Submitted:
12 May 2024
Posted:
13 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
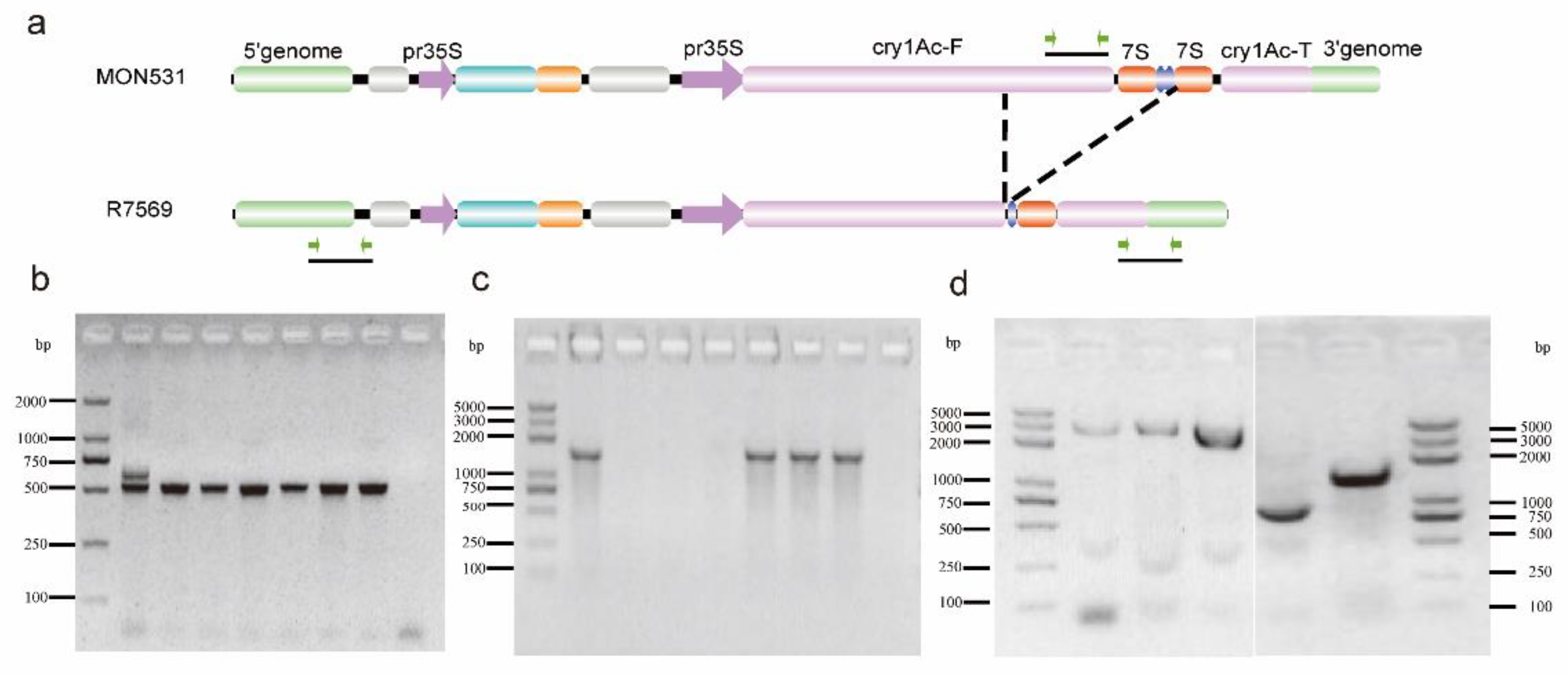
2.2. Validation of the Exogenous Insertion Structure of R7569
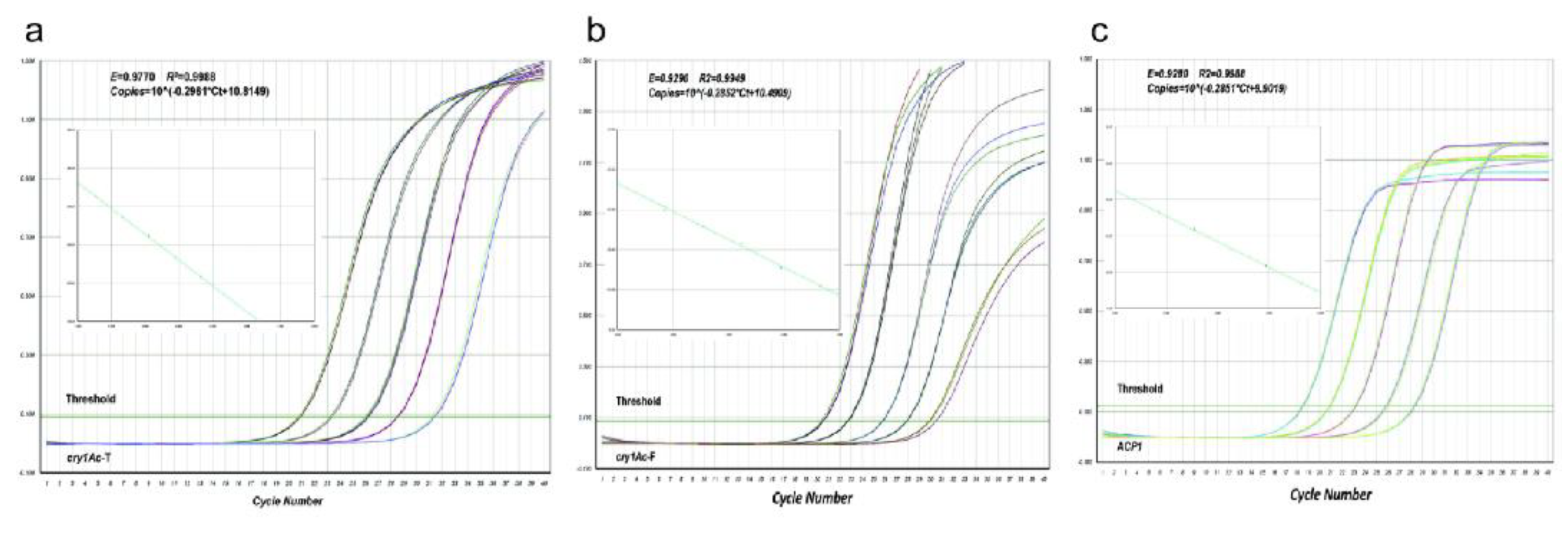
2.3. Establishment of Quantitative Testing Methods
2.4. RT-PCR Analysis of cry1Ac Gene Transcript Analysis in R7569
2.5. Determination of cry1Ac Insecticidal Protein by ELISA
2.6. Determination of Resistance to Bollworm for Cry1Ac Proteins
3. Results
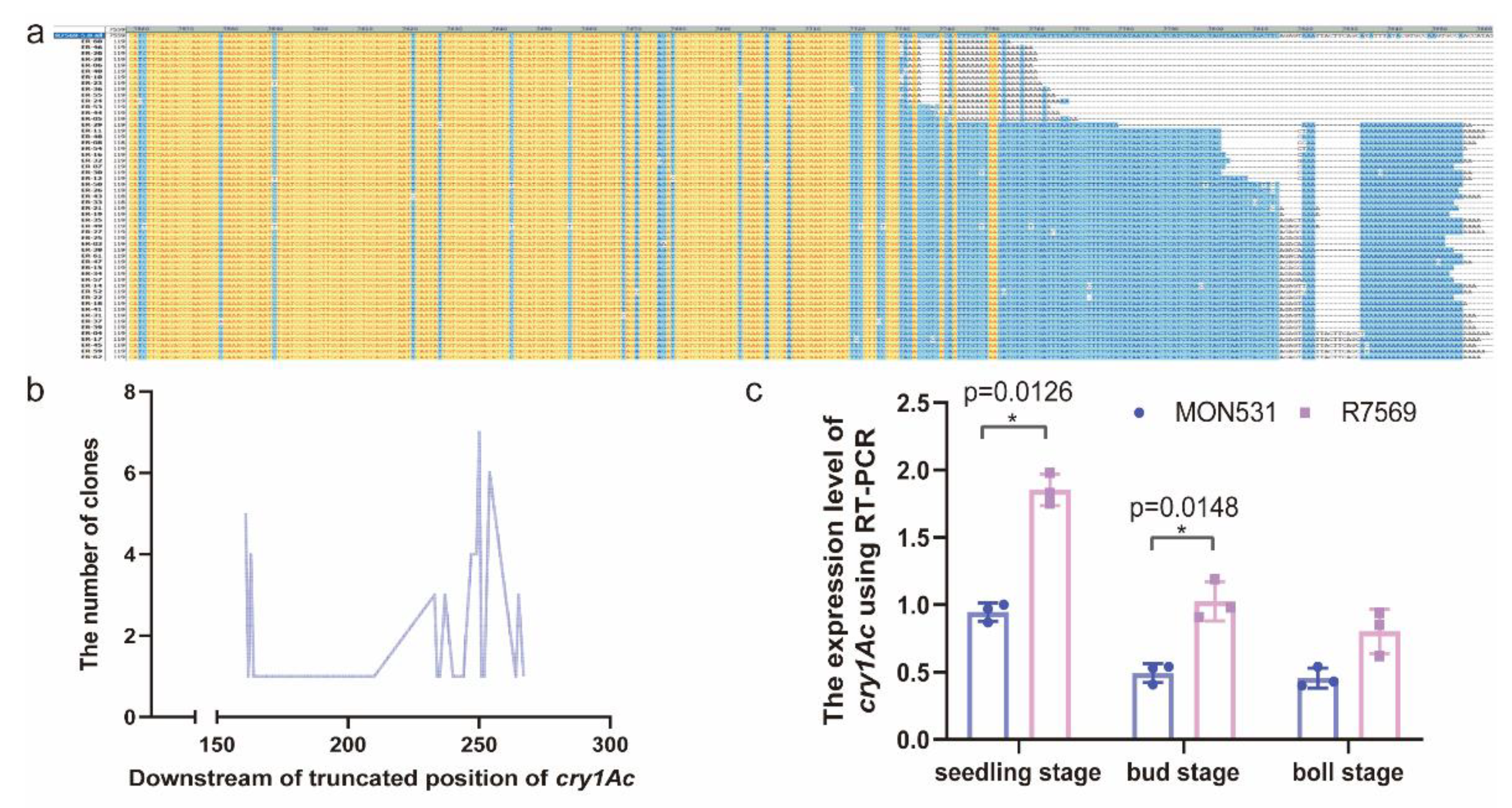
Transcription Levels of the Truncated cry1Ac Gene in R7569 Were Higher than Those of the Full-Length cry1Ac Gene
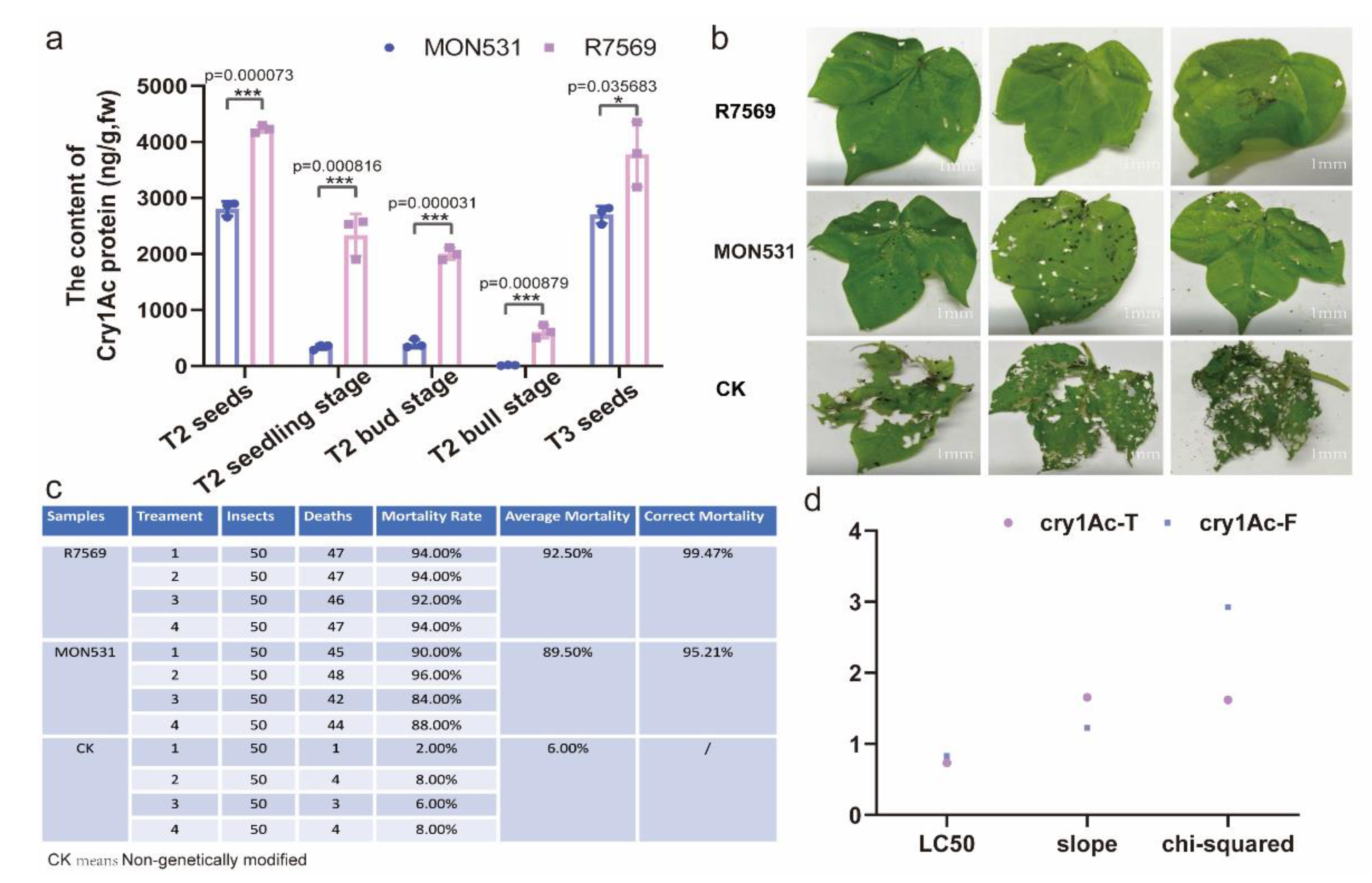
The Protein Content of the Truncated cry1Ac Gene Was Higher than That of the Full-Length cry1Ac Gene during the Cotton Growing Season
The Truncated Insecticidal Protein Cry1Ac Had a Higher Level of Biological Resistance than the Full-Length Insecticidal Protein Cry1Ac
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Hashmi, J.A.; Zafar, Y.; Arshad, M.; Mansoor, S.; Asad, S. Engineering Cotton (Gossypium Hirsutum L.) for Resistance to Cotton Leaf Curl Disease Using Viral Truncated AC1 DNA Sequences. Virus Genes 2011, 42, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.; Han, L.; Xie, J.; Chen, X. Sensitivities of Fall Armyworm (Spodoptera Frugiperda) Populations in Different Regions of China to Four Bt Proteins. Agronomy 2023, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Székács, A.; Lauber, É.; Juracsek, J.; Darvas, B. Cry1Ab Toxin Production of MON 810 Transgenic Maize. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- la Paz, J.L.; Pla, M.; Papazova, N.; Puigdomènech, P.; Vicient, C.M. Stability of the MON 810 Transgene in Maize. Plant Mol. Biol. 2010, 74, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, A.; Bogani, P.; Santarlasci, A.; Buiatti, M. Characterisation of 3′ Transgene Insertion Site and Derived MRNAs in MON810 YieldGard® Maize. Plant Mol. Biol. 2008, 67, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, B.; Yadav, R.; Sanyal, I.; Amla, D.V. Comparative Performance of Modified Full-Length and Truncated Bacillus Thuringiensis-Cry1Ac Genes in Transgenic Tomato. Springerplus 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Yang, L. Collaborative Ring Trial of the Applicability of a Reference Plasmid DNA Calibrant in the Quantitative Analysis of GM Maize Event MON810. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.R.; Berdal, K.G.; Bakke-Mckellep, A.M.; Holst-Jensen, A. Dietary DNA in Blood and Organs of Atlantic Salmon (Salmo Salar L.). Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2005, 221, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst-Jensen, A.; Bertheau, Y.; de Loose, M.; Grohmann, L.; Hamels, S.; Hougs, L.; Morisset, D.; Pecoraro, S.; Pla, M.; den Bulcke, M. Van; et al. Detecting Un-Authorized Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) and Derived Materials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 1318–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzanares-Palenzuela, C.L.; Mafra, I.; Costa, J.; Barroso, M.F.; De-Los-Santos-Álvarez, N.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; López-Ruiz, B. Electrochemical Magnetoassay Coupled to PCR as a Quantitative Approach to Detect the Soybean Transgenic Event GTS40-3-2 in Foods. Sensors Actuators, B Chem. 2016, 222, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahar, S. Ben; Salva, I.; Brants, I.O. Genetic Stability in Two Commercialized Transgenic Lines (MON810). Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Ye, W.; Fan, J.J. Event-Specific PCR Detection Methods of Genetically Modified Cotton ( Gossypium Hirsutum ) MON757 and Their Application. 2016, 24, 908–918. [CrossRef]
- Raman, R. The Impact of Genetically Modified (GM) Crops in Modern Agriculture: A Review. GM Crop. Food 2017, 8, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naranjo, S.E.; Ruberson, J.R.; Sharma, H.C.; Wilson, L. Integration of Insect-Resistant Genetically Modified Crops within IPM Programs; 2008; ISBN 9781402083730.
- VAN RIE, J.; JANSENS, S.; HÖFTE, H.; DEGHEELE, D.; VAN MELLAERT, H. Specificity of Bacillus Thuringiensisδ-endotoxins: Importance of Specific Receptors on the Brush Border Membrane of the Mid-gut of Target Insects. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 186, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, M.; Pla, M.; Esteve, T.; Prat, S.; Puigdomènech, P.; Ferrando, A. A Specific Real-Time Quantitative PCR Detection System for Event MON810 in Maize YieldGard® Based on the 3′-Transgene Integration Sequence. Transgenic Res. 2003, 12, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Paz, J.L.; Vicient, C.; Puigdomènech, P.; Pla, M. Characterization of Polyadenylated CryIA(b) Transcripts in Maize MON810 Commercial Varieties. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2125–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamoto, K.; Fukaya, T. Dynamic Interplay between Non-Coding Enhancer Transcription and Gene Activity in Development. bioRxiv 2022, 14, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamczyk, J.J.; Perera, O.; Meredith, W.R. Production of MRNA from the Cry1Ac Transgene Differs among Bollgard® Lines Which Correlates to the Level of Subsequent Protein. Transgenic Res. 2009, 18, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.; Choi, I.Y.; Kim, N.S. Detection of MPing Mobilization in Transgenic Rice Plants. Genes and Genomics 2020, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koul, B.; Srivastava, S.; Sanyal, I.; Tripathi, B.; Sharma, V.; Amla, D.V. Transgenic Tomato Line Expressing Modified Bacillus Thuringiensis Cry1Ab Gene Showing Complete Resistance to Two Lepidopteran Pests. Springerplus 2014, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




