1. Introduction:
Natural plants product extract, as pure or as standard extract, provide more than thousand opportunities for new drug discoveries. According to the world health organization (WHO), more than 80% of the world’s population use traditional medicine for their primary healthcare needs [
1].
Ziziphus spina-christi, commonly known as the Christ's Thorn Jujube or Sidr tree, is a species of flowering plant that has been used in traditional medicine for centuries across various regions of the world, particularly in the Middle East and North Africa [
2]. This evergreen tree, native to the Saharo-Arabian and Irano-Turanian regions, has long been revered for its diverse array of therapeutic properties and potential health benefits [
3].
One of the most intriguing aspects of Ziziphus spina-christi is its remarkable antimicrobial activity, which has garnered significant attention from the scientific community. The plant's ability to inhibit the growth and proliferation of various pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses, has made it a subject of intense research and exploration [
4].
The antimicrobial properties of Ziziphus spina-christi are believed to stem from the rich phytochemical composition of the plant, which includes a diverse array of bioactive compounds such as flavonoids, saponins, tannins, and triterpenes [
4]. These secondary metabolites have been found to exhibit potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, making the plant a promising candidate for the development of natural, plant-based antimicrobial agents [
5].
Moreover, the plant's traditional use in folk medicine for the treatment of various ailments, including skin infections, gastrointestinal disorders, and respiratory problems, further highlights its potential therapeutic applications [
6]. As the global healthcare system grapples with the challenge of antibiotic resistance, the exploration of natural antimicrobial agents like Ziziphus spina-christi has become increasingly crucial [
7].
Recent studies in drug discovery from medicinal plants have adopted a multi-layered approach, incorporating molecular, botanical, and phytochemical techniques [
8]. In this context, the present study focuses on the biochemical properties and antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi, a plant widely used in traditional medicine.
The aim of this study is to assess anti-microbial activity of leaves extract of Z. spina-christi and compare the biological activity of the plant. By employing a comprehensive approach that combines various analytical techniques, this study seeks to provide a deeper understanding of the biochemical characteristics and antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi. The findings presented here may serve as a foundation for future investigations, paving the way for the development of novel, plant-based antimicrobial agents that could revolutionize the way we approach infectious disease management.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Ziziphus Spina-Christi Leaves
Z. spina-christi leaves were collected randomly from Althawra area at Omdurman- Khartoum state. Leaves were allowed to air dried and transported to phytochemical laboratory at university of science and technology where extraction was done.
2.1.2. Extraction
Extraction was carried out according to method described by Sukhdev et. al. [
9]. Solvents (methanol 95%, petroleum ether, chloroform and ethyl-acetate), Petri dishes, conical flask, water bath, seperatory funnel, flitter papers, funnel, glass vials and dragendroff’s vials were prepared for the plant extraction and these material obtain from phytochemical lab (UST).
2.1.3. Thin Layer Chromatography Assay
Stationary phase: silica gel plate, solvent system: (toluene: EtAOC: formic acid) (5:4:1) Spray reagent: vanillin sulfuric beaker, capillary tubes, measuring cylinder, Ultra violet spectrometer, Oven, petri dish, aluminum foil [
10].
2.1.4. Materials Used in the Sensitivity Test
Mueller Hinton agar was used for bacterial culture. Tested organisms include S. typhi, E. coli and C. albicans was obtain as pure standard microorganisms from also from National Public Health laboratory. Standard antibiotic was used as control and in the experimental procedure is Ciprofloxacin disks and Ketoconazole of concentration 1mg\1ml.
2.2. Method
2.2.1. Extraction of the Plant
20g of the dry powder leaves was put on conical flask, covered with 130ml of 95% methanol and was put into water bath for 40 minutes, then the extract was filtered using filtered paper. The excess water was removed by few powder anhydrous sodium sulfate (mg) and the crude extract was re-filtered again. 1ml of the crude extract was transferred into glass vial and labeled as (Crude). Rest of the crude extract was fractionated with petroleum ether, chloroform and ethyl acetate.
128ml of petroleum ether was fractionated with the crude extract 4 times by seperatory funnel using 32ml on each. Petroleum ether layer was transferred into Petri dish and concentrated in water-bath. Excess water was removed by few powder anhydrous sodium sulfate (mg) and the pet-ether extract was re-filtered again, then 1ml of petroleum ether layer was taken and labeled as (Pet-ether). Remaining of aqueous layer was fractionated with chloroform. 96ml of chloroform was placed on seperatory funnel and fractionated three times 32ml on each fractionation. Chloroform layer was concentrated in Petri-dish on water-bath. Then excess water was removed by few powder anhydrous sodium sulfate and chloroform extract was re-filtered again and then 1ml of chloroform was taken and labeled as (CHCL3). Remaining aqueous layer was fractionated with ethyl-acetate. 128ml of ethyl-acetate was added to the aqueous extract 4 times 32ml on each, excess water was removed by using few of powder anhydrous sodium sulfate and the ethyl-acetate extract was re-filtered again. Then the ethyl acetate layer was concentrated in Petri dish and 1ml of ethyl-acetate was taken and labeled as (EtAOC). On the remaining aqueous extract, excess water was removed by using few milligrams of powder anhydrous sodium sulfate and the ethyl-acetate extract was re-filtered again. Extract concentrated in water bath, 1ml of aqueous extract was taken and labeled as (Aq).
Crude extraction and the fractionation were prepared for the sensitivity testing by evaporating the solvents until drying. Crude extract (17.7mg), petroleum ether (20.7mg), Chloroform (20.7mg), ethyl acetate (23.7mg), Aqueous (20.8mg) were obtained after being weighted then they were dissolved in 2% Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) to obtain 20 mg/1ml concentration for each extract.
2.2.2. Preparation of Media
Media used for culturing microorganisms (Mueller Hinton agar) was taken as powder, liquefied then transform into sterile petri dish 2mm layer of agar and kept at room temperature.
2.2.3. Preparation of the Microorganisms
Microorganisms as standard organisms were diluted in normal saline solution 0.9% then it was used for sensitivity test.
2.2.4. Sensitivity Testing
Methanol extract of Z. spina-christi was tested against each of the organisms. Microorganisms were cultured in the prepared media and allow to stand 1 minute then 6 wells were made in the media 5 peripheral for Z. spina-christi extract and 1 in the center for antibiotic-antifungal control, then by aid of micropipette into each well the extract was putted, Then the media containing microorganisms with extract were incubated at 37oc for 24 h for both bacteria and fungi.
2.2.5. Thin Layer Chromatography Assay (TLC)
15 ml of the solvent Toluene: ethyl acetate: Formic acid by ratio (15:4:1) was taken and put into borosilicate glass beaker(250ml) and allow to saturate the medium for 15 minutes.
Thin layer chromatography plate covered by silica gel the distances between spots were measured and divided to equal distance 5 spots and named as PE, CHCL3, Cr, EtAOC, Aq (petroleum ether extract, chloroform extract, crude extract, ethyl acetate extract, aqueous extract respectively).
On each spot that have been drawn a drop of each extract was put in its labeled place, by aided of capillary tubes. Then plate was taken and put into beaker contain the solvent system and running time was calculated until the solvent layer reach the upper plate line. The plate was taken out and allow for dryness.
Records was obtaining in UV in short and long wave (length 365nm). Plate was sprayed by special reagent vanillin/sulfuric acid and allow to stand 5min. The plate was taken and put into an oven for 5 minutes and RF value were calculated for each [
10].
3. Results
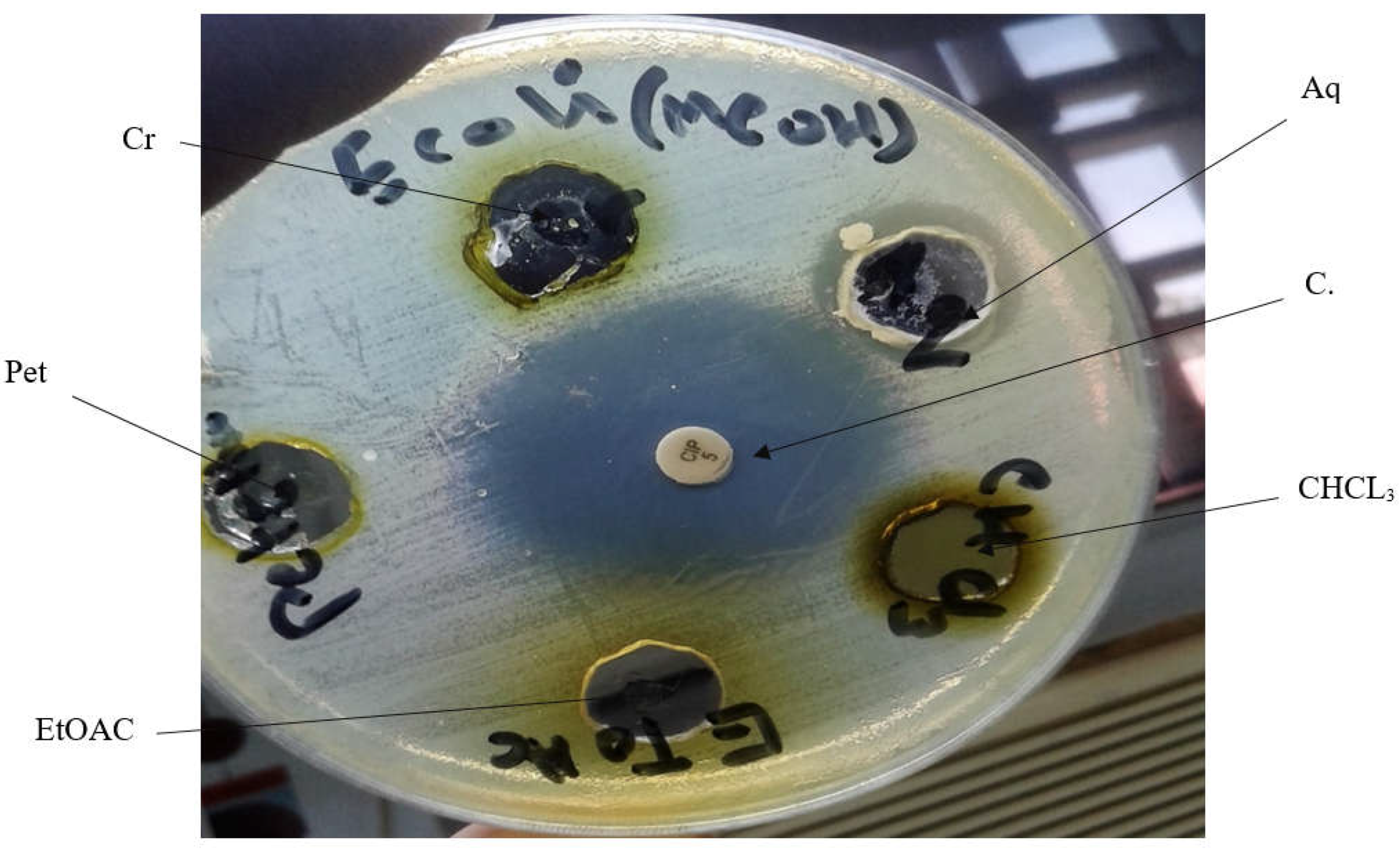
Methanolic extract of Z. spina-christi leaves were tested against three bacterial spices including Escherichia coli, Salmonella para typhi B and fungal species Candida albicans. Result revealed that the plant extract shows slight antibacterial activity against E. coli with 17mm zone of inhibition, while negative result was observed with Crude, petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate used against E. coli. Table No. 4 figure No. 2
Table 1.
Anti-microbial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract.
Table 1.
Anti-microbial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract.
| Methanol Extract of Z. spina-christi
|
Salmonella para typhi B |
E. coli |
Candida albicans |
| Crude |
- |
- |
- |
| Petroleum ether |
- |
- |
- |
| Chloroform |
- |
- |
- |
| Ethyl acetate |
- |
- |
- |
| Aqueous |
- |
17mm |
- |
| Antibiotic control |
Ciprofloxacin |
Ciprofloxacin |
Ketoconazole |
| 40mm |
35mm |
43mm |
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi crude and fractionations against E. Coli Cr= Crude, Pet ether= Petroleum ether, CHCL3= Chloroform, EtAOC=Ethyl acetate, Aq=Aqueous extract, C=control.
Figure 1.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi crude and fractionations against E. Coli Cr= Crude, Pet ether= Petroleum ether, CHCL3= Chloroform, EtAOC=Ethyl acetate, Aq=Aqueous extract, C=control.
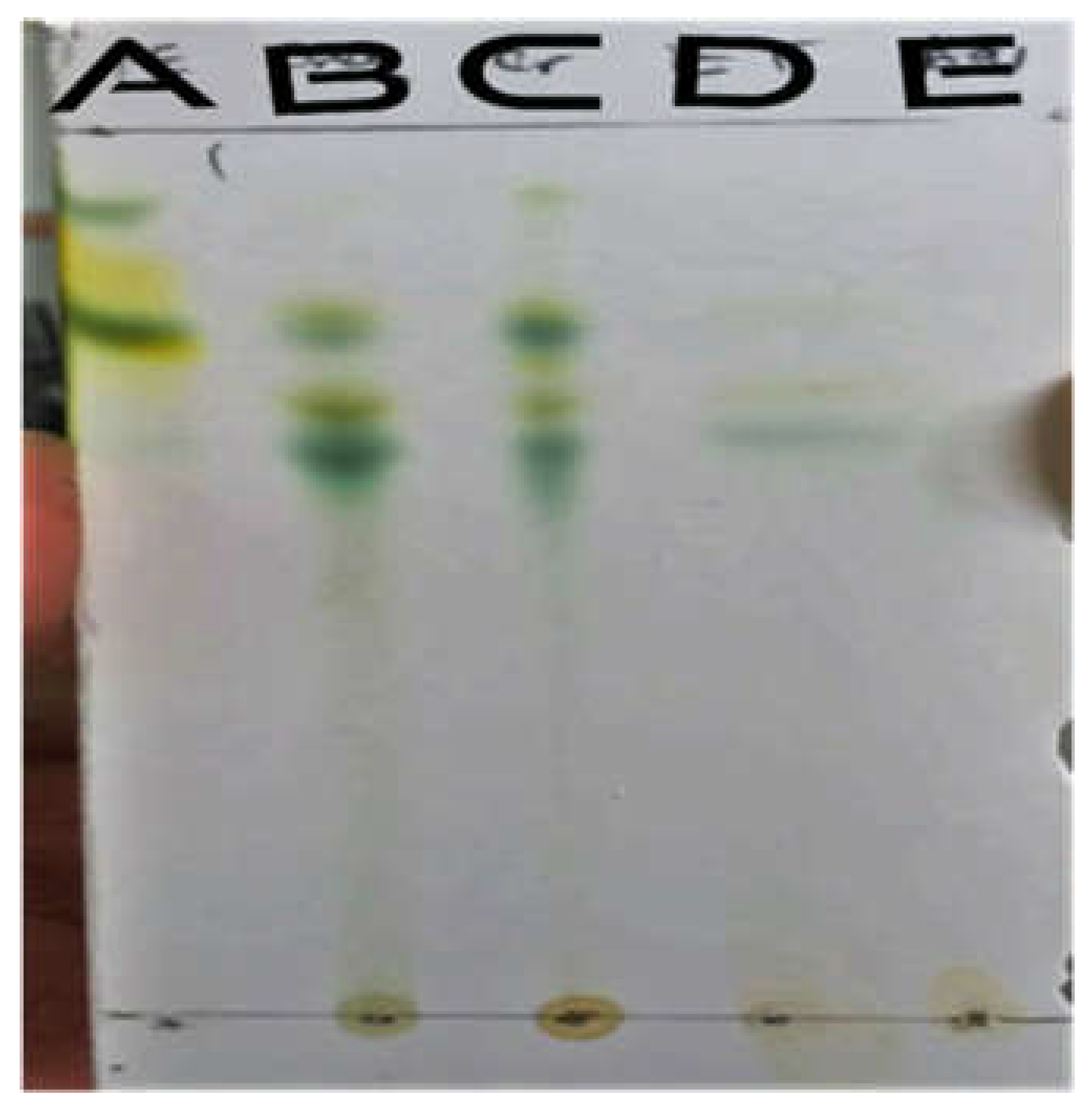
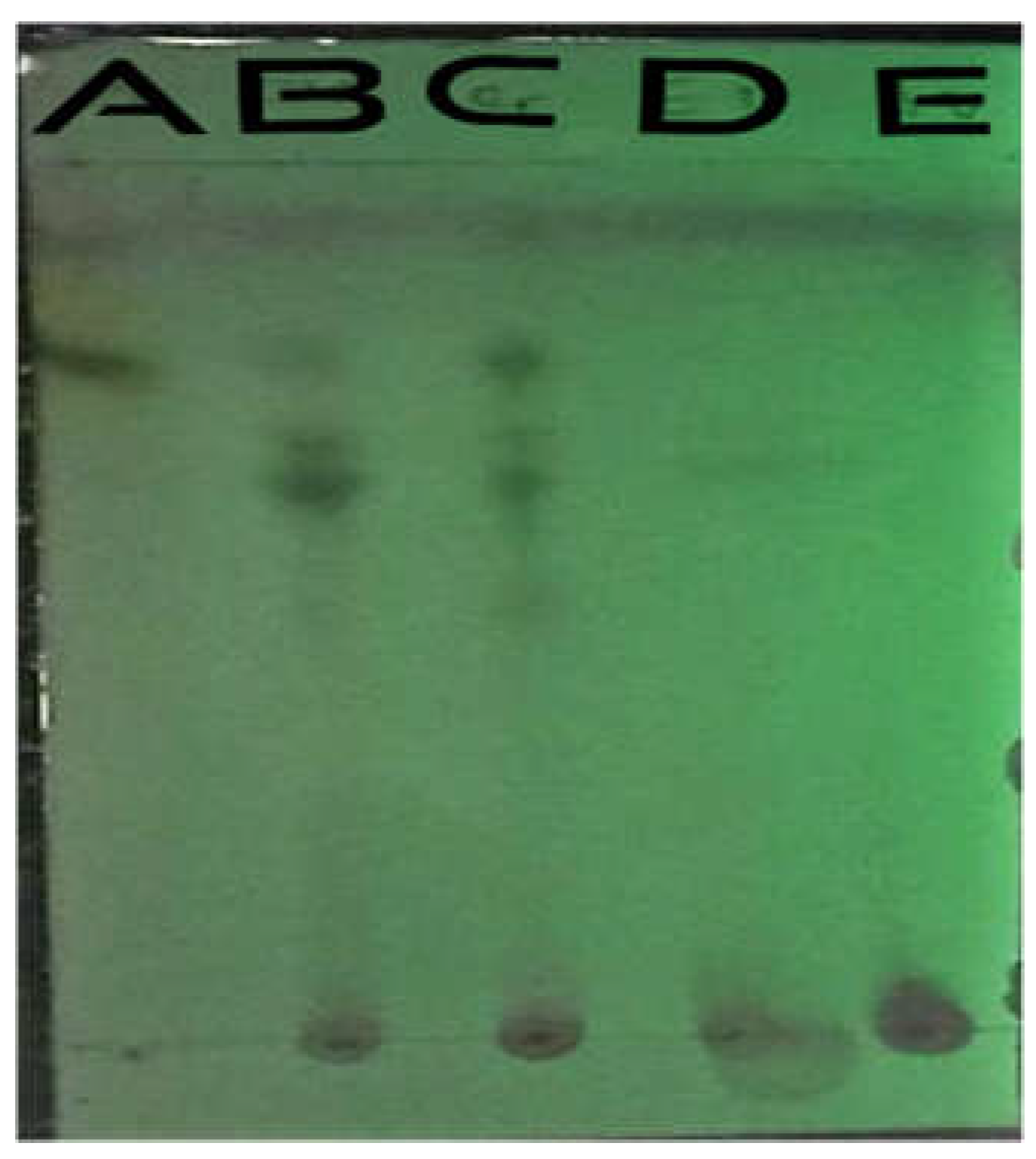
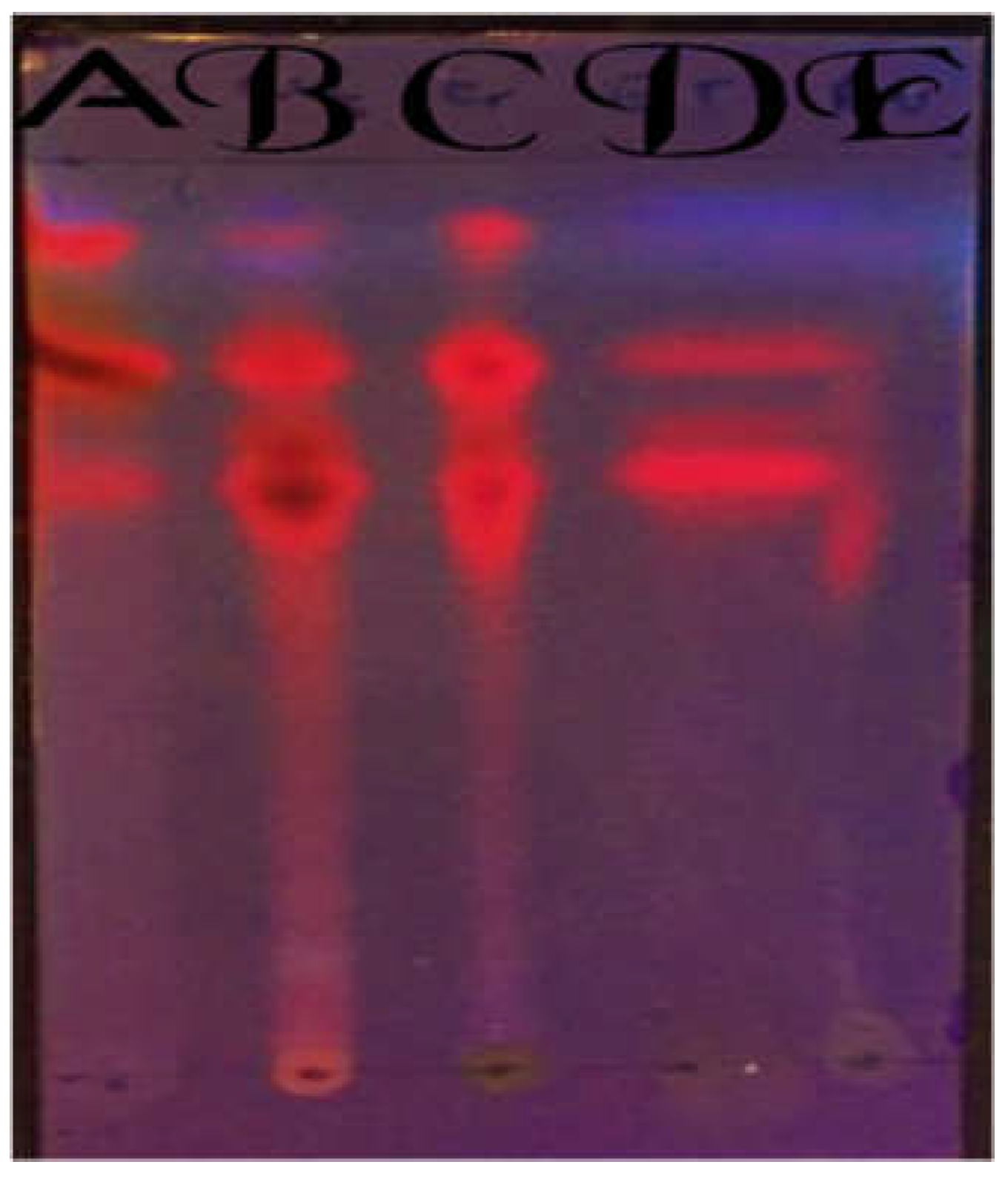
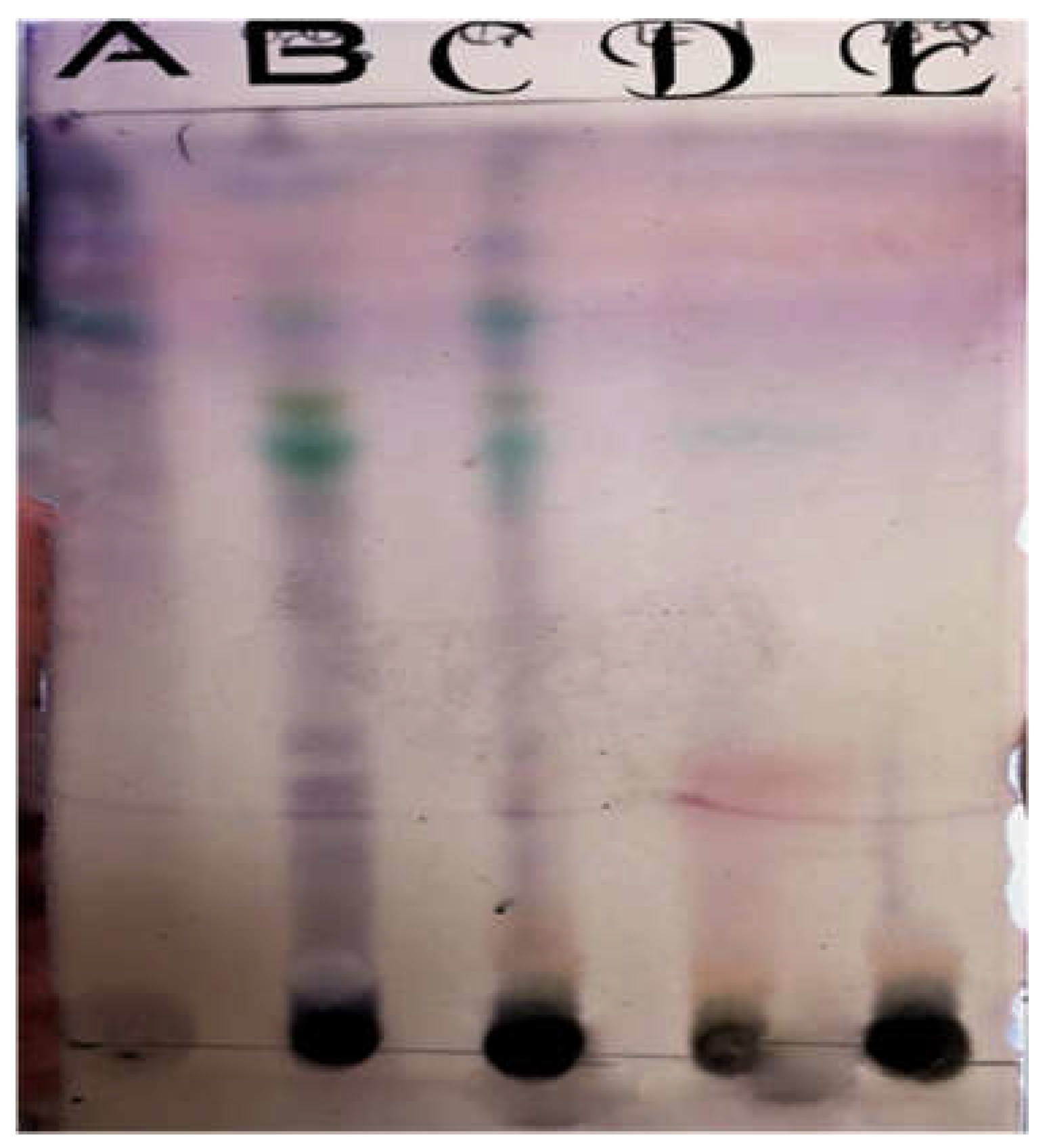
Inspection of the developed silica gel (fig,7,8,9,10) in the daylight followed by their visualization under UV (short and long wavelength) indicate that Z. spina-christi contains several chemical constituents. Anti-microbial effect of Z. spina-christi against E. coli might be due(Christinin-A), indicated by the spot in aqueous layer in the thin layer chromatography test (el-Din et al., 1996) table (5), figure (9).
Figure 2.
TLC in Day light before spraying. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 2.
TLC in Day light before spraying. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 3.
TLC before spraying under short wavelength UV. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 3.
TLC before spraying under short wavelength UV. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 4.
TLC before under long wavelength UV. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 4.
TLC before under long wavelength UV. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 5.
TLC on day light after spraying. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Figure 5.
TLC on day light after spraying. A=Petroleum ether, B= Chloroform, C=Crude, D=Ethyl acetate, E=Aqueous.
Table 2.
Represent the results of thin layer chromatography in toluene: ethyl acetate: Formic acid (5: 4: 1).
Table 2.
Represent the results of thin layer chromatography in toluene: ethyl acetate: Formic acid (5: 4: 1).
| Fractions |
Before spraying |
After spraying |
RF values |
| Toluene: EtAOC: Formic acid (5:4:1) solvent system |
Day light |
Short UV |
Long UV |
Day light |
Short UV |
Long UV |
|
| Crude |
Blue |
- |
Red florescence |
Green |
- |
- |
0.65 |
| Blue |
Quenching |
Red florescence |
Green |
- |
- |
0.75 |
| Green |
- |
Red florescence |
- |
- |
- |
0.95 |
| Pet. Ether |
Green |
Quenching |
Red florescence |
Green |
- |
- |
0.77 |
| Yellow |
- |
Red florescence |
Purple |
- |
- |
0.85 |
| Green |
- |
Blue florescence |
Green |
- |
- |
0.92 |
| Chloroform |
Blue |
Quenching |
Brown florescence |
Green |
|
|
0.65 |
| Blue |
Quenching |
Red florescence |
Green |
|
|
0.76 |
| EtAOC |
Green |
Quenching |
Brown florescence |
- |
- |
- |
- |
| Yellow |
Quenching |
Red florescence |
- |
- |
- |
0.75 |
| Aqueous |
- |
- |
Red florescence |
- |
- |
- |
0.54 |
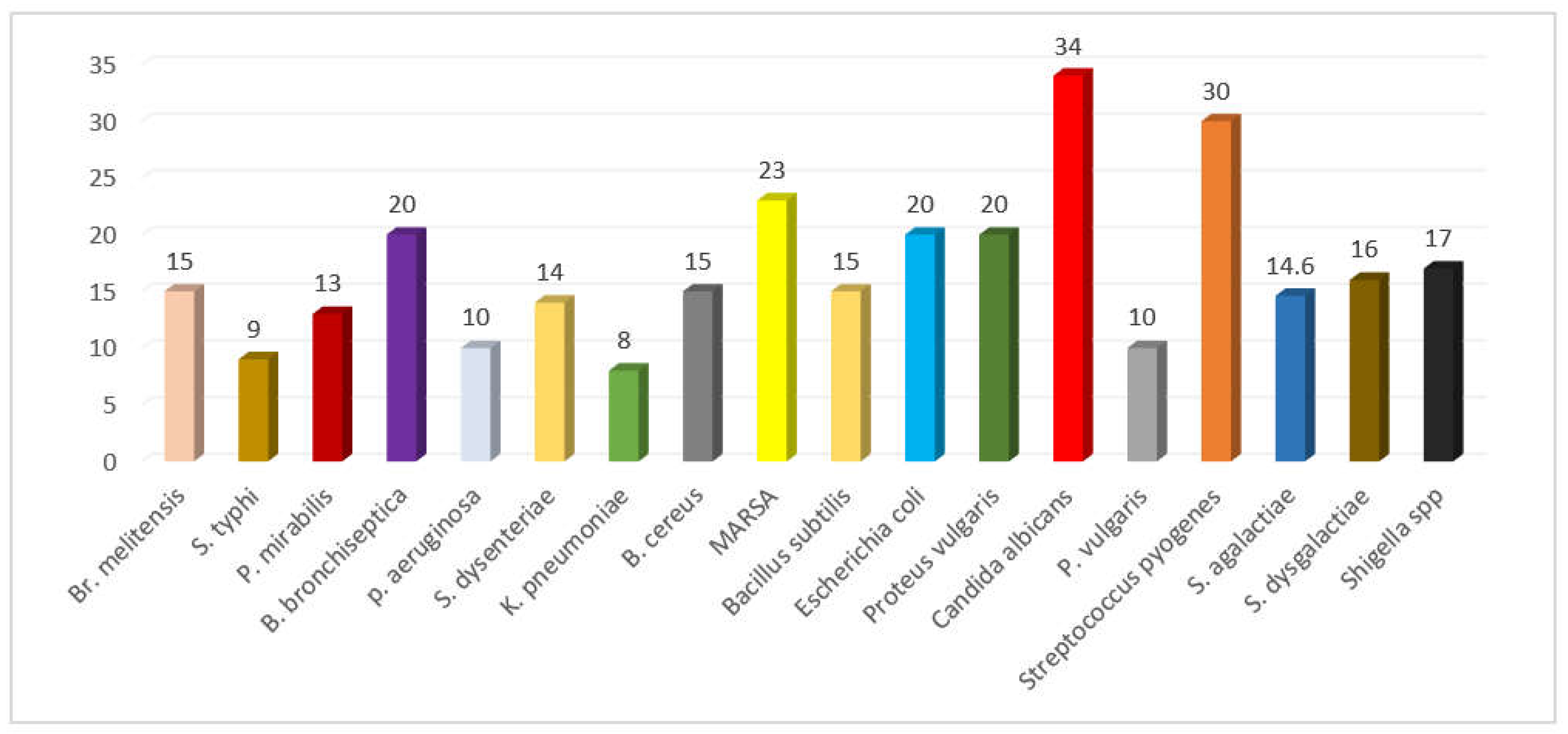
Figure 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves, barks, seeds, stems and fruits collected from different published data showing zone of inhibiton.
Figure 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves, barks, seeds, stems and fruits collected from different published data showing zone of inhibiton.
4. Discussion
The results of the study align with previous findings in the literature, providing further evidence that plant extracts from Z. spina-christi may not be effective against fungal species like C. albicans. However, the plant extract did demonstrate moderate activity against E. coli, albeit with a slight inhibition zone, suggesting it may have some antibacterial properties.
The data collected from the literature reveals that Z. spina-christi possesses antimicrobial activity when various plant parts (leaves, fruits, seeds, bark, stem, and root) are tested. This is likely due to the presence of bioactive compounds such as tannins, saponins, resins, polyphenols, cyclopeptide alkaloids, and flavonoids like furanocoumarins, glycosides, leucocyanidin, and triterpenoids [
11]. The beneficial medicinal effects of plant materials are typically attributed to a combination of these secondary metabolites rather than a single compound [
12].
The search for substances with high antibacterial properties is a crucial area of research, as the overuse of antibiotics has led to the development of resistant strains. Plant-derived compounds offer a promising alternative, as they are naturally toxic to bacteria but not to humans [
13]. This makes them a valuable resource for the development of new antimicrobial agents, which could help address the growing challenge of antibiotic resistance [
14].
The findings from this study, combined with the evidence from the literature, suggest that Z. spina-christi may have the potential to be a source of natural antimicrobial compounds, particularly against bacterial species [
15]. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the specific bioactive compounds responsible for the observed antimicrobial activities and to explore their potential therapeutic applications.
5. Conclusion
The present study aimed to assess the antimicrobial activity of the leaves of Ziziphus spina-christi, commonly known as Christ's Thorn Jujube, a plant widely used in traditional medicine. The leaves were extracted using various solvents, including methanol, petroleum ether, chloroform, ethyl acetate, and aqueous extracts, and their antimicrobial properties were evaluated against Escherichia coli, Salmonella Paratyphi B, and Candida albicans.
The results of the antimicrobial assays showed that the leaves of Z. spina-christi exhibited negative results against the fungal species C. albicans. Similarly, the bacterial species Salmonella Paratyphi B also showed no inhibition in the presence of the plant extracts. However, the aqueous extract of the leaves did demonstrate a slight inhibition zone against Escherichia coli.
These findings contrast with the existing literature, which has reported the antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi against various microorganisms. The authors suggest that this discrepancy could be due to the differences in environmental conditions affecting the plant material used in this study.
While the present study did not conclusively demonstrate the broad-spectrum antimicrobial properties of Z. spina-christi, it did provide evidence of its antibacterial effect, particularly against E. coli. Further studies are warranted to assess the clinical safety and biological effects of this plant species in vivo, using animal models and human subjects. Such investigations could help elucidate the full therapeutic potential of Z. spina-christi and its possible applications in the field of antimicrobial therapy.
Data Availability: All data underlying the results are available as part of the article and no additional source data are required.
References
- Bitwell, C., et al., A review of modern and conventional extraction techniques and their applications for extracting phytochemicals from plants. Scientific African, 2023. 19: p. e01585.
- Elhaj, Y.H., Exploring the Antimicrobial Activity of Ziziphus spina–christi: A Promising Natural Supply of Antimicrobial Agents. Egyptian Academic Journal of Biological Sciences, G. Microbiology, 2024. 16(1): p. 21-31.
- Al-Shaibani, E.A., D.A.A. Al-Ameri, and M.A. Al-Hegami, The Effect of Zizyphus spina-christi Extracts on hyperglycemia induced by hyperlipidemic diet in Albino rats. Sana'a University Journal of Applied Sciences and Technology, 2024. 2(1): p. 1-6.
- El Megdar, S., et al., Biological Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Lavandula mairei Humbert: Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Current Microbiology, 2024. 81(6): p. 151.
- Dawood, H.M., et al., Metabolomics and chemometrics approaches unravel the metabolic diversity and in-vitro antidiabetic potential of two Ziziphus species. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024. 212: p. 118288.
- Qari, S.H., A. Alqethami, and A.T. Qumsani, Ethnomedicinal evaluation of medicinal plants used for therapies by men and women in rural and urban communities in Makkah district. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2024. 32(1): p. 101881.
- Chaughule, R.S. and R.S. Barve, Role of herbal medicines in the treatment of infectious diseases. Vegetos, 2024. 37(1): p. 41-51.
- Khan, N., S.S. Dogra, and A. Saneja, The dawning era of oral thin films for nutraceutical delivery: From laboratory to clinic. Biotechnology Advances, 2024: p. 108362.
- Handa, S., et al., Extraction technologies for medicinal and aromatic plants. International centre for science and hightechnology. Trieste, 2014: p. 74-80.
- Kagan, I.A. and M.D. Flythe, Thin-layer chromatographic (TLC) separations and bioassays of plant extracts to identify antimicrobial compounds. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments), 2014(85): p. e51411.
- Ali, A.B., A.Z. Almagboul, and O.M. Mohammed, Antimicrobial activity of fruits, leaves, seeds and stems extracts of Ziziphus spina-christi. Arabian journal of medicinal and aromatic plants, 2015. 1(2): p. 94-107.
- Jain, C., S. Khatana, and R. Vijayvergia, Bioactivity of secondary metabolites of various plants: a review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res, 2019. 10(2): p. 494-504.
- AlSheikh, H.M.A., et al., Plant-based phytochemicals as possible alternative to antibiotics in combating bacterial drug resistance. Antibiotics, 2020. 9(8): p. 480.
- Álvarez-Martínez, F.J., et al., Plant-Derived Natural Products for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. 2024, Springer.
- El-Shahir, A.A., et al., Bioactive Compounds and Antifungal Activity of Leaves and Fruits Methanolic Extracts of Ziziphus spina-christi L. Plants, 2022. 11(6): p. 746.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).