1. Introduction
1.1. Nanoscale Messengers: Extracellular Vesicles and Exosomes
The immune system uses inflammation as a temporary defensive mechanism against infections and other triggers including tissue damage. Inflammation may occasionally last longer and result in chronic illness. Numerous illnesses, including diabetes, autoimmune disorders, obesity, chronic respiratory conditions, and cancer, have an etiology and mortality rate that are influenced by chronic inflammation. Common anti-inflammatory medications, such corticosteroids and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs), may generally be used to treat inflammation successfully. However, chronic use of NSAIDs or corticosteroids, especially in older persons, is linked to negative side effects such as diabetes, osteoporosis, stomach ulcers, renal failure, stroke, heart failure, and hypertension. Consequently, there is a growing demand for substitute pharmaceutical treatments to treat inflammation with fewer side effects (Emmanuela et al., 2024).
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) are categorized according to their physical characteristics and composition into many groupings, including microvesicles, exosomes, and apoptotic bodies. Exosomes, with a diameter ranging from 30 to 100 nm, are intraluminal vesicles (ILV) of multivesicular bodies (MVB). Advanced proteomic approaches in conjunction with high resolution electron microscopy analysis revealed the makeup of exosomes released from various cells (Mashouri et al., 2019). EVs have recently garnered significant attention in research, owing to their versatile involvement in numerous biological processes.
Exosomes are the tiniest category of EVs, smaller than micro vesicles, apoptotic bodies, and oncosomes, with a size range of 30 to 100 nm (Sarasati et al., 2023). These are double-layered vesicles, and the lipid bilayer that emerges from them is identical to the bilayer of the cell. At first, it was thought that exosomes were only waste products of cells that were produced in order to maintain cellular homeostasis and had no appreciable effect on nearby cells or tissues (Burtenshaw et al., 2022). Through this unique mechanism, which elicits a response and serves as a channel for intercellular communication, these cargos can be transferred to both proximal and distal cells and tissues.
Moreover, their payload is known to vary widely and is dependent upon the cell source. The discovery of exosomes in the 1980s revealed that they were produced by an internal process that took place inside the cell's endosomal compartment. To create multivesicular bodies (MVBs), this process begins with the commencement of inward membrane budding from an early endosome into the luminal compartment. Later, intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) within large MVBs are formed as a result of late endosomal membrane invagination (Johnstone et al., 1987).
1.2. Classification of Exosomes
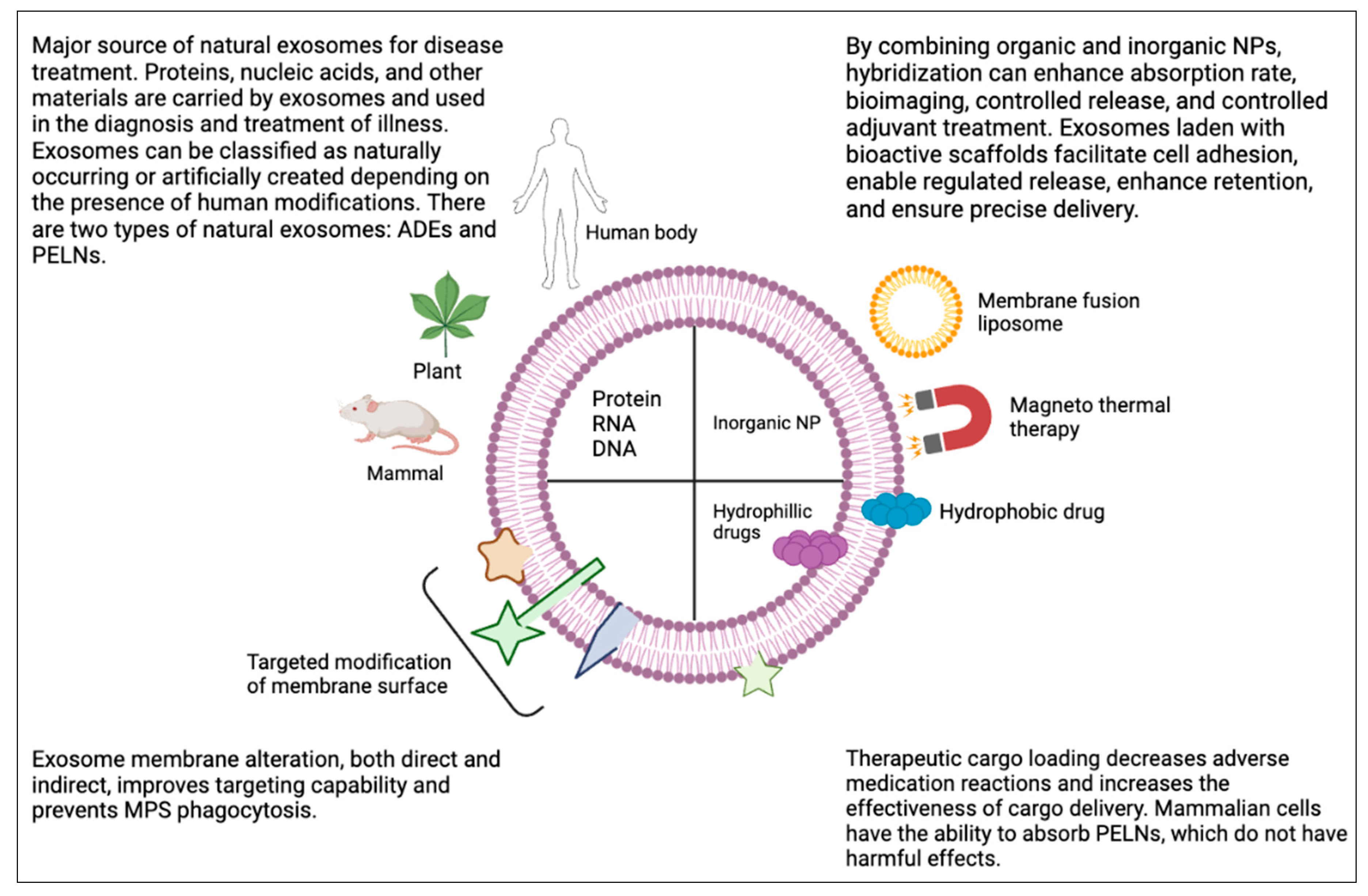
There is currently disagreement about how to categorize exosomes based on their properties and biological roles (Yi et al., 2023a). Based on the existence of manmade alterations, exosomes can be categorized as either natural or engineered. Animal-derived exosomes (ADEs) and plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PELNs) are two categories for natural exosomes. Animal-derived exosomes, which range in diameter from 30 to 150 nm, may be produced from nearly every type of cell, including cancer and normal cells, and they can be discharged into a wide range of bodily fluids, such as milk, bile, saliva, plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, seminal fluid, and malignant ascites (Kok & Yu, 2020). Research on PELNs to far has mostly concentrated on exosomes made from a variety of dietary items, such as broccoli, ginger, grape and grapefruit (Yi et al., 2023a).
1.2.1. Need for PLENs over ADEs
Mammalian exosomes have been intensively investigated in recent decades, and they undoubtedly constitute a melting pot of fresh scientific findings, particularly new understanding about the intricate and interwoven way our bodies operate. Exosomes are known to move throughout the body following their discharge from a tissue or compartment. This most likely reflects a dynamic network in which our bodily systems and compartments are always interacting to maintain a dynamic balance (Logozzi et al., 2021). However, using human exosomes to carry therapeutic compounds has drawn a lot of criticism. On the one hand, this results from the restricted large-scale synthesis of individual exosomes from healthy human cells (Logozzi et al., 2019). Conversely, data suggests that human exosomes could be one of our body's scavenging systems. Moreover, they frequently carry potentially hazardous substances including foreign nuclear acids, tumor-derived chemicals and transmissible agents. Thus, extracellular vesicles generated from plants are being used in addition to manufactured nanoparticles, as they seem safer and have similar structures and functions, such as that of an inherent interspecies transport system (Logozzi et al., 2022). Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles (PELNs) may be a preferable option to animal-derived exosomes (ADEs) because to their ubiquitous availability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of use. PELNs have the ability to facilitate interspecies communication by the transfer of diverse payloads, including proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, from plant tissues to mammalian tissues. PELNs may also significantly disrupt the dynamic balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory actions, helping to preserve the cellular immune microenvironment's equilibrium (Yi et al., 2023b). Plant-derived edible nanoparticles (PDENs) are vesicles found in the paramural region of plants that resemble their mammalian counterparts in both structure and function (Akuma et al., 2019). Many research conducted in the last few years have demonstrated that plant exosomes may improve the stability and insolubility of macromolecular medicines, prolong blood circulation, and enhance drug accumulation in target cells—all of which contribute to improved medication effectiveness (Wiklander et al., 2019). According to recent research, the application of nanoscale particles like exosomes in immunotherapy against cancer may offer a practical foundation for the creation of innovative cancer vaccines by triggering the immune system to identify and eliminate cancer cells using antigen-presenting cell technology. Incorporating nanotechnology with exosome engineering is emerging as a novel strategy for the creation of cancer vaccines. PELNs are excellent candidates for the creation of cancer vaccines because their biosafety surpasses that associated with other nanoparticles and they show promise as therapeutic nanocarriers (Cao et al., 2023)
Figure 1.
A brief overview of the primary sources and uses of natural exosomes, along with the primary methods of exosome distribution and engineering modification.
Figure 1.
A brief overview of the primary sources and uses of natural exosomes, along with the primary methods of exosome distribution and engineering modification.
2. Insights into Biogenesis
Research on Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanoparticles (PELNs) has been evolving since 1967, revealing their origin in multivesicular bodies and their subsequent release via plasmalemma fusion. PELN biogenesis involves the trans-Golgi network, evolving into multivesicular endosomes (MVBs), where RNAs, lipids, and DNA are selectively incorporated into intraluminal vesicles (ILVs). After vesicle budding, PELNs are released, either directly from the plasma membrane or through dysregulated intracellular plasma membrane-connected compartments. Exosomes, generated via endocytic pathways, are packed with carefully controlled cargo, facilitated by the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT). ESCRT-III, an essential component, triggers exosome release through membrane-binding spirals and ATPase activity. The similarities between ADEs and PELNs highlight the significance of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in their structures, influencing their cellular interactions. Understanding PELN biogenesis provides valuable insights for harnessing these nanoparticles in targeted drug delivery systems.
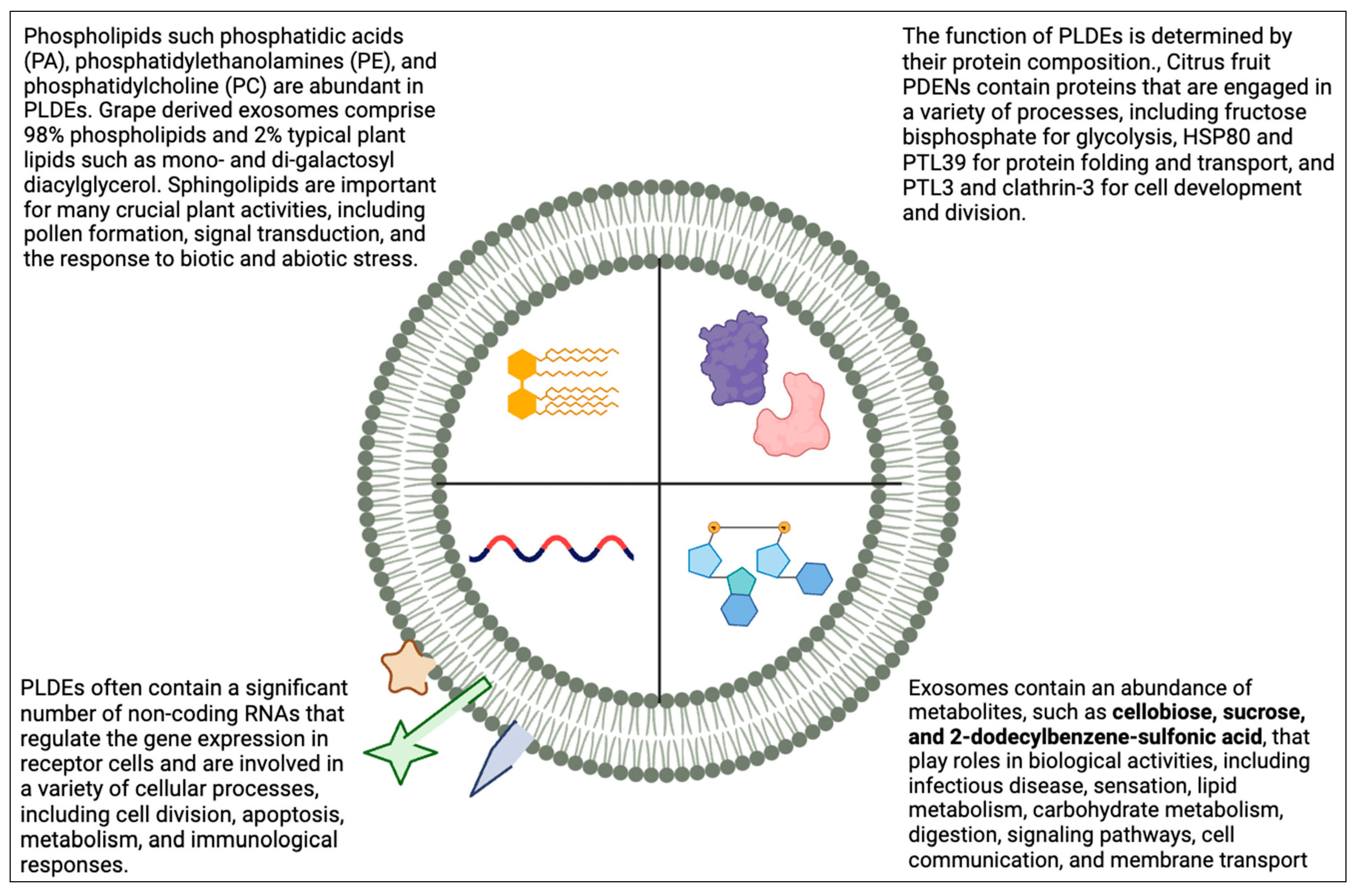
PELNs biogenesis is a tightly controlled process. PELNs are released from the plasma membrane as vesicular endosomes and enter the cell's interior following vesicle budding. Exosomes can proliferate from the plasma membrane in three different ways. Initially, when vesicles grow, individual endosomes transform into fully developed multi-vesicular bodies (MVBs), which release exosomes upon the fusion of the plasma membrane. Second, exosomes are directly released by vesicles that budding from the plasma membrane. Thirdly, they emerge right away from the dysregulated compartments associated to the intracellular plasma membrane (IPMC). These three techniques have varying levels of early effectiveness (X. Wei et al., 2023). Exosomes are produced via the endocytic pathway when intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) within Multivesicular Bodies (MVBs) are produced as a result of membrane invagination during late endocytosis (Y. Zhang et al., 2019). In vivo lipid droplets (ILVs) are created when the early endosomes fuse with the neighbouring membrane layer. Exosomes are enclosed in MVBs, where they eventually merge with the plasma membrane to release their contents into the extracellular milieu (Pegtel & Gould, 2019). Exosomes' contents are packed in a well regulated way rather than randomly, which means that the proteins within them regularly undergo post-translational modifications such ubiquitination (Joshi et al., 2020). Exosomes are produced in huge numbers by mammalian cells, and the cell mechanism involved in this process is well characterized. The cargo is sorted and transferred into the intraluminal compartments in large part by the endosomal sorting complex required for transport (ESCRT). ESCRT is made up of four complexes, ESCRT 0, -I, -II, and -III. Each complex is made up of many unique proteins. Since ESCRT-0 binds to and aggregates ubiquitinylated proteins, it is essential for removing them from the cell membrane's surface. The two molecules that make up ESCRT-0 are the Signal Transducing Adaptor Molecule (STAM), which may bind to the ubiquitinated loading, and Hepatocyte Growth-factor-regulated tyrosine kinase substrate (Hrs). Additionally, through its interaction with the ESCRT-1 protein TSG101, it delivers the complex to the location. The cargo is sorted into MVBs by the heterotetrametric complex ESCRT-1, which also interacts with the ESCRT-II complex to concentrate the cargo proteins. Moreover, the proteins EAP45, EAP30, and EAP 20 comprise the hetero-tetramer ESCRT-II. The release of exosomes is caused by the most important functional ingredient, ESCRT-III, which is an oligomer of the charged multivesicular body protein (CHMP). It also triggers the production of a similar ATPase called VpS4p/SKD1, which induces neck constriction and the release of the vesicle buds from the membrane. These spirals bind to membranes. This ATPase provides the energy required for the entire process of exosome release. When the vesicles attach themselves to a certain subset of SNAREs (N-ethylmaleimide Sensitive Factor Attachment Protein Receptors), they are released (Gurung et al., 2021). Animal exosomes' architectures resemble those of PELNs. PELNs primarily consist of lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The primary factor influencing the specificity of PELNs is their cellular source. These three chemicals are crucial, and each exosome component serves a specific purpose. The absorption process will typically be determined by the protein profiles. In recipient cells, nucleic acids function, and lipids are required for efficient cellular absorption. (X. Wei et al., 2023).
2.1. Generation and Preparation of PELNs
Few studies have examined the production of PELNs, despite the fact that exosomes generated from mammalian cells have been the subject of substantial research to date. The primary biogenesis process of PELNs is thought to be MVB-mediated secretion. When MVBs and the plasma membrane merge in plants, ILVs are released into the extracellular space (An et al., 2007). Furthermore, ELNs are located inside the cell wall. Nevertheless, it is still unknown how ELNs get through the cell wall. PELN production may include additional routes due to the existence of distinct components like the vacuole and cell wall. Currently, size-exclusion chromatography, field flow fractionation, immunoaffinity enrichment method, and co-precipitation, ultrafiltration, and ultracentrifugation are employed in the preparation of PELNs. A few novel technologies are being utilized (Yi et al., 2023a). PELN isolation requires the juice of fresh plant materials, such as fruits, roots, stems, leaves, and bark, which are crushed or pressed. Differential ultracentrifugation coupled with density gradient centrifugation is the most widely used technique for PELN separation and purification. The partitioning principle is determined by particle size and density; during centrifugation, various particle sizes sediments at varying rates (Berger et al., 2020). Once cell debris has been removed, the juice is centrifuged three times in short succession: once at a slower rate (500–3000grams for 10–20 min), once at a medium rate (10,000g for 20–30 min), and once at an elevated rate (100,000–150,000g for 1-2 hours) to collect pellets. The properties of a particular plant species determine the optimal centrifugation speed and duration during actual operation. Denser particles would settle while less dense particles would float, according to the basic principle of density gradient ultracentrifugation. The crude exosome pellets, tainted with accumulated proteins, nucleic acids, and other extracellular vesicles, are further processed by discontinuous sucrose gradient centrifugation (8 %/15 %, 30%, 45%, and 60%) after being ultracentrifuged and centrifuged at 150,000g for 1-2 hours (Cao et al., 2019). An ELN is often defined as the band that is collected within the thirty percent and forty-five percent sucrose layer. When compared to extracellular leaf extracts (ELNs) made from different plant samples using the same extraction method, mammal-derived exosomes exhibit far less variation in terms of production, purity, and particle size. This variety is a result of the significant differences in plant composition and structure. (Yi et al., 2023a).
Three main factors are used to evaluate the physical properties of PELNs: morphology, size distribution, and zeta potential. Compared to exosomes originating from mammals, PELNs have a much larger particle size distribution, between 30 to 400 nm in average particle diameter. PELNs have a negative zeta potential that varies from -70 mv to practically neutral (B. Wang et al., 2014). Two widely used techniques for determining zeta potential and particle size are Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) and dynamic light scattering (DLS). By assessing the distribution of hydrodynamic diameters changed by the particle's diffusion coefficient, DLS enables a quick assessment of the size distribution and zeta potential of PELNs. One drawback of DLS that cannot be ignored is its low resolution (Bhattacharjee, 2016). The NTA method is a high-throughput, single-particle methodology with good consistency for the quantitative assessment of particle diameter and concentration. In comparison to DLS, NTA offers a greater resolution and is less susceptible to strong particle scattering. The purity of the sample can be determined by comparing the ratio of particle counts to protein concentration; a higher particle-to-protein ratio indicates more purity. Purified ginger-derived exosomes like nanoparticles (GELNs) have a particle-to-protein ratio of approximately 1.3 × 1011 P/mg, or nanoparticles per milligram of protein (Webber & Clayton, 2013). Because there is a wide range of plant species, extraction methods, and circumstances used, it is challenging to determine the cut-off particle-to-protein ratio for assessing high purity. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is used to evaluate PELNs in order to determine their particle size and morphological properties. Particle size can be identified more precisely with TEM than with NTA because it has a narrower size distribution. The physics of size measurement, which rely on the mobility of particles in solution and is influenced by surface protein composition, may help to explain some of the wider variation in particle sizes observed by NTA. TEM produces pictures of excellent quality. To imitate the cup-shaped morphology of PELNs, TEM samples must be fixed and dehydrated prior to measurement. Furthermore, photographs are captured in a vacuum. The time-consuming and technically challenging nature of TEM's procedure is another disadvantage (Yi et al., 2023a).
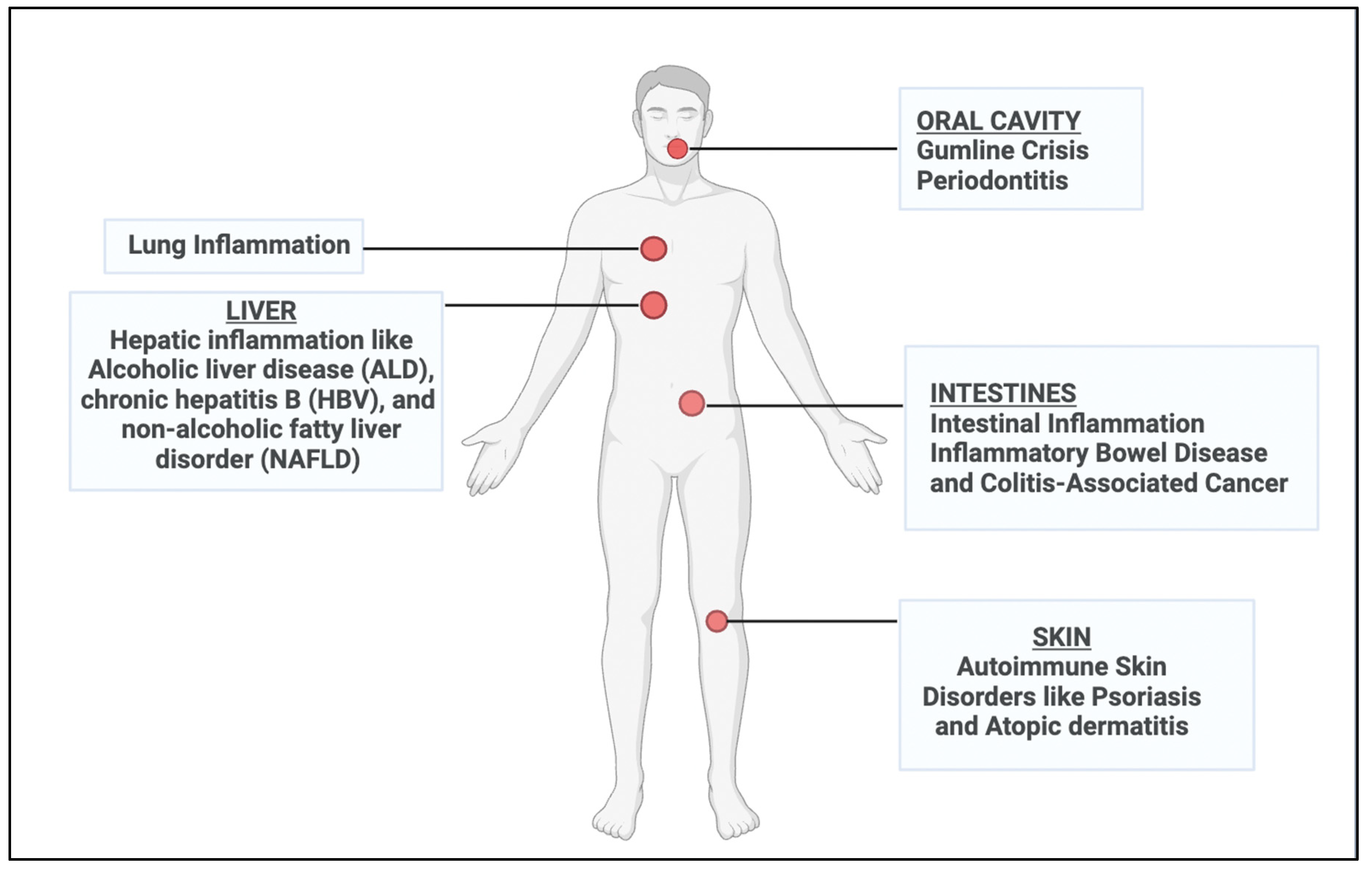
3. Novel Nanomedicine Approach at the Cusp of Therapeutic Breakthroughs in Inflammatory Disorders
3.1. Decoding the Complex Canvas of Autoimmune Skin Disorders
Psoriasis and Atopic dermatitis (AD) are two of the main autoimmune diseases that are increasingly endangering public health. Glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants, and monoclonal antibodies are often used therapeutic medications for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Nevertheless, their shortcomings include inadequate effectiveness and significant adverse reactions (Huang et al., 2023). MSC-derived EVs have been used to genetically modify target proteins and encapsulate medications that alleviate autoimmune disorders without causing adverse effects (Huang et al., 2023). Exosome-like nanovesicles produced from plant cells are also being acknowledged as the next generation of nanotherapeutics due to their advantages of low toxicity, low immunological risk, biocompatibility, low cost, and easy mass manufacture (Kim et al., 2022).
Grape exosome-like nanoparticles (GELNs) were used to test the notion and show that GELNs have special biological roles and transport characteristics. Oral administration of GELNs stimulates intestinal stem cells, shielding animals from dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. This discovery may pave the way for new avenues in food nanotechnology, including the development of innovative, cost-effective, and safe methods for using edible plant-derived nanoparticles as nanosized therapeutic agents or as an alternative drug delivery system. In the colitis model created in mice by DSS, GELNs significantly boosted the quantity of intestinal stem cells. This, in turn, significantly sped up the regeneration of the mucosal epithelium and promptly restored the intestinal architecture across the whole intestine. Moreover, Lgr5 is expressed on intestinal stem cells as well as other tissue-derived stem cells. Research indicates that intestinal stem cells expressing Lgr5 take up grape nanoparticles and multiply as a result. Thus, in theory, Lgr5+ stem cell growth driven by GELN may be used to additional illnesses where Lgr5+ stem cells are involved in the pathophysiology of the condition (Ju et al., 2013). Additionally, after administering GELNs in vitro or in vivo, there was a significant increase in the expression of genes encoding pluripotent stem cell markers, including SOX2, Nanog, OCT4, and KLF4, as well as the intestinal stem cell marker BMI1. Lgr5+ stem cells significantly contribute to homeostatic regeneration and are receptive to canonical Wnt regulation, whereas Bmi1+ stem cells play a less significant role in this process. Plant miRNA159 was shown to suppress keratinocyte proliferation and lower inflammatory cytokine production by controlling the expression of mammalian genes. This finding contributes to the increasing amount of evidence that supports plant miRNA control across species boundaries. This reinforces the increasing amount of evidence indicating that plant-active nucleic acids may enter human cells through PLEVs. Effects may also be observed from other biomolecules included in PLEVs, such as proteins and lipids. In addition, we found flavonoids, terpenes, and polysaccharides—natural metabolites—in GEVs. These are the main constituents in a lot of Chinese herbal medications, which suggests that exosomes from Chinese herbal medicines might be studied further and might serve similar purposes as extracts from Chinese herbal medicines. CX5461 was found to have an impact on keratinocytes, causing the cells to stop growing by stopping at the G2 phase. This indicates that CD4+T cells and keratinocytes can be prevented from multiplying by CX5461. Furthermore, results from animal experiments indicated that CX5461 may be employed as a therapeutic therapy for atopic dermatitis and psoriasis (Huang et al., 2023).
Recently, nanovesicle-mediated cell communication has gained popularity due to its capacity to transport various chemicals from generating cells to target cells via extracellular vesicles known as exosomes. The exosome-specific markers 79.91% HSP 70, 93.96% CD9, and 86.39% CD63 were expressed in wheat-derived nanovesicles. Cell proliferation was significantly increased in the primary human dermal fibroblast cell line (HDF), human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT), and human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in a dose-dependent manner. After being exposed to wheat exosomes for 24 hours, it was observed that HDF, HUVEC, and HaCaT cells migrated more quickly. The findings demonstrated that wheat exosomes play a crucial function in cell migration by promoting wound closure. Wheat exosomes have the capacity to significantly increase the number of branches, which increases the creation of tube-like structures. This suggests that wheat exosomes play a crucial part in the vascularization process during wound healing (Şahin et al., 2019).
3.2. Confronting Inflammatory Bowel Disease and the Looming Threat of Colitis-Associated Cancer
IBD, or inflammatory bowel disorder, is a recurrent, chronic digestive ailment that includes both ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn's disease. Current IBD therapy are somewhat limited and mostly focused on disease remission because of the complex etiology of colitis. Furthermore, it is impossible to overlook how conventional medications affect the body. Additionally, there is a correlation between IBD and colitis-associated cancer (CAC), and inflammatory cells have the capacity to generate a prodigious quantity of cytokines that facilitate the growth of tumours (Cai et al., 2022). Therapeutic medications are being delivered via both natural and synthetic dispersion systems (DDS), such as mammalian and plant-derived exosomes and liposomes and microspheres. However, the artificial nanoparticles may cause apoptosis, cell stress, inflammation, and other adverse consequences (Radmanesh et al., 2021). Exosomes from citrus and lemons have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties; exosomes from edible plants, such grapefruit, tomato, blueberries, and shiitake mushrooms, have anti-inflammatory properties and exosomes from apples and carrots may influence intestinal transporters (Y. Cai et al., 2022).
For example, TNFSF15 is expressed in a variety of organs, including myeloid cells, activated T cells, and endothelial cells. Due to its susceptibility, TNFSF15 might raise the risk of IBD by activating its receptor DR3, which in turn can trigger the release of cytokines (Richard et al., 2018). Furthermore, C1orf106 is a vulnerable gene for IBD, resulting in abnormalities in the intestinal epithelial barrier and an increased vulnerability to intestinal infections (Mohanan et al., 2018). It has been shown that miRNA21 (miR21) binds to certain mRNAs to regulate protein synthesis or start RNA cleavage. Exosomes containing miR21 derived from substance P-induced colonic epithelial cells exacerbate colitis by encouraging immune cell migration and proliferation. It might be an alternative strategy for treating IBD that prevents substance P-induced exosome production. Major cytokines like TGF-β1 have a strong immunosuppressive impact, and exosomes containing TGF-β1 may have therapeutic value for inflammatory bowel disease. Exosomes generated by DCs with the TGF-β1 gene altered can stop the progression of IBD by blocking Th17. Furthermore, the impacts of TGF-β1 inside these membrane exosome structures have also been demonstrated, indicating that exosome structure can boost TGF-β1's therapeutic potential in inflammatory bowel disease (Zhang et al., 2019). The expression of many colonic epithelial transporters was shown to be downregulated by apple-derived nanoparticles, including organic-anion-transporting polypeptide (OATP) 2B1, which is pharmacologically significant for humans since it transports the antihistaminic medication fexofenadine. APNPs inhibited the absorption of [3H] Estrone-3-sulfate as well as OATP2B1 as mRNA and protein. Subsequent research revealed that Caco-2 cells imported APNP-derived miRNAs, which then bound to the 3′-UTR of OATP2B1 gene to limit its expression. These findings suggest that food-derived NPs may be utilized to deliver big molecules to treat GI tract illnesses, in addition to the possibility that PDNVs may change the transport function of GI tract epithelial cells (Di Gioia et al., 2020). Exosomes generated from lemons have been demonstrated in recent studies to enhance lactobacillus's bile tolerance, which is critical for the formation of the microbes in the gut. The results of this study indicate that exosomes generated from lemons may also increase the stress tolerance of gut flora (Lei et al., 2021). Through the AhR/COPS8 pathway, the exosomes from edible mulberry bark can prevent colitis and hasten the intestinal mucosa's healing process (Sriwastva et al., 2022). Ginger-derived exosomes were able to encapsulate siRNA-CD98 with an encapsulation efficiency of 61 ± 8%, demonstrating the potential of ginger-derived exosomes as effective carriers of siRNA. The biological effects of siRNAs trapped in exosomes are indistinguishable in vivo. Oral delivery of siRNA-CD98/GDLV was used. The results clearly revealed the strong targeting of siRNA-CD98/GDLV to the intestine, as siRNA-CD98/GDLV maintained significant retention in the colon and ileum, but the free DIR control was only maintained in the gut. Moreover, siRNA-CD98/GDLV effectively reduced the level of inflammation and specifically decreased the level of expression of the CD98 gene in the mouse colon, treating colitis and colitis-related malignancies. In the present times, exosomes generated from plants are advancing quickly as a medicinal carrier, with a few of them even making it into clinical trials. There are still some significant obstacles to overcome before they develop into a mature DDS suitable for clinical application. The selection of appropriate plant sources and purifying processes for large-scale manufacturing require more investigation (Cai et al., 2022).
3.3. Gumline Crisis: Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an infectious dental illness that causes tooth loss and the deterioration of periodontal tissues. Dental plaque can be removed with the gold standard technique, scaling and root planning (SRP), which has a strong antibacterial impact and prevents the growth of periodontal disorders (Rosa et al., 2021). Although the indications and effectiveness of regenerative operations for stimulating osteogenesis and periodontal ligament repair are restricted (Zhang et al., 2022). Adjunctive pharmaceutical treatments have been employed in the treatment of periodontitis in order to address the shortcomings of current therapeutic techniques. PELNs possess antibacterial, immune-modulating, microbiota-modifying, and tissue-regeneration properties that may aid in the prevention and treatment of periodontitis. PELNs can be added to drug delivery systems to increase the drugs' accessibility and biological distribution, improving their therapeutic advantages against periodontitis. (Dad et al., 2021a). PELNs are more readily extracted, more readily purified, and more biocompatible than mammalian exosomes. Macrophages play a crucial role in the immune system. Macrophages' M1 and M2 polarization in periodontitis mediates the disease's onset and progression (Sun et al., 2021). M1 macrophages produce several anti-inflammatory compounds, such as TNF-α and IL-6, to eradicate germs, trigger inflammation, and elicit osteoclast activation, ultimately leading to alveolar ridge absorption. M2 macrophages, on the other hand, produce transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and IL-10, which have anti-inflammatory and thrombotic properties. They also encourage osteoblasts to produce new bone tissue. In macrophages, GELNs prevent the NLRP3 inflammasome from assembling. Furthermore, ELNs formed from ginseng reduce M2-like polarization of macrophages brought on by IL-4 and IL-13 and increase the production of cytokines linked to M1 macrophages, including TNF-α, IL-12, and IL-6 (Z. Zhang et al., 2022b). Numerous studies have indicated that ELNs produced from blueberries, carrots, ginger, grapefruit, and grapefruit have anti-inflammatory properties (Teng et al., 2021). GELNs significantly increase intestinal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, shielding animals from colitis produced by dextran sulfate sodium. ELNs produced from cabbage and red cabbage have definite anti-inflammatory properties by lowering the production of COX-2, IL-1β, and IL-6 in macrophages challenged with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Orange (Citrus sinensis)-derived ELNs modify the expression of HMOX-1, ICAM1, OCLN, CLDN1, and MLCK to reduce inflammation and repair the functional intestinal barrier (Z. Zhang et al., 2022b). Lipids in Broccoli-derived ELNs reduce gut inflammation by inducing CD11c tolerogenic dendritic cells (Deng et al., 2017). According to a recent study, PELN proteins have anti-inflammatory qualities too. Mulberry bark ELNs prevent mouse colitis via inducing the AhR/COPS8 pathway via the Mulberry bark ELNs-derived heat stock protein HSP8. Recent studies have shown that PELNs regulate tissue regeneration. Fibroblast migration, proliferation, and collagen type I synthesis are all enhanced by wheat-derived ELNs. Human dermal fibroblasts, human keratinocyte cells, and human keratinocyte cells are all subjected to anti-apoptotic action by wheat-derived ELNs. Furthermore, human umbilical vein endothelial cells exhibit angiogenesis in response to wheat-derived ELNs (Şahin et al., 2019). Additionally, PELNs stimulate the development of probiotics and inhibit a variety of pathogens, including, Porphyromonas gingivalis. GELNs bind to hemin-binding protein 35 (HBP35) on the surface of P. gingivalis to limit P. gingivalis growth through phosphatidic acid. PELNs exhibit microbiome regulatory qualities by encouraging probiotic development. Lemon-derived ELNs shield LGG from bile presumably by suppressing Msps protein production, triggering the degradation of certain bacterial tRNA, and stopping S.24-7 development.
3.4. Intestinal Inflammation
Acute and chronic intestinal inflammatory disorders (IBDs) might result from the gut's continuous immune response to invasive pathogens, which are present due to food and bacterial exposure. Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis are the two primary forms of inflammatory bowel disorders (IBDs). The precise etiology of many illnesses, however, are still unclear and vary greatly. While intestinal illnesses may now be treated with immunomodulators, anti-TNF medicines, and monoclonal antibodies, the adverse effects, prolonged treatment cycles, and high patient expenses are possible outcomes. On the other hand, natural exosomes extracted from traditional medicinal plants like bitter melon, garlic, and cannabis can get around many of these restrictions by offering long-lasting, secure, and affordable therapeutic options (X. Wei et al., 2023). Purified PELNs have been found to be present in miRNA-containing plant extracts from grapefruit, pineapple, and grapes, and these extracts are absorbed by intestinal cells in animals' small intestines (Ito et al., 2021). Treating intestinal inflammation by targeting PLDEs is a potential approach. Exosomal vesicles from the edible and medicinal ginger plant have been demonstrated to offer a number of therapeutic advantages in the treatment of inflammatory illnesses. Previous studies have shown that oral GELNs activated intestinal Wnt/TCF4 in mice and Nrf2 in macrophages, therefore selectively increasing the production of cytokines that are anti-inflammatory, such as IL-10 and HO-1 (Mu et al., 2014). Gut epithelial cells (IECs) are the principal site of invasion after inflammation and play a role in intestinal physical resistance. In a colitis model, GELNs increased the duration of survival and proliferation of IECs when administered orally. GELNs were mostly absorbed by macrophages and IECs. Their capacity to decrease the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β and to increase the expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines like IL-10 and IL-22 has been shown by research. Consequently, during intestinal inflammation, GELNs may be able to reduce damage factors while encouraging a healing response (M. Zhang, Viennois, et al., 2016). Another study shown that by suppressing the expression of CD98, GELNs were similarly successful in selectively targeting colonic tissue and reducing colitis (X. Wei et al., 2023). Using HO-1 overexpression, grapefruit-derived nanovesicles (GRELPs) were selectively absorbed by intestinal macrophages in a mouse model of dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. The process of TNF-α and IL-1β synthesis in intestinal macrophages was shown to be expressed and inhibited, which reduced colitis symptoms (B. Wang et al., 2014). Grape exosome-like nanoparticles (GrapeELNs) can penetrate the intestinal mucus barrier to operate on mouse intestinal stem cells (mISCs). Furthermore, they have the ability to be selectively absorbed, and via activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, they encourage the expansion of leucine-rich-repeat-containing G-protein-coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5) in the mouse gut. These vesicles were demonstrated to induce a dramatic growth of mISCs and result in mucosal epithelial regeneration as well as rapid remediation of intestinal architecture, based on the expression of mISC growth genes activated by GrapeELN in both steady-state and injury-induced colitis models in mice (Ju et al., 2013). Turmeric-derived nanoparticles (TNDPs) were administered orally to mice with LPS-induced colitis, and they were mostly absorbed by macrophages and colonic epithelial cells in the inflamed colon. TDNPs have been demonstrated to lessen the symptoms of colitis in mice by blocking the NF-κB pathway, regulating the generation of cytokines that are pro-inflammatory (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β), and the antioxidant gene HO-1 (C. Liu et al., 2022). Natural exosomes were isolated from tea leaves, and exosome-like nanotherapeutics that (ENTs) were synthesized with surface galactose groups to affect the growth of macrophages by selective internalization and galactose receptor-mediated endocytosis. Enteric neurons (ENTs) have been shown to alleviate inflammation in the colon and intestines. This method involves the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine expression, the reduction of reactive oxygen species production, and the rise in macrophages production of the anti-inflammatory properties factor IL-10 (Zu et al., 2021). In the gastrointestinal tract, PLDEs have the ability to elicit immunological responses not only from macrophages, intestinal epithelial cells, and other cell types, but also from the gut flora. One perennial plant in the ginger genus that contains anti-inflammatory and anti-vomiting properties is ginger. GELNs are preferentially absorbed by Lactobacillus bacteria via surface lipids. Additionally, these GELNs include microRNAs that target certain LGG (Lactobacillus rhamnosus) genes. When GELN mdo-miR7267-3p targets LGG monooxygenase ycnE, it raises the quantities of indole-3-carbaldehyde (I3A) produced. Colonic inflammation can be reduced by releasing IL-22, an anti-inflammatory agent, which is produced when GELN-RNA and I3A bind to aryl hydrocarbon receptors (Teng et al., 2021). Mulberry bark-extracted exosome-like nanovesicles (MBELNs) have the ability to bind to the unique protein of the pathogenic Lis-EGD (Listeria monocytogenes strain, EGD) and so prevent the production of bacterial mRNA. The capacity of MBELNs to induce species-specific growth inhibition of Lis-EGD (Listeria (L.) monocytogenes-EGD) and maintain gut microbial homeostasis.
T cells (Tregs) are the targets and functions of PLDEs, which interact with intestinal epithelial cells, macrophages, gut microbiota, and host immune cells collectively. Numerous processes, including microbial homeostasis and macrophage development, affect resistance to them. On the other hand, they can suppress intestinal inflammation and encourage the production and release of anti-inflammatory substances (X. Wei et al., 2023).
3.5. Lung Inflammation
It has been discovered that exosomes, which are generated by neutrophils, macrophages, pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells, and endogenous alveolar epithelial cells, control immunity when the lungs are injured and irritated (Lanyu & Feilong, 2019). It has been shown recently that PLDEs may interact with animal cells from a variety of species, and their significance for immunological control cannot be understated. Researchers found that in lung macrophages of mice infected with the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), exosomal Nsp12 and Nsp13 activated nuclear factor kappa B. Inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β were expressed as a consequence. The tracheal delivery method of miRNA aly-miR396a-5p was successfully delivered to the lungs by the use of ginger exosome-like nanoparticles (GELN). Cytopathic effects (CPEs) observed in Vero E6 cells infected with SARS-CoV-2 were avoided by GELN miRNAs by blocking the expression of the viral S and Nsp12. It was also shown that exposure to Nsp12 by itself did not trigger NF-κB; nevertheless, lung epithelial cells and macrophages may be specifically targeted with ginger miRNAs to suppress Nsp12 production and avert exosomal Nsp12-induced lung inflammation. By blocking the NF-κB pathway, GELN can also prevent and cure inflammation by reducing the production of TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β. It's important to remember that when a disease progresses, viral exosomes release a range of pro-inflammatory cytokines; however, GELN can inhibit this effect by releasing endogenous exosomes. This illustration demonstrates the potential interaction between PLDEs and endogenous host exosomes, although more research is still needed to fully understand the precise processes underlying these responses (Teng et al., 2021). The active elements of traditional Chinese medications used to treat lung disorders are typically stable and are given as a decoction made by boiling plants in water. In these concoctions, ELNs that are sourced from traditional Chinese medicinal herbs could also be involved. While ELNs from the latter source had stronger therapeutic benefits, both those extracted from decoctions and those produced in vitro shown therapeutic effects in vivo. HJT-sRNA-m7 and PGY-sRNA-6, two siRNA-containing ELNs, have shown to be highly effective in suppressing inflammation and fibrosis, respectively (X. Wei et al., 2023). The co-assembly of sphingosine-PGY-sRNA-6 and sphingosine-HJT-sRNA-m7 benzyl groups using sphingine and siRNAs may improve post-oral stroke in mice, based on the two essential components. The aforementioned effects were seen in both lung inflammation and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis (X. Li et al., 2019).
3.6. Liver Inflammation
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), chronic hepatitis B (HBV), and non-alcoholic fatty liver disorder (NAFLD) are all associated with hepatic inflammation. The anti-inflammatory processes that trigger hepatic inflammation are a key avenue for the pharmaceutical treatment of liver diseases (X. Wei et al., 2023). Ginger-derived nanoparticles (GDN) carry gingerol, a bioactive chemical that may be the reason behind GELP's ability to target liver cells. This gingerol is injected directly into the liver cells, where it dehydrates to generate 6-shogaol, which activates the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2). Instead of being acquired in its free state. In vitro mouse hepatocyte cultivation tests have shown that 6-shogaol is essential for GDN-mediated Nrf2 activation, and Nrf2 possesses anti-inflammatory characteristics. This was accomplished by blocking the TLR4/TRIF pathway, and the reduction of hepatocyte inflammation was demonstrated via lipid knock-in and knock-out methods (Zhuang et al., 2015). To confirm the role of surface proteins during endocytosis, garlic-derived nanovesicles (GDVs) that had eliminated all of these constituents were compared to non-trypsinized GDVs. Additionally, inhibiting CD98 receptors significantly reduced the GDV absorption of the HepG2 cell line. The mannose-saturated surface lectin (lectin II) on GDVs was observed, and it was shown that GDV internalization was suppressed when the CD98 receptor was blocked by CD98 antibodies. Research carried out in vitro has revealed the anti-inflammatory characteristics of GDVs. This is supported by the fact that pro-inflammatory factors including IL-6 and IFN-γ are down-regulated in HepG2 cells. This may be the result of GDVs targeting CD98 both in vitro and in vivo, which lowers pro-inflammatory cytokines associated with hepatitis such as TNF-α, IFN-γ, and IL-6. This inhibits liver inflammation (Song et al., 2020). Both medications and poisons, as well as pathogenic bacteria, can harm the liver. It has been shown that the pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome is overactivated, which leads to inflammation, facilitates the development of diseases, and ultimately harms the liver (X. Wei et al., 2023). The enormous molecular weight multi-protein complex known as the NLRP3 inflammasome recruits the apoptotic speck protein, which contains caspase 1 and the caspase recruitment domain (ASC). These substances are necessary for both acquired and innate immunity. Previous studies have shown that primary macrophages may be blocked from undergoing subsequent processes that result from inflammasome activation by delivering ginger rhizome exosome-like nanoparticles (G-ELNs). IL-1β and IL-18 are secreted as a result of caspase 1 self-cleavage, which inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome formation and activation (X. Chen et al., 2019). The study of shiitake mushroom exosomes shows that ELNs may be generated from a range of commonly occurring mushroom species, however only shiitake-derived ELNs (S-ELNs) have been demonstrated to substantially decrease NLRP3 by inhibiting the development of inflammasomes in primary macrophages. The goal of inflammasome activation, which lessens inflammation by preventing it via a different mechanism than lentinan, is AIM2 inflammasome-associated activity. The findings of the immunofluorescence staining showed that the formation of ASC in cells treated with S-ELN was greatly inhibited. This implies that S-ELN inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway's early stages in order to stop it from assembling. (X. Wei et al., 2023). The study discovered that pro-IL-1β and NLRP3 were reduced in the livers of mice subjected to stress produced by GalN/LPS after receiving pre-treatment with S-ELN. The findings suggest that S-ELN inhibits IL-6 secretion as well as IL-1β protein and mRNA expression levels. The findings imply that S-ELN could be able to lessen the degree of acute liver damage brought on by GalN/LPS in mice (B. Liu et al., 2020).
5. Conclusion and Future Prospects
Extracellular vesicles generated from plants have been the subject of an exponentially growing body of study in the past ten years. Previous studies have shown that plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PDEVs) are very complex, diverse, and offer a broad range of fascinating possible future uses. However, a variety of plant sources have been found to produce these nano-sized vesicles, which may have a wide range of applications in the management of health and sickness, as well as medicine delivery (Kameli et al., 2021). Recent research has revealed that PELNVs are implicated in several physiological and pathological processes that transpire not just among plant cells but also among cells of other species. There remains significant ambiguity over whether communication is stochastic or specific to recipient cells. Furthermore, a lot of attention has lately been paid to their use as nanotherapeutics or to transport drugs, proteins, and nucleic acids across diverse biological barriers. However, until recently, little was known about the cellular and molecular mechanisms controlling PELNV production, release, and functions. To achieve PELNV commercial and therapeutic translations, appropriate isolation techniques are currently time-consuming to get pure PELNVs and need to be improved (Dad et al., 2021a). PELNVs may be helpful in preventing immunogenicity, cytotoxicity, and long-term expression because of their small size, ability to cross robust biological barriers, and evasion of the mononuclear phagocyte system (MPS) (Dad et al., 2021a). Since proteins are the basic building blocks that primarily determine how EVs operate in biological systems, proteomics profiling might help us better understand EVs in biological situations. Until recently, this was a major issue because to the nanoscale size of the EVs. However, these days, tiny quantities of EVs may be used to assess EV proteins thanks to recent advances. Newly created methods for quantifying EV proteins, such as improved flow cytometry and optical, non-optical, microfluidic, and single vesicle detection approaches, are among these advancements (Kameli et al., 2021). PELNVs have a great deal of promise for use in drug delivery systems because of their intrinsic biological characteristics (Dad et al., 2021c). While markers such as outer membrane protein A (OmpA) and lipoteichoic acid (LTA) can be used to identify bacterial outer membrane vesicles, CD63, CD81, and CD9 are among the most commonly used markers in mammalian cells. However, when it comes to plant vesicles, we are aware of a notably dearth of literature about target marker proteins. Patellin-3-like proteins and clathrin heavy chain proteins are two examples of common marker proteins that have been effectively identified in one study that looked at the presence of surface proteins on vesicles formed from citrus. Contradictory findings have been observed in other investigations, though. PELNVs may be surface-tuned to selectively aggregate at distant and challenging-to-target tumours without producing any immunogenicity, thereby conferring target specificity. Furthermore, due to their ability to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and avoid the toxicity and complicated MPS processes associated with other nanocarriers, PELNVs have the potential to serve as a model medication delivery system in the future. Following that, given their structural similarity to liposomes and their capacity to permeate skin, PELNVs may also be useful as delivery nanoplatforms for transcutaneous immunization (Dad et al., 2021c). PELNVs are now a well-researched drug carrier in oral and drug-targeted administration; however, their use in transdermal drug delivery systems has received less attention. Future research will focus on developing a PELNV delivery system with high stability, transdermal volume, and convenience of use for this effective carrier (Y. Wang et al., 2023). Despite the limitations in the sector, exosomes provide several benefits in terms of biocompatibility, therapeutic efficacy, targeting capability, and cellular absorption. One is constantly looking for natural therapeutic substances that are safe and don't cause any adverse effects. Plant exosomes have the potential to become dependable medicinal agents for a variety of common illnesses if they are targeted and produced with multidisciplinary competence (Subha et al., 2023)