Submitted:
20 May 2024
Posted:
21 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Chemicals
2.1.1. Animals
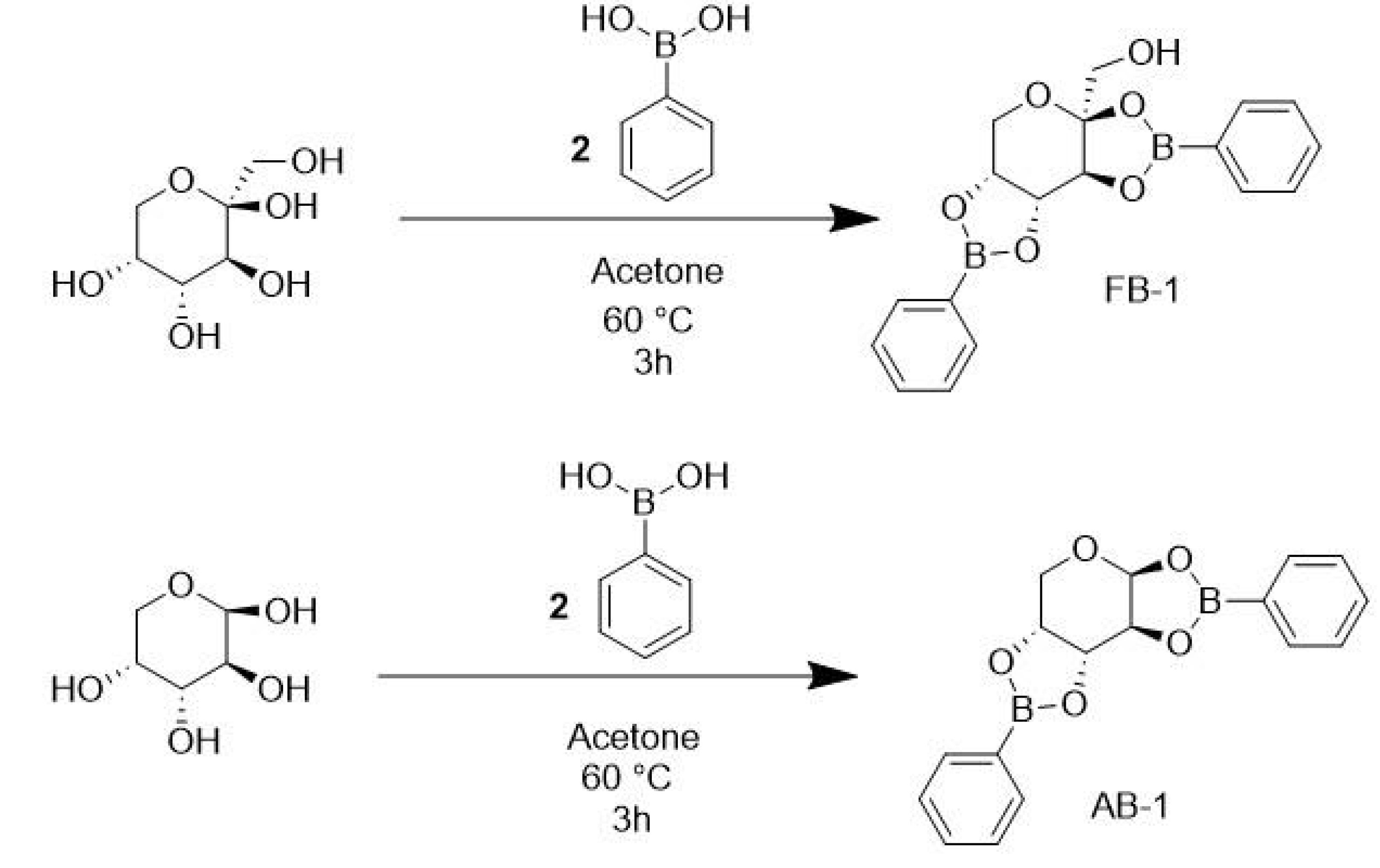
2.2. Synthesis and Chemical Characterization
2.3. Single Crystal X-ray Molecular Structure
2.4. In-Silico Prediction of the Physicochemical Properties
2.5. Biological Evaluation
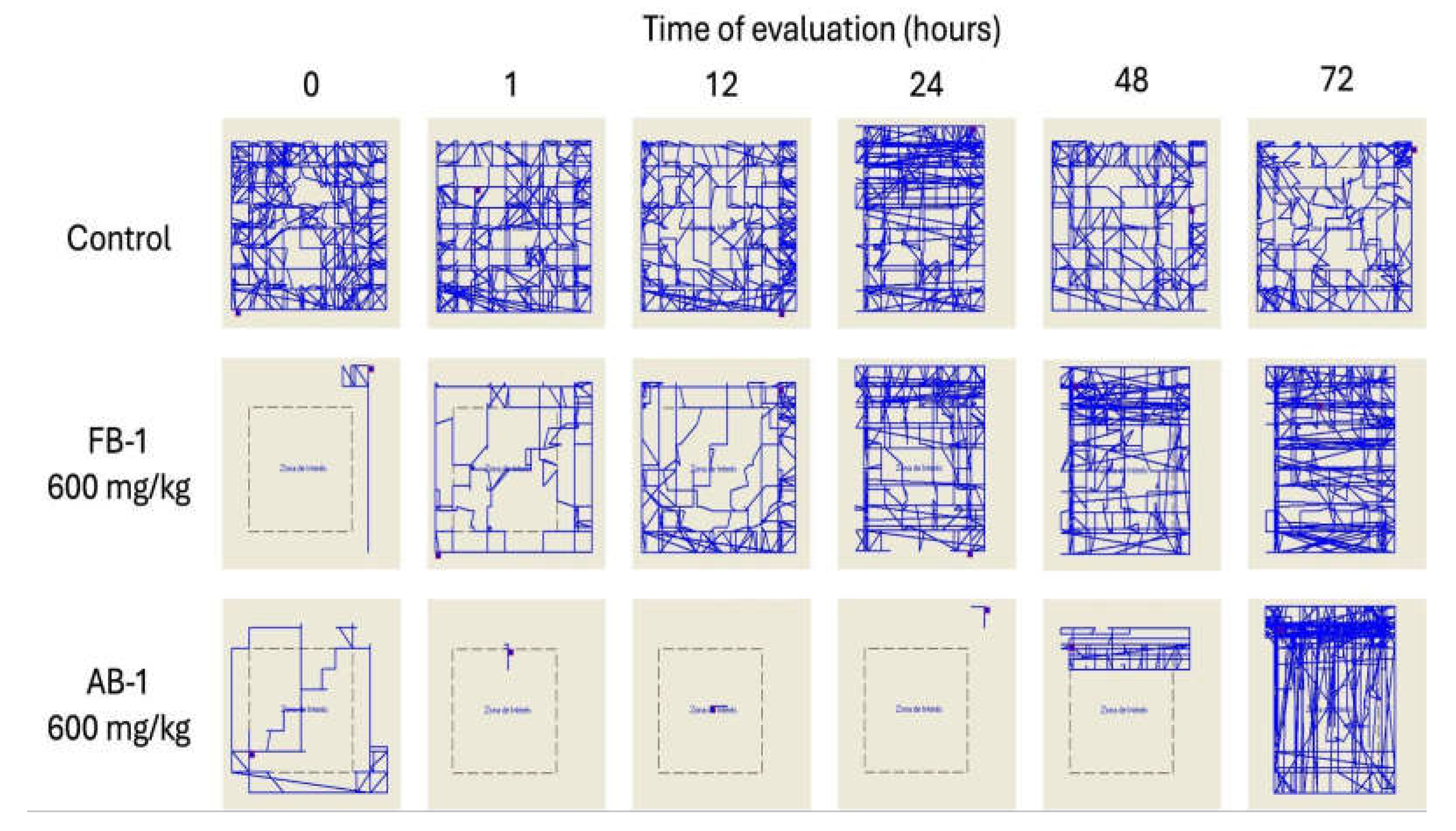
3. Results
3.1. Chemistry
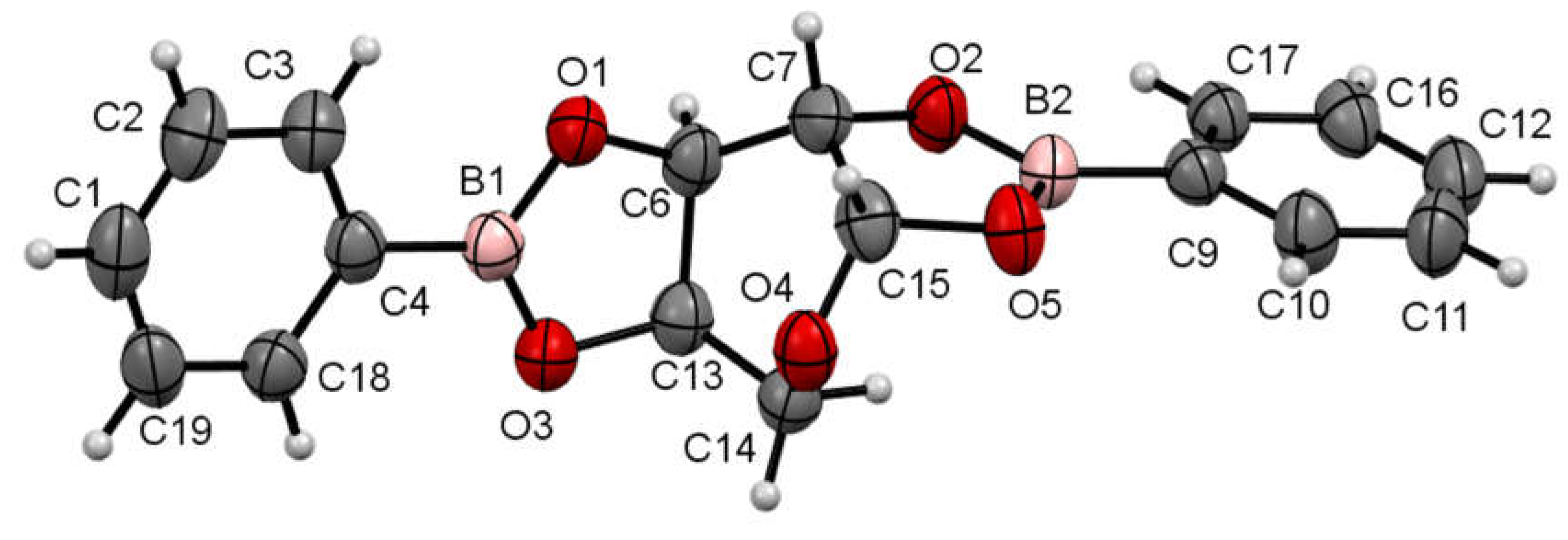
3.3. X-ray Diffraction Crystallography
3.4. In-Silico Predictions
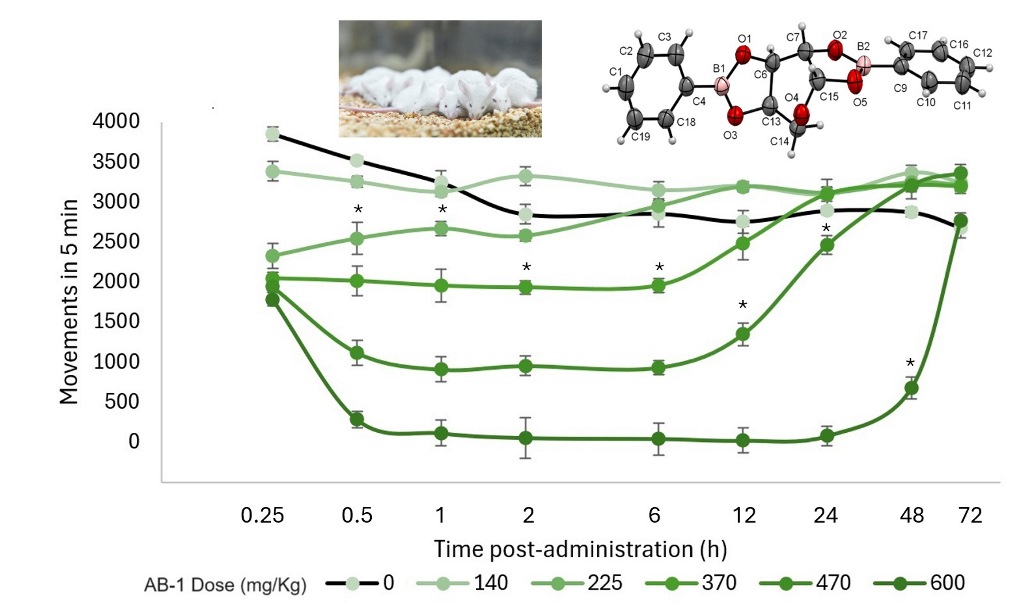
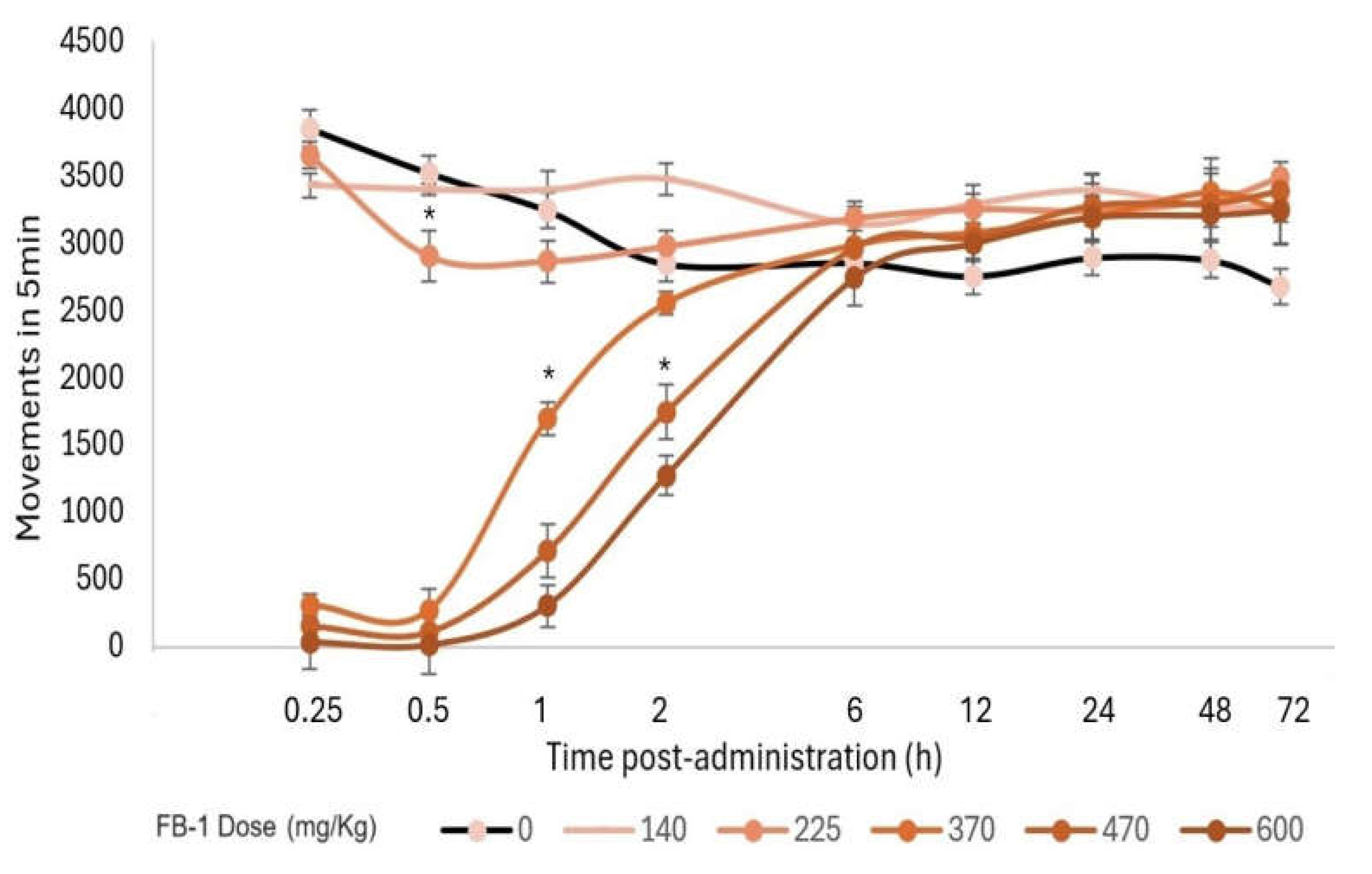
3.5. Acute Toxicity Test
3.6. Determination of the Median Effective Dose (ED50) for Hypnosis and Sedation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grams, R.J.; Santos, W.L.; Scorei, I.R.; Abad-García, A.; Rosenblum, C.A.; Bita, A.; Cerecetto, H.; Viñas, C.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. The Rise of Boron-Containing Compounds: Advancements in Synthesis, Medicinal Chemistry, and Emerging Pharmacology. Chemical reviews 2024, 124, 2441–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.J.; Ding, C.Z.; Akama, T.; Zhang, Y.K.; Hernandez, V.; Xia, Y. Therapeutic potential of boron-containing compounds. Future medicinal chemistry 2009, 1, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.M.; Nemzer, B.V.; Rangavajla, N.; Biţă, A.; Rogoveanu, O.C.; Neamţu, J.; Scorei, I.R.; Bejenaru, L.E.; Rău, G.; Bejenaru, C.; Mogoşanu, G.D. The Fructoborates: Part of a Family of Naturally Occurring Sugar-Borate Complexes-Biochemistry, Physiology, and Impact on Human Health: a Review. Biological trace element research 2019, 188, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, H.S.; Nakamura, H. Boron-Based Drug Design. Chemical record (New York, N.Y.) 2015, 15, 616–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, C. D. (2012). Dietary boron: progress in establishing essential roles in human physiology. Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology : organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS). [CrossRef]
- Draffin, S.P.; Duggan, P.J.; Fallon, G.D. O2,O3:O4,O5-Bis (phenylboranediyl)-β-D-fructo-pyranose acetone solvate. Acta Crystallographica. 2004, 60, 1520–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draffin, S.P.; Duggan, P.J.; Fallon, G.D.; Tyndall, E.M. O1,O2:O3,O5 - Bis (phenylboranediyl)-α-D-glucofuranose. Acta Crystallographica. 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichvilser, M.M.; Heinzl, C.; Klüfers, P. Boronic acid mono- and diesters of the aldopentoses. Carbohydrate research 2010, 345, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, X.X.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Jiang, Y.B. Selective sensing of saccharides using simple boronic acids and their aggregates. Chemical Society reviews 2013, 42, 8032–8048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks WL, A.; Deng, C.C.; Sumerlin, B.S. Structure-Reactivity Relationships in Boronic Acid-Diol Complexation. ACS omega 2018, 3, 17863–17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach, Ł.; Williams, G.T.; Fossey, J.S. Insulin Delivery Using Dynamic Covalent Boronic Acid/Ester-Controlled Release. Adv. Therap. 2021, 2100118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.R.; Ravikumar, A.; Peppas, N.A. Recent advances in glucose-responsive insulin delivery systems: novel hydrogels and future applications. Regenerative biomaterials 2022, 9, rbac056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, T.; Tamura, K.; Ueda, H.; Tanaka, T.; Sato, K.; Kuroda, R.; Aoki, S. Design and synthesis of boron containing monosaccharides by the hydroboration of d-glucal for use in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2018, 26, 5922–5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Ursúa, M.A.; Farfán-García, E.D.; Geninatti-Crich, S. Turning Fear of Boron Toxicity into Boron-containing Drug Design. Current medicinal chemistry 2019, 26, 5005–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farfán-García, E.D.; Castillo-Mendieta, N.T.; Ciprés-Flores, F.J.; Padilla-Martínez, I.I.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.G.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. Current data regarding the structure-toxicity relationship of boron-containing compounds. Toxicology letters 2016, 258, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soriano-Ursúa, M.A.; Farfán-García, E.D.; López-Cabrera, Y.; Querejeta, E.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.G. Boron-containing acids: preliminary evaluation of acute toxicity and access to the brain determined by Raman scattering spectroscopy. Neurotoxicology 2014, 40, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.P. The rise and fall of borax as an antiepileptic drug. Archives of neurology 2006, 63, 621–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrón-González, M.; Montes-Aparicio, A.V.; Cuevas-Galindo, M.E.; Orozco-Suárez, S.; Barrientos, R.; Alatorre, A.; Querejeta, E.; Trujillo-Ferrara, J.G.; Farfán-García, E.D.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. Boron-containing compounds on neurons: Actions and potential applications for treating neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of inorganic biochemistry 2023, 238, 112027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordova-Chávez, R.I.; Carrasco-Ruiz, M.F.; Rodríguez-Vera, D.; Pérez-Capistrán, T.; Tamay-Cach, F.; Score, I.R.; Abad-García, A.; Soriano-Ursúa, M.A. Boron-Containing Compounds for Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Human Metabolic Disorders. Biological trace element research 2023, 201, 2222–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruker. SAINT v8.37A, Bruker AXS Inc, Madison, WI, USA, 2015.
- R.H. Blessing, An empirical correction for absorption anisotropy. Acta Crystallogr 1995, A5, 33–38. [CrossRef]
- G.M. Sheldrick, A short history of SHELX, Acta Crystallogr. A64 (2008) 112–122. [CrossRef]
- L.J. Farrugia, WinGX and ORTEP for windows: an update, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 45 (2012) 849–854. [CrossRef]
- A.L. Spek, Structure validation in chemical crystallography, Acta Crystallogr. D65 (2009) 148–155. [CrossRef]
- C. F. Macrae, I.J. Bruno, J.A. Chisholm, P.R. Edgington, P. McCabe, E. Pidcock, L. Rodriguez-Monge, R. Taylor, J. van de Streek, P.A. Wood, Mercury–CSD, New features for the visualization and investigation of crystal structures, J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2008, 41, 466–470. [CrossRef]
- Arulanandam, C.D.; Hwang, J.S.; Rathinam, A.J.; et al. Evaluating different web applications to assess the toxicity of plasticizers. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 19684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gfeller, D.; Grosdidier, A.; Wirth, M.; Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissTargetPrediction: a web server for target prediction of bioactive small molecules. Nucleic acids research 2014, 42(Web Server issue), W32–W38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrahpour, A.; Motamedifar, M.; Zarei, M.; Youssoufi, M.H.; Mimouni, M.; Chohan, Z.H.; Ben Hadda, T. Petra, Osiris, and molinspiration together as a guide in drug design: predictions and correlation structure/antibacterial activity relationships of new N-sulfonyl monocyclic β-lactams, phosphorus. Sulfur. Silicon Relat. Elem 2010, 185, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Li, X.; Lin, X. A Review on Applications of Computational Methods in Drug Screening and Design. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 25, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sliwoski, G.; Kothiwale, S.; Meiler, J.; Lowe, E.W. , Jr Computational methods in drug discovery. Pharmacological reviews 2013, 66, 334–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorke, D. A new approach to practical acute toxicity testing. Archives of toxicology 1983, 54, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, C.; Xiaohui, W.; Mengrou, S.; Xin, L.; Ting, Z.; Ping, G. Preliminary evaluation of the efficacy and safety of brimonidine for general anesthesia. BMC anesthesiology 2021, 21, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prut, L.; Belzung, C. The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. European journal of pharmacology 2003, 463, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallop, P.M.; Paz, M.A.; Henson, E. Boradeption: a new procedure for transferring water-insoluble agents across cell membranes. Science (New York, N.Y.) 1982, 217, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altamore, T.M.; Duggan, P.J.; Krippner, G.Y. Improving the membrane permeability of sialic acid derivatives. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry 2006, 14, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggan, P.; Houston, T.; Kiefel-Levonis, S.; Smith-Szydzik, M.L. Enhanced Fructose, Glucose and Lactose Transport Promoted by a 2-(Aminomethyl) phenylboronic Acid. Tetrahedron. 2008, 6471227126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, B. Developments in the Karplus equation as they relate to the NMR coupling constants of carbohydrates. Advances in carbohydrate chemistry and biochemistry 2009, 62, 17–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.H.; Bhacca, N.S. Dependency of Vicinal Coupling Constants on the Configuration of Electronegative Substituents. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1964, 86, 2742–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, W.J.; Bayley, H. Single-Molecule Determination of the Isomers of d-Glucose and d-Fructose that Bind to Boronic Acids. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2018, 57, 2841–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorand, J.P.; Edwards, J.O. Polyol Complexes and Structure of the Benzeneboronate Ion. The Journal of Organic Chemistry 1959, 24, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyabu, R.; Kubo, Y.; James, T.D.; Fossey, J.S. Boronic acid building blocks: tools for sensing and separation. Chemical Communications 2011, 47, 1106–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, J.D.; Fossey, J.S.; James, T.D.; Brooks, B.R.; Bock, C.W. A computational investigation of the nitrogen-boron interaction in o-(N,N-dialkylaminomethyl)arylboronate systems. The journal of physical chemistry. A 2010, 114, 12531–12539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, S.D.; Davidson, M.G.; van den Elsen, J.M.; Fossey, J.S.; Jenkins, A.T.; Jiang, Y.B.; Kubo, Y.; Marken, F.; Sakurai, K.; Zhao, J.; James, T.D. Exploiting the reversible covalent bonding of boronic acids: recognition, sensing, and assembly. Accounts of chemical research 2013, 46, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, Y.; Shimizu, M.; Okamoto, T.; Sugaya, T.; Iwatsuki, S.; Inamo, M.; Takagi, H.D.; Odani, A.; Ishihara, K. Detailed Mechanism of the Reaction of Phenylboronic Acid Derivatives with D-Fructose in Aqueous Solution: A Comprehensive Kinetic Study. ChemistrySelect. 2016, 1, 5141–5151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, H.A.; Walker, T.E.; Fuentes, R.; O'Connor, J.; Serianni, A.; Barker, R. Carbon-13 as a tool for the study of carbohydrate structures, conformations and interactions. Journal of supramolecular structure 1977, 6, 535–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobre, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Rodrigues, L.R. New Trends and Technological Challenges in the Industrial Production and Purification of Fructo-oligosaccharides. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2015, 55, 1444–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues-Borges, M.; de Carvalho-Balaban, R. L-Arabinose (pyranose and furanose rings)-branched poly(vinyl alcohol): Enzymatic synthesis of the sugar esters followed by free radical polymerization. Journal of Biotechnology 2014, 192, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmitt, S.; Stampfer, H.; Martin, J.H. When less is more - efficacy with less toxicity at the ED50. British journal of clinical pharmacology 2017, 83, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, S.; Azim, Y.; Desiraju, G.R. Molecular complexes of alprazolam with carboxylic acids, boric acid, boronic acids, and phenols. Evaluation of supramolecular heterosynthons mediated by a triazole ring. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2010, 99, 3743–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldschen-Ohm, M.P. Benzodiazepine Modulation of GABAA Receptors: A Mechanistic Perspective. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisniak, J. Borax, Boric Acid and Boron-From Exotic to Commodity. Indian Journal of Chemical Technology 2005, 12, 488–500. [Google Scholar]
- Grand, R.S.; Wegner, E.S. Fatal case of boric acid poisoning. Am J Dis Child 1948, 6, 910–912. [Google Scholar]
- Bean, E.O. Accidental ingestion of boric acid. Clin Proc Child Hosp Dist Columbia 1949, 4, 101–103. [Google Scholar]
- Restuccio, A.; Mortensen, M.E.; Kelley, M.T. Fatal ingestion of boric acid in an adult. The American journal of emergency medicine 1992, 10, 545–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, R.A.; Wolf, B.C. Accidental boric acid poisoning following the ingestion of household pesticide. Journal of forensic sciences 2007, 52, 706–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duydu, Y.; Basaran, N.; Hermann, B.M. Human health risk assessment of boric acid and sodium borates. Toxicol Lett 2015, 238, S102–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, H.S.; Brown, S.D.; Woodhead, J.H.; Skeen, G.A.; Wolf, H.H. Topiramate modulates GABA-evoked currents in murine cortical neurons by a nonbenzodiazepine mechanism. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shank, R.P.; Gardocki; J. F.; Streeter; A. J.; Maryanoff; B.E. An overview of the preclinical aspects of topiramate: pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and mechanism of action. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 3–9. [CrossRef]
- Mula, M.; Cavanna, A.E.; Monaco, F. Psychopharmacology of topiramate: from epilepsy to bipolar disorder. Neuropsychiatric disease and treatment 2006, 2, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Velumian, A.A.; Jones, O.T.; Carlen, P.L. Modulation of high-voltage-activated calcium channels in dentate granule cells by topiramate. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodgson, S.J.; Shank, R.P.; Maryanoff, B.E. Topiramate as an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase isoenzymes. Epilepsia 2000, 41, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, J.W., 3rd.; Sombati, S.; DeLorenzo, R.J.; Coulter, D.A. Cellular actions of topiramate: blockade of kainate-evoked inward currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Epilepsia 2000, 41(S1), 10–16. [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




