Introduction
The total number of space launches per year has significantly increased in recent decades, reflecting the growing interest in and advancements in space exploration. Key drivers for the increased launch frequency include the deployment of Earth observation satellites, advancements in satellite miniaturization, and a surge in commercial satellite launches for communication and remote sensing purposes. Additionally, ambitious missions from various countries to explore Mars, the Moon, and beyond contribute to the escalating launch figures. Analyzing these trends is crucial for understanding the evolving landscape of space activities, offering insights into technological innovations, international collaborations, and the overall expansion of humanity's presence beyond Earth.
The prospect of space exploration has captivated humans for over a century, leading to the successful launch of numerous satellites and missions. Unfortunately, World War II's impact delayed the development of these missions by a decade during their early days. However, in 1957, the Russians launched their first successful satellite, Sputnik-1, followed by Sputnik-II in the same calendar year. This event marked the start of a heated space race between nations, each vying to be the foremost explorer in the world. The number of satellite launches has increased significantly in recent years, particularly within the past three decades. Today, space exploration has become a focal point for every nation, with each striving to be at the forefront of this exciting field.
Early Space Missions
Sputnik 1 successfully entered Earth's orbit on October 4, 1957 (
Figure 1), ushering in the space age. This launch was a shock to the world, as it made the former Soviet Union the first to put a human-made object into space. The word "Sputnik" originally meant "fellow traveler" but has since become synonymous with "satellite" in modern Russian. Sputnik 2 carried a dog named Laika into space, which gave rise to the idea of sending humans into space. This testing mission evaluated the requirements for sending humans into space. In 1959, Roscosmos (presently known by that name) performed a hard landing on the moon with their Luna 2 spacecraft, taking pictures of the moon, and discovering no evidence of radiation belts on the moon (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023).
By 1960, there had been a total of 20 launches worldwide, with the United States playing a leading role by launching 17 rockets into (Dunbar, 2011) (Figure1). However, there were many problems encountered during this time due to a lack of technology and limited communication among the space industries caused many problems during this time. In 1961, the Soviet Union decided to send astronauts into space, four years after their first launch. The United States then took a major step towards space exploration. On July 16th, 1969, NASA sent a group of three astronauts on an Apollo 11 mission to land on the moon (Dunbar, 2011), led by Neil Armstrong, which successfully landed after a 4-day journey. To reduce the payload weight, they left some equipment on the moon for future missions.
Only 17 astronauts have had the privilege of setting foot on the moon. The last time any astronauts or cosmonauts visited the moon was quite some time ago. Space agencies now provide planetary protection to prevent microbial issues. However, space agencies have been working on developing rockets that carry satellites to support various areas, such as deep space exploration, earth observation, navigation, communication, and radiation telescopes, among others. These technologies have been gradually improving over time (Berger, 2022).
Space Traffic
Since the start of the space age in 1957, around 6,500 rockets have been launched (excluding failures). These launches have placed several satellites into Earth's orbit, the exact number being 16,990. However, as the number of launches increases, space debris is also growing. Currently, there are around 11,500 satellites in space, of which around 9,000 are still operational. Unfortunately, the increase in space debris poses a significant threat to future missions. In the space environment, we can categorize objects into two broad categories: those tracing back to a launch event and those whose origin remains unknown. We refer to the latter objects as unidentified (UI). In 2002, the Inter-Agency Debris Committee (IADC) published its Space Debris Mitigation Guidelines, which served as a starting point for deriving technical standards and non-binding policy documents. In 2019, the United Nations Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (UNCOPUOS) published its Guidelines for the Long-Term Sustainability of Outer Space Activities, marking a significant step towards addressing the issue of space debris.
Statistical data of launches
The 1970s marked a new era with the Apollo Moon landings and advancements in space technology, including the development of space stations (e.g., Skylab). The average. number. of launches increased to around 100 per year in that decade. The 1980s decade marked the beginning of the Space Shuttle program, which led to an increase in the number of launches. The program reached its peak in the mid-1980s, but it suffered a brief setback following the tragic Challenger disaster in 1986. Seven crew members died in this mission. This prompted all space agencies to introduce new policies and some restrictions for space missions.
The Space Shuttle program's dominance ended in the 1990s, with a shift towards international collaborations like the International Space Station. Approximately 90–100 launches took place annually, with stable launch activity. In the early 2000s, the annual count was relatively modest, with around 60 to 70 launches per year (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023) globally (
Figure 2).
However, as space agencies, private companies, and international collaborations intensified their efforts, the numbers soared (Semanik & Crotty, 2023). By the mid-2010s, the annual launches had surpassed 100 (
Figure 3), indicating a significant uptrend. Commercial space enterprises like SpaceX and the diversification of spacefaring nations are responsible for this surge. The average number of launches increased to about 90–100 per year (Number of Satellites Launched by Year 2019, n.d.), with a significant spike toward the end of the decade. The space industry has recently undergone significant changes, with China's state-led program experiencing a remarkable expansion and SpaceX witnessing a surge in activity following the launch of its first Falcon 9 rocket in 2010.
In
Figure 4, we can see a huge increase in launches by both the USA and China (Berger, 2022). Additionally, newer commercial companies like Rocket Lab, based in the US, have emerged and have successfully launched six times in 2021. The trend continued into the 2020s, with an average annual launch count surpassing 150.
Despite the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, the pace of launches continued to increase, with more than 100 launches in 2020. In 2021, the number of launches rose to over 130 (
Figure 4), driven by large satellite constellations like Starlink and the growing role of commercial spaceflight.
Orbital Launches by a Country in 2023
Most orbital launchers are used to deliver satellites to Low Earth Orbit (LEO), which is usually below 900 km, or to Geosynchronous Orbit (GEO) at an altitude of approximately 36,000 km. To define where space begins, the Kármán line was proposed, which is situated at an altitude of 100 km. This line is now used by various international organizations as a boundary between Earth’s atmosphere and outer space. In 2015, only 1300 active satellites orbited Earth, while 82 rockets were successfully launched worldwide (Statista Research Department, 2023). Over 9000 satellites are active now.
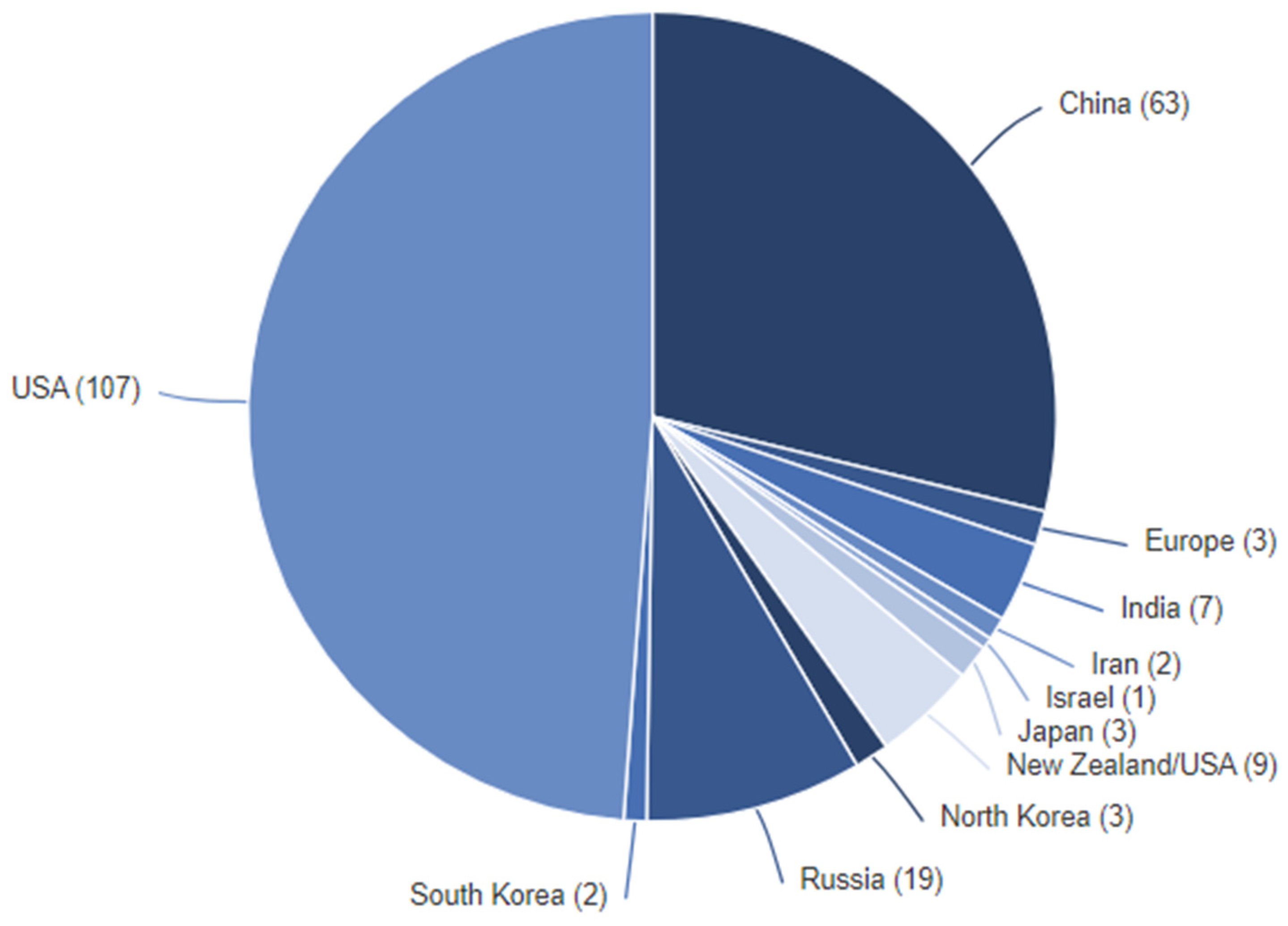
In 2023, the world embarked on a total of 212 successful launches (Orbital Launches of 2023, n.d.) (
Figure 5) among 223 with 2,664 satellites (McDowell, 2024), the highest record in one calendar year. SpaceX made 98 orbital launches with the Falcon 9, Falcon Heavy, and Starship rockets, representing 90% of all US launches this year (Sirieys et al., 2022). No other American company completed more than three launches, except Rocket Lab Electron from New Zealand. China logged 67 orbital launch attempts last year, continuing its steady climb up and to the right. The Long March 2D led the way (Sirieys et al., 2022) with 13 launches. Mainly commercially operated rockets were responsible for 65% of global launch attempts in 2023 (McDowell, 2024), up from 55% in 2022 (
Figure 6).
At the onset of Space 2.0 in the 1950s, the first space agencies emerged as the sole champions, primary actors, and investors of their respective national space sectors. The transition to Space 3.0 happened at NASA after the end of the Cold War when space organizations joined forces and began building space stations. Space 4.0 (Merhaba et al., 2019)has been happening since 2006 when the private and commercial sectors started investing in and building space missions.
Estimated Future Statistical Data
Mega-constellations, or large satellite networks, are improving global internet service. SpaceX has applied for 42,000 Starlink satellites, and Amazon has reserved 83 launches to deploy the majority of its Kuiper constellation in the next five years. By 2026, we can expect over 150 launches annually, with a significant portion coming from commercial entities like SpaceX and Rocket Lab. The proliferation of small satellites and CubeSats will continue, leading to multi-payload launches. Governments will increase their activities, especially for the Artemis program and interplanetary missions.
From 2027–2030, launches may reach 200 or more per year, driven by expanding satellite constellations, deep space exploration, and lunar activities. Expect more frequent launches of crewed missions to the International Space Station and early Artemis missions to the Moon. By 2040, there will be 250+ launches per year, with an expected range between 250 and 300. This increase reflects the expansion of commercial ventures, regular missions to the Moon and possibly Mars, and the rise of space tourism.
Conclusion
Technology advancements, expanding commercial opportunities, and international partnerships are driving the exponential growth of the space industry. The number of annual space launches has already surpassed 200 in 2023, signaling a promising upward trend for the future. The proliferation of satellite constellations for communication, Earth observation, and remote sensing, along with ambitious missions exploring the Moon, Mars, and beyond, fuels this rise in activity.
However, this surge in launch activity presents challenges that demand careful attention, particularly the accumulation of space debris. As the volume of objects in orbit increases, so do the risks to both existing satellites and new missions. To address this issue, space agencies and private companies must work together with guidelines like UNCOPUOS's 2019 recommendations, which serve as a foundational step toward sustainability in space operations.
Looking ahead, projections indicate that annual launches could reach between 250 and 300 by 2040, driven by commercial space ventures, deep space exploration, and space tourism. To ensure the long-term success and safety of space activities, stakeholders must prioritize strategies to mitigate space debris, foster international cooperation, and uphold the principles of responsible space exploration. This focus will be essential as humanity's presence in space continues to expand, enabling us to sustain and advance our exploration efforts for decades to come.
References
-
Annual number of objects launched into space. (2023). Our World in Data. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/yearly-number-of-objects-launched-into-outer-space.
- Berger, E. (2022, January 3). The world just set a record for sending the most rockets into orbit. Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/science/2022/01/thanks-to-china-and-spacex-the-world-set-an-orbital-launch-record-in-2021/.
- Dunbar, B. (2011). NASA: 60 Years & Counting - Human Spaceflight. NASA. https://www.nasa.gov/specials/60counting/spaceflight.html.
- McDowell, J. (2024, January 15). Report: Space Activities in 2023 (Jonathan McDowell 2024) page 4-14. New Space Economy. https://newspaceeconomy.ca/2024/01/15/report-2.
- Merhaba, A., Ainardi, M., & Aebi, T. (2019, March 28). The Space Agency of the Future. Arthur D Little. https://www.adlittle.com/en/insights/viewpoints/space-agency-future.
-
Number of satellites launched by year 2019. (n.d.). Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/896699/number-of-satellites-launched-by-year/.
-
Orbital Launches of 2023. (n.d.). Space.skyrocket.de. https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_chr/lau2023.htm.
- Semanik, M., & Crotty, P. (2023). International Trade Commission Executive Briefings on Trade. https://www.usitc.gov/publications/332/executive_briefings/ebot_us_private_space_launch_industry_is_out_of_this_world.pdf.
- Sirieys, E., Gentgen, C., Milton, J., & de Weck, O. (2022). Space sustainability isn’t just about space debris: On the atmospheric impact of space launches. MIT Science Policy Review, 3, 143–151. [CrossRef]
- Statista Research Department. (2023, December 1). Number of active satellites by year 1957-2020. Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/897719/number-of-active-satellites-by-year/.
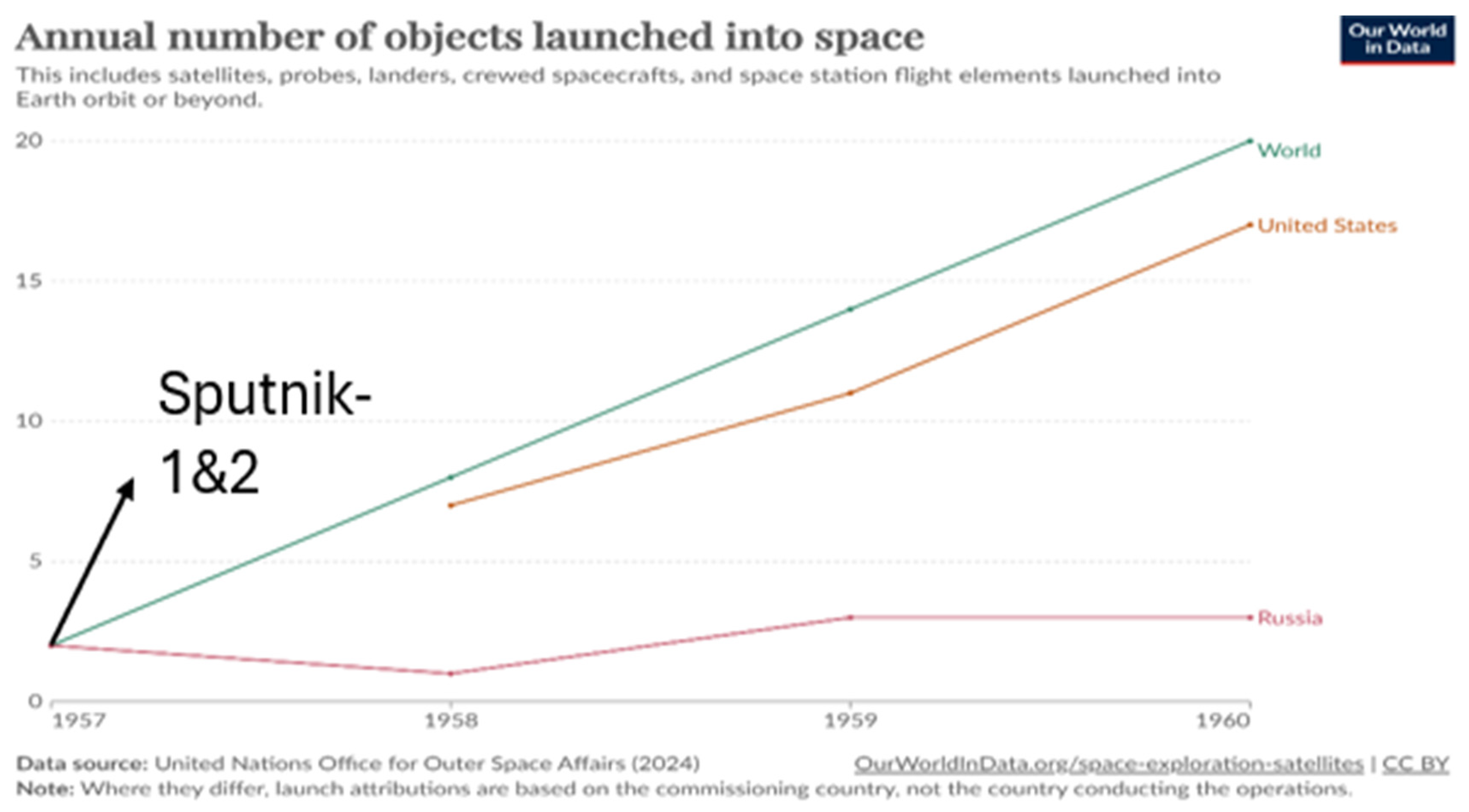
Figure 1.
| In 1957, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, launched the first object into space, followed by the founding of NASA by the USA in the subsequent year, which also saw their first launch. The USA's 15 successful launches by the end of the 1960s paved the way for the space race among different nations. Image credit (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023).
Figure 1.
| In 1957, Roscosmos, the Russian space agency, launched the first object into space, followed by the founding of NASA by the USA in the subsequent year, which also saw their first launch. The USA's 15 successful launches by the end of the 1960s paved the way for the space race among different nations. Image credit (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023).
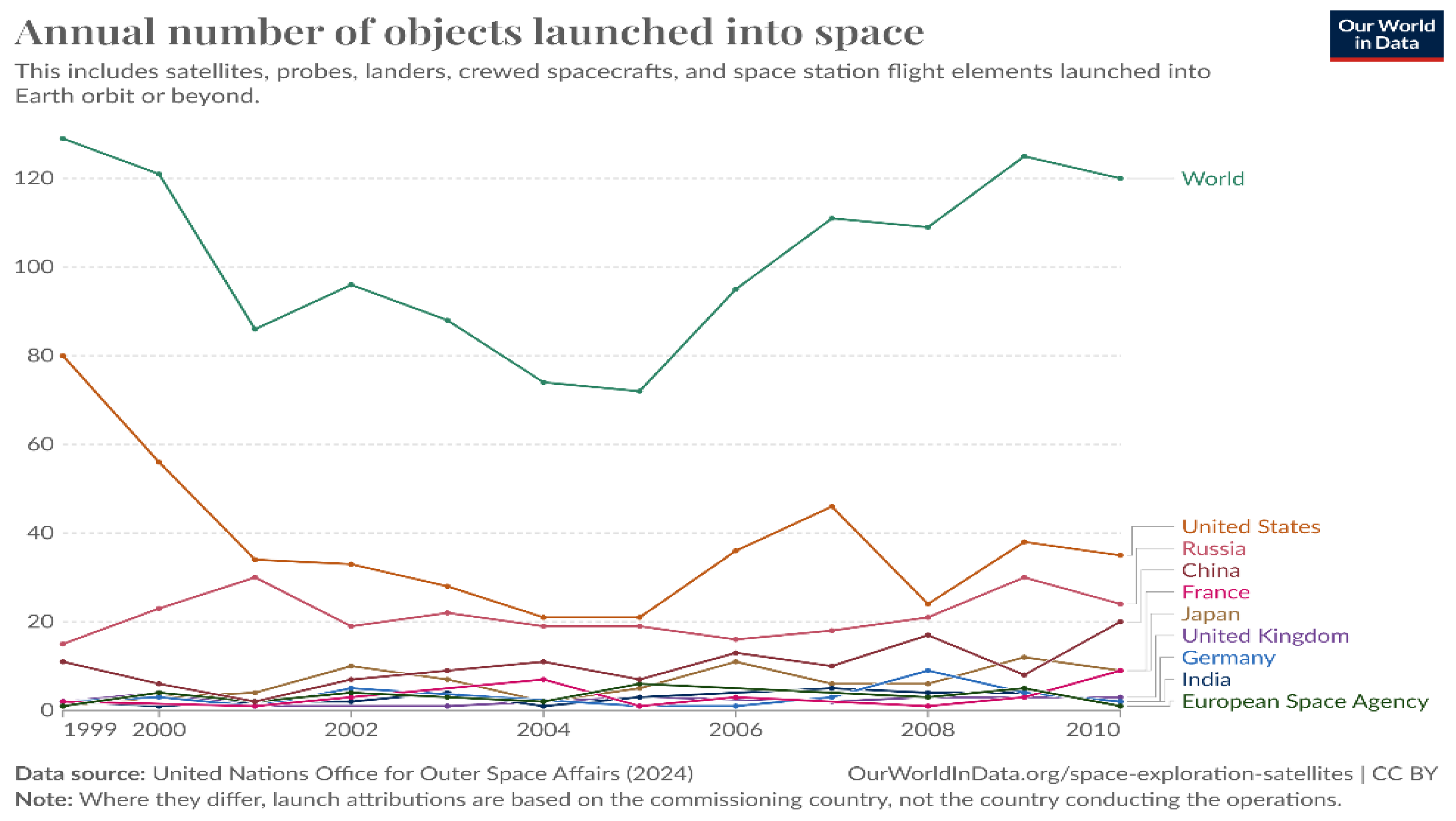
Figure 2.
| It shows the average number of launches from the early 2000s to 2010. In mid-2010 the launches decreased because of a lack of government funding for the space agencies. But, by including the private and commercial sectors made a huge growth as we can see clearly in this graph. Image credit (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023).
Figure 2.
| It shows the average number of launches from the early 2000s to 2010. In mid-2010 the launches decreased because of a lack of government funding for the space agencies. But, by including the private and commercial sectors made a huge growth as we can see clearly in this graph. Image credit (Annual Number of Objects Launched into Space, 2023).
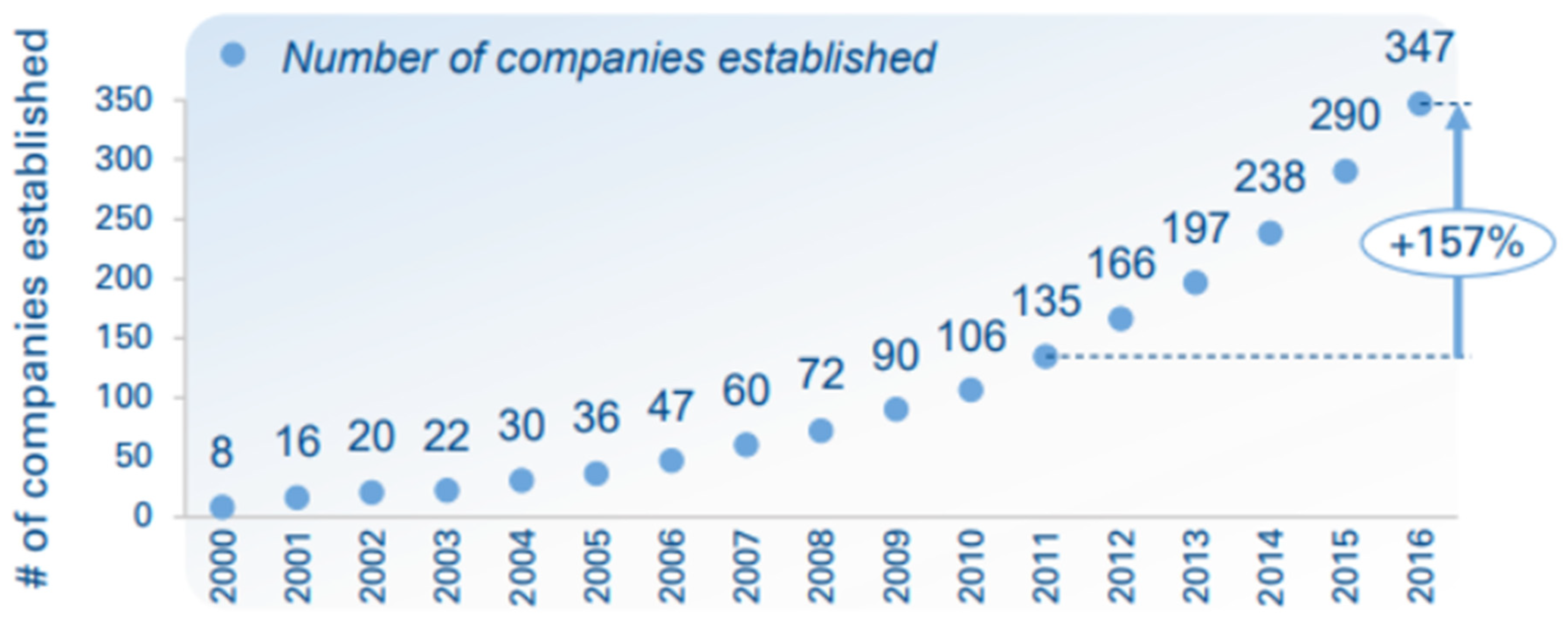
Figure 3.
| Displayed in the above graph is a representation of the annual establishment of companies spanning from 2000 to 2016. Notably, there was a substantial surge in growth from 2011 to 2016, with an astounding 157 percent increase occurring in 2016 alone. This data highlights the vital role that private companies occupy in the market (Merhaba et al., 2019).
Figure 3.
| Displayed in the above graph is a representation of the annual establishment of companies spanning from 2000 to 2016. Notably, there was a substantial surge in growth from 2011 to 2016, with an astounding 157 percent increase occurring in 2016 alone. This data highlights the vital role that private companies occupy in the market (Merhaba et al., 2019).
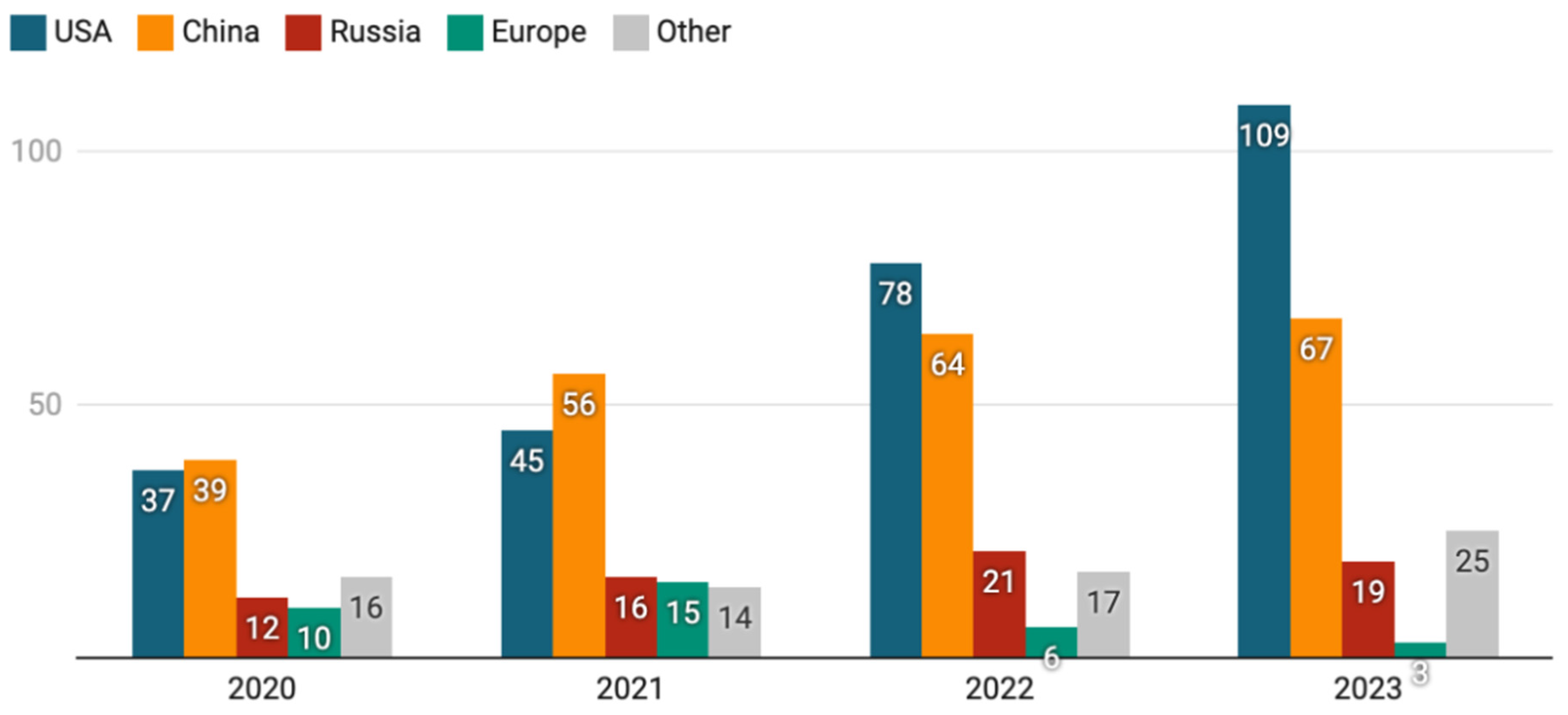
Figure 4.
| It shows the last 4 years data of USA, Cina, Russia, Europe and other countries as well. The highest record of 223 launches in a single year which is 2023 has been increased by 100 percent as compared to 2020. This is mainly because the launches were delayed in 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. A few of them were rescheduled to upcoming years. Also, companies like SpaceX. Blue Origin and more had a major impact.
Figure 4.
| It shows the last 4 years data of USA, Cina, Russia, Europe and other countries as well. The highest record of 223 launches in a single year which is 2023 has been increased by 100 percent as compared to 2020. This is mainly because the launches were delayed in 2020 and 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. A few of them were rescheduled to upcoming years. Also, companies like SpaceX. Blue Origin and more had a major impact.
Figure 5.
| Upon examination of the 2023 space launch records (Orbital Launches of 2023, n.d.), it has been determined that both the United States and China are at the forefront of space launches. Russia has also made a notable contribution of 10% to the overall tally. It is worth mentioning that the leading countries have predominantly opened up their space programs to private sectors (Semanik & Crotty, 2023), resulting in a more efficient outcome.
Figure 5.
| Upon examination of the 2023 space launch records (Orbital Launches of 2023, n.d.), it has been determined that both the United States and China are at the forefront of space launches. Russia has also made a notable contribution of 10% to the overall tally. It is worth mentioning that the leading countries have predominantly opened up their space programs to private sectors (Semanik & Crotty, 2023), resulting in a more efficient outcome.
Figure 6.
| The total number of successful orbital launches worldwide per year from 1957 to 2021, broken down by the primary propellants used (both first stage and booster(s), cumulatively). Commercial missions primarily drove the 54% growth since 2001.
Figure 6.
| The total number of successful orbital launches worldwide per year from 1957 to 2021, broken down by the primary propellants used (both first stage and booster(s), cumulatively). Commercial missions primarily drove the 54% growth since 2001.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).