Submitted:
11 May 2024
Posted:
14 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Library Construction
2.2. Data Analysis
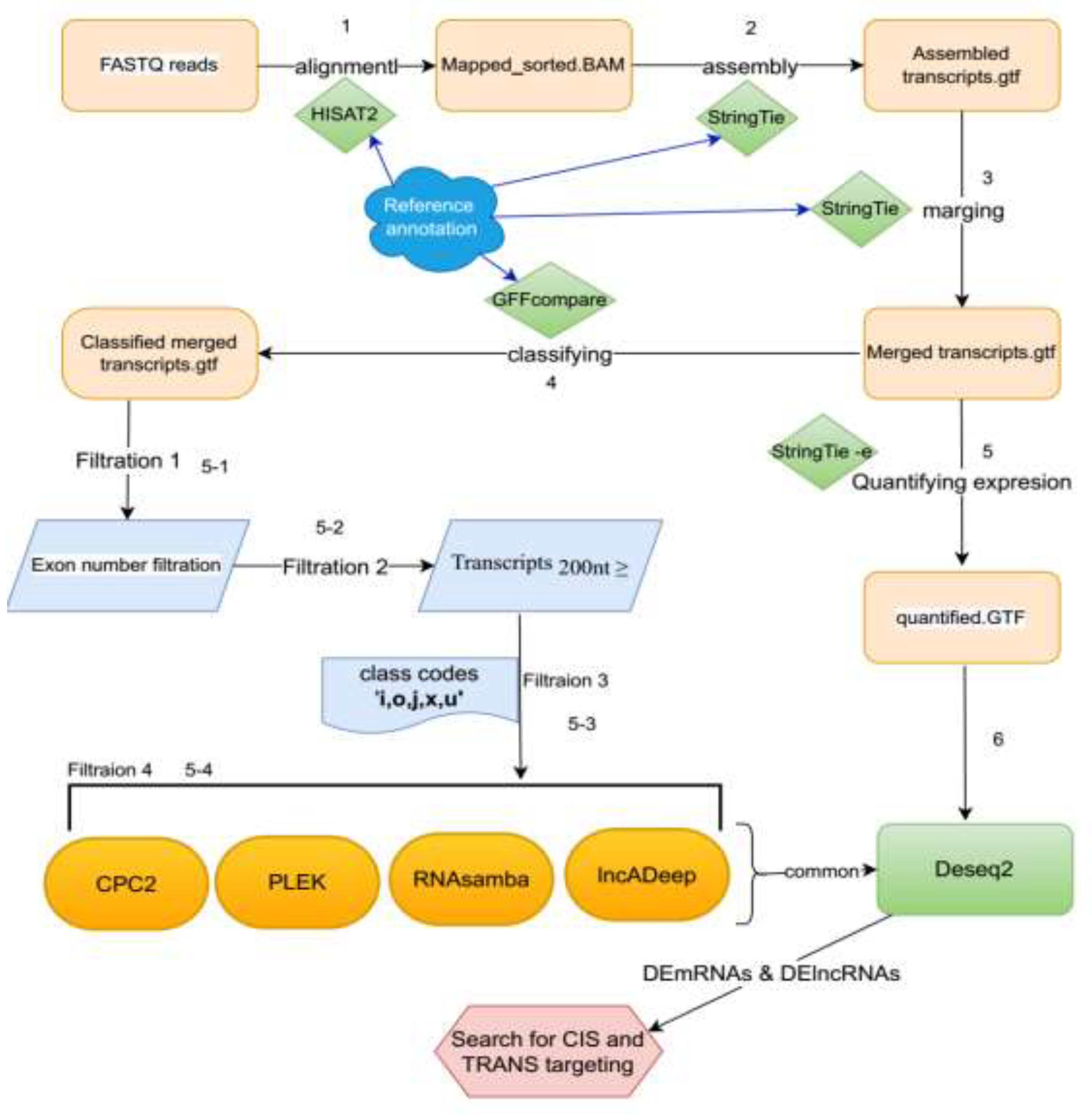
2.2.1. Read Alignment and Transcript Assembly
2.2.2. Transcript Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis
2.2.3. Identification and Classification of Putative lncRNAs
2.2.4. Target Gene Prediction and PPI Network
2.2.5. Gene Ontology and Networking Analysis
2.2.6. Novel lncRNAs and QTL Analysis
2.2.7. Q-RT-PCR Validation
3. Results
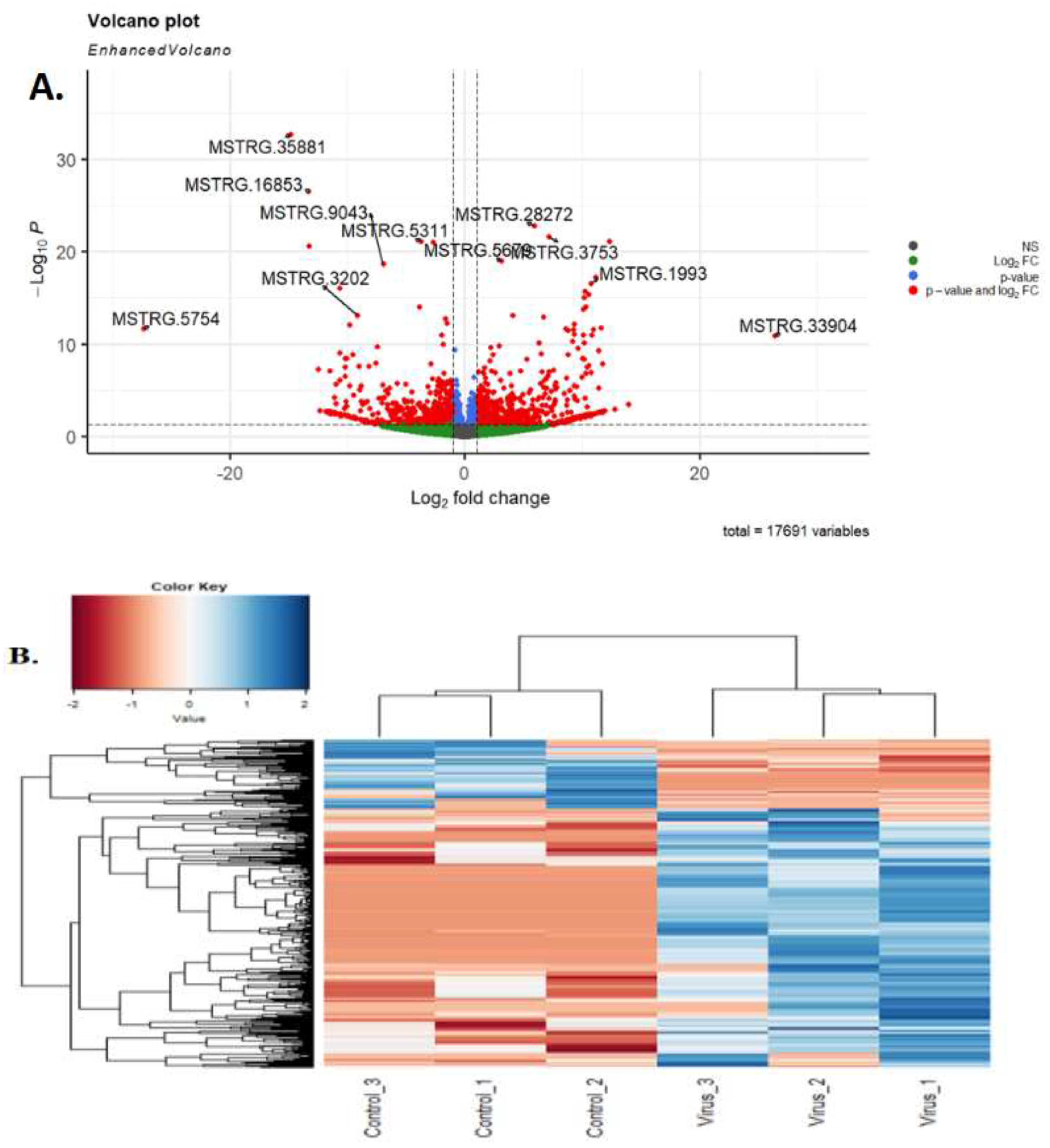
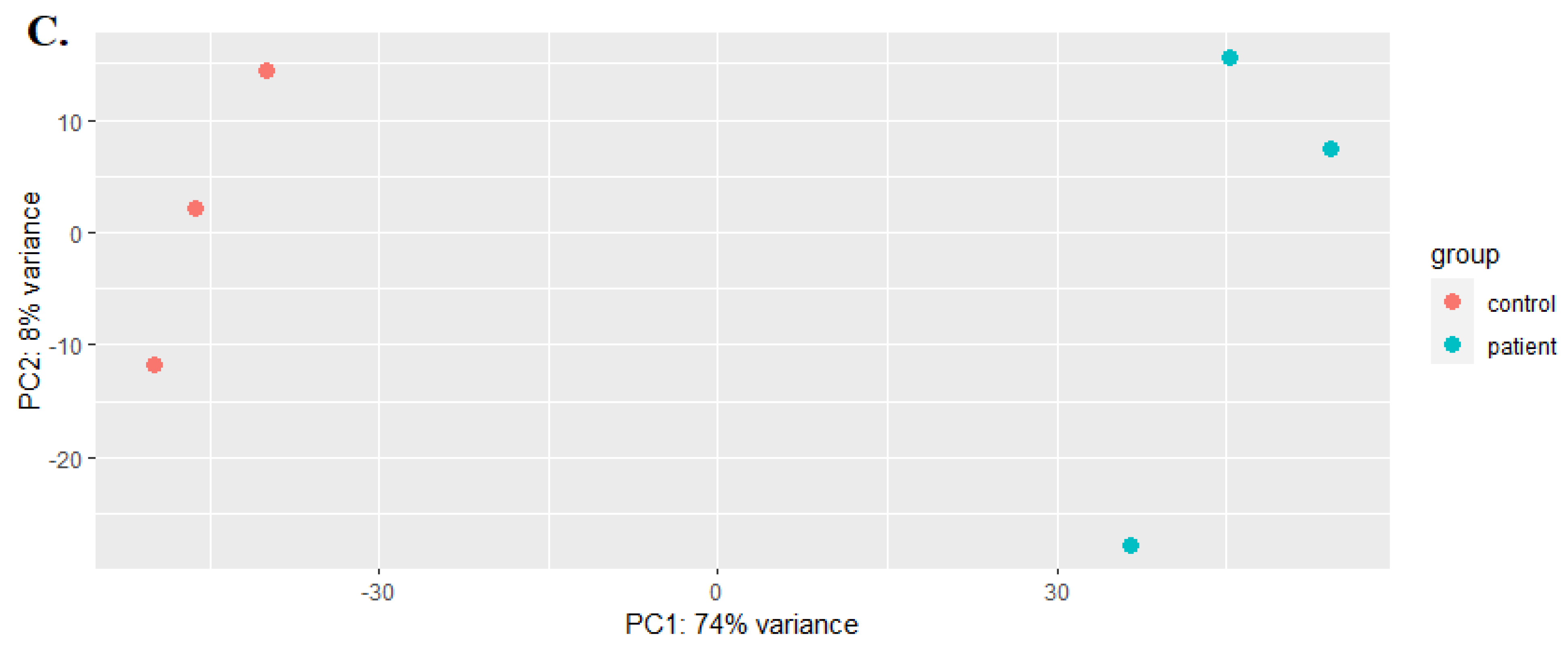
3.1. RNA-Seq Data Analysis
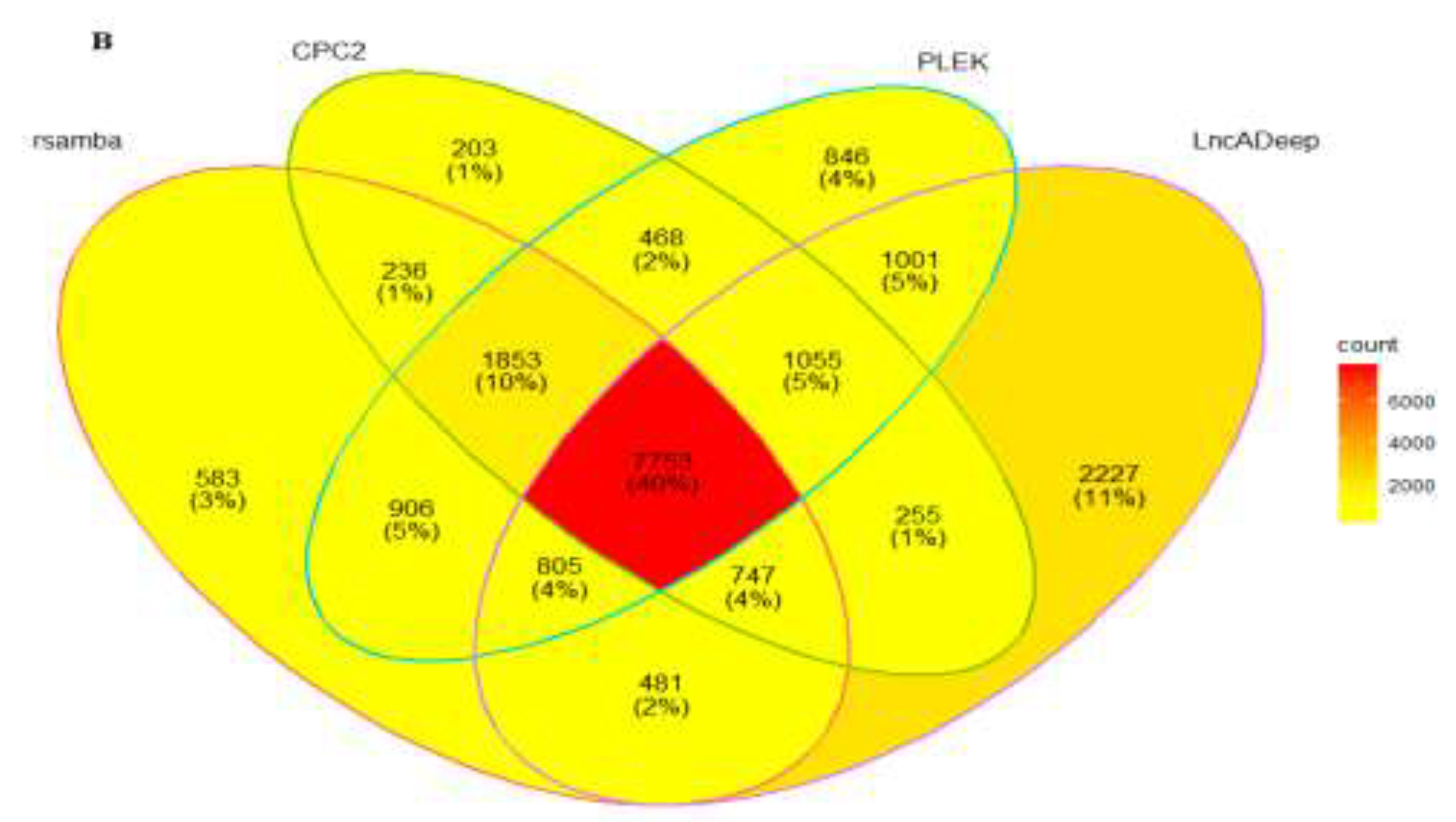
3.2. Identification and Classification of Putative lncRNAs
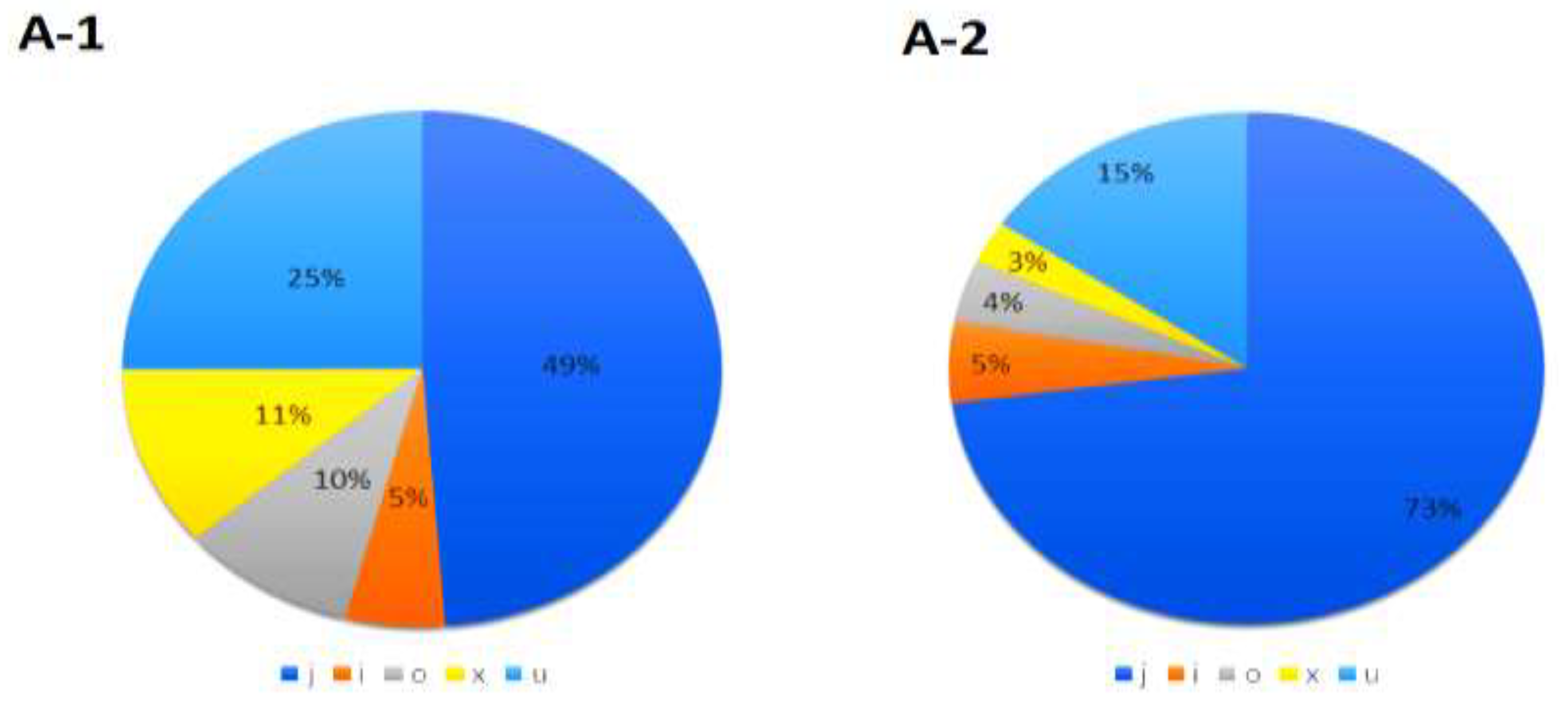
3.3. Differentially Expressed lncRNAs
3.4. Target Prediction of the Candidate lncRNAs and Gene Networking
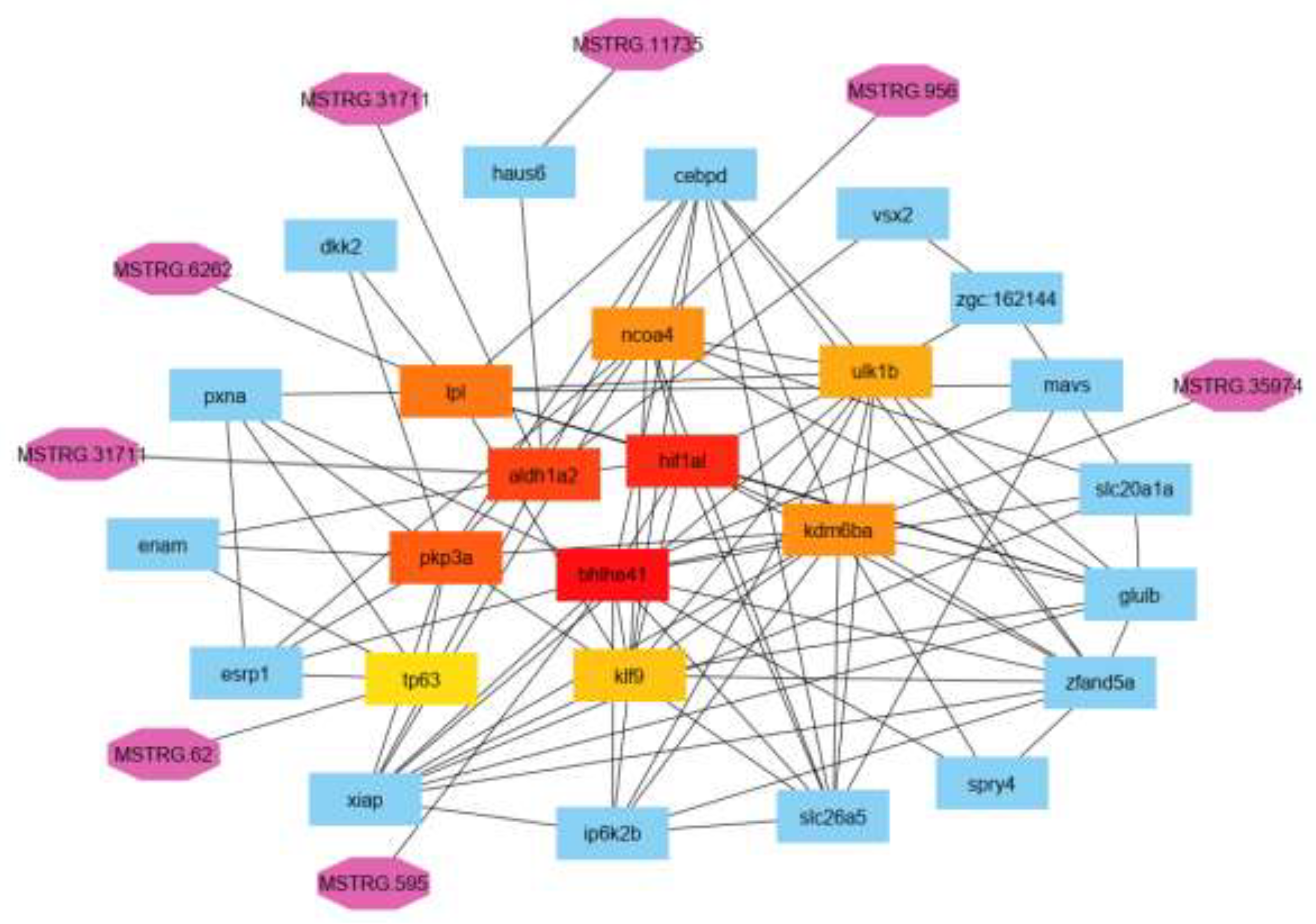
3.5. LncRNAs Target Gene Networking
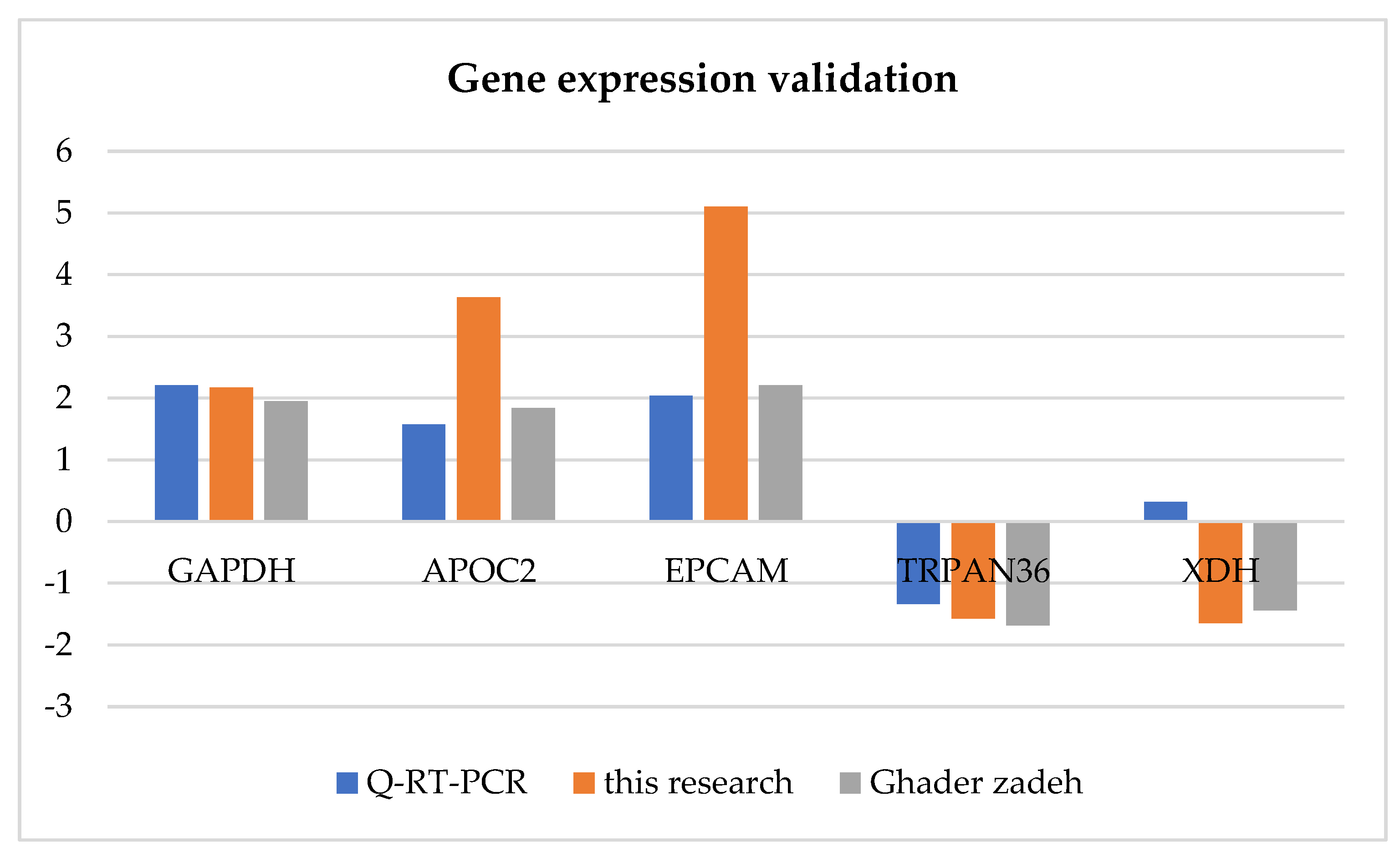
3.6. Validation of RNA-Seq by qRT‒PCR
3.7. QTL Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Funding
References
- Food and A.O.o.t.U.N.F. Department, The state of world fisheries and aquaculture. 1996: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- Smith, G.R.; Stearley, R.F. The Classification and Scientific Names of Rainbow and Cutthroat Trouts. Fisheries 1989, 14, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAllister, P. Fish Disease Leaflet 83. Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia of Fishes; US Fish and Wildlife Service, National Fisheries Research Center-Leetown, National Fish Health Research Laboratory: Kearneysville, VA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Olesen, N.J.; Korsholm, H. Control measures for viral diseases in aquaculture: eradication of VHS and IHN. Bulletin of the European Association of Fish Pathologists 1997, 17, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Bokaei, S.; et al. Investigation of Outbreaks of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia and Associated Risk Factors in Rainbow Trout Farms in Iran, 2014. Iranian Journal of Epidemiology 2017, 13, 253–261. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.-W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.-L. Cellular functions of long noncoding RNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cech, T.R.; Steitz, J.A. The Noncoding RNA Revolution—Trashing Old Rules to Forge New Ones. Cell 2014, 157, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Jiang, D.L.; Meng, Z.N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.X.; Lin, H.R.; Xia, J.H. Genome-wide identification and differentially expression analysis of lncRNAs in tilapia. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Kwon, Y.-K.; Nam, M.; Vaidya, B.; Kim, S.R.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.; Kim, D.; Hwang, G.-S. Integrated profiling of global metabolomic and transcriptomic responses to viral hemorrhagic septicemia virus infection in olive flounder. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2017, 71, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fu, L.; Koganti, P.P.; Wang, L.; Hand, J.M.; Ma, H.; Yao, J. Identification and Functional Prediction of Large Intergenic Noncoding RNAs (lincRNAs) in Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Mar. Biotechnol. 2016, 18, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, L. Integrated Analysis of lncRNA and circRNA Mediated ceRNA Regulatory Networks in Skin Reveals Innate Immunity Differences Between Wild-Type and Yellow Mutant Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 802731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.; Kang, Y.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Ma, F.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. Identification and characterization of long noncoding RNAs provide insight into the regulation of gene expression in response to heat stress in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D: Genom. Proteom. 2020, 36, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaderzadeh, M.; Rahimi Mianji, G.; Nejati Javaremi, A.; Shahbazian, N. Effect of Viral Hemorrhagic Septicemia (VHS) disease on the biometric parameters in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Veterinary Research & Biological Products 2021, 34, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovaka, S.; Zimin, A.V.; Pertea, G.M.; Razaghi, R.; Salzberg, S.L.; Pertea, M. Transcriptome assembly from long-read RNA-seq alignments with StringTie2. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.; Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential analysis of count data–the DESeq2 package. Genome Biology 2014, 15, 10.1186. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Yang, D.-C.; Kong, L.; Hou, M.; Meng, Y.-Q.; Wei, L.; Gao, G. CPC2: a fast and accurate coding potential calculator based on sequence intrinsic features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W12–W16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.P.; Sourkov, V.; Pereira, G.A.G.; Carazzolle, M.F. RNAsamba: neural network-based assessment of the protein-coding potential of RNA sequences. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqz024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, A.P.; Sourkov, V.; Pereira, G.A.G.; Carazzolle, M.F. RNAsamba: neural network-based assessment of the protein-coding potential of RNA sequences. NAR Genom. Bioinform. 2020, 2, lqz024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Z. PLEK: a tool for predicting long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs based on an improved k-mer scheme. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Chang, H.Y. Genome Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 145–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukunaga, T.; Hamada, M. RIblast: an ultrafast RNA–RNA interaction prediction system based on a seed-and-extension approach. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2666–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Wu, H.-H.; Ho, C.-W.; Ko, M.-T.; Lin, C.-Y. cytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst. Biol. 2014, 8 (Suppl. 4), S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-L.; Park, C.A.; Reecy, J.M. Developmental progress and current status of the Animal QTLdb. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 44, D827–D833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.-J.; Chen, L.-L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118, Correction in 2021, 22, 159, 10.1038/s41580-021-00330-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamarai, M.D.; Rajan, M.R.; Bharathi, P.V. Current risks of microbial infections in fish and their prevention methods: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2023, 185, 106400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Tang, Y.-D.; Hu, W.; Zheng, C. When Poly (A) Binding Proteins Meet Viral Infections, Including SARS-CoV-2. Journal of Virology 2022, 96, e00136-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, R.L.; Fragomeni, B.O.; Cheng, H.; Gao, G.; Long, R.L.; Shewbridge, K.L.; MacMillan, J.R.; Towner, R.; Palti, Y. Assessing Accuracy of Genomic Predictions for Resistance to Infectious Hematopoietic Necrosis Virus With Progeny Testing of Selection Candidates in a Commercial Rainbow Trout Breeding Population. Front. Veter- Sci. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S.; et al. Long non-coding RNAs: definitions, functions, challenges and recommendations. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2023, 24, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, H.; Lu, Y.; Feng, T.; Sun, W. LncRNA BC032020 suppresses the survival of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cells by targeting ZNF451. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1224–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadallah, S.; Eken, C.; Martin, P.J.; Schifferli, J.A. Microparticles (Ectosomes) Shed by Stored Human Platelets Downregulate Macrophages and Modify the Development of Dendritic Cells. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 6543–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; et al. Dynamic TF-lncRNA regulatory networks revealed prognostic signatures in the development of ovarian cancer. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2020, 8, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toni, M.; Cioni, C. Fish Synucleins: An Update. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 6665–6686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Ma, K. SARS-CoV-2 proteins interact with alpha synuclein and induce Lewy body-like pathology in vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasen, A.; et al. Upregulation of α-synuclein following immune activation: Possible trigger of Parkinson's disease. Neurobiology of Disease 2022, 166, 105654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reish, H.E.A.; Standaert, D.G. Role of α-Synuclein in Inducing Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Parkinson Disease. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grathwohl, S.; et al. Experimental colitis drives enteric alpha-synuclein accumulation and Parkinson-like brain pathology. bioRxiv 2018, 505164. [Google Scholar]
- Kunimura, K.; Uruno, T.; Fukui, Y. DOCK family proteins: key players in immune surveillance mechanisms. Int. Immunol. 2019, 32, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.-B.; Wang, D.; Han, T.; Wen, Z.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, Q.-L.; Zheng, J.-L.; Wang, P. Histological, antioxidant, apoptotic and transcriptomic responses under cold stress and the mitigation of blue wavelength light of zebrafish eyes. Aquac. Rep. 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, A.; Corrales, N.; Galvez, N.M.S.; Bueno, S.M.; Kalergis, A.M.; Gonzalez, P.A. Contribution of hypoxia inducible factor-1 during viral infections. Virulence 2020, 11, 1482–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, E.; Nde, C.; Ray, R.S.; Preciado, D.; Zohn, I.E. ALDH1A2-related disorder: A new genetic syndrome due to alteration of the retinoic acid pathway. Am. J. Med Genet. Part A 2022, 191, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, N.; Si, L.; Zhu, L.; Zeng, A.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X. INF2 regulates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in epidermal HaCaT cells by modulating the HIF1 signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 111, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Xia, Y.; Fan, K.; Liu, Y.; Liu, P.-F. Identification and expression analysis of a fibrinogen alpha chain-like gene in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). Aquac. Rep. 2021, 22, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Rui-Qiong, M.; Ye, X.; Cui, H.; Hong-Lan, Z.; Chang, X.-H. Fibrinogen alpha chain is up-regulated and affects the pathogenesis of endometriosis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2019, 39, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Weng, J.; Chen, L.; Hu, N.; Yuan, X.; Wang, J.; He, F.; Cai, Y.; Huang, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of SLC43A2 on the tumor immune microenvironment and prognosis of liver hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, N.; Ferreira-Martins, D.; McCormick, S.D.; Sheridan, M.A. Divergent genes encoding the putative receptors for growth hormone and prolactin in sea lamprey display distinct patterns of expression. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicenas, J.; et al. KRAS, TP53, CDKN2A, SMAD4, BRCA1, and BRCA2 mutations in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosic, J.; Dragicevic, S.; Miladinov, M.; Despotovic, J.; Bogdanovic, A.; Krivokapic, Z.; Nikolic, A. SMAD7 and SMAD4 expression in colorectal cancer progression and therapy response. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2021, 123, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Bradshaw, A.-D.; Gera, S.; Dewan, M.Z.; Xu, R. The TGF-β/Smad4 Signaling Pathway in Pancreatic Carcinogenesis and Its Clinical Significance. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kany, S.; Vollrath, J.T.; Relja, B. Cytokines in inflammatory disease. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, C.; Tang, Y.; Chen, F.; Yang, M.; Wang, K.-J. Identification of novel long non-coding RNAs involved in bisphenol A induced immunotoxicity in fish primary macrophages. Fish Shellfish. Immunol. 2020, 100, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daynes, R.A.; Jones, D.C. Emerging roles of PPARS in inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebl, A.; Goldammer, T.; Seyfert, H.-M. Toll-like receptor signaling in bony fish. Veter- Immunol. Immunopathol. 2010, 134, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Peter, S.; Jung, M.; Lewin, A.; Hemmrich-Stanisak, G.; Franke, A.; von Kleist, M.; Schütte, C.; Einspanier, R.; Sharbati, S.; et al. Analysis of long non-coding RNA and mRNA expression in bovine macrophages brings up novel aspects of Mycobacterium avium subspecies paratuberculosis infections. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Zhou, C.; Yin, H.; Song, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, S. Genome Wide Identification of Novel Long Non-coding RNAs and Their Potential Associations With Milk Proteins in Chinese Holstein Cows. Front. Genet. 2018, 9, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marancik, D.; Gao, G.; Paneru, B.; Ma, H.; Hernandez, A.G.; Salem, M.; Yao, J.; Palti, Y.; Wiens, G.D. Whole-body transcriptome of selectively bred, resistant-, control-, and susceptible-line rainbow trout following experimental challenge with Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Front. Genet. 2015, 5, 453–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paneru, B.; Al-Tobasei, R.; Palti, Y.; Wiens, G.D.; Salem, M. Differential expression of long non-coding RNAs in three genetic lines of rainbow trout in response to infection with Flavobacterium psychrophilum. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36032–36032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample | Raw Data | Valid Data | Valid Ratio (%) | Q20 (%) | Q30 (%) | Mapped Ratio (%) |
| Control | 42,374,402 | 42,087,999 | 99.32 | 99.88 | 92.25 | 91.17 |
| Control | 40,339,708 | 40,035,219 | 99.25 | 99.87 | 91.14 | 90.53 |
| Control | 54,456,286 | 53,829,279 | 98.85 | 99.85 | 91.07 | 90.25 |
| Treated | 45,502,028 | 45,364,200 | 99.70 | 99.91 | 91.87 | 89.92 |
| Treated | 48,998,728 | 48,930,236 | 99.86 | 99.93 | 91.77 | 90.23 |
| Treated | 44,135,524 | 43,796,603 | 99.23 | 99.88 | 91.40 | 88.89 |
| Tab. | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mRNA | Regulation | lncRNA | class code | Regulation | mRNA | Regulation | lncRNA | class code | Regulation |
| TP63 | Down | MSTRG.62 | j | Up | LOC118944460 | Down | MSTRG.32002 | o | Down |
| LOC110524396 | Down | MSTRG.148 | x | Up | LOC118944461 | Down | MSTRG.32002 | o | Down |
| BHLHE41 | Down | MSTRG.595 | u | Up | LOC110528420 | Up | MSTRG.9557 | j | Up |
| LOC110525089 | Down | MSTRG.785 | j | Down | IL10 | Up | MSTRG.9783 | j | Up |
| LOC110526498 | Down | MSTRG.896 | o | Down | IL10 | Up | MSTRG.9784 | u | Down |
| NCOA4 | Down | MSTRG.956 | j | Down | LOC110529378 | Up | MSTRG.9966 | j | Down |
| LOC110527687 | Down | MSTRG.982 | j | Down | LOC110529379 | Down | MSTRG.9966 | j | Down |
| LOC110512766 | Down | MSTRG.1363 | j | Down | LOC110529615 | Up | MSTRG.10141 | j | Up |
| LOC110525147 | Down | MSTRG.1563 | j | Down | LOC118936275 | Down | MSTRG.10832 | j | Down |
| TUFT1A | Down | MSTRG.1680 | j | Up | LOC110530481 | Down | MSTRG.10832 | j | Down |
| LOC118937935 | Up | MSTRG.1706 | j | Up | LOC110530704 | Up | MSTRG.11013 | j | Up |
| LOC110485723 | Up | MSTRG.1993 | j | Up | HAUS6 | Down | MSTRG.11735 | j | Down |
| LOC110502310 | Down | MSTRG.2952 | j | Down | LOC110532684 | Down | MSTRG.12397 | j | Up |
| LOC110521085 | Up | MSTRG.5084 | j | Up | E1 | Down | MSTRG.12464 | j | Down |
| EFNA1B | Up | MSTRG.1700 | u | Down | LOC110533701 | Up | MSTRG.13116 | j | Up |
| LOC118937935 | Up | MSTRG.3327 | j | Up | LOC110497318 | Up | MSTRG.25735 | j | Up |
| LOC110516769 | Down | MSTRG.3347 | j | Down | LOC110497317 | Up | MSTRG.25735 | j | Up |
| LOC110520884 | Down | MSTRG.3347 | j | Down | LOC110497274 | Down | MSTRG.13985 | j | Down |
| LOC110520883 | Down | MSTRG.3347 | j | Down | LOC110497275 | Down | MSTRG.13985 | j | Down |
| GHR1 | Up | MSTRG.5679 | j | Down | LOC110514189 | Up | MSTRG.14211 | j | Up |
| LOC110523752 | Down | MSTRG.5854 | j | Down | LOC110535281 | Up | MSTRG.14419 | j | Up |
| SID1 | Up | MSTRG.6203 | j | Up | LOC110535279 | Down | MSTRG.14419 | j | Up |
| LPL | Down | MSTRG.6262 | j | Down | LOC110535540 | Down | MSTRG.14622 | j | Down |
| LOC110526114 | Down | MSTRG.7664 | j | Down | SLC20A1A | Up | MSTRG.14967 | j | Up |
| ALDH1A2 | Up | MSTRG.31711 | j | Up | SLC25A37 | Up | MSTRG.14992 | j | Up |
| LOC110506541 | Down | MSTRG.31713 | j | Down | NAALADL1 | Up | MSTRG.15351 | j | Down |
| LOC110506917 | Down | MSTRG.32002 | o | Down | LOC110537350 | Down | MSTRG.15881 | j | Down |
| Dock10 | Up | MSTRG.30015 | j | Down | |||||
| lncRNAs | Expr | mRNAs | Expr | InEnergy | lncRNAs | Expr | mRNAs | Expr | InEnergy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSTRG.17204 | down | LOC110486166 | up | -20.1681 | MSTRG.24034 | down | LOC110503011 | down | -25.8338 |
| MSTRG.19333 | up | SI:DKEY-89B17.4 | down | -22.5963 | MSTRG.24034 | up | LOC110503701 | down | -22.4431 |
| MSTRG.19333 | up | LOC110486530 | up | -22.7976 | MSTRG.24034 | up | LOC110508925 | up | -23.4754 |
| MSTRG.19333 | up | LOC110486615 | up | -20.9064 | MSTRG.27872 | up | FAM78AB | down | -20.3565 |
| MSTRG.19333 | up | LOC110489230 | up | -20.1649 | MSTRG.27872 | up | LOC110504281 | up | -20.3359 |
| MSTRG.29125 | up | LOC110489230 | up | -21.5915 | MSTRG.34190 | up | ENPP2 | up | -21.8946 |
| MSTRG.29125 | up | LOC110490321 | down | -21.1108 | MSTRG.34190 | up | LOC110525147 | up | -22.0789 |
| MSTRG.29125 | up | LOC100136069 | up | -22.1927 | MSTRG.34190 | up | LOC110489230 | up | -27.3874 |
| MSTRG.34190 | down | MEOX2A | up | -20.8682 | MSTRG.34190 | down | TFAP2A | up | -20.5328 |
| MSTRG.34190 | down | CDH13 | down | -24.9856 | MSTRG.34190 | down | LOC118938874 | down | -20.3688 |
| MSTRG.34190 | down | LOC110500756 | down | -30.236 | MSTRG.34190 | down | LOC110491320 | up | -21.5654 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | SI:CH211-214J24.15 | down | -21.568 | MSTRG.34190 | down | LOC110493456 | up | -23.9436 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | LOC110485438 | down | -23.9051 | MSTRG.35974 | down | ANTXR1B | down | -22.1156 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | LOC110510746 | up | -21.2892 | MSTRG.35974 | down | LOC110510746 | up | -20.399 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | FAM78AB | down | -23.6439 | MSTRG.35974 | down | LOC110534579 | up | -22.3215 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | LOC101268921 | up | -20.3122 | MSTRG.35974 | down | CHRNA2A | down | -22.1661 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | PRLH2 | up | -20.1694 | MSTRG.35974 | down | KDM6BA | down | -21.7067 |
| MSTRG.36357 | down | LOC110534579 | up | -20.7044 | MSTRG.982 | down | LOC110506699 | down | -21.1293 |
| MSTRG.29125 | up | LOC110508925 | up | -20.2593 | MSTRG.982 | up | LOC110521060 | down | -20.433 |
| MSTRG.29125 | up | LOC110521826 | up | -28.0706 | MSTRG.982 | up | FAM78AB | down | -26.6405 |
| MSTRG.13869 | up | LOC100136069 | up | -25.5793 | MSTRG.982 | up | LOC110513729 | up | -20.1696 |
| MSTRG.13869 | up | LOC110534579 | up | -20.342 | MSTRG.982 | up | LOC110534814 | up | -22.5472 |
| MSTRG.13869 | up | SI:CH73-22O12.1 | up | -20.6675 | MSTRG.19333 | up | LOC110503011 | down | -21.2381 |
| MSTRG.22011 | up | LOC100136069 | up | -21.3084 | MSTRG.22011 | up | ZNF385A | up | -20.8434 |
| MSTRG.22011 | up | LOC118936283 | up | -21.8654 | MSTRG.22011 | up | LOC110510746 | up | -28.6177 |
| MSTRG.22011 | down | LOC110486615 | up | -20.4733 | MSTRG.24034 | down | LOC110489230 | up | -20.3093 |
| MSTRG.24034 | down | LOC110510746 | up | -31.7948 | MSTRG.24034 | down | PRLH2 | up | -21.9129 |
| MSTRG.24034 | down | ZNF385A | up | -20.3607 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





