Introduction
Sentiment analysis models have become very popular recently, especially due to the development of Transformer technologies that allow analyzing large amounts of textual information quickly and efficiently. The Hugging Face portal has published a huge variety of sentiment analysis models for a multitude of languages and subject areas. Sentiment analytics allows you to classify people's feedback by emotional tone for the industries of food service, telecom, healthcare, e-commerce, and so on. Depending on the task, the result of this categorization provides insight into the reaction of certain user groups to a certain phenomenon. But it is important to realize that there are a huge number of languages and dialects in the world, and not all of them have resources available to create and train an effective sentiment analysis model. In this paper, due to the limited training data, one of the low-resource languages - Kazakh - is considered.
The current approaches of sentiment analysis are based on the Transformer architecture. The aim of the study is to create a sentiment-analysis model for analyzing texts in Kazakh language. In this work, we aim to use fine-tuning methods on our own dataset for already existing models, thus improving their accuracy and efficiency for analyzing Kazakh language texts. The problem statement of sentiment analysis in the chosen subject area is as follows. There are reviews in the Internet in the Kazakh language. It is necessary to determine the polarity of the review (i.e. negative, positive or neutral) without human involvement. To achieve the goal of the work the following tasks were set:
Data collection and processing – since one of the main problems for low-resource languages is the lack of training data, the first step will be to systematically collect and annotate reviews in the Kazakh language from the city information service 2GIS [
1] into a single dataset called "KazIntTelCom".
Model selection and fine-tuning – it is planned to take multilingual models from the HuggingFace platform [
2] and adapt them to the specifics of the Kazakh language using the fine-tuning method.
Evaluation and comparison of the model – analysis of the results obtained and evaluation of efficiency.
Literature Review
There are many areas for which sentiment analysis methods are important. These include medicine, public services, hospitality and catering, and the movie industry. In the medical field, the most relevant research topic for sentiment analysis was the global pandemic COVID-19. People had to spend more time at home, the Internet became the main means of communication. Public attention focused on discussing current events, including restrictive measures, health status, and available services. People actively shared their opinions and feedback through social media. This created an urgent need for government agencies and businesses to understand public opinion in order to adequately respond to a rapidly changing situation. Studies [
3,
4,
5,
6,
7] analyze sentiment in tweets on COVID-19 by applying various NLP and machine learning models and techniques. The papers evaluate the effectiveness of BERTje and RobBERT models on Dutch, as well as recurrent neural networks and the Valence Aware and Sentiment Reasoner dictionary methods for classifying tweets based on emotional coloration. Results highlight the division of public sentiment regarding COVID-19 vaccination, expressed in fluctuations ranging from optimism to skepticism, and reveal geographic differences in vaccine perceptions, with the greatest optimism in the United Arab Emirates and predominant skepticism in Brazil. A particular focus of these studies is adapting and tuning models to analyze social media texts, which not only improves the accuracy of emotion classification, but also provides a deeper understanding of public opinion. These results demonstrate the importance of using advanced machine learning technologies to interpret complex social phenomena such as the COVID-19 pandemic and highlight the potential of these technologies to assess and predict changes in public sentiment in real time.
Studies [
8,
9,
10] analyze cultural aspects and sentiment in the hospitality and service industry using data from reviews on TripAdvisor and social media analysis. The study [
8] analyzed 390,236 terms from complaints from guests from 63 countries staying in 353 hotels in the UK to identify cultural differences in service perceptions between Asian and non-Asian customers. In [
9], a multimodal analysis of social media content in the hospitality industry was carried out, emphasizing the low engagement between hotel brands and users. The work of [
10] reveals the importance of Hispanic employees in the hospitality industry, emphasizing the need to address their needs to improve overall satisfaction and performance.
Studies [
11,
12,
13] analyze aspect-based sentiment analysis and government interaction with citizens through social media, using lexicons and rules to classify feedback and analyze emotions in the context of government projects and mobile applications. In [
11], an integrated lexicon and rule-based model is applied to identify explicit and implicit aspects of feedback to optimize intelligent services. [
12] uses social network analysis to assess public perception of the Statue of Unity project, and [
13] explores visualization techniques to analyze activity and reactions to tweets about government initiatives, showing how visual and emotional analysis can contribute to understanding civic participation and reactions to government actions. These studies emphasize the importance of sentiment analysis and social media interactions for improving government services and communication.
Regarding recent research on sentiment analysis for the Kazakh language, a number of studies [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18] have examined various methods for sentiment analysis of Kazakh language texts, including building a dictionary of Kazakh sentiment words and developing rules based on morphological and ontological models. Pre-trained transformer models like BERT and GPT were also investigated to compensate for the lack of specialized models and annotated datasets. Experiments showed that multilingual models pre-trained in multiple languages performed better in sentiment analysis than models specifically trained for other languages with linguistic similarities, such as Turkish. Moreover, even a small amount of fine-tuning on Kazakh samples significantly improved the models' performance, emphasizing the effectiveness of transfer learning methods for resource-limited languages.
Research Methods
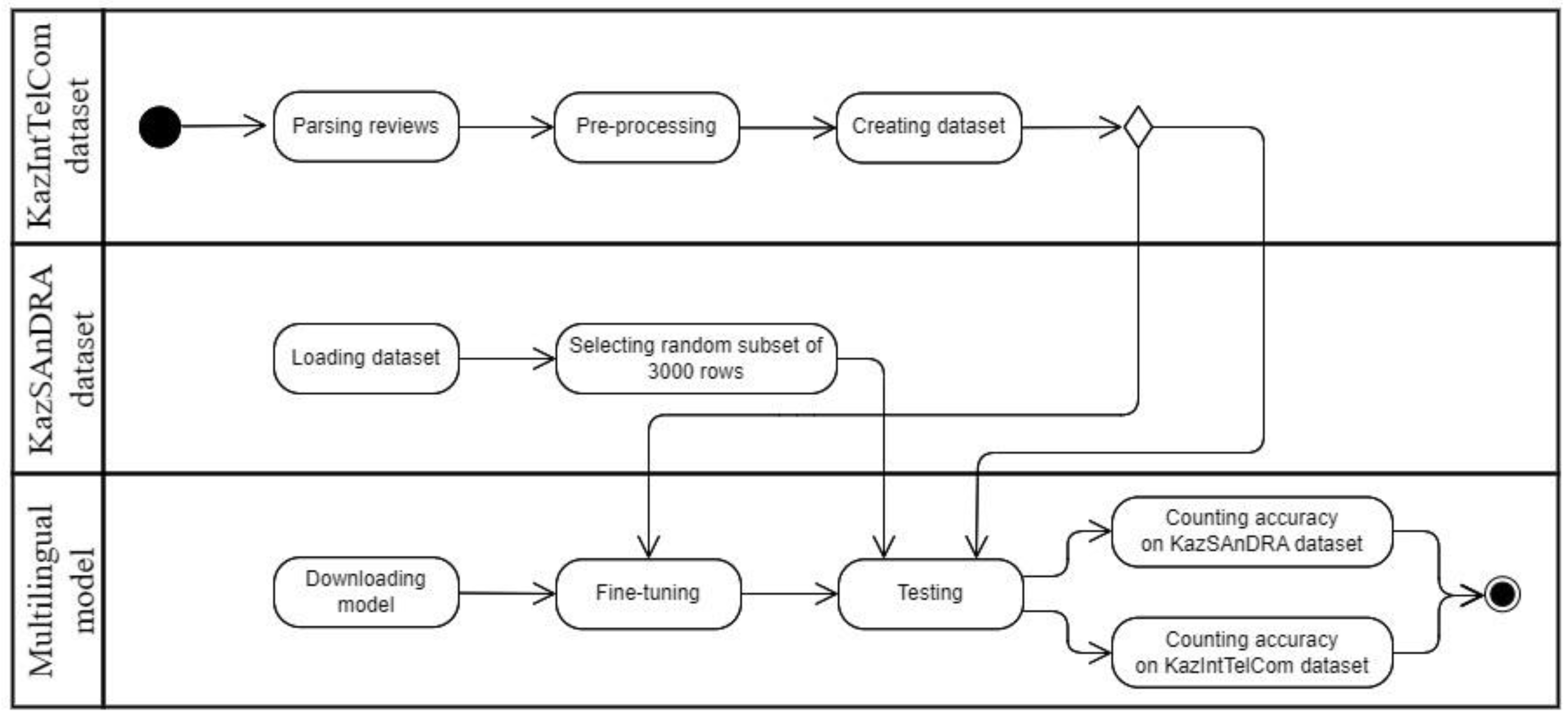
This section describes the methods used for the first and second tasks. The research scheme is shown in
Figure 1.
Data Collection and Processing
Due to the scarcity of the Kazakh language, there are very few high-quality datasets in the public domain, so we have collected the KazIntTelCom dataset consisting of reviews in the Kazakh language from the city information service 2GIS. A hand-selected dataset was focused on the topics of "Internet", "Communications", "Providers". Parsing has covered almost all large cities of Kazakhstan, this is due to the fact that the number of people writing reviews in the state language is generally low.
Figure 2 below shows a segment from the dataset.
Nevertheless, the volume of KazIntTelCom was just over 700 entries, which are lexically mixed in two forms: (a) words written entirely in Kazakh, (b) words. written in a mixture of Kazakh and Russian. After analyzing the dataset, each review was assigned a corresponding value: 1 – positive, -1 negative, 0 – neutral.
Selecting Models and Fine-Tuning
In the course of this work, two pre-trained BERT-based models were taken from the Transformers library from the HuggingFace platform. The first of these is "distilbert-base-multilingual-cased-sentiments-student", a multilingual sentiment analysis model developed by Lik Xun Yuan [
19]. From now on, we will call the first model "distilbert student". This model is trained on a multilingual-sentiments dataset compiled by Tay Yong Qiang [
20], which includes texts in 12 different languages: Arabic, Catalan, English, French, German, Hindi, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Malay, Portuguese, and Spanish. The dataset is a set of datasets of 13 different datasets, each of which covers different topics: "IndoNLU (EmoT)", "IndoNLU (SmSA)", "IndoNLU (CASA)", "IndoNLU (HoASA)", "Multilingual Amazon Reviews", "GoEmotions", "Offenseval Dravidian", "SemEval-2018 Task 1: Affect in Tweets", "Emotion", "IMDB", "Amazon Polarity", "Yelp Reviews", "Yelp Polarity". The second model is the multilingual model "twitter-XLM-roBERTa-base for Sentiment Analysis" created by Francesco Barbieri, Luis Espinosa Anke, Jose Camacho-Collados, based on XLM-roBERTa [
21]. From now on, we will call the second model "XLM roberta". Using the Twitter API, they managed to collect 198 million tweets in 65 languages published between May 18 and March 20, 2022. An important aspect of choosing the above models is their multilingualism, training on a rich dataset, and built-in zero-shot learning. These sentiment analysis models have not been trained to analyze reviews in the Kazakh language, and thanks to the zero-shot training built into their functionality, we can use them in the context of a research task.
In order for the model to more accurately determine the sentiment of reviews, it needs to be further trained, that is, fine-tuning on our dataset. We will perform Python code and debugging in the Google Colab cloud development service [
22], which provides the ability to run Jupyter notebooks in Python 3 online on Google servers. In this service, you can execute a certain piece of code in separate blocks and implement the project on CPU, GPU, and TPU capacities. Having a dataset consisting of 702 records, we take a little more than 75% – 538 records – to retrain the model using the T4 GPU. Out of 538 records, we select 10% as validation. The remaining 164 entries will be used for testing. We have defined the learning arguments as shown in
Figure 3. These hyperparameters will be used for two models.
Results
Using the accuracy function, we determined the performance of the models. The results of the pre- and post-training sentiment analysis are shown in
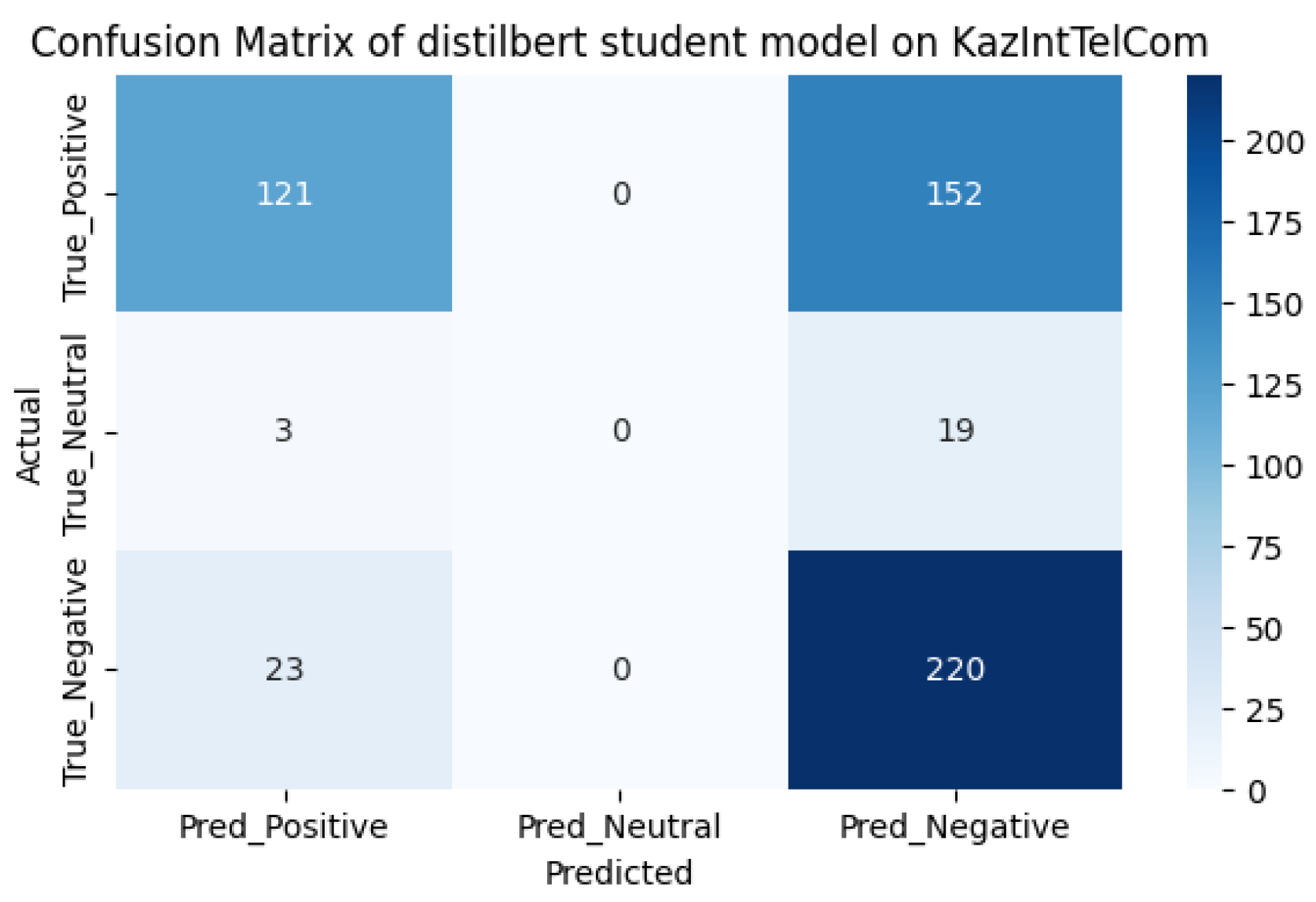
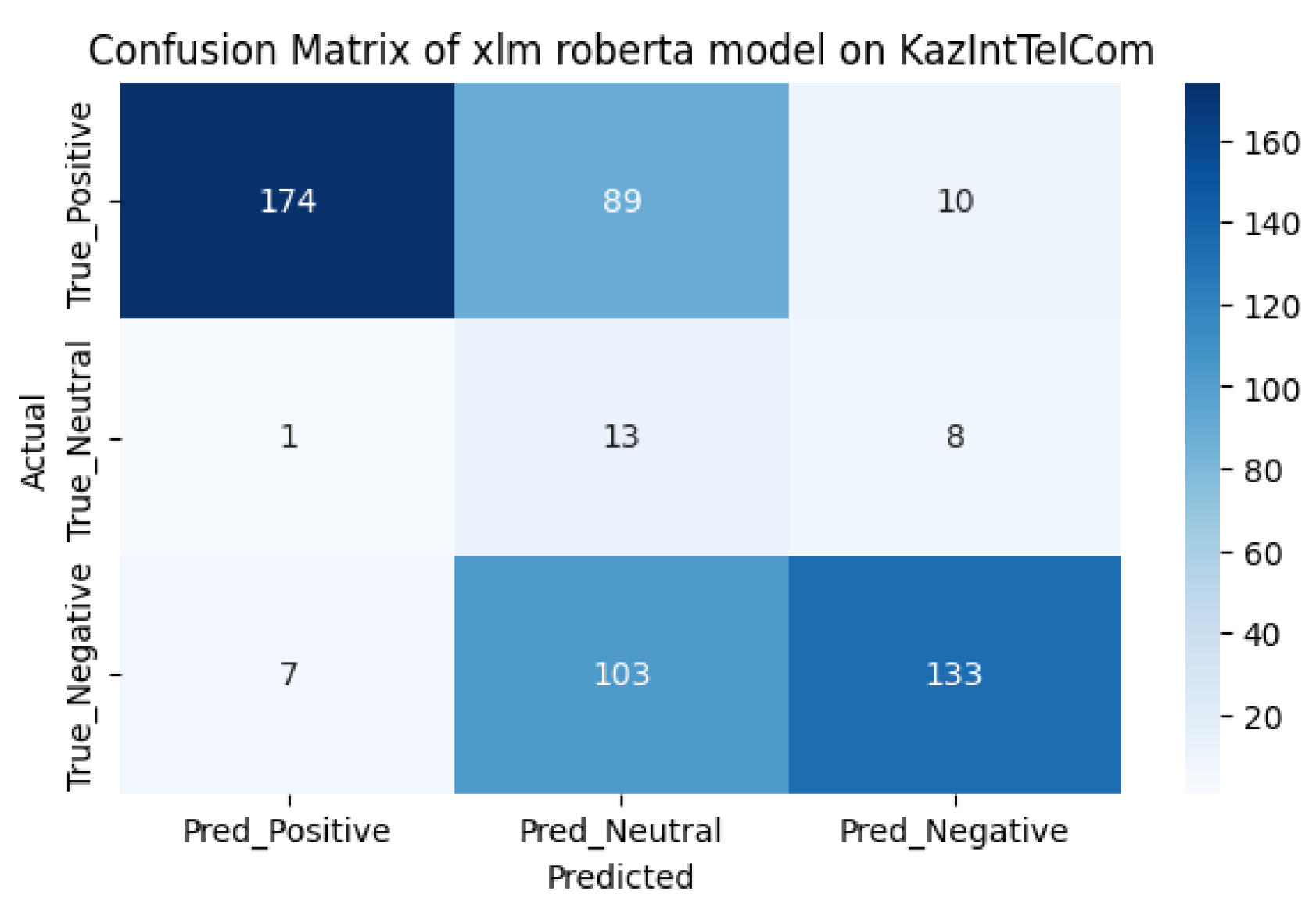
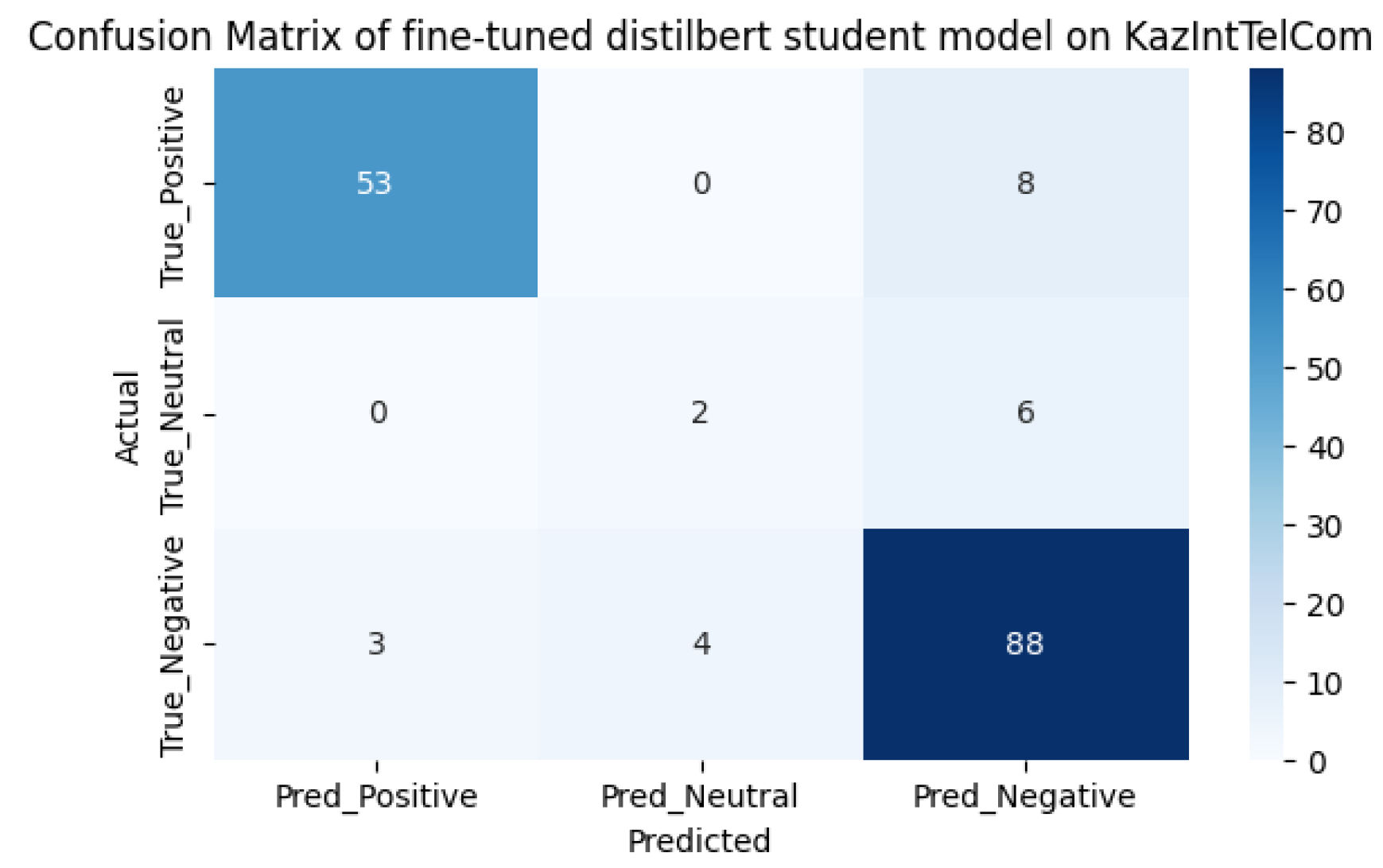
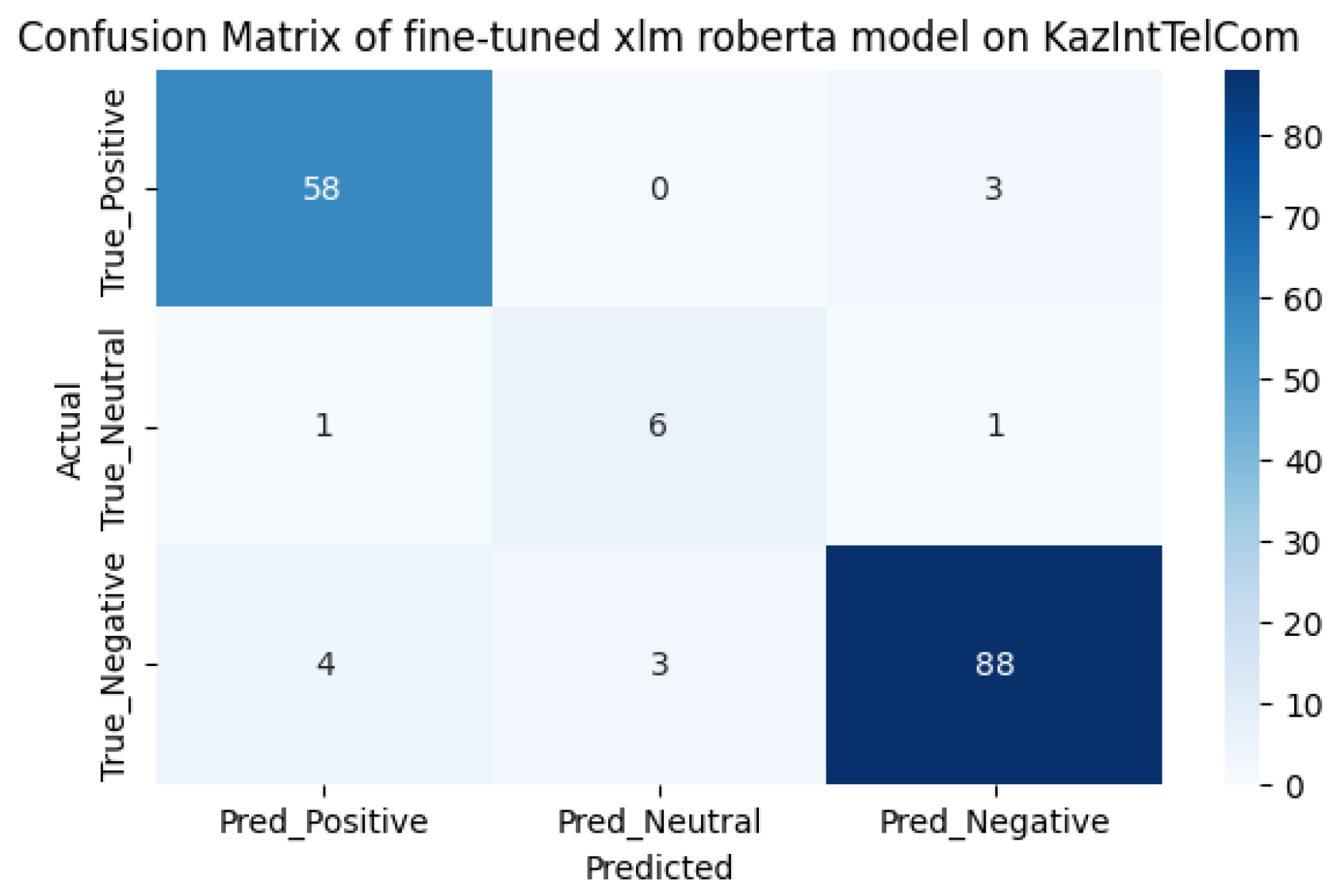
Table 1. The performance of the models has increased as expected. As can be seen from the comparison of models, the first model before additional training did better, showing an accuracy result of 63%, surpassing the second model with an accuracy of 59%. However, after additional training, the predictive power of the first model increased by 24%, showing a result of 87%, and the predictive power of the second model increased by 33%, showing a result of 92%. The inaccuracy matrices for the two models before and after fine-tuning are shown in
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6 and
Figure 7, respectively. It should be noted that the performance of the xlm roberta model after fine-tuning increases due to more accurate predictions for neutral samples.
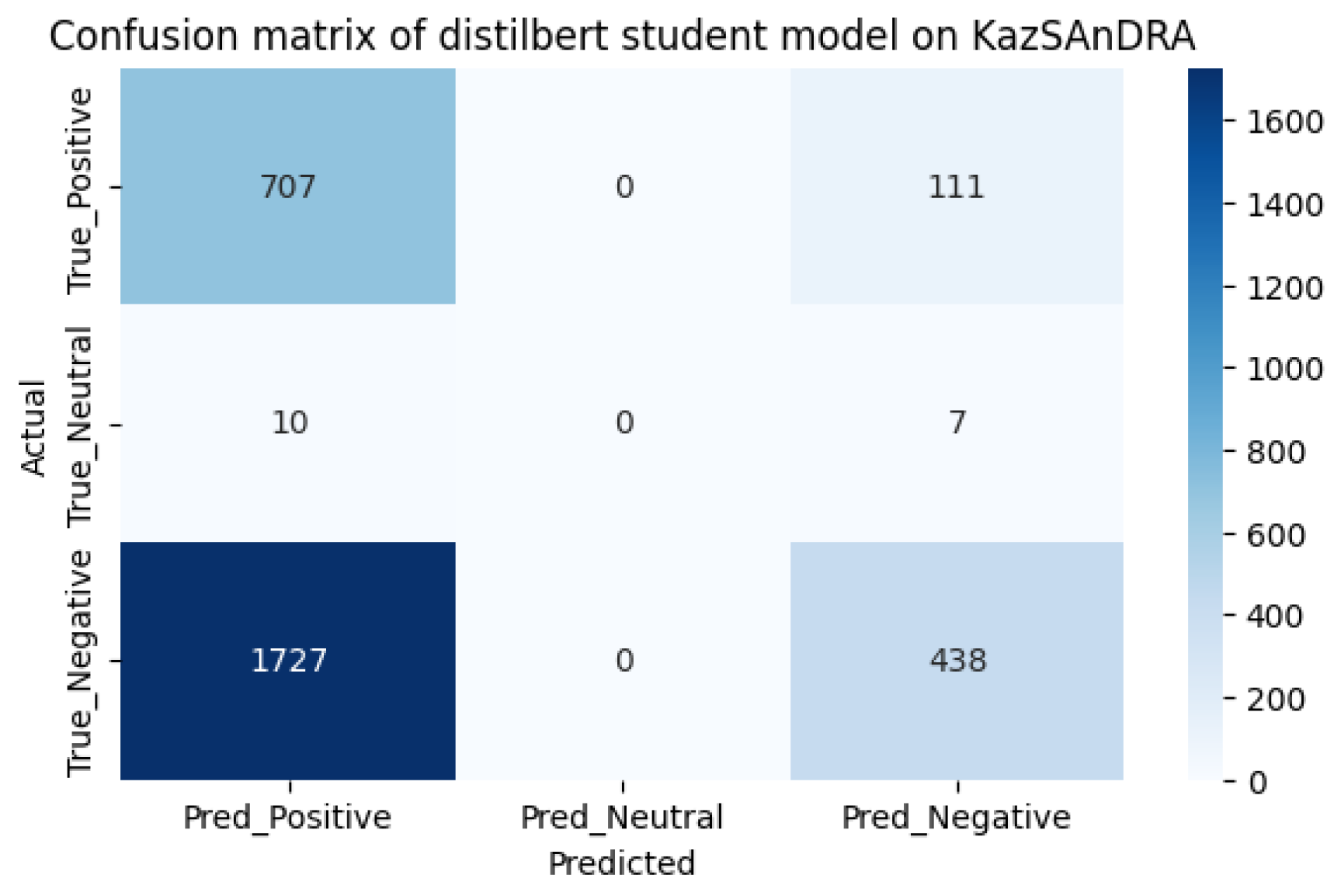
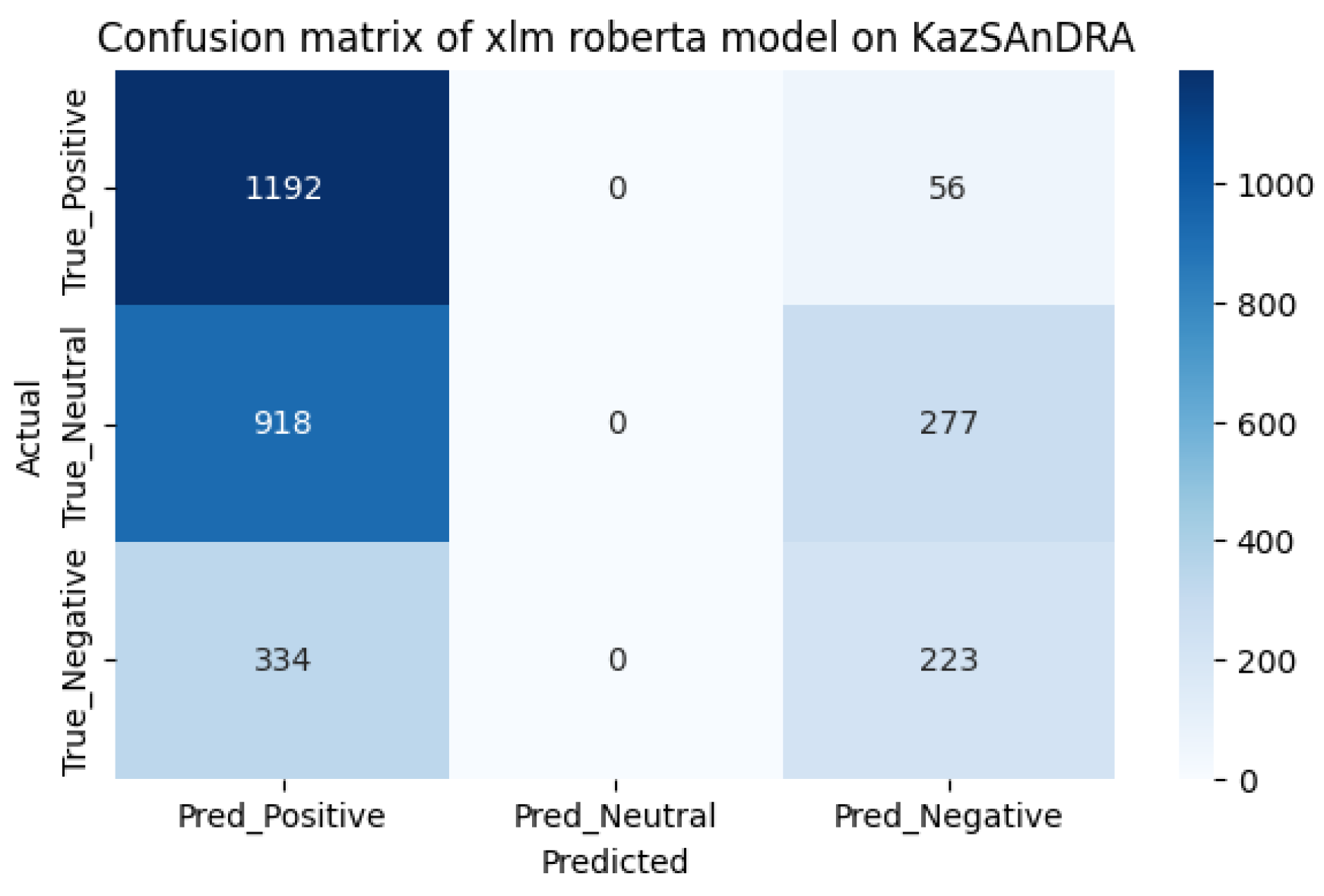
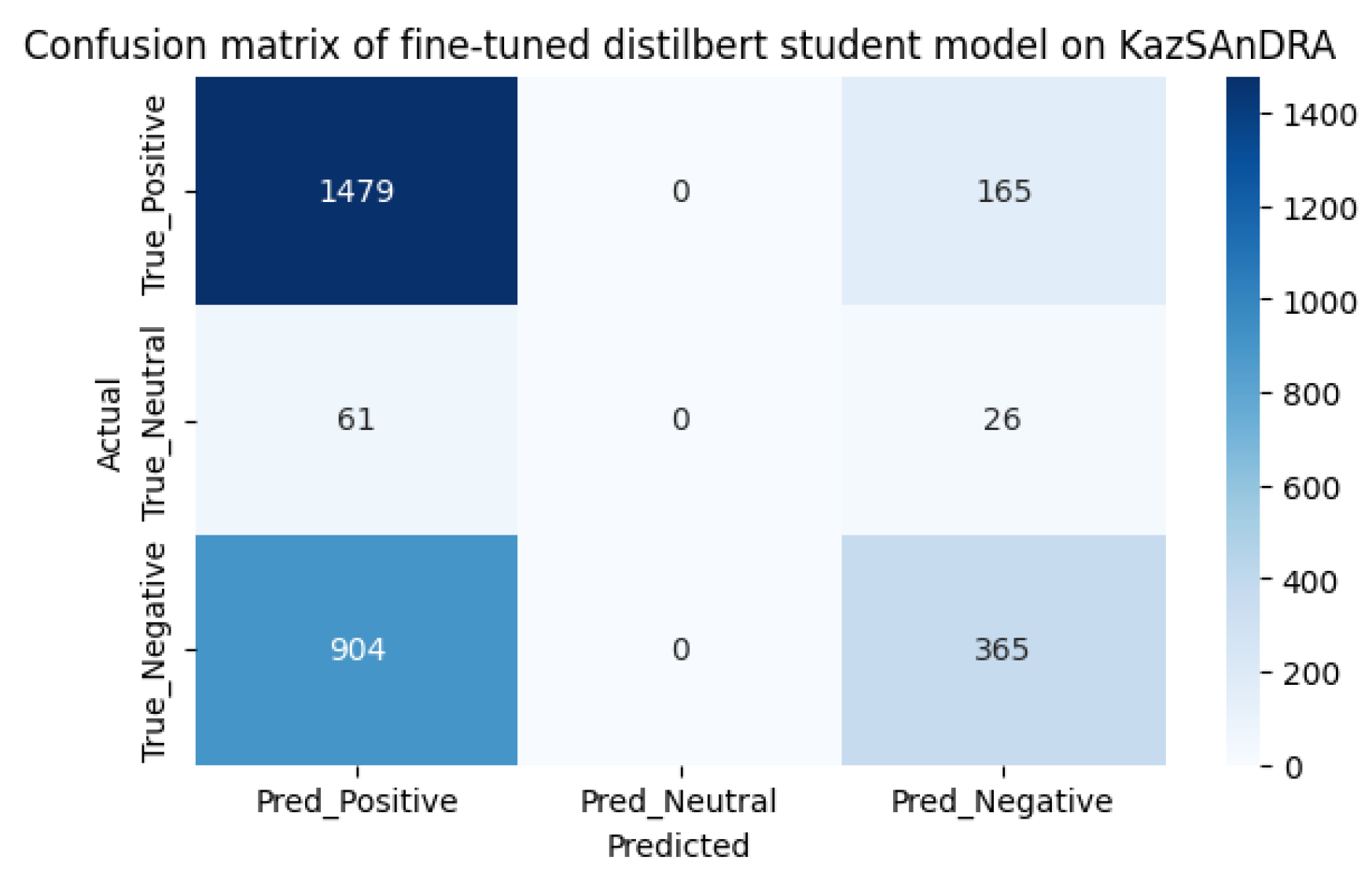
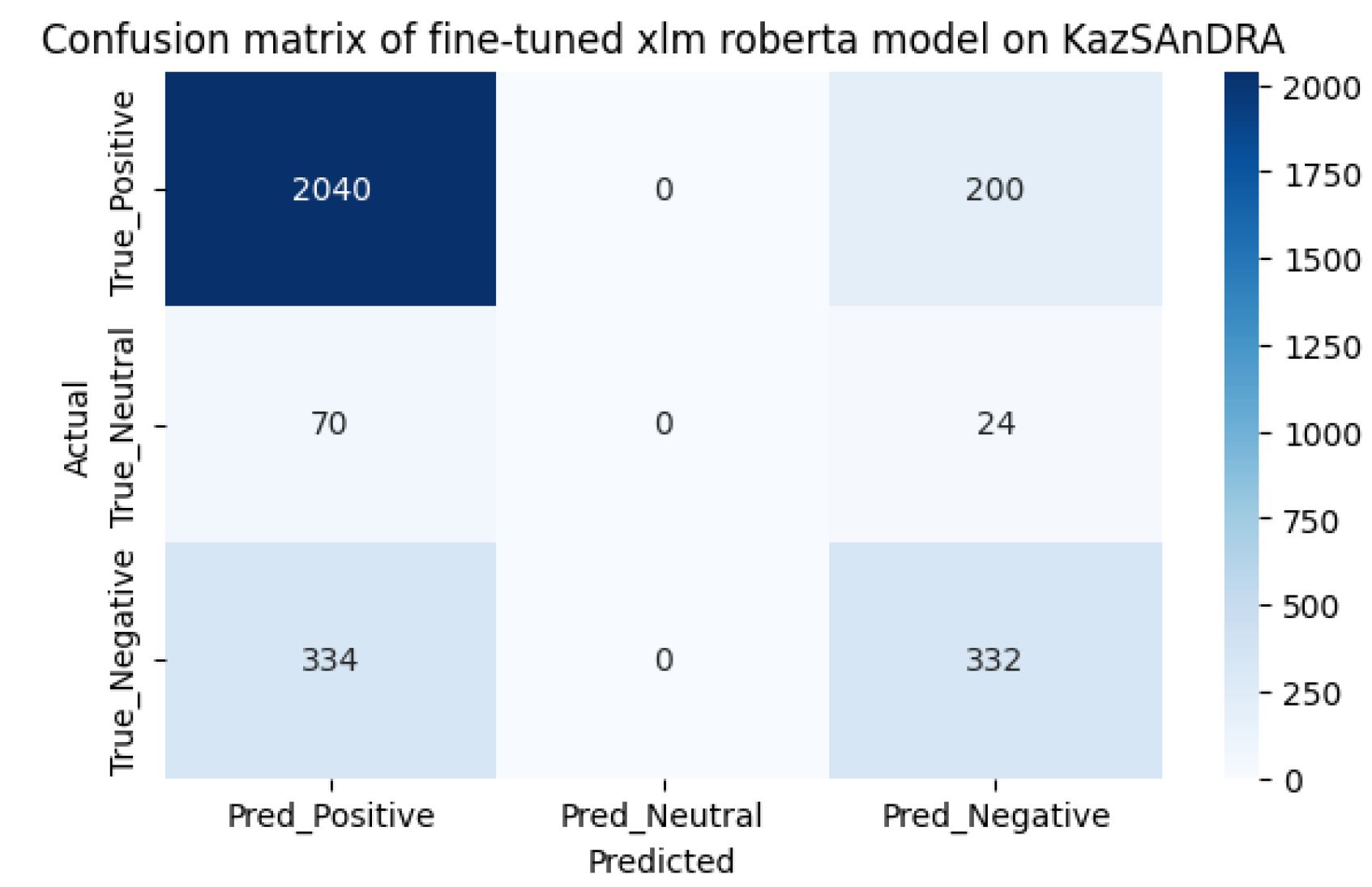
We also tested the models on the KazSAnDRA dataset provided in [
8], taking the first 3000 records and comparing the results with theirs. Testing was carried out in two stages: the first stage was preliminary testing of models, the second stage was testing models after additional training. The test results are shown in
Table 2.
The xlm roberta model turned out to be closer to the performance indicators [
8] than the first model. Confusion matrix before and after follow-up are shown in
Figure 8,
Figure 9,
Figure 10 and
Figure 11.
Discussion
As we can see from the model pre-use cofusion matrices on the KazIntTelCom dataset, the distilbert student model performs better in correctly identifying negative reviews, while the xlm roberta model performs better in identifying positive and non-truthful reviews. However, after fine-tuning models, the second model shows better results in identifying positive and non-truthful reviews, while with negative reviews both models showed almost the same results, perhaps this is due to the vocabulary of the dataset KazIntTelCom, namely case, emoji, language mix or the difference of words and letters. As for testing the models on the KazSAnDRA dataset, the inaccuracy matrices show that both models have difficulties in identifying neutral responses, which emphasizes the need to improve the processing algorithms or enrich the training dataset with examples of neutral statements. Perhaps a more balanced distribution of classes in the training samples would help avoid biasing the models towards more frequent classes. Although our pre-trained models are inferior to the pre-trained models from [
8], it is worth noting that their models are not trained to detect neutral reviews, unlike ours. It should also be noted that there is a difference in the volume of datasets. Thus, the fine-tuning method increases the efficiency of predictive power by 20-30% on average, which is not the limit if we adjust the hyperparameters of pre-training and train on a high-quality dataset.
Conclusions
This study demonstrated how multilingual machine learning models can be adapted to work with Kazakh language texts. The results before and after pre-training showed a significant improvement in the accuracy of the models, confirming the effectiveness of the fine-tuning method. The comparison of models showed that the second model, based on XLM-roBERTa, came out on top after pre-training, indicating that it is more flexible and adaptive to the dynamics of a dataset containing mixed language data. Also, the work on this study emphasized the importance of having a high-quality and high-dimensional dataset for model training and testing. The training dataset consisted of a total of 702 samples of positive, negative and neutral reviews, generated by random sampling from the 2GIS service. Also testing was conducted on the dataset KazSAnDRA in the volume of the first 3000 records from [
8] and was found an increase in predictive power by an average of 20-30% both when testing their own dataset and theirs. Even with such a small training sample, a performance gain in the predictive power of sentiment analysis was obtained. This promises the promise of this approach for future works. will be related to the improvement of training datasets. To achieve better performance and quality of models, further improvement of training datasets as well as learning and tuning of training hyperparameters is needed.
References
- Karta gorodov Kazahstana: Almaty, Astana, Shymkent i drugie goroda — 2GIS. (n.d.). https://2gis.kz/.
- Hugging Face – The AI community building the future. (n.d.). https://huggingface.co/.
- Rutte, M. (2022). Dutch sentiment analysis on Twitter (Doctoral dissertation, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam).
- Liu, S., & Liu, J. (2021). Public attitudes toward COVID-19 vaccines on English-language Twitter: A sentiment analysis. Vaccine, 39(39), 5499–5505. [CrossRef]
- Alsayat, A. (2021). Improving sentiment analysis for social media applications using an ensemble deep learning language model. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 47(2), 2499–2511. [CrossRef]
- Alamoodi, A., Zaidan, B., Zaidan, A., Albahri, O., Mohammed, K., Malik, R., Almahdi, E., Chyad, M., Tareq, Z., Albahri, A., Hameed, H., & Alaa, M. (2021). Sentiment analysis and its applications in fighting COVID-19 and infectious diseases: A systematic review. Expert Systems With Applications, 167, 114155. [CrossRef]
- Nemes, L., & Kiss, A. (2020). Social media sentiment analysis based on COVID-19. Journal of Information and Telecommunication, 5(1), 1–15. [CrossRef]
- Sann, R., & Lai, P. (2020). Understanding homophily of service failure within the hotel guest cycle: Applying NLP-aspect-based sentiment analysis to the hospitality industry. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 91, 102678. [CrossRef]
- Mušanović, J., Folgieri, R., & Gregorić, M. (2021). SENTIMENT ANALYSIS AND MULTIMODAL APPROACH APPLIED TO SOCIAL MEDIA CONTENT IN HOSPITALITY INDUSTRY. Tourism in South East Europe . . ./Tourism in Southern and Eastern Europe. [CrossRef]
- Young, L. M., & Gavade, S. R. (2018). Translating emotional insights from hospitality employees’ comments. International Hospitality Review, 32(1), 75–92. [CrossRef]
- Alqaryouti, O., Siyam, N., Monem, A. A., & Shaalan, K. (2020). Aspect-based sentiment analysis using smart government review data. Applied Computing and Informatics, 20(1/2), 142–161. [CrossRef]
- Verma, P., Khanday, A. M., Rabani, S. T., Hussain, M., & Jamwal, S. (2019). Twitter Sentiment Analysis on Indian Government Project using R. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(3), 8338–8341. [CrossRef]
- Hubert, R. B., Estevez, E., Maguitman, A., & Janowski, T. (2018, May). Examining government-citizen interactions on Twitter using visual and sentiment analysis. In Proceedings of the 19th annual international conference on digital government research: Governance in the data age (pp. 1-10). [CrossRef]
- Yergesh, B., Bekmanova, G., & Sharipbay, A. (2019). Sentiment analysis of Kazakh text and their polarity. Web Intelligence, 17(1), 9–15. [CrossRef]
- Bekmanova, G., Yelibayeva, G., Aubakirova, S., Dyussupova, N., Sharipbay, A., & Nyazova, R. (2019b). Methods for analyzing polarity of the Kazakh texts related to the terrorist threats. In Lecture notes in computer science (pp. 717–730). [CrossRef]
- Nugumanova, A., Baiburin, Y., & Alimzhanov, Y. (2022). Sentiment analysis of reviews in Kazakh with transfer learning techniques. 2022 International Conference on Smart Information Systems and Technologies (SIST). [CrossRef]
- Gimadi, D. (2021). Web-sentiment Analysis of Public Comments (PUblic Reviews) for languages with limited resources such as the Kazakh language. Student Research Workshop . . ./Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop . . [CrossRef]
- Yeshpanov, R., & Varol, H. A. (2024). KazSAnDRA: Kazakh Sentiment Analysis Dataset of Reviews and Attitudes. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.19335.
- lxyuan/distilbert-base-multilingual-cased-sentiments-student · Hugging Face. (2023, May 23). https://huggingface.co/lxyuan/distilbert-base-multilingual-cased-sentiments-student.
- tyqiangz/multilingual-sentiments Datasets at Hugging Face. (2023, June 24). https://huggingface.co/datasets/tyqiangz/multilingual-sentiments.
- Barbieri, F., Anke, L. E., & Camacho-Collados, J. (2021). XLM-T: Multilingual language models in Twitter for sentiment analysis and beyond. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.12250.
- Google Colab. (n.d.). https://colab.research.google.com/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).