Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
29 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
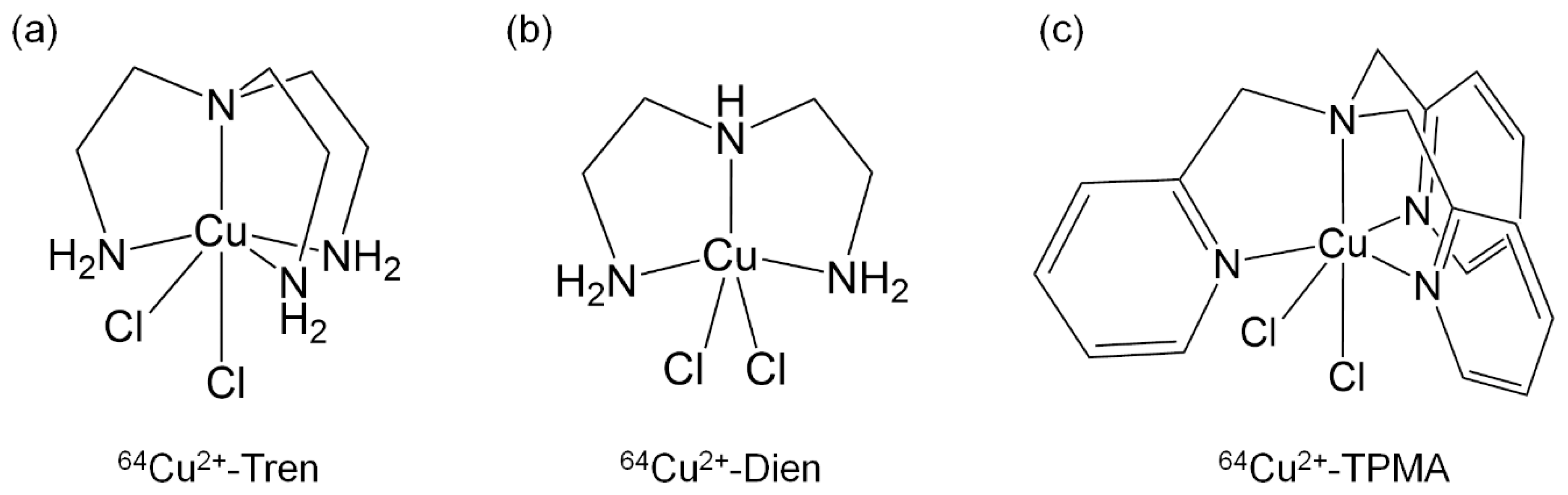
2. Results
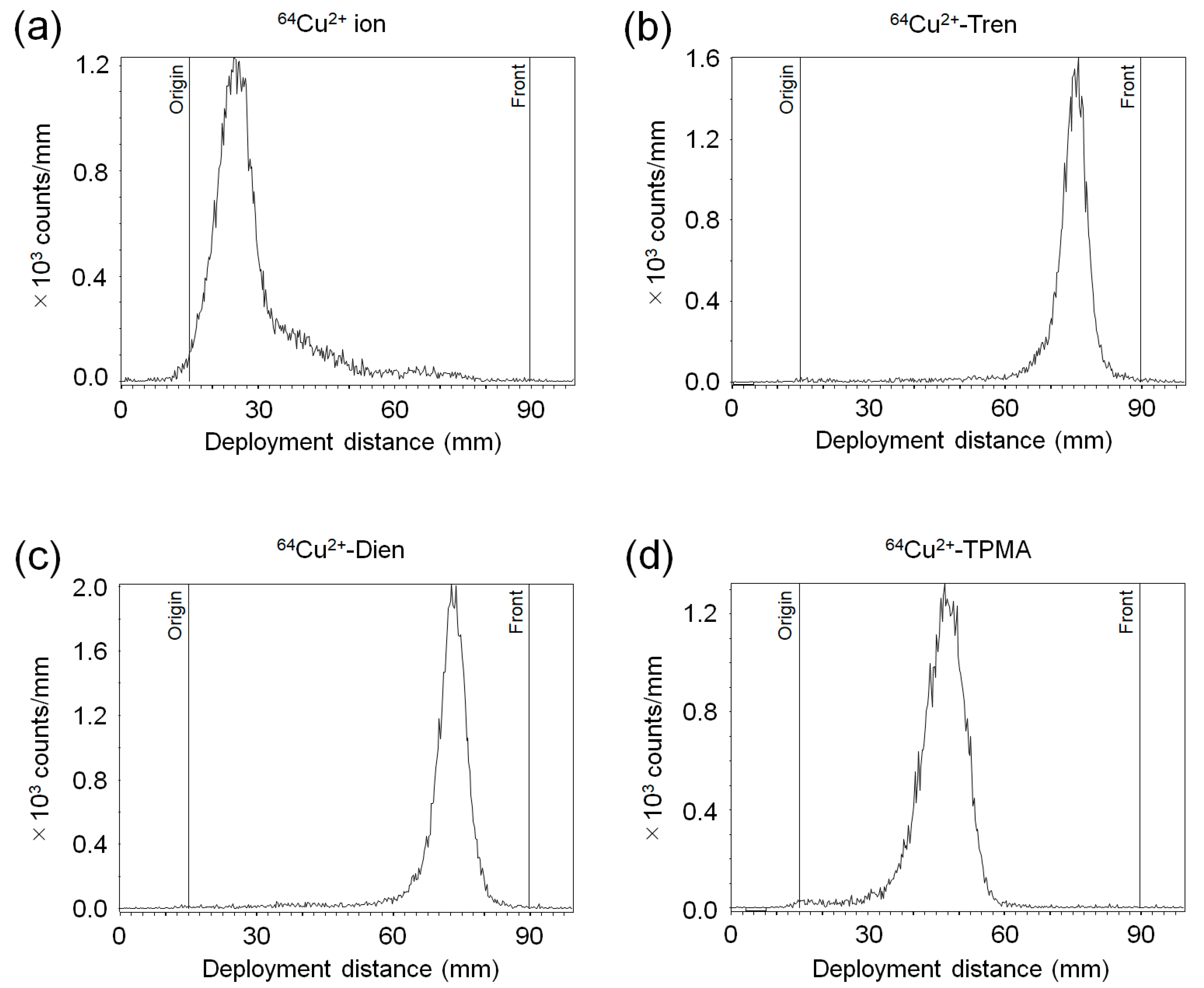
2.1. Determination of the Radiochemical Purity of 64Cu2+ Complexes
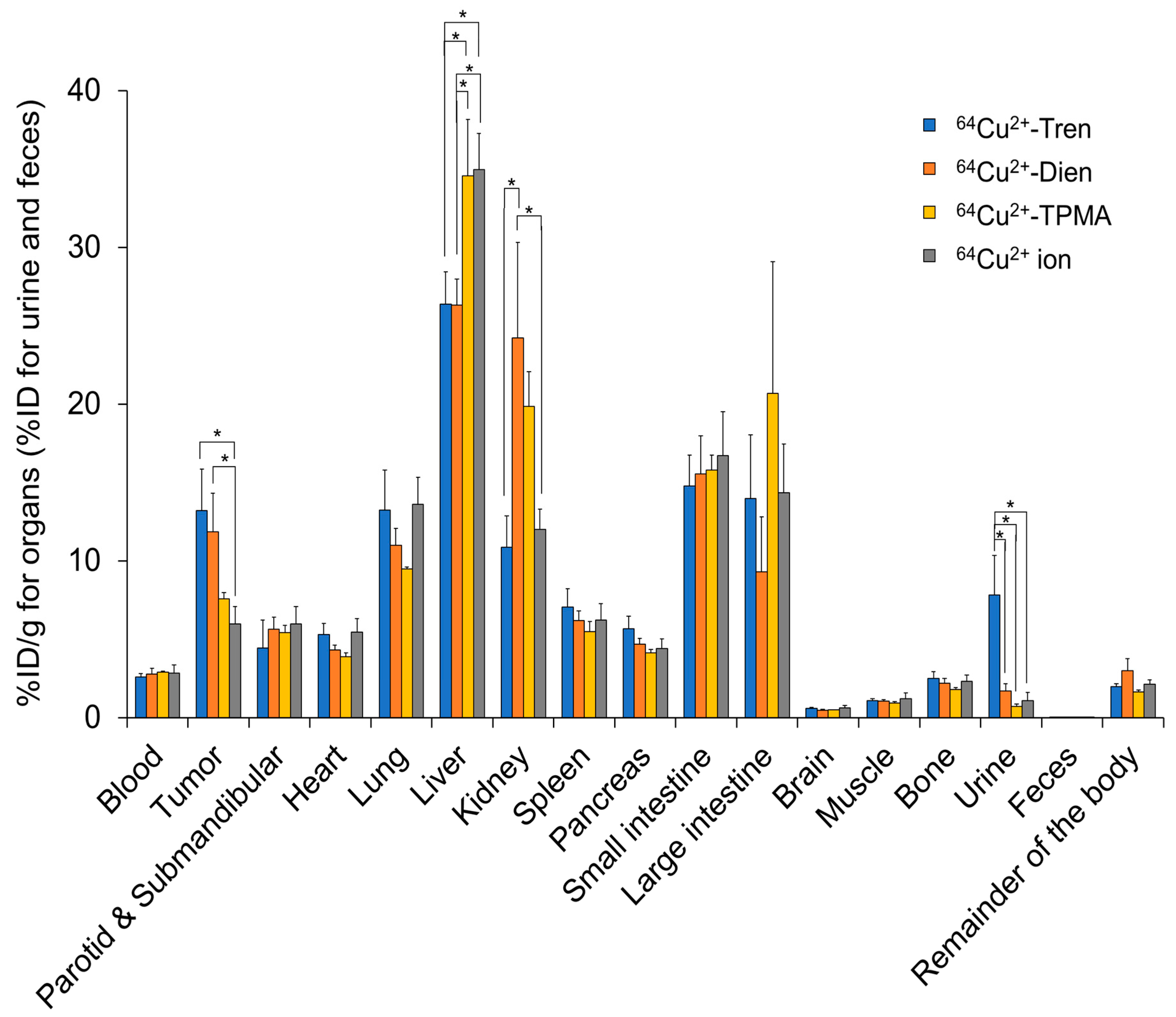
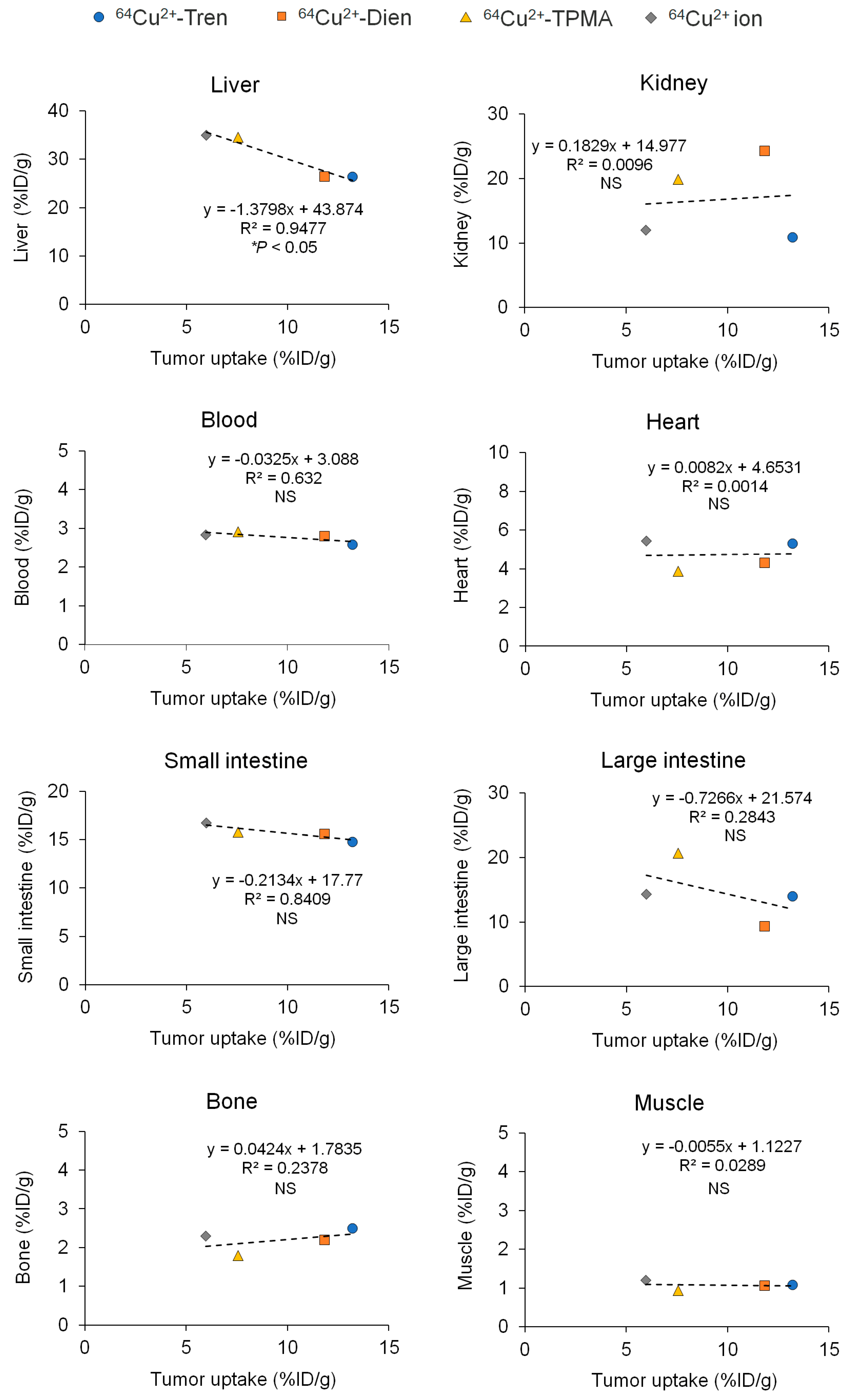
2.2. Tissue Distribution In Vivo
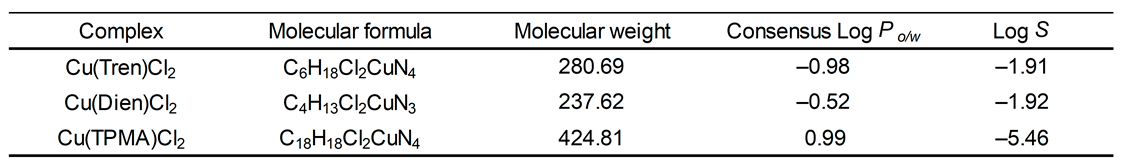
2.3. In Silico Log Po/w and Log S Studies of Cu2+ Complexes
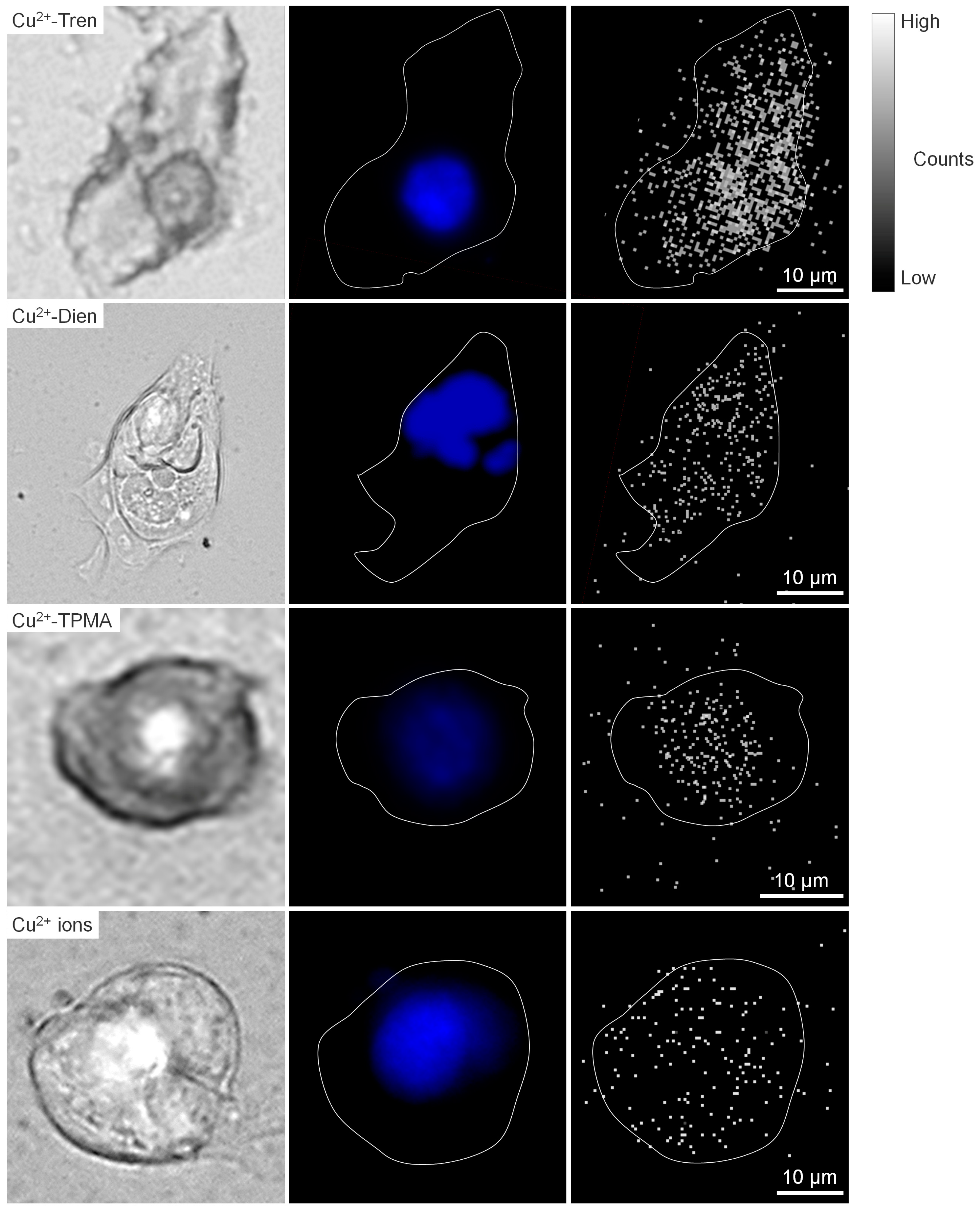
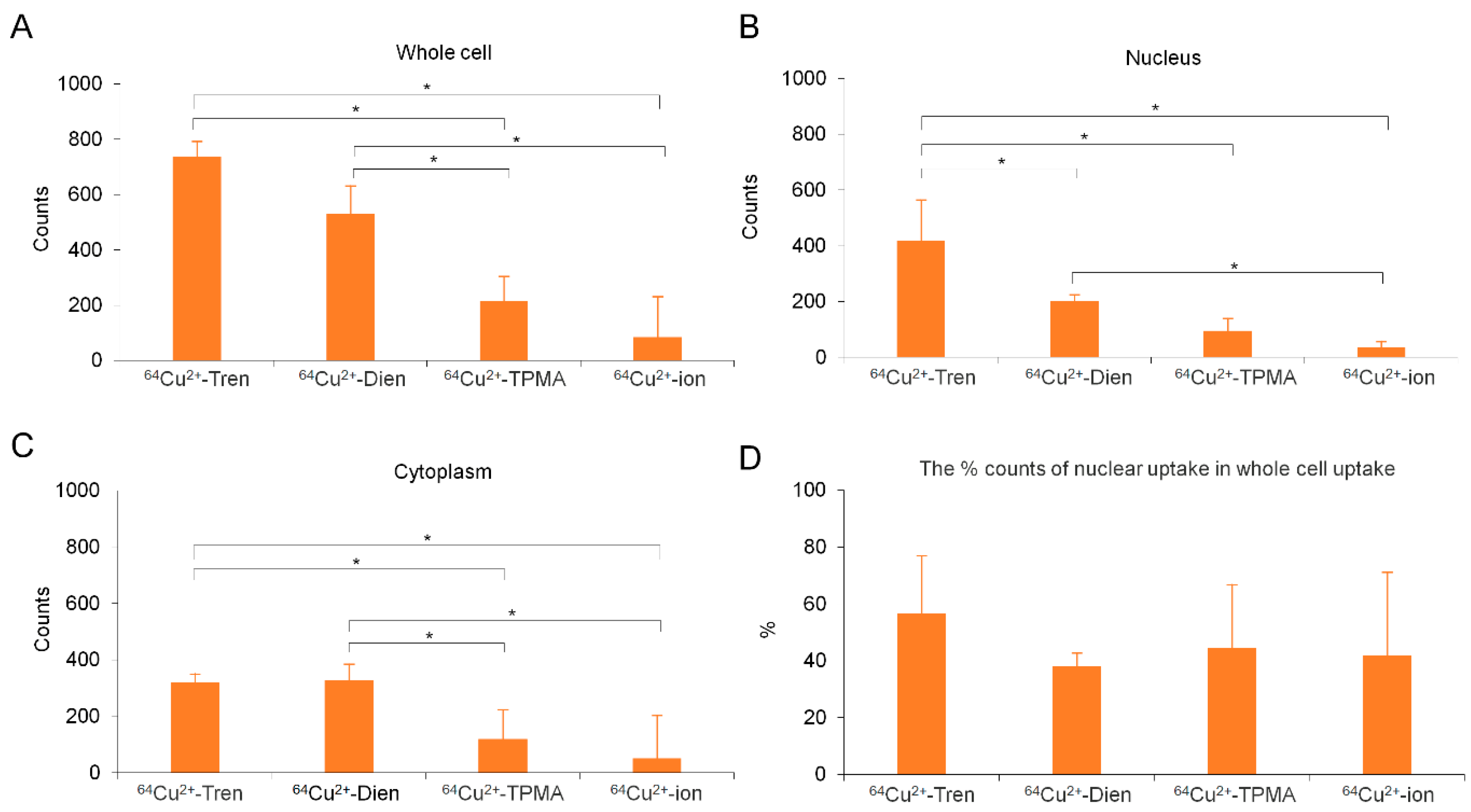
2.4. Intracellular Cu Distribution
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Materials
4.2. Preparation of 64Cu2+ Complexes
4.3. Cell Line and Culture
4.4. Animal Model
4.5. Tissue Distribution In Vivo
4.6. In Silico Log Po/w and Log S Studies of 64Cu2+ Tripodal Amine Complexes
4.7. Micro-PIXE Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lelievre, P.; Sancey, L.; Coll, J.L.; Deniaud, A.; Busser, B. The Multifaceted Roles of Copper in Cancer: A Trace Metal Element with Dysregulated Metabolism, but Also a Target or a Bullet for Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, J.S.; Tai, S.; Jin, L.; Teng, C.B. Blockage of SLC31A1-dependent copper absorption increases pancreatic cancer cell autophagy to resist cell death. Cell Prolif 2019, 52, e12568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Yan, Z.; Miao, Y.; Ha, W.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Mi, D. Copper in cancer: from limiting nutrient to therapeutic target. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1209156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2022, 7, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zablocka-Slowinska, K.; Prescha, A.; Placzkowska, S.; Porebska, I.; Kosacka, M.; Pawelczyk, K. Serum and Whole Blood Cu and Zn Status in Predicting Mortality in Lung Cancer Patients. Nutrients 2020, 13, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Chen, X.; Ma, K.; He, H.; Li, W.; Cui, J. Serum Copper Level and the Copper-to-Zinc Ratio Could Be Useful in the Prediction of Lung Cancer and Its Prognosis: A Case-Control Study in Northeast China. Nutr Cancer 2021, 73, 1908–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, A.P.; Chen, P.Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, D.M.; Luo, Y.; Liao, G.C.; Long, J.A.; Zhong, R.H.; Zhou, Z.G.; et al. Serum copper and zinc levels at diagnosis and hepatocellular carcinoma survival in the Guangdong Liver Cancer Cohort. Int J Cancer 2019, 144, 2823–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiya, T. Copper in the tumor microenvironment and tumor metastasis. J Clin Biochem Nutr 2022, 71, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriotti, G.; Piccardo, A.; Giovannelli, E.; Signore, A. Targeting Copper in Cancer Imaging and Therapy: A New Theragnostic Agent. J Clin Med 2022, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascia, M.; Villano, C.; De Francesco, V.; Schips, L.; Marchioni, M.; Cindolo, L. Efficacy and Safety of the 64Cu(II)Cl2 PET/CT for Urological Malignancies: Phase IIa Clinical Study. Clin Nucl Med 2021, 46, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Perez, F.O.; Medina-Ornelas, S.S.; Barron-Barron, F.; Arrieta-Rodriguez, O. Evaluation of non-small cell lung cancer by PET/CT with 64CuCl2: initial experience in humans. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020, 10, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiz, F.; Bottoni, G.; Ugolini, M.; Righi, S.; Cirone, A.; Garganese, M.C.; Verrico, A.; Rossi, A.; Milanaccio, C.; Ramaglia, A.; et al. Diagnostic and Dosimetry Features of [64Cu]CuCl2 in High-Grade Paediatric Infiltrative Gliomas. Mol Imaging Biol 2023, 25, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, C.I.G.; Bucar, S.; Alves, V.; Fonseca, A.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; da Silva, C.L.; Guerreiro, J.F.; Mendes, F. Copper-64 Chloride Exhibits Therapeutic Potential in Three-Dimensional Cellular Models of Prostate Cancer. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7, 609172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, J.; Laforest, R.; Buettner, T.; Song, S.; Fujibayashi, Y.; Connett, J.; Welch, M. Copper-64-diacetyl-bis(N4-methylthiosemicarbazone): An agent for radiotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001, 98, 1206–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.D.; Maeda, J.; Bell, J.J.; Genet, M.D.; Phoonswadi, G.; Mann, K.A.; Kraft, S.L.; Kitamura, H.; Fujimori, A.; Yoshii, Y.; et al. Validation of 64Cu-ATSM damaging DNA via high-LET Auger electron emission. J Radiat Res 2015, 56, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Liu, H.; Chen, K.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Z. Theranostics of malignant melanoma with 64CuCl2. J Nucl Med 2014, 55, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, J.F.; Alves, V.; Abrunhosa, A.J.; Paulo, A.; Gil, O.M.; Mendes, F. Radiobiological Characterization of 64CuCl2 as a Simple Tool for Prostate Cancer Theranostics. Molecules 2018, 23, 2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Tu, Y.; Hu, X.; Bao, A.; Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Doyle, T.; Shi, H.; Cheng, Z. Pilot Study of 64Cu(I) for PET Imaging of Melanoma. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, K.; Sandahl, T.D.; Frisch, K.; Vase, K.H.; Keiding, S.; Vilstrup, H.; Ott, P.; Gormsen, L.C.; Munk, O.L. Intravenous and oral copper kinetics, biodistribution and dosimetry in healthy humans studied by [64Cu]copper PET/CT. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriya, M.; Ho, Y.H.; Grana, A.; Nguyen, L.; Alvarez, A.; Jamil, R.; Ackland, M.L.; Michalczyk, A.; Hamer, P.; Ramos, D.; et al. Copper is taken up efficiently from albumin and alpha2-macroglobulin by cultured human cells by more than one mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2008, 295, C708–C721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovidis, I.; Delimaris, I.; Piperakis, S.M. Copper and its complexes in medicine: a biochemical approach. Mol Biol Int 2011, 2011, 594529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heroux, K.J.; Woodin, K.S.; Tranchemontagne, D.J.; Widger, P.C.B.; Southwick, E.; Wong, E.H.; Weisman, G.R.; Tomellini, S.A.; Wadas, T.J.; Anderson, C.J.; et al. The long and short of it: the influence of N-carboxyethyl versus N-carboxymethyl pendant arms on in vitro and in vivo behavior of copper complexes of cross-bridged tetraamine macrocycles. Dalton Trans 2007, 2150–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Qin, Z.; Wang, Z.; Wei, S.; Chen, H.; Zhu, T.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, B.; Song, W. Condensed tannins from Ulmus pumila L. leaves induce G2/M phase arrest and apoptosis via caspase-cascade activation in TFK-1 cholangiocarcinoma cells. J Food Biochem 2022, 46, e14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozel, M.; Baskol, G.; Baskol, M.; Gunes, F.; Ucar, C.; Dogru, B.N.; Akalin, H. SAHA induce hippo pathway in CCA cells without increasing cell proliferation. Mol Biol Rep 2022, 49, 3649–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, L.N.C.; Nooijen, L.E.; Ali, M.; Puik, J.R.; Moustaquim, J.; Fraga Rodrigues, S.M.; Broos, R.; Belkouz, A.; Meijer, L.L.; Le Large, T.Y.S.; et al. Prognostic and predictive value of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a translational study. Front Pharmacol 2023, 14, 1274692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oba, M.; Nakanishi, Y.; Mitsuhashi, T.; Sasaki, K.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Sasaki, M.; Nange, A.; Okumura, A.; Hayashi, M.; Yoshida, Y.; et al. CCR7 Mediates Cell Invasion and Migration in Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers 2023, 15, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Kim, S.W.; Park, D.J.; Ahn, Y.J.; Yoon, Y.S.; Choi, M.G.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, K.U.; Park, Y.H. Actual long-term outcome of extrahepatic bile duct cancer after surgical resection. Ann Surg 2005, 241, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Kang, K.M.; Jeong, B.K.; Jeong, H.; Lee, Y.H.; Ha, I.B.; Kim, T.G.; Song, J.H. Patterns of failure after resection of extrahepatic bile duct cancer: implications for adjuvant radiotherapy indication and treatment volumes. Radiat Oncol 2018, 13, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, I.W.; Jang, J.Y.; Kwon, W.; Park, T.; Kim, Y.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, S.W. Ceruloplasmin as a prognostic marker in patients with bile duct cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29028–29037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, J.G.; Chen, X.F.; Gu, D.H.; Liu, Z.M.; Gao, Y.D.; Zheng, B. Ceruloplasmin overexpression is associated with oncogenic pathways and poorer survival rates in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. FEBS Open Bio 2021, 11, 2988–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, M.C.; Moor, J.R.; Wright, K. Ceruloplasmin assays in diagnosis and treatment of human lung, breast, and gastrointestinal cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 1981, 67, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci Rep 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaney, J.S. ESOL: estimating aqueous solubility directly from molecular structure. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 2004, 44, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Kim, J.; Martell, A.E.; Welch, M.J.; Anderson, C.J. In vivo evaluation of copper-64-labeled monooxo-tetraazamacrocyclic ligands. Nucl Med Biol 2004, 31, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnott, J.A.; Planey, S.L. The influence of lipophilicity in drug discovery and design. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2012, 7, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafreshi, N.K.; Kil, H.; Pandya, D.N.; Tichacek, C.J.; Doligalski, M.L.; Budzevich, M.M.; Delva, N.C.; Langsen, M.L.; Vallas, J.A.; Boulware, D.C.; et al. Lipophilicity Determines Routes of Uptake and Clearance, and Toxicity of an Alpha-Particle-Emitting Peptide Receptor Radiotherapy. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2021, 4, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneria, M.; Rakholiya, K. ScienceDirect. In Nanotechnology and in silico tools; Elsevier: San Diego, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Sawant, P.D.; Luu, D.; Ye, R.; Buchta, R. Drug release from hydroethanolic gels. Effect of drug's lipophilicity (logP), polymer-drug interactions and solvent lipophilicity. Int J Pharm 2010, 396, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garza, A.Z.; Park, S.B.; Kocz, R. Drug Elimination. In StatPearls; Treasure Island: Florida, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, R.; Ohashi, R.; Esaki, T.; Kawashima, H.; Natsume-Kitatani, Y.; Nagao, C.; Mizuguchi, K. Development of an in silico prediction system of human renal excretion and clearance from chemical structure information incorporating fraction unbound in plasma as a descriptor. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 18782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vemula, V.R.; Lagishetty, V.; Lingala, S. Solubility enhancement techniques. Int J Pharma Sci Rev Res 2010, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, E.H.; Di, L. Drug-like properties: concepts, structure design and methods: from ADME to toxicity optimization; Academic Press: Amsterdam; Boston, 2008; pp. xix, 526 p., 522 p. of plates. [Google Scholar]
- Teles, R.H.G.; Graminha, A.E.; Rivera-Cruz, C.M.; Nakahata, D.H.; Formiga, A.L.B.; Corbi, P.P.; Figueiredo, M.L.; Cominetti, M.R. Copper transporter 1 affinity as a delivery strategy to improve the cytotoxic profile of rationally designed copper(II) complexes for cancer treatment. Toxicol In Vitro 2020, 67, 104922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopp, M.; Becker, J.; Becker, S.; Miska, A.; Gandin, V.; Marzano, C.; Schindler, S. Anticancer activity of a series of copper(II) complexes with tripodal ligands. Eur J Med Chem 2017, 132, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szilágyi, I.; Labádi, I.; Pálinkó, I. Thermal stabilities of nanocomposites: Mono- or binuclear Cu complexes intercalated or immobilised in/on siliceous materials. Nanopages 2009, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, F.H. Metal complexes based on macrocyclic ligands and their ability to hydrolyse phosphate esters. Ph.D. Thesis, Monash University, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Bew, M.J.; Hathaway, B.J.; Fereday, R.J. Electronic properties and stereochemistry of the copper(II) ion. Part VII. Mono(diethylenetriamine)copper(II) complexes. J Chem Soc Dalton 1972, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapley, J.R. Inorg Synth; Wiley: Hoboken, 2004; Volume 34, pp. 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Oikawa, M.; Suya, N.; Konishi, T.; Ishikawa, T.; Hamano, T.; Homma-Takeda, S. Micro-PIXE analysis system at NIRS-electrostatic accelerator facility for various applications. Int J PIXE 2015, 25, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, L.; Carmona, A.; Roudeau, S.; Ortega, R. Evaluation of sample preparation methods for single cell quantitative elemental imaging using proton or synchrotron radiation focused beams. J Anal Atom Spectrom 2015, 30, 2525–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




