Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
20 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Material Measurements
3.2. SI Characteristics
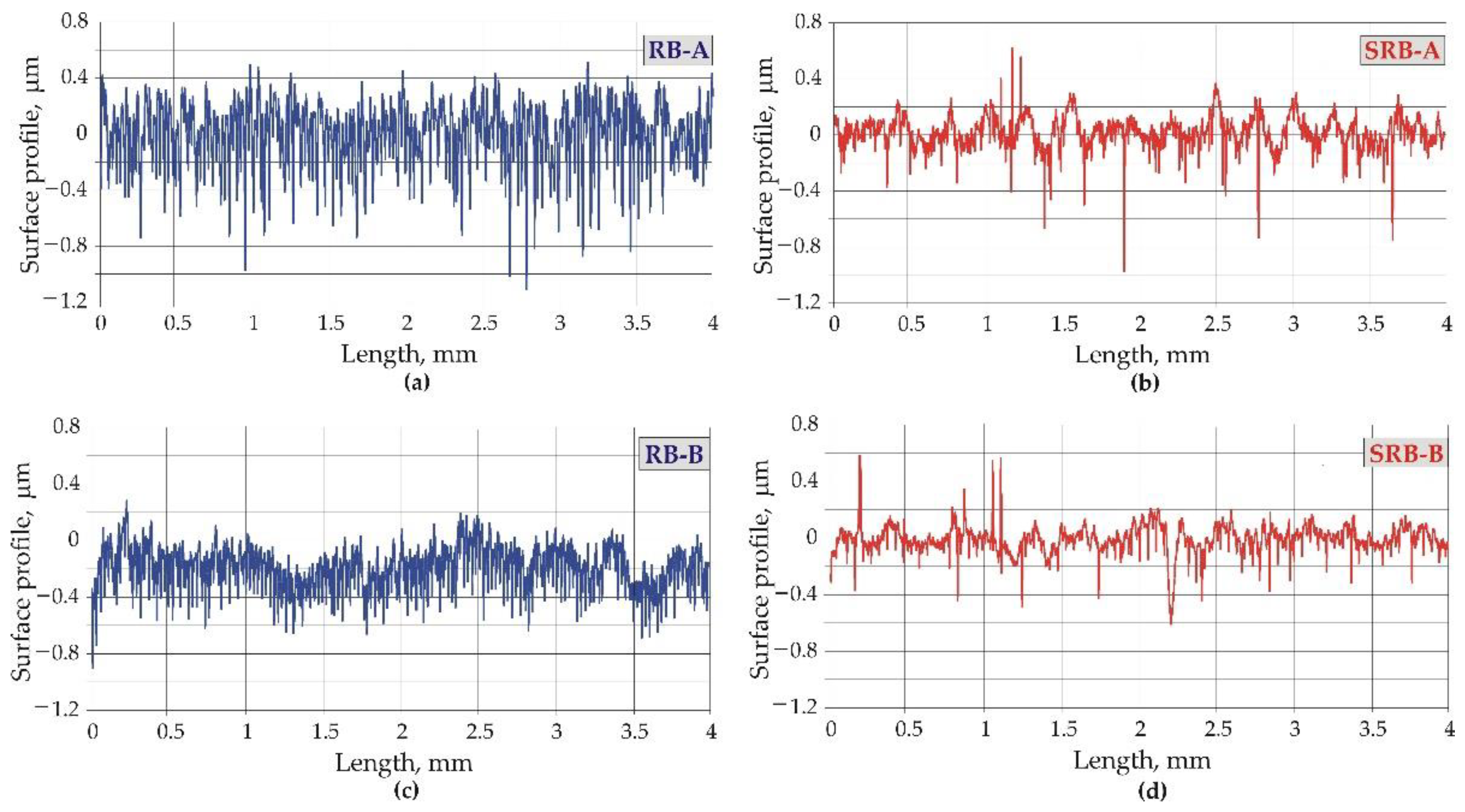
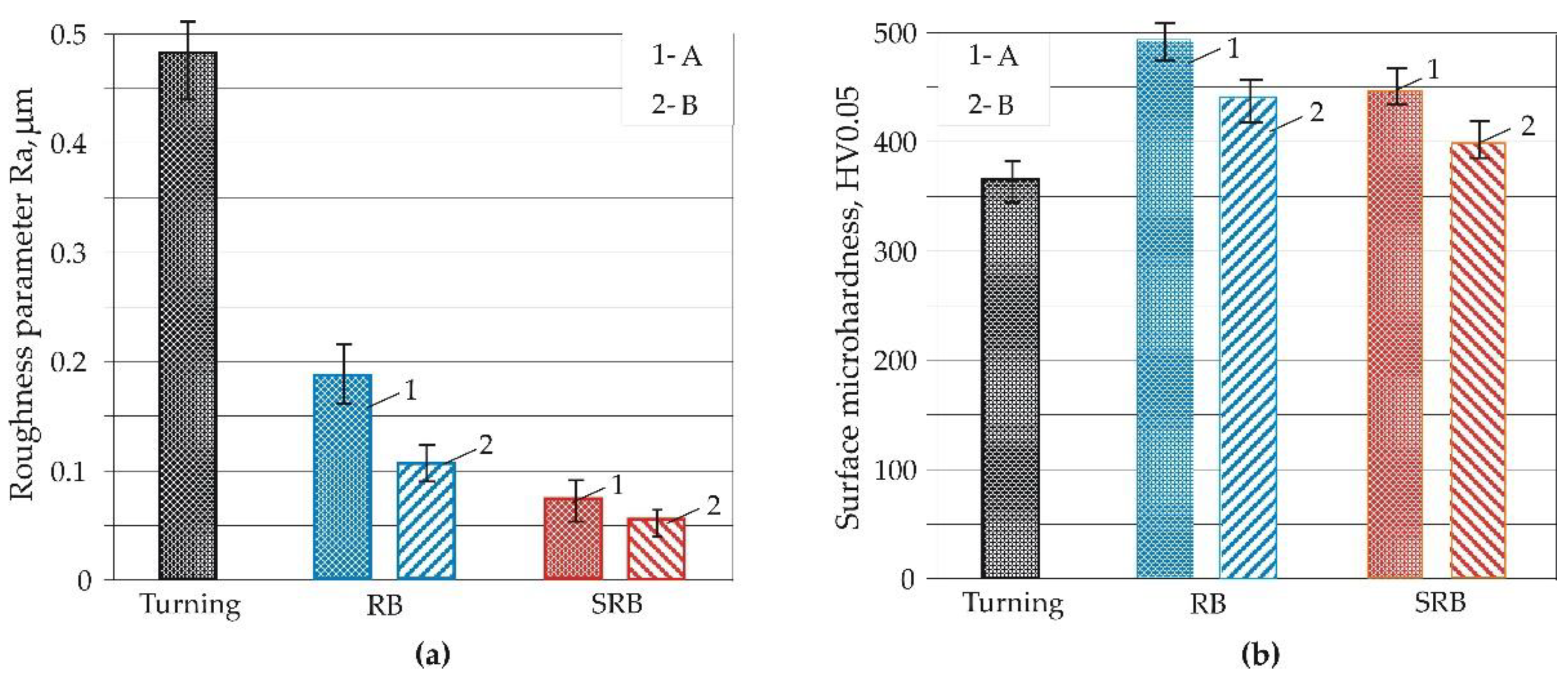
3.2.1. Roughness
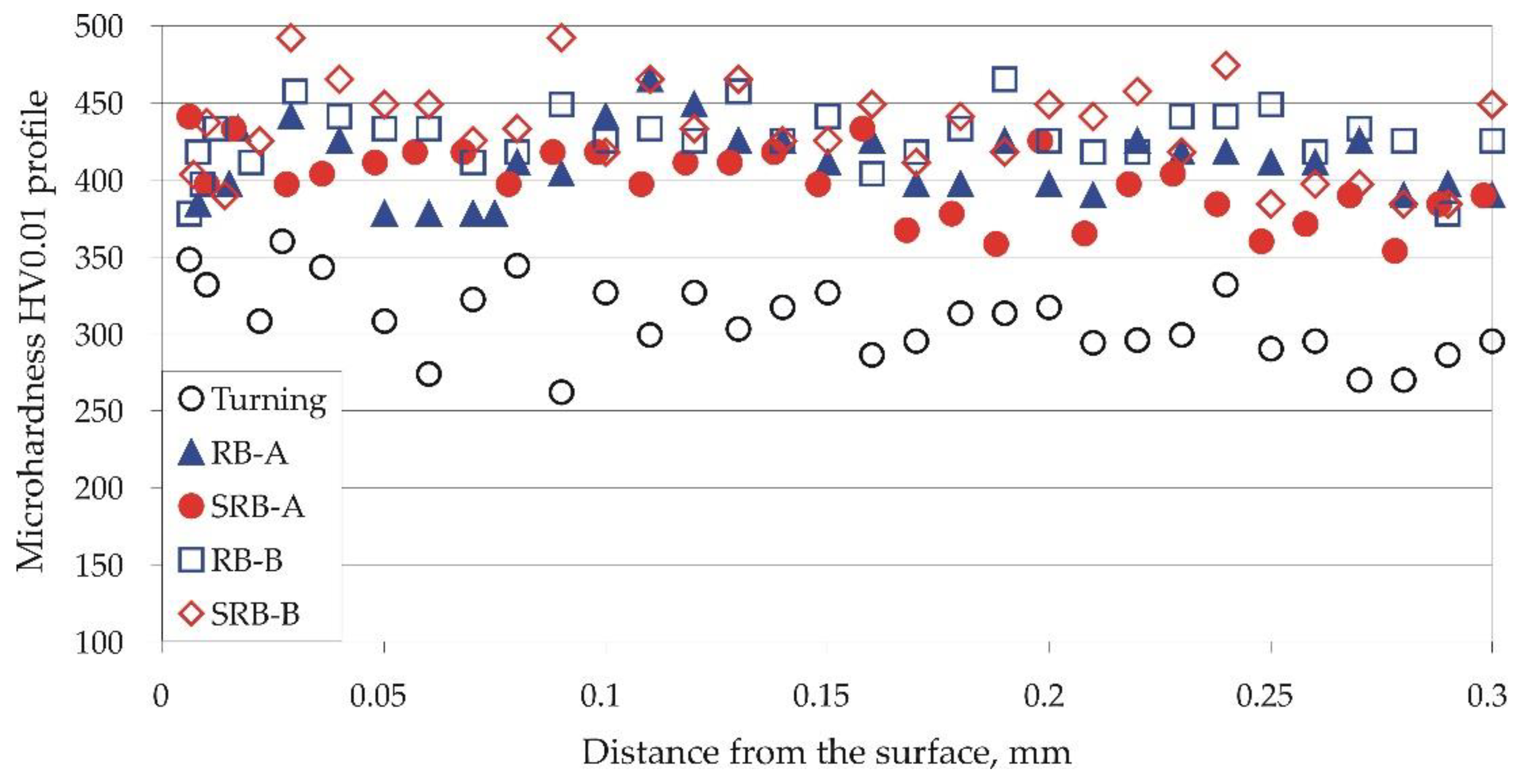
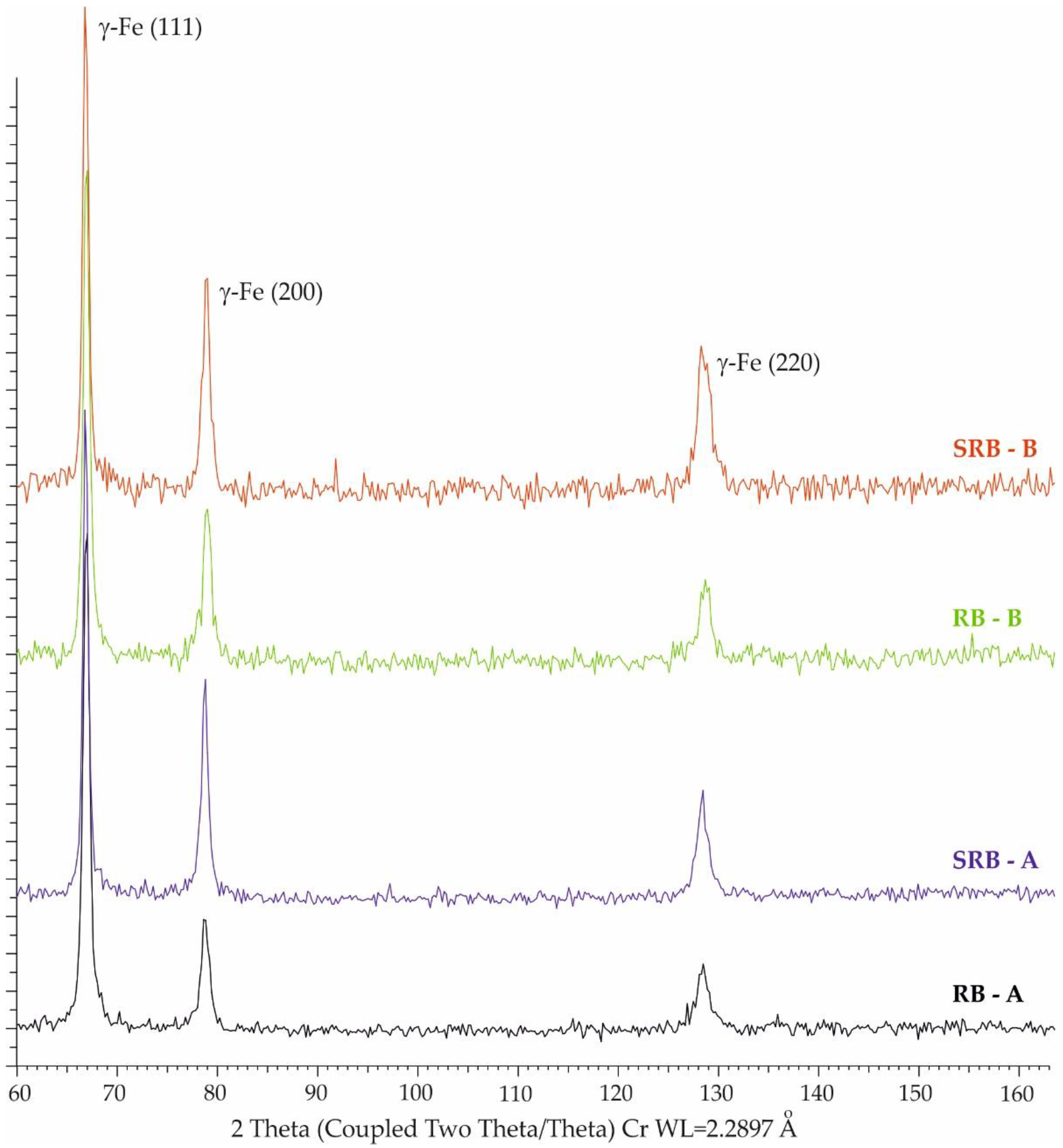
3.2.2. Microhardness and Phase Analysis Results
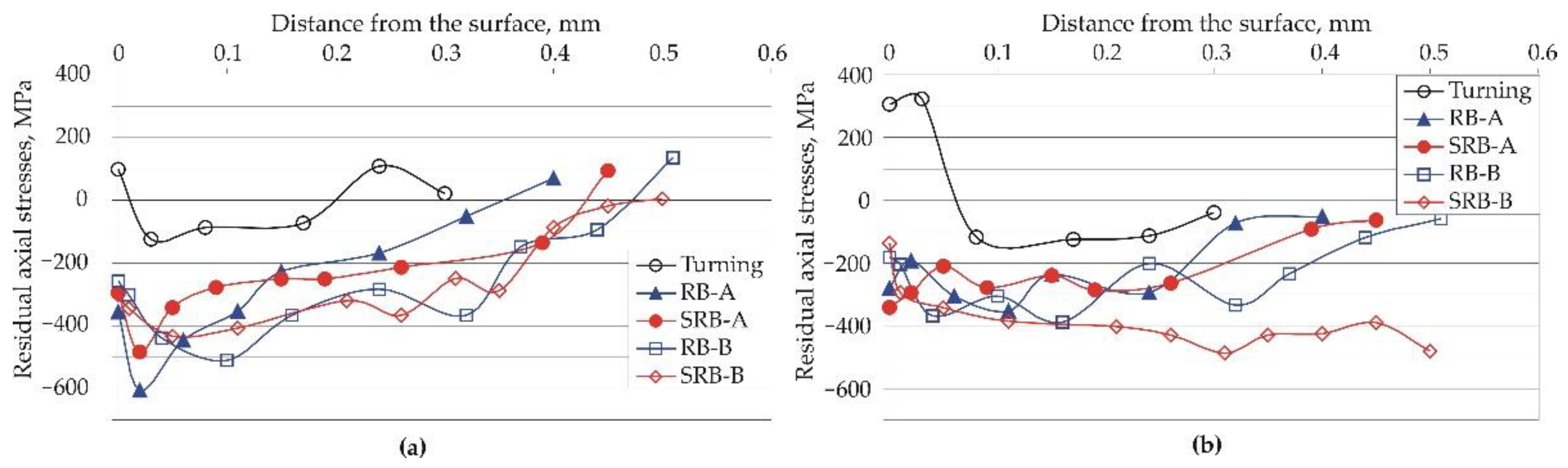
3.2.3. Residual Stresses
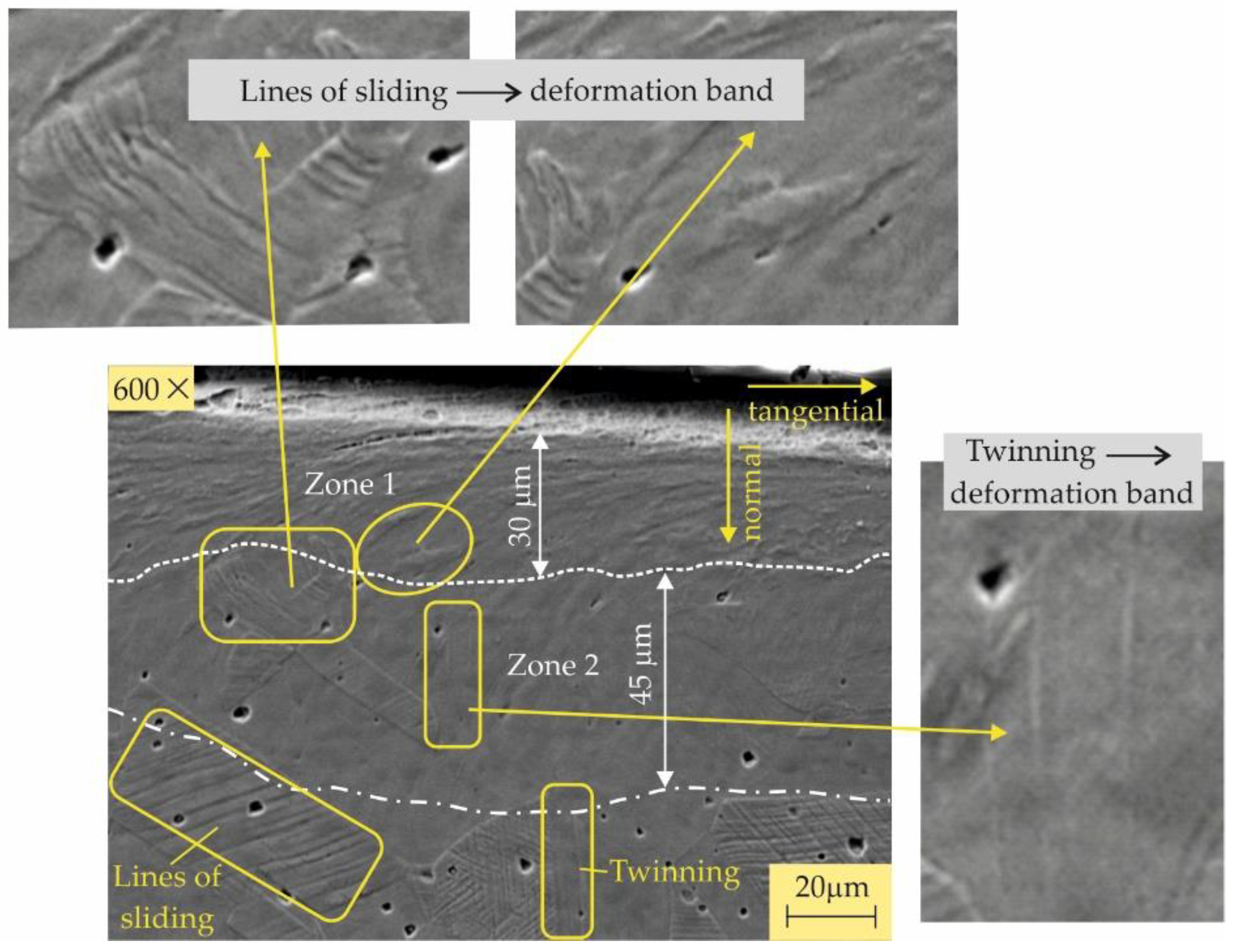
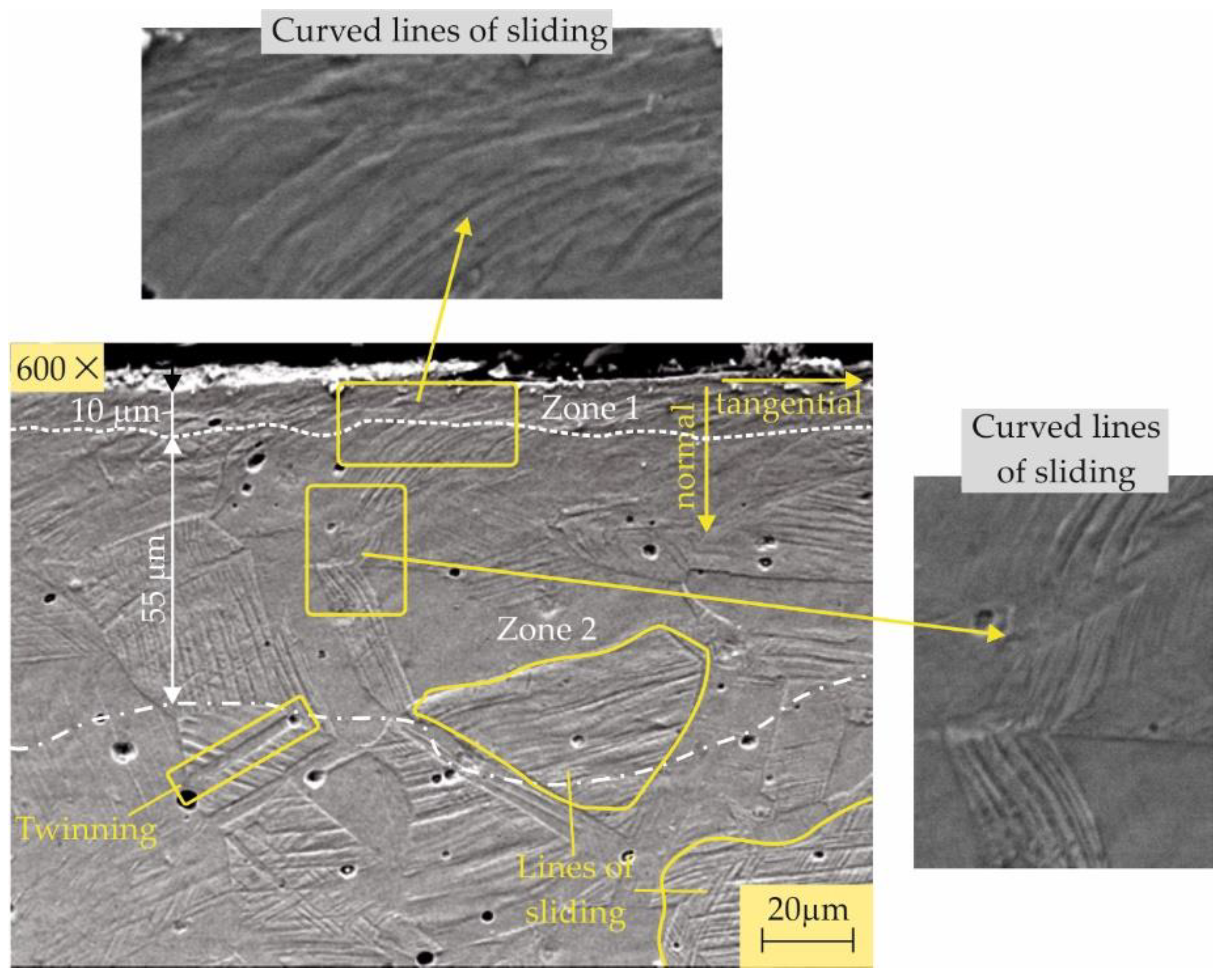
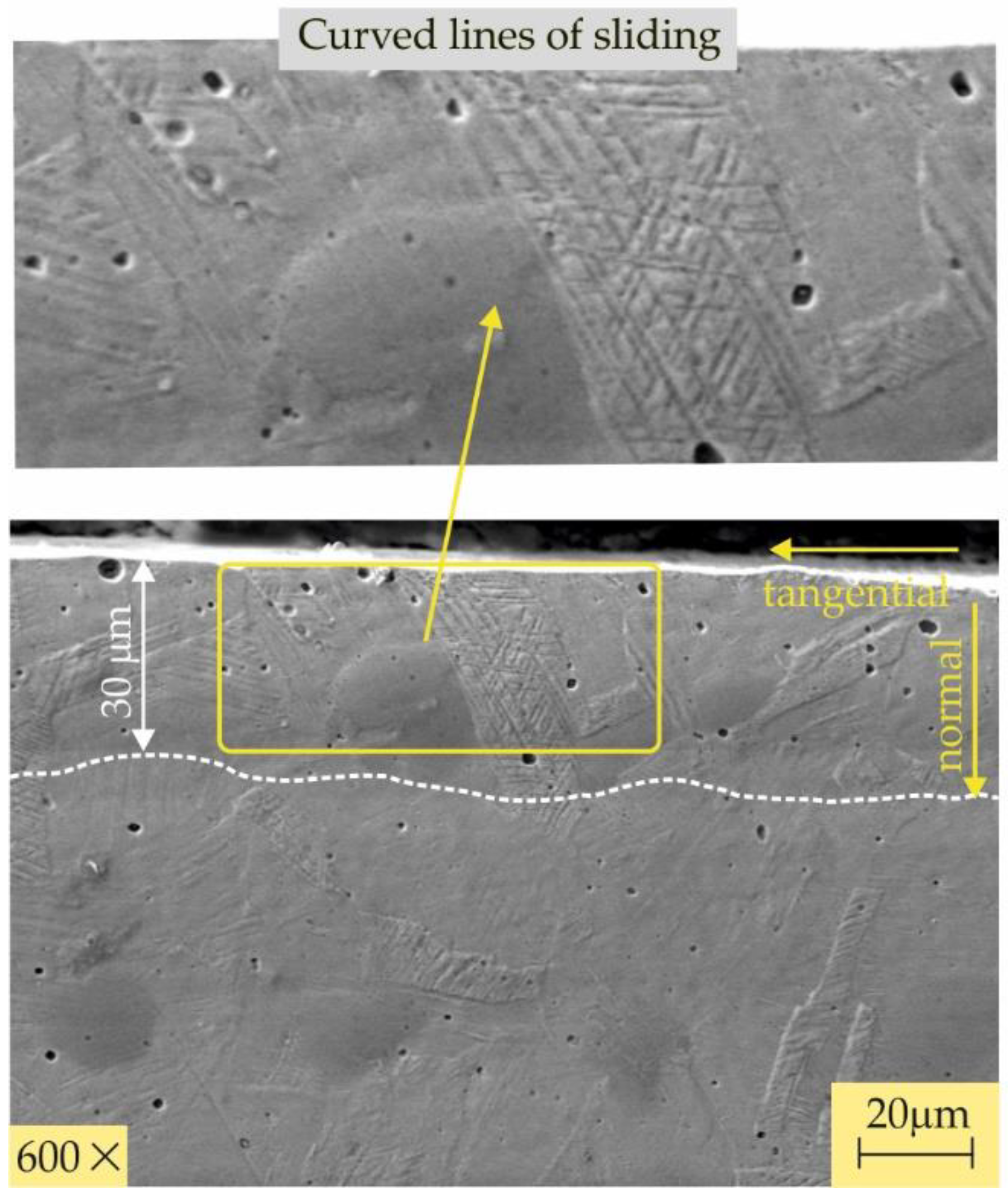
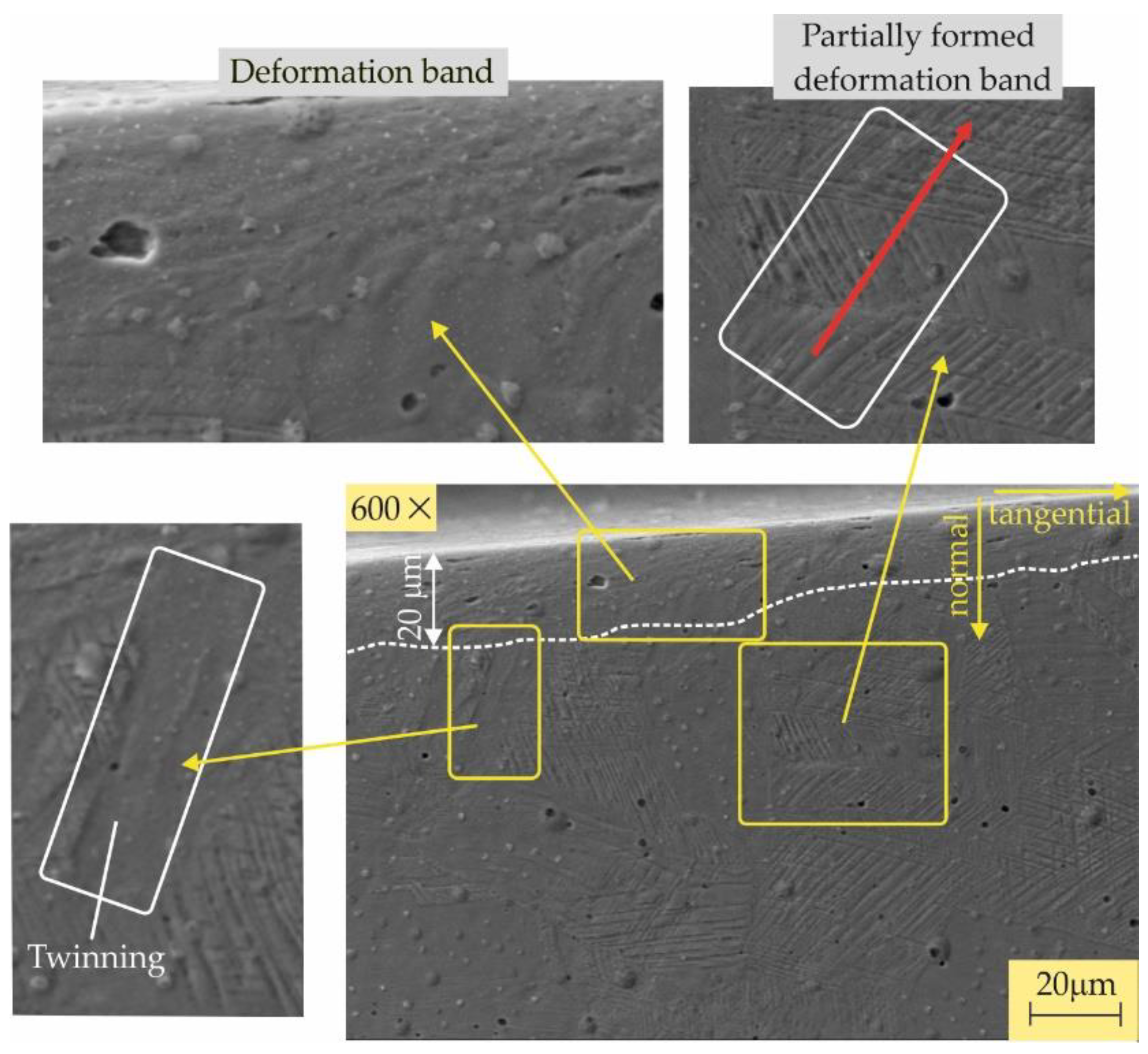
3.2.4. Microstructures
3.3. Fatigue Behavior
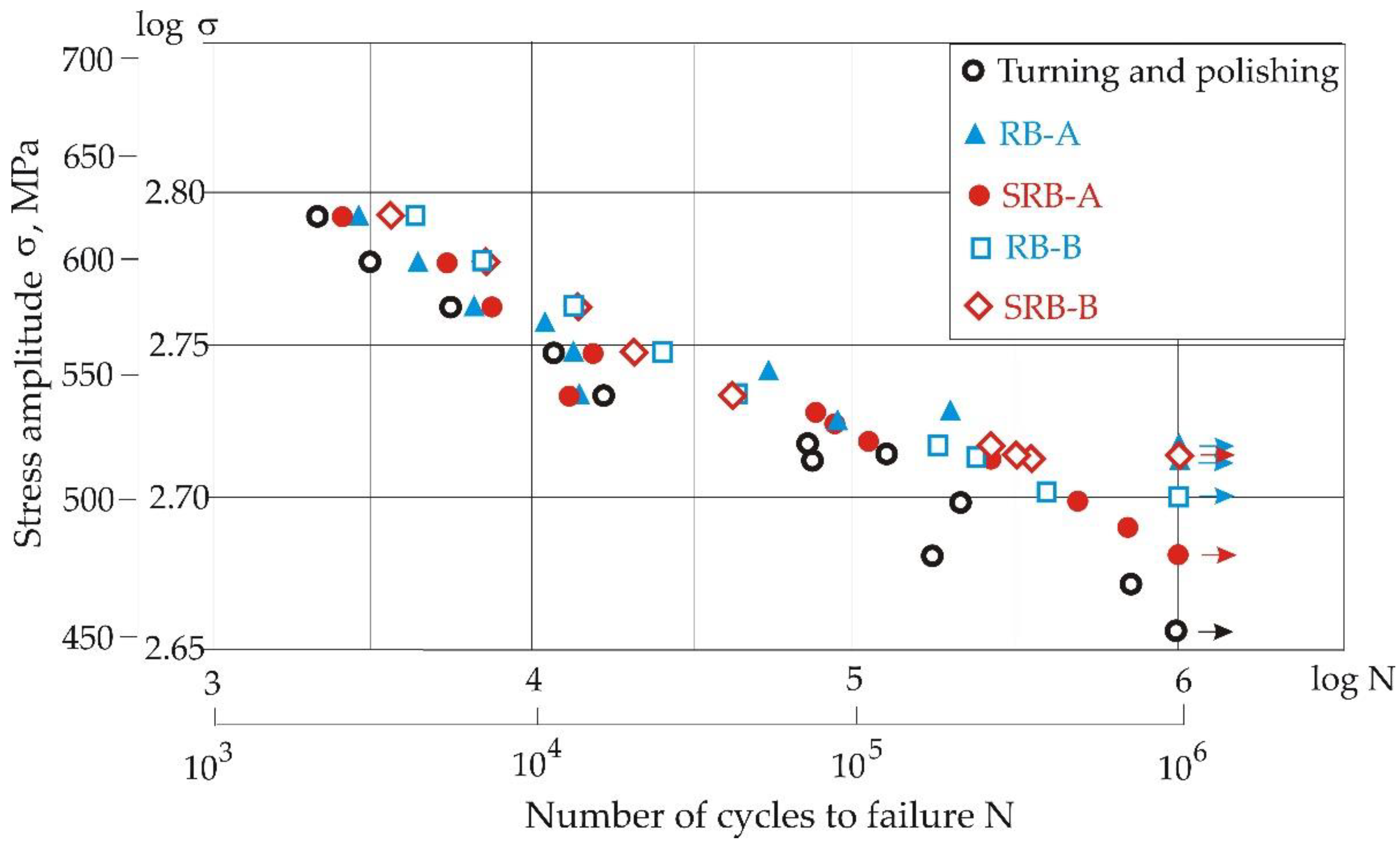
3.3.1. S-N Curves
- When the stress amplitude is above 520 MPa, the RB-А and SRB-А processes show practically the same efficiency regarding improvement in fatigue behavior compared to RC. As the stress amplitude decreases below 520 MPa, the performance of RB-A significantly increases. At smaller stress amplitudes, the residual stress relaxation is less. Thus, the larger surface compressive residual stresses and surface microhardness due to the RB-A process explain the higher fatigue strength.
- The situation is similar for the RB-B and SRB-B processes, but when the stress amplitude is below 540 MPa, the efficiency of SRB-B is markedly higher than that of RB-B.
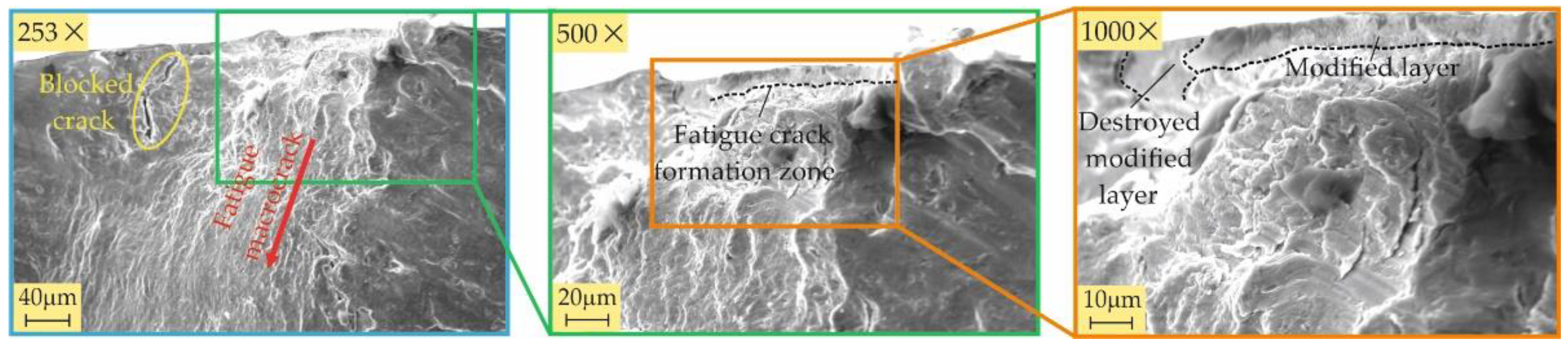
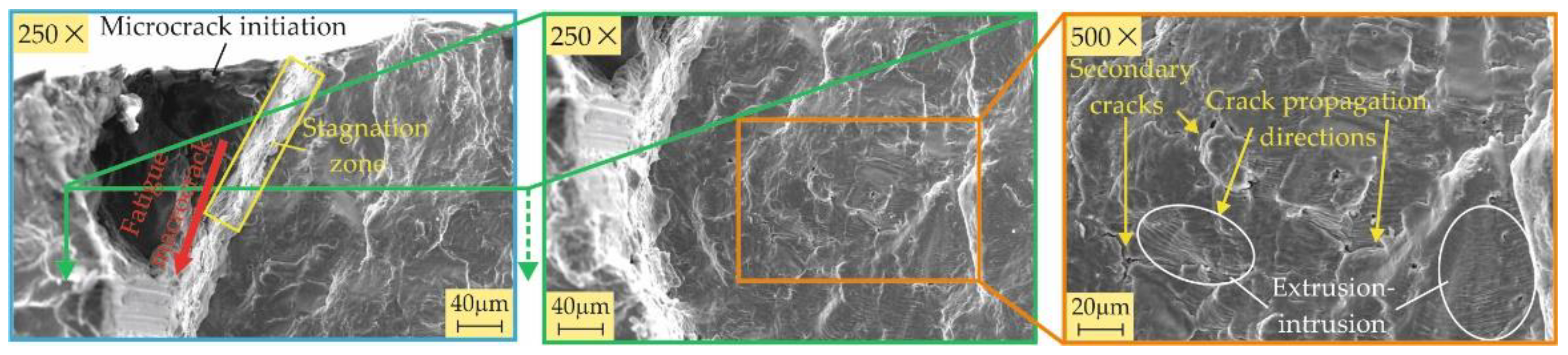
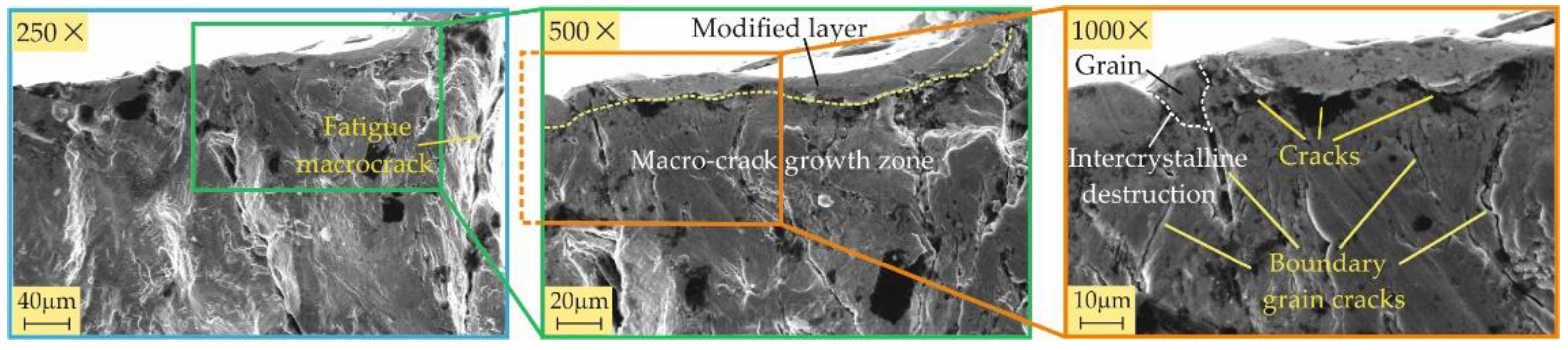
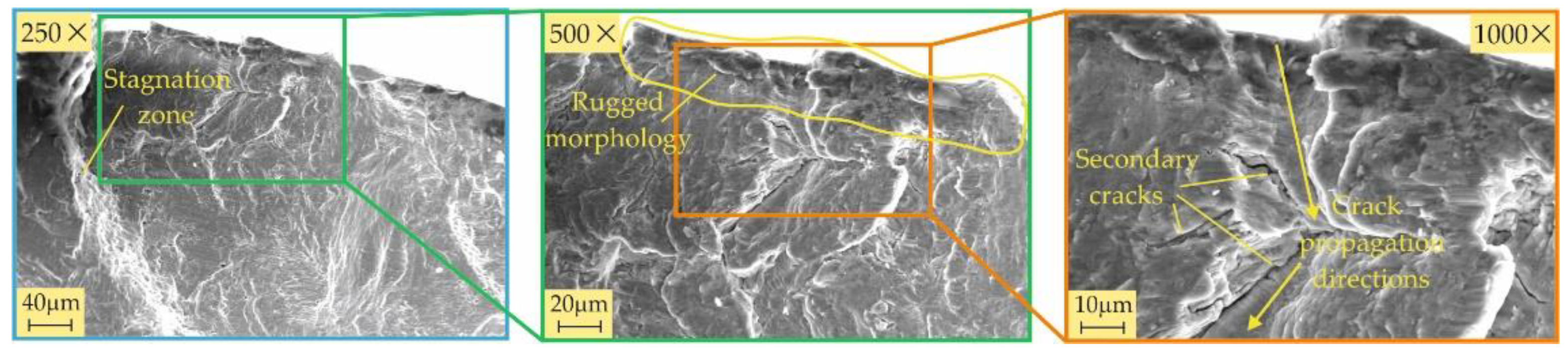
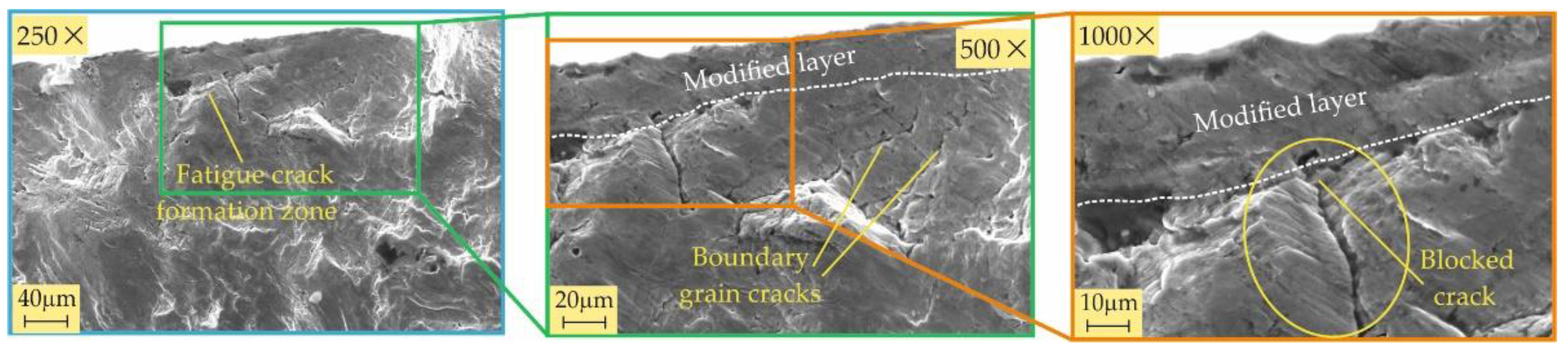
3.3.2. Fractography
4. Conclusions
- Compared to RB, both SRB processes lead to the following: 1) significantly lower amplitude and functional roughness parameters (mirror-finish surfaces); 2) lower surface microhardness but higher subsurface microhardness; and 3) a deeper zone of residual compressive stresses. These SI characteristics are a direct consequence of the larger contact area and relative sliding velocity in the SRB, owing to the crossing axes of the deforming roller and the workpiece.
- We found that the surface microhardness is affected to a greater extent by the feed rate than by the burnishing force, because of the so-called overlapping effect,which causes cyclic hardening. Conversely, the microhardness beneath the surface is more sensitive to the burnishing force than the feed rate because of the depth-attenuating overlapping effect.
- All four burnishing processes create a modified surface layer with thicknesses of about 10 μm from the RB-A, SRB-A, and RB-B processes and over 20 μm from the SRB-B process. This layer has the greatest crack resistance when created using SRB-B. The main fatigue macrocrack is formed at the interface between the modified layer and the remaining material for all specimens except the one treated by SRB-A. The reason is that SRB-A creates a surface with a large negative skewness (leading to micro-stress concentrators), which, in combination with smaller compressive residual stresses, is a prerequisite for the formation of a fatigue macro-crack from the surface.
- The technological possibilities of the SRB method for achieving desired SI characteristics according to the functional purpose of the burnished component have been experimentally shown achieving a mirror-finish surface (Ra=0.055 μm) but a fatigue strength lower than that of the conventional RB-A process. The SRB-B process achieves low height and functional roughness parameters (Ra=0.073 μm) and the greatest fatigue strength compared to other burnishing processes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RB | Roller burnishing |
| RB-A | Roller burnishing process A |
| RB-B | Roller burnishing process B |
| RC | Reference condition |
| SB | Slide burnishing |
| SCW | Surface cold working |
| SE | Surface engineering |
| SI | Surface integrity |
| SL | Surface layers |
| SRB | Slide roller burnishing |
| SRB-A | Slide roller burnishing process A |
| SRB-B | Slide roller burnishing process B |
References
- Miranda, R.M.; Gandra, J.P.; Vilaca, P.; Quintino, L.; Santos, T.G. Surface modification by solid state processing. Elsevier (Woodhead Publishing Limited) 2014 ISBN 978-0-85709-469-8.
- Dwivedi, D.K. Surface Engineering. In Enhancing Life of Tribological Components; Korzynski, M., Ed.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2018; ISBN 978-81-322-3779-2. [Google Scholar]
- Butz, G.A.; Lyst, J.O. Improvement in Fatigue Resistance of Aluminum Alloys by Surface Cold-Working. Materials Research & Standards.
- Semenchenko, I.V.; Grinchenko, I.G. Fatigue of the surface cold worked AK-4 alloy at elevated temperatures. Metal Science and Heat Treatment 1970, 12, 959–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saud, H.M.; Abdulrazzaq, M.A. Study the effect of cold working on the mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 2024 T4. IOP Conf. Ser.: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 928, 022125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, J.T.; Duncheva, G.V.; Anchev, A.P. , Ichkova, M. D. Slide burnishing—review and prospects. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 2019, 104, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.P. , Tarasov, S.Y.; Dmitriev, A.I. Nanostructuring burnishing and subsurface shear instability. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 217, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, M. Modeling and experimental validation of force – surface roughness relation for smoothing burnishing with a spherical tool. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2007, 47, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobola, D.; Kania, B. Phase composition and stress state in the surface layers of burnished and gas nitrided Sverker 21 and Vanadis 6 tool steels. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 353, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoczylas, A.; Zaleski, K.; Matuszak, J.; Ciecielag, K.; Zaleski, R.; Gorgol, M. Influence of Slide Burnishing Parameters on the Surface Layer Properties of Stainless Steel and Mean Positron Lifetime. Materials 2022, 15, 8131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Nishinaka, K.; Yanagi, K. Development of hydraulic burnishing tool for discontinuous surface finishing – machining characteristics of hydrostatic burnishing tool with single crystal diamond tip. J. Jpn Soc. Technol. Plast. 2012, 53, 924–928. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Nestler, A.; Schubert, A. Effect of machining parameters on surface properties in slide diamond burnishing of aluminium matrix composites. Materials Today: Proceedings 2015, 2S, S156–S161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsov, V.; Makarov, A.; Skorobogatov, A.; Skorinina, P.; Luchko, S.; Sirosh, V.; Chekan, N. Influence of normal force on smoothing and hardening of the surface layer of steel 03X16N15M3T1 during dry diamond smoothing with a spherical indenter. Met. Process. 2022, 24, 6–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dzierwa, A.; Gałda, L.; Tupaj, M.; Dudek, K. Investigation of wear resistance of selected materials after slide burnishing process. Eksploat. Niezawodn. 2020, 22, 432–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.-L.; Shen, X.-H.; Xu, G.-F.; Xu, C.-H.; Wang, B.-L.; Su, G.-S. Surface integrity enhancement of austenitic stainless steel treated by ultrasonic burnishing with two burnishing tips. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2020, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluz, R.; Antosz, K.; Trzepiecinski, T.; Bucior, M. Modelling the influence of slide burnishing parameters on the surface roughness of shafts made of 42CrMo4 heat-treatable steel. Materials 2021, 14, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, H.; Hirokawa, W.; Todaka, Y.; Yasunaga, K. Improvement in surface roughness and hardness for carbon steel by slide burnishing process. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovskij, I.; Bobrovskij, N.; Khaimovich, A.; Travieso-Rodriguez, J.A. Impacts of surface texture and nature of friction on energy-force efficiency of surface plastic deformation during burnishing. Metals, 2022, 12, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dy, T.; Wijata, M.; Kusmierska-Matyszczak, W. The slide broaching burnishing and the influence of deformation on roughness of 314L stainless steel sleeves. Sci. J. Gdyn. Marit. Univ. 2020, 116, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Cagan, S.C.; Tasci, U.; Pruncu, C.I.; Bostan, B. Investigation of the effects of eco-friendly MQL system to improve the mechanical performance of WE43 magnesium alloys by the burnishing process. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2022, 45, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, J.T.; Duncheva, G.V. The Correlation between Surface Integrity and Operating Behaviour of Slide Burnished Components—A Review and Prospects. Appl. Sci., 2023, 13, 3313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximov, J.T.; Duncheva, G.V.; Anchev, A.P.; Dunchev, V.P. , Anastasov, K.; Daskalova, P.H. Effect of Roller Burnishing and Slide Roller Burnishing on Surface Integrity of AISI 316 Steel: Theoretical and Experimental Comparative Analysis. Machines, 2024, 12, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juijerm, P.; Altenberger, I. Fatigue performance enhancement of steels using mechanical surface treatments. J. Met., Mater. Miner. 2007, 17, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Moussa, N.B.; Gharbi, K.; Chaieb. I.; Fredj, N.B. Improvement of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel low-cycle fatigue life by initial and intermitten deep rolling. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2019, 101, 435–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedlacek, M.; Podgornik, B.; Vizintin, J. Correlation between standard roughness parameters skewness and kurtosis and tribological behaviour of contact surface. Tribol. Int. 2012, 48, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korzynski, M.; Dudek, K.; Kruczek, B.; Kocurek, P. Equilibrium surface texture of valve stems and burnishingmethod to obtain it. Tribol. Int. 2018, 124, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.; Blunt, L.; Tato, W.; Aginagalde, A.; Gomez, X.; Llavori, I. The use of areal surface topography characterisation in relation to fatigue performance. MATEC Web of Conferences, 2018, 165, 14013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 6892-1:2019 Metallic materials. Tensile testing Part1: Method of test at room temperature.
- Ecoroll Catalogue. Tools and Solutions for Metal Surface Improvement; Ecoroll Corporation Tool Technology: Milford, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- DIFFRAC. DQUANT, Quantitative Analysis from Calibration to Reporting; Bruker AXS GmbH: Karlsrue, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bulgarian National Standard 5297:1983 Metals. Fatigue test methods (in Bulgarian).
- Pawlus, P.; Reizer, R.; Wieczorowski, M. Functional Importance of Surface TextureParameters. Materials 2021, 14, 5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pei, Z.J. Characterization Methods for Surface Integrity (Ed., J. Paulo), Surface Integrity in Mashining, 2010, Springer – Verlag London Limited e-ISBN 978-1-84-882-974-2.
- Maximov, J.T.; Duncheva, G.V.; Anchev, A.P.; Ganev, N.; Dunchev, V.P. Effect of cyclic hardening on fatigue performance of slide burnishing components made of low-alloy medium carbon steel. Fatigue Fract Eng Mater Struct, 2019, 42, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
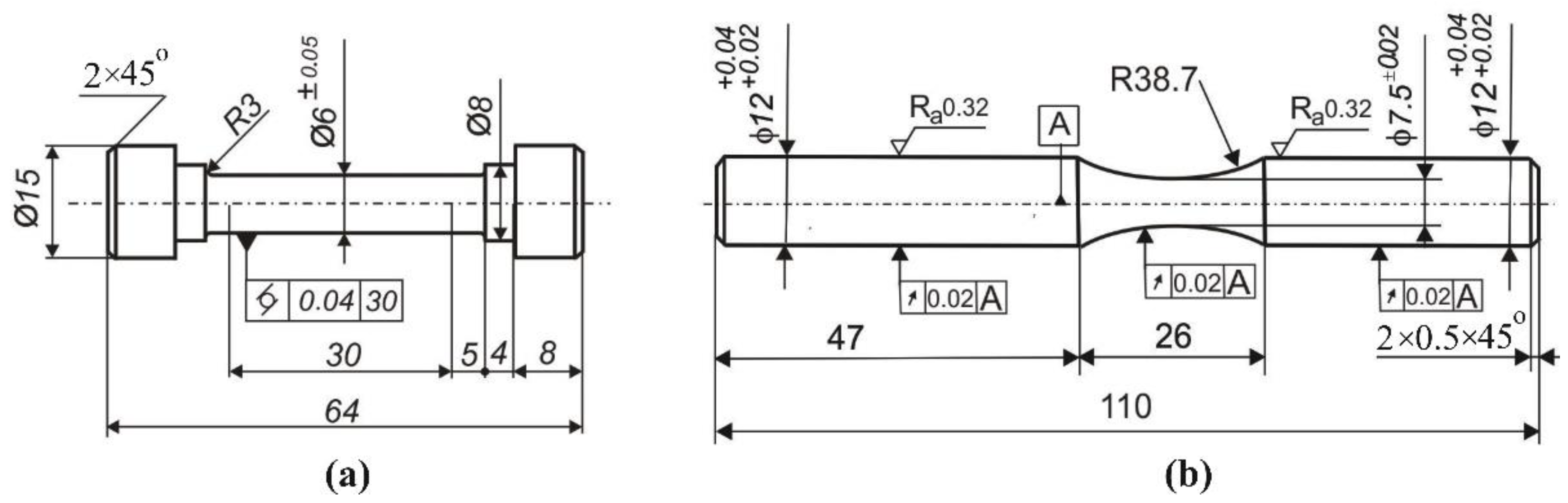
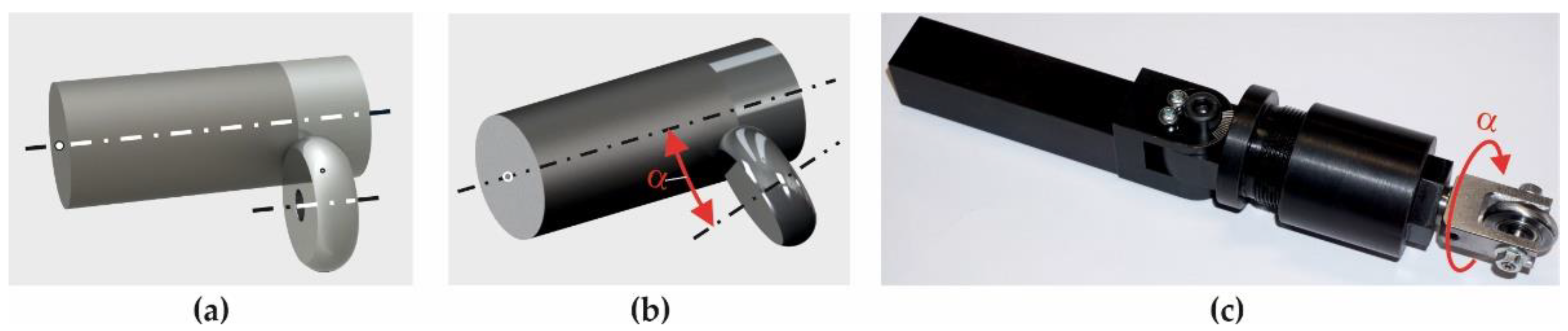

| Burnishing processes | r, mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RB-A, SRB-A | 3 | 250 | 0.05 | 60 |
| RB-B, SRB-B | 4 | 550 | 0.11 | 60 |
| Measuring device | Bruker D8 Advance diffractometer |
| X-ray tube | Long focus Cr – Kα |
| Crystallographic plane | Fe(γ) - (220) |
| Diffraction angle (2θ) | 128.78° (124° - 133°) |
| Measuring method | Offset coupled TwoTheta/Theta (sin2ψ method) |
| Scan mode | Continuous PSD fast |
| X-ray detector | SSD160-2 (1D scanning) |
| Collimator spot size | Standard Φ1.0 mm |
| Measurement time for single scan | Approx. 35 s |
| Elastic constant s1 | |
| Elastic constant 1/2s2 | |
| Voltage | 30 kV |
| Current | 40 mA |
| Step size | 0.5° |
| Time for step | 1 s |
| Fe | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Nb | Ti | Mo | Cu | Co | W | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68.7 | 0.0383 | 0.108 | 1.72 | 0.0299 | 0.0315 | 20.7 | 7.63 | 0.0356 | 0.0049 | 0.318 | 0.38 | 0.096 | 0.09 | 0.09 |
| Yield limit, MPa | Tensile strength, MPa | Elongation, % | Hardness, HB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processes | 2D roughness parameters | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Turning | 0.482 | 0.576 | 1.224 | 1.402 | -0.046 | 2.195 | 1.746 | 0.276 | 0.408 |
| RB-A | 0.186 | 0.237 | 0.470 | 0.885 | -0.791 | 3.703 | 0.545 | 0.142 | 0.378 |
| SRB-A | 0.073 | 0.098 | 0.229 | 0.526 | -1.072 | 7.117 | 0.219 | 0.093 | 0.166 |
| RB-B | 0.105 | 0.131 | 0.305 | 0.456 | -0.317 | 3.067 | 0.329 | 0.099 | 0.160 |
| SRB-B | 0.055 | 0.076 | 0.215 | 0.388 | -0.675 | 6.584 | 0.167 | 0.074 | 0.133 |
| Turning | RB-A | SRB-A | RB-B | SRB-B | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Depth mm |
Error, MPa | Depth mm |
Error, MPa | Depth mm |
Error, MPa | Depth mm |
Error, MPa | Depth mm |
Error, MPa | |||||
| Axial | Hoop | Axial | Hoop | Axial | Hoop | Axial | Hoop | Axial | Hoop | |||||
| 0 | 50 | 59 | 0 | 126 | 38 | 0 | 84.7 | 62.1 | 0 | 47.7 | 41.5 | 0 | 50.3 | 25.7 |
| 0.03 | 28.8 | 34.3 | 0.02 | 48 | 55.6 | 0.02 | 18.9 | 35.5 | 0.01 | 52.8 | 20.0 | 0.01 | 58.8 | 31.7 |
| 0.08 | 34.7 | 33.5 | 0.06 | 57.1 | 33.8 | 0.05 | 41.9 | 33.8 | 0.04 | 51.4 | 75.7 | 0.05 | 54.8 | 46.5 |
| 0.17 | 32.3 | 35.6 | 0.11 | 32.9 | 28.8 | 0.09 | 23.8 | 39.5 | 0.10 | 63.6 | 42.1 | 0.11 | 25.8 | 66.7 |
| 0.24 | 66.4 | 35.9 | 0.15 | 31.9 | 31.5 | 0.15 | 23.3 | 29.7 | 0.16 | 27.4 | 47.9 | 0.21 | 31.1 | 49.1 |
| 0.3 | 38.4 | 31.9 | 0.24 | 41 | 33.2 | 0.19 | 13.7 | 45.3 | 0.24 | 37.0 | 30.5 | 0.26 | 72.7 | 21.2 |
| - | - | - | 0.32 | 41.9 | 32.3 | 0.26 | 52.8 | 31.4 | 0.32 | 27.2 | 23.9 | 0.31 | 70.4 | 23.6 |
| - | - | - | 0.4 | 33.3 | 22.9 | 0.39 | 31.8 | 39.4 | 0.37 | 32.3 | 37.0 | 0.35 | 46.1 | 49.6 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.45 | 67.7 | 18.7 | 0.44 | 42.8 | 55.1 | 0.40 | 65.1 | 56.8 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.51 | 18.4 | 37.4 | 0.45 | 62.5 | 49.2 |
| - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.5 | 59.3 | 51.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





