1. Introduction
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) play an important role in the Indonesian economy. They account for more than 60% of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and employ about 97% of the total workforce. The growth and development of MSMEs can be influenced by various factors such as economic openness, investment, and the number of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia.
The qualitative review will involve an in-depth analysis of these factors and their impact on the economic growth of MSMEs. This study can include the trends, challenges and opportunities facing MSMEs.
The growth of MSMEs is an indicator of national economic conditions. The increase in the number of MSMEs indicates that the economy is improving, while a decline or stagnation can indicate a weakening economy.
This arrangement starts with the role of MSMEs in the economy, then discusses the factors influencing their growth, followed by the methods of studying these factors, and finally connects the growth of MSMEs to the overall economic conditions. This creates a coherent narrative that logically connects the different aspects of the concept.
The growth of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) plays a crucial role in the Indonesian economy. Understanding the number and growth rate of MSMEs is vital, not only for the Indonesian workforce but also for the overall economic development.
Assessing the Economic Growth Prospects of MSMEs At the University of Indonesia, the prospects for economic growth of MSMEs can be assessed based on several factors. These include the current condition of MSMEs, the support and resources available for their growth, and potential market opportunities. This assessment requires a forward-looking analysis, taking into account future trends and developments that may impact MSMEs.
The Role of MSME Data in Research and Policy Making For academics, MSME data is needed for both quantitative and qualitative research studies. These studies are generally used to observe and analyze trends related to economic and social issues. For the government, the use of MSME data extends even further. It is used for making strategic decisions and formulating public policies, especially those regarding economic development and empowerment at both national and regional levels.
The growth of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) is very important for the Indonesian economy. Understanding the number and growth rate of MSMEs is crucial. According to the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs of the Republic of Indonesia, MSMEs in Indonesia have increased from year to year.
Table 1.
Data on the number of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in Indonesia according to the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs:.
Table 1.
Data on the number of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in Indonesia according to the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs:.
| Year |
Number of MSMEs |
| 2021 |
64.2 million |
| 2023 |
65.4 million |
Universities such as the University of Indonesia can play an important role in supporting the growth and development of MSMEs. Educators from the University of Indonesia can provide research, innovation, and training that can help these companies grow and develop. Trainers can explore how the University of Indonesia contributes to this aspect.
The
Table 2 of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) specifically at the University of Indonesia in Depok, Jawa Barat.
| Year |
Total Number of MSMEs in Depok City |
| 2016 |
162,388 |
| 2021 |
219,238 |
The total number of MSMEs across the entire city of Depok.
The research entitled “Qualitative Overview and Prospects for Economic Growth of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia” aims to examine the important role of MSMEs in increasing economic growth in Indonesia. This research uses qualitative research methods with a literature study approach. The Indonesian workforce plays a significant role in this context.
MSMEs have become the backbone of the Indonesian economy, contributing many jobs and playing an important role in increasing the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). The research notes a number of positive impacts caused by the MSME sector in the context of economic growth. The results of this research show that the role of MSMEs in encouraging economic growth is quite significant through strengthening the quality of human resources, creating jobs, and implementing digitalization of MSMEs. Therefore, understanding the conditions and growth rate of MSMEs is very important for academics, government and policy makers. MSMEs data can be used to make strategic public policy decisions, especially regarding economic development and empowerment at the national and regional levels.
But on the other hand, there are also needs that MSME actors have noticed for increasing the role of MSMEs on a larger scale. As for the needs of MSMEs, according to research, Risnawaty, H., et all, (2023) determined that the condition of MSMEs in Indonesia and their needs are as follows:
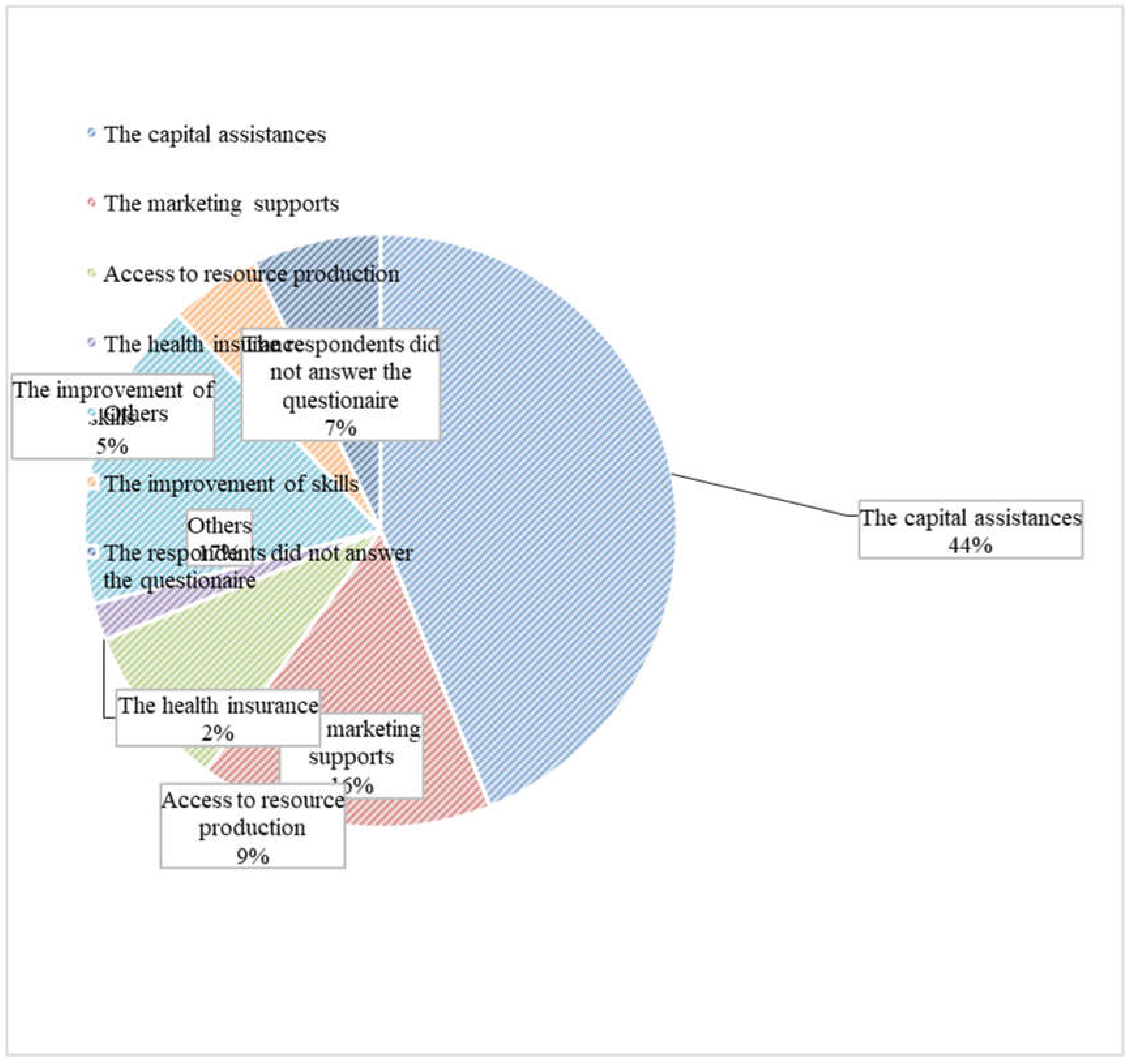
Referring to the graph below, 44 percent of MSMEs need capital assistance, 16 percent need marketing support, 9 percent need access to production resources, and 2 percent need health insurance.
Figure 1.
Challenges faced by MSMEs in West Java, Indonesia.
Figure 1.
Challenges faced by MSMEs in West Java, Indonesia.
Digitalization presents an opportunity for MSMEs to transition from traditional trade to new trends that incorporate technology. However, the readiness of MSMEs, particularly those associated with the University of Indonesia, to embrace digitalization remains a significant challenge. This highlights a gap in understanding how these MSMEs can effectively navigate digital transformation.
MSMEs commonly face the challenge of limited access to capital. It is crucial to explore strategies these enterprises, especially those within the University of Indonesia, can employ to overcome these financial obstacles. A majority of MSME owners encounter difficulties in marketing their products. The indicates is a gap in the implementation of effective marketing strategies for MSMEs at the University of Indonesia.
There is a pressing need for a more comprehensive benchmarking and gap analysis of the condition of MSMEs in Indonesia in comparison to other countries. Such an analysis could provide valuable insights for improving the conditions of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia. To address these challenges and enhance digitalization readiness, knowledge transfer activities from universities to MSMEs are essential. This underscores a gap in understanding the potential role of institutions like the University of Indonesia in actively supporting MSMEs. This gap presents opportunities for further research and exploration aimed at improving the economic growth prospects of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia. These points provide a clear direction for further research and potential solutions to improve the economic growth prospects of MSMEs associated with the University of Indonesia.
1.2. UI's Role in MSME Development
Even though the University of Indonesia (UI) is not directly involved in MSME operations, it plays an important role in supporting the development of MSMEs through research, education and collaboration. UI's academic programs, research centers and faculty expertise contribute to increasing the knowledge and skills of MSME entrepreneurs. UI can provide valuable insights, conduct studies, and provide recommendations to policy makers regarding MSME policies and strategies.
The concept of MSMEs itself is not new because small and medium businesses have existed for centuries. However, the new thing lies in MSMEs adapting to changes in the economic landscape, technological advances and market demand. Innovation in the MSME environment can take the form of: Digital Transformation: Utilizing technology for marketing, sales and operations. Sustainable Practices: Implement environmentally friendly processes and products. 1)Collaboration: Form partnerships with other businesses or research institutions. 2)Product Diversification: Offering unique products or services that stand out in the market. 3)Social Entrepreneurship: Addressing social or environmental issues while running a business.
MSMEs face challenges such as limited access to capital, lack of skilled labor, and regulatory obstacles. However, there are opportunities for MSMEs to develop: Government Support: Policies and programs that encourage the growth of MSMEs. Education and Training: Improve entrepreneurial skills. Networking: Collaborate with other businesses and institutions. Innovation Ecosystem: Access to research, technology, and mentorship.
MSMEs lies in their ability to adapt, innovate and contribute to the development of the Indonesian economy. UI's role in supporting MSMEs is very important and continuous efforts are needed to overcome challenges to seize opportunities.
The research questions are as follows;
What is the current condition of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia?
What factors influence the economic growth of SMEs at the University of Indonesia?
What are the challenges faced by UKM University of Indonesia in achieving economic growth?
What are the future economic growth prospects for University of Indonesia UKM?
How can the University of Indonesia support the economic growth of SMEs? These questions aim to understand the current situation, challenges and prospects for MSMEs at the University of Indonesia in the future.
2. Research Methods
This study is conducted at the University of Indonesia, focuses on the role of Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) within the campus environment. Ten MSME actors were selected as interview subjects to provide a comprehensive understanding of the dynamics of MSMEs.
The methodology adopted for this research is a qualitative approach, designed to answer the research questions effectively. Various methods, including in-depth interviews, case studies, participant observation, and document analysis of both primary and secondary data, were utilized.
Data collection involved identifying potential interviewees or subjects for observation. These could include MSME owners, employees, students involved in UKM (Unit of Universities activities) or other relevant parties.
The data analysis process may involve coding and categorizing responses from interviews or analyzing findings from observations. A key aspect of this research is the proposition, a statement about the relationship between concepts derived from theory. In the context of MSMEs, these theories and propositions can help researchers understand and analyze the dynamics of MSMEs, their role in the economy, and the factors that influence their success or failure.
MSME actors play a crucial role in both the theoretical and empirical research process. The theoretical process involves concepts, propositions, and theories, while the empirical process involves hypotheses and variables. Understanding these elements is critical for researchers to simplify complex realities into manageable units of analysis.
The insights gained from this understanding can then be used to inform policies and strategies to support the growth and development of MSMEs. This is particularly relevant in the context of the University of Indonesia, where the study is located, and where MSMEs play a significant role in the campus environment.
3. Discussion and Analysis
Research Questions:
1)
What is the current condition of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia?
A study of the University of Indonesia researched quality entrepreneurship - motivation, orientation entrepreneurship, and behavior risk - in deep connection with opportunity performance MSMEs finance in Indonesia. The main results show that in a normal economic environment, the more intrinsic and continuity-oriented an entrepreneur is, the more likely an MSME will reach financial growth compared to remaining stagnant.
Digitalization of MSMEs The Management Institute Faculty of Economics and Business at the University of Indonesia (LM FEB UI) held an exclusive discussion forum to get a comprehensive picture about the development of digitalization of SMEs in Indonesia. Survey results show that SMEs have started to actively use instant messaging applications and social media but are still not very familiar with e-commerce, both in buying and selling activities.
Structural Problems of MSMEs Discoveries show that MSMEs at the beginning stage face relatively simple problems. However, many have experienced failure due to inadequate financing.
- 2.
What Factors Influence the Economic Growth of MSMEs at the University of Indonesia?
MSMEs that manage working capital optimally tend to increase profitability and growth. MSMEs involved in foreign trade enjoy higher profitability. Bank loans encourage profitability and sales of SMEs to become higher, but collateral can limit growth. The involvement of the owner in the business does not affect growth but can increase profitability. The Human Capital Index, especially the education index as well as workforce, level of ethnic group interest, the value of the Indonesian Rupiah exchange rate, and inflation have no significant effect on MSME investment. Business units, personnel employment, investment, and exports of MSMEs have a positive and significant influence on economic growth in Indonesia.
- 3.
What are the Challenges Faced by UKM University of Indonesia in Achieving Economic Growth?
Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in Indonesia, including those at the University of Indonesia, are facing a number of challenges in reaching economic growth. Some of the challenges they face: (1) MSMEs often experience difficulty in getting access to financing. This can be a barrier to business growth and expansion. (2) In today’s digital era, the readiness of MSMEs to adapt and exploit digital technology is very important. However, many MSMEs are still not yet ready to undergo digital transformation. (3) Marketing Access: MSMEs also often face challenges in marketing matters. They need an effective marketing strategy to be able to compete in a growing and competitive market. (4) Innovation and Technology: MSMEs need to continuously innovate and exploit technology to increase productivity and efficiency. (5) The quality of HR is also a challenge for MSMEs. They require competent human resources possessing the required skills to operate the business. (5) Problems with legality or licensing also frequently become challenges for MSMEs. (6) Standardization and Certification: MSMEs need to fulfill standards and get relevant certification for their products or services. (7) Environmental Awareness: In a global context, MSMEs need to implement environmentally friendly processes in their operations.
All these challenges need to be addressed so that MSMEs can achieve optimal economic growth. Cooperation between the government, private sector, and educational institutions like the University of Indonesia is required to help MSMEs cope with these challenges.
- 4.
What are the Future Economic Growth Prospects for University of Indonesia MSMEs?
Prospect growth UMKM economics (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) University of Indonesia apparently is enough promising. Following a number of points that can be used consideration:
The role of MSMEs in Economy: MSMEs, in particular industry home, have role important in push Indonesian economy. Industry home create field work, build rural, add diversification activity economy , and contribute to Product Gross Domestic (GDP)
Enhancement Consumption During Ramadan: During the month of Ramadan, occurs enhancement consumption various products and services, esp related with preparation break the fast fasting and celebration Eid Fitri . This matter utilized by MSMEs for expand his business. Digitalization of MSMEs: Although Still There is challenges , such as lack of knowledge , sources power, and infrastructure, digitalization of MSMEs can become opportunities for MSMEs to develop. With so, prospects growth University of Indonesia MSME economics apparently Enough bright
How can the University of Indonesia respond to the challenges and economic growth of MSMEs? challenges and prospects for the University of Indonesia in the future.
The University of Indonesia (UI) has role active in support growth MSME economy in Indonesia. Following is a number of how to do it by UI:
Collaboration with the Ministry of Cooperatives and MSMEs: UI has collaborate with the Ministry of Cooperatives and SMEs of the Republic of Indonesia for print businessman young based higher education 1. this collaboration covers education and training, mentoring, internships and development in the field cooperatives, micro, small, medium, and entrepreneurship.
Center for Community Services and Empowerment: UI has Directorate Community Services and Empowerment that play a role in help MSME development.
Innovation and Science Techno Park Center : This center role in push the birth of innovative MSMEs national.
The Current Situation is University of Indonesia has intertwine cooperation with the Ministry of Cooperatives and MSMEs and several other universities in Indonesia for support growth and development of MSMEs. Apart from that, the UI also does it study For understand influencing factors profitability and growth of MSMEs in Indonesia .
Challenges: Several challenges faced by MSMEs in Indonesia include ability source Power human , understanding technology information , and business model transformation. Plus, it 's a challenge other is security , logistics and delivery , as well trust from side consumer .
Future Prospects : UI is hopeful cooperation this can provide benefit inclusive to the community UI academics and Indonesian society . UI also hopes to help in development of start-ups and MSMEs that innovate, so they can compete with MSME products that already exist on the market.
The study of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), also known as Usaha Mikro, Kecil, dan Menengah, (UMKM) in Indonesian, is encapsulated in the UMKM Theory. This theory underscores the significant role that MSMEs play in various aspects of the economy, including entrepreneurship, production, and the evaluation of project costs and benefits.
In Indonesia, the definition of MSMEs is typically based on net assets and annual sales. According to the Law of the Republic of Indonesia no. 20 of 2008, small businesses are defined as those with net assets between IDR 50 million and IDR 500 million, excluding land and business premises, or with annual sales between IDR 300 million and IDR 2.5 billion. On the other hand, medium-sized companies are those with a net worth of between IDR 500 million and IDR 10 billion, excluding land and business premises, or with annual sales between IDR 2.5 billion and IDR 50 billion.
Research indicates that one of the main challenges faced by MSME actors is the inability to secure external assistance and educational support from universities. This issue is a key area of focus in the ongoing study of MSMEs and their impact on economic growth and entrepreneurship.
Conducting a survey with 10 respondents from MSMEs in an Indonesian University, as a result, for each statement, 8 out of 10 respondents agreed (which is 80%), and 2 out of 10 disagreed (which is 20%).
The study shows that there have been several failures in the program from both parties, namely from the university and MSME players. Universities, particularly the University of Indonesia (UI), play a crucial role in supporting Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs). There are several reasons why universities should assist MSMEs:
Increasing MSME Capacity: Universities can enhance the managerial, marketing, and information technology capabilities of MSMEs through training, research, and consulting programs.
Encouraging Innovation: With their resources and expertise, universities can catalyze the creation of new products and services by MSMEs.
Helping Access to Capital: The role of universities is not to provide capital, but to foster the capabilities of small industries, thereby enhancing their ability to access capital.
Building Networks: MSMEs can connect with wider business networks, potential investors, and export markets through collaboration with universities.
However, achieving optimal synergy requires strong commitment and cooperation from both parties. Universities need to strengthen their engagement with MSMEs through relevant and sustainable programs. Conversely, MSMEs also need to be open to collaboration with universities, recognizing the added value these educational institutions can provide.
If MSMEs agree to receive assistance, UI can provide various forms of support, including:
Business Development Assistance Through the Internet of Things (IoT): UI has aided the development of MSMEs through the implementation of IoT, enabling MSMEs to continue to develop and compete in the digital era. This program involves UI students and lecturers in providing training and assistance to MSMEs.
Training and Education: UI can offer training and education to MSMEs, such as basic computer introductions, website and packaging material design, digital promotion techniques, and improving the quality of raw materials.
Research and Development: UI can assist MSMEs in conducting research and development of the products or services they offer, helping MSMEs improve the quality and competitiveness of their products or services.
Business Consulting: UI can provide business assistance and consultation to MSMEs, helping them overcome various challenges and obstacles faced in running their businesses.
Collaboration with Other Parties: UI can assist MSMEs in establishing collaborations with other parties, such as government and business people, helping MSMEs gain access to various resources and business opportunities.
Universities, especially UI, have a significant role in supporting the growth and development of MSMEs. However, this requires a mutual understanding and willingness to collaborate from both the universities and the MSMEs.
When it comes to the assistance provided by the University of Indonesia to Micro, Small, and Medium-sized Enterprises (MSMEs) in Indonesia, there are several obstacles that may arise, especially if the MSMEs do not agree with the assistance. These obstacles include:
Capacity of Business Actors: Business actors may find it difficult to adapt to an increasingly large business scale.
Availability of Workers: The workers recruited might not be able to meet the needs of company management.
Regulatory Knowledge: Knowledge regarding regulations, such as taxes, licensing, and export regulations, may not be well socialized.
Lack of Capital: These businesses are often individual entities whose business capital is their own, making it difficult to obtain loan capital from financial institutions due to the administrative and technical requirements requested by banks.
Access to Financing: There are obstacles in the aspect of minimal capital and difficulty in accessing financing.
Effective mentoring requires a deep understanding of these challenges and strategies to overcome them. The University of Indonesia has attempted to support MSMEs through various initiatives, such as the preparation of parameters for MSMEs to be promoted to class, complete with a mentoring and training curriculum. However, if MSMEs do not agree with the assistance, the process of assistance can become more complex and challenging.
Conclusions
The study shows that entrepreneurial qualities, including motivation, entrepreneurial orientation, and risk behavior, have a positive impact on the financial performance of MSMEs in Indonesia. In a normal economic environment, the higher an entrepreneur’s motivation and entrepreneurial orientation, the greater the likelihood that their MSME will achieve financial growth. However, nearly 90% of micro-enterprises and 66% of SMEs report worker shortages as one of their main operational difficulties. MSMEs that manage working capital optimally tend to increase profitability and growth, a strategy known as Optimal Working Capital Management.
Additionally, MSMEs involved in foreign trade usually get higher profitability. Bank loans can drive profitability and higher sales of MSMEs, but the requirement for collateral can limit growth. Interestingly, the owner’s involvement in the business does not affect growth, but it can add to profitability. Factors such as the Human Capital Index, especially the education and labor index, interest rates, the Indonesian Rupiah exchange rate, and inflation do not have a significant effect on MSME investment. Business units, labor, investment, and exports of MSMEs have a positive and significant influence on economic growth in Indonesia. Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), particularly home industries, play a significant role in driving Indonesia's economy. These industries create jobs, develop rural areas, add to the diversification of economic activities, and contribute to the Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Optimal working capital management, foreign trade, and bank loans can increase the profitability of MSMEs. Meanwhile, owner involvement can increase profitability but does not affect growth. Despite challenges such as limited access to financing, digital readiness, marketing access, innovation and technology adoption, human resource quality, legality issues, standardization and certification, and environmental awareness, MSMEs in Indonesia have the potential to achieve sustainable growth and contribute more significantly to the Indonesian economy. To overcome these challenges, MSMEs need to improve their strategies and operations. This includes enhancing their digital capabilities, adopting effective marketing strategies, continuously innovating, improving the quality of their human resources, resolving legality issues, meeting relevant standards and certifications, and implementing environmentally friendly processes. Factors such as education, labor, interest rates, exchange rates, and inflation do not have a significant effect on MSME investment. However, MSME business units, workforce, investment, and exports can drive economic growth in Indonesia. During Ramadan, there is an increase in the consumption of various products and services, especially those related to breaking the fast and Eid al-Fitr celebrations. MSMEs take advantage of this to expand their businesses. Despite, challenges such as lack of knowledge, resources, and infrastructure, the digitalization of MSMEs can provide opportunities for these businesses to grow.
The University of Indonesia (UI) has taken strategic steps to support and advance the MSME sector in Indonesia. Through collaboration with the Ministry of Cooperatives and MSMEs, UI is committed to creating young entrepreneurs who are well educated and trained. This initiative includes education, training, mentoring, and internship programs designed to develop skills in the fields of cooperatives and entrepreneurship. Apart from that, UI has also established a Directorate of Community Services and Empowerment which functions as a service center to help and empower MSMEs. The UI Innovation and Science Techno Park Center plays an important role in encouraging innovation and technology among MSMEs. With this center, UI strives to produce MSMEs that are innovative and able to compete at the national level. Overall, UI's efforts have reflected the commitment of higher education institutions to support national economic growth through the empowerment of innovative and sustainable MSMEs.
References
- Arifin, R., Ningsih, AAT, & Putri, AK (2021). The Important Role Of MSMEs In Improving The Economy. East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics and Law.
- Subagyo, Kumar, V, & Ernestivita, G. (2020). Entrepreneurial parameters and performance of MSMEs in East Java province of Indonesia. ( 23(2), 267–282. [CrossRef]
- Tambunan, T. (2020). MSMEs in times of crisis. Evidence from Indonesia. Journal of Developing Economies.
- 4. Sari, NTP, & Kusumawati, A. (2022). Literature review: The efforts to strengthen micro, small and medium-sized enterprises (MSME) in Indonesia. Asian Journal of Management, Entrepreneurship and Social Science.
- S. Saiful, Hotma Napitupulu, & Sabar Napitupulu. (2023). Empowering MSMEs in Depok City through Government Support and External Aid. ( 44 (S3), 1512–1519. [CrossRef]
- Risnawaty, H., AbdulRohman, HN, Yanto, SN, & Saiful, HIS The Role of External Assistance in Enhancing the Innovation Capacity to MSMEs in West Java, Indonesia.
- Risnawaty, H., AbdulRohman, HN, Yanto, SN, & Saiful, HIS The Role of External Assistance in Enhancing the Innovation Capacity to MSMEs in West Java, Indonesia.
- Hasanuddin, Adam, Rahman, A., Napitupulu, S., Sari, HI, & Saiful, S. (2022). Mentoring MSME as a Pivotal Role to Achieve Comprehensive Results; A Case Study in Depok. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science. [CrossRef]
- 9. Yin Jh, Song Hy, Zeng Kx (2022) Does a smart business environment promote corporate investment? a case study of Hangzhou. PLoS ONE. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).