Introduction
As an esteemed variety of traditional Chinese liquor, strong-aroma Baijiu is renowned for its distinctive fragrance derived from fermentation pits, its refreshing taste, and its complex layers of flavor (Ao et al., 2022; Xu et al., 2024). The fermentation process occurs in proprietary mud pits utilizing the solid-state fermentation technique and continuous batch feeding method. This involves mixing rice husks and a new batch of freshly crushed grains with the fermented grains (Zaopei) from the prior fermentation cycle, followed by steaming and distillation to extract the liquor. Additionally, Daqu powder is incorporated into the steamed and cooled grains to initiate the subsequent fermentation cycle, typically lasting 60-90 days (Ding et al., 2015).
The brewing process of strong-flavor liquor results in the formation of Huangshui, a brown viscous liquid containing a variety of acids, alcohols, esters, and other substances (Wu et al., 2022). Various microorganisms can be found in Huangshui, such as yeasts, lactic acid bacteria, butyric acid bacteria, caproic acid bacteria, and Bacillus strains (Zou et al., 2018). It is estimated that approximately 400 liters of Huangshui are generated for every 1,000 liters of strong-flavor liquor produced (Kang et al., 2022).
Given the substantial production of Huangshui, inadequate treatment could result in resource wastage and environmental pollution (He et al., 2020). Presently, many distilleries utilize Huangshui for various purposes, including preservation of fermentation pits, creation of new mud pits, and cultivation of bacteria that produce caproic acid (Gao et al., 2020). It has also been reported that Huangshui was used to produce vinegar, prepare propionic acid, and serve as a preservative, showcasing viable methods for reusing Huangshui to bolster resource utilization efficiency and economic gains (Li et al., 2017). Moreover, Huangshui contains a rich array of flavor substances that can augment the taste and aroma of liquor. A flavoring substance derived from Huangshui has been incorporated into Baijiu to enhance its flavor and quality (Xie et al., 2020).
In recent years, Huangshui has gained significant research attention due to its abundance in bioactive molecules, such as Huangshui polysaccharides. These compounds exhibit diverse biological effects, including antioxidant (Huo et al., 2022), anti-inflammatory (Pei et al., 2023), and immunomodulatory activities (Huo et al., 2020). While current research on Huangshui primarily centers around its practical applications in brewing, microbial culture, and utilization of flavor substances, there is a notable gap in studies focusing on its water source and formation process. Herein, we analyzed the chemical components of Huangshui. Additionally, we developed two laboratory solid-state fermentation models to elucidate the water source and formation process of Huangshui. This study sheds light on the water source in Huangshui and its formation process, offering insights for adjusting the initial moisture content of fermented grains and exploring methods for reutilizing Huangshui in solid-state brewing.
Methods and Materials
Collection of Huangshui samples from a strong-flavor Baijiu distillery
Five Huangshui samples, each 2 liters in volume, were collected from the bottom of five fermentation pits at a strong-flavor Baijiu distillery located in Yibin, Sichuan Province, China. These pits were randomly selected from the same batch of fermentation pits operating under identical conditions. To facilitate the chemical component analysis of Huangshui, the five samples were combined into one, totaling 10 liters, and stored at 4% until further use.
The design of two fermentation devices
To study the impact of initial water contents on
Huangshui yield and explore its water source, we developed two fermentation devices. Fermentation device 1 (Model 1, depicted in
Figure 2A) is constructed from acrylic plastic glazing, featuring a height of 2.5 m and a diameter of 0.5 m. The side wall is marked with scale indicators to monitor liquid levels, while an automatic exhaust valve at the top facilitates the release of carbon dioxide and other gases produced by fermentation.
Fermentation device 2 (Model 2, shown in
Figure 2C) is crafted from stainless steel, measuring 180 mm in height and 150 mm in diameter. Equipped with a sieve plate, this container allows
Huangshui produced during fermentation to drip down. Additionally, a sampling port at the bottom facilitates Huangshui sampling, and an automatic exhaust valve at the top ensures efficient gas release.
Preparation of fermented grains
Following standard procedures, 200 kg of ready-to-use Daqu powder was obtained from the same distillery mentioned above and transported to the Sichuan University of Science and Engineering (Yibin, China) at room temperature. The Daqu powder was promptly packaged into plastic bags upon arrival and stored at -20°C until use. Sorghum and husks for brewing were purchased from local markets. The sorghum was crushed until 20-30% of it could pass through a 20-mesh sieve. Husks were steamed in a liquor distiller for 30 minutes and cooled down before use. Once the starting materials were prepared, a mixture comprising 100 kg sorghum, 60 kg husks, and 100 kg Huangshui (provided by the same distillery) was thoroughly blended. The mixture was then stacked at room temperature for two hours to allow the sorghum and husks to absorb water. Subsequently, the mixture was steamed for 90 minutes.
For fermented grains with initial water contents of 55%, 60%, and 65%, hot water (90°C) was added to adjust their weight to 332 kg, 376 kg, and 432 kg, respectively. The hot water and steamed grains were mixed continuously for 10 minutes to facilitate water absorption into the raw materials. Cold air was employed to rapidly cool the mixture to 22°C, and cold boiled water was added to compensate for water loss due to evaporation. Finally, 20 kg of Daqu powder was incorporated into the mixture and thoroughly blended to obtain the starting fermented grains.
The production and collection of Huangshui in two fermentation devices
350 kg and 2.1 kg starting fermented grains were transferred to fermentation container 1 (Model 1) and fermentation container 2 (Model 2), respectively. The two fermentation devices were placed in a constant temperature environment at 25°C. The Huangshui level in fermentation Model 1 was recorded daily for 40 days to track the production of Huangshui. In fermentation Model 2, Huangshui was collected at the bottom, and its volume was measured daily for the first 20 days to monitor production. To investigate the effects of initial water contents on Huangshui production, fifteen fermentation containers (Model 2) were prepared for each test group. Three containers from each group were sampled every four days (Day 4, Day 8, Day 12, Day 16, and Day 20) to conduct component analysis of Huangshui and fermented grains.
Chemical component analysis of Huangshui and fermented grains
The main components of Huangshui collected from the Baijiu distillery, including water, alcohols, acids, reducing sugars, starch, and amino acids, were analyzed. Similarly, the water content, solid contents, starch, alcohols, and acids were analyzed for the fermented grains and Huangshui collected from the fermentation Model 2.
Alcohols. To measure the yield of ethanol, 100 g of either fermented grains or Huangshui were transferred to a 500 mL distillation flask, followed by the addition of 200 mL of water. The mixture was distilled until 100 mL of distillate was obtained, and the alcohol content was determined using the density method (Xu et al., 2022). Other alcohols were detected and quantified using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS, Agilent 7890A-5975B) equipped with a chromatographic column DB-WAX (60 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm) and a Mass Selective Detector. Tertiary butanol was used as an internal standard for quantification (Qin et al., 2019).
Acids. The production of total acids was assessed using the acid-base neutralization titration method, with results presented as the amount of NaOH (mmol) consumed during titration (Ji et al., 2023). In Huangshui collected from the distillery, lactic acid predominates among the total acids; hence, the total acid content is calculated based on lactic acid. Other acids were detected and quantified using high-performance liquid chromatography (Shimadzu Prominence-i LC-2030C), featuring a Waters Atlantis dC18 reversed-phase chromatography column and a Diode Array Detector. The mobile phase consisted of acetonitrile (95%, v/v) in 10 mM KH2PO4 buffer (pH 2.8), with a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. The column temperature was maintained at 25°C, and detection occurred at a wavelength of 215 nm (Kassahun et al., 2024).
Starch and reducing sugars. For starch content determination, samples underwent acid hydrolysis, and reducing sugars were assessed using the Fehling reagent substitution method (Liu et al., 2024).
Amino acids. The total amino acids were quantified by first measuring total nitrogen using the Kjeldahl method (González-Weller et al., 2023), followed by the detection of ammonium nitrogen via Nessler’s reagent colorimetry (Gong et al., 2022). The content of total amino acids was then calculated using the formula: the content of total amino acids = 6.25 × (total nitrogen-ammonium nitrogen).
To quantify the peptide content, the Huangshui sample (10 mL) was centrifuged at 12,000 rpm for 10 min, filtered with a 0.22 μm microporous membrane, and concentrated through an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube (10 kDa, Millipore). The peptide content in the resulting filtrate was analyzed using the biuret method (Liu and Pan, 2017).
Free amino acids in Huangshui were detected and quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography (Shimadzu Prominence-i LC-2030C). Before sample injection, free amino acids were derivatized using phenyl isothiocyanate (Ding et al., 2023). A 10 µL sample was injected into a Waters Atlantis dC18 reversed-phase chromatography column (250 mm × 4.6 mm × 5 μm). Two mobile phase solutions were employed: mobile phase A (3.6 mM triethylamine, 20 mM acetic acid, pH 6.20) and mobile phase B (acetonitrile-water, 80:20, v/v) (Liu et al., 2023). The flow rate was maintained at 1 mL/min, and the column temperature was set to 40°C. Detection occurred at a wavelength of 254 nm. To quantify the amino acids, a standard curve was prepared using commercially available amino acid standards (GBW(E)100062, National Research Center For Certified Reference Materials, Beijing, China), which were loaded into the same column.
Esters. Esters were detected and quantified using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS, Agilent 7890A-5975B) equipped with a chromatographic column DB-WAX (60 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 µm). n-amyl acetate was used as an internal standard for quantification (Tang et al., 2014).
Solid contents. For solid contents analysis, 100 g of fermented grains from the fermentation devices were dried at 105°C to a constant weight.
Water. The measurement of water content followed a similar method to that used for measuring solid contents. The weight loss after drying represented the total weight of water and ethanol. Therefore, the weight of ethanol was subtracted to obtain the weight of water.
Results and Discussion
Huangshui contains a variety of biological components
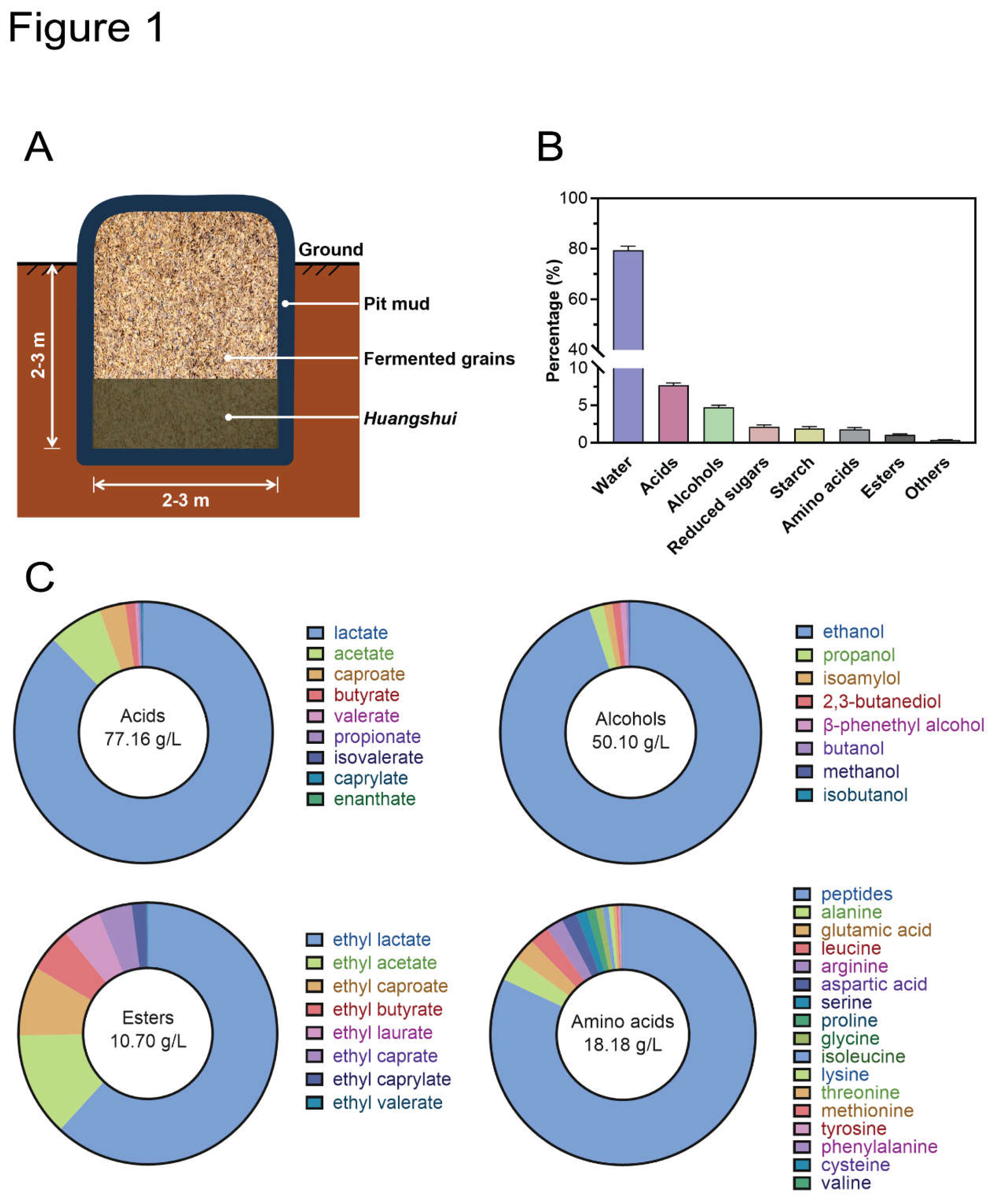
The fermentation of Chinese strong-flavor liquor is carried out in fermentation pits (Chai et al., 2021). Illustrated in the schematic diagram (
Figure 1A), a significant portion of the fermentation pit lies underground, with the fermented grains encased in a layer of mud measuring 15-30 cm in thickness, which hosts various anaerobic microorganisms. Following each fermentation cycle,
Huangshui, or “yellow water”, accumulates at the bottom of the pits (Ma et al., 2023). Composition analysis revealed
Huangshui to be a blend of acids, alcohols, esters, starches, reducing sugars, and other substances (
Figure 1B).
Water constitutes the majority of
Huangshui, comprising 80% of its mass. Various acids contribute to approximately 8% of
Huangshui’s mass, including lactic acid, acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid, valeric acid, and caproic acid. Notably, lactic acid exhibits the highest concentration, followed by acetic acid (
Figure 1C). Alcohols are also present in
Huangshui, accounting for 3.5-5.0% of its mass, with ethanol being the predominant component (
Figure 1C). Additionally, a range of ester compounds is detected in
Huangshui, with ethyl lactate being the most abundant, followed by ethyl acetate (
Figure 1C). This observation may be attributed to the substantial presence of lactic acid and acetic acid in
Huangshui. Amino acids within
Huangshui primarily exist in peptides (
Figure 1C).
Figure 1.
The chemical component analysis of Huangshui. (A). A schematic diagram of Huangshui production in a strong aroma liquor fermentation pit. (B). The chemical components of Huangshui and their contents. (C). The concentration and content of acids, alcohols, esters, and amino acids in Huangshui.
Figure 1.
The chemical component analysis of Huangshui. (A). A schematic diagram of Huangshui production in a strong aroma liquor fermentation pit. (B). The chemical components of Huangshui and their contents. (C). The concentration and content of acids, alcohols, esters, and amino acids in Huangshui.
The yield of Huangshui positively correlates with the initial moisture content of fermented grains
During the fermentation process of strong-aroma
Baijiu, the fermentation pits remain sealed to prevent interference from environmental microorganisms (Cheng et al., 2024). Consequently, direct observation of
Huangshui production in real fermentation pits is not feasible. To investigate the production of
Huangshui in this solid-state fermentation process, we devised two models that simulate real fermentation scenarios (
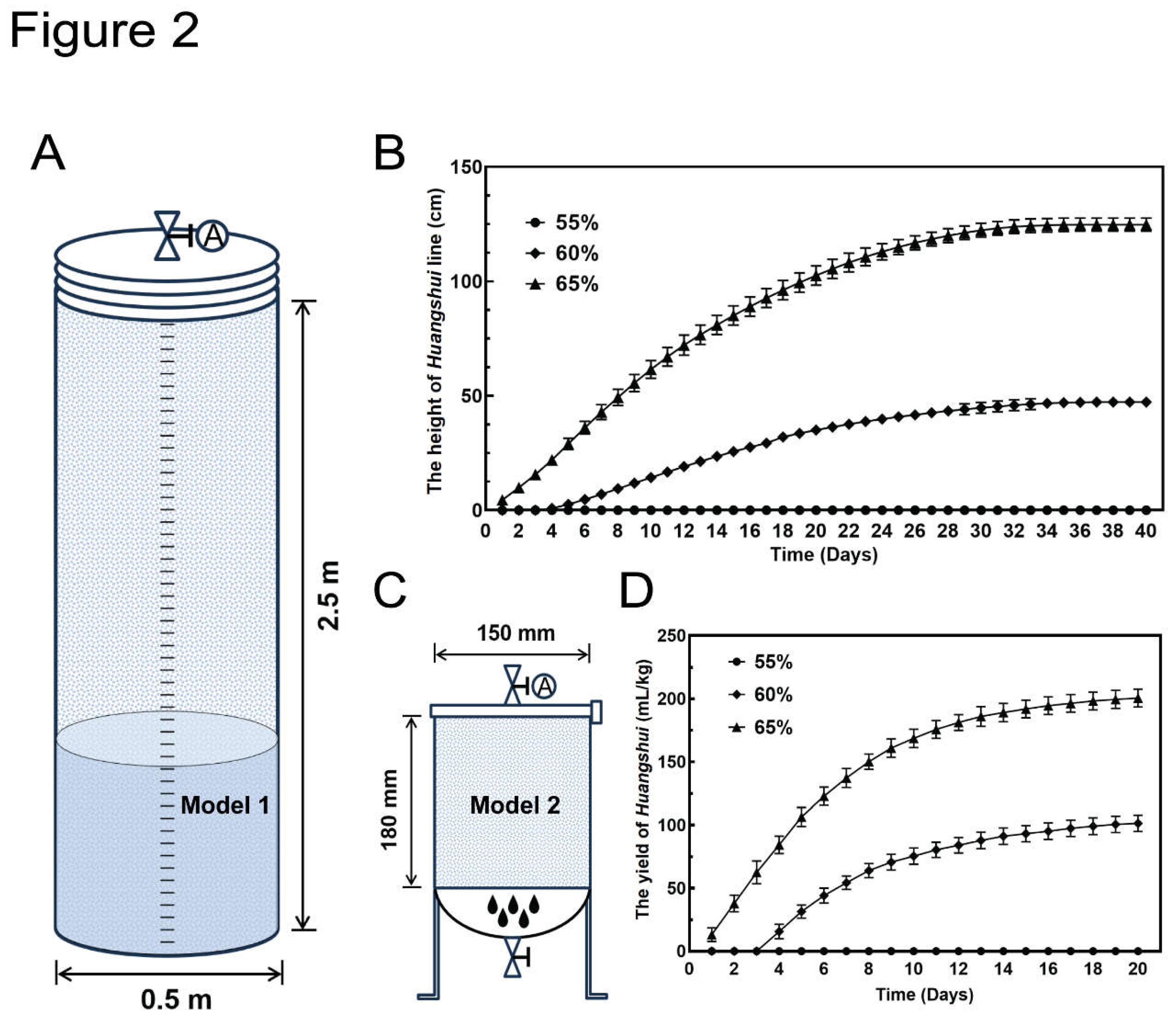
Figure 2A,C).
In Model 1, the fermentation apparatus, with a height of 2.5 m resembling real fermentation pits, consists of a transparent organic glass tank allowing daily monitoring of the
Huangshui liquid level. Fermented grains with varying initial moisture contents were introduced into the device, and changes in the
Huangshui level were monitored. When the initial moisture content of the fermented grains was 55%, no discernible liquid level was observed (
Figure 2B). With a 60% initial moisture content, the liquid level gradually rose, reaching a plateau at a height of 47 cm after 30 days of fermentation. By contrast, fermented grains with a 65% initial moisture content exhibited quicker and earlier accumulation of
Huangshui, reaching a plateau at 125 cm after 30 days (
Figure 2B).
Although the yield of
Huangshui was estimated based on the liquid level in Model 1, direct measurement of
Huangshui volume during fermentation was not possible. To address this, we designed Model 2, featuring a sieve plate and valve at the bottom for collecting and measuring
Huangshui (
Figure 2C). For fermented grains with a 55% initial moisture content, no
Huangshui was collected at the bottom (
Figure 2D). Consistent with Model 1, higher moisture content in the fermented grains resulted in faster production and higher yield of
Huangshui (
Figure 2B,D). Thus, it can be concluded that the yield of
Huangshui positively correlates with the initial water content of the fermented grains.
Figure 2.
Two solid-state fermentation models and the yield of Huangshui. (A). A schematic diagram of solid-state fermentation Model 1. (B). The yield of Huangshui in Model 1 within 40 days of fermentation. (C). A schematic diagram of solid-state fermentation Model 2. (D). The yield of Huangshui in Model 2 within 20 days of fermentation. The starting fermented grains have three water contents: 55%, 60%, and 65%. The yield of Huangshui was calculated as the amount of Huangshui produced per 1 kg of starting fermented grains.
Figure 2.
Two solid-state fermentation models and the yield of Huangshui. (A). A schematic diagram of solid-state fermentation Model 1. (B). The yield of Huangshui in Model 1 within 40 days of fermentation. (C). A schematic diagram of solid-state fermentation Model 2. (D). The yield of Huangshui in Model 2 within 20 days of fermentation. The starting fermented grains have three water contents: 55%, 60%, and 65%. The yield of Huangshui was calculated as the amount of Huangshui produced per 1 kg of starting fermented grains.
The effect of initial moisture content on fermentation
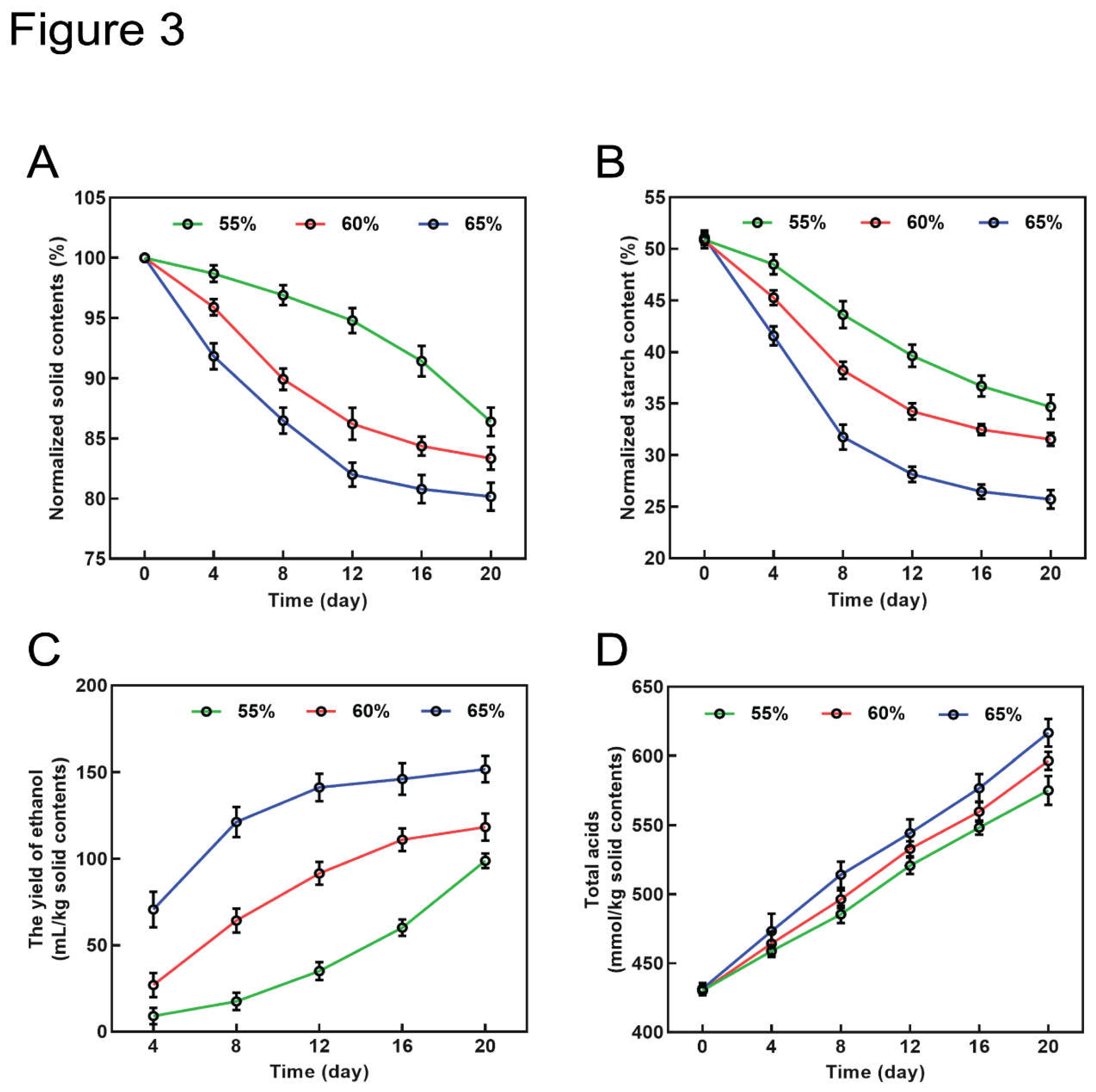
Fermented grains undergo degradation during the fermentation process due to the combined action of microorganisms and various enzymes . To investigate whether the initial moisture content of fermented grains affects fermentation, we measured solid content, starch content, and ethanol production during the fermentation process using fermented grains with different water contents.
The solid content in fermented grains, representing the proportion of non-volatile substances, reflects the utilization of fermented grains in the brewing process (Li et al., 2023). For the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 55%, the normalized solid content decreased from 100% on Day 0 to 86.4% on Day 20 (
Figure 3A). Similarly, the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 60% exhibited a decrease from 100% to 83.3% over the same period (
Figure 3A). Notably, fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 65% experienced a more pronounced decrease, with the solid content dropping from 100% to 80.2% (
Figure 3A), which suggests that higher water content benefits the utilization of fermented grains during fermentation.
Fermentation involves saccharification and starch decomposition, making the starch content in fermented grains crucial for liquor brewing (Wang et al., 2020). We monitored the amount of starch in solid content every four days during fermentation. The starch content showed a gradual decrease across all moisture levels. For the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 55% and 60%, the starch content decreased from 51.1% on Day 0 to 34.7% and 31.5% on Day 20, respectively (
Figure 3B). Notably, fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 65% exhibited the most rapid reduction in starch, decreasing from 51.1% to 25.7% (
Figure 3B).
Ethanol, the primary product in liquor brewing, serves as a significant parameter for fermentation efficiency (Wang et al., 2024). The yield of ethanol varied among fermented grains with different initial moisture levels. Fermented grains with initial moisture contents of 65% and 60% showed faster ethanol production from Day 4 to Day 8 compared to the fermented grains with a 55% moisture content (
Figure 3C). Additionally, ethanol production differed among moisture levels, with fermented grains at 65% moisture level producing the most ethanol, reaching a yield of 151.8 mL/kg of fermented grains on Day 20; followed by fermented grains with initial moisture of 60%, showing a yield of 118.4 mL/kg of fermented grains, and fermented grains with initial moisture of 55% produced the least amount of ethanol with a yield of 98.8 mL/kg of fermented grains (
Figure 3C). Overall, higher initial moisture content favors ethanol production during fermentation.
Organic acids are the main by-products in liquor brewing (Wu et al., 2024). Yeasts in
Daqu are the primary microorganisms responsible for ethanol production, while bacteria in
Daqu utilize starch, reducing sugar and other substances in fermented grains to produce organic acids such as acetic acid and lactic acid (Ren et al., 2024). The accumulation of ethanol and various acids in the fermentation system exerts a survival pressure on active microorganisms, leading to the establishment of a steady state until fermentation concludes (Song et al., 2019). We measured the production of total acids during fermentation using fermented grains with three initial moisture contents. At the onset of fermentation, every 1.0 kg of fermented grains (dry weight) contains approximately 430 mmol of total acid. Total acid production steadily increased from Day 0 to Day 20, with higher initial moisture levels resulting in greater acid production (
Figure 3D). For the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 55%, 60%, and 65%, the yield of total acids is 144.92, 166.38, and 185.10 mmol/kg of fermented grains, respectively.
In the factory production of Chinese
Baijiu, the period from Day 0 to Day 20 holds significant importance. During this phase, active yeasts efficiently produce ethanol, while ethanol suppresses the activity of acid-forming bacteria (Jiang et al., 2023). The ratio between ethanol and total acids on Day 20 was estimated to be 11.75:1, 12.08:1, and 14.07:1 for fermented grains with initial moisture contents of 55%, 60%, and 65%, respectively. This indicates that ethanol production predominates in the initial 20 days of fermentation (
Figure 3C, 3D).
Figure 3.
The effect of initial water contents in starting fermented grains on fermentation. (A). The changes in solid contents; normalized to the solid contents in starting fermented grains. (B). The changes in the starch content; normalized to the solid contents in starting fermented grains. (C). The yield of ethanol; calculated as the amount of ethanol produced per 1 kg of solid contents in starting fermented grains. (D). The production of total acids; calculated as the amount of acids produced per 1 kg of solid contents in starting fermented grains.
Figure 3.
The effect of initial water contents in starting fermented grains on fermentation. (A). The changes in solid contents; normalized to the solid contents in starting fermented grains. (B). The changes in the starch content; normalized to the solid contents in starting fermented grains. (C). The yield of ethanol; calculated as the amount of ethanol produced per 1 kg of solid contents in starting fermented grains. (D). The production of total acids; calculated as the amount of acids produced per 1 kg of solid contents in starting fermented grains.
Huangshui is fermentation percolate in the solid-state fermentation
Considering the initial water content of fermented grains shows a significant effect on the solid-state fermentation of Chinese
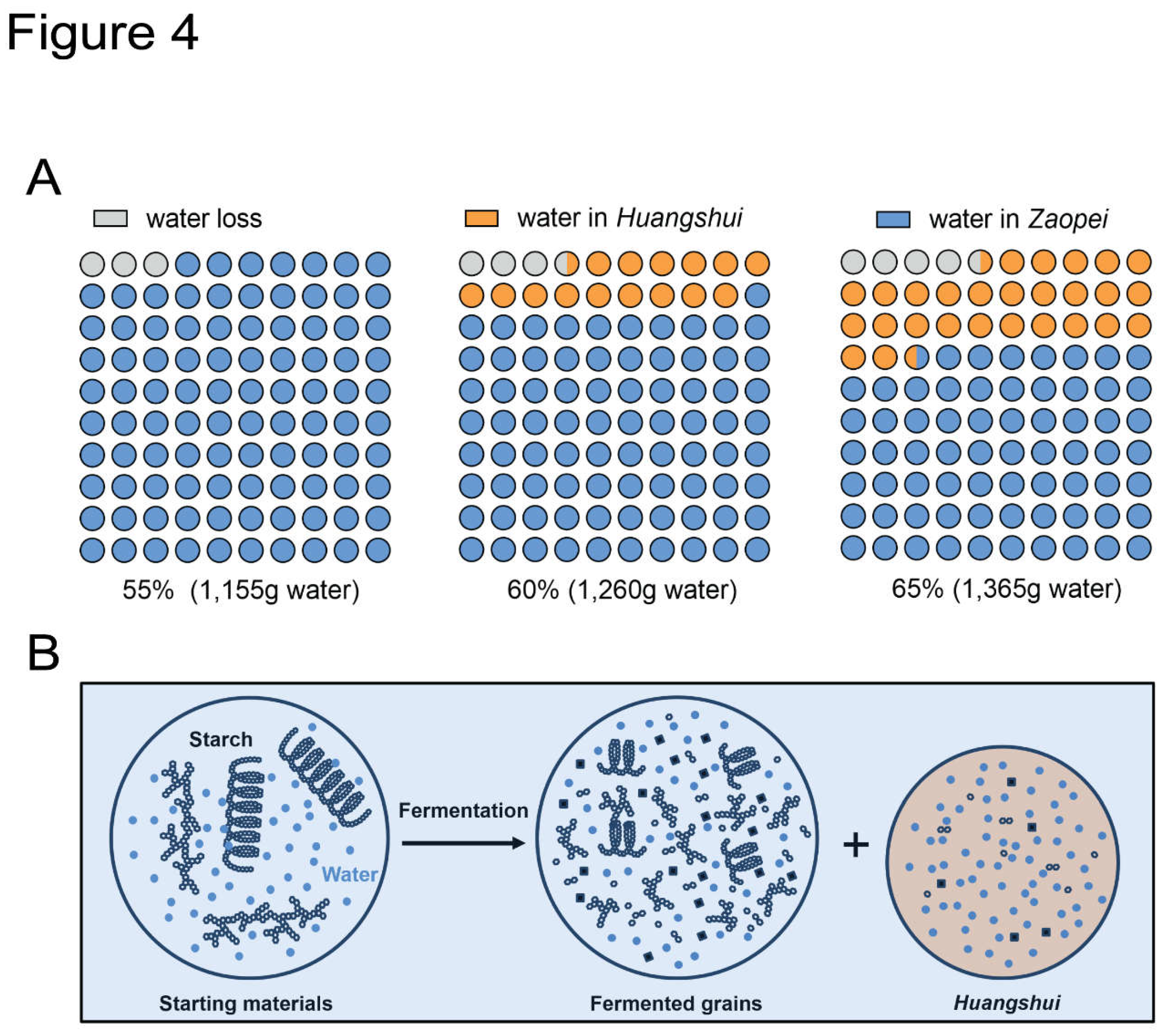
Baijiu (Zheng et al., 2014), we monitored water content changes during fermentation using 2.1 kg of fermented grains with moisture contents of 55%, 60%, and 65% in fermentation device Model 2. For the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 55%, negligible
Huangshui was collected, with 97% of water retained in fermented grains after 20 days of fermentation (
Figure 4A). Water loss, estimated at approximately 3% of total water, likely includes consumption during fermentation, evaporation, and experimental error. For the fermented grains with an initial moisture content of 60%, water loss, water in
Huangshui, and water in
Zaopei accounted for 3.7%, 15.3%, and 81% of total water, respectively (
Figure 4A). Increasing the initial moisture to 65% resulted in water loss, water in
Huangshui, and water in
Zaopei constituting 4.7%, 28.0%, and 67.3% of total water, respectively (
Figure 4A). Consistent with previous results (
Figure 2D), higher initial water content led to increased
Huangshui production and reduced water detected in
Zaopei. Minimal differences in water loss among the three experimental groups suggest only a small fraction of water content was utilized in fermentation.
Figure 4.
The water utilization in solid-state fermentation. (A). Tracking the water utilization in solid-state fermentation; (B). Huangshui is the percolate of solid-state fermentation.
Figure 4.
The water utilization in solid-state fermentation. (A). Tracking the water utilization in solid-state fermentation; (B). Huangshui is the percolate of solid-state fermentation.
Comparing the water contents of
Huangshui and
Zaopei in the 60% and 65% groups, the decrease (13.7%) in
Zaopei water was roughly equivalent to the increase (12.7%) in
Huangshui water. Assuming consistent water evaporation and experimental error across groups, this 1% moisture difference may stem from water consumption during fermentation, as evidenced by increased ethanol and acid production in the 65% group (
Figure 3C and 3D). Consequently, we propose a water utilization model for the solid-state fermentation of Chinese
Baijiu (
Figure 4B). Water is absorbed in solid matter, primarily starch in fermented grains before the solid-state fermentation starts. The hydrolysis of starch into glucose is a water-consuming process ((C
6H
10O
5)n + n H
2O → n C
6H
12O
6) and absorbed water molecules are released due to starch depletion (Liu et al., 2014). During the fermentation process, the water released is much more than the water consumed by the same amount of starch. Excessive water, along with unused starch, microorganisms, and fermentation products such as alcohols, acids, esters, reducing sugars, proteins, amino acids, and other substances, moves downward under gravity, forming
Huangshui at the bottom of fermentation pits. Thus,
Huangshui is the percolate of solid-state fermentation, and its water comes from the initial moisture content of fermented grains.
In summary, this study analyzed the main chemical components of Huangshui from a strong-flavor liquor factory and utilized two solid-state fermentation devices to investigate the water source of Huangshui and the impact of initial water content on Huangshui yield during fermentation. The results demonstrate that solid-state fermentation is a water-consuming process, with the water in Huangshui originating from the initial fermented grains. Starch and other substances in the fermented grains absorb a large number of water molecules. As fermentation proceeds, starch is degraded and the absorbed water is released. Fermentation products, unused starch, and other substances in the fermented grains are carried in water, ultimately forming Huangshui. Thus, it is concluded that Huangshui is fermentation percolate in the solid-state fermentation of Chinese liquor. Furthermore, the yield of Huangshui positively correlates with the moisture content of the initial fermented grains. This study provides novel insights into the water source and formation process of Huangshui in solid-state fermentation of strong-flavor liquor, with implications for Huangshui utilization and solid-state brewing practices.