Submitted:
06 May 2024
Posted:
08 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Predicted Analytics Models for O&G
2.1. Application of Artificial Neural Network Models
2.2. Application of Deep Learning Models
2.3. Application of Fuzzy Logic and Neuro-Fuzzy Models
2.4. Application of Decision Tree, Random Forest, and Hybrid Models
2.5. Application of Interrelated AI Models
2.6. Application of Statistical Models
2.7. Alternative ML Models Utilized for Predictive Analytics in the O&G
3. Literature Review Assessment
- Table 1, Table 2, Table 3, Table 4, Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7 provides a comprehensive overview of the reviewed papers, presenting essential details such as author names, applied AI model types, the temporality of the dataset, field of the O&G involved, dataset sources and the number of samples of data, parameters for input and output, measures for performance employed, the best models found, and the advantages or drawbacks of the performing models. Researchers consistently focused on carefully selecting input combinations for O&G predictive analytics modelling.
- ANN models can be expanded from binary to multiclass cases. Furthermore, the complexity of ANN models may be easily changed by modifying model structure and learning methods and assigning transfer functions using empirical evidence or correlation analysis. The findings revealed that ANN could effectively predict, classify, or cluster O&G cases, including crater width in buried gas pipelines, corrosion defect depth, flowing bottom-hole pressure in vertical oil wells, concentrations of gas-phase pollutants for contamination removal, drilling-related occurrences based on epochs, age, formation, lithology, and fields, as well as predicting gas routes and chimneys in drilling activities, and DGA datasets. ANN may be compared to various models, like SARIMA and QDA.
- Reviewed articles from 2021 to 2023. RF has become much more popular in the predictive analytics O&G than other modeling techniques like MLP, DT, and LSTM because it prevents overfitting and is more accurate in prediction. In the O&G sector, RF appears to be a typical, flexible, and effective ML framework because of its capacity to handle complicated O&G datasets that may be fragmented. The O&G industry has become another data scarcity for modeling. In pipeline failure risk prediction and transformer fault classification, RF is included in model ensembles to help achieve good results. Its use in drilling, well data analysis, lithology identification, crude oil data analysis, and burst pressure prediction demonstrates RF's robust application performance. RF stands out for its dependability, obtaining excellent accuracy, precision, and recall values in many applications within the O&G area, emphasizing its applicability for multiple data formats such as binary or multi-class cases.
- The O&G industry has seen a rise in the use of DL, an effective subset of ML, especially for predicting the lifespan of equipment and modeling groundwater levels. DL frameworks, especially CNN and LSTM, outperform other models in prediction accuracy. Industry uses of DL include assessing algorithm performance, integrating data into DL algorithms, and developing simulation frameworks. Significant studies demonstrate DL's efficacy in estimating oil output and pressure in wells, identifying pipeline fractures, and producing hydrocarbons in the gas sector. Evaluations of hybrid models, such as DCNN+LSTM and LSTM+Seq2Seq, show outstanding accuracy, indicating DL's potential for optimizing operations and decision-making processes in the O&G field. The hybrid model is more efficient due to feature extraction and the capacity to learn patterns in extended data sequences.
- AI models are swiftly employed in the O&G sector to deliver predictive analytics. In non-linear modeling, SVR is a kernel-based ML method often used to translate data to a higher-dimensional space. This makes it an effective tool for regression problems with complicated input and interaction of target variables. MLR is still an excellent approach for examining dependencies since it is a powerful tool for analyzing the connection between dependent and several independent variables. Non-temporal gas well data is analyzed using MLR, SVR, and GPR models because they provide a good blend of interpretability, simplicity, performance, and adaptability. However, the decision between these models is ultimately determined by the dataset's particular properties and the problem's needs. The other research focused on the temporal prediction of corrosion in pipes using several AI models, with RNN showing promise but requiring improvement. Non-temporal O&G production categorization, reservoir data analysis, and transformer fault prediction were all explored using various AI models, demonstrating industry flexibility.
- According to the previous literature, the O&G sector replicates real-world system behavior with mathematical models, namely regression and time-series analysis. Statistical models such as SARIMA, AR, and ARIMA are more accurate since they account for temporal relationships. Research validated the efficacy of SARIMA in forecasting DGA gas concentration in transformers, highlighting its ability to capture seasonal fluctuations based on each temporal data point. These techniques forecast shale gas output, producing a satisfactory mean outcome. It is proved that statistical approaches are adaptable to dealing with temporal dependencies and forecasting concerns in the O&G area.
- According to the previously reviewed publications, there are just a few input characteristics employed in the studies they conducted to detect defects in wells utilizing various sensors in predictive analytics models, whether classed, clustered, or forecasted. Because of the data's accessibility and availability, researchers regularly employ P-PDG, P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, and P-MON-CKP (5 parameters) as input parameters. Data limitations are widespread due to the difficulty of digging wells in severe environments such as the deep sea. However, in some other models, such as RF, data such as T-JUS-CKP, T-JUS-CKGL, P-JUS-CKGL, P-CKGL, and QGL, which totals 15 input parameters, were used as input parameters, and the results were compared to those models that only used the five input parameters mentioned previously. The outcomes of employing the 15 input parameters with the DT model were superior to the five input parameter models. Table 8 outlines the input parameters utilized by the researchers in their research papers.Table 8. Input Parameters of Undesirable Well Events from 3W Datasets.
Input Parameter of Undesirable Well Events [82] [68] [19] [96] [128] [83] [84] [7] [81] [133] P-PDG ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü P-TPT ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü T-TPT ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü P-MON-CKP ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü T-JUS-CKP ü ü ü ü ü ü ü T-JUS-CKGL ü ü ü P-JUS-CKGL ü ü ü P-CKGL ü QGL ü ü ü ü T-PDG ü T-PCK ü ü - Detecting internal transformer failures is another O&G-related topic that has been the subject of several previous studies. Specifically, a few gas compositions were used as input variables, including acetylene (C2H2), ethylene (C2H4), ethane (C2H6), methane (CH4), and hydrogen (H2), which are mainly applied across the studies because of the high correlation between the input variables and the target variables in detecting the fault in the transformer. However, the detection of other parameters such as total hydrocarbon (TH), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), ammonia (NH3), acetaldehyde (CH3CHO), acetone (CH32CO), toluene (C6H5CH3), oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), and ethanol (CH3CH2OH) vary between studies. The selection of the parameters is because the ranking of the correlation between the target and input variables is not strong, so not all studies implemented the gas compositions mentioned earlier. The comparison of the models in the study article employed few input variables such as C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, CH4, and H2 (5 variables) revealed that there are few models used such as KNN, QDA, and LGBM, with accuracies of 88%, 99.29%, and 87.06%, respectively. In contrast, the accuracies of MTGNN, KNN+SMOTE, and RF with 92%, 98%, and 96.2%, respectively, were obtained when the models employed C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, CH4, H2, TH, CO, CO2, NH3, CH3CHO, CH32CO, C6H5CH3, O2, N2, and CH3CH2OH (15 variables) in their research. As can be observed from the average accuracies, the use of 15 variables produces superior outcomes than five variable models. Previous research publications may be found in Table 9.Table 9. Input Parameters for Fault Detection of Transformer Oil from DGA Dataset.
Input Parameter of Internal Transformer Defect [32] [119] [37] [79] [94] [95] [56] [137] [61] [107] Acetylene (C2H2) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Ethylene (C2H4) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Ethane (C2H6) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Methane (CH4) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Hydrogen (H2) ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Total Hydrocarbon (TH) ü Carbon Monoxide (CO) ü ü ü ü ü Carbon Dioxide (CO2) ü ü ü ü ü Ammonia (NH3) ü Acetaldehyde (CH3CHO) ü Acetone (CH32CO) ü Nitrogen (N2) ü Ethanol (CH3CH2OH) ü - Table 10 summarizes the input parameters for a well-logging predictive analytics model. Researchers commonly use 14 parameters for well-logging, including Gamma Ray (GR), Sonic (Vp), Deep and Shallow Resistivities (LLD and LLS), Neuro-porosity (NPHI), Density (RHOB), Calliper (CALI), Neutron (NEU), Sonic, Transit-Time (DT), Bulk Density (DEN), Deep Resistivity (RD), True Resistivity (RT), Shallow Resistivity (RES SLW), Total Porosity (PHIT), and Water Saturation (SW). The correlation coefficient between the input parameters and the target variables is essential to determine which parameters are appropriate for predictive analytics and the data type, whether numerical or categorical. This way, a few important variables can be chosen to construct the best model for increased accuracy. However, the model using 14 variables produced a substantial result of 97% by including XGBoost in their research, but the study that utilized just GR, Vp, LLD&LLS, NPHI, and RHOB and used LSTM achieved a slightly lower result of 94%. These three well-known datasets utilized in recent research on the O&G sector demonstrate the importance of determining the correlation between target and input parameters to compare which variables are appropriate for models to provide significant outcomes in the research.Table 10. Input Parameters of Well-Logging.
Input Parameter of Well-logging [59] [102] [100] [138] [97] [104] Gamma Ray (GR) ü ü ü ü ü ü Sonic (Vp) ü ü Deep and Shallow Resistivities (LLD and LLS) ü ü Neuro-porosity (NPHI) ü ü Density (RHOB) ü ü ü ü Calliper (CALI) ü ü ü Neutron (NEU) ü ü ü Sonic Transit-Time (DT) ü ü ü ü Bulk Density (DEN) ü ü Deep Resistivity (RD) ü True Resistivity (RT) ü Shallow Resistivity (RES SLW) ü ü Total Porosity (PHIT) ü Water Saturation (SW) ü Compressional Slowness (DTC) ü Depth ü - The assessment of O&G research revealed an increase in published papers over time. As seen in Figure 2, the rise in O&G discoveries due to the dependence of technological advancements on the usage of gas and petroleum, as well as the annual progress of ML and AI tools, has resulted in more studies in this field utilizing AI-based models. According to Figure 2, there was an increase in growth throughout 2021, with 32 research publications published in this field. However, the number of articles released in 2022 decreased by seven, with just 25 published research papers. This reduction can be attributed to the continued development of AI and the gradual progression of interest in O&G research. It exhibits a positive trend, with 34 articles published in this field by 2023. This increase may be impacted by recognizing the necessity for improvement in the AI-based model in the O&G area. Many O&G companies have followed the IR4.0 road to integrate their organization with AI and reduce the likelihood of future expense utilization by forecasting future events.
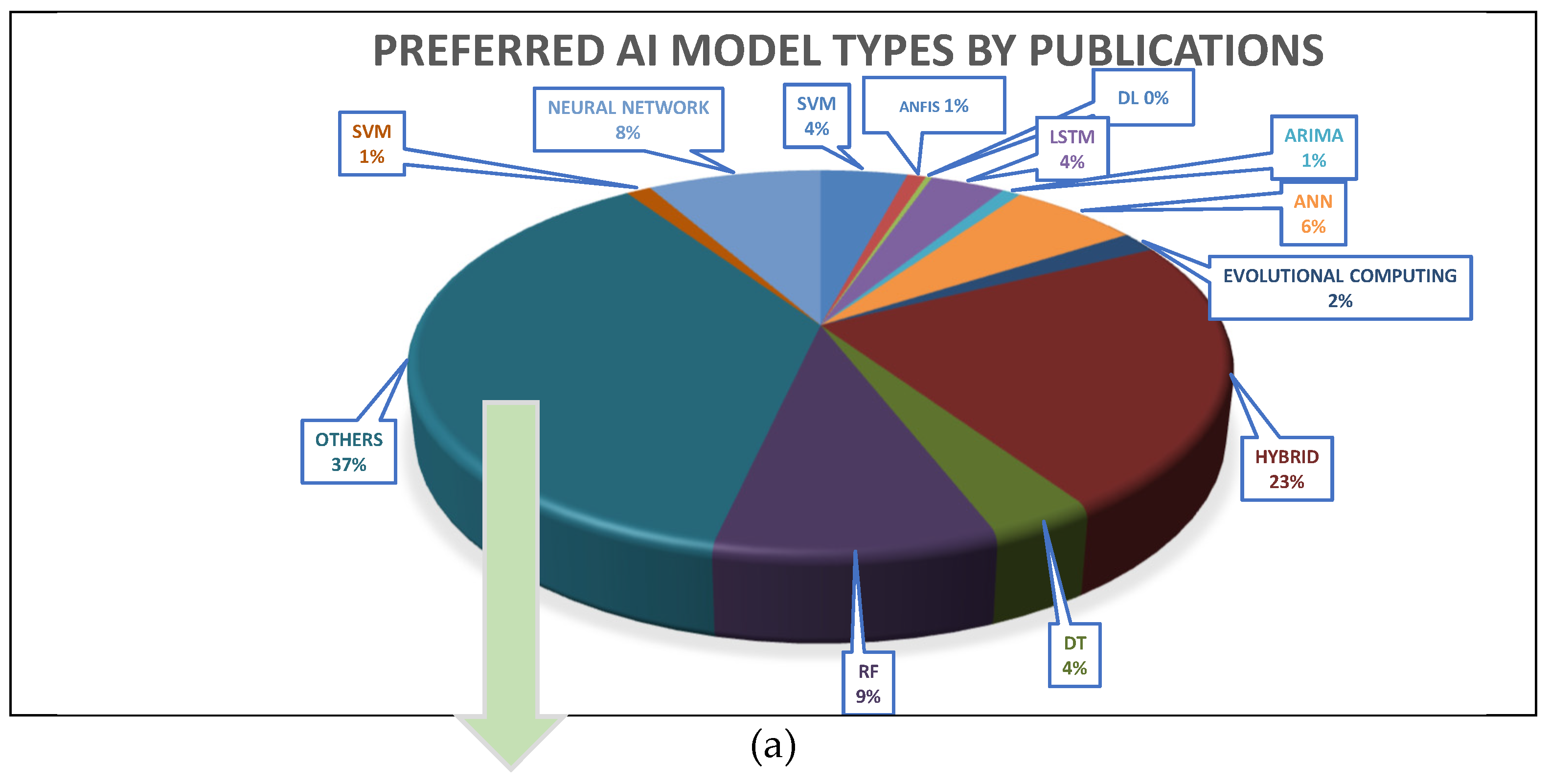
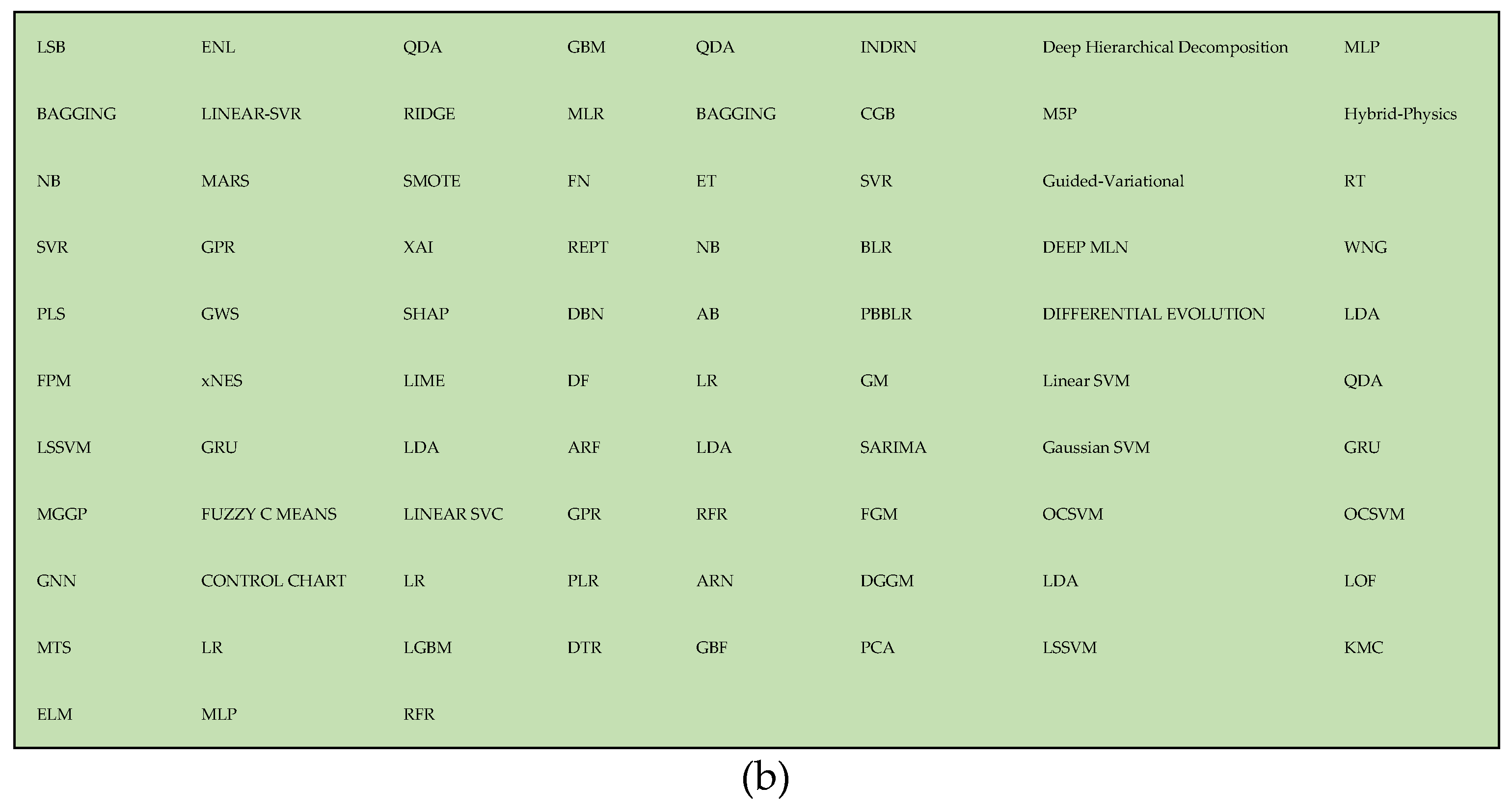
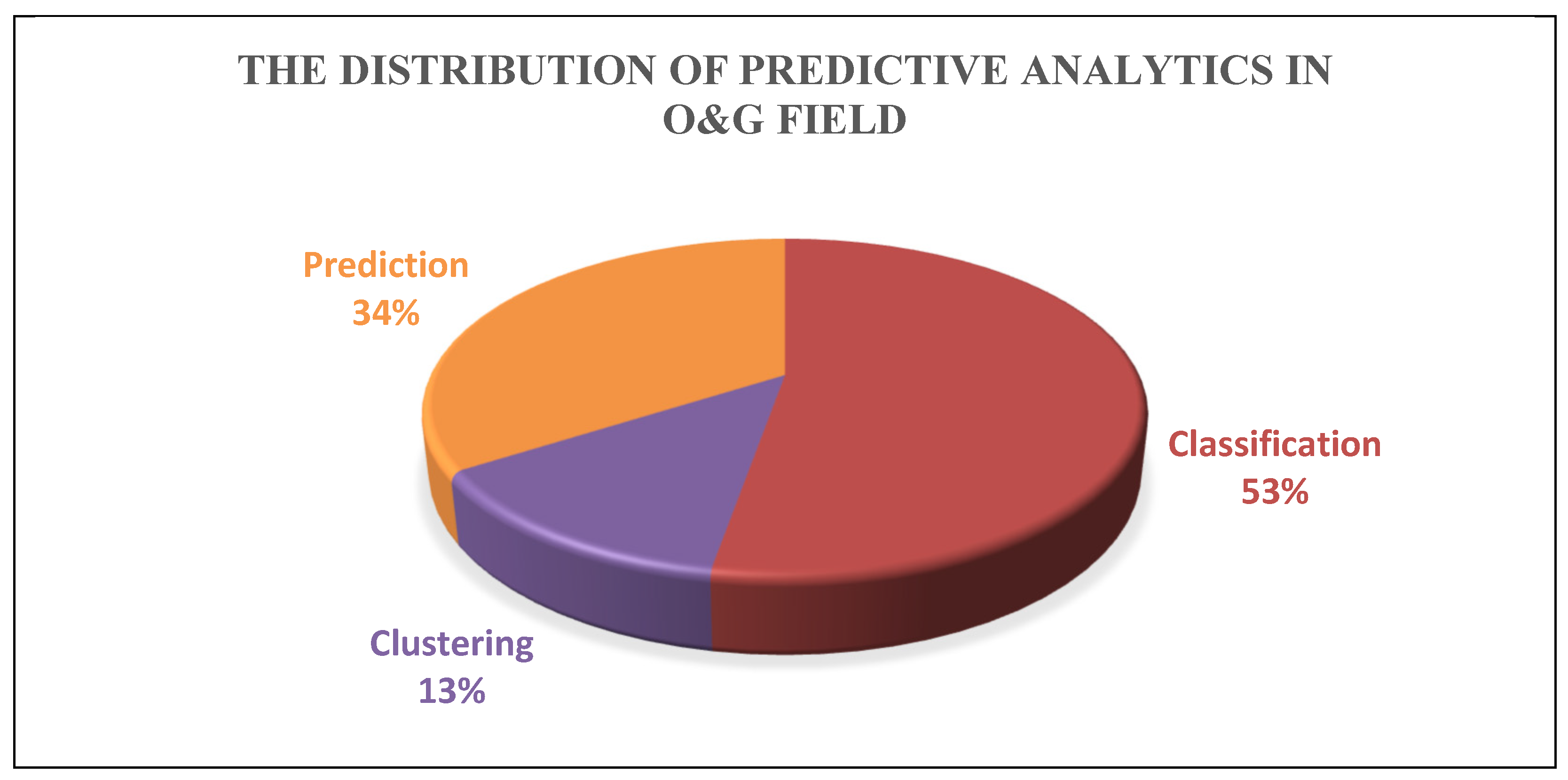
- Throughout the research period, developments in AI models resulted in more complicated and interconnected models, giving researchers tools to construct more exact and resilient models. A similar finding was reached while investigating the use of various models in predictive analytics in the O&G industry during the last three years. Figure 4 (a) depicts a thorough breakdown, illustrated by a pie chart, of the most common model types used for predictive analytics in the O&G industry. The chart shows that the most widely used models, 37%, are classified as "others," which primarily include foundational models such as SVR, GRU, MLP, and boosting-based models (shown in Figure 4 (b)). Due to their improved efficiency, accuracy, and capacity to handle non-linear datasets, these models have become quite popular. Due to their improved efficiency, accuracy, and capacity to handle non-linear datasets, these models have become quite popular. This selection of models shows that there is still a lot of remaining potential in this field.Figure 4. Preferred AI Model Types in the Research Articles about Predictive Analytics in O&G: (a) The overview of the AI models used in publications. (b) The extended “others” section.Figure 4. Preferred AI Model Types in the Research Articles about Predictive Analytics in O&G: (a) The overview of the AI models used in publications. (b) The extended “others” section.
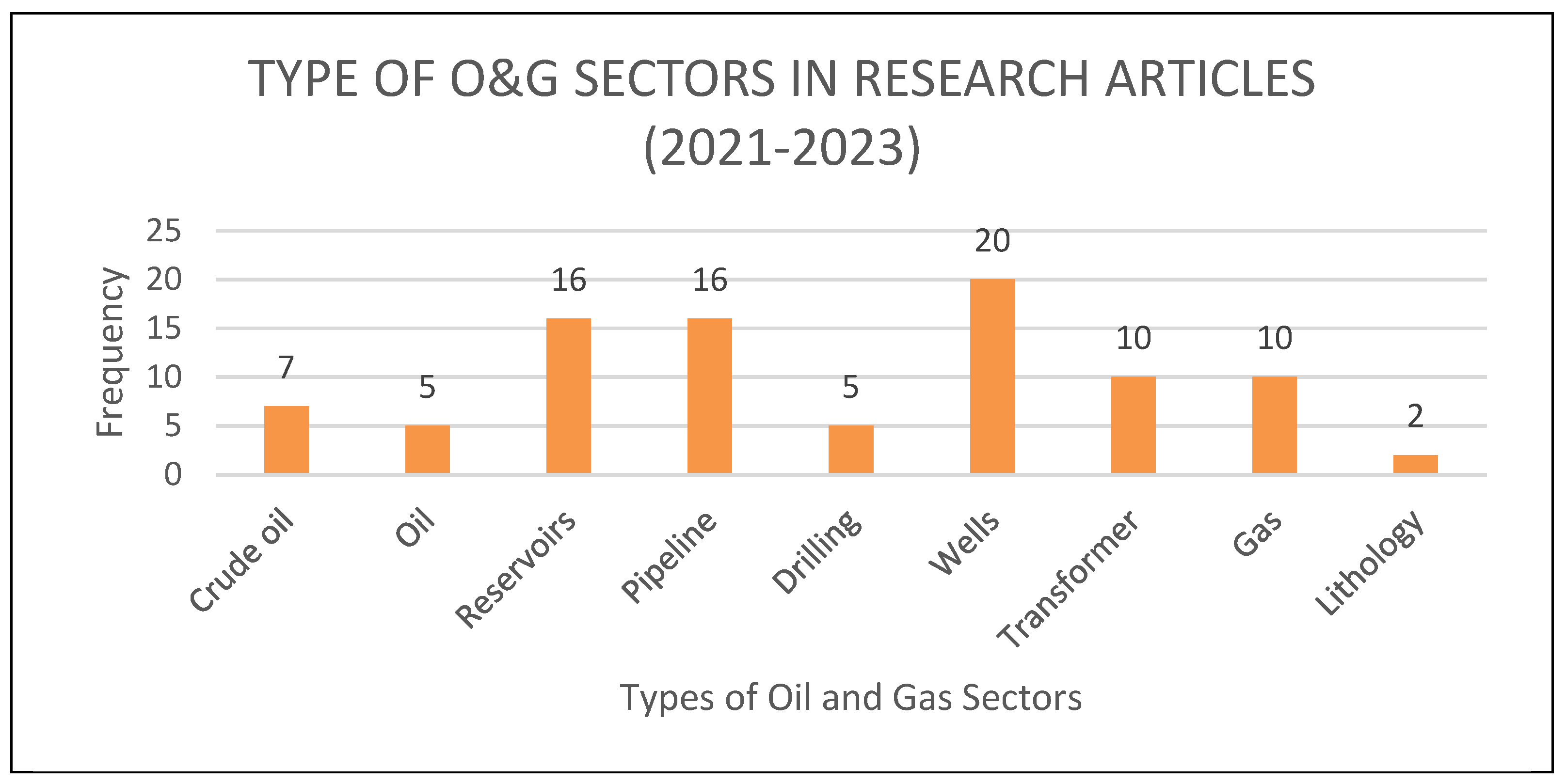
- The analysis of predictive analytics research publications from 2021 to 2023 focuses heavily on several areas of the O&G sector. Crude oils (7), oil (5), reservoirs (16), pipelines (16), drilling (5), wells (20), transformers (10), gas (10), and lithology (2) all appear as recurring topics in various research. The frequency of these terms demonstrates the industry's strong interest in using predictive analytics to optimize operations and decision-making in various sectors, including reservoir management, drilling procedures, pipeline integrity, and transformer health. This trend represents a deliberate effort in the O&G industry to use sophisticated analytics for greater efficiency, risk management, and overall operational excellence. Figure 5 is the graphical summary of the types of O&G sectors in research articles.Figure 5. Types of O&G Sectors in Research Articles from 2021 to 2023.
- Several performance measures have been utilized in O&G sector research, demonstrating diverse assessment criteria for predictive analytics models (see Figure 6). The performance metrics help understand the models' performance since they might show many model characteristics. Figure 6 (a), which shows the various performance measures used in the research, demonstrates that accuracy (49) was the most preferred for calculating the correctly predicted value versus the actual. This performance measure is appropriate for categorical data types and classification predictive analysis because it is simple to grasp and indicates whether all classes are balanced. However, utilizing accuracy for unbalanced classes has limitations since it can be deceptive; alternative measures like precision, recall, F1-score, or area under the AUC may be more helpful. Aside from that, the researchers' second chosen performance indicator in their research is R2 (41). This performance indicator is commonly employed in regression analysis and numerical data since it measures the relationship between the independent and dependent variables.Figure 6. Preferred Performance Metrics by Researcher: (a) Combination of Performance Metrics used in publications. (b) Display all the other performance metrics beyond the most common ones.Figure 6. Preferred Performance Metrics by Researcher: (a) Combination of Performance Metrics used in publications. (b) Display all the other performance metrics beyond the most common ones.
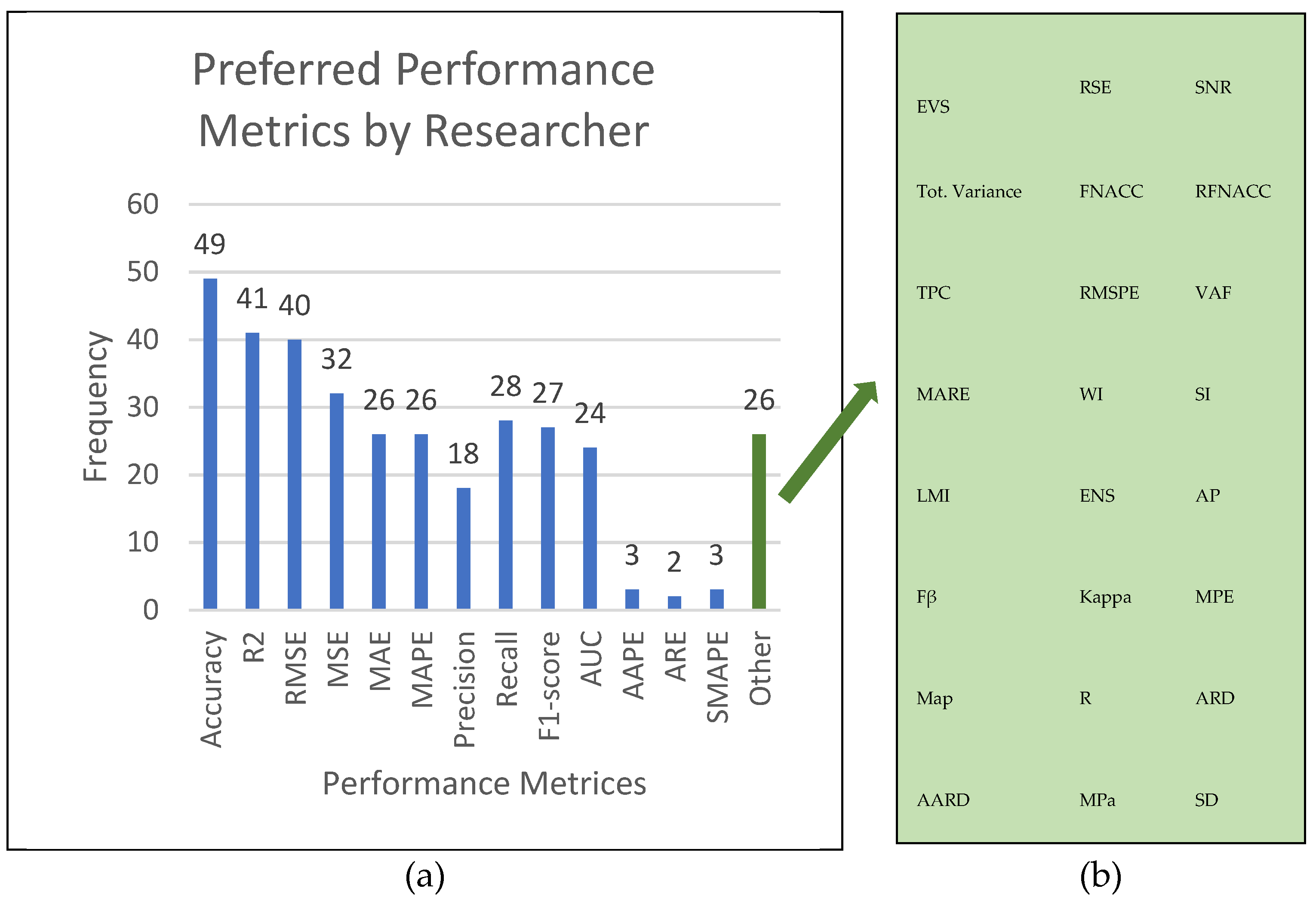
- Furthermore, R2 is simple to read because it ranges from 0 to 1, with closer results to 1 indicating perfect variability between independent and dependent variables. However, there is a disadvantage to using only R2 to demonstrate how effectively the model reacts. One of the disadvantages is that it is vulnerable to outliers; even a single outlier might alter the results. Figure 6 (b) is an expansion of "others" that depicts the additional performance indicators used in the previous studies.
4. Future Research Direction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Abbreviations | Definition | Abbreviations | Definition |
|---|---|---|---|
| RF | Random Forest | DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| GAM | Generalized Additive Model | MELM | Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition |
| NN | Neural Network | ANFIS | Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System |
| SVR-GA | Support Vector Regression with Genetic Algorithm | SOM | Self-Organizing Map |
| SVR-PSO | Support Vector Regression with Particle Swarm Optimization | ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| SVR-FFA | Support Vector Regression with Firefly Algorithm | MRGC | Maximum Relevant Gain Clustering |
| GB | Gradient Boosting | CatBoost | Categorical Boosting |
| LSSVM-CSA | Least Squares Support Vector Machine with Cuckoo Search Algorithm | MLR | Multiple Linear Regression |
| AHC | Agglomerative Hierarchical Clustering | SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| XGBoost | Extreme Gradient Boosting | FN | Fuzzy Network |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression | LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LWQPSO-ANN | Linearly Weighted Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization with Artificial Neural Network | LSSVM | Least Squares Support Vector Machine |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis | DL | Deep Learning |
| MLP-ANN | Multilayer Perceptron with Artificial Neural Network | MLSTM | Multilayer Long Short-Term Memory |
| MLP-PSO | Multilayer Perceptron with Particle Swarm Optimization | GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| DT | Decision Tree | AdaBoost | Adaptive Boosting |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory | LSTM-AE-IF | Long Short-Term Memory Autoencoder with Isolation Forest |
| KNN | k-Nearest Neighbors | DNN | Deep Neural Network |
| NB | Naive Bayes | CNN | Convolutional Neural Network |
| GP | Genetic Programming | O&G | Oil and Gas |
| ELM | Extreme Learning Machine | AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| DF | Deep Forest | MSE | Mean Squared Error |
| QDA | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| ML | Machine Learning | AAPE | Arithmetic Average Percentage Error |
| DGA | Dissolved Gas Analysis | SMAPE | Symmetric Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| RMSE | Root Mean Squared Error | RSE | Relative Squared Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error | RFR | Random Forest Regression |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve | FNACC | Faulty-normal accuracy |
| ARE | Absolute Relative Error | TPC | Total Percent of Correct |
| EVS | Explained Variance Score | VAF | Variance Accounted For |
| DTR | Decision Tree Regression | WI | Weighted Index |
| PLR | Polynomial Linear Regression | LMI | Linear Mean Index |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio | AP | Average Precision |
| RFNACC | Real Faulty-Normal Accuracy | MAP | Mean Average Percentage |
| RMSPE | Root Mean Square Percentage Error | ARD | Absolute Relative Difference |
| MARE | Mean Absolute Relative Error | Mpa | Megapascal |
| SI | Severity Index | P-JUS-CKGL | Pressure downstream of gas lift choke |
| ENS | Energy Normalized Score | P-CKGL | Pressure downstream of gas lift choke CKGL |
| MPE | Mean Percentage Error | QGL | Gas lift flow rate |
| R | Correlation of Coefficient | T-PDG | Temperature at the permanent downhole gauge sensor |
| AARD | Average Absolute Relative Deviation | T-PCK | Temperature downstream of the production choke |
| P-PDG | Pressure at permanent downhole gauge PDG | LSB | Least Square Boosting |
| P-TPT | Pressure at temperature/pressure transducer TPT | PLS | Partial Least Squares |
| T-TPT | Temperature at TPT | FPM | Feature Projection Model |
| P-MON-CKP | Pressure upstream of production choke CKP | FP-DNN | Feature Projection-Deep Neural Network |
| T-JUS-CKP | Pressure downstream of CKP | GNN | Graph Neural Network |
| T-JUS-CKGL | Temperature downstream of CKGL | MLP | Multilayer perceptron |
| FP-PLS | Feature Projection-PLS | Bi-LSTM | Bidirectional Long Short-Term |
| MGGP | Multi-Gene Genetic Programming | SHAP | Shapley Additive Explanation |
| xNES | Exponential natural evolution strategies | LR | Logistic Regression |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Network | LOF | Local Outlier Factor |
| LGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine | ICA | Imperialist Competitive Algorithm |
| SMOTE | Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique | SFLA | Shuffled Frog-Leaping Algorithm |
| LIME | Local Interpretable Model-Agnostic Explanations | SA | Simulated Annealing |
| XAI | Explainable Artificial Intelligence | PBBLR | Physics-Based Bayesian Linear Regression |
| GSK | Gaining-sharing knowledge-based algorithm | ARIMA | Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| BayesOpt-XGBoost | Bayesian optimization XGBoost | GM | Generalized Method of Moments |
| FA | Firefly Algorithm | PSO-FDGGM | PSO-based data grouping grey model with a fractional order accumulation |
| COA | Cuckoo Optimization Algorithm | PSOGM | PSO for Grey Model |
| GWO | Grey Wolf Optimizer | LSSVM | Least-Square Support Vector Machine |
| HAS | Harmony Search | GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| BLR | Bayesian Linear Regression | OCSVM | One-Class Support Vector Machine |
| SARIMA | Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average | BAE | Basic Autoencoder |
| GM | Grey model | CAE | Convolutional Autoencoder |
| FGM | Fractional grey model | AE | Autoencoder |
| DGGM | Data Grouping-Based Grey Modelling Method | VAE | Variational Autoencoders |
| GPR | Gaussian Process Regression | MARS | Multivariate Adaptive Regression Splines |
References
- J. Liang et al., “Activation of mixed sawdust and spirulina with or without a pre-carbonization step: Probing roles of volatile-char interaction on evolution of pyrolytic products,” Fuel Process. Technol., vol. 250, no. July, p. 107926, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Xu, Y. Wang, L. Mo, Y. Tang, F. Wang, and C. Li, “The research progress and prospect of data mining methods on corrosion prediction of oil and gas pipelines,” Eng. Fail. Anal., vol. 144, no. June 2022, p. 106951, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Sharma and B. Villányi, “Evaluation of corporate requirements for smart manufacturing systems using predictive analytics,” Internet of Things (Netherlands), vol. 19. Elsevier B.V., Aug. 01, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Henrys, “Role of Predictive Analytics in Business,” SSRN Electron. J., no. March, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Tewari, U. D. Dwivedi, and S. Biswas, “A novel application of ensemble methods with data resampling techniques for drill bit selection in the oil and gas industry,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 2, 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Allouche, Q. Zheng, N. Yoosef-Ghodsi, M. Fowler, Y. Li, and S. Adeeb, “Enhanced predictive method for pipeline strain demand subject to permanent ground displacements with internal pressure & temperature: a finite difference approach,” J. Infrastruct. Intell. Resil., vol. 2, no. 4, p. 100030, 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. G. Carvalho, R. E. Vaz Vargas, R. M. Salgado, C. J. Munaro, and F. M. Varejao, “Flow Instability Detection in Offshore Oil Wells with Multivariate Time Series Machine Learning Classifiers,” IEEE Int. Symp. Ind. Electron., vol. 2021-June, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nzubechukwu Chukwudum Ohalete, Adebayo Olusegun Aderibigbe, Emmanuel Chigozie Ani, Peter Efosa Ohenhen, and Abiodun Akinoso, “Advancements in predictive maintenance in the oil and gas industry: A review of AI and data science applications,” World J. Adv. Res. Rev., vol. 20, no. 3, pp. 167–181, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Tariq et al., A systematic review of data science and machine learning applications to the oil and gas industry, vol. 11, no. 12. Springer International Publishing, 2021.
- X. Yu, J. Wang, Q.-Q. Hong, R. Teku, S.-H. Wang, and Y.-D. Zhang, “Transfer learning for medical images analyses: A survey,” Neurocomputing, vol. 489, pp. 230–254, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. D. Barkana, Y. Ozkan, and J. A. Badara, “Analysis of working memory from EEG signals under different emotional states,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 71, p. 103249, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Chen, H. Huang, J. Huang, K. Wang, H. Qin, and K. K. L. Wong, “Deep learning-based medical image segmentation of the aorta using XR-MSF-U-Net,” Comput. Methods Programs Biomed., vol. 225, p. 107073, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Huang, B. Gu, Y. Chen, X. Tan, and L. Feng, “Energy return on energy, carbon, and water investment in oil and gas resource extraction: Methods and applications to the Daqing and Shengli oilfields,” Energy Policy, vol. 134, p. 110979, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Hazboun and H. Boudet, “Chapter 8 - A ‘thin green line’ of resistance? Assessing public views on oil, natural gas, and coal export in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States and Canada,” in Public Responses to Fossil Fuel Export, H. Boudet and S. Hazboun, Eds. Elsevier, 2022, pp. 121–139.
- A. Champeecharoensuk, S. Dhakal, N. Chollacoop, and A. Phdungsilp, “Greenhouse gas emissions trends and drivers insights from the domestic aviation in Thailand,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 2, p. e24206, 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. Centobelli, R. Cerchione, P. Del Vecchio, E. Oropallo, and G. Secundo, “Blockchain technology for bridging trust, traceability and transparency in circular supply chain,” Inf. Manag., vol. 59, no. 7, p. 103508, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Majed, S. Al-Janabi, and S. Mahmood, “Data Science for Genomics (GSK- XGBoost) for Prediction Six Types of Gas Based on Intelligent Analytics,” 2022, pp. 28–34. [CrossRef]
- A. Waterworth and M. J. Bradshaw, “Unconventional trade-offs? National oil companies, foreign investment and oil and gas development in Argentina and Brazil,” Energy Policy, vol. 122, pp. 7–16, 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Marins et al., “Fault detection and classification in oil wells and production/service lines using random forest,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 197, no. August 2020, p. 107879, 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. K. Dhaked, S. Dadhich, and D. Birla, “Power output forecasting of solar photovoltaic plant using LSTM,” Green Energy Intell. Transp., vol. 2, no. 5, p. 100113, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Yan, S. Wang, and C. Peng, “An Artificial Intelligence Model Considering Data Imbalance for Ship Selection in Port State Control Based on Detention Probabilities,” J. Comput. Sci., vol. 48, no. July 2020, p. 101257, 2021. [CrossRef]
- O. E. Agwu, E. E. Okoro, and S. E. Sanni, “Modelling oil and gas flow rate through chokes: A critical review of extant models,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 208, p. 109775, 2022. [CrossRef]
- K. Nandhini and G. Tamilpavai, “Hybrid CNN-LSTM and modified wild horse herd Model-based prediction of genome sequences for genetic disorders,” Biomed. Signal Process. Control, vol. 78, p. 103840, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Balaji and S. Karthik, “Deep Learning Based Energy Consumption Prediction on Internet of Things Environment,” Intell. Autom. SOFT Comput., vol. 37, no. 1, pp. 727–743, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Yang et al., “Optimization of tight gas reservoir fracturing parameters via gradient boosting regression modeling,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 5, p. e27015, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. de los Ángeles Sánchez Morales and F. I. Soler Anguiano, “Data science - time series analysis of oil & gas production in mexican fields,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 200, pp. 21–30, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Y. Tan, A. A. Al-Huqail, Q. S. Chen, H. S. Majdi, J. S. Algethami, and H. E. Ali, “Analysis of groundwater pollution in a petroleum refinery energy contributed in rock mechanics through ANFIS-AHP,” Int. J. ENERGY Res., vol. 46, no. 15, pp. 20928–20938, 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Wu, G. Wang, and H. Liu, “Research on Transformer Fault Diagnosis Based on SMOTE and Random Forest,” Proc. - 2022 4th Int. Conf. Electr. Eng. Control Technol. CEECT 2022, pp. 359–363, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Q. Dashti et al., “Data Analytics into Hydraulic Modelling for Better Understanding of Well/Surface Network Limits, Proactively Identify Challenges and, Provide Solutions for Improved System Performance in the Greater Burgan Field,” 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Wang, M. Daryapour, A. Shahrabadi, S. Pirasteh, and F. Razavirad, “Artificial neural networks in predicting of the gas molecular diffusion coefficient,” Chem. Eng. Res. Des., vol. 200, pp. 407–418, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. Kamarudin et al., “Influence of oxyhydrogen gas retrofit into two-stroke engine on emissions and exhaust gas temperature variations,” Heliyon, vol. 10, no. 5, p. e26597, 2024. [CrossRef]
- R. Raghuraman and A. Darvishi, “Detecting Transformer Fault Types from Dissolved Gas Analysis Data Using Machine Learning Techniques,” 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Mukherjee, T. Burgett, T. Ghanchi, C. Donegan, and T. Ward, “Predicting Gas Production Using Machine Learning Methods: A Case Study,” 2019, pp. 2248–2252. [CrossRef]
- N. Dixit, P. McColgan, and K. Kusler, “Machine Learning-Based Probabilistic Lithofacies Prediction from Conventional Well Logs: A Case from the Umiat Oil Field of Alaska,” Energies, vol. 13, no. 18, p. 4862, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. Aldosari, R. Elfouly, and R. Ammar, “Evaluation of Machine Learning-Based Regression Techniques for Prediction of Oil and Gas Pipelines Defect,” in 2020 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Dec. 2020, pp. 1452–1456. [CrossRef]
- H. H. Elmousalami and M. Elaskary, “Drilling stuck pipe classification and mitigation in the Gulf of Suez oil fields using artificial intelligence,” J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol., vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 2055–2068, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- I. B. M. Taha and D.-E. A. Mansour, “Novel Power Transformer Fault Diagnosis Using Optimized Machine LearningMethods,” Intell. Autom. SOFT Comput., vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 739–752, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Tiyasha, T. M. Tung, and Z. M. Yaseen, “A survey on river water quality modelling using artificial intelligence models: 2000–2020,” J. Hydrol., vol. 585, p. 124670, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Agatonovic-Kustrin and R. Beresford, “Basic concepts of artificial neural network (ANN) modeling and its application in pharmaceutical research,” J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., vol. 22, no. 5, pp. 717–727, 2000. [CrossRef]
- H. Tao et al., “Groundwater level prediction using machine learning models: A comprehensive review,” Neurocomputing, vol. 489, pp. 271–308, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Kalam, U. Yousuf, S. A. Abu-Khamsin, U. Bin Waheed, and R. A. Khan, “An ANN model to predict oil recovery from a 5-spot waterflood of a heterogeneous reservoir,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 210, p. 110012, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Eckert, Z. Bělohlav, T. Vaněk, P. Zámostný, and T. Herink, “ANN modelling of pyrolysis utilising the characterisation of atmospheric gas oil based on incomplete data,” Chem. Eng. Sci., vol. 62, no. 18, pp. 5021–5025, 2007. [CrossRef]
- G. Qin, A. Xia, H. Lu, Y. Wang, R. Li, and C. Wang, “A hybrid machine learning model for predicting crater width formed by explosions of natural gas pipelines,” J. Loss Prev. Process Ind., vol. 82, p. 104994, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Wang et al., “Evolution of corrosion prediction models for oil and gas pipelines: From empirical-driven to data-driven,” Eng. Fail. Anal., vol. 146, p. 107097, 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Sami and D. S. Ibrahim, “Forecasting multiphase flowing bottom-hole pressure of vertical oil wells using three machine learning techniques,” Pet. Res., vol. 6, no. 4, pp. 417–422, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Qayyum Chohan, I. Ahmad, N. Mohammad, D. Manca, and H. Caliskan, “An integrated approach of artificial neural networks and polynomial chaos expansion for prediction and analysis of yield and environmental impact of oil shale retorting process under uncertainty,” Fuel, vol. 329, p. 125351, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. de A. Carvalho, P. J. Minnett, N. F. F. Ebecken, and L. Landau, “Machine-Learning Classification of SAR Remotely-Sensed Sea-Surface Petroleum Signatures—Part 1: Training and Testing Cross Validation,” Remote Sens., vol. 14, no. 13, 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, W. Han, W. Shao, L. Chen, and D. Zhao, “Data-Driven Predictive Model for Mixed Oil Length Prediction in Long-Distance Transportation Pipeline,” in 2021 IEEE 10th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference (DDCLS), May 2021, pp. 1486–1491. [CrossRef]
- J. H. Mendoza, R. Tariq, L. F. S. Espinosa, F. Anguebes, A. Bassam, and IEEE, “Soft Computing Tools for Multiobjective Optimization of Offshore Crude Oil and Gas Separation Plant for the Best Operational Condition,” 2021 18TH INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING, COMPUTING SCIENCE AND AUTOMATIC CONTROL (CCE 2021), no. 18th International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Computing Science and Automatic Control (CCE). 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Sakhaei, S. M. Zamir, E. R. Rene, M. C. Veiga, and C. Kennes, “Neural network-based performance assessment of one- and two-liquid phase biotrickling filters for the removal of a waste-gas mixture containing methanol, α-pinene, and hydrogen sulfide,” Environ. Res., vol. 237, p. 116978, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Hasanzadeh and M. Madani, “Deterministic tools to predict gas assisted gravity drainage recovery factor,” Energy Geosci., p. 100267, 2023. [CrossRef]
- X.-Q. Zhang, Q.-L. Cheng, W. Sun, Y. Zhao, and Z.-M. Li, “Research on a TOPSIS energy efficiency evaluation system for crude oil gathering and transportation systems based on a GA-BP neural network,” Pet. Sci., 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Ismail, H. F. Ewida, S. Nazeri, M. G. Al-Ibiary, and A. Zollo, “Gas channels and chimneys prediction using artificial neural networks and multi-seismic attributes, offshore West Nile Delta, Egypt,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 208, 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Goliatt, C. M. Saporetti, L. C. Oliveira, and E. Pereira, “Performance of evolutionary optimized machine learning for modeling total organic carbon in core samples of shale gas fields,” Petroleum, 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. N. Amar, A. J. Ghahfarokhi, C. S. W. Ng, and N. Zeraibi, “Optimization of WAG in real geological field using rigorous soft computing techniques and nature-inspired algorithms,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 206, 2021. [CrossRef]
- W. Mao et al., “Power transformers fault diagnosis using graph neural networks based on dissolved gas data,” in Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022, vol. 2387, no. 1. [CrossRef]
- I. Ghosh, T. D. Chaudhuri, E. Alfaro-Cortés, M. Gámez, and N. García, “A hybrid approach to forecasting futures prices with simultaneous consideration of optimality in ensemble feature selection and advanced artificial intelligence,” Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change, vol. 181, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. Wang, Y. Guo, D. Wang, Y. Zhang, R. He, and J. Chen, “Prediction model of natural gas pipeline crack evolution based on optimized DCNN-LSTM,” Mech. Syst. Signal Process., vol. 181, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Antariksa, R. Muammar, A. Nugraha, and J. Lee, “Deep sequence model-based approach to well log data imputation and petrophysical analysis: A case study on the West Natuna Basin, Indonesia,” J. Appl. Geophys., vol. 218, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. de O. Werneck et al., “Data-driven deep-learning forecasting for oil production and pressure,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 210, p. 109937, Mar. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Das, A. Paramane, S. Chatterjee, and U. M. Rao, “Accurate Identification of Transformer Faults From Dissolved Gas Data Using Recursive Feature Elimination Method,” IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., vol. 30, no. 1, pp. 466–473, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. S. Barjouei et al., “Prediction performance advantages of deep machine learning algorithms for two-phase flow rates through wellhead chokes,” J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol., vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1233–1261, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- V. Martinez and A. Rocha, “The Golem: A General Data-Driven Model for Oil & Gas Forecasting Based on Recurrent Neural Networks,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 41105 – 41132, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. B. Wang et al., “Optimized faster R-CNN for oil wells detection from high-resolution remote sensing images,” Int. J. Remote Sens., vol. 44, no. 22, pp. 6897–6928, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Hiassat, A. Diabat, and I. Rahwan, “A genetic algorithm approach for location-inventory-routing problem with perishable products,” J. Manuf. Syst., vol. 42, pp. 93–103, 2017. [CrossRef]
- V. Sharma, Ü. Cali, B. Sardana, M. Kuzlu, D. Banga, and M. Pipattanasomporn, “Data-driven short-term natural gas demand forecasting with machine learning techniques,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 206, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Phan and H. T. Duong, “Predicting burst pressure of defected pipeline with Principal Component Analysis and adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System,” Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip., vol. 189, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. O. De Salvo Castro, M. De Jesus Rocha Santos, F. R. Leta, C. B. C. Lima, and G. B. A. Lima, “Unsupervised Methods to Classify Real Data from Offshore Wells,” Am. J. Oper. Res., vol. 11, no. 05, pp. 227–241, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Hamedi, S. Zendehboudi, N. Rezaei, N. M. C. Saady, and B. Zhang, “Modeling and optimization of oil adsorption capacity on functionalized magnetic nanoparticles using machine learning approach,” J. Mol. Liq., vol. 392, p. 123378, Dec. 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. Ma, J. Shuai, D. Liu, and K. Xu, “Assessment on failure pressure of high strength pipeline with corrosion defects,” Eng. Fail. Anal., vol. 32, pp. 209–219, 2013.
- Y. Shuai, J. Shuai, and K. Xu, “Probabilistic analysis of corroded pipelines based on a new failure pressure model,” Eng. Fail. Anal., vol. 81, pp. 216–233, 2017.
- H. C. Phan, A. S. Dhar, and B. C. Mondal, “Revisiting burst pressure models for corroded pipelines,” Can. J. Civ. Eng., vol. 44, no. 7, pp. 485–494, 2017.
- J. L. F. Freire, R. D. Vieira, J. T. P. Castro, and A. C. Benjamin, “Part 3: Burst tests of pipeline with extensive longitudinal metal loss,” Exp. Tech., vol. 30, pp. 60–65, 2006.
- D. S. Cronin, “Assessment of corrosion defects in pipelines,” 2000.
- A. Ghasemieh, A. Lloyed, P. Bahrami, P. Vajar, and R. Kashef, “A novel machine learning model with Stacking Ensemble Learner for predicting emergency readmission of heart-disease patients,” Decis. Anal. J., vol. 7, p. 100242, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. R. V. Jeny, N. S. Reddy, P. Aishwarya, and Samreen, “A Classification Approach for Heart Disease Diagnosis using Machine Learning,” Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Signal Process. Control, vol. 2021-Octob, pp. 456–459, 2021. [CrossRef]
- R. K. Mazumder, A. M. Salman, and Y. Li, “Failure risk analysis of pipelines using data-driven machine learning algorithms,” Struct. Saf., vol. 89, p. 102047, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Liu, Y. Zhao, and Z. Wang, “Artificial Intelligence Method for Shear Wave Travel Time Prediction considering Reservoir Geological Continuity,” Math. Probl. Eng., vol. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Saroja, S. Haseena, and R. Madavan, “Dissolved Gas Analysis of Transformer: An Approach Based on ML and MCDM,” IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., Oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Raj, D. Sarathkumar, S. K. Venkatachary, and L. J. B. Andrews, “Classification and Prediction of Incipient Faults in Transformer Oil by Supervised Machine Learning using Decision Tree,” 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Aslam et al., “Anomaly Detection Using Explainable Random Forest for the Prediction of Undesirable Events in Oil Wells,” Appl. Comput. Intell. Soft Comput., vol. 2022, 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Turan and J. Jaschke, “Classification of undesirable events in oil well operation,” Proc. 2021 23rd Int. Conf. Process Control. PC 2021, pp. 157–162, 2021. [CrossRef]
- F. Gatta, F. Giampaolo, D. Chiaro, and F. Piccialli, “Predictive maintenance for offshore oil wells by means of deep learning features extraction,” Expert Syst., no. August, pp. 1–13, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Brønstad, S. L. Netto, and A. L. L. Ramos, “Data-driven Detection and Identification of Undesirable Events in Subsea Oil Wells,” SENSORDEVICES 2021 Twelfth Int. Conf. Sens. Device Technol. Appl., no. c, pp. 1–6, 2021.
- S. Ben Jabeur, R. Khalfaoui, and W. Ben Arfi, “The effect of green energy, global environmental indexes, and stock markets in predicting oil price crashes: Evidence from explainable machine learning,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 298, p. 113511, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. K. Hassan Baabbad, E. Artun, and B. Kulga, “Understanding the Controlling Factors for CO2 Sequestration in Depleted Shale Reservoirs Using Data Analytics and Machine Learning,” Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Alsaihati, S. Elkatatny, A. A. Mahmoud, and A. Abdulraheem, “Use of Machine Learning and Data Analytics to Detect Downhole Abnormalities while Drilling Horizontal Wells, with Real Case Study,” J. Energy Resour. Technol. Trans. ASME, vol. 143, no. 4, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Kumar and H. Hassanzadeh, “A qualitative study of the impact of random shale barriers on SAGD performance using data analytics and machine learning,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 205, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Ma, H. Wang, M. Geng, Y. Ai, W. Zhang, and W. Zheng, “A new hybrid approach model for predicting burst pressure of corroded pipelines of gas and oil,” Eng. Fail. Anal., vol. 149, p. 107248, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Canonaco et al., “A Machine-Learning Approach for the Prediction of Internal Corrosion in Pipeline Infrastructures,” in 2021 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), May 2021, vol. 2021-May, pp. 1–6. [CrossRef]
- J. Fang, X. Cheng, H. Gai, S. Lin, and H. Lou, “Development of machine learning algorithms for predicting internal corrosion of crude oil and natural gas pipelines,” Comput. Chem. Eng., vol. 177, p. 108358, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Q. Lv et al., “Modelling minimum miscibility pressure of CO2-crude oil systems using deep learning, tree-based, and thermodynamic models: Application to CO2 sequestration and enhanced oil recovery,” Sep. Purif. Technol., vol. 310, p. 123086, 2023. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhu et al., “An automatic identification method of imbalanced lithology based on Deep Forest and K-means SMOTE,” Geoenergy Sci. Eng., vol. 224, no. May 2022, p. 211595, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. Majed, S. Al-Janabi, and S. Mahmood, “Data Science for Genomics (GSK- XGBoost) for Prediction Six Types of Gas Based on Intelligent Analytics,” in 2022 22nd International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications (ICCSA), 2022, pp. 28–34. [CrossRef]
- P. Chanchotisatien and C. Vong, “Feature engineering and feature selection for fault type classification from dissolved gas values in transformer oil,” in ICSEC 2021 - 25th International Computer Science and Engineering Conference, 2021, pp. 75–80. [CrossRef]
- M. de J. R. Santos et al., “Statistical analysis of offshore production sensors for failure detection applications / Análise estatística dos sensores de produção offshore para aplicações de detecção de falhas,” Brazilian J. Dev., vol. 7, no. 8, pp. 85880–85898, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Ali et al., “Reservoir characterization through comprehensive modeling of elastic logs prediction in heterogeneous rocks using unsupervised clustering and class-based ensemble machine learning,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 148, 2023. [CrossRef]
- C. Ashayeri and B. Jha, “Evaluation of transfer learning in data-driven methods in the assessment of unconventional resources,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 207, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Vuttipittayamongkol, A. Tung, and E. Elyan, “A Data-Driven Decision Support Tool for Offshore Oil and Gas Decommissioning,” IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 137063–137082, 2021. [CrossRef]
- T. Song et al., “A novel well-logging data generation model integrated with random forests and adaptive domain clustering algorithms,” Geoenergy Sci. Eng., vol. 231, 2023. [CrossRef]
- B. Awuku, Y. Huang, and N. Yodo, “Predicting Natural Gas Pipeline Failures Caused by Natural Forces: An Artificial Intelligence Classification Approach,” Appl. Sci., vol. 13, no. 7, 2023. [CrossRef]
- W. J. Al-Mudhafar, M. A. Abbas, and D. A. Wood, “Performance evaluation of boosting machine learning algorithms for lithofacies classification in heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs,” Mar. Pet. Geol., vol. 145, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Wen, L. Liu, J. Zhang, J. Hu, and X. Huang, “A hybrid machine learning model for landslide-oriented risk assessment of long-distance pipelines,” J. Environ. Manage., vol. 342, 2023. [CrossRef]
- D. A. Otchere, T. O. A. Ganat, V. Nta, E. T. Brantson, and T. Sharma, “Data analytics and Bayesian Optimised Extreme Gradient Boosting approach to estimate cut-offs from wireline logs for net reservoir and pay classification,” Appl. Soft Comput., vol. 120, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Gamal, S. Elkatatny, A. Alsaihati, and A. Abdulraheem, “Intelligent Prediction for Rock Porosity while Drilling Complex Lithology in Real Time,” Comput. Intell. Neurosci., vol. 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. F. H. Ismail, Z. May, V. S. Asirvadam, and N. A. Nayan, “Machine-Learning-Based Classification for Pipeline Corrosion with Monte Carlo Probabilistic Analysis,” Energies, vol. 16, no. 8, 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Prasojo et al., “Precise transformer fault diagnosis via random forest model enhanced by synthetic minority over-sampling technique,” Electr. Power Syst. Res., vol. 220, p. 109361, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Ali Salamai, “Deep learning framework for predictive modeling of crude oil price for sustainable management in oil markets,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 211, p. 118658, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Ma et al., “Very Short-Term Renewable Energy Power Prediction Using XGBoost Optimized by TPE Algorithm,” 2020 4th Int. Conf. HVDC, HVDC 2020, pp. 1236–1241, 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. Ma, Z. Jiang, and W. Liu, “Modeling Drying-Energy Consumption in Automotive Painting Line Based on ANN and MLR for Real-Time Prediction,” Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. - Green Technol., vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 241–254, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Z. Guo, H. Wang, X. Kong, L. Shen, and Y. Jia, “Machine Learning-Based Production Prediction Model and Its Application in Duvernay Formation,” Energies, vol. 14, no. 17, p. 5509, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. M. Ibrahim et al., “Well Performance Classification and Prediction: Deep Learning and Machine Learning Long Term Regression Experiments on Oil, Gas, and Water Production,” Sensors, vol. 22, no. 14, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Yin, C. Liu, W. Wu, K. Song, Y. Dan, and G. Cheng, “An integrated framework for criticality evaluation of oil & gas pipelines based on fuzzy logic inference and machine learning,” J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng., vol. 96, p. 104264, 2021. [CrossRef]
- H. Chen, C. Zhang, N. Jia, I. Duncan, S. Yang, and Y. Yang, “A machine learning model for predicting the minimum miscibility pressure of CO2 and crude oil system based on a support vector machine algorithm approach,” Fuel, vol. 290, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Naserzadeh and A. Nohegar, “Development of HGAPSO-SVR corrosion prediction approach for offshore oil and gas pipelines,” J. Loss Prev. Process Ind., vol. 84, p. 105092, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yuan, L. Chen, G. Liu, W. Shao, Y. Zhang, and W. Yang, “Physics-based Bayesian linear regression model for predicting length of mixed oil,” Geoenergy Sci. Eng., vol. 223, p. 211466, 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. E. P. Box, G. M. Jenkins, G. C. Reinsel, and G. M. Ljung, Time series analysis: forecasting and control. John Wiley \& Sons, 2015.
- R. H. McCuen, Modeling Hydrologic Change: Statistical Methods. CRC Press, 2016.
- J. Liu, Z. Zhao, Y. Zhong, C. Zhao, and G. Zhang, “Prediction of the dissolved gas concentration in power transformer oil based on SARIMA model,” Energy Reports, vol. 8, pp. 1360–1367, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Yang, X. Liu, R. Yu, Z. Hu, and X. Duan, “Long short-term memory suggests a model for predicting shale gas production,” Appl. Energy, vol. 322, p. 119415, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, X. Guo, L. Liu, Y. Cao, and B. Yang, “A novel seasonal grey model for forecasting the quarterly natural gas production in China,” Energy Reports, vol. 8, pp. 9142–9157, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Rashidi et al., “Determination of bubble point pressure & oil formation volume factor of crude oils applying multiple hidden layers extreme learning machine algorithms,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 202, p. 108425, Jul. 2021. [CrossRef]
- X. Gong et al., “A Leak Sample Dataset Construction Method for Gas Pipeline Leakage Estimation Using Pipeline Studio,” in International Conference on Advanced Mechatronic Systems, ICAMechS, 2021, vol. 2021-Decem, pp. 28–32. [CrossRef]
- S. Chung et al., “Capillary flow velocity profile analysis on paper-based microfluidic chips for screening oil types using machine learning,” J. Hazard. Mater., vol. 447, p. 130806, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- N. Mohamadian et al., “A geomechanical approach to casing collapse prediction in oil and gas wells aided by machine learning,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 196, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Sabah, M. Mehrad, S. B. Ashrafi, D. A. Wood, and S. Fathi, “Hybrid machine learning algorithms to enhance lost-circulation prediction and management in the Marun oil field,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 198, p. 108125, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Shi et al., “Real-time natural gas release forecasting by using physics-guided deep learning probability model,” J. Clean. Prod., vol. 368, Sep. 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. P. F. Machado, R. E. V. Vargas, P. M. Ciarelli, and C. J. Munaro, “Improving performance of one-class classifiers applied to anomaly detection in oil wells,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 218, no. December 2021, p. 110983, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Zhou, B. Liu, M. Shao, C. Yin, Y. Jiang, and Y. Song, “Lithologic classification of pyroclastic rocks: A case study for the third member of the Huoshiling Formation, Dehui fault depression, Songliao Basin, NE China,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 214, 2022. [CrossRef]
- G. Zhang, Z. Wang, S. Mohaghegh, C. Lin, Y. Sun, and S. Pei, “Pattern visualization and understanding of machine learning models for permeability prediction in tight sandstone reservoirs,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 200, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zuo, L. Ma, S. Liang, J. Liang, H. Zhang, and T. Liu, “A semi-supervised leakage detection method driven by multivariate time series for natural gas gathering pipeline,” Process Saf. Environ. Prot., vol. 164, pp. 468 – 478, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Z. Chen, W. Yu, J.-T. Liang, S. Wang, and H. Liang, “Application of statistical machine learning clustering algorithms to improve EUR predictions using decline curve analysis in shale-gas reservoirs,” J. Pet. Sci. Eng., vol. 208, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Fernandes, K. S. Komati, and K. de Souza Gazolli, “Anomaly detection in oil-producing wells: a comparative study of one-class classifiers in a multivariate time series dataset,” J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol., 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Z. Gao et al., “Application of GMDH model to predict pore pressure,” Front. EARTH Sci., vol. 10, 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Cirac, J. Farfan, G. D. Avansi, D. J. Schiozer, and A. Rocha, “Deep hierarchical distillation proxy-oil modeling for heterogeneous carbonate reservoirs,” Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell., vol. 126, p. 107076, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Z. Dayev et al., “Modeling the flow rate of dry part in the wet gas mixture using decision tree/kernel/non-parametric regression-based soft-computing techniques,” FLOW Meas. Instrum., vol. 86, 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Das, A. Paramane, S. Chatterjee, and U. M. Rao, “Sensing Incipient Faults in Power Transformers Using Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory Network,” IEEE Sensors Lett., vol. 7, no. 1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Gao, Z. Li, M. Zhang, Y. Gao, and W. Gao, “Unsupervised Seismic Random Noise Suppression Based on Local Similarity and Replacement Strategy,” IEEE Access, vol. 11, pp. 48924 – 48934, 2023, [Online]. Available: https://www.scopus.com/inward/record.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85159843987&doi=10.1109%2FACCESS.2023.3272905&partnerID=40&md5=6f6bfe47d0797b04b4fa925bc730880e.

| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | SVM, QPSO-ANN, WQPSO-ANN, LWQPSO-ANN | Non-temporal | Pipeline | Buried gas pipeline. 99 samples |
Prediction | Pipe diameter (mm), Operating pressure (MPa), Cover depth (m), Crater width (m) | crater width | Map, R2, MSE. RMSE, MAPE, MAE | LWQPSO-ANN | The proposed method outperformed the other method by more than 95%. |
| [45] | RF, KNN, ANN | Non-temporal | Wells | Middle East fields: for vertical wells 206 samples |
Prediction | oil gravity (API), well perforation depth (Depth (ft), Surface temperature (ST (F)), well bottom-hole temperature (BT (F)), flowing gas rate (Qg (Mscf/day), flowing water rate (Qw (bbl/day), production tubing internal diameter (ID (inches) and wellhead pressure (Pwh (psia)). | vertical oil wells' flowing bottom-hole pressure Pwf (psia) | MSE, R2 | ANN R2 = 97% (training) and 93% (testing) |
The suggested model has a much greater value than the other models. |
| [46] | ANN, LSB, Bagging | Non-temporal | Oil | Oil shale. 2,600 sample |
Prediction | Air molar flowrate, illite silica, carbon, hydrogen content, feed preheater temp, air preheater temp | Petroleum output with CO2 emissions | RMSE | ANN Correlation correlations of 99.6% for oil yield and 99.9% for CO |
The suggested model's precision outperformed the performance of the remaining models. |
| [47] | NB, KNN, DT, RF, SVM, ANN | Temporal | Oil | Ocean slick signature 769 samples |
Classification | Data is confidential | Sea-Surface Petroleum Signatures | Accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and predictive values | ANN Accuracy = 90% |
The proposed model did not give significant results. |
| [44] | ANN, SVM, EL, and SVR | Non-temporal | Pipeline | Data is confidential | Classification | CO2, temperature, pH, liquid velocity, pressure, stress, glycol concentration. H2S, organic acid, oil type, water chemistry, hydraulic diameter | Corrosion defect depth. | MSE, R2 | EL, ANN, and SVR | The proposed methods have a low error rate. |
| [48] | PLS, DNN, FPM, FP-DNN, FP-PLS | Non-temporal | Pipeline | long-distance pipelines 2,093 samples |
Prediction | Mixed oil length, inner diameter, pipeline width, Reynolds number, equivalent length, and actual mixed oil length. | Mixed oil length. | RMSE | DNN RMSE = 146% |
The error rate is not convincing and is the highest. |
| [49] | ANN, GA | Non-temporal | Crude Oil | ASPEN HYSYS V11 process simulator |
Prediction | Well, feed flow rate, The pressure of gas products, Interstage gas discharge pressure, Isentropic efficiency of centrifugal compressor. |
Enhance petroleum production. | R2 | ANN | The performance enhancement of the variable using the ANN+GA has improved. |
| [50] | ANN | Non-temporal | Gas | Data is confidential. 104 samples |
Prediction | Sulphur dioxide, methanol, and α-pinene. | The removal of gas-phase M, P, and H in an OLP-BTF and a TLP-BTF. | R2, MSE | ANN+PSO R2 > 99% |
The proposed model is good, and the author suggested improving the model with real-world applications. |
| [51] | ANN, LSSVM, and MGGP | Temporal | Reservoir | Previous experimental and simulation studies 223 samples |
Prediction | Height, dip angle, wetting phase viscosity, non-wetting phase viscosity, wetting phase density, non-wetting phase density, matrix porosity, fracture porosity, matrix permeability, fracture permeability, Injection rate, production time, and recovery factor. | gas-assisted gravity drainage (GAGD) | R2, RMSE, MSE, ARE, and AARE | ANN R2 = 97% RMSE = 0.0520 |
The ANN is outperformed the proposed method (MGGP = 89% (R2) and 0.0846 (RMSE) |
| [56] | GNN, Multivariate Time Series | Temporal | Transformer | DGA 1,408 samples |
Clustering | H2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, C2H2, CO, CO2 | Power transformer fault diagnosis | Accuracy | MTGNN Accuracy = 92% |
The model has proven to be effective in its application. |
| [30] | ANN, Multilayer Perceptron with Backpropagate | Non-temporal | Crude Oil | recent literature 172 samples |
Prediction | Pressure (P)[Kpa], Temperature (T) [C], Liquid Viscosity (uL)[c.p.], Gas Viscosity (uG)[c.p.], Liquid Molar Volume (VL) [m3/kmol], Gas Molar Volume (VG) [m3/kmol], Liquid Molecular Weight (MWL) [kg/kmol], Gas Molecular Weight (MWG) [kg/kmol], and Interfacial Tension (o) [Dyne] | Diffusion Coefficient (D) [m2/s] | MSE, RMSE | Multilayer Perceptron with Backpropagate R2 for training is 88%, and testing is 89% |
The suggested model has low accuracy. The hybrid does not improve the model's accuracy. |
| [52] | GA with backpropagation neural network | Temporal | Crude oil | crude oil gathering and transportation system. 509 samples |
Prediction | The inlet temp of the combined system, outlet temp of the combined system, the inlet pressure of the combined system, outlet pressure of the combined system, inlet and outlet temp for the transfer station system, inlet and outlet pressure of the transfer station system, inlet and outlet of oil gathering wellhead system, treatment liquid volume, tot power consumption, and tot gas consumption | Energy = 99% Heat = 99% Power = 97% |
R2 | GA with backpropagation neural network | The model provides considerable results. |
| [53] | MLP, ANN | Temporal | Drilling | Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC) 1,045 samples |
Clustering and Classification | Epoch, age, formation, lithology, fields | Gas channels and chimneys prediction | RMSPE | MLP RMSE = 0.10 |
The proposed model has a lower error rate and outperforms the other method. |
| [54] | ELM, Elastic Net Linear, Linear-SVR, Multivariate Adaptive Regression Spline, Artificial Bee Colony, PSO, Differential Evolution, Simple Genetic Algorithm, GWO, xNES | Temporal | Shale gas | YuDong-Nan shale gas field | Prediction | The following minerals are quartz, calcite, dolomite, barite, pyrite, siderite, clay, and K-feldspar. | total organic carbon | R2, RMSE, MAE, MAPE, MARE, WI | DE+ELM = 0.497 (RMSE) | Acceptable results for ELM models hybrid with the proposed method except for GWO |
| [55] | MLP, Radial Basis Functions Neural Network | Temporal | Reservoir | Gullfaks” in the North Sea | Prediction | Injection rate for water, gas, and half-cycle time. Downtime. | Water alternating gas | Average absolute relative deviation (AARD) | MLP-LMA | The proposed model outperforms the other two proxy models and significantly reduces simulation time. |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [60] | LSTM and GRU | Temporal | Reservoir | The Metro Interstate Traffic Volume Data set, The Appliances Energy Prediction Dataset, UNISIM-II-M-CO 301 samples |
Prediction | Fluid production (oil, gas, and water), pressure (bottom-hole), and their ratios (water cut, gas-oil ratio, and gas-liquid ratio). | Oil production and pressure | MAE, RMSE, SMAPE | LSTM + Seq2Seq andGRU2architectures | The author suggested looking at another metaheuristic method, such as GA. |
| [58] | DCNN + LSTM, ANN, SVR, LSTM, RNN | Temporal | Pipeline | Real-time pipeline crack 90,000 data samples |
Prediction | Pipeline condition, label, crack size, data length, sampling frequency, tube pressure | Natural gas pipeline crack | RMSE, MAPE, MAE, MSE, SNR | Optimized DCNN + LSTM Accuracy = 99.37% |
The model showcases impressive performance. |
| [59] | LSTM, Bi-LSTM, GRU | Temporal | Well | West Natuna Basin dataset 11,497 samples |
Prediction | GR, Vp, LLD, LLS, NPHI, and RHOB. | Well-log data imputation | MAE, RMSE, MAPE, R2 | LSTM RMSE = 94% |
The suggested model provides a greater accuracy. |
| [61] | KNN, SVM, XGBoost | Non-temporal | Transformer | DGA local power utilities and IEC TC 10 data set 1,530 samples |
Classification | F7, F10, F17, F18, F19, F21, F24, F34, F36, and F40 |
Transformer Faults | Accuracy, Precision, Recall | KNN + SMOTE Accuracy: DGA = 98% IEC TC 10 = 97% |
The proposed model outperforms the other model. |
| [62] | DL, DT, RF, ANN, SVR | Non-temporal | Reservoir | Sorush oil field and oil field of south Iran 7,245 samples |
Prediction | Measure choke size (D64), wellhead pressure (Pwh), oil specific gravity (γo), and gas-liquid ratio (GLR). | Wellhead choke flow rates | RMSE, R2 | DL R2 = 99% |
Compared to the other model, the accuracy of the suggested model is greater. |
| [63] | LSTM, GRU | Temporal | Reservoirs | UNISIM-IIH and Volve Oilfield 3,257 samples |
Classification | oil, gas, water, or pressure | oil & gas forecasting |
SMAPE, R2 | GRU R2 = 99% |
The proposed model gives the highest accuracy. |
| [64] | Faster R-CNN_Res50, Faster R-CNN_Res50_DC, Faster R-CNN_Res50_FPN, With Edge detection, Cluster+Soft-NMS |
Non-temporal | Well | Google Earth Imagery 439 samples |
Clustering | Width and height | clustered oil wells | Precision, Recall, F1-measure, AP | Faster R-CNN with ClusterRPN = 71% | The proposed method’s running time higher than the other models and accuracy less than 90%. |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [69] | ANFIS, LSSVM-CSA, Gene Expression Programming | Non-temporal | Oil | Data is confidential | Prediction | Mixing time (min), MNP dosage (g/L), Oil concentration (ppm) | Oil adsorption capacity (mg/g adsorbent) | R2, MPE, MAPE | LSSVM-CSA R2 = 99% |
The proposed method is outperformed by the other two models. |
| [67] | ANFIS, ANFIS+PCA | Non-temporal | Pipeline | Published studies. [70,71,72,73,74] 217 samples |
Classification | Pipe dimension, burst pressure, pipe wall thickness, defect depth, defect width | Pressure | RMSE, MAE, R2 | ANFIS+PCA R2 = 99% |
The proposed method outdistanced other models and significantly improved the model accuracy. |
| [41] | ANN, SVR, ANFIS | Non-temporal | Reservoir | CPG's waterflooding research group at the King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals in Saudi Arabia. 9,000 samples |
Clustering | Reservoir heterogeneity degree (V), mobility ratio (M), permeability anisotropy ratio (kz/kx), wettability indicator (WI), production water cut (fw), and oil/water density ratio (DR). | The effectiveness of moveable oil recovery during a flood (RFM). | MAPE, MAE, MSE, R2 | ANN | The proposed model has a better accuracy than the other models and saves the runtime and cost. |
| [68] | RF, Fuzzy C Means, Control Chart | Temporal | Well | 3W dataset 50,000 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, T-PDG, and T-PCK, grouping three classes (“normal,” “high fault,” “high fault”) | failure detection applications | Total Variance | Control chart + RF Specificity = 99% Sensitivity = 100% |
The proposed method has shown higher sensitivity and specificity. |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [77] | KNN, DT, RF, NB, AdaBoost, XGBoost, and CatBoost | Non-temporal | Pipeline | National Science Foundation (NSF) Critical Resilient Interdependent Infrastructure Systems and Processes (CRISP) 959 samples |
Classification | Pipe diameter, wall thickness, defect depth, defect length, yield strength, ultimate tensile strength, operating pressure | Failure risk pipeline | Precision, Recall, Mean accuracy | XGBoost Accuracy = 85% |
The proposed model needs to have an improvement in accuracy. |
| [78] | LR, RF, SVM, XGBoost, ANN | Non-temporal | Reservoir | Well-log data from North China 1,500 samples |
Classification | CAL, CNL, AC, GR, PE, RD, RMLL, RS, SP, DEN, DTS, and SP | Shear wave travel time (DTS) | R2 | XGBoost R2 = 99% (Training) and 96% (Testing) |
The best model is significant. |
| [37] | ELM, SVM, KNN, DT, RF, EL | Temporal | Transformer | DGA 542 samples |
Classification | C2H2, C2H6, CH4, H2 | Power transformer fault | Mean Accuracy | EN Accuracy = 78% (Training) and 84% (Testing) |
The proposed model’s performance accuracy is not above 90%. |
| [79] | DT, LDA, GB, Ensemble Tree, LGBM, RF, KNN, NB, LR, QDA, Ridge, SVM-Linear | Non-temporal | Transformer | DGA 3,147 samples |
Classification | C2H2, C2H4, C2H6, CH4 | Transformer fault | Accuracy, AUC, Recall, Precision, F1-Measure, Kappa, MCC, and Time-taken. | QDA Accuracy = 99.29% |
The proposed method has the best accuracy classifier model. |
| [80] | DT | Temporal | Well | KG Composition 180 samples |
Classification | KG, including hydrogen (H2), methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), ethylene (C2H4), and acetylene (C2H2) | Incipient Faults in Transformer Oil. | Accuracy. AUC | DT Accuracy = 62.9% |
The current model exhibits potential, and we recommend exploring opportunities for refinement to enhance its overall efficacy. |
| [81] | LR, DT, RF, KNN, SMOTE, XAI, SHAP, LIME | Non-temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, P-MON- PCK, T-JUS, PCK, P-JUS- CKGL, T-JUS- CKGL, QGL | Detect anomalies in oil wells | accuracy, recall, precision, F1-score, and AUC | RF Accuracy = 99.6%, recall = 99.64%, precision = 99.91%, F1-score = 99.77%, and AUC = 1.00%. |
The result of the proposed model is significant. |
| [82] | LDA, QDA, Linear SVC, LR, DT, RF, Adaboost | Temporal | Well | 3W dataset 2,000 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, P-MON-CKP, T-JUS-CKP | Undesirable events | F1-score, Accuracy | DT Accuracy = 97% |
The feature selection did not boost accuracy, and training time was increased with feature selection. The proposed method struggles with class 2 due to limited data and mismatched labels from calculated features. |
| [106] | DT, ANN, SVM. LR. KNN, NB | Temporal | Pipeline | external defects of pipelines in the United States 7,000 samples |
Classification | Consider the defect's length, breadth, and pipeline's nominal thickness. | Classification for pipeline corrosion | Accuracy | DT Accuracy = 99.9% |
The accuracy of the model is significant to the research. |
| [85] | LGBM, CatBoost, XGBoost, RF, and NN | Temporal | Crude oil | WTI crude oil 2,687 samples |
Classification | Gold, silver, crude oil, platinum, copper, the dollar index, the volatility index, and the euro Bitcoin: Green Energy Resources ESG. | Oil prices | accuracy, and AUC | LGBM and RF | The proposed method indicates superiority over traditional methods. |
| [86] | GB, RF, MLR | Non-temporal | Reservoir | Shale gas reservoirs 1,400 samples |
Prediction | Horizontal wellbore length, hydraulic fracture length, reservoir length, SRV fracture porosity, permeability, spacing, and pressure, total production time. | CO2 | MSE | RF | The best method is surpassing the other method in ML. |
| [87] | RF, ANN, FN | Temporal | Drilling | Real time Well-1 data 8,983 samples |
Classification | Standpipe pressure (SPP), weight-on-bit (WOB), rotary speed (RS), flow rate (Q), hook load (HL), rate of penetration (ROP), and rotary speed (RS). | torque and drag (T&D) | R and AAPE | RF | The proposed model has higher accuracy than the other two models. |
| [88] | RF | Temporal | Reservoir | 2D simulation in STARS 240 samples |
Prediction | Formation compressibility, volumetric heat capacity, rock, water, oil, and thermal conductivity. | Shale barrier | R2, RMSE | RF | The author suggested that incorporating more training data and features can improve the proposed method. |
| [89] | RF, XGBoost, SVM, LGBM | Non-temporal | Pipeline | full-scale corroded O&G pipelines 314 samples |
Prediction | Depth, length, and width of corrosion defects, wall thickness, pipe diameter, steel grade, and burst pressure. | Corroded pipelines of gas and oil of burst pressure. | R2, RMSE, MAE, MAPE | XGBoost R2 = 99% (training) and 98% (testing) |
The hybrid proposed model has significantly higher prediction accuracy. |
| [90] | XGBoost, SVM, NN | Non-temporal | Pipeline | OLGA data and PIG data 1,700 samples |
Classification | Geometrical variables: Odometry begins, ends, latitude, longitude, elevation, and bar length.Water volumetric flow rate, continuous velocity, water film shear stress, hold-up, flow regime, pressure, total mass and volumetric flow rates inclination, temperature, section area, gas mass and volumetric flow rates, gas velocity, wall shear stress, total water mass and flow rate (including vapor), | Internal Corrosion in Pipeline Infrastructures | Mean accuracy and F1 score | XGBoost Accuracy = 62% |
The proposed model needs an improvement in the accuracy. |
| [91] | RF, CatBoost | Non-temporal | Pipeline | Crude oil dataset 3,240 samples |
Prediction | stream compositions (nO2, nH2S, nCO2), pressure (P), velocity (v), and temperature (T) | Corrosion rates | R2, MSE MAE RMSE | CatBoost Accuracy = 99.9% training and testing |
The proposed model’s accuracy is outperformed the other models. |
| [32] | RF, KNN | Temporal | Transformer | DGA 11,400 samples |
Classification | Acetylene (𝐶𝐶2𝐻𝐻2), Ethylene (𝐶𝐶2𝐻𝐻4), Ethane (𝐶𝐶2𝐻𝐻6), Methane (𝐶𝐶𝐻𝐻4), and Hydrogen (𝐻𝐻2) |
Identify transformer fault types | Mean accuracy | KNN Accuracy = 88% |
The proposed model needs an improvement on the accuracy. |
| [92] | XGBoost, CatBoost, LGBM, RF, deep MLN, DBN, CNN | Non-Temporal | Crude-oil | Previous studies on CO2-oil MMP databank 310 samples |
Classification | Crude oil fractions (N2, C1, H2S, CO2, C2-C5), average critical injection gas temperature (Tcave), reservoir temperature (Tres), molecular weight of C5+ fraction (MWc5+). | Estimating the MMP of CO2-crude oil system | ARD, AARD, RMSE, MPa, SD |
CatBoost R2 = 99% |
The proposed model confirms its superiority against other models. |
| [93] | DF + K-means, RF, SVM, DNN, DF | Non-temporal | Lithology | Lithology dataset from Pearl River Mouth Basin 601 samples |
Classification | Sandstone (S00), siltstone (S06), grey siltstone (S37), mudstone (N00), sandy mudstone (N01), and limestone (H00). | lithology identification | Precision, recall and Fβ | DF + K-means Accuracy = 90% |
The baseline method cannot predict well on the minority class, small amount data label, error labelling, and noisy data |
| [94] | GSK- XGBoost | Temporal | Transformer | DGA 128 samples |
Classification | ammonia, acetaldehyde, acetone, ethylene, ethanol, and toluene | Ethanol, Ethylene. Ammonia, Acetaldehyde. Acetone and Toluene | Accuracy, precision, recall, f-measurement, beta-factor | GSK- XGBoost Mean accuracy = 50% |
The computational time is increased and the proposed model’s accuracy after use the develop method does not exceed to 90% |
| [95] | LGBM, XGBoost, RF, LR, SVM, NB, KNN, DT | Non-temporal | Transformer | DGA 796 samples |
Classification | H2, CH4, C2H2, C2H4, and C2H6 | fault type classification | accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 scores | LGBM Accuracy = 87.06% |
The model demonstrates a high level of competence. |
| [5] | Adaboost, RF, KNN, NB, MLP, SVM | Non-temporal | Drilling | Drill bit type in Norwegian Wells 4,312 samples |
Classification | Depth as Measured (DT), Ve rtical True Depth (TVD) Penetration Rate (ROP) Bit weight (WOB) Minutes per round (RPM) torque (TQ) SPP, or standpipe pressure Mud mass (MW) Rate of Flow in (FR) Totalized Gas (TG) Bit kind (BT) Bit Quantity (BS) DEXP stands for D-exponent. Area of total flow (TFA) Specific Mechanical Energy (MSE) Cut Depth (DC) Aggressiveness of Drill Bit (DBA). |
Drill Bit Selection | Accuracy, Precision, F1 Score, Recall, MCC, G-mean | RF Accuracy = 97% (Training) and 91% (Testing) |
The proposed method is more reliable, stable, and accurate than previous models. |
| [96] | RF | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, P-PCK, T-PCK, P-JUS-CKGL, T-JUS-CKGL, and gas lift flow | Early fault detection | Accuracy, Faulty-normal accuracy (FNACC), Real faulty-normal accuracy (RFNACC) | RF Accuracy = 94% |
The proposed method gives a good result for detecting the early fault. |
| [83] | One Directional, CNN, RF, GNN, QDA | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, T-TPT, P-MON-CKP, T-JUS-CKP, P-JUS-CKGL, QGL. | Anomalous events in oi | Accuracy, precision, recall, F1 score | RF Mean accuracy = 95% |
Time windows increase |
| [84] | RF, PCA | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, P-MON-CKP, T-PCK | Anomalous events in oil wells | Accuracy | RF+PCA Accuracy = 90% |
The proposed method’s accuracy > 95% for all classes. |
| [97] | SVM, LOF, RF | Temporal | Reservoir | Well log data. 37 samples |
Clustering | Depth, gammar ray, shallow resistivity, deep resistivity, neutron, density, CALI, DTS | Sonic (DTC) | R2 | KMeans+RF R2=0.92 to R2=0.98 |
The proposed hybrid approach outperformed several baseline methods. |
| [98] | RF | Temporal | Well | Field and well-scale data from a significant US 934 samples |
Clustering | API, On-stream date, Surface latitude and longitude, Formation thickness, TVD, Lateral length, Total proppant mass, Total injected fluid volume, API gravity, Porosity, Permeability, TOC, VClay, Oil production rate, Gas production rate, Water production rate, GPI, Frac fluid. | barrel of oil equivalent (BOE) | RMSE, R2 | RF RMSE: Train = 7.25% Test = 17.49% |
The proposed method needs an improvement of accuracy, and the model is overfitting. |
| [100] | RF with Analog-to-digital converters | Non-temporal | Well | Well-logging dataset 100 samples |
Clustering | neutron (CNL), gamma ray (GR), density (DEN), and compres sional slowness (DTC) | well-logging data generation | RMSE, MAE, MAPE, MSE | RF with Analog-to-digital converters RMSE = 9%, MAE = 6%, MAPE = 0.031% MSE = 86% |
The proposed model needs an improvement on the accuracy for clustering. |
| [107] | RF | Temporal | Transformer | DPM1 and DPM2 for DGA 2,123 samples |
Classification | H2 (hydrogen), CH4 (methane), C2H2 (acetylene), C2H4 (ethylene), C2H6 (ethane), CO (carbon monoxide), CO2 (carbon dioxide), O2 (oxygen) and N2 (nitrogen) | transformer fault diagnosis | Accuracy | RF Accuracy = DPM1 = 96.2% DPM2 = 96.5% |
For the evaluation dataset, the suggested models diagnose errors with a satisfactory level of performance. |
| [101] | KNN, Multilayer Perceptron Neural Network, multiclass SVM, XGBoost | Temporal | Pipeline | climate change data 81 samples |
Classification | location, time, pipeline age, pipeline material, temperature, humidity, and wind speed. | gas pipeline | Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1-Score | XGBOOST Accuracy = 92% |
The model outperformed other models however it needs to have an improvement. |
| [102] | LogitBoost, GBM, XGBoost, AdaBoost, KNN | Temporal | Well | Lithofacies and Well-log dataset 399 samples |
Classification | GR, CALI, NEU, DT, DEN, RES DEP, RES SLW, PHIT and SW | lithofacies predictions | total percent of correct (TPC) | XGBoost TPC = 97% |
The model gives significantly results to the proposed method. |
| [103] | recursive feature elimination and particle swarm optimization-AdaBoost | Non-temporal | Pipeline | Changshou-Fuling-Wulong-Nanchuan (CN) gas pipeline dataset 3,986 samples |
Clustering | Landslide susceptibility Area, Percentage, and Historical landslides. | long-distance pipelines | Accuracy, sensitivity, precision. F1 score | recursive feature elimination and particle swarm optimization-AdaBoost Accuracy = 90% (Training) and 83% (Testing) |
The proposed model needs an improvement on the accuracy. |
| [108] | LSTM, AdaBoost, LR, SVR, DNN, RF, adaptive RF | Temporal | Crude Oil | United states’ Energy Information Administration Brent COP data |
Prediction | Shape, location, scale | crude oil price (COP) | MAPE, MSE, RMSE, MAE, EVS | Adaptive RF MAPE = 112.31%; MAE = 52%; MSE = 53%; RMSE =73%; R2 = 99%; EVS = 99% |
The proposed model is outperformed than others however the running time is highest than the other models |
| [105] | RF, DT | Temporal | Drilling | Data is confidential | Prediction | WOB, torque, standpipe pressure, drill string rotation speed, rate of penetration, and pump rate. | Rock porosity | R2, AAPE, VAF | RF Accuracy = 99% training and 90% testing |
The model stands out for its exceptional performance. |
| [104] | BayesOpt-XGBoost, XGBoost | Non-temporal | Reservoir | The Equinor Volve Field Datasets 2,853 samples |
Classification | DT, GR, NPHI, RT, and RHOB. | vshale, porosity, horizontal permeability (KLOGH), and water saturation. | RMSE, MAE |
BayesOpt-XGBoost Accuracy = 93%, precision score = 98%, recall score = 86%, and combined F1-score = 93% |
The proposed method does not robust enough to predict all the output. |
| [99] | RF, KNN, NB, DT, NN | Temporal | Transformer | New O&G decommissioning dataset from GitHub 1,846 samples |
Classification | Size, diameter, length, metal, plastic, concrete, residues, position, and decision of the company, organization name, type, technical, safety, sociological, environmental, cost, weight, | predictive decommissioning options | Recall, Precision, F1-score, AUC | RF Accuracy: Full features = 80.06% Redundant removed = 80.66% |
The proposed method needs an improvement. |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [111] | MLR, SVR, GPR | Non-temporal | Gas | M6COND and M6GAS 129 samples |
Clustering | Condensate-gas ratio, total horizontal lateral length, gas saturation, total organic carbon content, cluster and stage counts, proppant amount, fluid volume, and total horizontal lateral length. | Gas well. | RMSE, R2 | GPR | The proposed method needs improvement in the accuracy. |
| [112] | XGBoost, ANN, RNN, MLR, PLR, SVR, DTR, RFR | Temporal | O&G production | Saudi Aramco of five well reservoirs 1,968 samples |
Classification | Location, contact, average permeability, volume, production, pressure ratio between the wellhead and bottomhole, and production. | Oil, gas, and water. | R2, MAE, MSE, RMSE | RNN R2: Oil = 98% Gas = 87% Water = 92% |
The proposed model needs an improvement on the output. |
| [113] | MLP, RF, SVR | Non-temporal | Pipeline | History record of pipeline failure 149,940 samples |
Classification | Effects of transportation disruptions on safety and health, the environment and ecology, and equipment maintenance. | Natural gas pipeline failure. | RMSE, MAE. MSE. R2 | RF | The proposed methods have shortest computing time and best fitting results. |
| [114] | SVM | Non-temporal | Reservoir | MMP data 147 samples |
Classification | reservoir temperature, oil composition and gas composition | Minimum miscibility pressure of CO2 and crude oil. | MSE | SVM- POLY kernel | The proposed model’s accuracy is outperformed the other models. |
| [19] | RF, ARN, LSTM, Independently Recurrent Neural Network, component-wise gradient | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, T-TPT, P-TPT, Initial Normal, Steady state, transient | Oil wells production. | Accuracy, precision, recall, f-measure | ARN Accuracy = 96% Precision = 88% Recall = 84% F-measure = 85% |
The proposed model is not robust because misclassification for undesirable events for type 3 and type 8. |
| [115] | SVR-GA-PSO, SVR, SVR-GA, SVR-FA, SVR-PSO, SVR-ABC, SVR-BAT, SVR-COA, SVR-GWO, SVR-HAS, SVR-ICA, SVR-SFLA | Temporal | Pipeline | Iranian Oilfields 340 samples |
Classification | Onshore oil and gas pipelines: Pit depths, exposure times, pitting start times, operational pressures, temperatures, water cuts, redox potentials, resistivities, pH, concentrations of sulfate and chloride ions, production rates. | Carbon steel corrosion rate | MSE, RMSE, MAE, EVS, R2, RSE | SVR-GA-PSO R2 = 99% RMSE = 0.0099 MSE = 9.84*10−5 MAE = 0.008 RSE = 0.001 EVS = 0.955 |
The proposed model shows a good result than others |
| [116] | BLR, PBBLR, ANN, Gradient Boosting DT | Non-temporal | Pipeline | SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) system 728 samples |
Prediction | Diameter, Reynolds number, transportation distance, mixed oil length. | Actual mixed oil length | RMSE, MAE, R2 | PBBLR | The proposed model is required to improve accuracy |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [119] | SARIMA, LSTM, AR | Temporal | Transformer | DGA 610 samples |
Prediction | H2, CH4, C2H4, C2H6, CO, CO2, and total hydrocarbon (TH). | dissolved gas concentration | ARE | SARIMA | The proposed method provides a good means. |
| [120] | LSTM, ARIMA | Temporal | Wells | Longmaxi Formation of the Sichuan Basin 3,650 samples |
Prediction | Date, Daily production | Shale gas production | MAE, RMSE, R2 | LSTM Accuracy = 0.63% |
The accuracy of the model needs more improvement. |
| [121] | GM, FGM, DGGM, ARIMA, PSOGM, PSO-FDGGM | Temporal | Gas | quarterly production of natural gas in China | Prediction | Training period, natural gas production | Natural gas production | MAPE | PSO-FDGGM MAPE = 3.19% |
The model's performance is noteworthy and reliable. |
| Research | Applied AI models | Temporality | Field | Dataset | Class/ Clustering/ Prediction |
Input Parameter | Output Parameter | Performance Metrics | Best Model | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [122] | Multivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition with Genetic Algorithm, LSSVM-GA and LSSVM-PSO | Non-temporal | Crude oils | Bubble point pressure & oil formation volume factor. 638 samples |
Clustering | Temperature (T), oil gravity (API), gas specific gravity (γg), and solution gas oil ratio (Rs). | bubble point pressure & oil formation volume factor of crude oils | RMSE | MELM-PSO | The hybrid proposed model outperform the empirical method. |
| [124] | PCA, SVM, LDA | Temporal | Oil | Real time oil samples 30 samples |
Classification | pore size remains the same, the capillary flow rate (l2/t) is a function of interfacial properties (γLG and θ) and viscosity (μ). | Oil types | Accuracy | SVM Accuracy = 90% |
The proposed model needs an improvement on the accuracy because the accuracy < 95%. |
| [125] | MLP-PSO, MLP-GA | Non-temporal | Well-log | Three wellbores drilled. 2,2323 samples |
Prediction | Depth DTC (Vp) DTS (Vs) RHOB (ρ) Pp | probable depth of casing collapse | R2, RMSE | MLP-PSO | The proposed model outperformed the other models’ accuracy. |
| [126] | LSSVM-COA, LSSVM-PSO, LSSVM-GA, MLP-COA, MLP-PSO, MLP-GA, LSSVM, MLP | Non-temporal | Drilling | 305 drilled wells in the Marun oil field 2,820 samples |
Prediction | Northing, easting, depth, meterage, formation type, hole size, WOB, flow rate, MW, MFVIS, retort solid, pore pressure, drilling time, fracture pressure, fan 600/fan 300, gel10min/gel10s, pump pressure, RPM. | severity of mud loss | R2 and RMSE | MLP-GA RMSE = 93% |
The accuracy of the proposed model can be improved. |
| [127] | Hybrid-Physics Guided-Variational Bayesian Spatial- Temporal neural network | Temporal | Gas | Natural gas 600 samples |
Prediction | Geometry size, location of release point, release diameter, released gas, volumetric release rate, release during, release duration, location of sensor | Natural gas concentration | R2 | Hybrid_PG_VBSTnn R2 = 99% |
The proposed integration enhances the spatiotemporal forecasting performance. |
| [123] | CNN, Linear SVM, Gaussian SVM, SVM+CNN | Temporal | Gas | Leakage dataset 1,000 samples |
Classification | Methane, Ethane, Propane, Isobutane, Butane, Helium, Nitrogen, Hydrogen Sulphide, Carbon Dioxide | Gas Pipeline Leakage Estimation | Accuracy | SVM Accuracy = 95.5% |
The model stands out for its exceptional performance. |
| [128] | LSTM, OCSVM | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG P-TPT T-TPT P-MON-CKP T-JUS-CKP |
Identify two types of faults | Recall, Specificity, Accuracy | OCSVM Accuracy = 91% |
The use of feature selection did not improve the classifier accuracy, the proposed model is not robust enough to classify 2 types of wells. |
| [7] | Ordered Nearest Neighbors, Weighted Nearest Neighbors, LDA, QDA | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, P-MON-CKP, T-JUS-CKP, CLASS | Predicting flow instability | Recall, Specificity, Accuracy | ONN Accuracy = 81% |
The author suggested to investigate another metaheuristic method. |
| [130] | CNN, SVM and SVM+CNN | Temporal | Pipeline | Leakage dataset 1,000 samples |
Prediction | Length, outer diameter, wall thickness, location in the model | Prediction in tight sandstone reservoirs | Accuracy | SVMCNN model, achieved 95.5% | The proposed method is outperformed other method. |
| [129] | DT, SVM | Non-temporal | Reservoir | high-resolution FMI data | Classification | Response of logging, Pyroclastic lava, Normal pyroclastic rock Sedimentary pyroclastic rock | Lithologic classification of pyroclastic rocks | Accuracy | SVM Accuracy = 98.6% |
The proposed model is higher than 95%. |
| [131] | BAE-OCSVM, CAE-OCSVM, LSTM-AE- OCSVM, RD-OCSVM, RF-OCSVM, PCA-OCSVM, VAE-OCSVM, LSTM-AE-IF | Temporal | Gas | Data from SCADA 9,980 samples |
Classification | Diameter, Wall thickness, length | Leakage of natural gas | AUC, Accuracy, F1 score, precision, TPR, FPR | LSTM- AE-OCSVM Accuracy = 98% |
The best model achieves higher accuracy and author suggested to use abnormal data for future work. |
| [63] | LSTM, GRU | Temporal | Reservoirs | UNISIM-IIH and Volve oilfield 3,257 samples |
Classification | Oil, gas, water, or pressure | oil & gas forecasting |
SMAPE, R2 | GRU R2 = 99% |
The proposed model gives a highest accuracy. |
| [133] | OCSVM, LOF, Elliptical Envelope, and Autoencoder with feedforward and LSTM | Temporal | Well | 3W 1,984 samples |
Classification | P-PDG, P-TPT, T-TPT, P-MON-CKP, T-JUS-CKP, P-JUS-CKGL, T-JUS-CKGL, QGL, Label vector | Fault detection | F1 score | LOF F1 score = 85% |
The proposed method need an improvement on the accuracy. |
| [132] | K-Means Clustering and KNN | Temporal | Reservoirs | Antrim, Barnett, Eager Ford, Woodford, Fayetteville, Haynesville, Marcellus 55,623 samples |
Clustering | Well location, well depth, well length, and production starting year | EUR predictions | R2 | K-MC R2 = 0.18 |
The proposed model outperformed the other models using average fitting parameters. |
| [134] | GS-GMDH | Non-temporal | Well | oil fields located in the Middle East 2,748 samples |
Prediction | Laterolog (LLS), photoelectric index (PEF), compressional wave velocity (Vp), porosity (NPHI), gamma ray (spectral) (SGR), density (RHOB), gamma ray (corrected) (CGR), shear wave velocity (Vs), caliper (CALI), resistivity (ILD), and sonic transit time (DT). |
Pore Pressure | RMSE, R2, MSE, SI, ENS | GS-GMDH RMSE = 1.88 psi and R2 = 0.9997 |
The proposed method shows the higher accuracy. |
| [135] | RF, Gradient Boosting Regressor , bagging, CNN, KNN, Deep Hierarchical Decomposition | Temporal | Reservoir | Geological data 180 samples |
Classification | Porosity, fracture porosity, fracture permeability, rocky type, net gross, matrix permeability, water relative permeability, formation volume factor, rock compressibility, pressure dependence of water viscosity, gas density, water density, vertical continuity, relative permeability curves, oil-water contact, fluid viscosity. | Oil production, water production, water injection, and liquid production | MAE, SMAPE | Deep Hierarchical Decomposition MAE: OP = 0.76% |
The proposed method has decreased the computational speed. |
| [136] | M5P tree model, RF, Random Tree, Reduced error pruning tree, GPR, SVM, and MARS | Non-temporal | Gas | Coriolis flow meter 201 samples |
Classification | wet gas flow rate (kg/h) and absolute gas humidity (g/m3) | estimation of the dry gas flow rate (kg/h) | RMSE, MAE, LMI, WI | GPR-RBKF MAE = 163.3266 kg/h,RMSE = 483.1359 kg/h, CC = 0.9915 for the testing data set |
The best model superior rather than the other models and the author suggested to explore other soft-computing method. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





