Submitted:
28 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Model
- LANDSCAPE INITIALIZATION
- 2.
- RRN INIZIALIZATION
- 3.
- COLONY EVOLUTION
- the amount of energy distributed in the landscape, being larger for larger energy, thus producing an autocatalytic effect;
- the difference of energy between the considered agents, being larger for smaller differences, thus allowing a better distribution of activated links among nodes similar in energy;
- the productivity of the agent, which represents the canalization of resources, in offspring or public goods production, thus producing less active links for higher productivity .
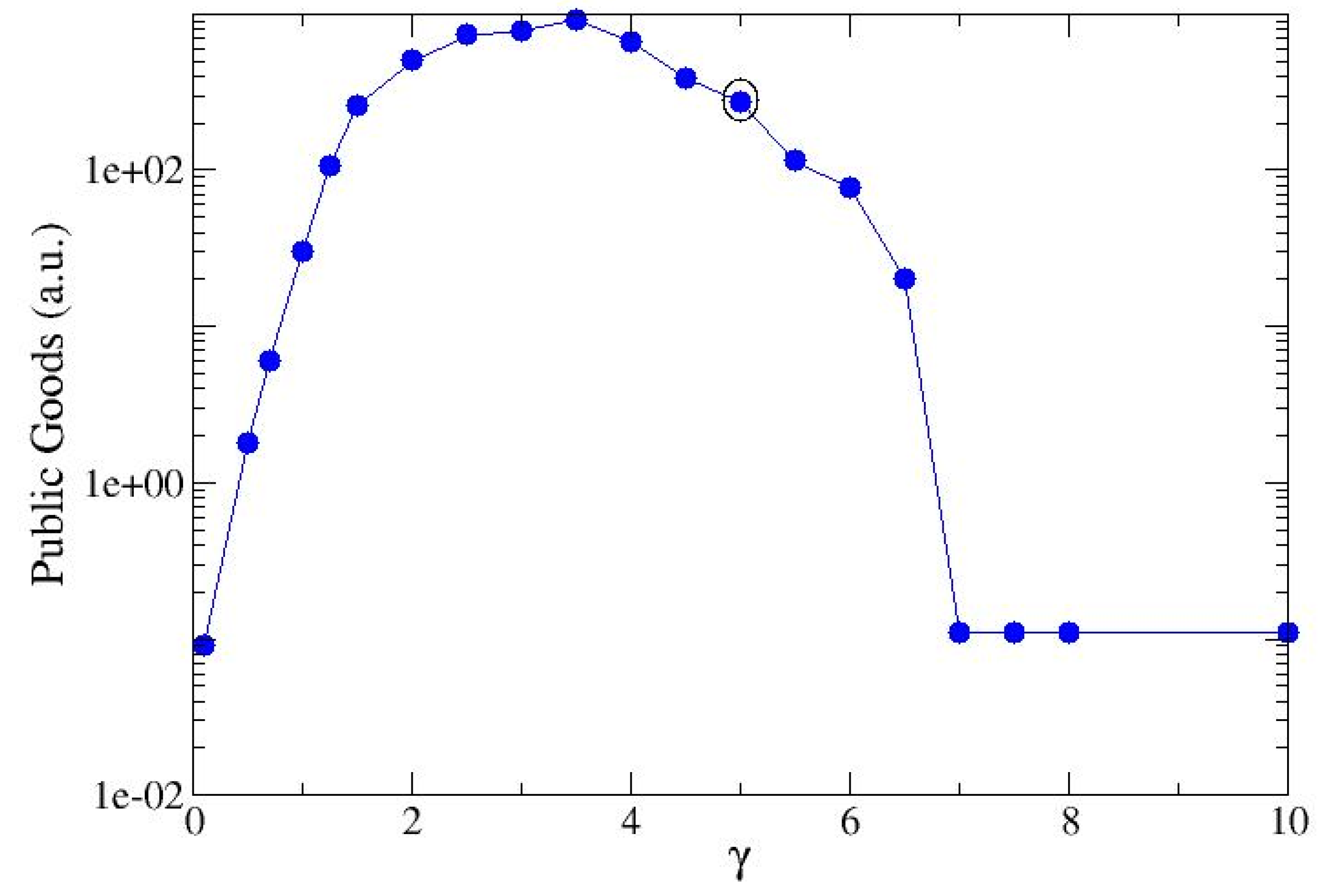
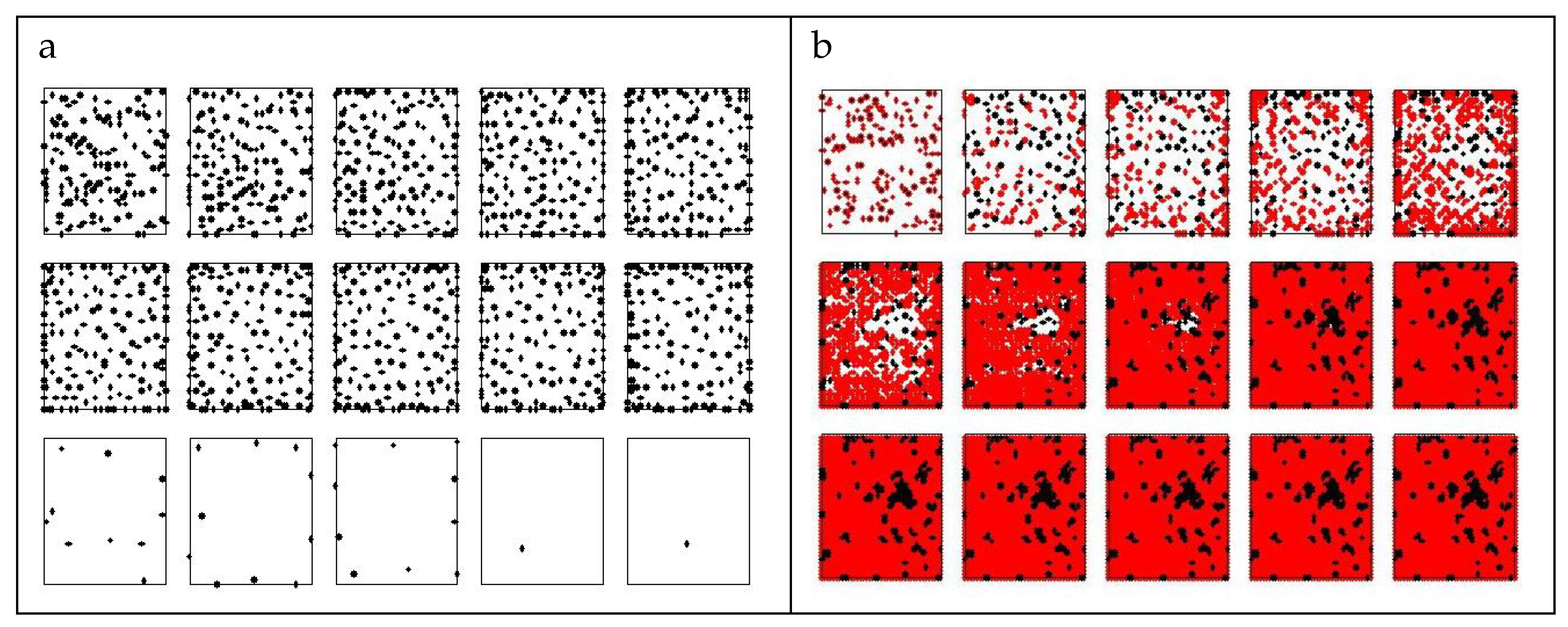
3. Results
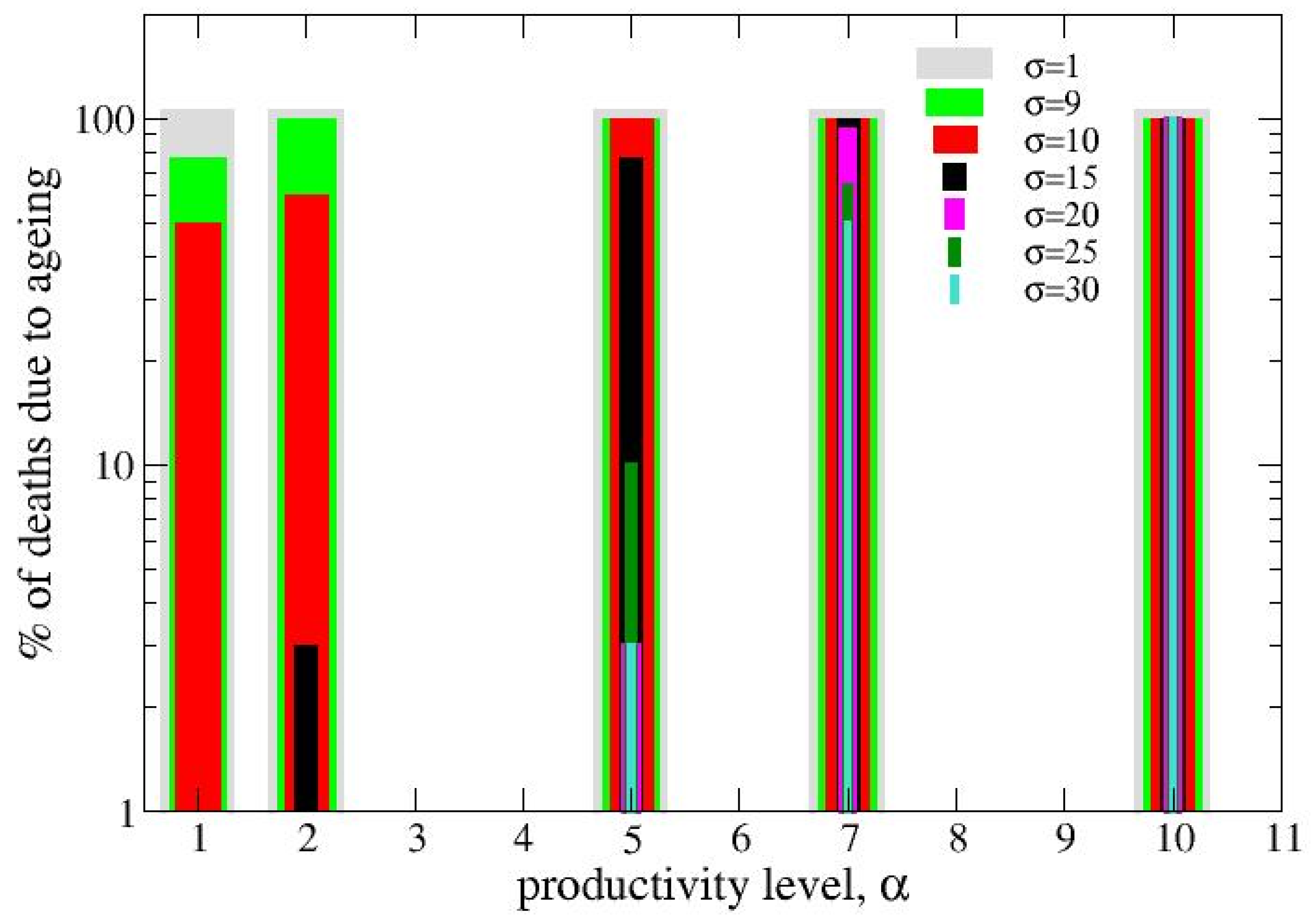
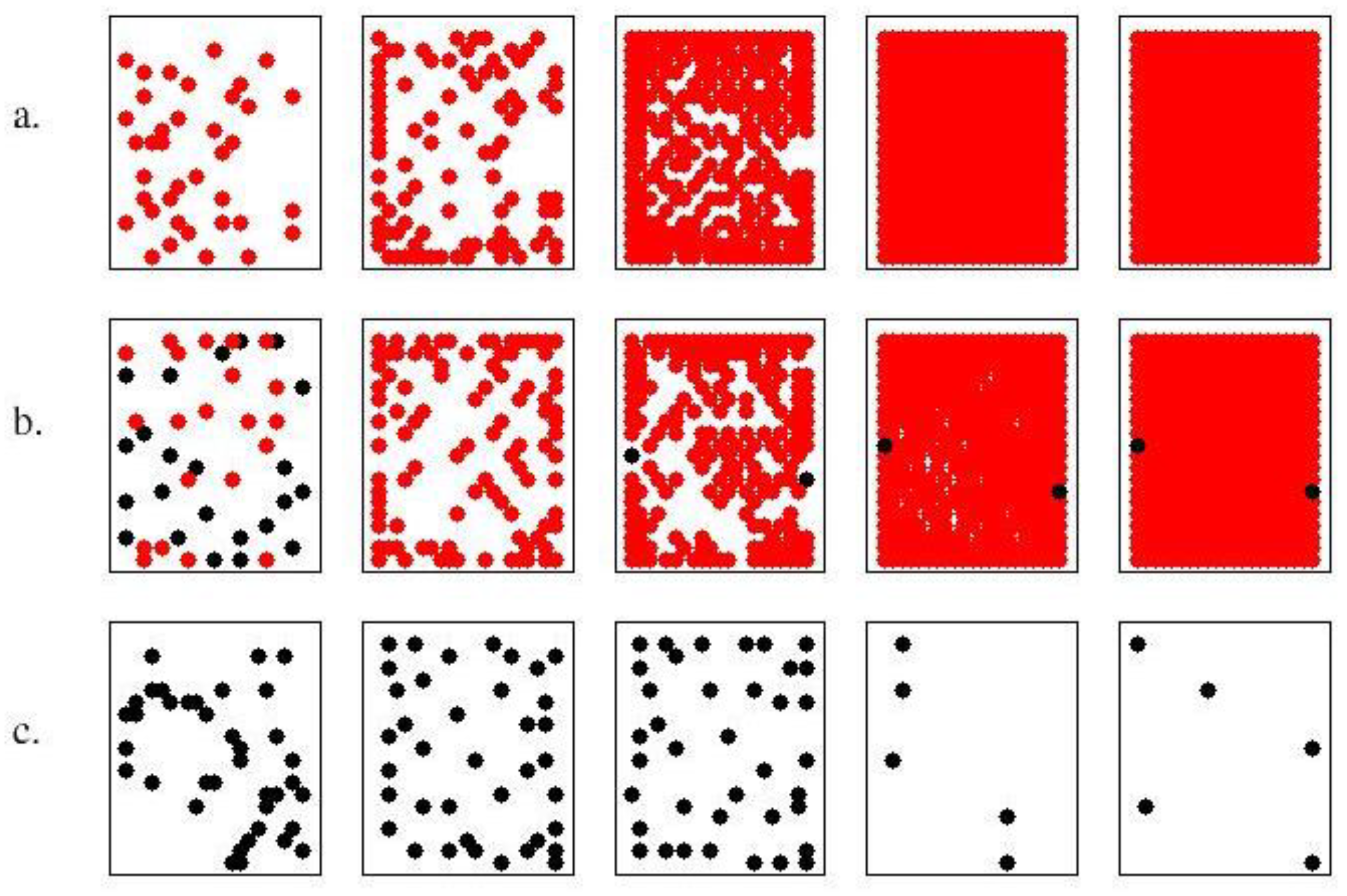
3.1. Single-Strain Colonies (SSC): Investigation on the Conditions for Reproduction
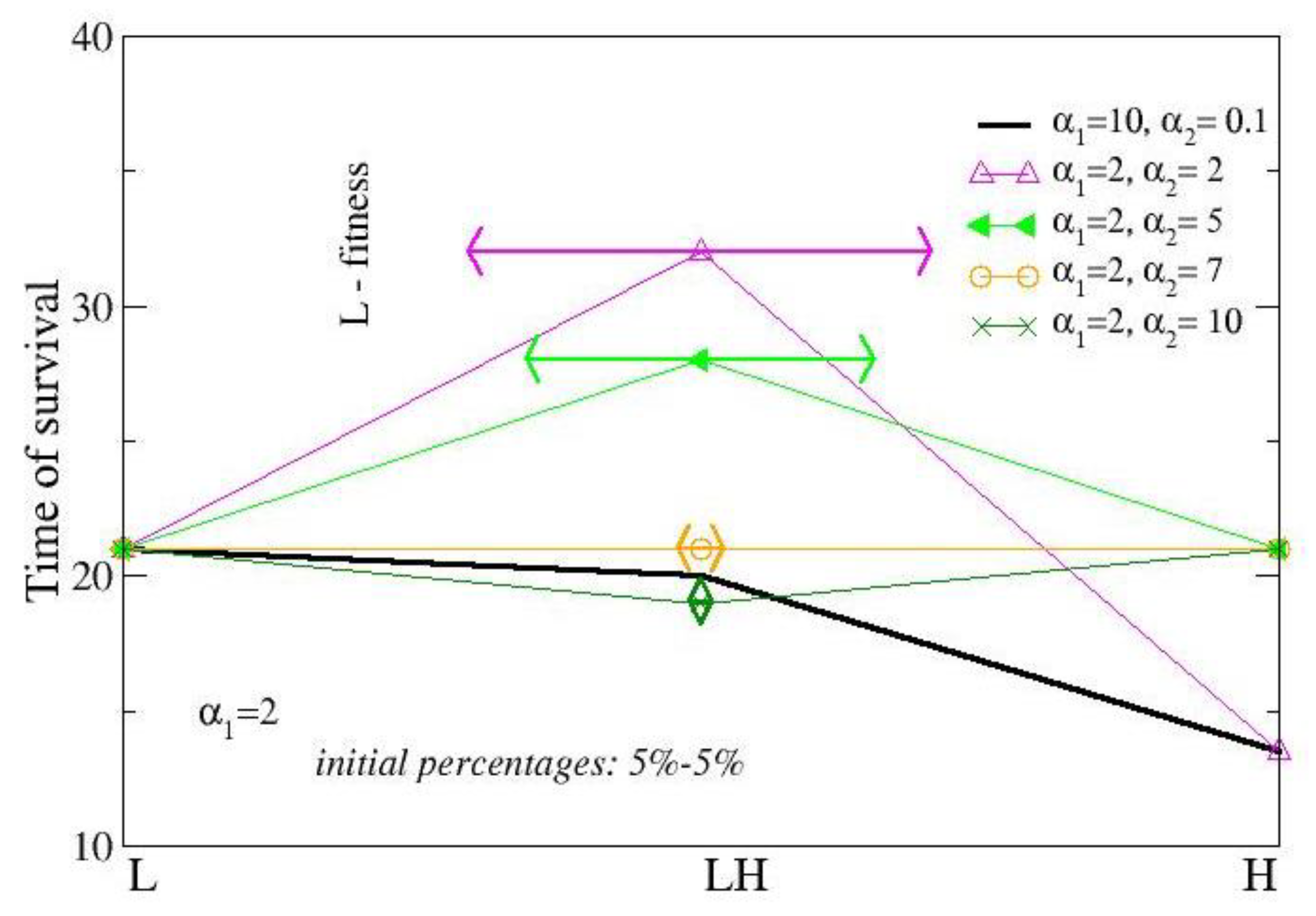
3.2. Two-Strain Colonies
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, K.; Zang, X.-H. Quorum quenching agents: resources for antivirulence therapy. Mar. Drugs, 2014, 12.6: 3245-3282.
- Appelbaum, P. C. 2012 and beyond: potential for the start of a second pre-antibiotic era?. J. Antimicrob. Chemothera., 2012, 67.9: 2062-2068. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen,T. H.; Goycoolea, F. M. Chitosan/Cyclodextrin/TPP nanoparticles loaded with quercetin as novel bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors. Molecules, 2017, 22(11), 1975.
- Nguyen, H. T.; Hensel, A.; Goycoolea, F. M. Chitosan/cyclodextrin surface-adsorbed naringenin-loaded nanocapsules enhance bacterial quorum quenching and anti-biofilm activities. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2022, 211, 112281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfinito, E.; Barra, A.; Beccaria, M., Fachechi, A.; Macorini, G. An evolutionary game model for behavioral gambit of loyalists: Global awareness and risk-aversion. Europhys. Lett., 2018, 121.3: 38001. [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. M. The theory of games and the evolution of animal conflicts. J. Theor. Biol. 1974, 47(1), 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weibull, J. W. Evolutionary game theory. MIT press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, USA, 1997.
- Parsek, M. R.; Greenberg, E. P. (2005). Sociomicrobiology: the connections between quorum sensing and biofilms. Trends Microbiol,2005,13(1), 27-33. [CrossRef]
- Henke, J. M.; Bassler, B.L. Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in Vibrio harveyi,J. Bacteriol.,2004,186 (20), 6902-6914. [CrossRef]
- Miller, M. B.; Bassler, B. L. Quorum sensing in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2001, 55(1), 165–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornforth, D. M; Foster, K. R. Competition sensing: the social side of bacterial stress responses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2013, 11(4), 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruger, E. L.; Snyder, D. J.; Cooper, V. S.; Waters, C. M. Quorum sensing provides a molecular mechanism for evolution to tune and maintain investment in cooperation. The ISME Journal, 2021, 15(4), 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruger, E. L.; Waters, C. M. Maximizing growth yield and dispersal via quorum sensing promotes cooperation in Vibrio bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. , 2018, 84(14), e00402-18. [CrossRef]
- Bruger, E. L.; Waters, C. M. Bacterial quorum sensing stabilizes cooperation by optimizing growth strategies. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016; 82.22, 6498–6506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, A. A.; Chugani, S.; Greenberg, E. P. Bacterial quorum sensing and metabolic incentives to cooperate. Science, 2012, 338(6104), 264-266. [CrossRef]
- Hibbing, M. E.; Fuqua, C.; Parsek, M. R.; Peterson, S. B. Bacterial competition: surviving and thriving in the microbial jungle. Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 2010 , 8(1), 15-25. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Rattray, J. B.; Thomas, S. A.; Gurney, J.; Brown, S. P. (2020). In silico bacteria evolve robust cooperation via complex quorum-sensing strategies. Scientific reports, 2020, 10(1), 8628. [CrossRef]
- Foster, K. R.; Wenseleers, T. A general model for the evolution of mutualisms. Journal of evolutionary biology, 2006, 19(4), 1283-1293. [CrossRef]
- Stone, L. The stability of mutualism. Nature communications, 2020, 11(1), 2648. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, C.; Zhang, H. Mutualism between antagonists: its ecological and evolutionary implications. Integrative Zoology, 2021, 16(1), 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watkins, E. R.; Maiden, M. C.; Gupta, S. (2016). Metabolic competition as a driver of bacterial population structure. Future Microbiol., 2016, 11(10), 1339-1357. [CrossRef]
- Rosenzweig, M. L. Paradox of enrichment: destabilization of exploitation ecosystems in ecological time. Science, 1971, 171(3969), 385-387. [CrossRef]
- Lempp, M.; Lubrano, P.; Bange, G.; Link, H. Metabolism of non-growing bacteria. Biol. Chem., 2020, 401(12), 1479-1485. [CrossRef]
- Alfinito, E.; Cesaria, M.; Beccaria, M. Did Maxwell dream of electrical bacteria?. Biophysica, 2022, 2(3), 281-291. [CrossRef]
- Alfinito, E.; Beccaria, M.; Cesaria, M. Cooperation in bioluminescence: understanding the role of autoinducers by a stochastic random resistor model. EPJ E, 2023,46(10), 94. [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Parker, M.; Bourret, R. B.; Giddings, M. C. An agent-based model of signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. PloS one, 2010, 5(5), e9454. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rattray, J. B.; Thomas, S. A.; Gurney, J.; Brown, S. P. (2020). In silico bacteria evolve robust cooperation via complex quorum-sensing strategies. Scientific Rep., 2020, 10(1), 8628. [CrossRef]
- Leaman, E. J.; Geuther, B. Q.; Behkam, B. Hybrid centralized/decentralized control of a network of bacteria-based bio-hybrid microrobots. J. Micro-Bio Robot., 2019, 15, 1-12. [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D. ; Aharony,A. Introduction to percolation theory, 2rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca-Raton, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Alfinito, E.; Reggiani, L.; Pousset, J. Proteotronics: Electronic devices based on proteins. In Sensors: Proceedings of the Second National Conference on Sensors, Rome 19-21 February, 2014 (pp. 3-7). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Cataldo, R., Leuzzi, M.; Alfinito, E. Modelling and development of electrical aptasensors: a short review. Chemosensors ,2018, 6(2), 20.
- Alfinito, E.; Beccaria, M.; Fachechi, A.; Macorini, G. Reactive immunization on complex networks. Europhys. Lett., 2017 , 117(1), 18002. [CrossRef]
- Hill,V. A new mathematical treatment of changes of ionic concentration in muscle and nerve under the action of electric currents, with a theory as to their mode of excitation, J. Physiol.1910, 40 (3), 190-224.
- Goutelle, S.; Maurin, M.; Rougier,F.; Barbaut,X.; Bourguignon,L.; Ducher, M; P. Maire,P. The Hill equation: a review of its capabilities in pharmacological modelling, Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol., 2008, 22(6), 633-648 (2008). [CrossRef]
- Dockery, J. D.; Keener, J. P. Mathematical model for quorum sensing in Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Bull. Math. Biol., 2001, 63 (1), 95-116. [CrossRef]
- Ward, J. P. ; King, J. R.; Koerber, A. J. ; Williams, P.; Croft, J. M.; Sockett, R. E. Mathematical modelling of quorum sensing in bacteria, IMA J. Math. Med. Biol., 2001, 18(3), 263-292. [CrossRef]
- Frederick, M. R.; Kuttler, C. ; Hense ,B. A.; Eberl, H. J. , A mathematical model of quorum sensing regulated EPS production in biofilm communities, Theor. Biol. Medical Model. 2011, 8, 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Goryachev, A. B. Understanding Bacterial Cell-Cell Communication with Computational Modeling, Chem. Rev. , 2011, 111(1), 238-250 (2011). [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, P.; C. A. Brackley, C.A.; Carballo-Pacheco, M.; Allen, R. J. Model for quorum-sensing mediated stochastic biofilm nucleation, Phys. Rev. Lett, 2022, 129(19),198102.
- E. Ben-Jacob, O. Schochet, A. Tenenbaum, I. Cohen, A. Czirok and T. Vicsek, Generic modelling of cooperative growth patterns in bacterial colonies, Nature 368(6466), 1994, 46-49. [CrossRef]
- J. Pérez-Velázquez, J.; Gölgeli, M.; García-Contreras,R. Mathematical modelling of bacterial quorum sensing: a review, Bull. Math. Biol. 2016, 78, 1585-1639.
| Lx, Ly | Dimensions of the rectangular grid | 20x20 |
| f0 | Initial fraction of occupied nodes | 0.1 |
| α | productivity coefficient | variable |
| rmax, rmin | Resistance values entering the link resistance formula | rmax=1000, rmin=1(a.u.) |
| g | Parameter in the Hill-like function, controlling the resistance interpolation | 0.01 |
| σ | Activation efficiency | variable |
| Qmax | Maximum value of the activity triggering death or biofilm formation | 80 |
| τ | Ageing time | 10 |
| Max(E) | Maximal fraction of energy to be used | 0.9 |
| Qmin | Minimal reproduction size | 2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





