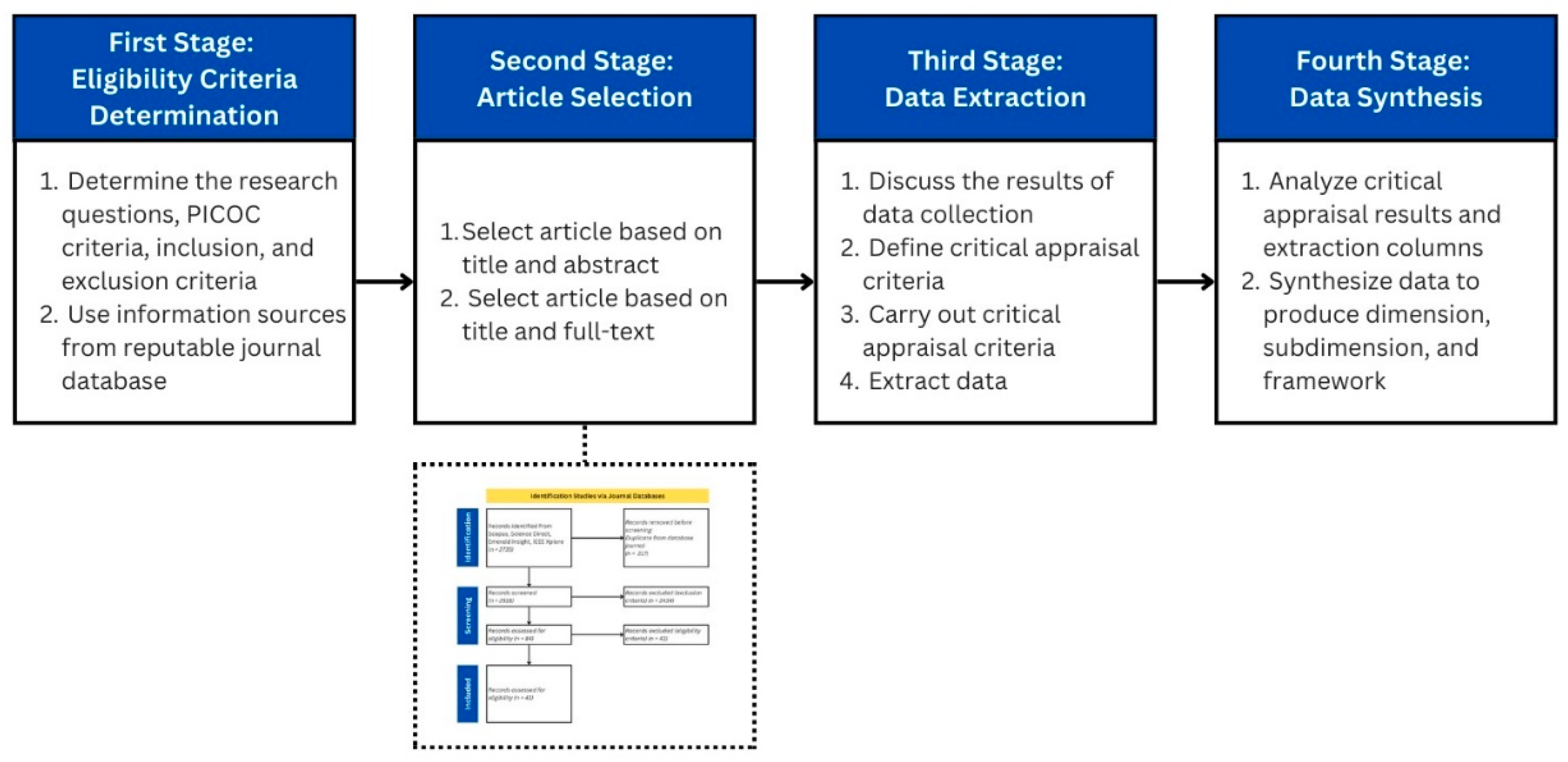
2. Materials and Methods
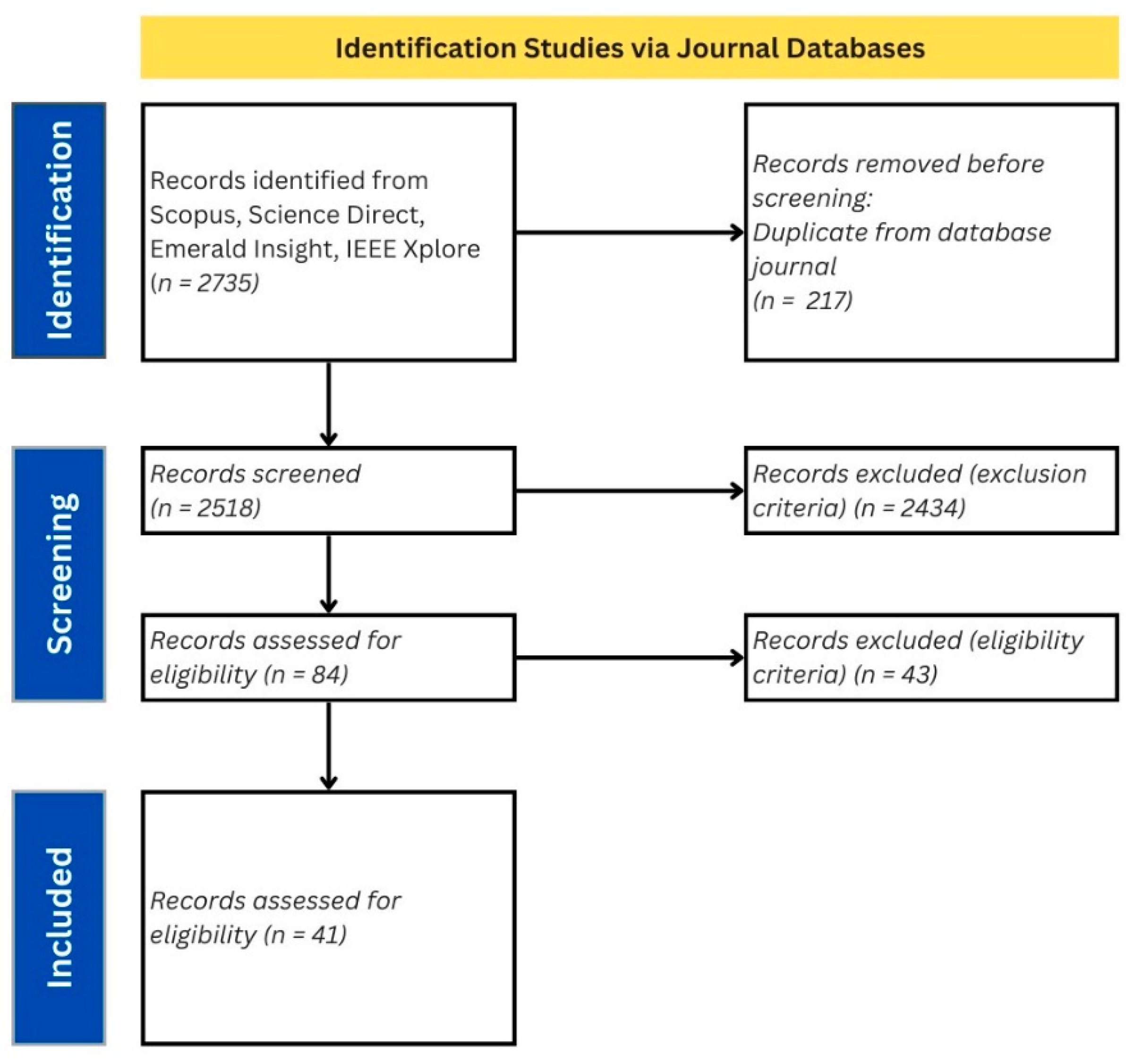
2.1. Determining Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Article Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.3. Data Synthesis
2.4. Validation Method for Framework
3. Results
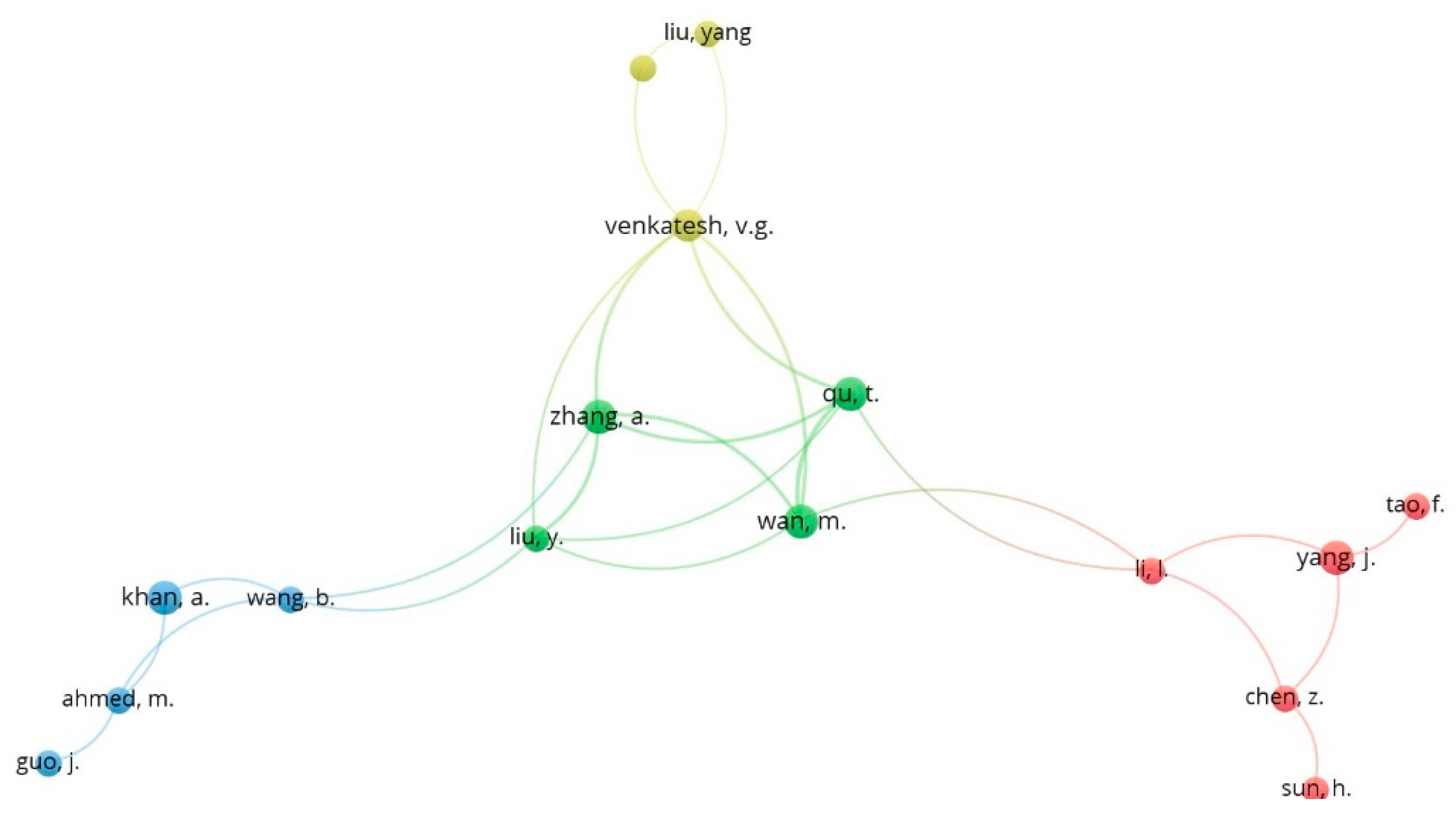
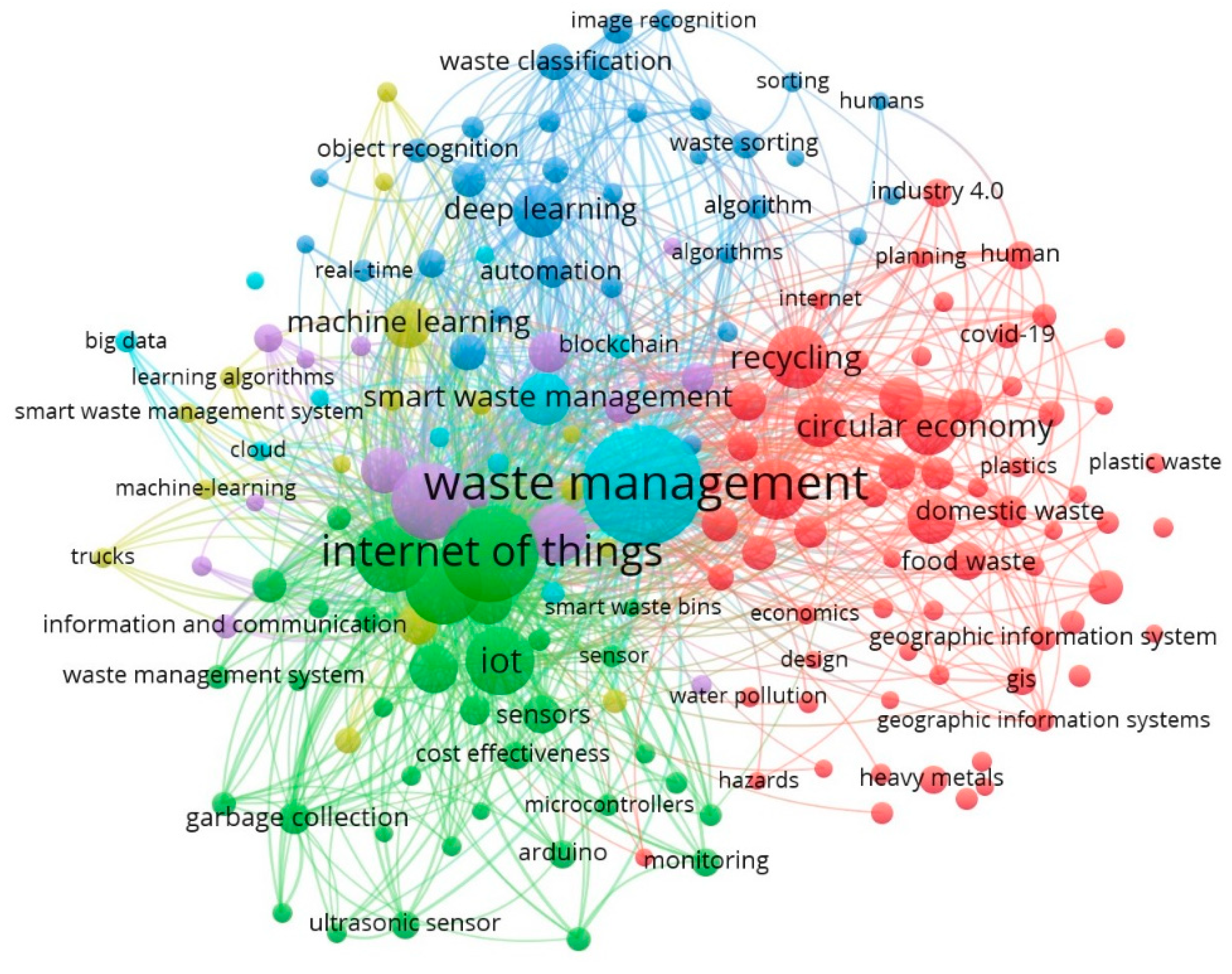
3.1. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1. Previous Research Demographics
3.2. Waste Types in Smart Household Waste Management System
3.3. Waste Managemen Process Type
3.3. Features of Smarrt Household Waste Management
3.4. Data Managed by Smart Household Waste Management System
3.5. Stakeholders Involved in Smart Household Waste Management System
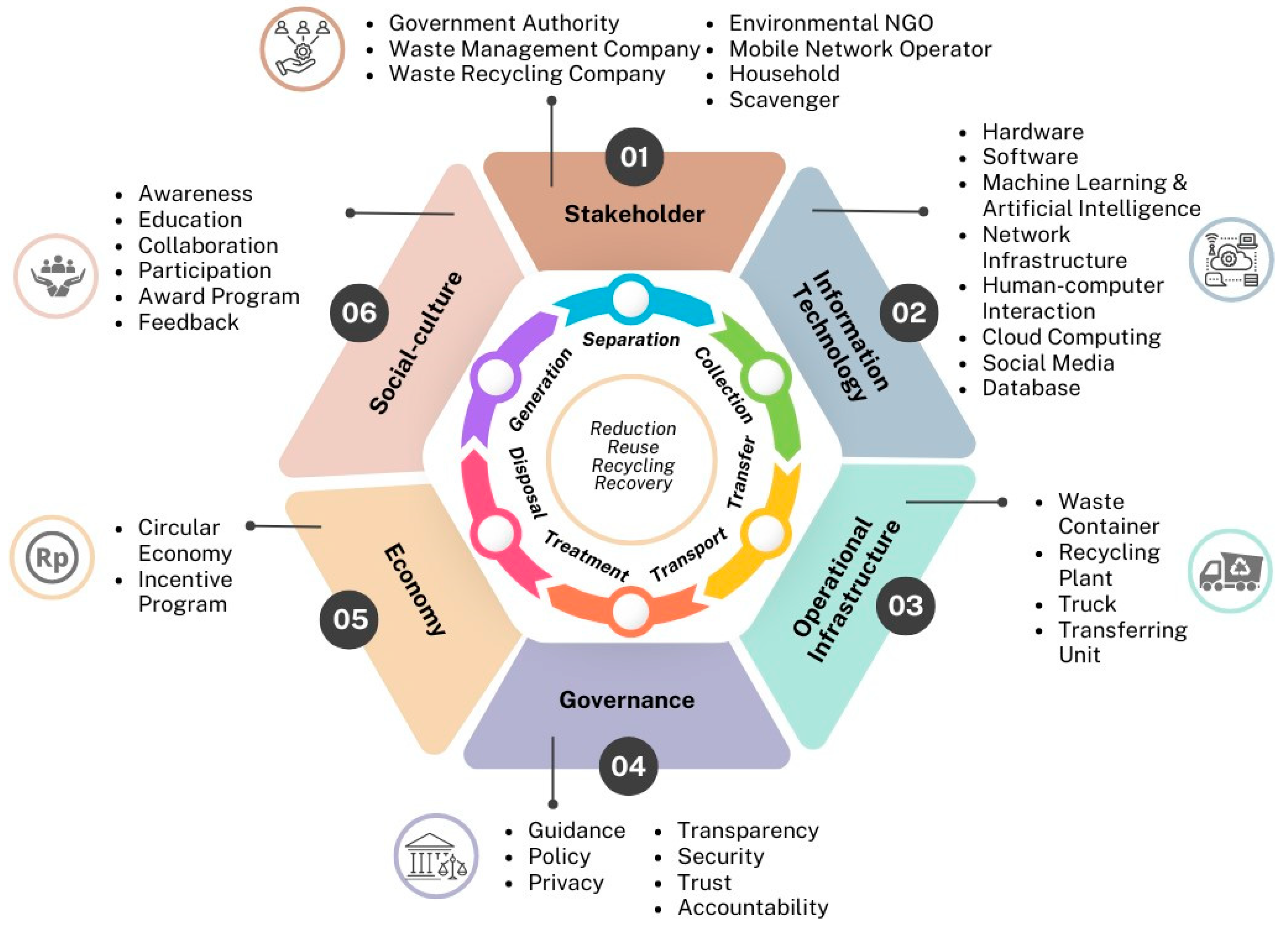
3.6. Frameworks for Smart and Integrated Household Waste Management System
3.6.1. Information Technology Dimension
3.6.2. Operational Infrastructure Dimension
3.6.3. Governance Dimensions
3.6.4. Economy Dimensions
3.6.1. Social-Culture Dimensions
3.6.4. Validation Results of the Smart and Integrated Household Waste Management System Framework
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Critical Appraisal Criteria
| Criteria | Addressed bias/element of external validity |
|
The study context should identify household, domestic, or family waste |
|
The study should identify data about the waste managed in smart waste management |
|
The study should identify the category of business processes supported by smart waste management. The Integrated Solid Waste Management (ISWM) framework identifies the business process category |
|
Show components of smart waste management architecture: Sensors and IoT Devices, Data Collection and Communication, Data Processing and Analytics, Cloud-Based Platform, Machine Learning and AI, Routing and Scheduling Optimization, User Interfaces, Alerts and Notifications, Integration with Fleet Management, Energy Management and Sustainability, Security and Privacy, Remote Management and Updates, Feedback and Continuous Improvement, Reporting and Analytics, Regulatory Compliance, Incentive Programs |
|
The study identifies stakeholders involved in the system, such as households, governments, waste management companies, scavengers |
Appendix B. Features of Smart Household Waste Management System
|
Process: Reduction |
|
Process: Reduction, Reuse, Recycling, and Recovery |
|
Process: Separation |
|
Process: Separation & Collection |
|
Process: Collection |
Process: Collection & Transport
|
|
Process: Transfer & Transport |
|
Process: Generation Predict the amount of waste in a certain period [14,15,20] |
|
Process: Treatment |
|
Process: Disposal |
References
- Tang, D.; Cai, X.; Nketiah, E.; Adjei, M.; Adu-Gyamfi, G.; Obuobi, B. Separate Your Waste: A Comprehensive Conceptual Framework Investigating Residents’ Intention to Adopt Household Waste Separation. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2023, 39, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Cheng, S.; Shi, R. Decision-Making Behavior of Rural Residents’ Domestic Waste Classification in Northwestern of China ——Analysis Based on Environmental Responsibility and Pollution Perception. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 326, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knickmeyer, D. Social Factors Influencing Household Waste Separation: A Literature Review on Good Practices to Improve the Recycling Performance of Urban Areas. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhullah, W.; Imran, N.I.N.; Ismail, S.N.S.; Jaafar, M.H.; Abdullah, H. Household Solid Waste Management Practices and Perceptions among Residents in the East Coast of Malaysia. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Deng, X. Can the Implementation of Household Waste Classification Mitigate Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Beijing? A Comprehensive Analysis of Recent Trends and Future Scenarios. Heliyon 2023, 9, e23132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations SDGs Report 2023. Sustain. Dev. Goals Rep. 2023 Spec. Ed. 2023, 80.
- Anjum, M.; Shahab, S.; Umar, M.S. Smart Waste Management Paradigm in Perspective of IoT and Forecasting Models. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2022, 29, 34–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razip, M.M.; Savita, K.S.; Kalid, K.S.; Ahmad, M.N.; Zaffar, M.; Abdul Rahim, E.E.; Baleanu, D.; Ahmadian, A. The Development of Sustainable IoT E-Waste Management Guideline for Households. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Gumabay, M.V.N. Smart Household Waste Classification System Using Artificial Intelligence. Proc. - 2022 5th Int. Conf. Adv. Electron. Mater. Comput. Softw. Eng. AEMCSE 2022. [CrossRef]
- Blazquez, C.; Paredes-Belmar, G. Network Design of a Household Waste Collection System: A Case Study of the Commune of Renca in Santiago, Chile. Waste Manag. 2020, 116, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janela, J.; Mourão, M.C.; Santiago Pinto, L. Arc Routing with Trip-Balancing and Attractiveness Measures — A Waste Collection Case Study. Comput. Oper. Res. 2022, 147, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjoseputro, Y.; Julianto, E.; Handarkho, Y.D.; Ritonga, Y.I.T. Design and Implementation of Smart Waste Recycling Bin for the Household Environment Based on IoT. Sens. Rev. 2020, 40, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edderkaoui, R.; Khomsi, D.; Hamidi, A.; Baiti, H.B.; Souidi, H.; Elhachmi, D.; Aqil, M. Application of Analytical Hierarchy Process and GIS to Analyse Management Plans for Household and Similar Waste in Marrakech Prefecture, Morocco. Proc. - 2020 IEEE Int. Conf. Moroccan Geomatics, MORGEO 2020. [CrossRef]
- Cubillos, M. Multi-Site Household Waste Generation Forecasting Using a Deep Learning Approach. Waste Manag. 2020, 115, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namoun, A.; Hussein, B.R.; Tufail, A.; Alrehaili, A.; Syed, T.A.; Benrhouma, O. An Ensemble Learning Based Classification Approach for the Prediction of Household Solid Waste Generation. Sensors 2022, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijah, U.L.M.; Abeygunawardhana, P.K.W. Smart Waste Segregation for Home Environment. ICARC 2023 - 3rd Int. Conf. Adv. Res. Comput. Digit. Transform. Sustain. Dev. [CrossRef]
- Sallem, R.; Serbaji, M.M.; Alamri, A.M.; Kallel, A.; Trabelsi, I. Optimal Routing of Household Waste Collection Using ArcGIS Application: A Case Study of El Bousten District, Sfax City, Tunisia. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Liu, X. Designing a Smart Incentive-Based Recycling System for Household Recyclable Waste. Waste Manag. 2021, 123, 142–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crome, C.; Graf-Drasch, V.; Hawlitschek, F.; Zinsbacher, D. Circular Economy Is Key! Designing a Digital Artifact to Foster Smarter Household Biowaste Sorting. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, X.C.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; La, D.D.; Kumar, G.; Rene, E.R.; Nguyen, D.D.; Chang, S.W.; Chung, W.J.; Nguyen, X.H.; Nguyen, V.K. Development of Machine Learning - Based Models to Forecast Solid Waste Generation in Residential Areas: A Case Study from Vietnam. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, A.Z.Z.; Othman, M.F.I.; Hassan, A.; Murdianingsih, Y.; Suryadi, U.T.; Faizal, M. LoRa-Based Smart Waste Bins Placement Using Clustering Method in Rural Areas of Indonesia. Int. J. Adv. Soft Comput. its Appl. 2022, 14, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.D.; Kang, H.; Ilankoon, I.M.S.K.; Chong, C.Y. Electronic Waste Collection Systems Using Internet of Things (IoT): Household Electronic Waste Management in Malaysia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, H.; Wan, X.; Skitmore, M.; Sun, H. An Intelligent Waste Removal System for Smarter Communities. Sustain. 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatimah, Y.A.; Govindan, K.; Murniningsih, R.; Setiawan, A. Industry 4.0 Based Sustainable Circular Economy Approach for Smart Waste Management System to Achieve Sustainable Development Goals: A Case Study of Indonesia. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and Explanation. 2015, 7647, 1–25. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols ( PRISMA-P ) 2015 Statement. 2015, 4, 1–9. 4. [CrossRef]
- Kohl, C.; Mcintosh, E.J.; Unger, S.; Haddaway, N.R.; Kecke, S.; Schiemann, J.; Wilhelm, R. Online Tools Supporting the Conduct and Reporting of Systematic Reviews and Systematic Maps : A Case Study on CADIMA and Review of Existing Tools. Environ. Evid. 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry Organization Available online:. Available online: https://www.menlhk.go.id/profile/organization/ (accessed on 26 March 2024).
- Barnett-Page, E.; Thomas, J. Methods for the Synthesis of Qualitative Research: A Critical Review. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2009, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry Waste Management Performance Achievements Available online:. Available online: https://sipsn.menlhk.go.id/sipsn/ (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Maghsoudi, M.; Shokouhyar, S.; Khanizadeh, S.; Shokoohyar, S. Towards a Taxonomy of Waste Management Research: An Application of Community Detection in Keyword Network. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 401, 136587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargar, T.I.; Alam, P.; Khan, A.H.; Alam, S.S.; Abutaleb, A.; Abul Hasan, M.; Khan, N.A. Characterization of Municipal Solid Waste: Measures towards Management Strategies Using Statistical Analysis. J. Environ. Manage. 2023, 342, 118331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeabai, N.; Siripaiboon, C.; Taweengern, K.; Buttanoo, C.; Sujirapatpong, W.; Yimyam, D.; Takahashi, F.; Areeprasert, C. The Integrated Study of the Effects of Infographic Design on Waste Separation Behavior and the Behavioral Outcome Implementation on Waste Composting. Waste Manag. 2023, 169, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.M.; Ukundimana, Z.; Wamyil, F.B.; Yusuf, A.A.; Telesphore, K. Quantification and Characterization of Solid Waste Generated within Mulago National Referral Hospital, Uganda, East Africa. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023, 7, 100334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Li, L. Migration and Transformation of Main Components during Perishable Waste Bio-Drying Process. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 319, 115720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurkadem, K.; Karymsakova, N.; Mansurova, M. Disposal of Solid Household Waste Using Computer Vision. 2023 IEEE Int. Conf. Smart Inf. Syst. Technol. 2023, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamnenko, J.; Kurdecha, V.; Gvozdetska, N. Domestic Solid Waste Disposal Logistic Optimization Using Internet of Things Technologies. UkrMiCo 2021 - 2021 IEEE Int. Conf. Inf. Telecommun. Technol. Radio Electron. Proc. [CrossRef]
- Benezzine, G.; Zouhri, A.; Koulali, Y. AHP and GIS-Based Site Selection for a Sanitary Landfill: Case of Settat Province, Morocco. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Farooque, M.; Zhong, R.Y.; Zhang, A.; Liu, Y. Internet of Things (IoT) -Enabled Accountability in Source Separation of Household Waste for a Circular Economy in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 300, 126773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L. Design and Development of Intelligent Community Management Service Platform Integrating Garbage Image Recognition and Classification. Int. Conf. Appl. Mach. Learn. Des. 2022, 4th. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Li, S.; Xu, W.; Duan, X. A Household Garbage Classification and Collection Device Based on Machine Vision and Deep Learning. 2022 4th Int. Conf. Robot. Comput. Vision, ICRCV 2022. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yang, J.; Yu, K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B.; Zheng, H. Evaluation of a Data Driven Intelligent Waste Classification System for Scientific Management of Garbage Recycling in a Chinese Community. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 87913–87924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.Y.; Han, H.; Cheng, K.M.; Koo, A.C.; Yussof, S. ESS-IoT: The Smart Waste Management System for General Household. Pertanika J. Sci. Technol. 2023, 31, 311–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. An Intelligent Waste-Sorting and Recycling Device Based on Improved EfficientNet. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Li, Q. Design of Voice Recognition of Intelligent Household Waste Classification System. 2022, 113. [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Zhang, F. Design of Intelligent Household Separated-Waste Containers Based on Deep Learning. 5th Int. Conf. Intell. Robot. Control Eng. IRCE 2022 2022, 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, M.; Qu, T.; Huang, M.; Li, L.; Huang, G.Q. Cloud-Based Product-Service Systems Platform for Household Solid Waste Classification Management. IET Collab. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 2, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, S.; Singh, P.; Yadav, P.; Singh, K.K. Household Waste Management System Using IoT and Machine Learning. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 167, 1950–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, S.; MacHado, S. IoT Based Automatic Waste Segregator. 2019 6th IEEE Int. Conf. Adv. Comput. Commun. Control. ICAC3 2019 2019, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneswari, M.; Tansin, K.; Ahamed, S.T.; Ram, N.T.S.; Prasath, S.V. Internet of Things Based Intelligent Waste Segregation and Management System for Smart Home Application. Proc. Seventh Int. Conf. Commun. Electron. Syst. (ICCES 2022).
- Jayanth, S.; Jayalakshmi, C.; Parthive, M.; Chandra Kala, V.; Uhasushma, B. An Android Application for Smart Garbage Monitoring System Using Internet of Things (IoT). Proc. - 7th Int. Conf. Comput. Methodol. Commun. ICCMC 2023, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Crespo, J.; Álvarez-Mendoza, C.I.; Soto, M.; Amaya-Rivas, J.L. Quantification and Mapping of Domestic Plastic Waste Using GIS/GPS Approach at the City of Guayaquil. Procedia CIRP 2022, 105, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Sheng, B.; Li, P.; Yang, P.; Feng, D.D.; Qi, J. Automatic Detection and Classification System of Domestic Waste via Multimodel Cascaded Convolutional Neural Network. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informatics 2022, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, F.; Papetti, A.; Rossi, M.; Germani, M. Smart Strategies for Household Food Waste Management. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 200, 887–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Cao, X.; Huang, L.; Zou, L.; Yang, S. Research on Computer Vision-Based Waste Sorting System. 2020 5th Int. Conf. Control. Robot. Cybern. CRC 2020 2020, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, I.J.; de Castro Neto, M.; Pinheiro, F.L. Bringing Trust and Transparency to the Opaque World of Waste Management with Blockchain: A Polkadot Parathread Application. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 182, 109347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letelier, C.; Blazquez, C.; Paredes-Belmar, G. Solving the Bin Location–Allocation Problem for Household and Recycle Waste Generated in the Commune of Renca in Santiago, Chile Waste. Waste Manag. Res. 2022, 40, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y. Sen; Mukherjee, S. A Reward-Based Framework for Recovery and Utilization of Recyclable Wastes Using Blockchain. Proc. - 2022 OITS Int. Conf. Inf. Technol. OCIT 2022. [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, T.; Hernawati, E.; Aditya, B.R. IoT-Based Waste Height and Weight Monitoring System. J. Comput. Sci. 2021, 17, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anschütz, J.; IJgosse, J.; Scheinberg, A. Putting Integrated Sustainable Waste Management into Practice; 2004; ISBN 9076639051.
- Mir, I.S.; Cheema, P.P.S.; Singh, S.P. Implementation Analysis of Solid Waste Management in Ludhiana City of Punjab. Environ. Challenges 2021, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatuschtschenko, E. Electronic Waste in China, Japan, and Vietnam: A Comparative Analysis of Waste Management Strategies. Vienna J. East Asian Stud. 2018, 9, 29–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Human Settlements Programme Solid Waste Management in the World’s Cities – Water and Sanitation in the World’s Cities 2010; 2010; Vol. 21; ISBN 9781849711692.
- Wilson, D.C.; Velis, C.A.; Rodic, L. Integrated Sustainable Waste Management in Developing Countries. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Waste Resour. Manag. 2013, 166, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lühr Sierra, D. V.; Balinos, M.; Gatica, J.; Lagomarsino, C. Ciudad Limpia Valdivia: A Mobile and Web Based Smart Solution Based on Foss Technology To Support Municipal And Household Waste Collection. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. - ISPRS Arch. 2021, 46, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benezzine, G.; Zouhri, A.; Koulali, Y. Use of Gis for Digital Mapping and Spatial Analysis of Landfills: Case of the Settat Province in Morocco. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phiri, G.; Trevorrow, P. Sustainable Household Food Management Using Smart Technology. Conf. Proc. 2019 10th Int. Conf. Dependable Syst. Serv. Technol. DESSERT 2019 2019, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobeva, D.; Scott, I.J.; Oliveira, T.; Neto, M. Adoption of New Household Waste Management Technologies: The Role of Financial Incentives and pro-Environmental Behavior. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Criteria | Category | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | The physical condition of the waste | Solid waste | |
| |||
| 2. | The risk level of waste | Hazardous waste | Hazardous waste [22,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47] |
| Electronic waste | Electronic waste [8] | ||
| 3. | Composition of waste materials | Inorganic waste | |
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| Organic waste | |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| |||
| 4. | Recovery feasibility of waste | Recyclable waste | Recycled waste [9,10,13,18,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,56,57,58,59] |
| Non-recyclable waste |
|
||
| |||
|
| No | Process | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Separation | [9,19,36,40,41,43,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,53,55,59] |
| 2. | Collection | [10,18,21,22,52,56,57,65,66] |
| 3. | Separation & collection | [16,39,42,45,58] |
| 4. | Transfer | [17] |
| 5. | Transport | [17] |
| 6. | Collection & transport | [11,37] |
| 7. | Treatment | [12] |
| 8. | Disposal | [13] |
| 9. | Generation | [14,20] [15] |
| 10. | Reduction | [8,54] [67] |
| 11. | Reuse | [8] |
| 12. | Recycling | [8] |
| 13. | Recovery | [8] |
| Actor’s role |
|---|
Process: reduction, reuse, recycling, and recovery
|
| Actor’s role |
|---|
Process:separation
|
| Actor’s role |
|---|
Process:separation and collection
|
| Actor’s role |
|---|
Process: Collection
|
| Actor’s role |
|---|
|
Process: collection and transport |
| Actor’s role |
|---|
|
Process: generation |
| Description | Devices | |
|---|---|---|
| Subdimension: hardware | ||
|
Digital camera | |
|
Sensor | |
| Subdimension: software | ||
|
Alert and notification | |
|
MILP/MCLP algorithm | |
|
Data analytic | |
|
GIS | |
|
Mobile & web application | |
|
Algoritma MCARP | |
|
Blockchain | |
|
Voice recognition | |
|
Gamification | |
| Subdimension: machine learning & AI | ||
|
CNN, MC-CNN, Lightweight CNN, GECM-EfficientNet, KNN, data recognition model | |
|
LSTM neural network, RF, KNN, ensemble learning | |
| Subdimension: network infrastructure | ||
|
QR code, barcode, NFC reader with communication node | |
|
NB-IoT, GSM, LoRA, Wi-Fi, smart gateway, Bluetooth | |
| Subdimension: human-computer interaction | ||
|
Mobile or web application prototype, gamification | |
| Subdimension: cloud computing | ||
|
Application platforms based on cloud computing | |
| Subdimension: social media | ||
|
Telegram | |
| Subdimension: database | ||
|
Cloud-based database | |
| Description | Devices |
|---|---|
|
Subdimension: Waste container The availability of waste containers with specific characteristics can make it easier for household actors to manage waste |
RFID-based key, user identity via QR code/RFID |
|
Subdimension: Recycling plant Availability of industrial facilities to process waste into new products through waste recycling activities |
Recycling facilities with location and product status data |
|
Subdimension: Transferring unit A tool can be used to move waste from one place to another |
Conveyor |
|
Subdimension: Truck Availability of tools to transport waste from one location to another |
Waste transport trucks |
| Description | Devices |
|---|---|
|
Subdimension: Guidance There are guidelines for managing waste sustainably |
Guidelines for sustainable waste management |
|
Subdimension: policy Implement policies made by the government for all stakeholders |
Waste management policy |
|
Subdimension: Privacy Availability of efforts to protect personal data from users when using the system |
Using pseudonyms when making transactions |
|
Subdimension: Transparency Availability of information transparency of waste management carried out by household actors and connected to the policy of giving penalties and awards |
Transparency of user recycling performance |
|
Subdimension: Security There are efforts to prevent unwanted user behavior, such as DDos or spam |
Economic security through charging transaction fees |
|
Subdimension: Trust There is an element of trust in information disclosure in the system |
Using blockchain to increase trust |
|
Subdimension: Accountability Availability of responsibility from stakeholders for waste management performance |
Accountability of waste collectors and household actors |
| Description | Devices |
|---|---|
|
Subdimension: Circular economy There is a strategy to reuse recycled waste into resources |
Implementation of circular economy strategies in digital applications |
|
Subdimension: Incentive program There is a program to provide rewards and punishments for the recycling performance of household actors |
Implementation of rewards and punishments through blockchain |
| Description | Devices |
|---|---|
|
Subdimension: Awareness There are efforts to support the level of awareness of waste management |
Use of AI to support awareness |
|
Subdimension: Education There is a program to increase household knowledge regarding types of waste, how to manage it, and how to use smart systems |
Tips and information features |
|
Subdimension: Collaboration Various stakeholders have made collaborative efforts to solve household waste problems |
Collaboration in sharing information and monitoring household behavior |
|
Subdimension: Participation There is involvement of household actors to play a role in waste management |
A system with fair point acquisition and a system that protects personal data |
|
Subdimension: Award program There is a program that can encourage the involvement of household actors in managing their waste |
Publication of winners' names |
|
Subdimension: Feedback Availability of mechanisms to provide input or criticism of household waste management performance, services, and policies |
Feedback on performance, services, and management policies |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





