Preprint
Article
A New Retrieval Algorithm of Fractional Snow over the Tibetan plateau Derived from AVH09C1
Altmetrics
Downloads
68
Views
17
Comments
0
A peer-reviewed article of this preprint also exists.
Submitted:
27 May 2024
Posted:
28 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
Snow cover products are primarily derived from the Moderate-resolution Imaging Spectrometer (MODIS) and Advanced Very High-Resolution Radiometer (AVHRR) datasets. MODIS achieves both snow/non-snow discrimination and snow cover fractional retrieval, while early AVHRR-based snow cover products only focused on snow/non-snow discrimination. The AVHRR Climate Data Record (AVHRR -CDR) provides a nearly 40-year global dataset that has a potential to fill a gap in long term snow cover fractional monitoring. Our study selects the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau as the experimental area, utilizing AVHRR-CDR surface reflectance data (AVH09C1) and calibrating with MODIS snow product MOD10A1. The snow cover percentage retrieval from the AVHRR dataset is performed using Surface reflectance at 0.64μm (SR1) and Surface reflectance at 0.86μm (SR2), along with a simulated Normalized Difference Snow Index (NDSI) model. Also, in order to detect the effects of land cover type and topography on snow inversion, we tested the accuracy of the algorithm with and without these influences, respectively (vanilla algorithm & improved algorithm). The accuracy of the AVHRR snow cover percentage data product is evaluated using MOD10A1、 ground snow-depth measurements and ERA5. Results indicate that the logic model based on NDSI has the best fitting effect, with R-square and RMSE values of 0.83 and 0.10, respectively. Meanwhile, the accuracy was improved after taking into account the effects of land cover type and topography. The model is validated using MOD10A1 snow-covered areas, showing snow cover area differences of less than 4% across 6 temporal phases. Improved algorithm results in better consistency with MOD10A1 than vanilla algorithm. Moreover, the RMSE reaches greater levels when the elevation is below 2,000 meters or above 6,000 meters, and is lower when the slope is between 16° and 20°. Using ground snow-depth measurements as ground truth, the multi-year recall rates are mostly above 0.7, with an average recall rate of 0.81. Results also show a high degree of consistency with ERA5. The validation results demonstrate that the AVHRR snow cover percentage remote sensing product proposed in this study exhibits high accuracy in the Tibetan Plateau region, also demonstrating that land cover type and topographic factors are important to the algorithm. Our study lays the foundation for the global snow cover percentage product based on AVHRR-CDR,furthermore lays a basic work for generating a long-term AVHRR-MODIS fractional snow cover dataset.
Keywords:
Subject: Environmental and Earth Sciences - Remote Sensing
1. Introduction
Since the first generation of AVHRR was sent to space in 1976, daily snow monitoring products are possible to be applied in global scale based on space remote sensors (Hall, Riggs, Salomonson, Digirolamo, et al., 2002; Kelly & Chang, 2003; Simpson et al., 1998).Among these, snow monitoring based on optical sensors mainly focuses on the inversion of snow cover area, such as AVHRR, MODIS, VIIRS, etc (Hüsler et al., 2014; Marchane et al., 2015; Riggs et al., 2017a). Through systematic data processing flow, these sensors can generate long term series snow cover products, such as Northern Hemisphere Weekly Snow Cover and Sea Ice Extent (NHSCE) (Helfrich et al., 2007; Robinson et al., 1993), Interactive Multi-sensor Snow and Ice Mapping System(IMS)(Helfrich et al., 2007), Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer(MODIS)(Hall, Riggs, Salomonson, DiGirolamo, et al., 2002; Stroeve et al., 2005; X. Wang et al., 2008) and Global Snow Monitoring for Climate Research (GlobSnow)(Solberg et al., 2010). NHSCE’s snow cover product provides weekly SCE from 1966 to 1997 with a spatial resolution of 190 kilometers (Robinson et al., 1993). IMS provides daily SCE imagery at 24, 4 and 1 kilometer spatial resolution from 1997 to the present day(Helfrich et al., 2007; Ramsay, 1998). The MODIS/Terra Snow Cover Daily L3 Global 500 m Grid (MOD10A1, recently version 6) is a global, gridded fractional snow cover area (FSCA) product produced daily by the National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) (Hall, Riggs, Salomonson, Digirolamo, et al., 2002; Riggs et al., 2017b). It apples the normalized difference snow index (NDSI) to extract snow cover area, which leverages the contrasting reflectance of snow in the visible and shortwave infrared regions of the spectrum. FSCA is estimated using an empirical relationship between FSCA and NDSI, which apples TM data as the true data. MOD10A2 which revealed maximum snow cover is generated by reading 8 days of 500m resolution MOD10A1 tiles (Hall et al., 2006). Although the accuracy of MOD10A1 has reached a relative high level (Riggs et al., 2015),its time series can only cover about twenty years. Current researches in the field of global climate change, especially in the related studies of vegetation variation in conjunction with long term NDVI data, there are many researches exhibits of last 40 years of long time series research when it comes to long time series remote sensing data (Alkama et al., 2022; Qiu et al., 2019; Zhao et al., 2022). It is therefore necessary to extend the snow product to a 40-year term length.
Earlier studies based on AVHRR snow cover inversion mostly used thresholding methods. Khlopenkov et al. implemented AVHRR-based snow cover inversion based on snow reflectivity characteristics in visible and infrared bands through the thresholding method and SPARC probability maps, and removed cloud contamination in combination with bright temperature data (Khlopenkov & Trishchenko, 2007). Husler et al. developed a snow extent retrieval method to identify Alpine snow extent using a 1km AVHRR dataset based on Khlopenkov's research (Hüsler et al., 2012). Zhou et al. developed a long time series snow extent recognition algorithm (Zhou et al., 2013) based on 1km resolution AVHRR-LAC and HRPT data, in Central Asia area, which uses an aggregated rating method that normalized the image class range from 0 to 1. Their method still belongs to the snow vs. non-snow binary classification. Hori et al. used the 3.7μm band to replace the missing 1.64μm band to simulate NDSI (NDSIAVHRR) and set the discrimination threshold to 0.8 to produce a Northern Hemisphere snow cover dataset (Hori et al., 2017). Chen et al. calibrated the data using Landsat and adjusted the threshold for NDSIAVHRR to 0.77 based on Hori’s research, creating the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau dataset (Chen et al., 2018). Prior to year 2018, research predominantly focused on qualitative inversion, with the quantitative inversion of snow cover in long time series of AVHRR gradually emerging in 2018. Hao et al. utilized NDSIAVHRR as the primary test for snow discrimination, creating a nationwide snow cover dataset for China. They adjusted the NDSIAVHRR threshold to 0.73 and 0.65 around the year 2000, and combined information from bands such as Surface Reflectance at 0.64μm (SR1) and Surface reflectance at 0.86μm (SR2) to identify snow cover (Hao et al., 2021).
Previous studies tended to opt for using SR3 as substitute for the near-infrared band in MODIS to calculate the NDSI value for AVHRR. Simultaneously, combining information from bands such as SR1 and SR2 serves as the primary basis for snow cover identification. Most snow cover products based on AVHRR still primarily involve binary classification into snowy or non-snowy conditions (Harrison & Lucas, 1989; Ranzi et al., 1999; L. Wang et al., 2005; S. Wang et al., 2017). However, NDSIAVHRR can be employed not only for distinguishing between snow and non-snow but also for determining the percentage of snow cover. Therefore, it is essential to explore the feasibility of constructing an FSC dataset based on NDSIAVHRR. The aim of our study is to assess the feasibility of generating FSC data based on AVHRR data in the Tibetan Plateau region. Additionally, precision evaluation of retrieval results will be conducted by incorporating MODIS snow cover products and ground observations.
This study comprises six sections. Section 2 describes study area and data sets used in the study. Section 3 presents the details of main algorithm. In Section 4, based on MODIS, ground observations and reanalysis data, we analyze the accuracies of AVHRR_FSC. Further discussion about the algorithm and its precision are listed in section 6,as well as the potential problems of AVHRR_FSC long term dataset. Finally, in Section 6, we summarize this study and present our conclusions.
2. Materials
2.1. Study Area
The Tibetan Plateau, with an average elevation of 4000 meters, is the third pole on Earth after the Arctic and Antarctic, formed by the collision and compression of the Indian plate against the Asian plate. During the exceptionally long winter, vast areas of the Tibetan Plateau are covered by snow. The snowmelt from this region serves as the source for many rivers, including the Yangtze, Yellow River, Indus, Ganges, and Mekong. Moreover, the snow cover on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau is a primary water supply for vegetation growth on the plateau, providing crucial water resources for the ecosystem and human societies in the surrounding countries. Its rugged terrain makes it an ideal testing area. The selected region corresponds to the geographic definition of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, encompassing parts of China, Pakistan, India, Nepal, and other countries. It also includes the Pamir Plateau, the Himalayas, the Kunlun Mountains, and the Tanggula Mountains. We chose three experimental areas, namely, the Pamir Plateau, the central part of the Gangdise Mountains, and the central part of the Nyainqentanglha Mountains (Figure 1), to establish the relationship between AVH09C1 band information and snow cover percentage. These areas are characterized by perennial snow cover (Pu et al., 2007; You et al., 2020), making them ideal experimental regions.
2.2. AVHRR Dataset
Recently, the Long Term Data Record project (LTDR), funded by NASA, created a 0.05° global daily dataset. This LTDR version 5 covers the years 1982 to 2020, and includes improved atmospheric correction and inter-calibration between sensors. It includes three main products: AVH02C1 (Level 1 product), AVH09C1 (Daily Surface Reflectance), AVH13C1 (Daily NDVI).
The AVH09C1 dataset provides continuous daily surface reflectance and brightness temperature, sourced from AVHRR sensors on NOAA polar-orbiting satellites such as NOAA-7 to NOAA-19. Additionally, AVH09C1 has calibrated data from various instruments since 1981 (Vermote et al., 2019). According to previous research, the utility error of AVH09C1 surface reflectance is comparable to MODIS (Franch et al., 2017; Vermote et al., 2019). Therefore, we choose AVH09C1 as the primary data source for snow cover percentage retrieval.
2.3. MODIS Dataset
In the MODIS remote sensing product series, there are primarily two snow cover percentage products: MO/YD10A1 and MO/YD10C1 (Rittger et al., 2013; X. Wang et al., 2014). Among them, MO/YD10C1 is in Climate Modeling Grid format, derived from calculations based on MO/YD10A1 snow observation values. The spatial resolution of MO/YD10A1 is 500 meters. Under ideal illumination, clear sky, and smooth surface conditions, the overall absolute accuracy of MOD10A1 exceeds 95% (Gao et al., 2010; Tong et al., 2009).
In this study, we selected MOD10A1 data from six temporal phases corresponding to AVH09C1 for curve fitting in the training dataset. Additionally, we chose MOD10A1 data from another six temporal phases as the validation dataset. Both the training and validation datasets (Table 2) consist of two temporal phases for each test area (Figure 1).
2.4. Ground Observations & Reanalysis Dataset
After all, MOD10A1 serves only as a simulated result. In addition to our use of MOD10A1 data for validation, we also require actual ground data to evaluate the accuracy of our snow cover product. Consequently, ground snow depth measurement data provided by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA) for the years 2000 to 2012 were utilized to validate the AVHRR FSC product. Daily snow depth measurements were taken near each station using a professional meter stick at 8:00 AM Beijing time, provided that the day's snow cover in the field of view exceeded 50%. The CMA stations selected for validation were carefully chosen to avoid an overrepresentation of non-snow samples, which could affect the accuracy of the assessment. To ensure the reliability of the validation, only the measured data from stations with more than 20 days of snow coverage and a depth greater than 1 centimeter were selected. Additionally, we utilized the ERA5 snow cover data. ERA5 is the fifth generation of reanalysis data (Hersbach et al., 2020). According to previous research, ERA5 is effective in representing variables such as weather events (Lei et al., 2020, 2023). Therefore, we incorporated the ERA5 snow cover dataset as a comparative data source for accuracy validation.
2.5. Land Cover Type
According to previous studies (Dietz et al., 2012; Shreve et al., 2009), the complexity of surface conditions affects snow cover inversion accuracy. Surface conditions are primarily classified into two categories: topographic conditions and vegetation cover conditions. Topography is mainly about elevation and slope. Vegetation cover conditions usually refer to vegetation types. For instance, in forest areas, trees will partially obscure snow-covered surface, and the effect of trees should be considered when mapping snow cover in forests, otherwise, the snow cover in forested areas may be underestimated, such as the results observed by Solberg et al. in Norway (Solberg et al., 1997). For the effect of elevation, we used DEM data in representing elevation and also generated slope data based on DEM data. For the effect of surface vegetation cover, we used MCD10C1 Land Cover Type products based on MODIS data to reflect the surface vegetation cover types. Based on previous research (Chen et al., 2018), we roughly classified the vegetation cover types as forest, grassland and bareland.
3. Methods
The framework of this study mainly consists of three parts: data preprocessing, dataset production, and accuracy validation. Data preprocessing includes quality control, cloud detection, and the construction of fishnet. Quality control is primarily based on QA data from AVH09C1 to obtain valid pixels. Cloud detection will be detailed in section 3.1. Due to the different resolutions between AVH09C1 and MOD10A1, and the much lower spatial resolution of AVH09C1 compared to MOD10A1, we construct fishnet (vector data) based on AVH09C1 to calculate statistical values for fitting and accuracy evaluation work. Dataset production mainly involves fitting core formulas and comparative analysis, with detailed content presented in section 3.2. Accuracy analysis relies primarily on MOD10A1, ground observation data, and ERA5 data, while also examining the stability of accuracy under different land surface vegetation cover types, elevations, and slope conditions. .
3.1. Cloud Detection
Due to potential issues of significant cloud cover overestimation in AVHRR (Chen et al., 2018; Hori et al., 2017), many studies have re-identified clouds, leading us to not directly adopt the cloudy flags. Cloud detection using AVHRR data remains a challenge due to the limited number of spectral bands. Effective cloud detection is crucial as it directly impacts the inversion results of target features, especially since the reflectance of snow in the visible spectrum overlaps with cloud altitudes. Currently, there are two mainstream methods for cloud monitoring: one categorizes clouds into high, medium, low, and thin clouds, setting different thresholds for different cloud types (Zhu et al., 2022). Another approach, represented by Hori's work, differentiates cloud monitoring between alpine and non-alpine regions and has achieved global cloud monitoring. Chen et al.'s study in the Tibetan Plateau has confirmed the adaptability of Hori's method in the region (Chen et al., 2018). Furthermore, Hao et al. have conducted a spectral analysis of cloud characteristics over China based on Hori's method, making adjustments primarily focused on the threshold selection between BT3 and BT4 (Hao et al., 2021). This study integrates the identification methods of Hori and Hao, presenting the following cloud identification method (as in Table 2). The cloud detector scans from the top to the bottom of the list for each target; a flag switch set to on indicates "cloudy," while off indicates "no cloud." A total of nine variables are used for cloud identification. It is important to note that NDSIAVHRR is a variant of NDSI, using the 3.7 μm infrared band instead of the 1.6 μm near-infrared band.
3.2. Inversion Algorithm of AVHRR FSC
First of all, we selected SR1 and SR2 along with NDSIAVHRR for fitting the snow cover percentage. By examining the distribution characteristics of the scatter plots, we performed both linear and logistic model fittings on the results. All pixel-based sampling points are averaged every 10 values to better illustrate the fitting effect. The findings indicate that the logistic model provided a better fit for B1, B2, and NDSIAVHRR. Among these, NDSIAVHRR achieved the best fitting results, with an R-squared and RMSE (Root Mean Square Error) of 0.92 and 0.078, respectively; B2 showed the poorest fit, with an R-squared and RMSE of 0.89 and 0.095, respectively, while B1's results were intermediate. Both in terms of R-squared and RMSE, NDSIAVHRR exhibited the best fitting results, although the outcomes of the three fitting parameters were very close. Ultimately, we selected NDSIAVHRR as the key parameter for the inversion of snow cover percentage.
The above formula can be regard as the vanilla algorithm. Although it achieves a high fitting effect, it does not consider the influence of the complex state of the ground surface on the snowpack inversion. In order to recognize these influences, we add other factors to improve the algorithm. According to previous studies, the main influences on snow cover inversion are elevation, slope, surface vegetation type, and seasonal influence. Among them, the seasonal influence is mainly the difference in inversion models caused by different surface temperatures, and here we use BT4 as a rough characterization of surface temperature, combined with elevation and slope, which are continuous variables, and we use them together with NDSIAVHRR as variables in the logistic model. Multivariate fitting was performed separately for different vegetation cover types. The fitting results showed that the fitting results considering multiple factors were better than Eq. 1. Further, we fitted the model for different vegetation cover types. Grassland had the best fit, followed by bare ground and forest, but all arrived at higher R-square, while RMSE was maintained at a low level, and finally, we used Equations 3 to 5 as the official inverse model (regard as the improved algorithm).
Equation 2 incorporates the influences of topography and surface temperature variations. Equations 3 through 5 present the fitting results under various surface vegetation cover conditions. The fitting outcomes of Equations 2 to 5 are depicted in Figure 4.
Comparing the results of Figure 3 and Figure 4, when elevation, slope and BT4 are added as variables, R-squared and RMSE are improved. Figure 4 also shows the fitting results under different vegetation cover types, among which Grass has the widest distribution and the largest number of sampling points on the Tibetan Plateau, and has the best fitting effect, with R-squared and RMSE reaching 0.92 and 0.0745 respectively. Forest is not the main vegetation cover type, but the R-squared and RMSE also reach 0.73 and 0.0745 respectively. Finally, we used Eq. (3) to Eq. (5) as the improved algorithms for the AVHRR-FSC dataset.
4. Accuracies of the AVHRR FSC Product
We compared the FSC inversion results of both vanilla algorithm and improved algorithm for six temporal phases between AVHRR and MODIS. As shown in Figure 5, across three test areas on the Tibetan Plateau, the trends in snow cover percentage distribution were largely consistent between the two, with areas identified as cloudy in AVHRR also marked as non-snow in corresponding MODIS data, suggesting alignment in cloud identification outcomes. This indicates the snow detection algorithm's spatial reliability.
Figure 5 presents a comparison between AVHRR-FSC images of vanilla algorithm and sub-pixel snow mapping images of MOD10A1. The visual comparison highlights differences in snow distribution, suggesting that significant discrepancies would question the sub-pixel snow spectroscopy's reliability. Based on Figure 4, snow distribution from visual interpretation of AVHRR/2 images corresponds with sub-pixel snow mapping outcomes, further affirming the sub-pixel snow mapping algorithm's validity.
Additionally, we analyzed the standard deviation between AVHRR and MOD10A1 data for these phases, finding the largest standard deviation to be 28.68 and the smallest 15.05%. The most significant difference in snow-covered area among the test sites occurred on 14/12/2014, at less than 4%, with all other discrepancies below 3%. These findings, from both spatial distribution and statistical metrics, demonstrate a high congruence between AVHRR and MOD10A1 products.
Although Figure 5 demonstrates that the vanilla algorithm achieves high accuracy, the improved algorithm gets a better result (Figure 6). For all the six data, the snow cover area from improved algorithm is closer to MOD10A1. Taking the time-phase data of 10/12/2009 and 6/12/2004 as examples, the vanilla algorithm recognizes the snow cover area of 8.62% and 4.41%, respectively, while the improved algorithm recognizes snow coverage of 11.26% and 6.04%, respectively. Despite the high RMSE values for both the vanilla and improved algorithms, it is important to note that RMSE values are calculated based on pixel size. This calculation method is over stringent due to the differences in spatial resolution between AVHRR and MODIS data. Even a minor misalignment in geographic coordinates can significantly increase the RMSE value, making it more appropriate as a reference rather than an absolute measure of accuracy. Nevertheless, the statistical values of snow-covered areas and the results from visual interpretation exhibit a high degree of consistency between AVHRR-FSC data and MOD10A1.
To provide a more comprehensive comparison of the accuracy between the vanilla algorithm and the improved algorithm, we evaluated their performance under varying conditions of elevation, slope, and vegetation cover types. As illustrated in Figure 7, regardless of elevation or slope, the RMSE remained below 30%. Under different elevation and slope conditions, the improved algorithm consistently exhibited lower RMSE values compared to the vanilla algorithm, and its estimates of snow-covered area were more closely aligned with MOD10A1 data.
In various elevation intervals, the RMSE values for both the vanilla and improved algorithms were highest at elevations below 2 kilometers and above 6 kilometers, with the lowest values occurring between 2 and 3 kilometers. Regarding slope, the RMSE of the vanilla algorithm initially increased and then decreased, peaking for slopes between 12° and 16°, and reaching its lowest point for slopes between 16° and 20°. In contrast, the RMSE of the improved algorithm remained consistently lower than that of the vanilla algorithm within the 0° to 16° slope range, without significant variation, indicating greater stability.
As shown in Figure 8, the RMSE for different vegetation cover types remains below 20%. The RMSE of the improved algorithm is consistently lower than that of the baseline algorithm, and its snow cover area is closer to that of MOD10A1. For both the baseline and the improved algorithms, bareland exhibits the lowest RMSE, although the differences among the three are minimal. Based on the comprehensive analysis from multiple perspectives, the improved algorithm outperforms the baseline algorithm. Therefore, we have adopted the improved algorithm as the core algorithm for the AVHRR-FSC dataset.
After completing the creation of the AVHRR-FSC dataset for the years 1982-2020, we used ground observation data and reanalysis data as supplementary validation methods. We employed snow depth measurement data from 103 sites over 13 years, provided by the China Meteorological Administration (CMA), to validate our new AVHRR snow product. The overview of the validation results, as presented in Table 8, shows that although kappa coefficients were generally low, the recall values were significantly higher. Notably, the peak recall value was recorded in 2008 at 0.90, while the lowest was in 2012, at 0.66, with the recall values for the other years all above 0.73. This indicates that the inversion results demonstrated a high level of stability.
The daily data from ERA5 for the year 2012 were used in our study. Due to cloud interference, the two datasets could not be directly compared. Therefore, we only compared the number of snow-covered pixels under cloud-free conditions between the two datasets. The results indicate that the temporal variation trends of the two datasets are highly consistent (Figure 9). However, the number of snow-covered pixels in the ERA5 data is significantly higher, which is expected as ERA5 is known to have an overestimation issue. It is important to note that both the ground observation data and the ERA5 data are based on observations from meteorological stations. There is a substantial difference in spatial scale between point data and raster data. Therefore, the accuracy assessment of the AVHRR-FSC* dataset needs to be comprehensively evaluated using Figure 6, Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9 and Table 4.
5. Discussion
Through comparison and validation with MODIS and meteorological station data, we have confirmed that AVHRR-derived snow cover percentages exhibit high accuracy. It is important to note that MODIS and meteorological stations offer different perspectives for data validation. MODIS data primarily assesses the spatial consistency of snow inversion results. However, since the MOD10A1 does not contain cloud identification information (Riggs et al., 2015), we did not directly evaluate the accuracy of cloud identification. The ability to correctly exclude cloud interference may represent one of the main challenges for AVHRR in snow inversion. In the example from December 10, 2009, in Figure 6, we observe that MODIS identified parts of western Nyingchi Tanggula mountain as snow-free, whereas AVHRR results indicated significant cloud interference in this area, with more consistent identification results in other areas.
While many studies use meteorological station data to validate the accuracy of remotely sensed snow products (Orsolini et al., 2019; Parajka & Blöschl, 2006; Simic et al., 2004), meteorological station snow depth measurements are theoretically not ideal for validation purposes. This is because the stations provide point data, whereas AVHRR has a spatial resolution of 0.05°. Within a grid, the position of the station and the actual distribution of snow cover can greatly affect the accuracy assessment. However, the recall metric is very important for data from meteorological stations. This is because if a station measures a certain snow depth, it confirms the presence of snow cover in that area, implying the AVHRR-detected snow cover percentage should be greater than 0. However, a snow depth of 0 at a station does not mean that there is no snow cover within the entire 0.05° × 0.05° grid of the station's location. Therefore, for accuracy assessments based on meteorological stations, the significance of Recall is greater than that of Precision, Kappa, and other evaluation metrics. In this study, the Recall values of the AVHRR snow cover product relative to meteorological station snow depth data are at a high level, indicating that our algorithm has a high rate of snow cover detection.
Metsämäki et al., based on AVHRR and observational data, performed linear interpolation between reference reflectances under full snow cover conditions (SCA=100%) and no snow conditions (SCA=0%), different from the logistic model-based interpolation method used in our study, to estimate the Snow Cover Area (SCA) (Metsämäki et al., 2002). When validated against in situ SCA measurements from snow tracks, the overall accuracy was 85%, and when validated against snow measurements from meteorological stations, the accuracy was 64.4%. With the overall accuracy above 99% in our study (calculated from Figure 6), our sub-pixel snow mapping algorithm should be considered reliable and feasible.
The most significant finding of our study is the determination that the percentage of snow cover exhibits a logistic curve relationship with NDSIAVHRR, whereas previous research results were often linear, such as when Hall et al. used a linear equation to simulate snow cover percentage with NDSI for MODIS data inversion. Additionally, spectral mixture models also differ from logistic models, which might relate to the data processing workflow and the selection of validation datasets. Nevertheless, this study has confirmed that the logistic model based on NDSIAVHRR achieves high accuracy.
It is worth mentioning that Hüsler's algorithm for inverting snow cover probability also utilized a logistic model and validated it with on-site data captured by network cameras. However, their logistic model was primarily used for calculating snow cover probability (Hüsler et al., 2012). Logistic regression is more commonly applied in classification problems, and we employed it only because the fitting curve more accurately matched the characteristics of the scatter distribution. Currently, it is unclear whether their findings are in any way related to our research, which remains an area for future investigation.
The accuracy of snow cover detection algorithms is associated with various factors, such as elevation, surface roughness, etc. (Parajka et al., 2010; Veitinger et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2021). This study systematically analyzes, by distinguishing between vanilla and improved algorithms, the effects of vegetation cover type and topographic elements on the accuracy of FSC inversion. The importance of considering these factors in the algorithm is demonstrated. In this study, slope is used as a proxy for surface roughness. Previous research has shown that elevation significantly influences accuracy, with snow detection precision tending to decrease as elevation increases. Despite the reduced snow detection accuracy at elevations above 6,000 meters in this study, this phenomenon is attributed to the unique geographical environment of the high mountain regions in Asia and the selection of validation images by date. Due to the high elevations in the high mountain regions of Asia, areas above 5,000 meters are predominantly covered by grasslands, leading to severe fragmentation of snow cover. This finding is consistent with previous research for elevations significantly below the 2,000 to 6,000 meters range (Pan et al., 2022; Wu et al., 2021). However, there was no significant decrease in accuracy within the 2,000 to 6,000 meters range, and accuracy was lower at elevations below 2,000 meters. In the Tibetan Plateau region, areas below 2,000 meters, such as the Qaidam Basin and valleys on the southern edge of the plateau transitioning to the high plateau, experience climates transitioning from subtropical arid to subtropical forest climates to high plateau climates. Therefore, snow fragmentation is particularly severe in these areas. Additionally, it is important to note that the validation images selected were from the winter season when snow cover is more extensive, resulting in more concentrated snow cover in these areas and higher validation accuracy.
Due to cloud interference, the dataset created in this study cannot yet be directly applied to global change researches (Jing et al., 2019). Future work could involve the creation of long-term, cloud-free datasets through the fusion of multi-temporal and multi-source data. It is important to note that current long-term cloud-free snow cover datasets are based on a binary snow/no-snow classification, utilizing multi-temporal fusion to mitigate some cloud effects and further integrating with passive microwave data to completely eliminate cloud influences (Hall et al., 2010; Huang et al., 2017; Kumar et al., 2015). However, for snow cover percentage data, while multi-temporal fusion allows for averaging pixel values, establishing a conversion relationship between snow depth measurements and snow cover percentages when fusing with passive microwave data remains a technical challenge and a potential direction for future research.
In this study, we used MODIS snow products as training samples instead of selecting higher-resolution TM data, as many studies did, which could be seen as contentious. It's worth mentioning that our choice of the MODIS dataset was driven by two main reasons. Firstly, the MODIS snow product has undergone numerous iterations and updates, and its accuracy has been validated across many global regions, offering strong reliability (Hall & Riggs, 2007; Klein & Barnett, 2003; Parajka & Blöschl, 2006). Secondly, using MODIS as a training sample allows for easier balancing of RMSE to ensure consistency between AVHRR and MODIS inversion results, laying the groundwork for the next step of creating a long-term AVHRR-MODIS-VIIRS dataset. In the future, we plan to reference the NDVI dataset to create a global long-term FSC data product starting from 1981 and spanning over 40 years.
6. Conclusion
This study developed a snow cover dataset for the Tibetan Plateau region based on the long-term AVHRR dataset. Using MODIS data as ground truth, we fitted Bands 1, 2, and NDSIAVHRR, and the results indicated that Band 1's logistic curve fitting was the most optimal, achieving an R-squared of 0.9 for the training dataset and an RMSE of less than 0.5 for the prediction dataset. Furthermore, we analyzed the influence of factors such as surface vegetation cover type, elevation, and slope on the algorithm by distinguishing between the vanilla algorithm and the improved algorithm. We assessed the importance of these factors and ultimately adopted the improved algorithm as the core algorithm for the AVHRR-FSC dataset. Through spatial comparison analysis with the MODIS dataset, we observed that the spatial distribution of AVHRR snow cover inversion results was consistent with those from MOD10A1, with a standard deviation of less than 0.2 for each spatial pixel. Considering that terrain might impact inversion accuracy, we analyzed accuracy under different elevation conditions, revealing that consistency between AVHRR and MOD10A1 inversion results increased with elevation. Comparison analysis with actual meteorological station data showed that except for a Recall value of 0.66 in 2012, all other values were greater than 0.73, indicating that most snow-covered areas were detected. Additionally, the results also show a high degree of consistency with ERA5. This study demonstrates the feasibility of AVHRR inversion for snow cover percentage and provides the optimal fitting curve. The operational snow inversion technique designed in this study lays the foundation for future global AVHRR snow cover percentage product development.
Data Availability Statement
We encourage all authors of articles published in MDPI journals to share their research data. In this section, please provide details regarding where data supporting reported results can be found, including links to publicly archived datasets analyzed or generated during the study. Where no new data were created, or where data is unavailable due to privacy or ethical restrictions, a statement is still required. Suggested Data Availability Statements are available in section “MDPI Research Data Policies” at https://www.mdpi.com/ethics.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Alkama, R.; Forzieri, G.; Duveiller, G.; Grassi, G.; Liang, S.; Cescatti, A. Vegetation-based climate mitigation in a warmer and greener World. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Long, D.; Liang, S.; He, L.; Zeng, C.; Hao, X.; Hong, Y. Developing a composite daily snow cover extent record over the Tibetan Plateau from 1981 to 2016 using multisource data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2018, 215, 284–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietz, A.J.; Kuenzer, C.; Gessner, U.; Dech, S. Remote sensing of snow–a review of available methods. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2012, 33, 4094–4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franch, B.; Vermote, E.F.; Roger, J.-C.; Murphy, E.; Becker-Reshef, I.; Justice, C.; Claverie, M.; Nagol, J.; Csiszar, I.; Meyer, D. A 30+ year AVHRR land surface reflectance climate data record and its application to wheat yield monitoring. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Xie, H.; Lu, N.; Yao, T.; Liang, T. Toward advanced daily cloud-free snow cover and snow water equivalent products from Terra–Aqua MODIS and Aqua AMSR-E measurements. Journal of Hydrology 2010, 385, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A. Accuracy assessment of the MODIS snow products. Hydrological Processes: An International Journal 2007, 21, 1534–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Foster, J.L.; Kumar, S.V. Development and evaluation of a cloud-gap-filled MODIS daily snow-cover product. Remote Sensing of Environment 2010, 114, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V. V.; Digirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Riggs, G.A.; Salomonson, V. V.; DiGirolamo, N.E.; Bayr, K.J. MODIS snow-cover products. Remote Sensing of Environment 2002, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Salomonson, V. V, Riggs, G.A. MODIS/Terra snow cover 8-day l3 global 500m grid, version 5. Tile H12v12]. Boulder, Colorado USA: National Snow and Ice Data Center. 2006.
- Hao, X.; Huang, G.; Che, T.; Ji, W.; Sun, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Yang, Q. The NIEER AVHRR snow cover extent product over China - A long-term daily snow record for regional climate research. Earth System Science Data 2021, 13, 4711–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, A.R.; Lucas, R.M. Multi-spectral classification of snow using NOAA AVHRR imagery. International Journal of Remote Sensing 1989, 10, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, S.R.; McNamara, D.; Ramsay, B.H.; Baldwin, T.; Kasheta, T. Enhancements to, and forthcoming developments in the Interactive Multisensor Snow and Ice Mapping System (IMS). Hydrological Processes: An International Journal 2007, 21, 1576–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, M.; Sugiura, K.; Kobayashi, K.; Aoki, T.; Tanikawa, T.; Kuchiki, K.; Niwano, M.; Enomoto, H. A 38-year (1978–2015) Northern Hemisphere daily snow cover extent product derived using consistent objective criteria from satellite-borne optical sensors. Remote Sensing of Environment 2017, 191, 402–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Feng, Q.; Liang, T. Impact of climate and elevation on snow cover using integrated remote sensing snow products in Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing of Environment 2017, 190, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsler, F.; Jonas, T.; Riffler, M.; Musial, J.P.; Wunderle, S. A satellite-based snow cover climatology (1985–2011) for the European Alps derived from AVHRR data. The Cryosphere 2014, 8, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hüsler, F.; Jonas, T.; Wunderle, S.; Albrecht, S. Validation of a modified snow cover retrieval algorithm from historical 1-km AVHRR data over the European Alps. Remote Sensing of Environment 2012, 121, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Shen, H.; Li, X.; Guan, X. A two-stage fusion framework to generate a spatio–temporally continuous MODIS NDSI product over the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.E.J.; Chang, A.T.C. Development of a passive microwave global snow depth retrieval algorithm for Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) and Advanced Microwave Scanning Radiometer-EOS (AMSR-E) data. Radio Science 2003, 38, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlopenkov, K. V.; Trishchenko, A.P. SPARC: New cloud, snow, and cloud shadow detection scheme for historical 1-km AVHHR data over Canada. Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology 2007, 24, 322–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.G.; Barnett, A.C. Validation of daily MODIS snow cover maps of the Upper Rio Grande River Basin for the 2000–2001 snow year. Remote Sensing of Environment 2003, 86, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S. V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Arsenault, K.R.; Getirana, A.; Mocko, D.; Liu, Y. Quantifying the added value of snow cover area observations in passive microwave snow depth data assimilation. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2015, 16, 1736–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Letu, H.; Shang, H.; Shi, J. Cloud cover over the Tibetan Plateau and eastern China: a comparison of ERA5 and ERA Interim with satellite observations. Climate Dynamics 2020, 54, 2941–2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Pan, J.; Xiong, C.; Jiang, L.; Shi, J. Snow depth and snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau observed from space in against ERA5: matters of scale. Climate Dynamics 2023, 60, 1523–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchane, A.; Jarlan, L.; Hanich, L.; Boudhar, A.; Gascoin, S.; Tavernier, A.; Filali, N.; Le Page, M.; Hagolle, O.; Berjamy, B. (). Assessment of daily MODIS snow cover products to monitor snow cover dynamics over the Moroccan Atlas mountain range. Remote Sensing of Environment 2015, 160, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsämäki, S.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Pulliainen, J.; Sucksdorff, Y. Improved linear interpolation method for the estimation of snow-covered area from optical data. Remote Sensing of Environment 2002, 82, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsolini, Y.; Wegmann, M.; Dutra, E.; Liu, B.; Balsamo, G.; Yang, K.; de Rosnay, P.; Zhu, C.; Wang, W.; Senan, R. (). Evaluation of snow depth and snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau in global reanalyses using in situ and satellite remote sensing observations. The Cryosphere 2019, 13, 2221–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Jiang, L.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, G.; Cui, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, J. Retrieval of Fractional Snow Cover over High Mountain Asia Using 1 km and 5 km AVHRR/2 with Simulated Mid-Infrared Reflective Band. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Blöschl, G. Validation of MODIS snow cover images over Austria. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2006, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajka, J.; Dadson, S.; Lafon, T.; Essery, R. Evaluation of snow cover and depth simulated by a land surface model using detailed regional snow observations from Austria. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Z.; Xu, L.; Salomonson, V.V. MODIS/Terra observed seasonal variations of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau. Geophysical Research Letters 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Li, W.; Wang, X.; Shang, L.; Song, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Y. Satellite-observed solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence reveals higher sensitivity of alpine ecosystems to snow cover on the Tibetan Plateau. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology 2019, 271, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, B.H. The interactive multisensor snow and ice mapping system. Hydrological Processes 1998, 12, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranzi, R.; Grossi, G.; Bacchi, B. Ten years of monitoring areal snowpack in the Southern Alps using NOAA-AVHRR imagery, ground measurements and hydrological data. Hydrological Processes 1999, 13, 2079–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. MODIS snow products collection 6 user guide. National Snow and Ice Data Center: Boulder, CO, USA, 2015; p. 66.
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. Overview of NASA’s MODIS and visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) snow-cover earth system data records. Earth System Science Data 2017, 9, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, G.A.; Hall, D.K.; Román, M.O. Overview of NASA’s MODIS and Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) snow-cover Earth System Data Records. Earth System Science Data 2017, 9, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittger, K.; Painter, T.H.; Dozier, J. Assessment of methods for mapping snow cover from MODIS. Advances in Water Resources 2013, 51, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Dewey, K.F.; Heim, R.R. Global snow cover monitoring: an update. Bulletin - American Meteorological Society 1993, 74, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreve, C.M.; Okin, G.S.; Painter, T.H. Indices for estimating fractional snow cover in the western Tibetan Plateau. Journal of Glaciology 2009, 55, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, A.; Fernandes, R.; Brown, R.; Romanov, P.; Park, W. Validation of VEGETATION, MODIS, and GOES+ SSM/I snow-cover products over Canada based on surface snow depth observations. Hydrological Processes 2004, 18, 1089–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, J.J.; Stitt, J.R.; Sienko, M. Improved estimates of the areal extent of snow cover from AVHRR data. Journal of Hydrology 1998, 204, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solberg, R.; Wangensteen, B.; Amlien, J.; Koren, H.; Metsämäki, S.; Nagler, T.; Luojus, K.; Pulliainen, J. A new global snow extent product. Proceedings of ESA Living Planet Symposium, ESA Special Publication SP-686, Bergen, Norway, 26 June–02 July 2010.
- Stroeve, J.; Box, J.E.; Gao, F.; Liang, S.; Nolin, A.; Schaaf, C. Accuracy assessment of the MODIS 16-day albedo product for snow: comparisons with Greenland in situ measurements. Remote Sensing of Environment 2005, 94, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Déry, S.J.; Jackson, P.L. Interrelationships between MODIS/Terra remotely sensed snow cover and the hydrometeorology of the Quesnel River Basin, British Columbia, Canada. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences 2009, 13, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veitinger, J.; Sovilla, B.; Purves, R.S. Influence of snow depth distribution on surface roughness in alpine terrain: a multi-scale approach. The Cryosphere 2014, 8, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.; Justice, C.; Csiszar, I.; Eidenshink, J.; Myneni, R.; Baret, F.; Masuoka, E.; Wolfe, R.; Claverie, M. NOAA Climate Data Record (CDR) of AVHRR Surface Reflectance, Version 5. NOAA National Centers for Environmental Information: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Wang, L.; Sharp, M.; Brown, R.; Derksen, C.; Rivard, B. Evaluation of spring snow covered area depletion in the Canadian Arctic from NOAA snow charts. Remote Sensing of Environment 2005, 95, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Yang, Q.; Wang, B.; Ma, Y.; Shen, M. Complex responses of spring alpine vegetation phenology to snow cover dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau, China. Science of the Total Environment 2017, 593, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xie, H.; Liang, T. Evaluation of MODIS snow cover and cloud mask and its application in Northern Xinjiang, China. Remote Sensing of Environment 2008, 112, 1497–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, L.; Huang, H.; Liu, K. Mapping snow cover variations using a MODIS daily cloud-free snow cover product in northeast China. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing 2014, 8, 84681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Naegeli, K.; Premier, V.; Marin, C.; Ma, D.; Wang, J.; Wunderle, S. Evaluation of snow extent time series derived from Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer global area coverage data (1982–2018) in the Hindu Kush Himalayas. The Cryosphere 2021, 15, 4261–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Wu, T.; Shen, L.; Pepin, N.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Kang, S.; AghaKouchak, A. Review of snow cover variation over the Tibetan Plateau and its influence on the broad climate system. Earth-Science Reviews 2020, 201, 103043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Hao, X.; He, D.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Wang, X. The Relationship between the Temporal and Spatial Changes of Snow Cover and Climate and Vegetation in Northern Xinjiang from 1980 to 2019. Remote Sensing Technology and Application 2022, 36, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Aizen, E.; Aizen, V. Deriving long term snow cover extent dataset from AVHRR and MODIS data: Central Asia case study. Remote Sensing of Environment 2013, 136, 146–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Cao, S.; Shang, G.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, C.; Yang, H.; Xie, B. Subpixel Snow Mapping Using Daily AVHRR/2 Data over Qinghai–Tibet Plateau. Remote Sensing 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Study area and test areas for regression.
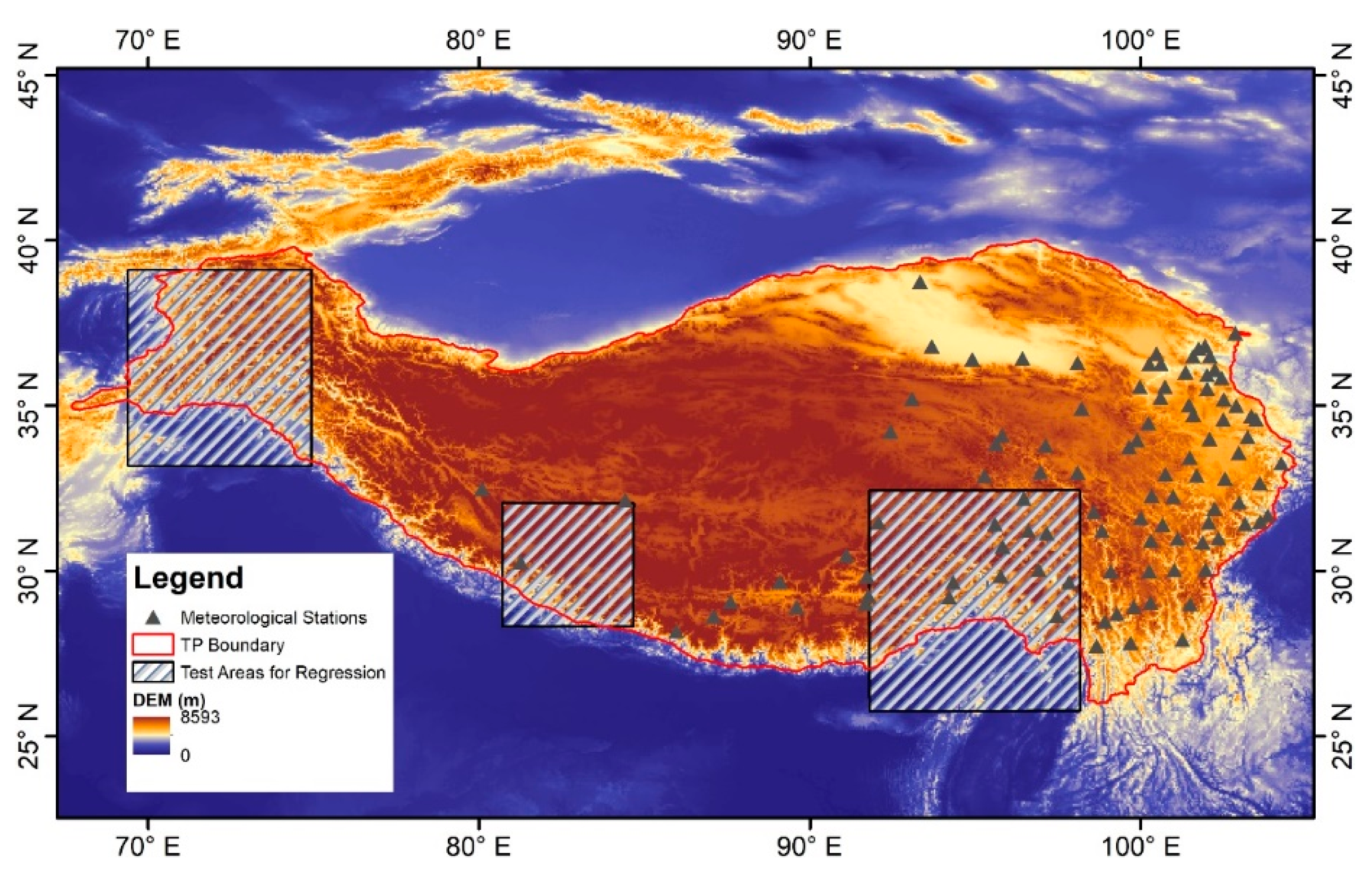
Figure 2.
Flowchart of AVHRR-FSC generation and accuracy analysis in this study.
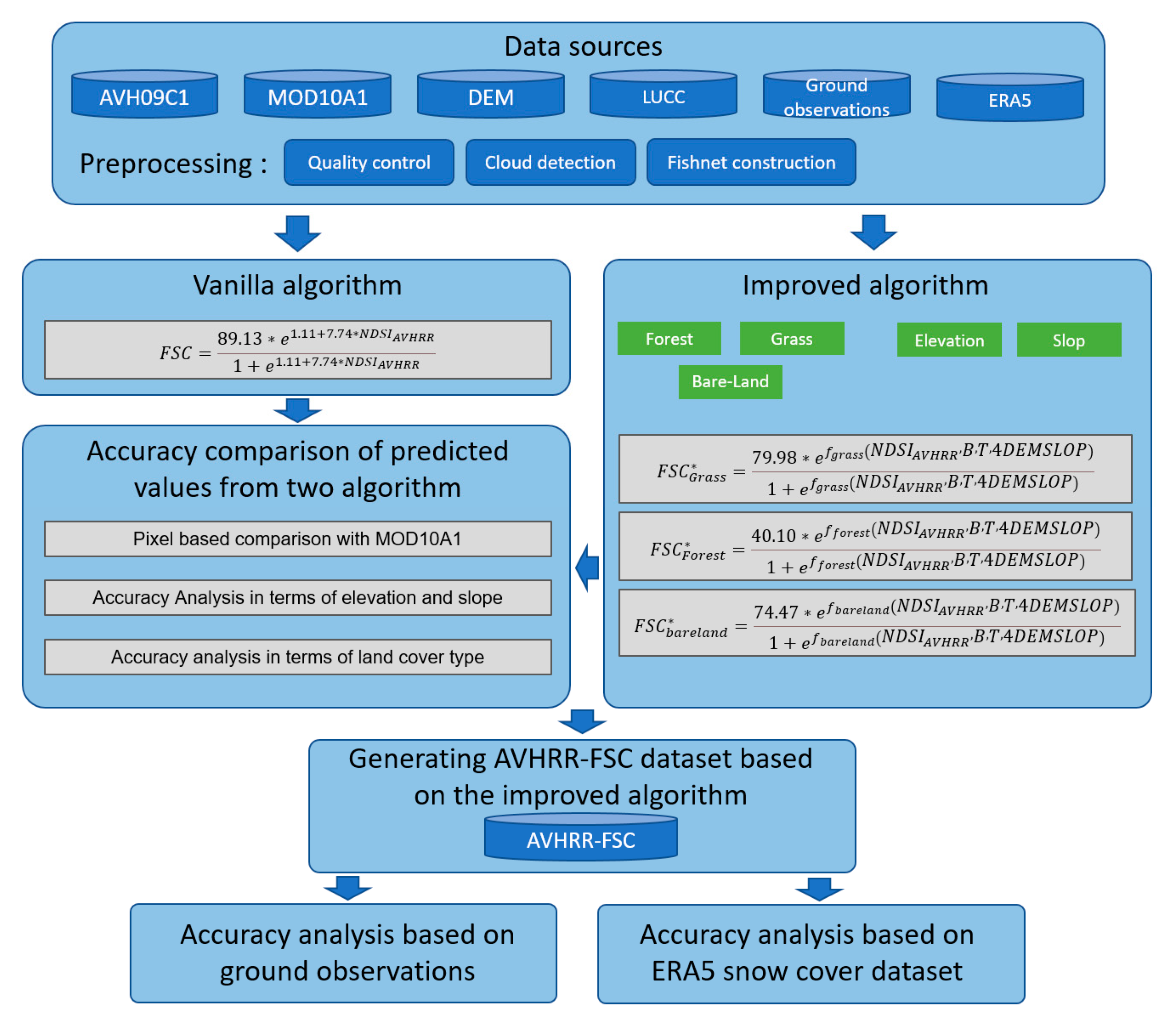
Figure 3.
Linear fitting of SR1, SR2 and NDSIAVHRR with MOD10A1 for training data.
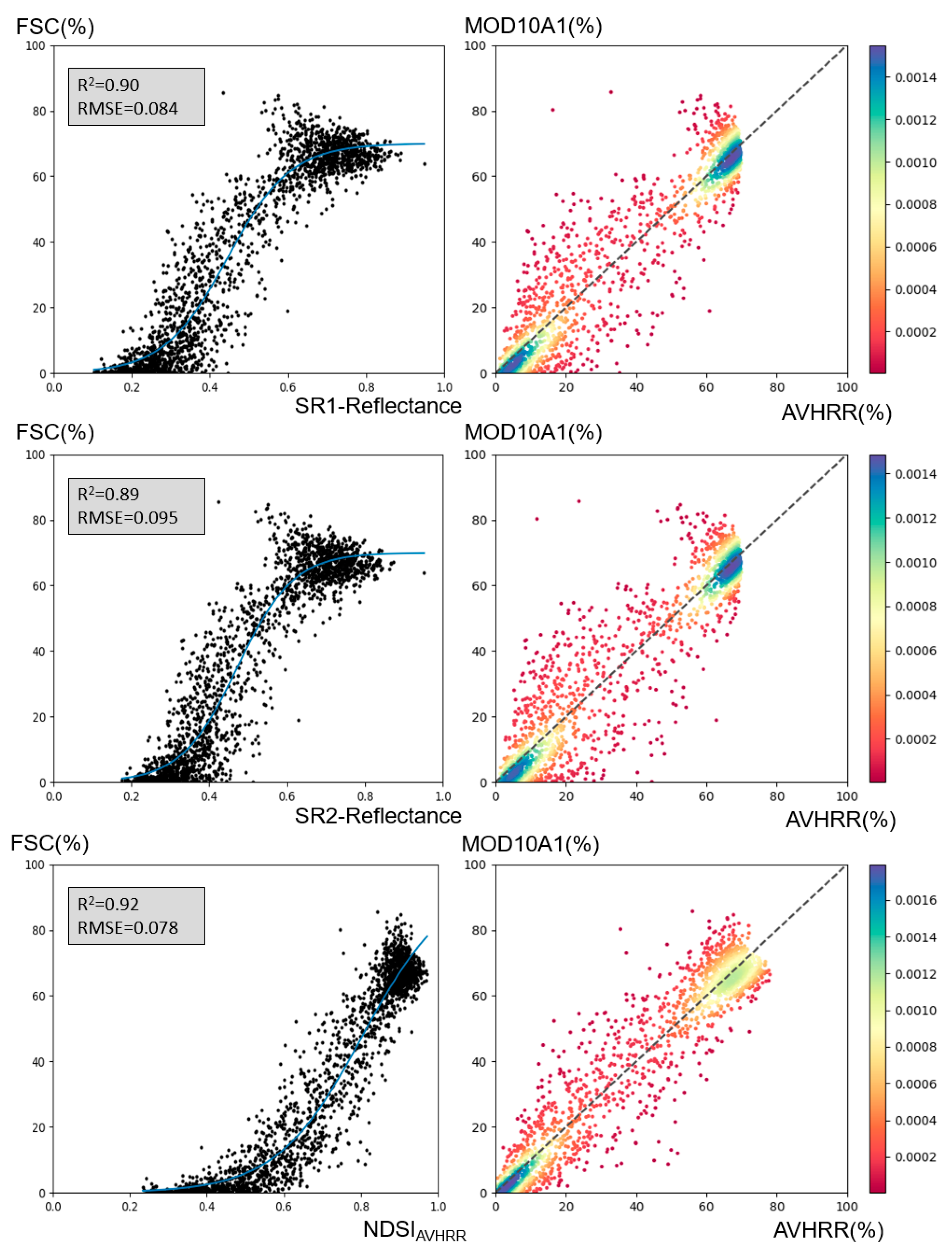
Figure 4.
Scatter density plots for Logistic fitting results after considering elevation, slop, BT4 and comparison of predicted values with MOD10A1. Four subplots were related to uncategorized, grass, forest and bareland for vegetation cover types.
Figure 4.
Scatter density plots for Logistic fitting results after considering elevation, slop, BT4 and comparison of predicted values with MOD10A1. Four subplots were related to uncategorized, grass, forest and bareland for vegetation cover types.
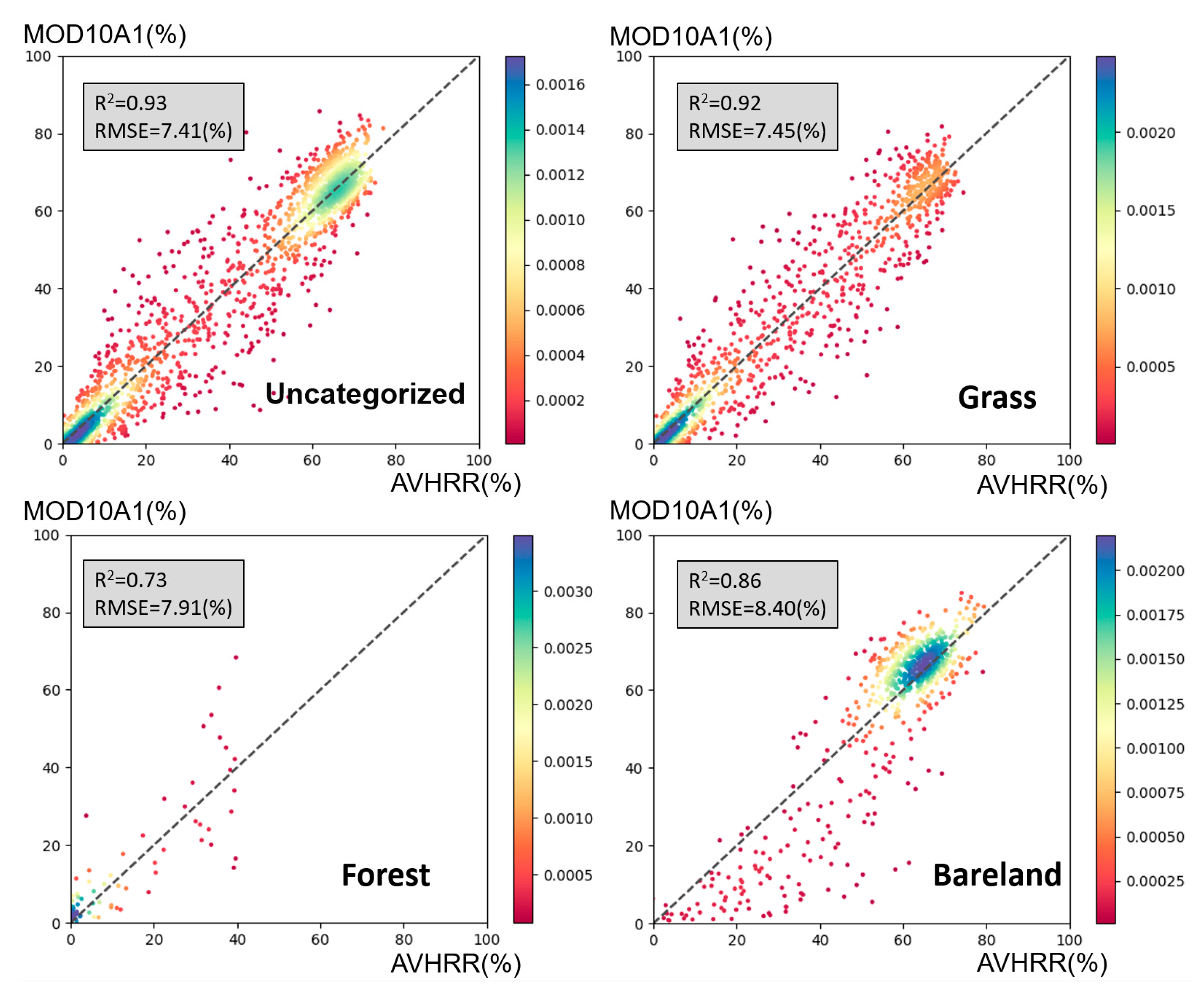
Figure 5.
Comparison of AVHRR_FSC(the vanilla algorithm) and MODIS_FSC mapping, AVHRR_FSC & MODIS_FSC stand for total snow cover area, RMSE is pixel-based calculated.
Figure 5.
Comparison of AVHRR_FSC(the vanilla algorithm) and MODIS_FSC mapping, AVHRR_FSC & MODIS_FSC stand for total snow cover area, RMSE is pixel-based calculated.
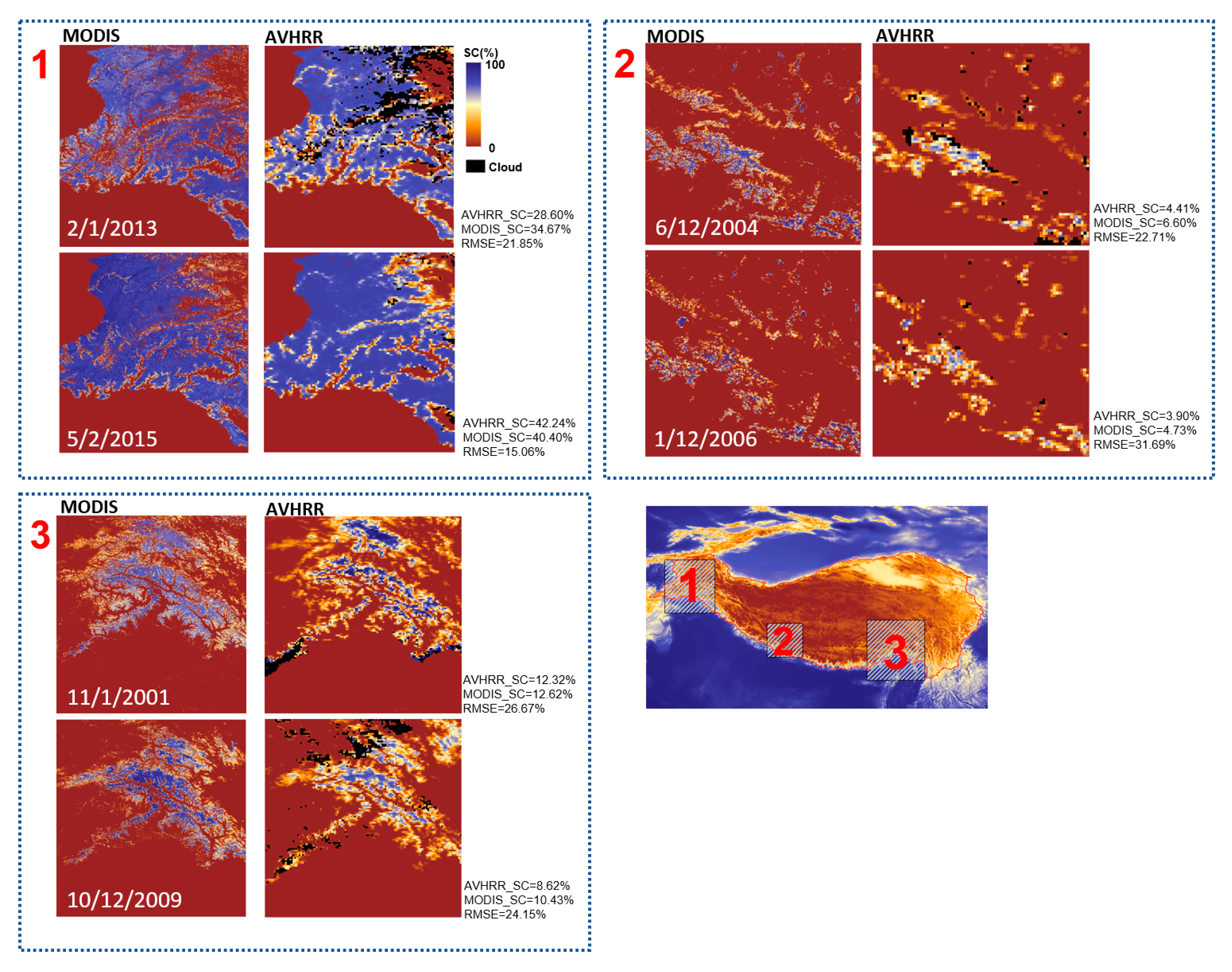
Figure 6.
Comparison of AVHRR_FSC*(the improved algorithm) and MODIS_FSC mapping, AVHRR_FSC* & MODIS_FSC stand for total snow cover area, RMSE is pixel-based calculated.
Figure 6.
Comparison of AVHRR_FSC*(the improved algorithm) and MODIS_FSC mapping, AVHRR_FSC* & MODIS_FSC stand for total snow cover area, RMSE is pixel-based calculated.
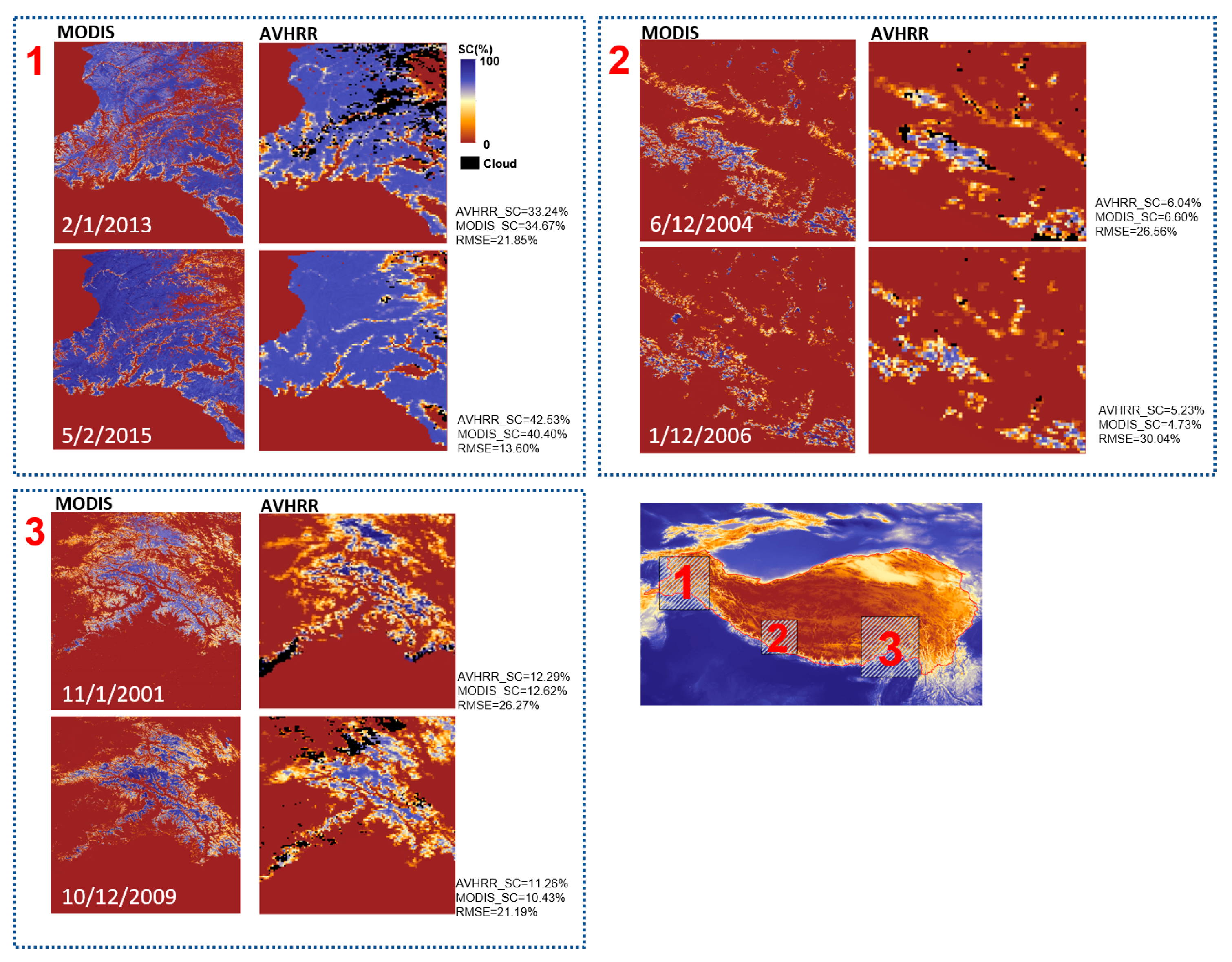
Figure 7.
Trends in RMSE of AVHRR FSC inversion results with elevation and slope variation, using MOD10A1 as the ground truth. RMSE & AVHRR_FSC stand for the vanilla algorithm,RMSE* & AVHRR_FSC* stand for the improved algorithm.
Figure 7.
Trends in RMSE of AVHRR FSC inversion results with elevation and slope variation, using MOD10A1 as the ground truth. RMSE & AVHRR_FSC stand for the vanilla algorithm,RMSE* & AVHRR_FSC* stand for the improved algorithm.
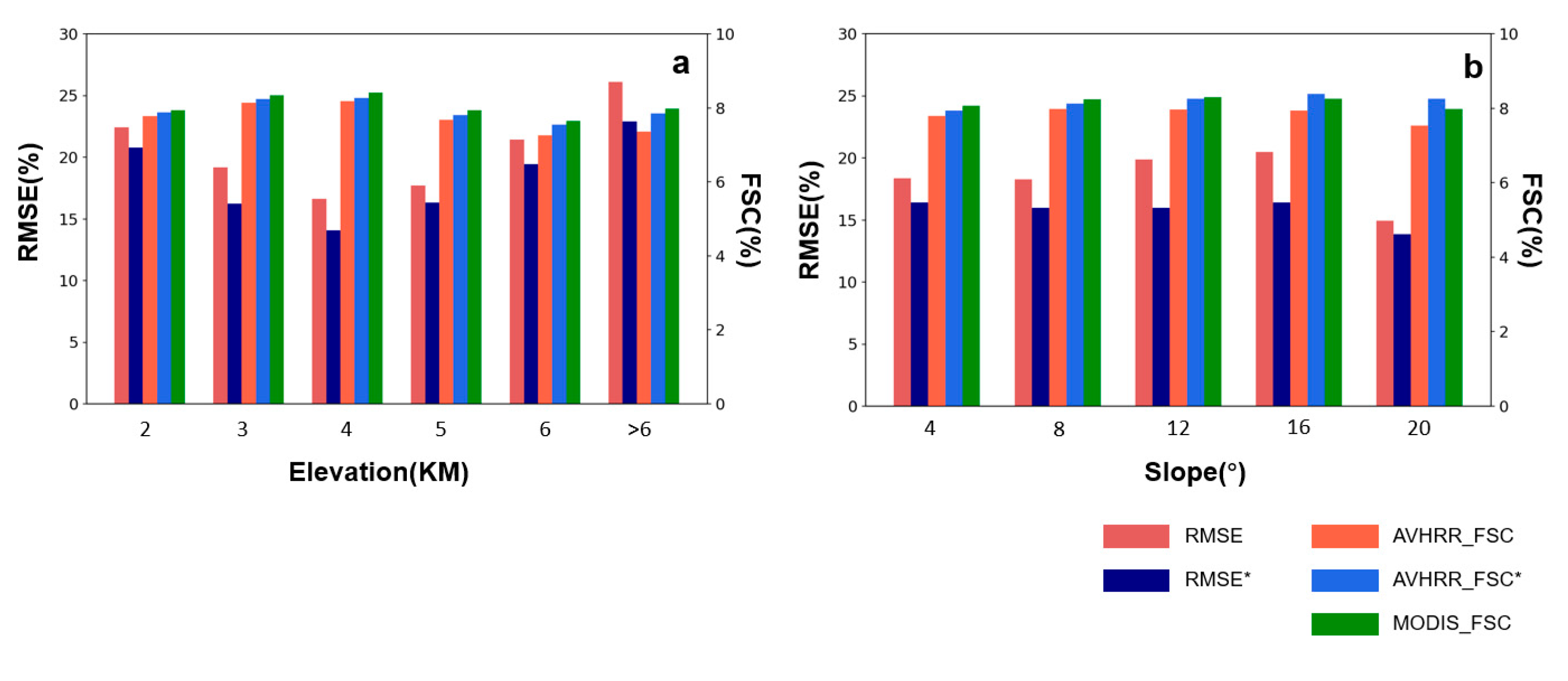
Figure 8.
Trends in RMSE of AVHRR FSC inversion results with different vegetation types, using MOD10A1 as the ground truth. RMSE & AVHRR_FSC stand for the vanilla algorithm,RMSE* & AVHRR_FSC* stand for improved algorithm.
Figure 8.
Trends in RMSE of AVHRR FSC inversion results with different vegetation types, using MOD10A1 as the ground truth. RMSE & AVHRR_FSC stand for the vanilla algorithm,RMSE* & AVHRR_FSC* stand for improved algorithm.
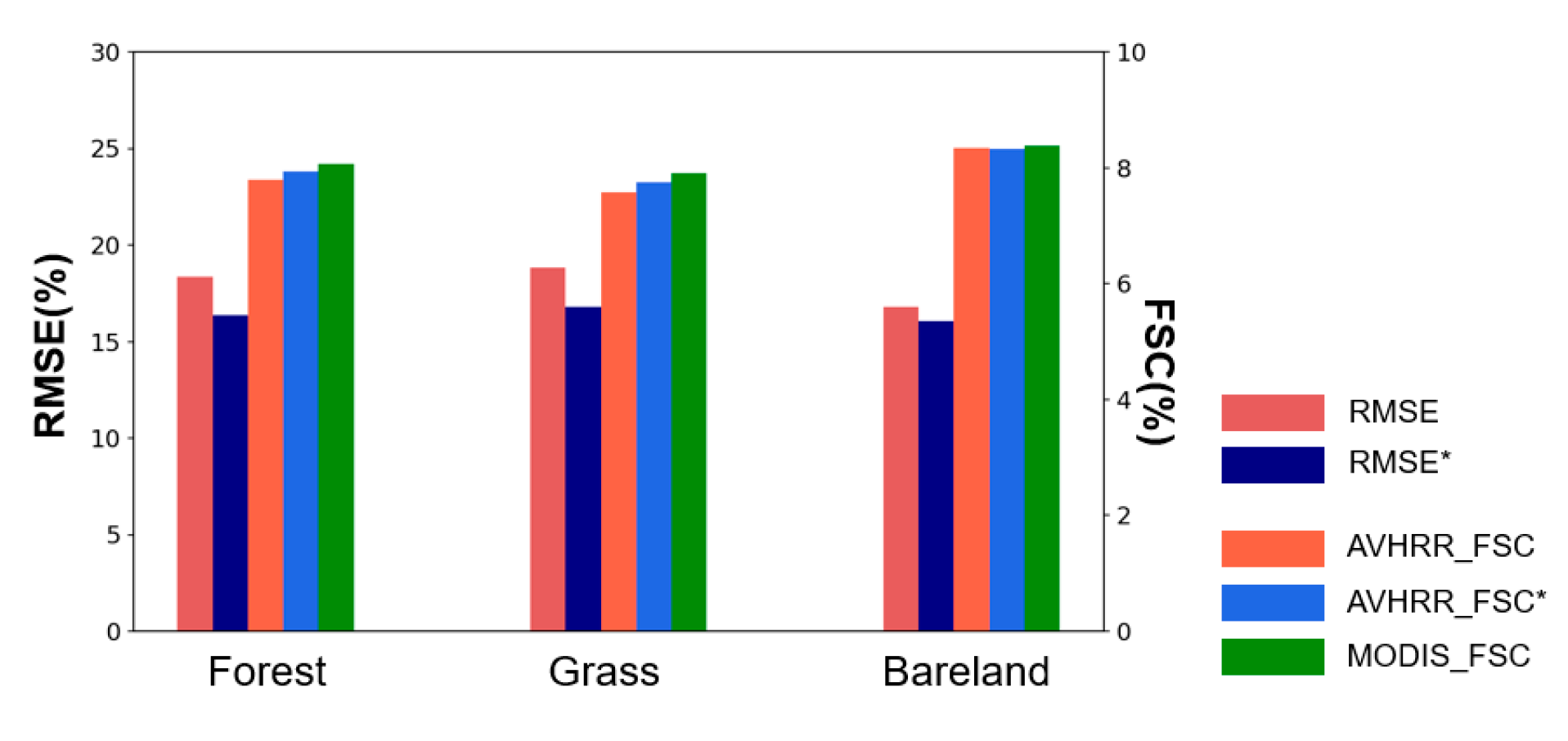
Figure 9.
Snow cover pixel count of AVHRR-FSC* compared to ERA5. AVHRR-FSC* is the result of the improved algorithm.
Figure 9.
Snow cover pixel count of AVHRR-FSC* compared to ERA5. AVHRR-FSC* is the result of the improved algorithm.
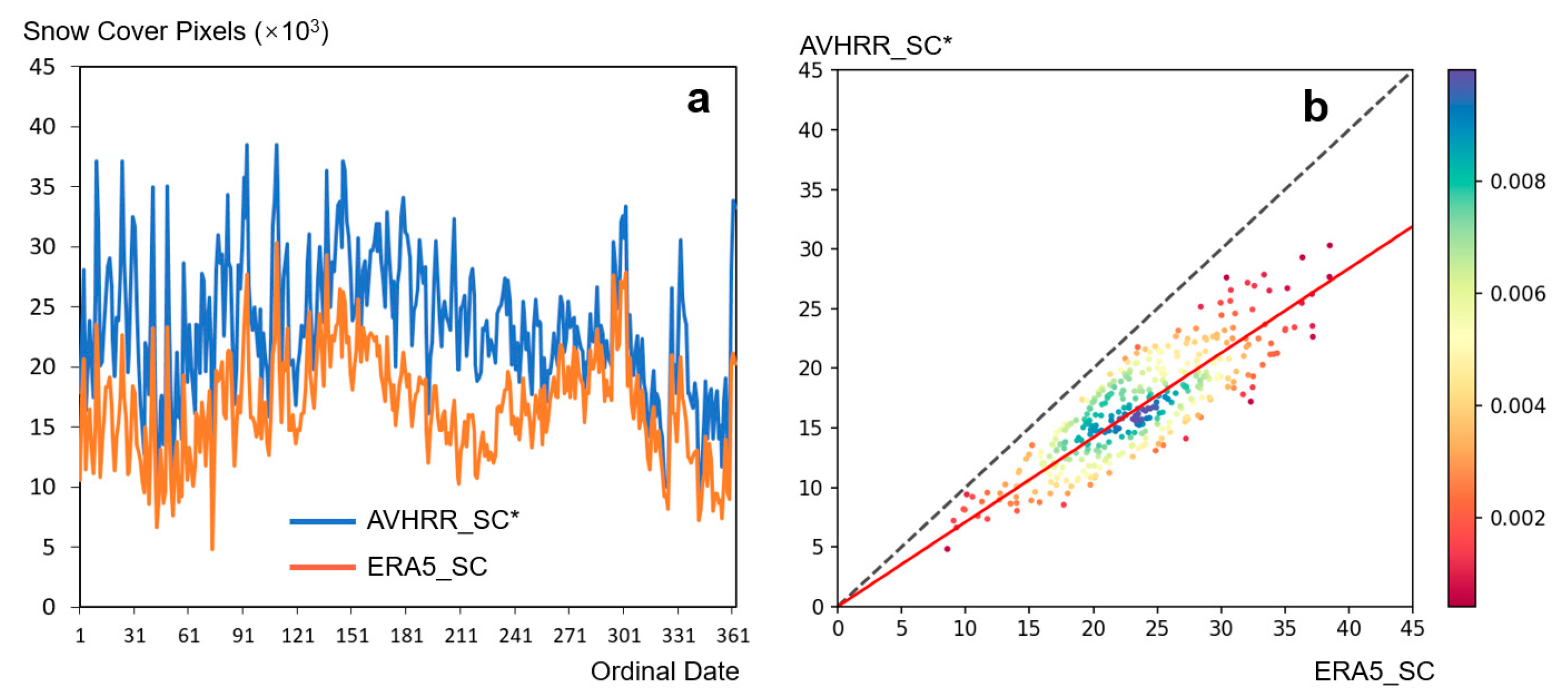
Table 1.
The band information of AVH09C1.
| Band | Abbreviation | Wavelength(μm) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SREFL_CH1 | SR1 | 0.58~0.68 | Surface reflectance at 0.64μm |
| SREFL_CH2 | SR2 | 0.725~1.00 | Surface reflectance at 0.86μm |
| SREFL_CH3 | SR3 | 3.55~3.93 | Surface reflectance at 3.75μm |
| BT_CH3 | BT3 | 3.55~3.93 | Brightness temperature at 3.75μm |
| BT_CH4 | BT4 | 10.30~11.30 | Brightness temperature at 11.0μm |
| BT_CH5 | BT5 | 11.50~12.50 | Brightness temperature at 12.0μm |
Table 2.
Data sources and discreptions.
| Dataset | Date | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AVHRR | Year:1982~2020 | 0.05° | Daily | Surface reflectance: AVH09C1 |
| MODIS | Training: 13/2/2003 6/1/2004 28/3/2007 5/1/2010 14/1/2010 16/3/2011 |
500m | Daily | Fractional Snow Cover: MOD10A1 |
| Predicting: 11/1/2001 1/12/2004 1/12/2006 10/12/2009 2/1/2013 5/2/2015 | ||||
| DEM/Slop | \ | 30m Resampled to 0.05° |
\ | |
| LUCC | Year:2000~2020 | 0.05° | Yearly | Land Cover Type: MCD12C1 |
| Ground snow depth records | Year:2000~2012 | Points | Daily | Depth greater than 1cm is considered valid. |
| Reanalysis dataset | Year:2012 | 0.05° | daily | ERA5 snow cover dataset |
Table 3.
Cloud detection tests and corresponding thresholds.
| Target | Switch | DEM | SR1 | SR2 | SR3 | SR1-SR2 | NDVI | NDSI | BT4(K) | BT3-BT4 | BT3-BT4 | BT4-BT5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEM>300m&BT11<260K | On | <3000 | ≥240 | >14.5 | >19.5 | |||||||
| On | ≥300 | ≥240 | >15.5 | >20 | ||||||||
| On | <240 | >21.5 | >31 | |||||||||
| On | >0.1 | >-0.02 | <0.88 | >25.5 | >33.5 | |||||||
| Off | >0.5 | >288 | ||||||||||
| Off | >310 | |||||||||||
| DEM<300m&BT11≥260K | On | <260 | >14 | >16 | ||||||||
| On | >-0.02 | <310 | >10.5 | >16.5 | ||||||||
| On | >0.3 | >-0.02 | <293 | >11.5 | >17.5 | |||||||
| On | >0.4 | >-0.03 | <293 | >11.5 | >18 | >-1 | ||||||
| On | >0.4 | <278 | >11.5 | >19.5 | >-1 | |||||||
| On | >0.3 | >0.2 | <263 | >11.5 | >18 | |||||||
| Off | >0.5 | >288 | ||||||||||
| Off | >310 | |||||||||||
| Off | >1000 | <0.4 | <-0.04 | >275 |
Table 4.
The validation results of the AVHRR_FSC* based on ground snow-depth measurements.
| Year | AVHRRsnow~Stationsnow | AVHRRnon-snow~Stationsnow | AVHRRsnow~Stationnon-snow | AVHRRnon-now~Stationnon-snow | K | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2007 | 17183 | 423 | 15169 | 0.07 | 0.83 |
| 2001 | 1615 | 17730 | 350 | 15276 | 0.06 | 0.82 |
| 2002 | 1748 | 17749 | 286 | 15010 | 0.06 | 0.86 |
| 2003 | 1252 | 16970 | 276 | 12265 | 0.04 | 0.82 |
| 2004 | 1532 | 18666 | 329 | 13521 | 0.04 | 0.82 |
| 2005 | 2324 | 18896 | 392 | 13261 | 0.07 | 0.86 |
| 2006 | 2038 | 18702 | 579 | 13673 | 0.05 | 0.79 |
| 2007 | 1447 | 17211 | 334 | 16267 | 0.05 | 0.81 |
| 2008 | 2412 | 18060 | 287 | 14598 | 0.08 | 0.90 |
| 2009 | 1687 | 17178 | 344 | 16115 | 0.06 | 0.83 |
| 2010 | 1079 | 17772 | 346 | 16367 | 0.03 | 0.76 |
| 2011 | 2123 | 17394 | 766 | 15786 | 0.06 | 0.73 |
| 2012 | 3737 | 16459 | 1943 | 13810 | 0.06 | 0.66 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated






