Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Mechanical Properties Testing
2.1. Compression Strength Testing: Determines the Material's Ability to Withstand Compression Loads
2.2. Tensile Strength Testing: Measures the Material's Resistance to Being Pulled Apart and Determines Tensile Strength
2.3. Flexural Strength Testing: Assesses the material's ability to bear bending forces.
2.4. Shear Strength Testing: Evaluates the Material's Ability to Withstand Sliding Forces
2.5. Modulus of Elasticity: Assesses the Material's Ability to Deform Elastically under Stress
2.6. Hardness Test: Measures the Resistance of a Material to Deformation, Particularly Permanent Deformation, Indentation, or Scratching
2.7. Impact Resistance Test: Evaluates a Material's Ability to Resist Sudden Impacts or Shocks
2.8. Creep Test: Measures the Time-Dependent Deformation of Materials under Constant Stress
2.9. Fatigue Test: Assesses the Material's Ability to Withstand Cyclic Loading and Determines its Fatigue Life
3. Chemical Properties Testing
3.1. Spectroscopy: Identifies the Chemical Composition of Materials
3.2. Chromatography: Used to Separate and Analyze Compounds That Can Be Vaporized without Decomposition
3.3. X-ray Fluorescence: Determines the Elemental Composition of Materials
3.4. pH Measurement: Determines the Acidity or Alkalinity of Aqueous Solutions in Materials
4. Thermal Properties Testing
4.1. Thermogravimetric Analysis: Measures Changes in Weight in Relation to Changes in Temperature
4.2. Differential Scanning Calorimetry: Determines the Energy Absorbed or Released by a Material as It Is Heated or Cooled
4.3. Thermal Conductivity Test: Measures the rate at which heat passes through a material.
4.4. Thermal Expansion Test: Determines the Expansion Rate of Materials When Subjected to Temperature Changes
4.5. Hot Disk Thermal Constants Analyzer: Measures Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Diffusivity, and Specific Heat of Materials
5. Microstructural Properties Testing
5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy: Provides Detailed Images of the Material's Surface and Microstructure
5.2. X-ray Diffraction: Identifies the Crystalline Phases and Orientation of Crystals within the Material
5.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy: Offers High-Resolution Images of the Material, Allowing for the Study of Its Nanostructure
5.4. Atomic Force Microscopy: Provides Nanoscale Surface Profiling and Analysis to Understand Material Behavior at a Microscopic level
6. Durability Properties Testing
6.1. Freeze-Thaw Testing: Assesses the Material's Resistance to Freezing and Thawing Cycles
6.2. Sulfate Attack Testing: Evaluates the material's durability against sulfate ions.
6.3. Chemical Resistance Test: Evaluates the Material's Resistance to Chemicals
6.4. Corrosion Testing: Assesses the Susceptibility of Materials to Corrosion under Various Environmental Conditions
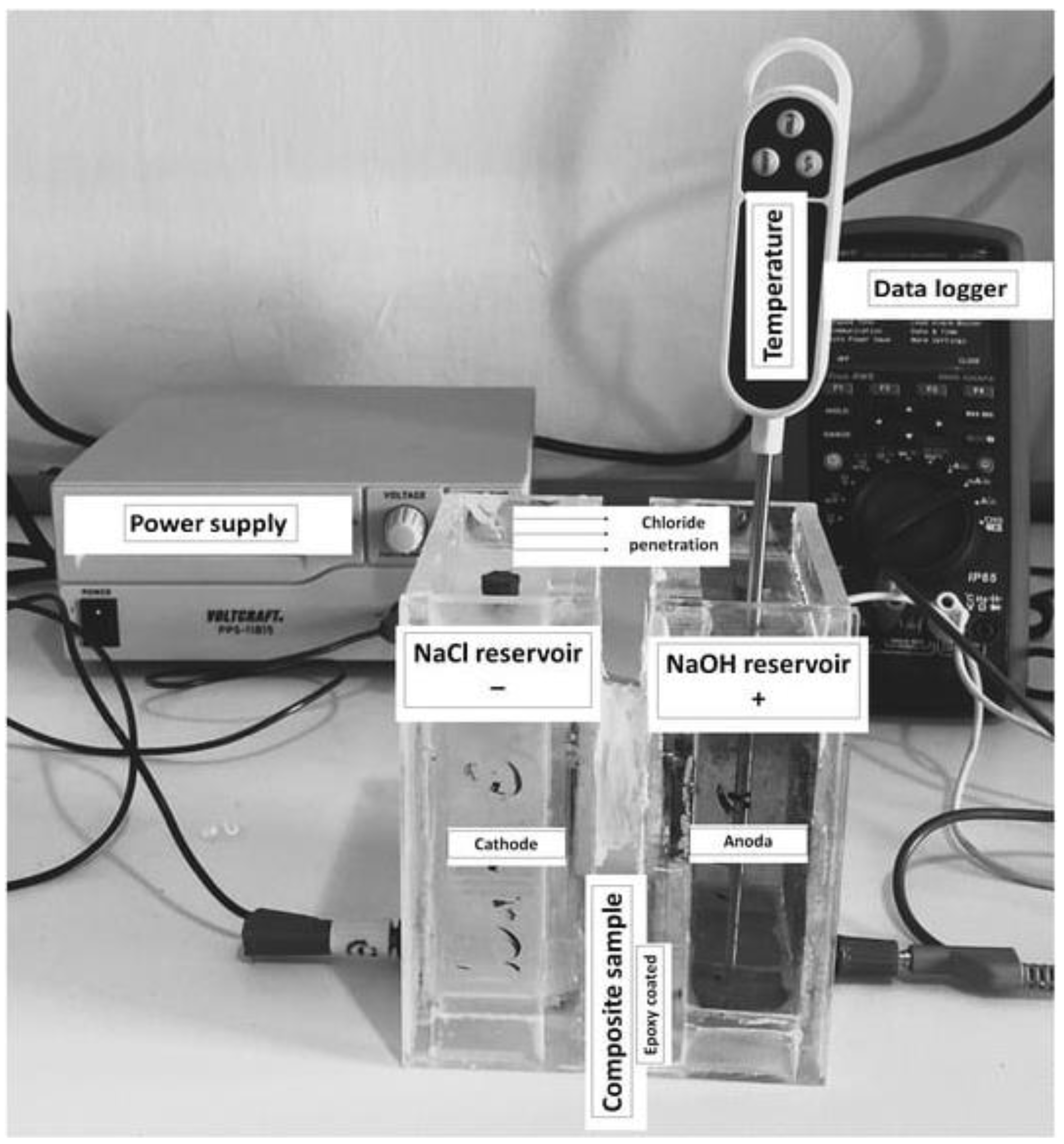
6.5. Chloride Penetration Testing: Measures the Material's Resistance to Chloride ion Penetration, Relevant for Corrosion Resistance in Steel Reinforcement
6.6. Carbonation Testing: Assesses the Depth of Carbonation in Concrete, Which Can Affect its Durability and Steel Reinforcement Corrosion
6.7. Moisture Absorption Test: Evaluates the Amount of Moisture Absorbed by Materials under Specific Conditions
6.8. Salt Spray Test: Tests the material's Resistance to Corrosion Caused by Salt or Saline Environments, Often Used for Metals
7. Physical Properties Testing
7.1. Porosity and Density Measurements: Determine the Void Spaces within a Material and Its Mass per Volume
7.2. Water Absorption Test: Assesses the Porosity of Materials by Measuring the Amount of Water Absorbed under Specified Conditions
7.3. Shrinkage Test: Measures the Change in Dimensions of Materials, Particularly Concrete, Mortar, and Grout, as They Dry or React to Temperature Changes
8. Rheological Properties Testing
8.1. Viscosity Measurement: Determines the Material's Resistance to Flow
8.2. Workability Tests: Assess the Ease with Which a Concrete Mix Can Be Mixed, Placed, Compacted, and Finished
9. Non-destructive Testing
9.1. Ultrasonic Testing: Utilizes High-Frequency Sound Waves to Detect Internal Flaws or Characterize Properties of Materials
9.2. Radiography: Employs X-rays or Gamma Rays to Capture Images of a Material's Internal Structure and Reveal Defects or Irregularities
9.3. Ground Penetrating Radar: Uses Radar Pulses to Image the Subsurface and Identify Changes in Material Properties, Voids, and Cracks
9.4. Free Vibration Testing: Measures the Natural Frequencies and Damping Ratios of the Material to Determine the Dynamic Characteristics and Potential Structural Weaknesses
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talaat, A.; Emad, A.; Tarek, A.; Masbouba, M.; Essam, A.; Kohail, M. Factors affecting the results of concrete compression testing: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comminal, R. , da Silva, W. ( 138, 106256.
- Rajabi, A.M.; Moaf, F.O.; Abdelgader, H.S. Evaluation of Mechanical Properties of Two-Stage Concrete and Conventional Concrete Using Nondestructive Tests. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2020, 32, 04020185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, M. C. (2002). Non contact ultrasound: the final frontier in non destructive analysis. Boalsburg: Second Wave Systems.
- Hou, S.; Duan, Z.; Xiao, J.; Ye, J. A review of 3D printed concrete: Performance requirements, testing measurements and mix design. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 273, 121745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM, A. (2018). ASTM C39/C39M-18 standard test method for compressive strength of cylindrical concrete specimens. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA ASTM, AI.
- BS 12390-3 (2009) Testing hardened concrete. Compressive Strength of Test Specimens. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- CSN, E. (2009). 12390-3: Testing hardened concrete-Part 3: Compressive strength of test specimens. The Czech Republic.
- ASTM, A. (2016). ASTM C78/C78M-16 standard test method for flexural strength of concrete (using simple beam with third-point loading ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA ASTM, AI.
- BS 12390-5 (2019) Testing hardened concrete. Flexural strength of test specimens. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- de Normalisation, C. E. (2009). EN 12390–5: Testing Hardened Concrete—Part 5: Flexural Strength of Test Specimens. CEN: Brussels, Belgium.
- ASTM, A. (2010). ASTM C732/C732M-10 standard test method for shear strength of plastics by punch tool. ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA ASTM, AI.
- BS 7991 (2001). Determination of the mode I adhesive fracture energy GIC of structure adhesives using the double cantilever beam (DCB) and tapered double cantilever beam (TDCB) specimens. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2018). 1922:2018 Rigid cellular plastics–determination of shear properties. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2017). ASTM E111-17 Standard test method for young's modulus, tangent modulus, and chord modulus, in, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 527-1 (2012) Plastics. Determination of tensile properties. General principles. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 527-1:2019 Determination of tensile properties – Part 1: General principles. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2023). ASTM D785-23 Standard Test Method for Rockwell Hardness of Plastics and Electrical Insulating Materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 2039-1 (2003) Plastics Determination of hardness Part 1: Ball indentation method. General principles. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2003). 2039-1:2003 Plastics Determination of hardness Part 1: Ball indentation method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2023). ASTM D256- 23e1 Standard Test Methods for Determining the Izod Pendulum Impact Resistance of Plastics, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 179-1 (2023) Plastics. Determination of Charpy impact properties Non-instrumented impact test. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2023). 179-1:2023 Plastics. Determination of Charpy impact properties Non-instrumented impact test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2015). ASTM C512- C512M-15 Standard Test Method for Creep of Concrete in Compression, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 1881-122 (2011) Testing concrete Part 122: Method for determination of water absorption. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 13791:2019 Assessment of in-situ compressive strength in structures and precast concrete components. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM E466-21 Standard Practice for Conducting Force Controlled Constant Amplitude Axial Fatigue Tests of Metallic Materials, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 7270 (2006) Metallic materials - Constant amplitude strain controlled axial fatigue - Method of test. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2010). 6072:2010 Aerospace series - Metallic materials - Test methods - Constant amplitude fatigue testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM E1252-98(2021) Standard Practice for General Techniques for Obtaining Infrared Spectra for Qualitative Analysis, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 3696 (1995) Water for analytical laboratory use. Specification and test methods. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (1995). 3696:1995 Water for analytical laboratory use. Specification and test methods. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM D6581-18 Standard Test Methods for Bromate, Bromide, Chlorate, and Chlorite in Drinking Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 12341 (2014) Ambient air — Standard gravimetric measurement method for the determination of the PM10 or PM2,5 mass concentration of suspended particulate matter. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2014). 12341:2014 Ambient air — Standard gravimetric measurement method for the determination of the PM10 or PM2,5 mass concentration of suspended particulate matter. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2017). ASTM D4327-17 Standard Test Method for Anions in Water by Suppressed Ion Chromatography, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 11885 (2009) Water quality. Determination of selected elements by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2009). 11885:2009 Water quality. Determination of selected elements by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2019). ASTM E70-19 Standard Test Method for pH of Aqueous Solutions with the Glass Electrode, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 3978 (1987) Specification for water for laboratory use. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2012). 10523:2012 Water quality - Determination of pH. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM E1131-20 Standard Test Method for Compositional Analysis by Thermogravimetry, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 8201 (2011) Code of practice for installation of flooring of wood and wood-based panels.
- ISO. (2011). 8201:2011 Code of practice for installation of flooring of wood and wood-based panels. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM D3418-21 Standard Test Method for Transition Temperatures and Enthalpies of Fusion and Crystallization of Polymers by Differential Scanning Calorimetry, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 11357 (1997) Plastics. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). General principles.
- ISO. (1997). 11357: 1997 Plastics. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). General principles. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM C518-21 Standard Test Method for Steady-State Thermal Transmission Properties by Means of the Heat Flow Meter Apparatus, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 12667 (2001) Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Products - Determination of Thermal Resistance by Means of Guarded Hot Plate and Heat Flow Meter Methods - Products of High and Medium Thermal Resistance. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2001). 12667: 2001 Thermal Performance of Building Materials and Products - Determination of Thermal Resistance by Means of Guarded Hot Plate and Heat Flow Meter Methods - Products of High and Medium Thermal Resistance. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2019). ASTM E831-19 Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials by Thermomechanical Analysis, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 11359-1 (2014) Plastics - Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) - Part 1: General Principles. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2014). 11359-1: 2014 Plastics - Thermomechanical Analysis (TMA) - Part 1: General Principles. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2019). ASTM D7896-19 Standard Test Method for Thermal Conductivity, Thermal Diffusivity, and Volumetric Heat Capacity of Engine Coolants and Related Fluids by Transient Hot Wire Liquid Thermal Conductivity Method, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- ASTM, A. (2022). ASTM E2809-22 Standard Guide for Using Scanning Electron Microscopy/Energy Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (SEM/EDS) in Forensic Polymer Examinations, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 340-1 (1979) Specification for Precast Concrete Kerbs, Channels, Edgings and Quadrants. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (1979). 340-1: 1979 Specification for Precast Concrete Kerbs, Channels, Edgings and Quadrants. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2022). ASTM D8-22a Standard Terminology Relating to Materials for Roads and Pavements, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 13925-1 (2003) Non-destructive testing - X-ray diffraction from polycrystalline and amorphous materials - Part 1: General principles. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2003). 13925-1: 2003 Non-destructive testing - X-ray diffraction from polycrystalline and amorphous materials - Part 1: General principles. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM E2015-04(2021) Standard Guide for Preparation of Plastics and Polymeric Specimens for Microstructural Examination, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- ISO. (2019). ISO 21432 Non-destructive testing: Standard test method for determining residual stresses by neutron diffraction, ISO.
- ASTM. (2021). ASTM E1621-21 Standard Guide for Elemental Analysis by Wavelength Dispersive X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM E2382-04(2020) Standard Guide to Scanner and Tip Related Artifacts in Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and Atomic Force Microscopy, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 20903 (2019) Surface chemical analysis - Auger electron spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - Methods used to determine peak intensities and information required when reporting results. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 20903: 2019 Surface chemical analysis - Auger electron spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy - Methods used to determine peak intensities and information required when reporting results. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (1997). ASTM C666-97 Standard Test Method for Resistance of Concrete to Rapid Freezing and Thawing, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 1367-1 (2007) Tests for thermal and weathering properties of aggregates - Part 1: Determination of resistance to freezing and thawing. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2007). 1367-1: 2007 Tests for thermal and weathering properties of aggregates - Part 1: Determination of resistance to freezing and thawing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2004). ASTM C1012-04 Standard Test Method for Length Change of Hydraulic-Cement Mortars Exposed to a Sulfate Solution, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 13295 (2004) Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures Test methods Determination of resistance to carbonation. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2004). 13295: 2004 Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures Test methods Determination of resistance to carbonation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2021). ASTM G31-21 Standard Guide for Laboratory Immersion Corrosion Testing of Metals, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- ASTM. (2020). ASTM C267-20 Standard Test Methods for Chemical Resistance of Mortars, Grouts, and Monolithic Surfacings and Polymer Concretes.
- ISO. (2010). ISO 175:2010 Plastics Methods of test for the determination of the effects of immersion in liquid chemicals.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM G48-11(2020) e1 Standard Test Methods for Pitting and Crevice Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steels and Related Alloys by Use of Ferric Chloride Solution, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- ASTM. (2017). ASTM G1-03(2017)e1 Standard Practice for Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test Specimens.
- ISO. (2017). 9227: 2017 Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres — Salt spray tests. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2022). ASTM C1202-22e1 (2022) Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete’s Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 12390-8 (2019) Testing hardened concrete Part 8: Depth of penetration of water under pressure. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 12390-8: 2019 Testing hardened concrete Part 8: Depth of penetration of water under pressure. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM C1583/C1583M-20 (2020) Standard Test Method for Tensile Strength of Concrete Surfaces and the Bond Strength or Tensile Strength of Concrete Repair and Overlay Materials by Direct Tension (Pull-off Method), ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 13295 (2004) Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures Test methods Determination of resistance to carbonation. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2004). 13295: 2004 Products and systems for the protection and repair of concrete structures Test methods Determination of resistance to carbonation. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM C1585-20 (2020) Standard Test Method for Measurement of Rate of Absorption of Water by Hydraulic-Cement Concretes, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 1881-124 (2015) Testing Concrete - Part 124: Methods for analysis of hardened concrete. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 13791: 2019 Assessment of in-situ compressive strength in structures and precast concrete components. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2019). ASTM B117-19 (2019) Standard Practice for Operating Salt Spray (Fog) Apparatus, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 9227 (2017) Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2017). 9227: 2017 Corrosion tests in artificial atmospheres - Salt spray tests. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM. (2020). ASTM D792-20 Standard Test Methods for Density and Specific Gravity (Relative Density) of Plastics by Displacement.
- BS 1936 (2007) Natural stone test methods - Determination of real density and apparent density, and of total and open porosity. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2007). 1936: 2007 Natural stone test methods - Determination of real density and apparent density, and of total and open porosity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- BS 13755 (2008) Natural Stone Test Methods - Determination of Water Absorption at Atmospheric Pressure. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2008). 13755: 2008 Natural Stone Test Methods - Determination of Water Absorption at Atmospheric Pressure. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (1975). ASTM C157-75 (1975) Standard Test Method for Length Change Of Hardened Cement Mortar And Concrete, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 12617-4 (2002) Products and Systems for the Protection and Repair of Concrete Structures - Test Methods - Part 4: Determination of Shrinkage and Expansion. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2002). 12617-4: 2002 Products and Systems for the Protection and Repair of Concrete Structures - Test Methods - Part 4: Determination of Shrinkage and Expansion. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2024). ASTM D445-24 (2024) Standard Test Method for Kinematic Viscosity of Transparent and Opaque Liquids (and Calculation of Dynamic Viscosity), ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 3104 (2020) Petroleum products – Transparent and opaque liquids – Determination of kinematic viscosity and calculation of dynamic viscosity. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2020). 3104: 2020 Petroleum products – Transparent and opaque liquids – Determination of kinematic viscosity and calculation of dynamic viscosity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM C143/C143M-20 (2020) Standard Test Method for Slump of Hydraulic-Cement Concrete, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 12350-2 (2019) Testing fresh concrete Part 2: Slump-test. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 12350-2: 2019 Testing fresh concrete Part 2: Slump-test. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2020). ASTM E494-20 (2020) Standard Practice for Measuring Ultrasonic Velocity in Materials by Comparative Pulse-Echo Method, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 583-2 (2001) Non-Destructive Testing - Ultrasonic Examination - Part 2: Sensitivity and Range Setting. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2001). 583-2: 2001 Non-Destructive Testing - Ultrasonic Examination - Part 2: Sensitivity and Range Setting. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2018). ASTM E1742/E1742M-18 (2018) Standard Practice for Radiographic Examination, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 444 (1994) Non-destructive testing - General principles for radiographic examination of metallic materials by X- and gamma-rays. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (1994). 444: 1994 Non-destructive testing - General principles for radiographic examination of metallic materials by X- and gamma-rays. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2019). ASTM D6432-19 (2019) Standard Guide for Using the Surface Ground Penetrating Radar Method for Subsurface Investigation, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 5930 (2015) Code of practice for ground investigations. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2007). 1997-2: 2007 Eurocode 7. Geotechnical design Ground investigation and testing. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ASTM, A. (2017). ASTM E289-17 (2017) Standard Test Method for Linear Thermal Expansion of Rigid Solids with Interferometry, ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, ASTM, AI.
- BS 7626-5 (2019) Mechanical vibration and shock — Experimental determination of mechanical mobility — Part 5: Measurements using impact excitation with an exciter which is not attached to the structure. British Standards Institution (BSI), London, UK.
- ISO. (2019). 7626-5: 2019 Mechanical vibration and shock — Experimental determination of mechanical mobility — Part 5: Measurements using impact excitation with an exciter which is not attached to the structure. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Mata-Falcón, J.; Haefliger, S.; Lee, M.; Galkovski, T.; Gehri, N. Combined application of distributed fibre optical and digital image correlation measurements to structural concrete experiments. Eng. Struct. 2020, 225, 111309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Yildirim, U. Simplified modeling of rubberized concrete properties using multivariable regression analysis. Mater. De Construccion 2022, 72, e289–e289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; AL Houri, A.; Habib, M.; Elzokra, A.; Yildirim, U. Structural Performance and Finite Element Modeling of Roller Compacted Concrete Dams: A Review. Lat. Am. J. Solids Struct. 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadyan-Yasouj, S.E.; Ghaderi, A. Experimental investigation of waste glass powder, basalt fibre, and carbon nanotube on the mechanical properties of concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, B.; Han, L.-H.; Lam, D. Experimental study on the performance of steel-concrete interfaces in circular concrete-filled double skin steel tube. Thin-Walled Struct. 2020, 149, 106660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Chen, M.; Pang, L.; Sun, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, X. Exploring temperature-resilient recycled aggregate concrete with waste rubber: An experimental and multi-objective optimization analysis. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2023, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X. Experimental and numerical study of hooked-end steel fiber-reinforced concrete based on the meso- and macro-models. Compos. Struct. 2023, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Kong, X.; Fang, Q. Experimental and numerical investigation on the attenuation of blast waves in concrete induced by cylindrical charge explosion. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2023, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khakimov, S. R. (2023). The Influence of Temperature on the Surrounding Environment and Process Hardening of Concrete. Excellencia: International Multi-disciplinary Journal of Education (2994-9521), 1(6), 314-321.
- Habib, A.; Yildirim, U.; Habib, M. Applying Kernel Principal Component Analysis for Enhanced Multivariable Regression Modeling of Rubberized Concrete Properties. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2022, 48, 5383–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, Q.-B.; Morel, J.-C.; Hans, S.; Meunier, N. Compression behaviour of non-industrial materials in civil engineering by three scale experiments: the case of rammed earth. Mater. Struct. 2008, 42, 1101–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Chen, C.; Shi, J.; Mei, C.; Kibleur, P.; Van Acker, J.; Van den Bulcke, J. Understanding the mechanical performance of OSB in compression tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubert, J.E.; Maillard, P.; Morel, J.-C.; Al Rafii, M. Towards a simple compressive strength test for earth bricks? Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 1641–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorramian, K.; Sadeghian, P. Material Characterization of GFRP Bars in Compression Using a New Test Method. J. Test. Evaluation 2021, 49, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Adams, D.F. Effect of Loading Method on Compression Testing of Composite Materials. J. Compos. Mater. 1995, 29, 1581–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, L. Compressive Test Investigation and Numerical Simulation of Polyvinyl-Alcohol (PVA)-Fiber-Reinforced Rubber Concrete. Buildings 2023, 13, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Houri, A.; Habib, A.; Elzokra, A.; Habib, M. Tensile Testing of Soils: History, Equipment and Methodologies. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussainy, F.; Hasan, H.A.; Rogic, S.; Sheikh, M.N.; Hadi, M.N. Direct tensile testing of Self-Compacting Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussainy, F.; Hasan, H.A.; Sheikh, M.N.; Hadi, M.N.S. A New Method for Direct Tensile Testing of Concrete. J. Test. Evaluation 2019, 47, 704–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Pellegrino, A.; Heisserer, U.; Duke, P.W.; Curtis, P.T.; Morton, J.; Petrinic, N.; Tagarielli, V.L. A new technique for tensile testing of engineering materials and composites at high strain rates. Proc. R. Soc. A: Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2019, 475, 20190310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Peled, A.; Mobasher, B. Dynamic tensile testing of fabric–cement composites. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 25, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betaubun, P. (2018). Compressive Strength And Tensile Tests For Concrete Made From Local Materials From Toftof, Eligobel District. International Journal of Civil Engineering and Technology (IJCIET), 9(8), 574-579.
- Rao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Yi, W.; Xie, W. A New Flattened Cylinder Specimen for Direct Tensile Test of Rock. Sensors 2021, 21, 4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, T.; Tinjum, J.M.; Gokce, A.; Edil, T.B. Protocol for Testing Flexural Strength, Flexural Modulus, and Fatigue Failure of Cementitiously Stabilized Materials Using Third-Point Flexural Beam Tests. Geotech. Test. J. 2016, 39, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkawi, A. B. , Habib, M. ( 18(65), 132–139.
- Kang, T.H.-K.; Kim, W.; Kwak, Y.-K.; Hong, S.-G. Flexural Testing of Reinforced Concrete Beams with Recycled Concrete Aggregates. ACI Struct. J. 2014, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, J. (2011). Flexural testing of sustainable and alternative materials for surfboard construction, in comparison to current industry standard materials.
- Ding, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Dai, J.; Xu, H. Investigation into the Flexural Toughness and Methods of Evaluating Ductile Concrete. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piratheepan, J.; Arulrajah, A.; Disfani, M.M. Large-Scale Direct Shear Testing of Recycled Construction and Demolition Materials. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2013, 2, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arulrajah, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Piratheepan, J.; Bo, M.W.; Imteaz, M.A. Evaluation of Interface Shear Strength Properties of Geogrid-Reinforced Construction and Demolition Materials Using a Modified Large-Scale Direct Shear Testing Apparatus. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradler, P.R.; Fischer, J.; Wan-Wendner, R.; Lang, R.W. Shear test equipment for testing various polymeric materials by using standardized multipurpose specimens with minor adaptions. Polym. Test. 2019, 75, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, J. S. J. , Walker, P., Heath, A., & Morgan, T. K. K. B. (2012). Evaluating shear test methods for stabilised rammed earth. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers-Construction Materials, 165(6), 325-334.
- Ma, S.; Wong, R.; Chau, K. Shear strength components of concrete under direct shearing. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, O.A. Comparison between the Behaviors of Different Concrete Types in Various Shear Tests. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, V.V.; Singh, B.; Patel, V.; Trivedi, A. Evaluation of modulus of elasticity for normal and high strength concrete with granite and calc-granulite aggregate. Struct. Concr. 2020, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.I.; Morais, J.; Morais, P.; Veiga, M.D.R.; Santos, C.; Candeias, P.; Ferreira, J.G. Modulus of elasticity of mortars: Static and dynamic analyses. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 232, 117216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lu, L.; Qiao, P. Assessment of wave modulus of elasticity of concrete with surface-bonded piezoelectric transducers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 242, 118033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shires, G.A. Hardness Tests Research: Some Practical Aspects of the Scratch Test for Hardness. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. 1925, 108, 647–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, D. The physical meaning of indentation and scratch hardness. Br. J. Appl. Phys. 1956, 7, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, B.J.; Sinha, S.K. Scratch Resistance and Localised Damage Characteristics of Polymer Surfaces – a Review. Mater. und Werkst. 2003, 34, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broitman, E. Indentation Hardness Measurements at Macro-, Micro-, and Nanoscale: A Critical Overview. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachurski, Z. H. (2006). Testing materials’ hardness science, technology & application. In Mater Forum (Vol. 30, pp. 118-125).
- Xu, X.; van der Zwaag, S.; Xu, W. Prediction of the abrasion resistance of construction steels on the basis of the subsurface deformation layer in a multi-pass dual-indenter scratch test. Wear 2015, 338-339, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanu, L. , Badita, L. L., & Florescu, V. (2018). The abrasion resistance estimation of the C120 steel by a multi-pass dual-indenter scratch test. Jurnal Tribologi, 16, 30-41.
- Atkinson, R. H. (1993). Hardness tests for rock characterization. In Rock testing and site characterization (pp. 105-117). Pergamon.
- Narayanaswamy, B.; Ghaderi, A.; Hodgson, P.; Cizek, P.; Chao, Q.; Safi, M.; Beladi, H. Abrasive Wear Resistance of Ferrous Microstructures with Similar Bulk Hardness Levels Evaluated by a Scratch-Tester Method. Met. Mater. Trans. A 2019, 50, 4839–4850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, A. F. , Hassan, M. K., Alshamrani, A. H., Azam, S. A., Abdellah, M. Y., & Backar, A. H. (2022). Assessment of the Wear Behavior and Surface Roughness of Epoxy/Date Seed's Powder Bio-composites. American Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 10(1), 41-48.
- Mathias, L. (2023). Material Characterization with Digital Image Correlation: Understanding the properties and behavior of materials through various testing methods, such as tensile, hardness, and impact testing, to determine their mechanical, thermal, and chemical characteristics. SSRN Journal.
- Rajendran, R.; Narasimhan, K. Deformation and fracture behaviour of plate specimens subjected to underwater explosion—a review. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2006, 32, 1945–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Lu, Y. Evaluation of typical concrete material models used in hydrocodes for high dynamic response simulations. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2009, 36, 132–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milionis, A.; Loth, E.; Bayer, I.S. Recent advances in the mechanical durability of superhydrophobic materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 229, 57–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabir, H.A.; Abid, S.R.; Murali, G.; Ali, S.H.; Klyuev, S.; Fediuk, R.; Vatin, N.; Promakhov, V.; Vasilev, Y. Experimental Tests and Reliability Analysis of the Cracking Impact Resistance of UHPFRC. Fibers 2020, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Wang, S. Time-Dependent Behavior of Diabase and a Nonlinear Creep Model. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2013, 47, 1211–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Sun, B.; Chen, L. Creep characteristics and time-dependent creep model of tunnel lining structure concrete. Mech. Time-Dependent Mater. 2020, 25, 365–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.-S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Zhai, H.-R.; Wang, G.-Y.; Su, Y.-J.; Dai, L.; Ogata, S.; Zhang, T.-Y. Time-, stress-, and temperature-dependent deformation in nanostructured copper: Creep tests and simulations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2016, 94, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, C. Time-dependent tests on intact rocks in uniaxial compression. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Géoméch. Abstr. 2000, 37, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.-H.; Tong, F. Constitutive modeling of time-dependent stress–strain behaviour of saturated soils exhibiting both creep and swelling. Can. Geotech. J. 2011, 48, 1870–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabre, G. , & Pellet, F. (2006). Creep and time-dependent damage in argillaceous rocks. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 43(6), 950-960.
- Lucas, B.N.; Oliver, W.C.; Pharr, G.M.; Loubet, J.-L. Time Dependent Deformation During Indentation Testing. MRS Proc. 1996, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshoff, W. P. , & Van Zijl, G. P. (2007). Time-dependent response of ECC: Characterisation of creep and rate dependence. Cement and concrete research, 37(5), 725-734.
- Zhang, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Z.; Han, Z.; Weng, X.; Wang, L. Uniaxial Creep Test Analysis on Creep Characteristics of Fully Weathered Sandy Shale. Processes 2023, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raske, D. T. , & Morrow, J. (1969). Mechanics of materials in low cycle fatigue testing. In Manual on low cycle fatigue testing. ASTM International.
- Manson, S.; Halford, G. Fatigue and Durability of Structural Materials; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, United States, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas, T. (2006). High cycle fatigue: a mechanics of materials perspective. Elsevier.
- Teixeira, E.C.; Piascik, J.R.; Stoner, B.R.; Thompson, J.Y. Dynamic fatigue and strength characterization of three ceramic materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 1219–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, G.; Huang, P.; Zhou, G.; Lv, S. Experimental Research on Fatigue Behavior of Existing Reinforced Concrete Beams. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carrasco, L. , Torrens-Martín, D., Morales, L. M., & Martínez-Ramírez, S. (2012). Infrared spectroscopy in the analysis of building and construction materials. Infrared spectroscopy–Materials science, engineering and technology, 510.
- Zofka, A.; Chrysochoou, M.; Yut, I.; Johnston, C.; Shaw, M.; Sun, S.-P.; Mahoney, J.; Farquharson, S.; Donahue, M. ; Strategic Highway Research Program Renewal Focus Area; et al. Evaluating Applications of Field Spectroscopy Devices to Fingerprint Commonly Used Construction Materials; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, United States, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Abina, A.; Puc, U.; Jeglič, A.; Zidanšek, A. Applications of Terahertz Spectroscopy in the Field of Construction and Building Materials. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2014, 50, 279–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politano, G.G.; Versace, C. Spectroscopic Ellipsometry: Advancements, Applications and Future Prospects in Optical Characterization. Spectrosc. J. 2023, 1, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, G.; Sun, D.; Yu, F.; Hu, M.; Lu, T. Application of gel permeation chromatography technology in asphalt materials: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leninskii, M.A.; Savelieva, E.I.; Karakashev, G.V.; Vasilieva, I.A.; Samchenko, N.A. Determination of the Conversion Products of Toxic organophosphorus substances in Construction Materials Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 77, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, X.; Ling, S.; Guo, D. Deterioration and Oxidation Characteristics of Black Shale under Immersion and Its Impact on the Strength of Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulusoy, Ö. , Akça, B., & Erzeneoğlu, S. Z. (2019). Analysis of various construction materials used in turkey with wavelength dispersive x-ray fluorescence spectrometer. JMEST, 6, 10994-11002.
- Garcia-Florentino, C.; Maguregui, M.; Margui, E.; Torrent, L.; Queralt, I.; Madariaga, J.M. Development of Total Reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry quantitative methodologies for elemental characterization of building materials and their degradation products. Spectrochim. Acta Part B: At. Spectrosc. 2018, 143, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eshaikh, M.A.; Kadachi, A. Elemental analysis of steel products using X-ray fluorescence (XRF) technique. J. King Saud Univ. - Eng. Sci. 2011, 23, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudbrink, B.; Khanzadeh Moradllo, M.; Hu, Q.; Ley, M.T.; Davis, J.M.; Materer, N.; Apblett, A. Imaging the presence of silane coatings in concrete with micro X-ray fluorescence. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 92, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradllo, M.K.; Sudbrink, B.; Hu, Q.; Aboustait, M.; Tabb, B.; Ley, M.T.; Davis, J.M. Using micro X-ray fluorescence to image chloride profiles in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 92, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, S. A. , Provis, J. L., Rose, V., & de Gutiérrez, R. M. (2013). High-resolution X-ray diffraction and fluorescence microscopy characterization of alkali-activated slag-metakaolin binders. Journal of the american ceramic society, 96(6), 1951-1957.
- Yang, T.; Yao, X.; Zhang, Z. Quantification of chloride diffusion in fly ash–slag-based geopolymers by X-ray fluorescence (XRF). Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 69, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Núñez, R. Portable X-ray Fluorescence Analysis of Organic Amendments: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, C. S. , & Cravotta III, C. A. (2005b). Net alkalinity and net acidity 2: practical considerations. Applied Geochemistry, 20(10), 1941-1964.
- Grubb, J. A. , Limaye, H. S., & Kakade, A. M. (2007). Testing pH of concrete. Concrete International-Detroit-, 29(4), 78.
- Karastogianni, S. , Girousi, S., & Sotiropoulos, S. (2016). pH: Principles and measurement. Encyclopedia of Food and Health, 4, 333-338.
- Behnood, A. , Van Tittelboom, K., & De Belie, N. (2016). Methods for measuring pH in concrete: A review. Construction and Building Materials, 105, 176-188.
- Stojanović, G.; Radovanović, M.; Krstić, D.; Ignjatovic, I.; Dragaš, J.; Carević, V. Determination of pH in Powdered Concrete Samples or in Suspension. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B. , Durdzinski, P. ( 1, 177–211.
- Villain, G.; Thiery, M.; Platret, G. Measurement methods of carbonation profiles in concrete: Thermogravimetry, chemical analysis and gammadensimetry. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chazallon, C.; Braymand, S.; Hornych, P. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) for characterization of self-cementation of recycled concrete aggregates in pavement. Thermochim. Acta 2024, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrachero, M. , Paya, J., Bonilla, M., & Monzó, J. (2008). The use of thermogravimetric analysis technique for the characterization of construction materials: the gypsum case. Journal of thermal analysis and Calorimetry, 91(2), 503-509.
- Tobón, J.I.; Paya, J.; Borrachero, M.V.; Soriano, L.; Restrepo, O.J. Determination of the optimum parameters in the high resolution thermogravimetric analysis (HRTG) for cementitious materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 107, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veliseicik, T.; Zurauskiene, R.; Valentukeviciene, M. Determining the Impact of High Temperature Fire Conditions on Fibre Cement Boards Using Thermogravimetric Analysis. Symmetry 2020, 12, 1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, D.S.; Ray, A.; Guerbois, J.-P. Differential scanning calorimetry evaluation of autoclaved cement based building materials made with construction and demolition waste. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 389, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, P.; Liu, X.; Erkens, S.; Scarpas, A. Characterization of epoxy-asphalt binders by differential scanning calorimetry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 249, 118800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, W. (2002). Differential scanning calorimetry study of the hydration products in Portland cement pastes with metakaolin replacement. In Advances in building technology (pp. 881-888). Elsevier.
- Sha, W.; Pereira, G. Differential scanning calorimetry study of ordinary Portland cement paste containing metakaolin and theoretical approach of metakaolin activity. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2001, 23, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wanasekara, N.; Yu, X. (. Thermal Properties of Thermochromic Asphalt Binders by Modulated Differential Scanning Calorimetry. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2014, 2444, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Zhang, C.; Shangguan, F.; Li, X. A Differential Scanning Calorimetry Method for Construction of Continuous Cooling Transformation Diagram of Blast Furnace Slag. Met. Mater. Trans. B 2012, 43, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atamanov, M.K.; Noboru, I.; Shotaro, T.; Amrousse, R.; Tulepov, M.Y.; Kerimkulova, A.R.; Hobosyan, M.A.; Hori, K.; Martirosyan, K.S.; Mansurov, Z.A. Investigation of Сombustion and Thermal Analysis of Ammonium Nitrate with Carbonaceous Materials. Combust. Sci. Technol. 2016, 188, 2003–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksel, N. (2016). The review of some commonly used methods and techniques to measure the thermal conductivity of insulation materials. In Insulation materials in context of sustainability. IntechOpen.
- Zhao, D.; Qian, X.; Gu, X.; Jajja, S.A.; Yang, R. Measurement techniques for thermal conductivity and interfacial thermal conductance of bulk and thin film materials. J. Electron. Packag. 2016, 138, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios, A.; Cong, L.; Navarro, M.E.; Ding, Y.; Barreneche, C. Thermal conductivity measurement techniques for characterizing thermal energy storage materials - A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2019, 108, 32–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eithun, C. F. (2012). Development of a thermal conductivity apparatus: Analysis and design (Master's thesis, Institutt for energi-og prosessteknikk).
- Sharma, V.; Singh, S.; Narad, S. Instruments to Measure Thermal Conductivity of Engineering Materials - A Brief Review. J. Adv. Res. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2020, 07, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, I.; Shafigh, P.; Hassan, Z.F.A.B.; Mahyuddin, N.B. Thermal conductivity of concrete – A review. J. Build. Eng. 2018, 20, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Gao, P.; Geng, F.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. Thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of porous concrete materials. Mater. Lett. 2017, 209, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, S.; Nantasai, B. Thermal Conductivity of Pervious Concrete for Various Porosities. ACI Mater. J. 2017, 114, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castán-Fernández, C.; Marcos-Robredo, G.; Castro-García, M.P.; Rey-Ronco, M.A.; Alonso-Sánchez, T. Apparatus Development for the Measurement of the Thermal Conductivity of Geothermal Backfill Materials. Inventions 2023, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowayed, Y.; Zou, W.; Gross, S. An analytical approach to evaluate the coefficients of thermal expansion of textile composite materials. Polym. Compos. 2000, 21, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viviani, M.; Glisic, B.; Smith, I.F.C. System for monitoring the evolution of the thermal expansion coefficient and autogenous deformation of hardening materials. Smart Mater. Struct. 2006, 15, N137–N146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhutovsky, S.; Kovler, K. Evaluation of the Thermal Expansion Coefficient Using Non-Destructive Testing. 10th International Conference on Mechanics and Physics of Creep, Shrinkage, and Durability of Concrete and Concrete Structures. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, AustriaDATE OF CONFERENCE;
- Crawford, G.L.; Gudimettla, J.M.; Tanesi, J. Interlaboratory Study on Measuring Coefficient of Thermal Expansion of Concrete. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2164, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Reis, J.; Ferreira, A.; Marques, A. Thermal expansion of epoxy and polyester polymer mortars—plain mortars and fibre-reinforced mortars. Polym. Test. 2003, 22, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, H.; Young, J.F.; Scherer, G.W. Thermal Expansion Kinetics: Method to Measure Permeability of Cementitious Materials: II, Application to Hardened Cement Pastes. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 385–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsolakis, E.; Kalligeros, C.; Tzouganakis, P.; Koulocheris, D.; Spitas, V. A novel experimental setup for the determination of the thermal expansion coefficient of concrete at cryogenic temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 309, 125134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakyi-Bekoe, K. (2008). Assessment of the coefficient of thermal expansion of Alabama concrete (Doctoral dissertation).
- Siddiqui, S.; Grasley, Z.; Fowler, D.W. Internal water pressure development in saturated concrete cylinder subjected to coefficient of thermal expansion tests: Poroelastic model. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aly, H.A.; Seleman, M.M.E.-S.; Bakkar, A.; Albaijan, I.; Ahmed, M.M.Z.; Ibrahim, K.M. Effect of Si Content on the Thermal Expansion of Ti15Mo(0–2 Si) Biomaterial Alloys during Different Heating Rates. Materials 2023, 16, 4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xue, S.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, G. Robust Interferometry for Testing Thermal Expansion of Dual-Material Lattices. Materials 2020, 13, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, M.; Karawacki, E.; Gustafsson, S.E. Thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, and specific heat of thin samples from transient measurements with hot disk sensors. Rev. Sci. Instruments 1994, 65, 3856–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavsson, M.; Gustavsson, J.; Gustafsson, S.; Hälldahl, L. Recent developments and applications of the hot disk thermal constants analyser for measuring thermal transport properties of solids. High Temp. Press. 2000, 32, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trofimov, A.A.; Atchley, J.; Shrestha, S.S.; Desjarlais, A.O.; Wang, H. Evaluation of measuring thermal conductivity of isotropic and anisotropic thermally insulating materials by transient plane source (Hot Disk) technique. J. Porous Mater. 2020, 27, 1791–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Tsunetsugu, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Shibusawa, T. Thermal properties of wood measured by the hot-disk method: comparison with thermal properties measured by the steady-state method. J. Wood Sci. 2021, 67, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xu, G.; Tao, Z. Effect on the Thermal Properties of Building Mortars with Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials for Radiant Floors. Buildings 2023, 13, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendran, R.; Pang, H.; Wen, H. Use of scanning electron microscopy in concrete studies. Struct. Surv. 1998, 16, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospíšil, K.; Frýbort, A.; Kratochvíl, A.; Macháčková, J. Scanning Electron Microscopy Method as a Tool for the Evaluation of Selected Materials Microstructure. Trans. Transp. Sci. 2008, 1, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A. , & Abdullah, A. In (2018). Scanning electron microscopy (SEM): A review. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Hydraulics and Pneumatics—HERVEX, Băile Govora, Romania (Vol. 2018; pp. 7–9. [Google Scholar]
- Aboustait, M.; Kim, T.; Ley, M.T.; Davis, J.M. Physical and chemical characteristics of fly ash using automated scanning electron microscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 106, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, D.C.; Kleib, J.; Amar, M.; Benzerzour, M.; Abriak, N.-E. Determination of the degree of hydration of Portland cement using three different approaches: Scanning electron microscopy (SEM-BSE) and Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangaru, S.S.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Hassan, M. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) image segmentation for microstructure analysis of concrete using U-net convolutional neural network. Autom. Constr. 2022, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imtiaz, T.; Ahmed, A.; Hossain, S.; Faysal, M. Microstructure Analysis and Strength Characterization of Recycled Base and Sub-Base Materials Using Scanning Electron Microscope. Infrastructures 2020, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, F. T. (1974). X ray diffraction. Applications to construction quality control. Materiales de Construcción, 24(155), 63-84.
- Bunaciu, A.A.; Udriştioiu, E.g.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. X-Ray Diffraction: Instrumentation and Applications. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2014, 45, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epp, J. (2016). X-ray diffraction (XRD) techniques for materials characterization. In Materials characterization using nondestructive evaluation (NDE) methods (pp. 81-124). Woodhead Publishing.
- Snellings, R.; Salze, A.; Scrivener, K. Use of X-ray diffraction to quantify amorphous supplementary cementitious materials in anhydrous and hydrated blended cements. Cem. Concr. Res. 2014, 64, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhapekar, N. K. , & Chopkar, D. M. (2016). Structural health monitoring of ordinary portland cement concrete structures using X-ray diffraction. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 11(9), 6128-6131.
- Uzbaş, B.; Aydin, A.C. Analysis of Fly Ash Concrete With Scanning Electron Microscopy and X-Ray Diffraction. Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J. 2019, 13, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, K.; Mitsui, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Watanabe, K. X-ray powder diffraction camera for high-field experiments. J. Physics: Conf. Ser. 2009, 156, 012018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilkes, R. J. (1994). Transmission electron microscope analysis of soil materials. Quantitative methods in soil mineralogy, 177-204.
- Mathur, P. C. (2007). Study of cementitious materials using transmission electron microscopy. École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne.
- Stutzman, P. E. , & Clifton, J. R. (1999, April). Specimen preparation for scanning electron microscopy. In Proceedings of the international conference on cement microscopy (Vol. 21; pp. 10–22.
- Lam, J. , Katti, P. ( 10(9), 2177. [PubMed]
- Magonov, S.N.; Reneker, D.H. CHARACTERIZATION OF POLYMER SURFACES WITH ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1997, 27, 175–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B. Nano- to microscale wear and mechanical characterization using scanning probe microscopy. Wear 2001, 251, 1105–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chung, H.; Sow, C.; Wee, A. Nanoscale materials patterning and engineering by atomic force microscopy nanolithography. Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Rep. 2006, 54, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugstad, G. (2012). Atomic force microscopy: understanding basic modes and advanced applications. John Wiley & Sons.
- Gulati, K.; Adachi, T. Profiling to Probing: Atomic force microscopy to characterize nano-engineered implants. Acta Biomater. 2023, 170, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Balogun, O.; Shah, S.P. Atomic Force Acoustic Microscopy to Measure Nanoscale Mechanical Properties of Cement Pastes. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2010, 2141, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trtik, P.; Kaufmann, J.; Volz, U. On the use of peak-force tapping atomic force microscopy for quantification of the local elastic modulus in hardened cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peled, A.; Castro, J.; Weiss, W. Atomic force and lateral force microscopy (AFM and LFM) examinations of cement and cement hydration products. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2013, 36, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, K.; Siddique, S.; Ramana, P.V. Employing atomic force microscopy technique and X-ray diffraction analysis to examine nanostructure and phase of glass concrete. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2019, 26, 700–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Cai, M.; Tong, T.; Wang, H. Progress in the Correlative Atomic Force Microscopy and Optical Microscopy. Sensors 2017, 17, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Petersson, P.-. .-E. Slab test: Freeze/thaw resistance of concrete—Internal deterioration. Mater. Struct. 2004, 37, 754–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Coventry, K.; Bacon, J. Freeze/thaw durability of concrete with recycled demolition aggregate compared to virgin aggregate concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Rikabi, F.T.; Sargand, S.M.; Khoury, I.; Hussein, H.H. Material Properties of Synthetic Fiber-Reinforced Concrete under Freeze-Thaw Conditions. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-C.; Meng, S.-P.; Cao, D.-F.; Tu, Y.-M.; Sabourova, N.; Grip, N.; Ohlsson, U.; Blanksvärd, T.; Sas, G.; Elfgren, L. Evaluation of freeze-thaw damage on concrete material and prestressed concrete specimens. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 892–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tu, Y.; Sas, G.; Elfgren, L. Freeze-thaw damage evaluation and model creation for concrete exposed to freeze–thaw cycles at early-age. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 312, 125352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, G. Experimental investigation on the freeze–thaw durability of concrete under compressive load and with joints. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Pan, X.; Pan, Y.; Jia, P. Effects of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Permeability Behavior and Desiccation Cracking of Dalian Red Clay in China Considering Saline Intrusion. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Elahi, M.; Shearer, C.R.; Reza, A.N.R.; Saha, A.K.; Khan, N.N.; Hossain, M.; Sarker, P.K. Improving the sulfate attack resistance of concrete by using supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs): A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 281, 122628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhutovsky, S.; Hooton, R.D. Accelerated testing of cementitious materials for resistance to physical sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.H.; Alrashidi, R.S.; Mosavi, H.; Almarshoud, M.A.; Riding, K.A. Potential accelerated test methods for physical sulfate attack on concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, M.; Metalssi, O.O.; Quiertant, M.; Baroghel-Bouny, V. A Critical Review of Existing Test-Methods for External Sulfate Attack. Materials 2022, 15, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedriks, A. J. (1996). Corrosion of stainless steels (Vol. 15). John Wiley & Sons.
- Blawert, C.; Dietzel, W.; Ghali, E.; Song, G. Anodizing Treatments for Magnesium Alloys and Their Effect on Corrosion Resistance in Various Environments. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2006, 8, 511–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiromoto, S.; Yamamoto, A. High corrosion resistance of magnesium coated with hydroxyapatite directly synthesized in an aqueous solution. Electrochimica Acta 2009, 54, 7085–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghali, E. (2010). Corrosion resistance of aluminum and magnesium alloys: understanding, performance, and testing. John Wiley & Sons.
- Bakar, B. H. A. , Jaya, R. P., & Aziz, H. A. (2011, August). Malaysian rice husk ash–improving the durability and corrosion resistance of concrete: Pre-review. In EACEF-International Conference of Civil Engineering (Vol. 1, pp. 607-612).
- Erofeev, V.; Yausheva, L.; Bulgakov, A.; Bobryshev, A.; Shafigullin, L.; Afonin, V. Chemical resistance of sulfur concrete. THE THIRD INTERNATIONAL SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE CONSTRUCTION MECHANICS, HYDRAULICS AND WATER RESOURCES ENGINEERING (CONMECHYDRO 2021 AS). LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, UzbekistanDATE OF CONFERENCE; p. 060021.
- Lee, H.B.; Lee, K.S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, B.I.; Go, B.R.; Rhu, C.J.; Han, T.H. Effect of Chemical Agents on the Morphology and Chemical Structures of Microplastics. Polymers 2022, 14, 4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, B. D. , & Anderson, D. S. (Eds.). (1994). Handbook of corrosion data. ASM international.
- Ghali, E.; Dietzel, W.; Kainer, K.-U. Testing of General and Localized Corrosion of Magnesium Alloys: A Critical Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2004, 13, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Deng, H.; Lan, W.; Cao, P. Electrochemical investigation on atmospheric corrosion of carbon steel under different environmental parameters. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater. 2013, 60, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniyal; Akhtar, S. Corrosion assessment and control techniques for reinforced concrete structures: a review. J. Build. Pathol. Rehabilitation 2019, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulsada, S.A.; Fazakas. ; Török, T.I. Corrosion testing on steel reinforced XD3 concrete samples prepared with a green inhibitor and two different superplasticizers. Mater. Corros. 2019, 70, 1262–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa-Sánchez, A.; Bosch, J.; Baltazar-Zamora, M.A.; Croche, R.; Landa-Ruiz, L.; Santiago-Hurtado, G.; Moreno-Landeros, V.M.; Olguín-Coca, J.; López-Léon, L.; Bastidas, J.M.; et al. Corrosion Behavior of Steel-Reinforced Green Concrete Containing Recycled Coarse Aggregate Additions in Sulfate Media. Materials 2020, 13, 4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.; Mamidi, S.K.; Kamat, S.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Bijukumar, D.; Tsai, P.-I.; Wu, M.-H.; Orías, A.A.E.; Mathew, M.T. Mechanical, Electrochemical and Biological Behavior of 3D Printed-Porous Titanium for Biomedical Applications. J. Bio- Tribo-Corrosion 2021, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, E. W. (2011). Comparison of two methods for the assessment of chloride ion penetration in concrete: A field study.
- Bhaskar, S. (2013). Study of chloride induced corrosion of reinforcement steel in cracked concrete (Doctoral dissertation, Ph. D. thesis, Indian Institute of Technology Madras, Chennai, India).
- Rengaraju, S. R. I. P. R. I. Y. A. (2019). Electrochemical response and chloride threshold of steel in highly resistive concrete systems. Indian Institute of Technology Madras, 36.
- Güneyisi, E.; Özturan, T.; Gesogˇlu, M. Effect of initial curing on chloride ingress and corrosion resistance characteristics of concretes made with plain and blended cements. J. Affect. Disord. 2007, 42, 2676–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioubakhsh, S. (2011). The penetration of chloride in concrete subject to wetting and drying: measurement and modelling (Doctoral dissertation, UCL (University College London)).
- Wang, B. (2019). Corrosion Behavior of Corrosion-Resistant Steel Reinforcements in High and Ultra-High Performance Concrete in Chloride Attack Environments (Doctoral dissertation).
- Paul, S. C. , & van Zijl, G. P. (2016). Chloride-induced corrosion modelling of cracked reinforced SHCC. Archives of Civil and Mechanical Engineering, 16, 734-742.
- Berrocal, C.G.; Lundgren, K.; Löfgren, I. Corrosion of steel bars embedded in fibre reinforced concrete under chloride attack: State of the art. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 80, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hološová, M. .; Eštoková, A.; Lupták, M. Rapid Chloride Permeability Test of Mortar Samples with Various Admixtures. The 4th International Conference on Advances in Environmental Engineering. LOCATION OF CONFERENCE, COUNTRYDATE OF CONFERENCE; p. 36.
- Zych, T. (2015). Test methods of concrete resistance to chloride ingress. Czasopismo Techniczne.
- Moreno, E. I. (1997). Carbonation in Concrete and Effect on Steel Corrosion.
- Parrott, L.J. A study of carbonation-induced corrosion. Mag. Concr. Res. 1994, 46, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heiyantuduwa, R.; Alexander, M.G.; Mackechnie, J.R. Performance of a Penetrating Corrosion Inhibitor in Concrete Affected by Carbonation-Induced Corrosion. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2006, 18, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikotun, J. O. (2017). Effects of concrete quality and cover depth on carbonation-induced reinforcement corrosion and initiation of concrete cover cracking in reinforced concrete structures (Doctoral dissertation, University of the Witwatersrand, Faculty of Engineering and the Built Environment, School of Civil and Environmental Engineering).
- Mizzi, B.; Wang, Y.; Borg, R.P. Effects of climate change on structures; analysis of carbonation-induced corrosion in Reinforced Concrete Structures in Malta. IOP Conf. Series: Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 442, 012023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortolan, T.L.P.; Borges, P.M.; Silvestro, L.; da Silva, S.R.; Possan, E.; Andrade, J.J.d.O. Durability of concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregates: carbonation and service life prediction under chloride-induced corrosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, S. (2013). The effects of global climate change on carbonation induced corrosion of reinforced concrete structures (Doctoral dissertation, University of British Columbia).
- Zhu, X.; Zi, G.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Kong, J. Probabilistic analysis of reinforcement corrosion due to the combined action of carbonation and chloride ingress in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C. Evaluation of the degree of carbonation of concretes in three environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 230, 116804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgacem, M. E. G. (2021). Correlation permeability/carbonation and its influence on the service life of reinforced concrete structures (Doctoral dissertation).
- Zhang, P.; Li, Q.-F. Effect of polypropylene fiber on durability of concrete composite containing fly ash and silica fume. Compos. Part B: Eng. 2013, 45, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krus, M. (1996). Moisture transport and storage coefficients of porous mineral building materials. Theoretical Principles and New Test Methods. IRB-Verlag Stuttgart.
- Wan, Y.Z.; Luo, H.; He, F.; Liang, H.; Huang, Y.; Li, X.L. Mechanical, moisture absorption, and biodegradation behaviours of bacterial cellulose fibre-reinforced starch biocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1212–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q. (2005). Investigation of conditions for moisture damage in asphalt concrete and appropriate laboratory test methods.
- Yorseng, K.; Rangappa, S.M.; Pulikkalparambil, H.; Siengchin, S.; Parameswaranpillai, J. Accelerated weathering studies of kenaf/sisal fiber fabric reinforced fully biobased hybrid bioepoxy composites for semi-structural applications: Morphology, thermo-mechanical, water absorption behavior and surface hydrophobicity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 235, 117464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslinda, A.; Majid, M.A.; Ridzuan, M.; Afendi, M.; Gibson, A. Effect of water absorption on the mechanical properties of hybrid interwoven cellulosic-cellulosic fibre reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Struct. 2017, 167, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, M.R.; Velosa, A.; Magalhães, A. Experimental applications of mortars with pozzolanic additions: Characterization and performance evaluation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 23, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, R.; Singh, M. The dynamic properties of fibre-reinforced polymers exposed to hot, wet conditions. Compos. Sci. Technol. 1996, 56, 977–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chia, K.S.; Zhang, M.-H. Water absorption, permeability, and resistance to chloride-ion penetration of lightweight aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 25, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnaik, A.; Mvubu, M.; Muniyasamy, S.; Botha, A.; Anandjiwala, R.D. Thermal and sound insulation materials from waste wool and recycled polyester fibers and their biodegradation studies. Energy Build. 2015, 92, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.-P.M.; Kan, C.-W.; Fan, J.-T. Comparison of test methods for measuring water absorption and transport test methods of fabrics. Measurement 2017, 97, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egtvedt, S. (2011). Thermally sprayed aluminum (TSA) with cathodic protection as corrosion protection for steel in natural seawater: characterization of properties on TSA and calcareous deposit (Master's thesis, Institutt for materialteknologi).
- Malik, A.U.; Al-Fozan, S.A. Corrosion and materials selection in MSF desalination plants. Corros. Rev. 2011, 29, 153–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surowska, B.; Ostapiuk, M.; Jakubczak, P.; Droździel, M. The Durability of an Organic–Inorganic Sol–Gel Interlayer in Al-GFRP-CFRP Laminates in a Saline Environment. Materials 2019, 12, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.; Hsu, H.; Young, M.; Huang, J. Mechanical degradation of cold-worked 304 stainless steel in salt spray environments. J. Nucl. Mater. 2012, 422, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagui, S.; Ray, A.; Sahu, J.; Parida, N.; Swaminathan, J.; Tamilselvi, M.; Mannan, S. Influence of saline environment on creep rupture life of Nimonic-263 for marine turbine application. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 566, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karafyllias, G. (2017). The effect of acidity and salinity level in erosion-corrosion performance of metals.
- Chen, H.; Gao, W.; Liu, T.; Lin, W.; Li, M. An experimental study on the effect of salt spray testing on the optical properties of solar selective absorber coatings produced with different manufacturing technologies. Int. J. Energy Environ. Eng. 2019, 10, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar-Ozbek, A.S.; Weerheijm, J.; Schlangen, E.; van Breugel, K. Investigating porous concrete with improved strength: Testing at different scales. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 41, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, G.; Zhang, H. Preparation and characterization of high porosity cement-based foam material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, C.; Zhuge, Y.; Beecham, S. The relationship between porosity and strength for porous concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2011, 25, 4294–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, S.C.; Carrijo, P.M.; Figueiredo, A.D.; Chaves, A.P.; John, V.M. On the classification of mixed construction and demolition waste aggregate by porosity and its impact on the mechanical performance of concrete. Mater. Struct. 2009, 43, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, S.; Li, S. Design and Application of a Rock Porosity Measurement Apparatus under High Isostatic Pressure. Minerals 2022, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.P.; Zong, L. Evaluation of Relationship between Water Absorption and Durability of Concrete Materials. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2014, 2014, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golewski, G.L. Assessing of water absorption on concrete composites containing fly ash up to 30 % in regards to structures completely immersed in water. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurain Izzati, M. Y. , Suraya Hani, A., Shahiron, S., Sallehuddin Shah, A., Mohamad Hairi, O., Zalipah, J.,... & Nurul Amirah, K. (2019, April). Strength and water absorption properties of lightweight concrete brick. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 513, p. 012005). IOP Publishing.
- Pachideh, G.; Gholhaki, M. Effect of pozzolanic materials on mechanical properties and water absorption of autoclaved aerated concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 26, 100856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benazzouk, A.; Douzane, O.; Langlet, T.; Mezreb, K.; Roucoult, J.; Quéneudec, M. Physico-mechanical properties and water absorption of cement composite containing shredded rubber wastes. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2007, 29, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, N.; Siddique, R.; Rajor, A. Influence of bacteria on the compressive strength, water absorption and rapid chloride permeability of fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. A new method to determine the density and water absorption of fine recycled aggregates. Mater. Res. 2013, 16, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elzokra, A.A.E.; Al Houri, A.; Habib, A.; Habib, M.; Malkawi, A.B. Shrinkage Behavior of Conventional and Nonconventional Concrete: A Review. Civ. Eng. J. 2020, 6, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetzel, A.; Herwegh, M.; Zurbriggen, R.; Winnefeld, F. Influence of shrinkage and water transport mechanisms on microstructure and crack formation of tile adhesive mortars. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 42, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, P.-M.; He, Z.-H. Application of shrinkage reducing admixture in concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szlachetka, O.; Witkowska-Dobrev, J.; Dohojda, M.; Cała, A. Influence of compressive strength and maturity conditions on shrinkage of ordinary concrete. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghourchian, S.; Wyrzykowski, M.; Baquerizo, L.; Lura, P. Susceptibility of Portland cement and blended cement concretes to plastic shrinkage cracking. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 85, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulayt, A.; Jaafri, R.; Samouh, H.; El Idrissi, A.C.; Roziere, E.; Moussa, R.; Loukili, A. Stability of a new geopolymer grout: Rheological and mechanical performances of metakaolin-fly ash binary mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 181, 420–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Zeid, M. , Fowler, D. J. ( 224, 12–16.
- Emmons, P. H. , & Vaysburd, A. M. (1995). Performance Criteria for Concrete Repair Materials: Phase I. US Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station.
- Bertolini, L. , Elsener, B., Pedeferri, P., Redaelli, E., & Polder, R. B. (2013). Corrosion of steel in concrete: prevention, diagnosis, repair. John Wiley & Sons.
- Mohammed, A. W. , Ibralebbe, R. M., & Aminayi, P. (2012). Evaluation of Potential use of Waste Powder Paint (WPP) in Cement Grout and Mortar.
- Barabanshchikov, Y.; Pham, H.; Usanova, K. Influence of Microfibrillated Cellulose Additive on Strength, Elastic Modulus, Heat Release, and Shrinkage of Mortar and Concrete. Materials 2021, 14, 6933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraris, C. F. , & Martys, N. S. ( 108(3), 229.
- Khayat, K.H. Viscosity-enhancing admixtures for cement-based materials — An overview. Cem. Concr. Compos. 1998, 20, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tregger, N. , Ferrara, L., & Shah, S. P. (2008). Identifying viscosity of cement paste from mini-slump-flow test. ACI Materials Journal, 105(6), 558.
- Bhattad, A. (2023). Review on viscosity measurement: devices, methods and models. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 1-17.
- Khayat, K. H. (1999). Workability, testing, and performance of self-consolidating concrete. Materials Journal, 96(3), 346-353.
- Papachristoforou, M.; Mitsopoulos, V.; Stefanidou, M. Evaluation of workability parameters in 3D printing concrete. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2018, 10, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domone, P.L.J.; Yongmo, X.; Banfill, P.F.G. Developments of the two-point workability test for high-performance concrete. Mag. Concr. Res. 1999, 51, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, D. G. (2006). Factors influencing concrete workability. In Significance of tests and properties of concrete and concrete-making materials. ASTM International.
- Ahmed, S.; Yehia, S. Evaluation of Workability and Structuration Rate of Locally Developed 3D Printing Concrete Using Conventional Methods. Materials 2022, 15, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautkrämer, J. , & Krautkrämer, H. (2013). Ultrasonic testing of materials. Springer Science & Business Media.
- Ensminger, D. , & Bond, L. J. (2024). Ultrasonics: fundamentals, technologies, and applications. CRC press.
- Schmerr, L. , & Song, J. S. (2007). Ultrasonic nondestructive evaluation systems.
- Chaplin, R. (2017). Industrial Ultrasonic Inspection: Levels 1 and 2. FriesenPress.
- Blitz, J. , & Simpson, G. (1995). Ultrasonic methods of non-destructive testing (Vol. 2). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Gessesew, F. (2007). Non-Destructive Testing of Metallic Structures (Doctoral dissertation, Addis Ababa University).
- Guo, C.; Xu, C.; Hao, J.; Xiao, D.; Yang, W. Ultrasonic Non-Destructive Testing System of Semi-Enclosed Workpiece with Dual-Robot Testing System. Sensors 2019, 19, 3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halmshaw, R. (1995). Industrial radiology: theory and practice (Vol. 1). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Al-Zubaidy, F. R. S. (2010). X-ray Radiographic Study of Simulated Voids–Like Defects in Aluminum Casting and Welded Joints in Steel (Doctoral dissertation, Ministry of Higher Education).
- Berger, H. , & Iddings, F. ( 17, 387–395.
- Low, I.M.; Azman, N.Z.N. Polymer Composites and Nanocomposites for X-Rays Shielding; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Dordrecht, GX, Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Kourra, N. (2016). The application of x-ray computed tomography in aerospace industry: innovation report (Doctoral dissertation, University of Warwick).
- Seeram, E. , & Seeram, E. (2019). Continuous quality improvement for digital radiography. Digital Radiography: Physical Principles and Quality Control, 185-211.
- Mery, D. , & Pieringer, C. (2020). Computer vision for x-ray testing: Imaging, systems, image databases, and algorithms. Springer Nature.
- Urone, P. P. , & Hinrichs, R. (2016). 30.4 X Rays: Atomic Origins and Applications. College Physics.
- Wittmann, F. H. , Zhang, P. , Lehmann, E., & Zhao, Geneva, ASMES Aedification Publishers (pp. 155-174)., T. (2011). Visualisation of frost damage in concrete by means of neutron radiography. In Proceedings of a Workshop on Basic Research on Concrete and Applications. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.-H.; Heo, D.-W.; Jeong, C.-W.; Ryu, J.-H.; Jun, H.Y.; Han, S.-J.; Ha, T.; Yoon, K.-H. Development of Portable Digital Radiography System with a Device for Monitoring X-ray Source-Detector Angle and Its Application in Chest Imaging. Sensors 2017, 17, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenschmidt, J. (2010). Geophysics and non-destructive testing for transport infrastructure, with special emphasis on ground penetrating radar (Doctoral dissertation, ETH Zurich).
- Topczewski, L. (2007). Improvement and application of ground penetrating radar non-destructive technique for the concrete brigde inspection.
- Huston, D. , Fuhr, P. ( 2002). Nondestructive testing of reinforced concrete bridges using radar imaging techniques. The New England Transportation Consortium Report, 15.
- Rasol, M. A. R. (2021). Development of new GPR methodologies for soil and cement concrete pavement assessment.
- Aziz, A. S. (2016). 3D Ground-Penetrating Radar (Gpr) Investigations: Buried Culverts, Historical Graves, A Sandstone Reservoir Analog, And An Impact Crater (Doctoral dissertation).
- Seren, A. , & Acikgoz, A. D. ( 7(40), 3368–3381.
- Suarez, P. F. (2004). Investigation of ground penetrating radar for detection of leaking pipelines under roadway pavements and development of fiber-wrapping repair technique.
- Wang, S. (2021). Prediction of asphalt concrete pavement density from processing ground-penetrating radar compaction data (Doctoral dissertation, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign).
- Lombardi, F.; Ortuani, B.; Facchi, A.; Lualdi, M. Assessing the Perspectives of Ground Penetrating Radar for Precision Farming. Remote. Sens. 2022, 14, 6066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, A.; Yildirim, U.; Eren, O. Mechanical and dynamic properties of high strength concrete with well graded coarse and fine tire rubber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig Jr, R. R. , & Kurdila, A. J. (2006). Fundamentals of structural dynamics. John Wiley & Sons.
- Avitabile, P. (2017). Modal testing: a practitioner's guide. John Wiley & Sons.
- Buzdugan, G. , Mihailescu, E., & Rades, M. (2013). Vibration measurement (Vol. 8). Springer Science & Business Media.
- Araiza Garaygordobil, J. C. (2003). Dynamic assessment of structural building components. Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya.
- Ashory, M. R. (1999). High quality modal testing methods (Doctoral dissertation, University of London).
- Rajasekaran, S. (2009). Structural dynamics of earthquake engineering: theory and application using MATHEMATICA and MATLAB. Elsevier.
- Inman, D. J. (2017). Vibration with control. John Wiley & Sons.
- Baz, A.M. Active and Passive Vibration Damping; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, United States, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Genta, G. (2009). Vibration dynamics and control (Vol. 616). New York: Springer.
- Merzuki, M.N.M.; Rejab, M.R.M.; Sani, M.S.M.; Zhang, B.; Quanjin, M. Experimental investigation of free vibration analysis on fibre metal composite laminates. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2019, 13, 5753–5763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
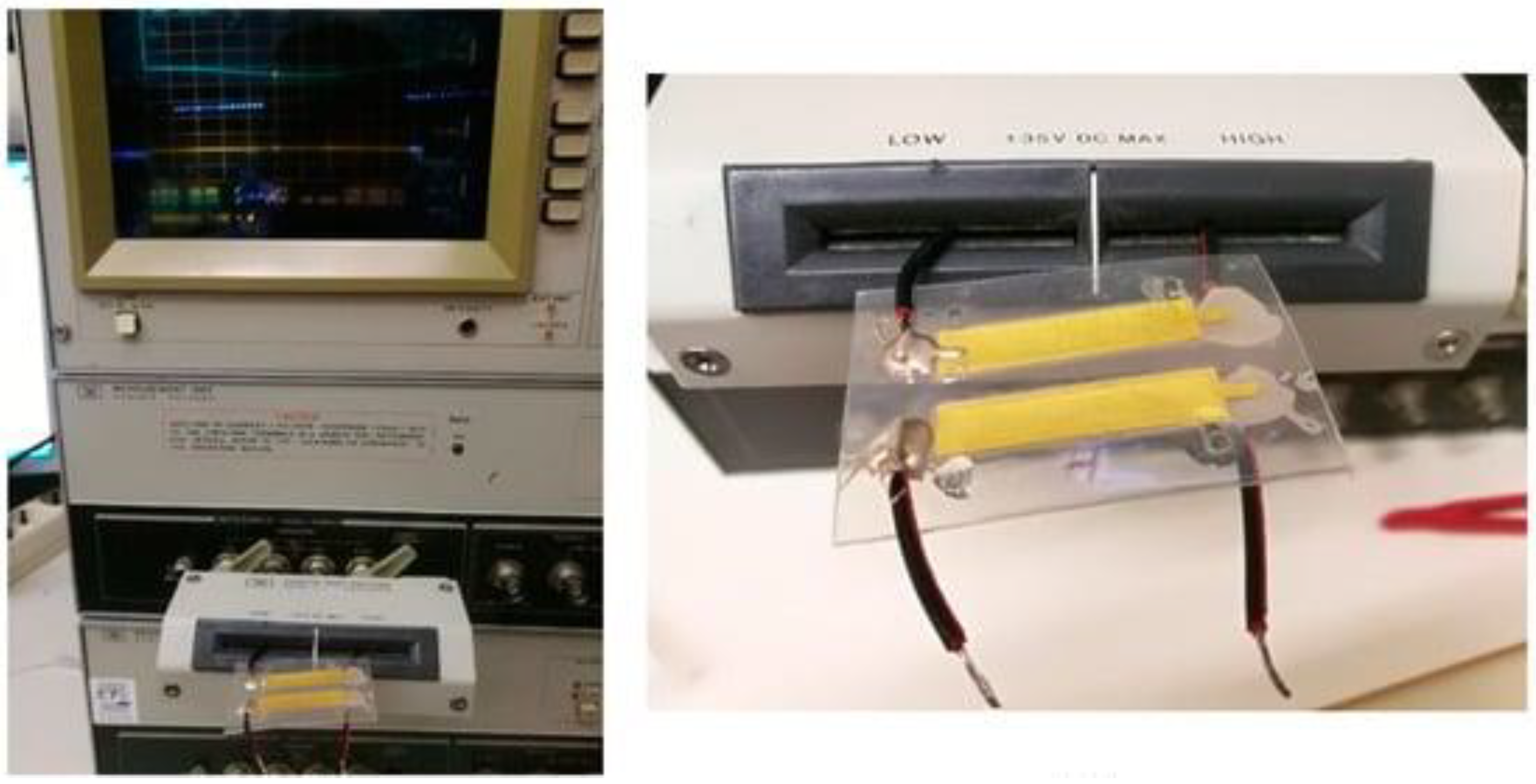
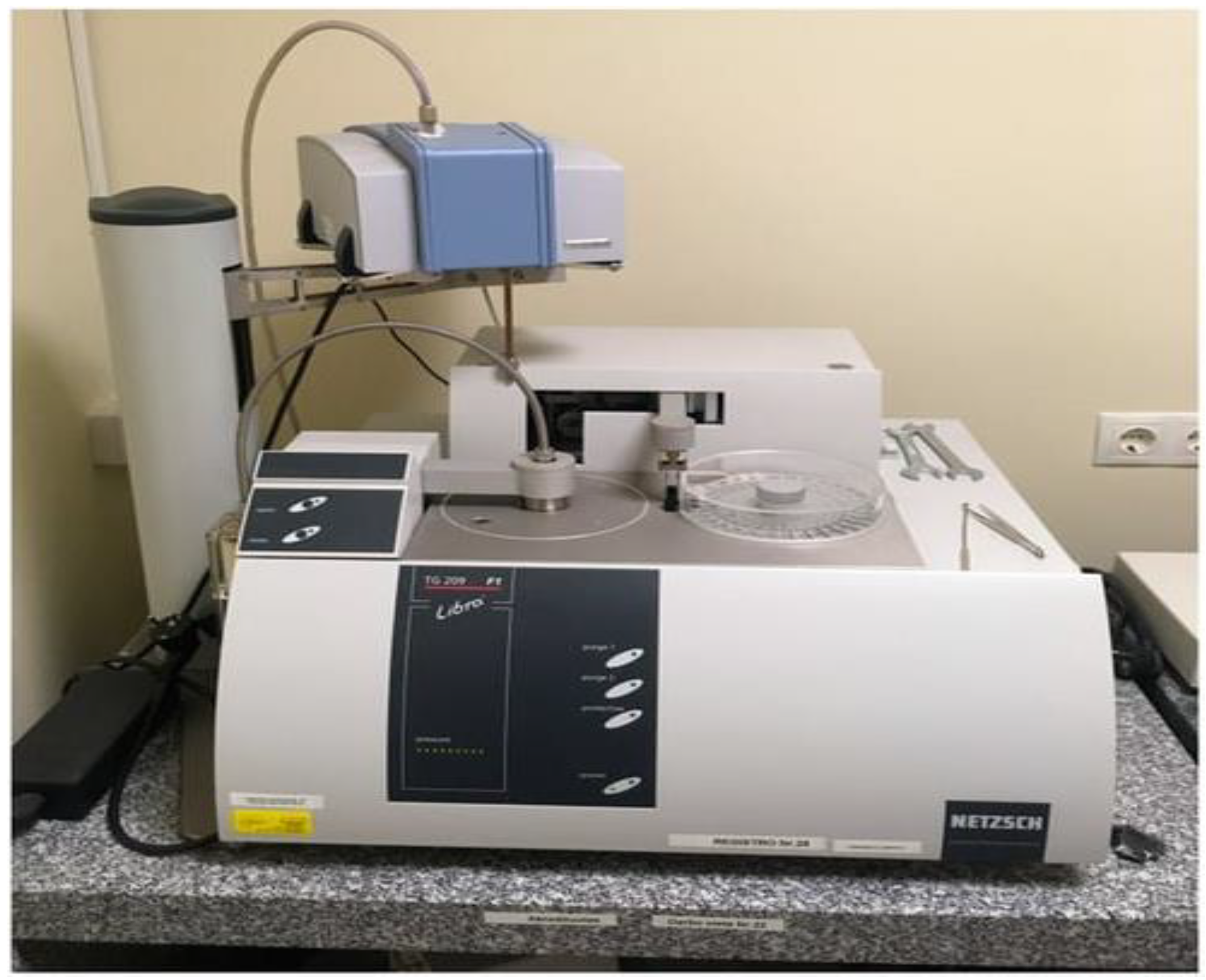
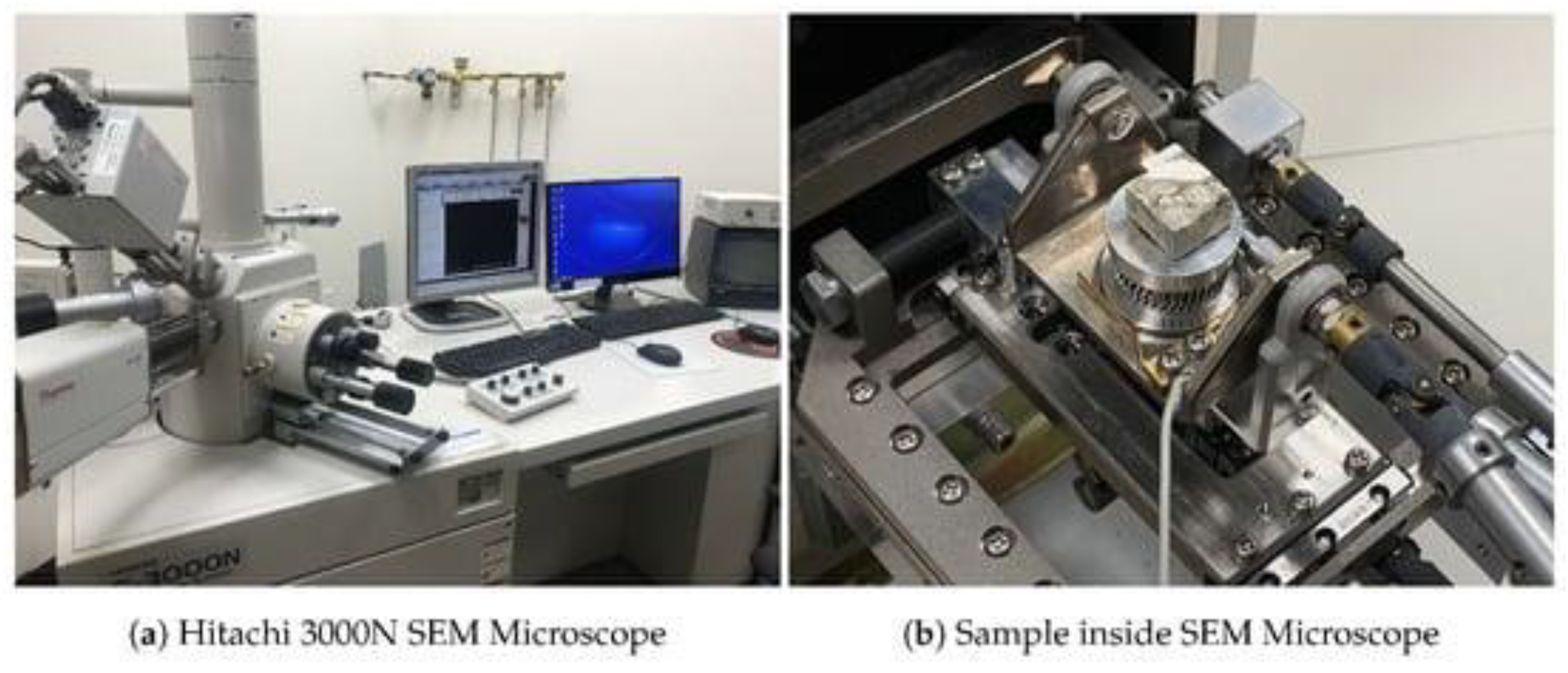
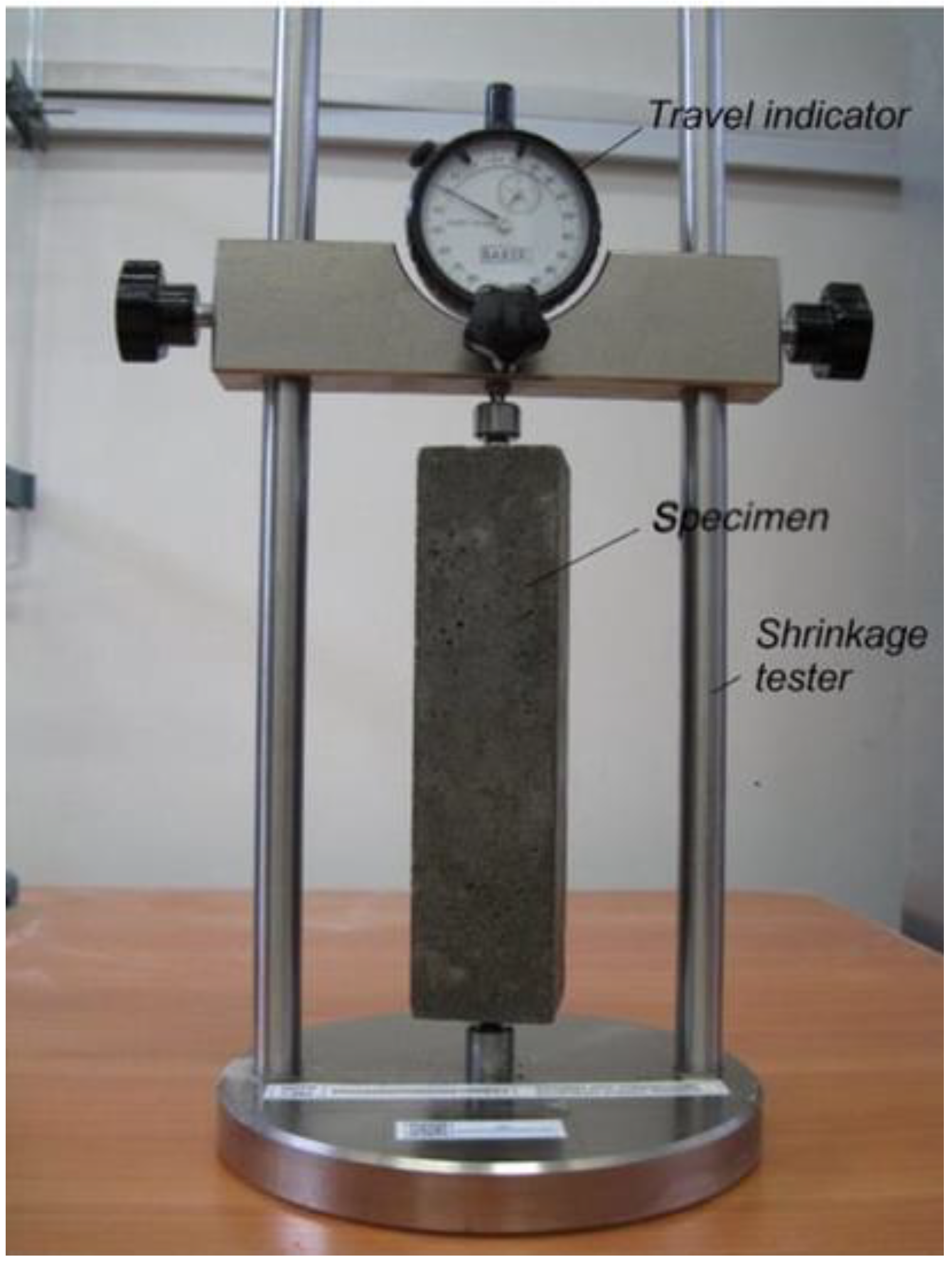
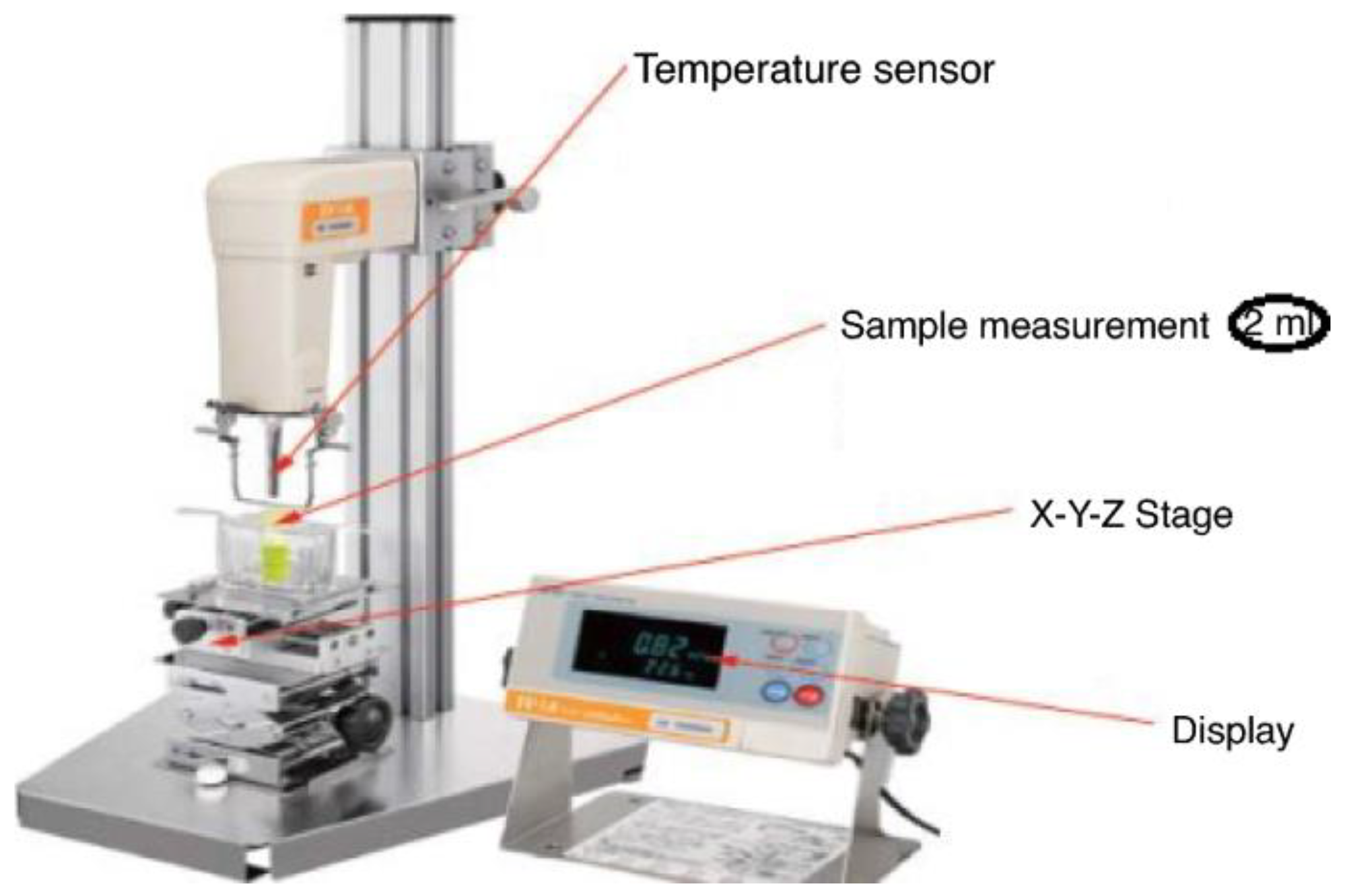
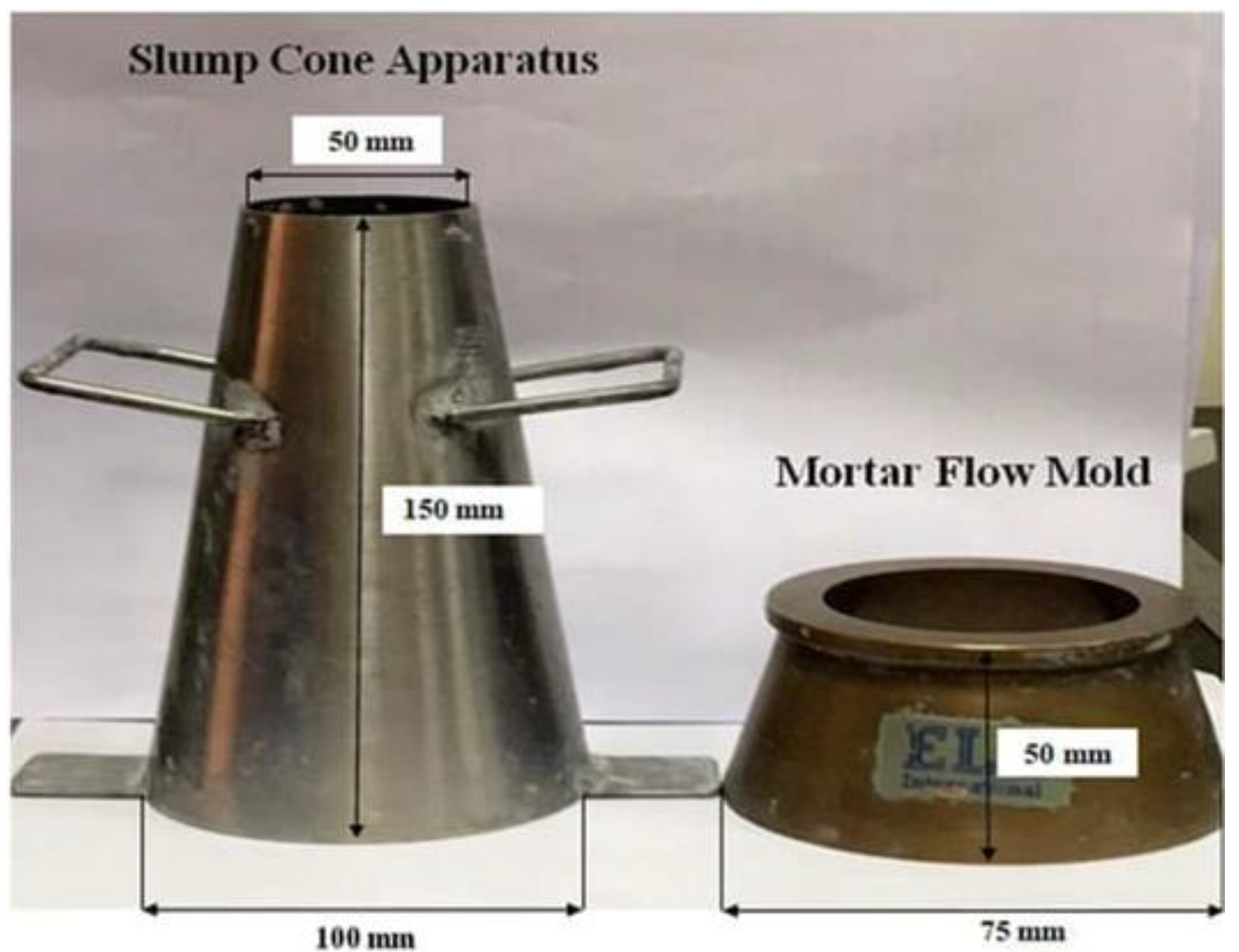
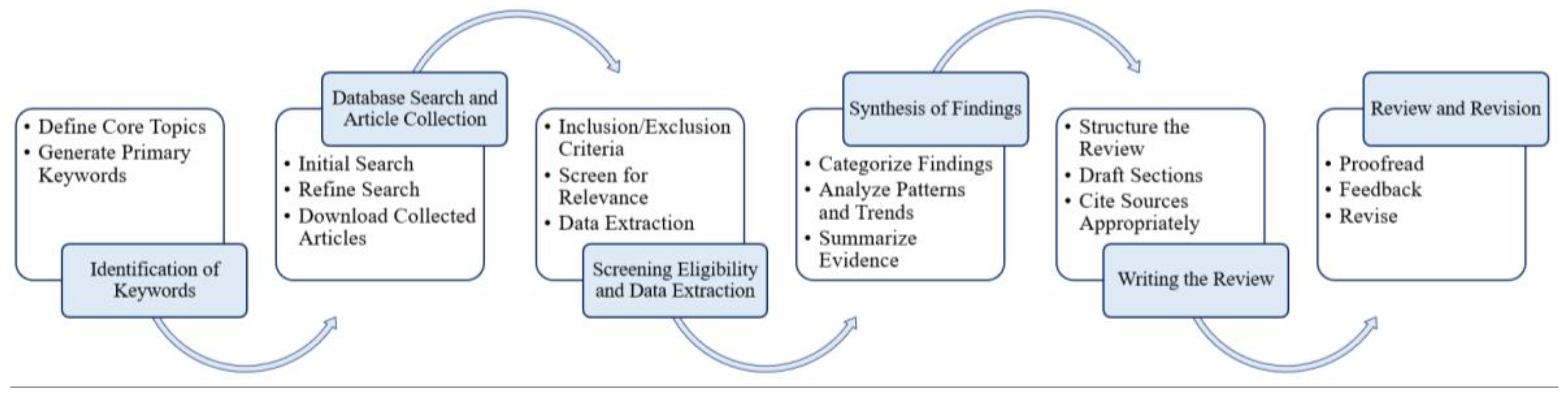
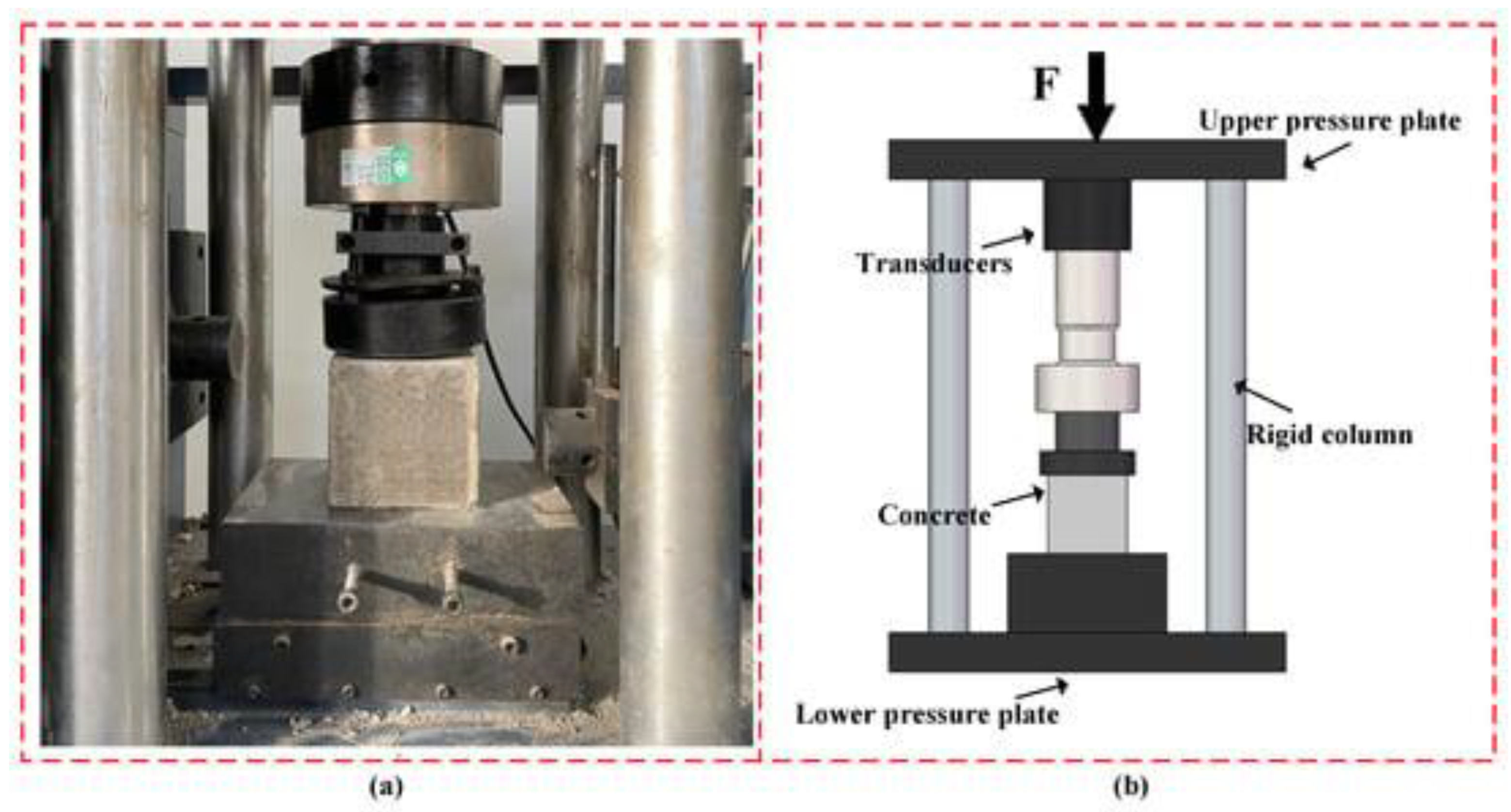

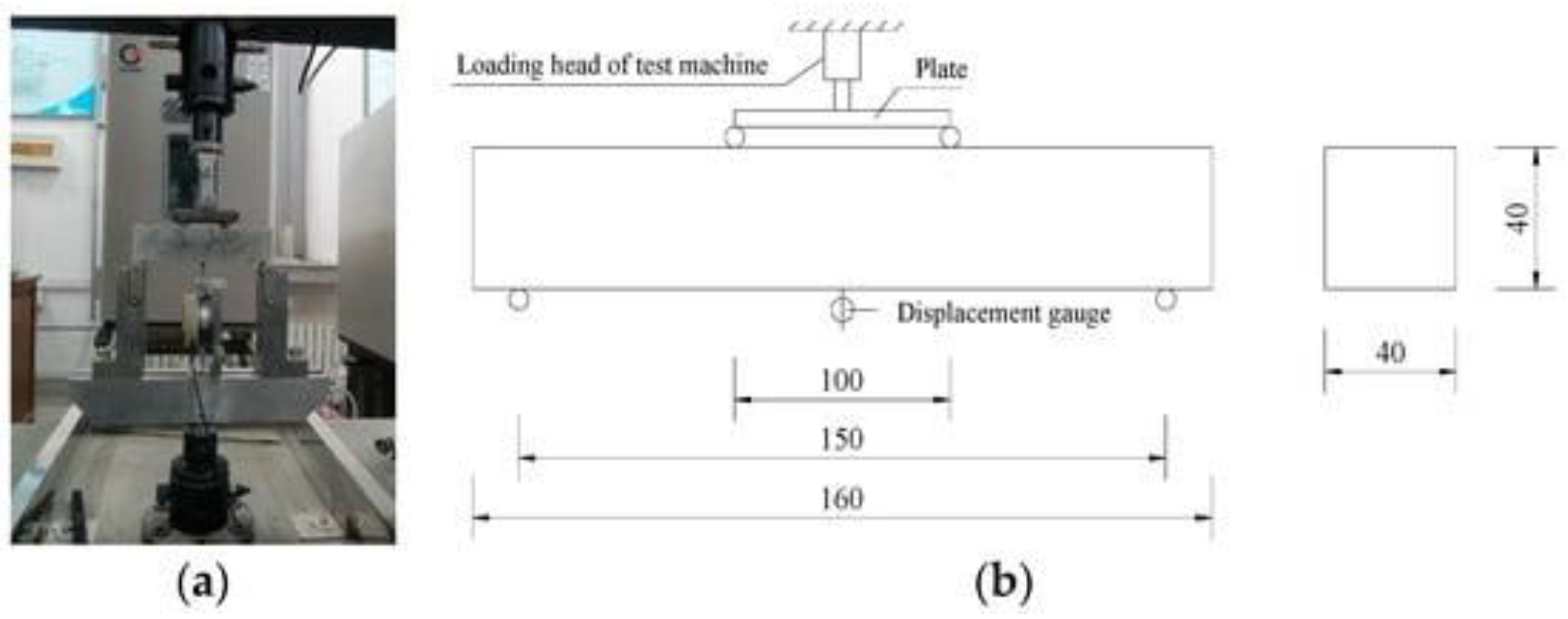
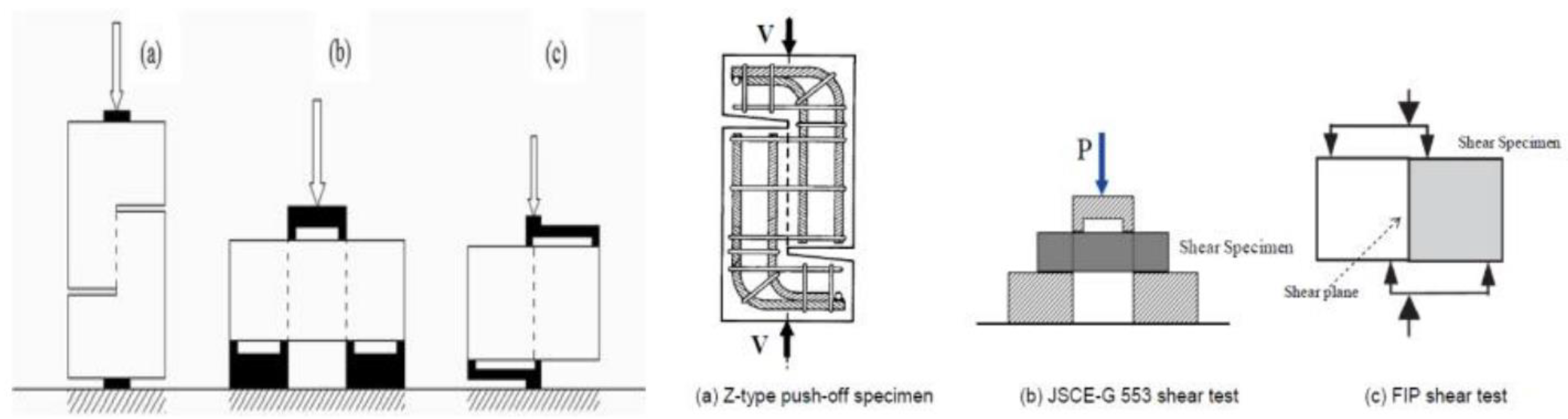
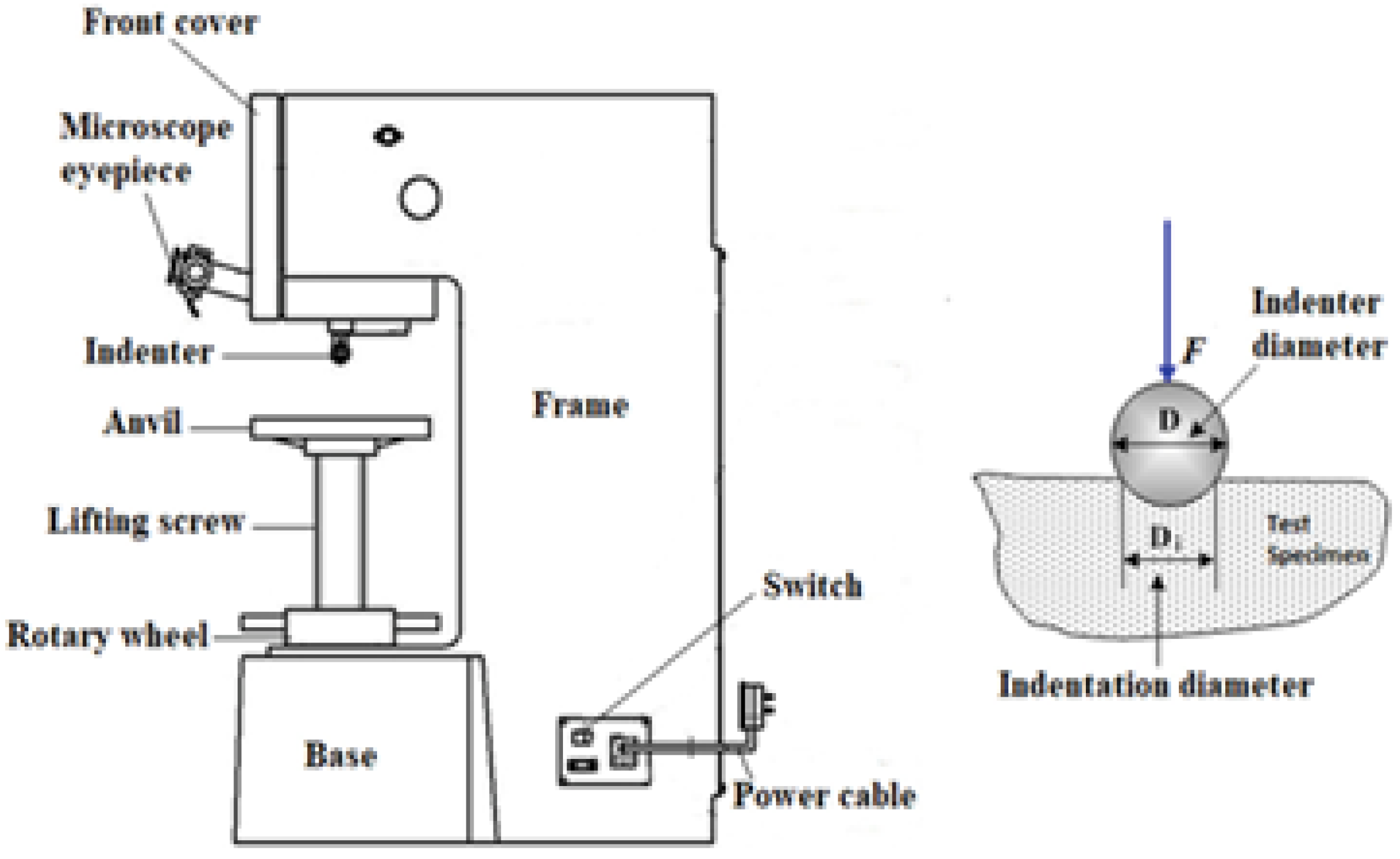
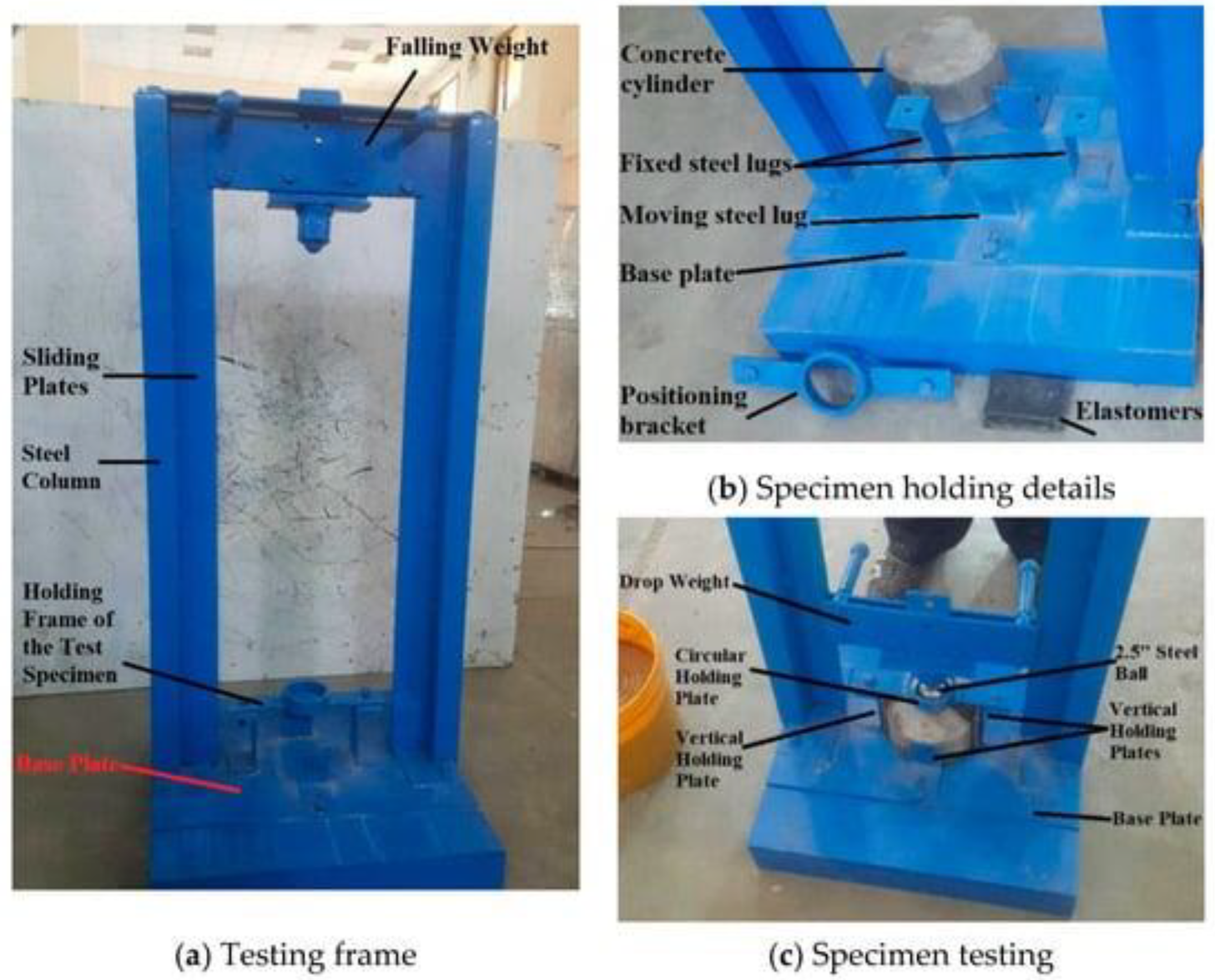
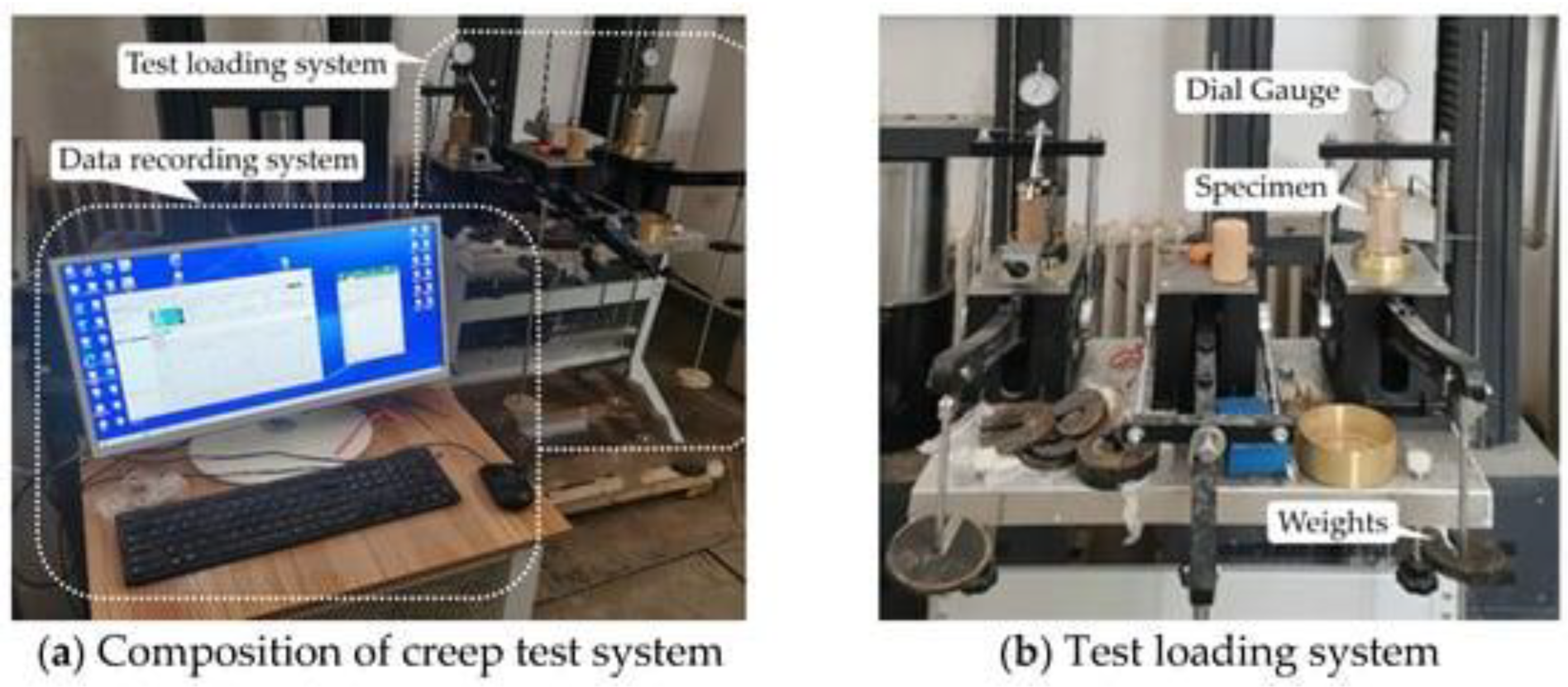
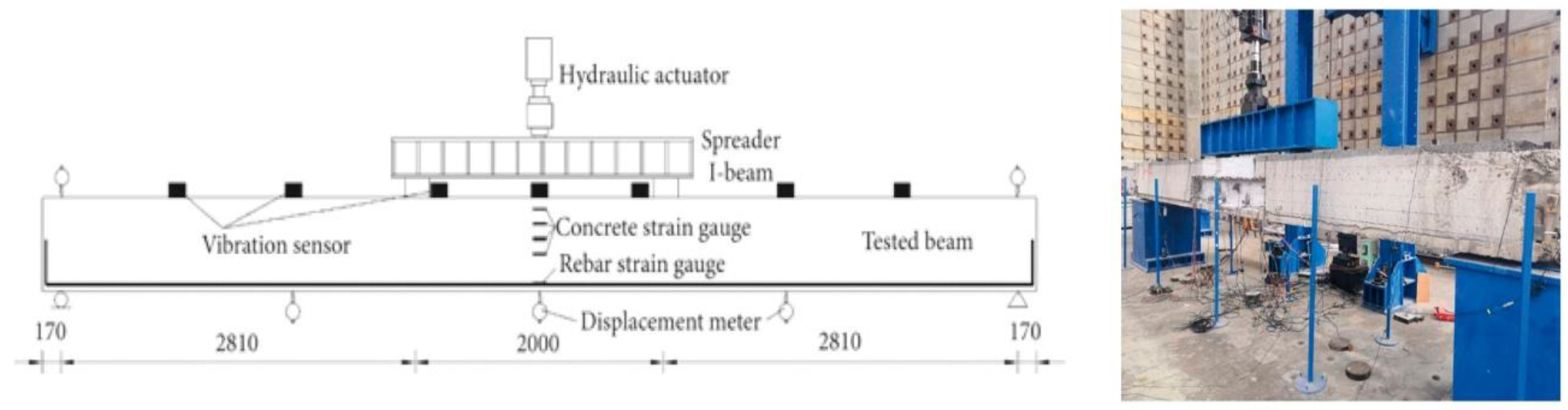
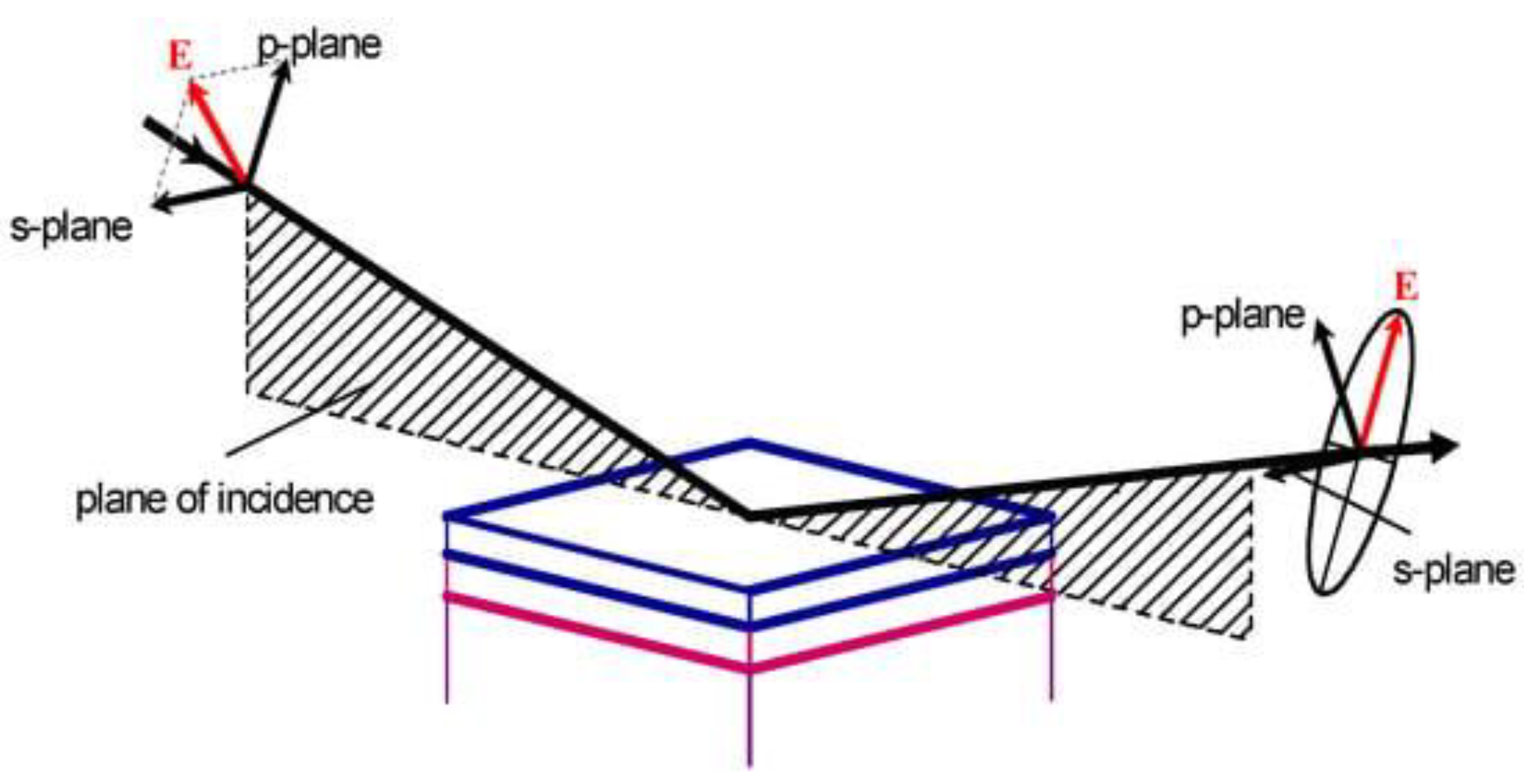
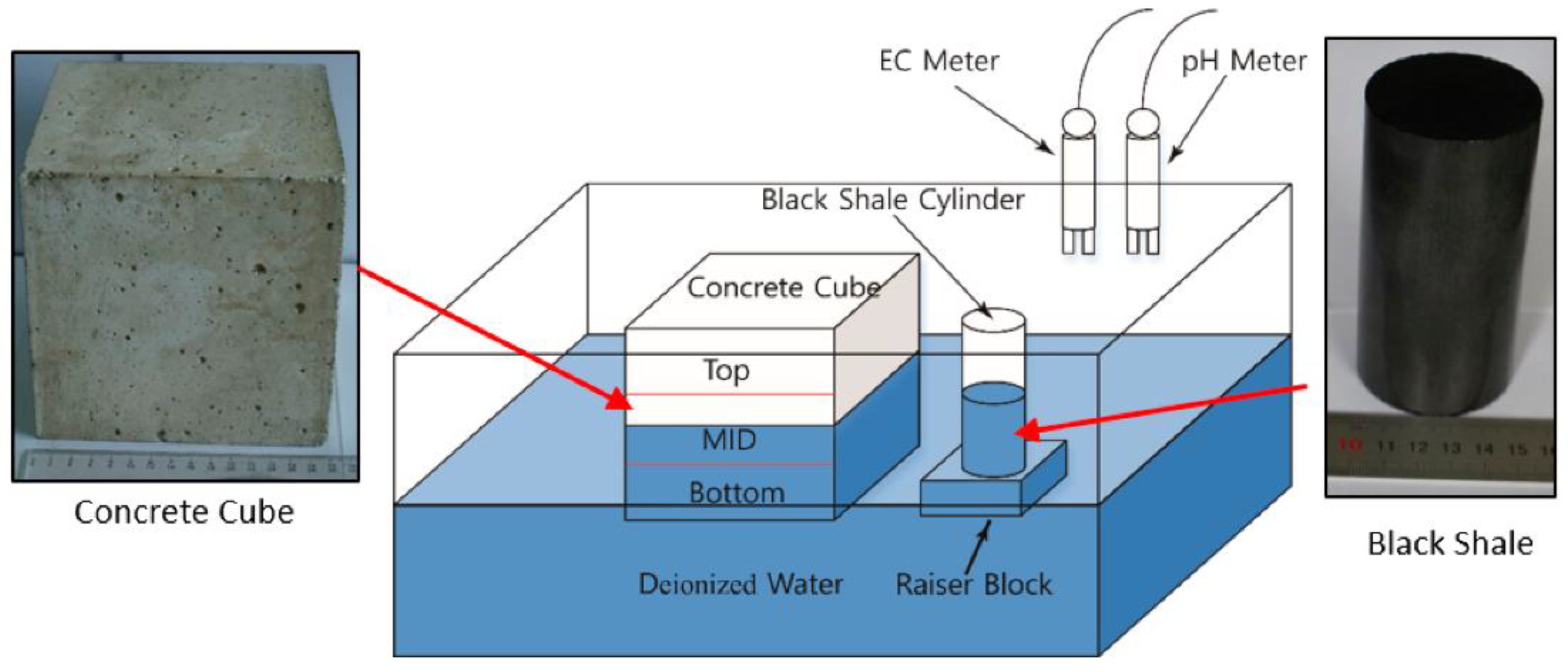
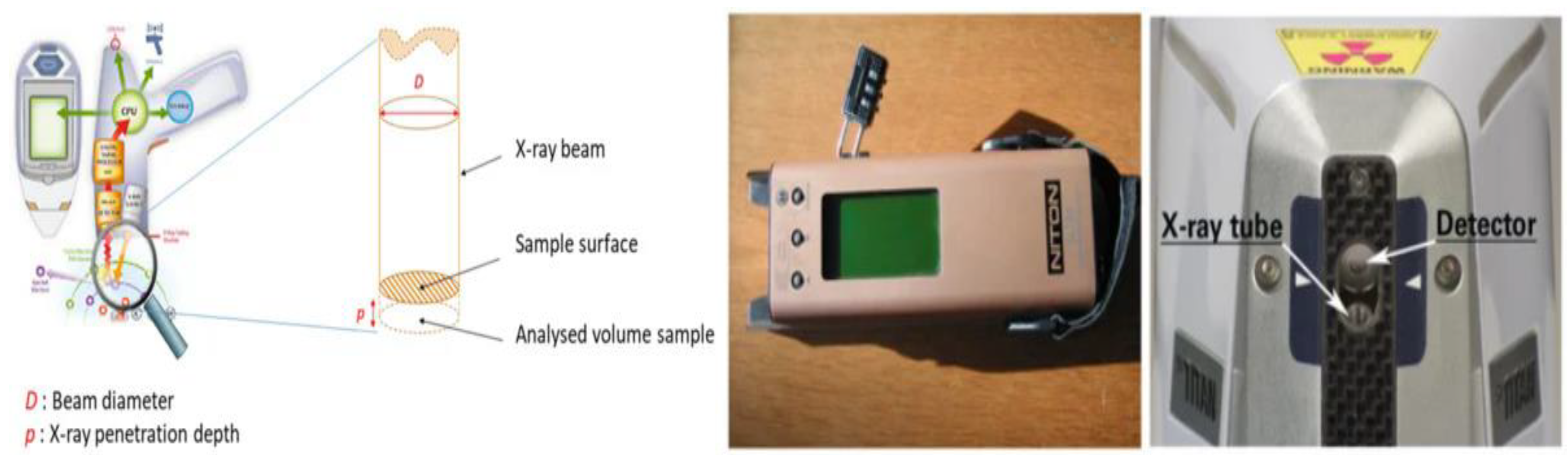


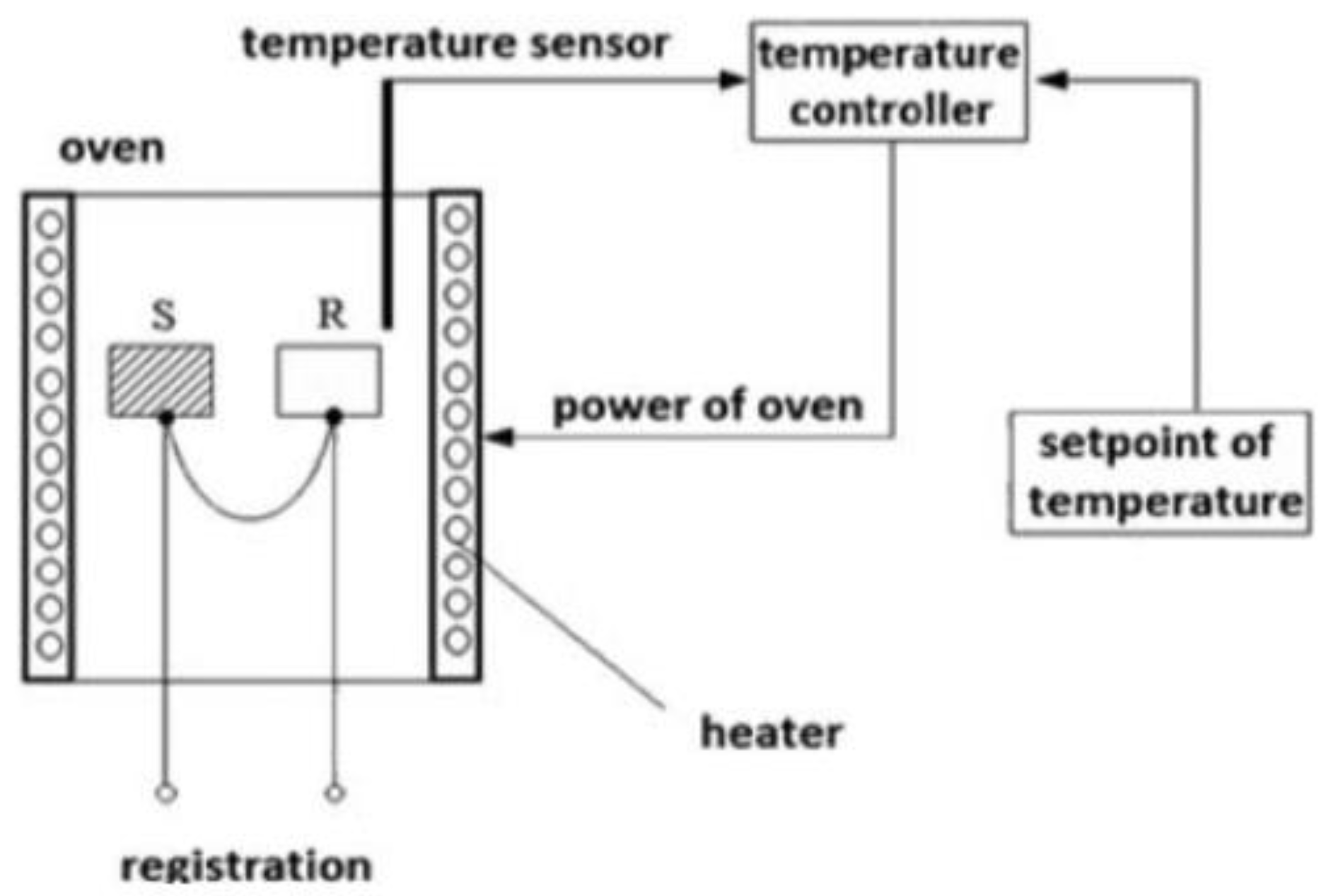
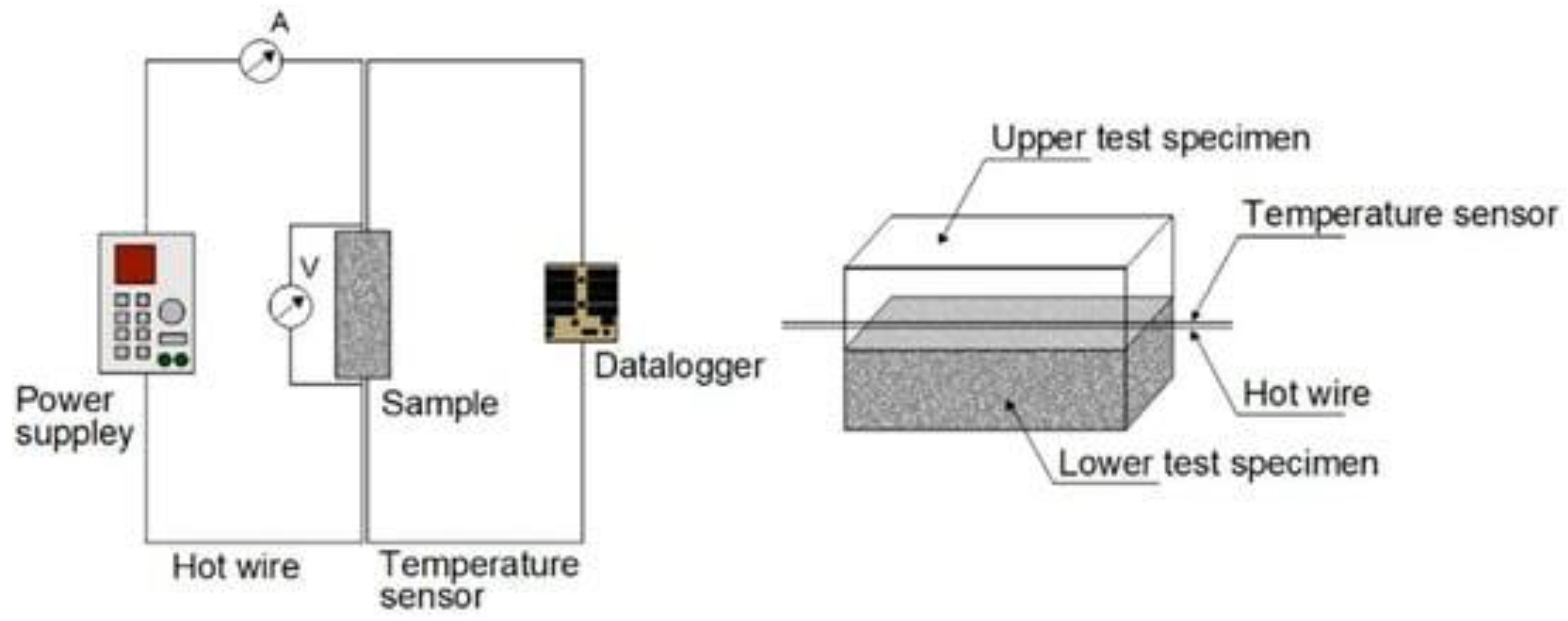
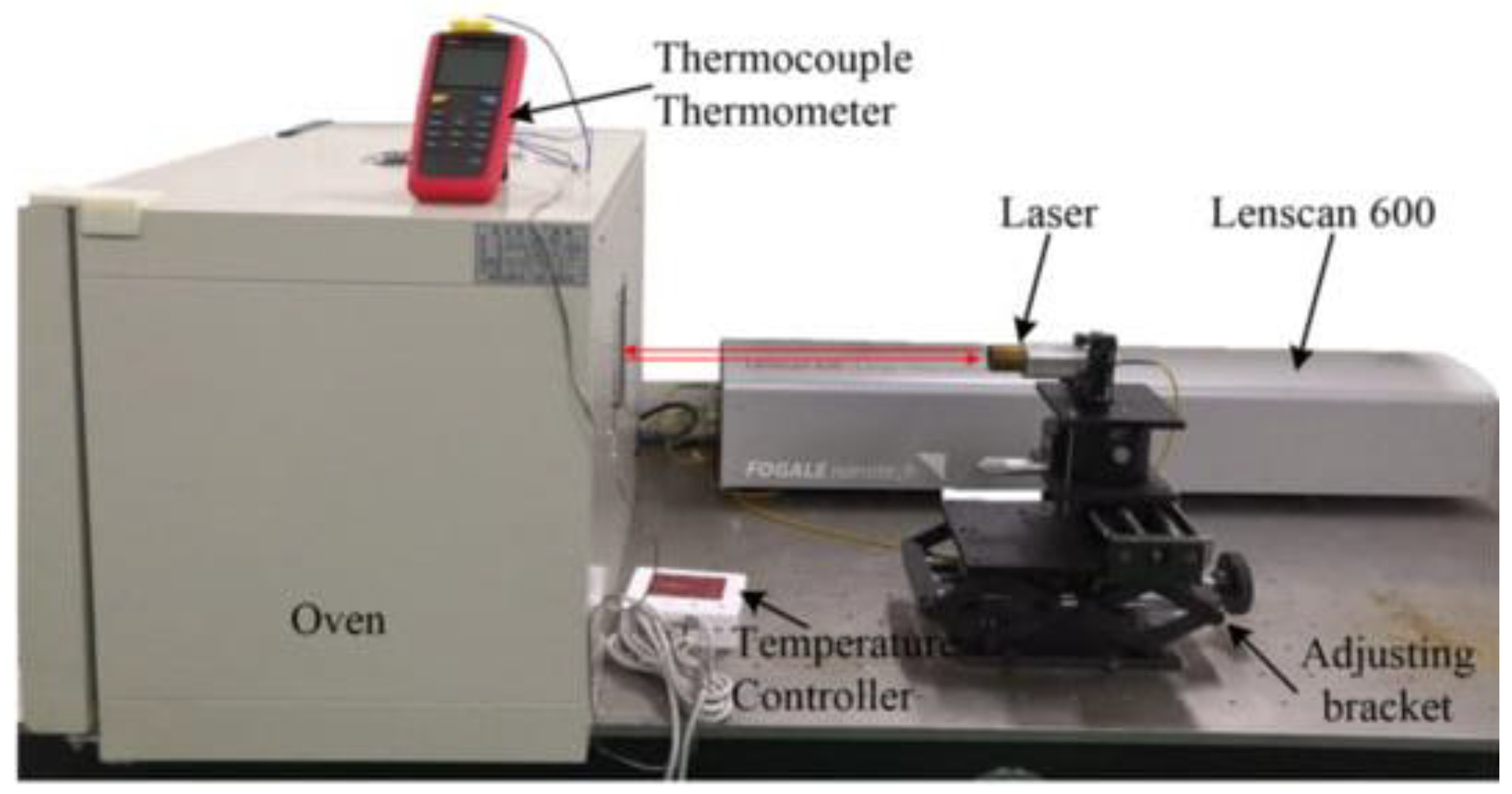


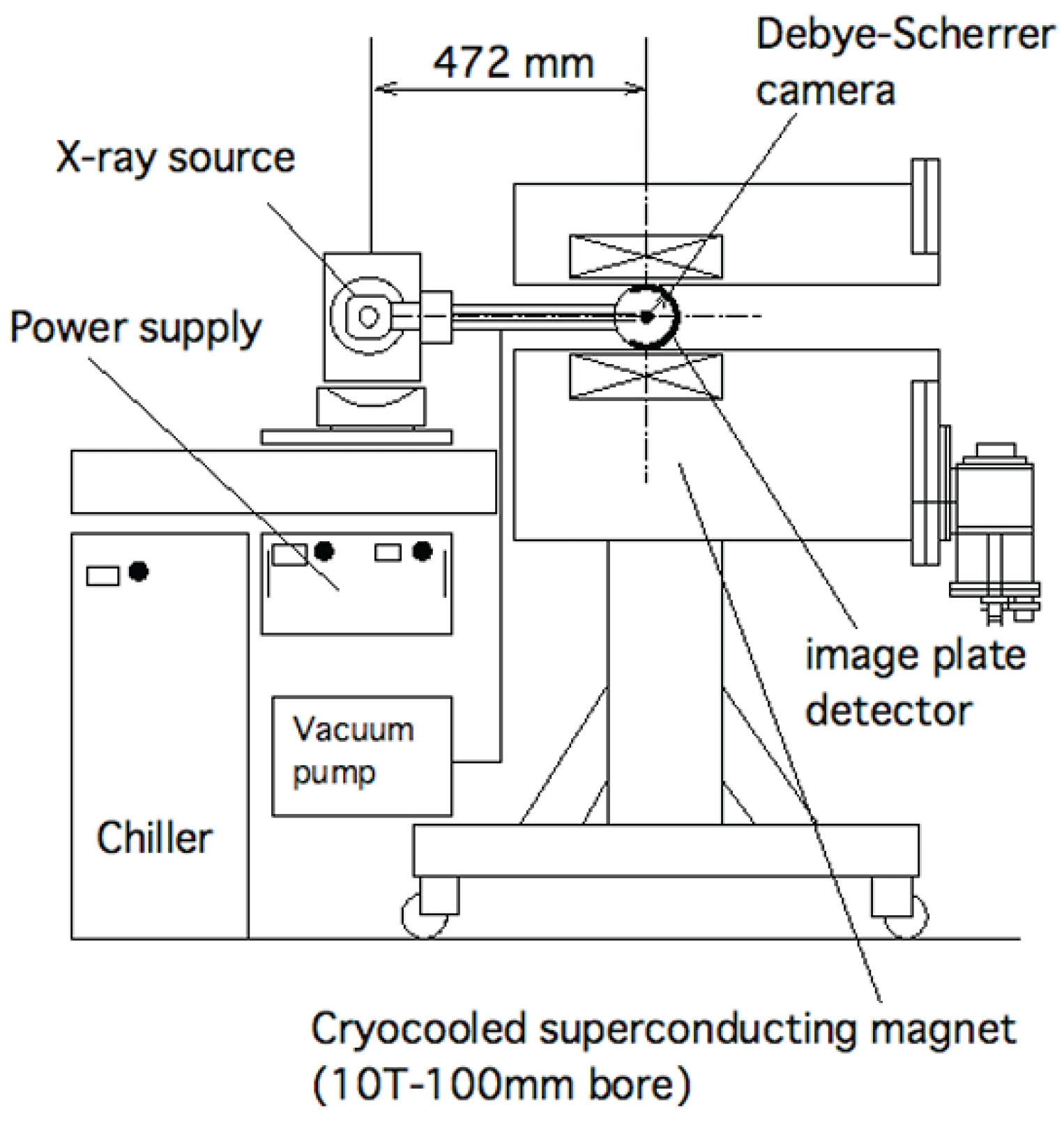
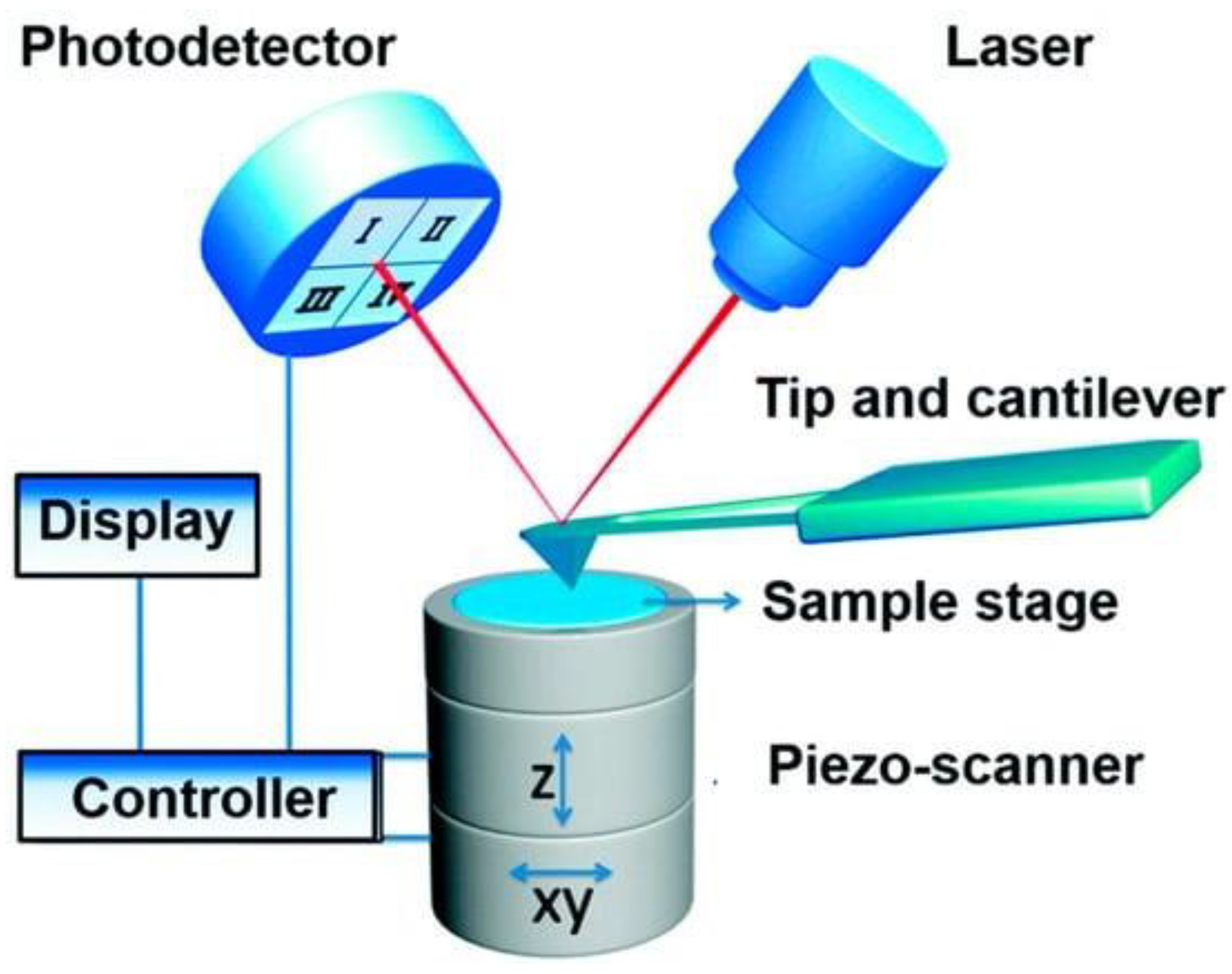
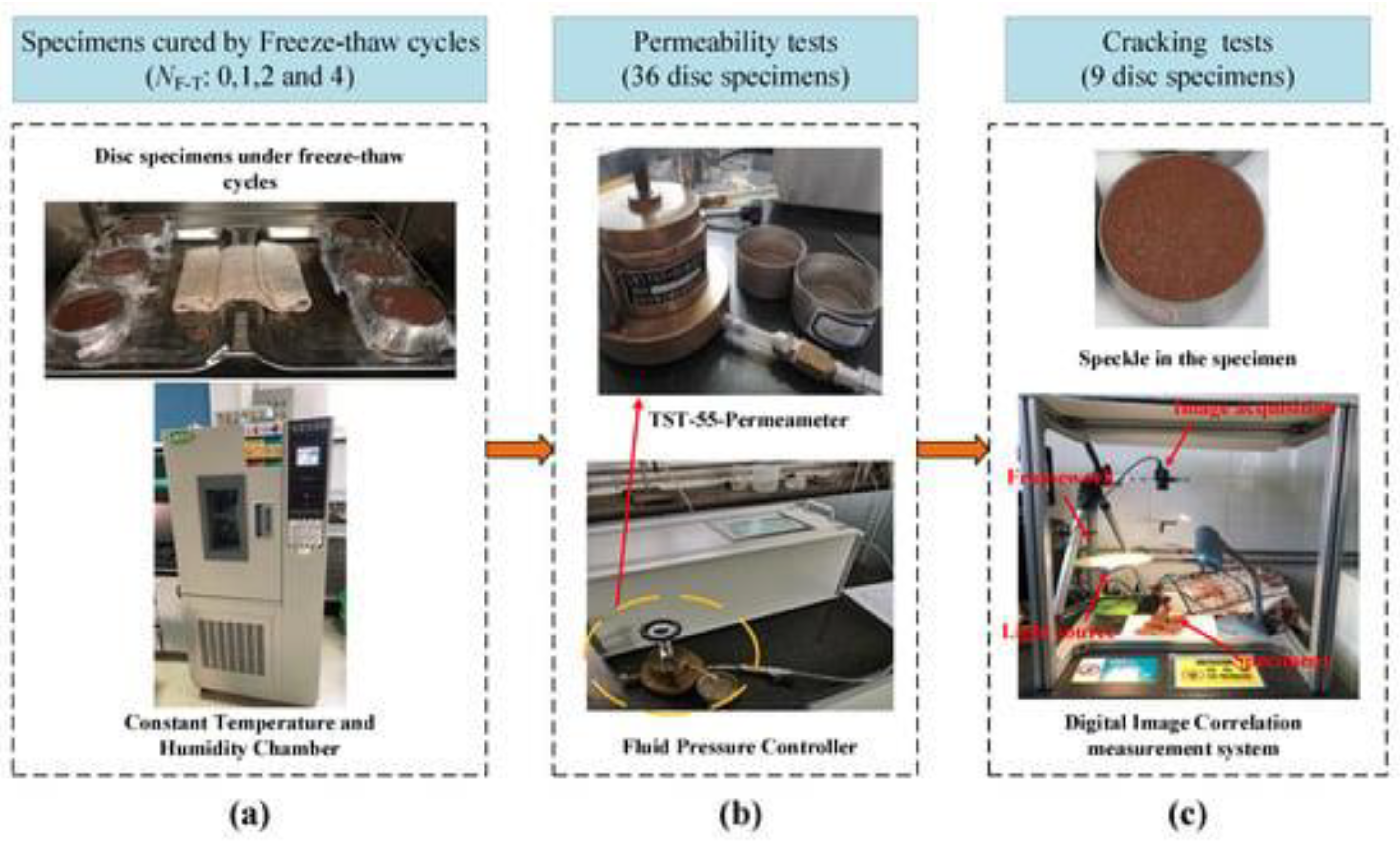
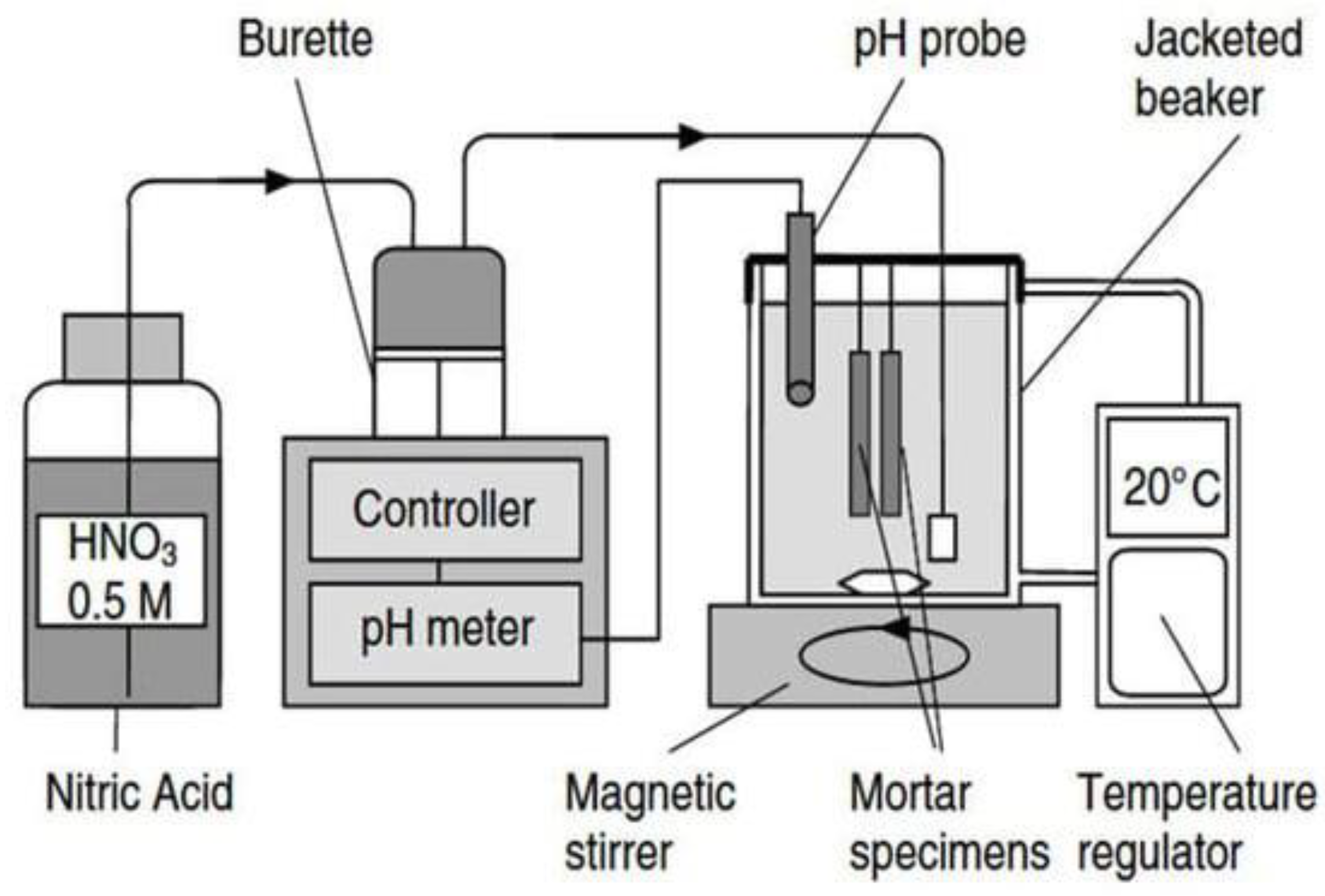
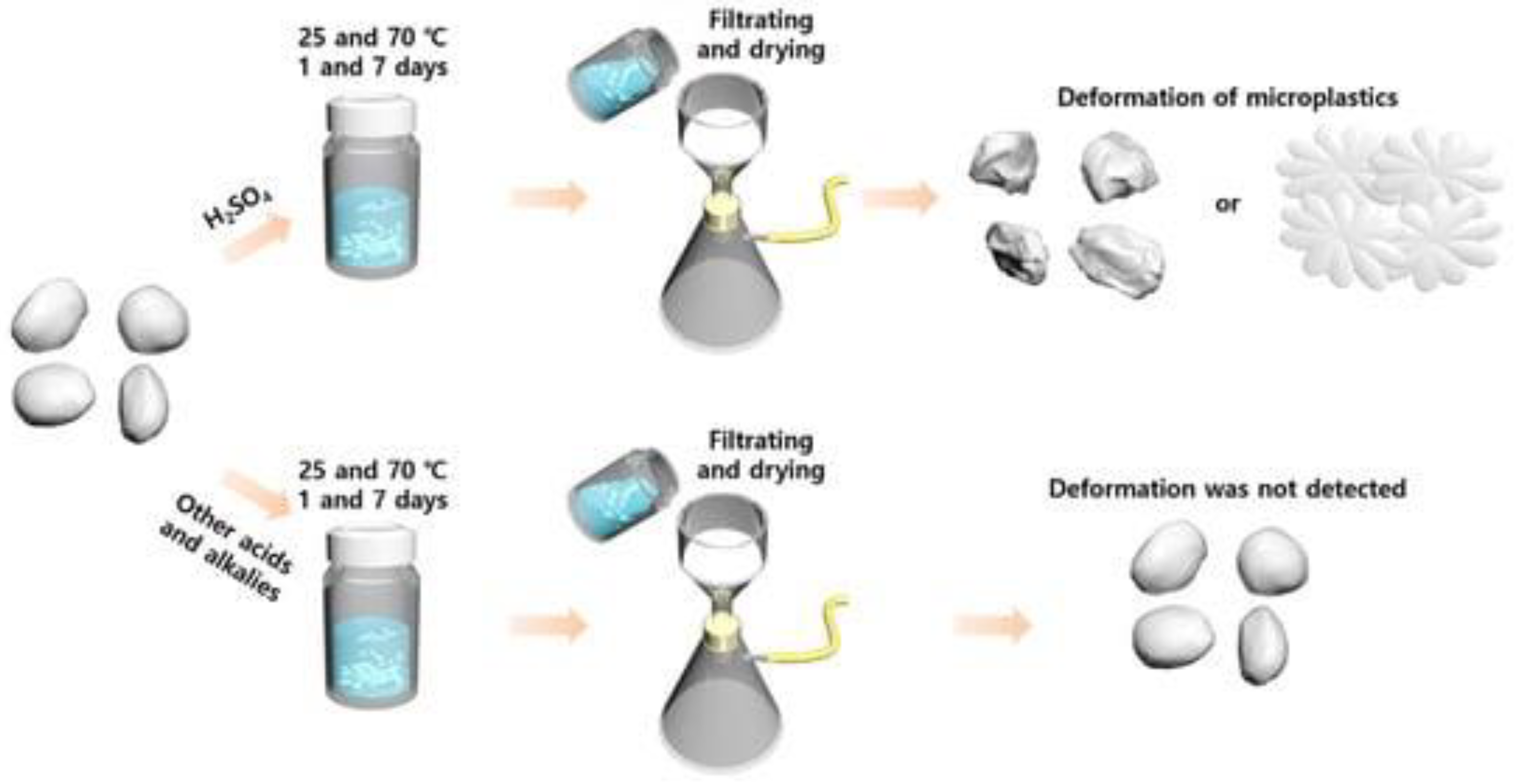
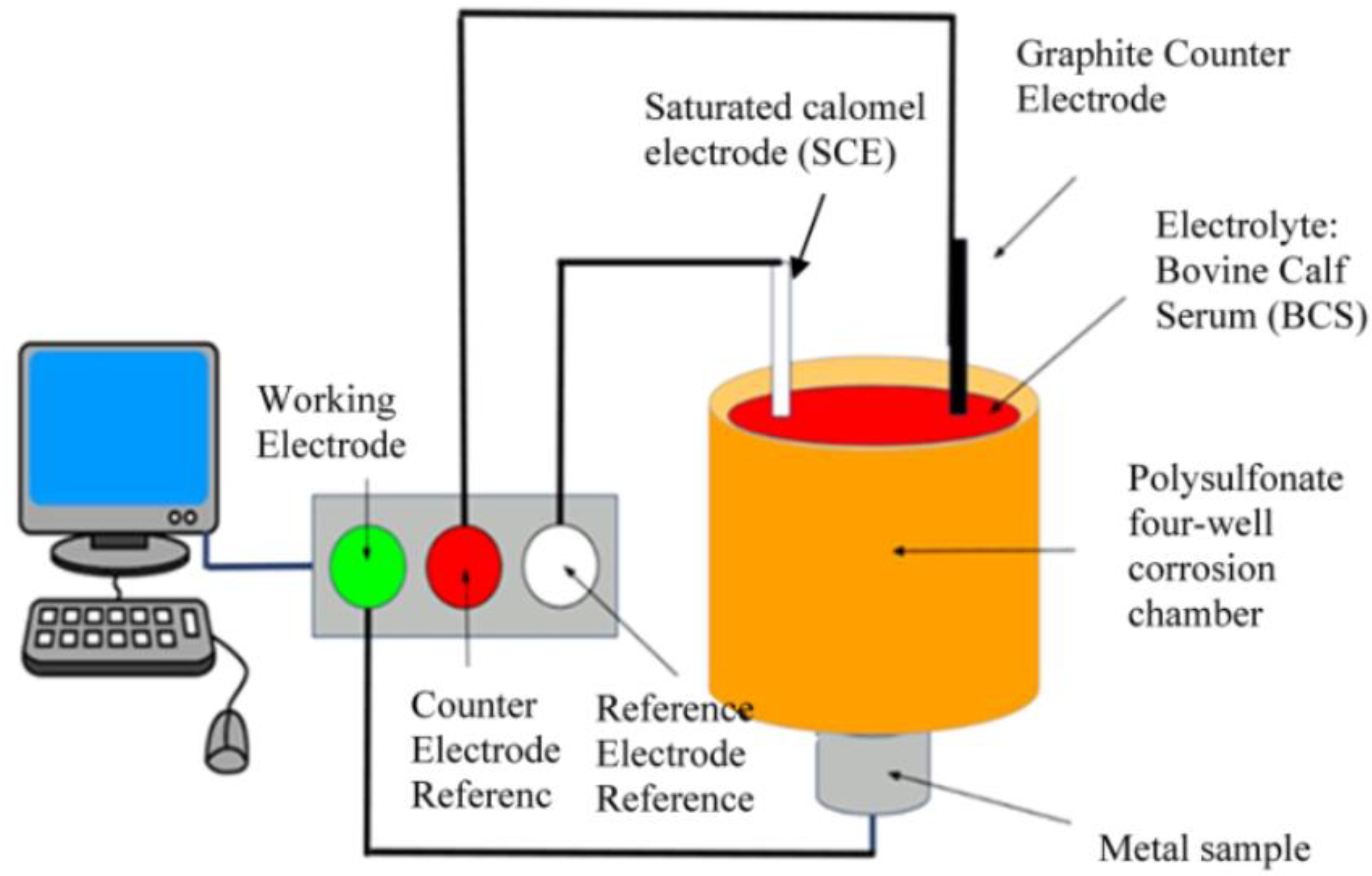

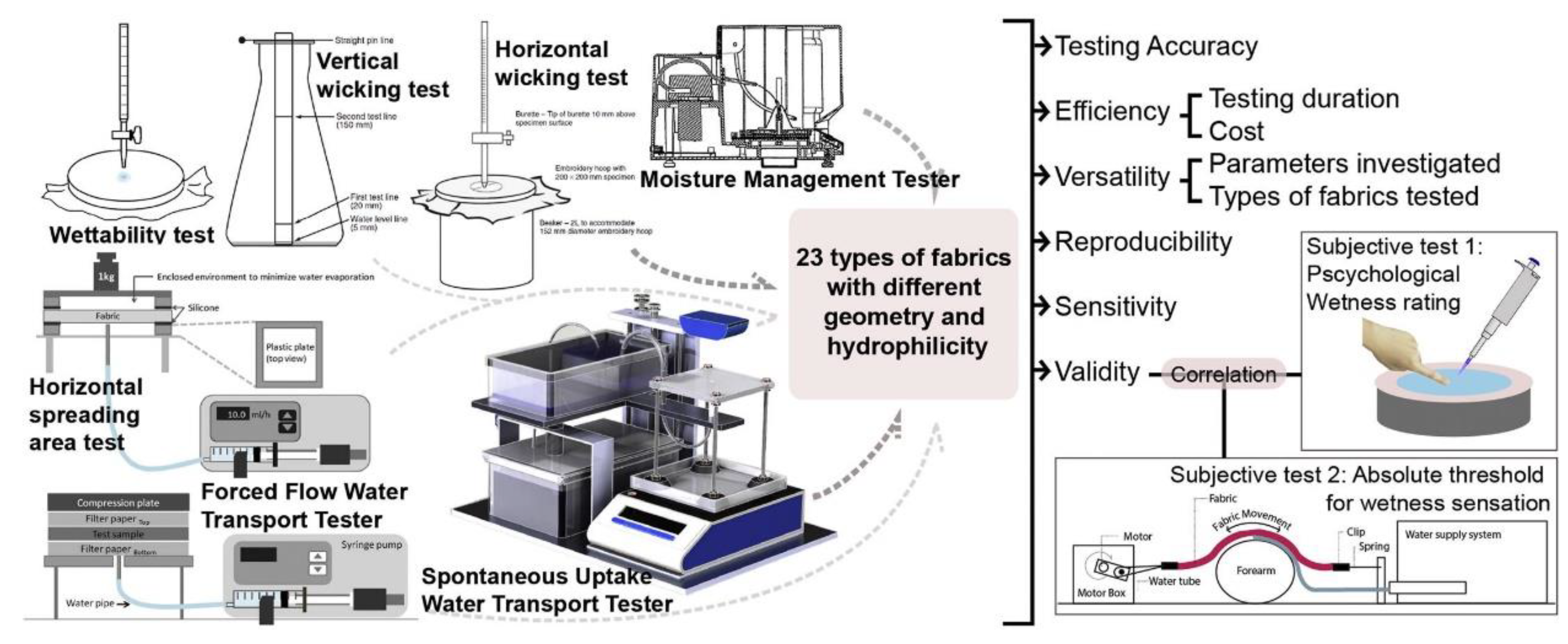


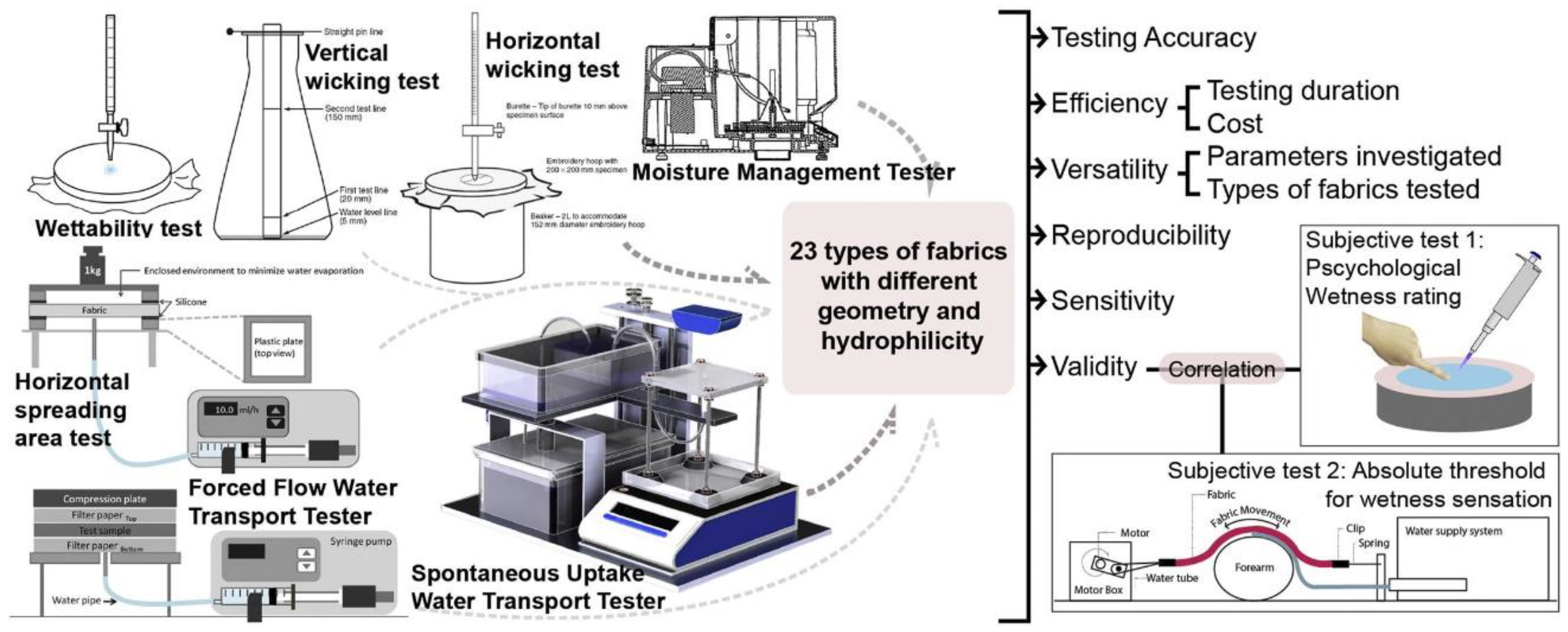



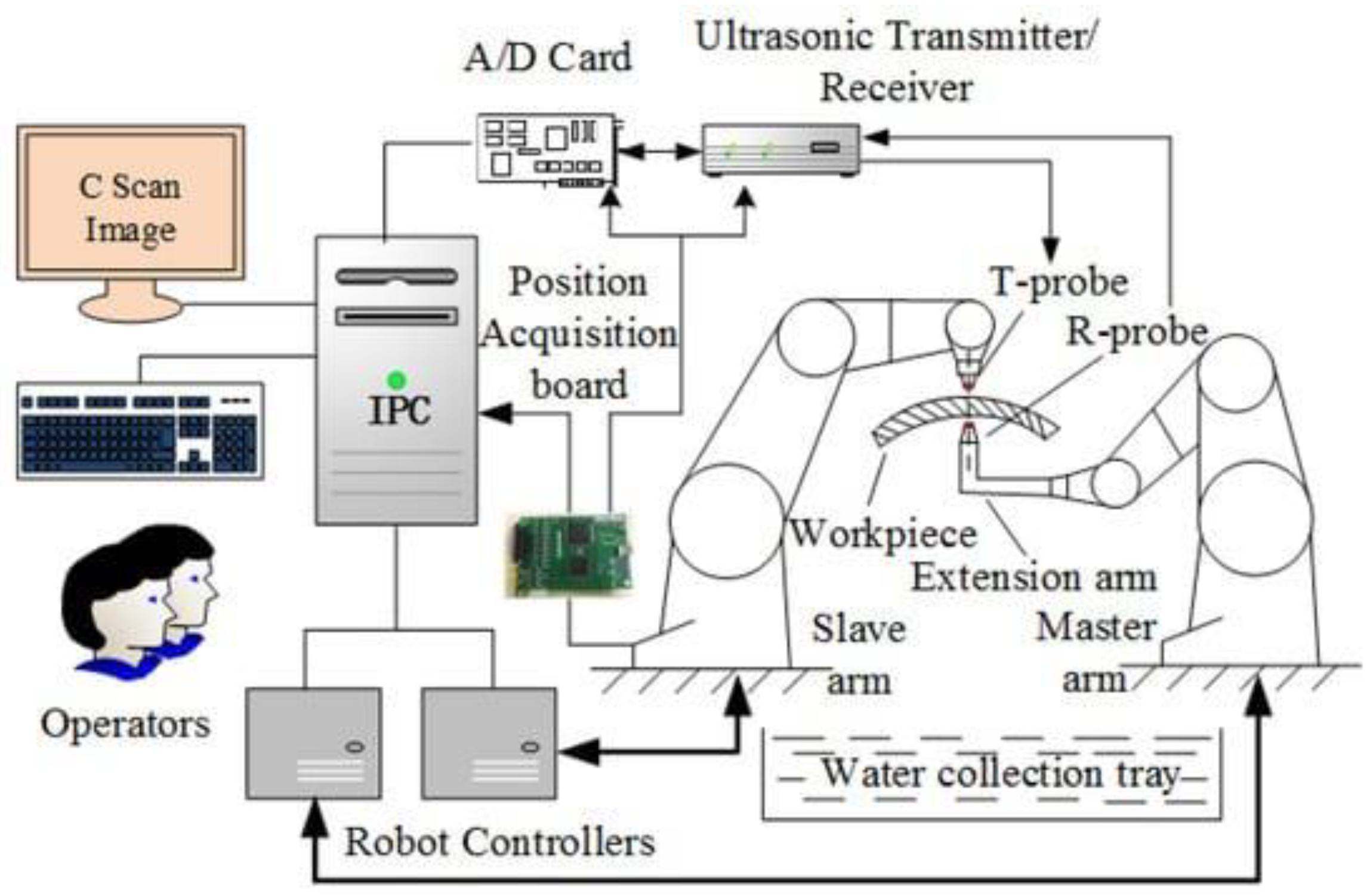
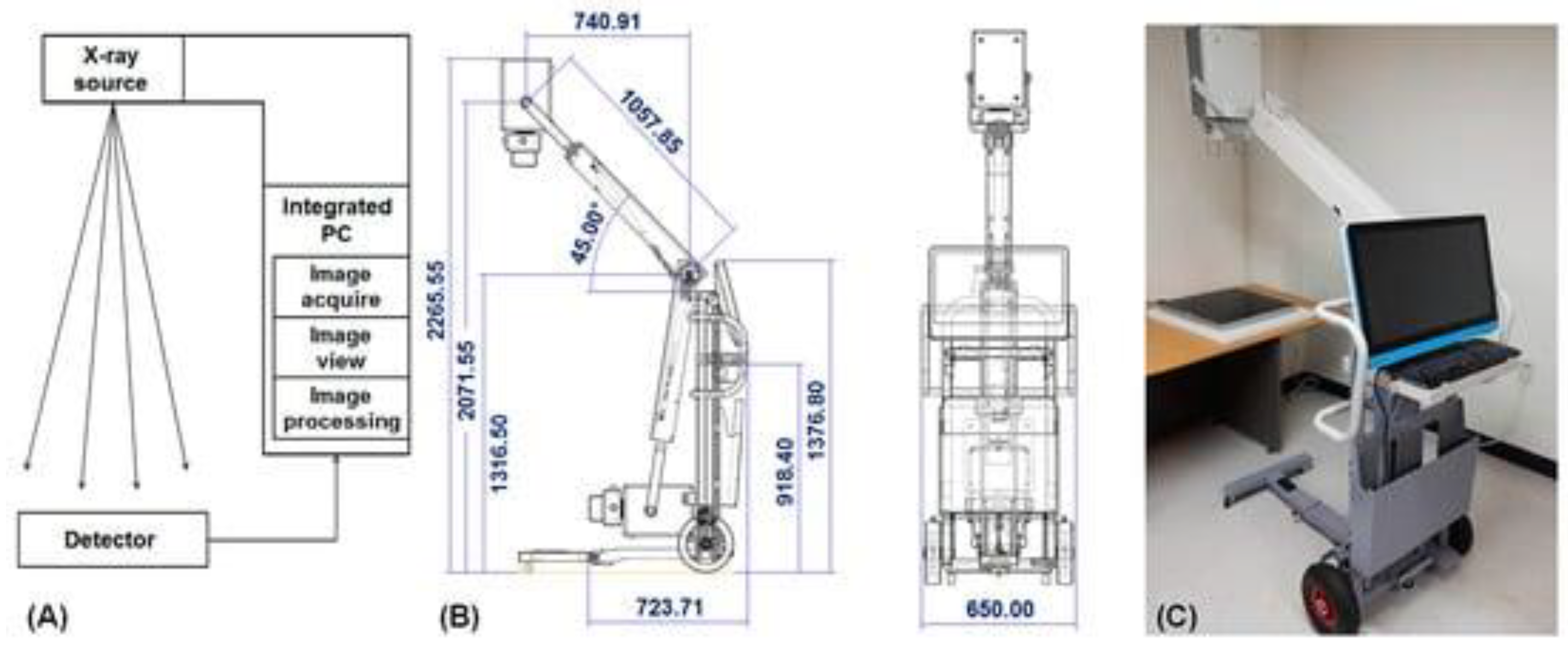
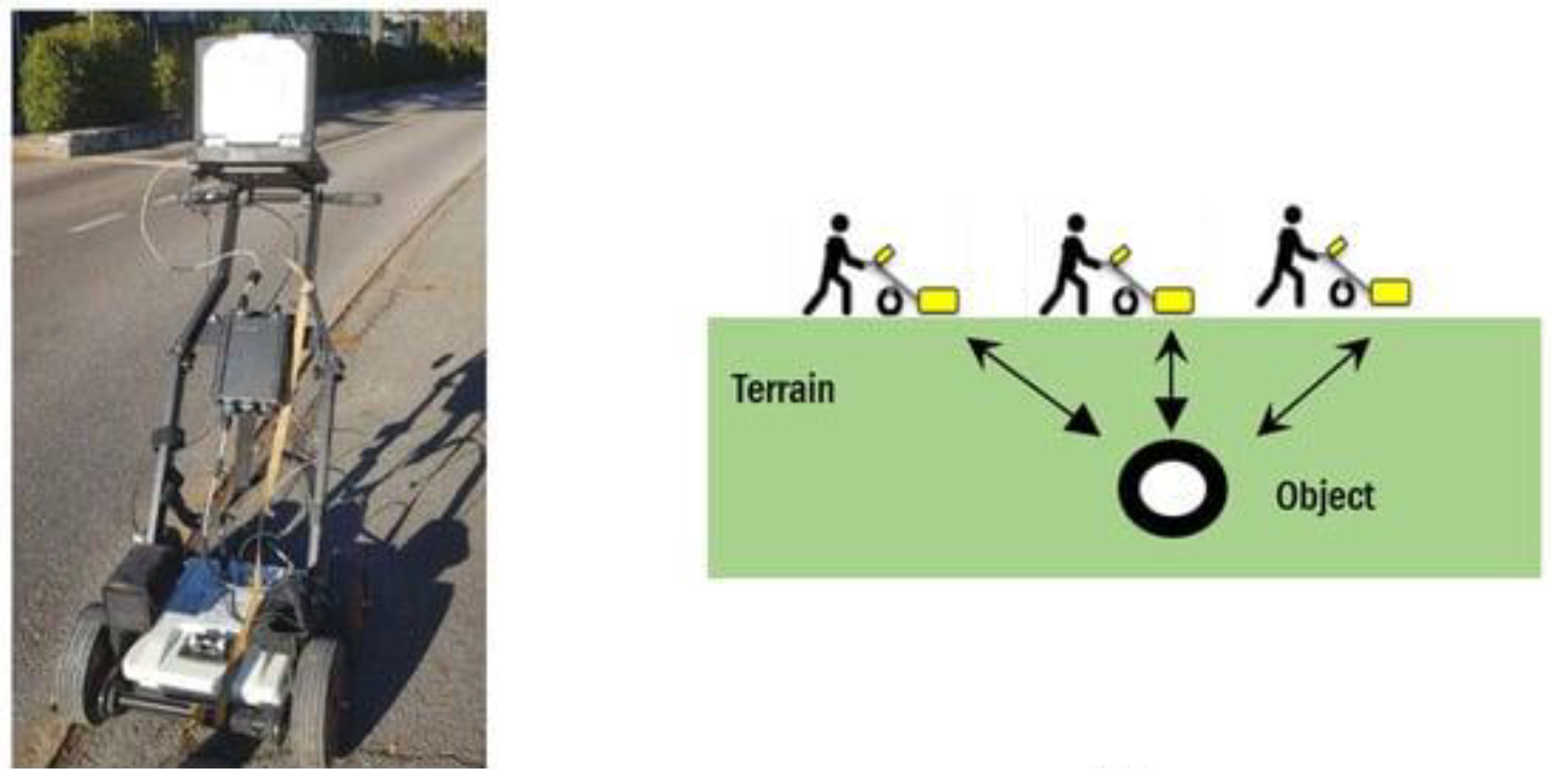
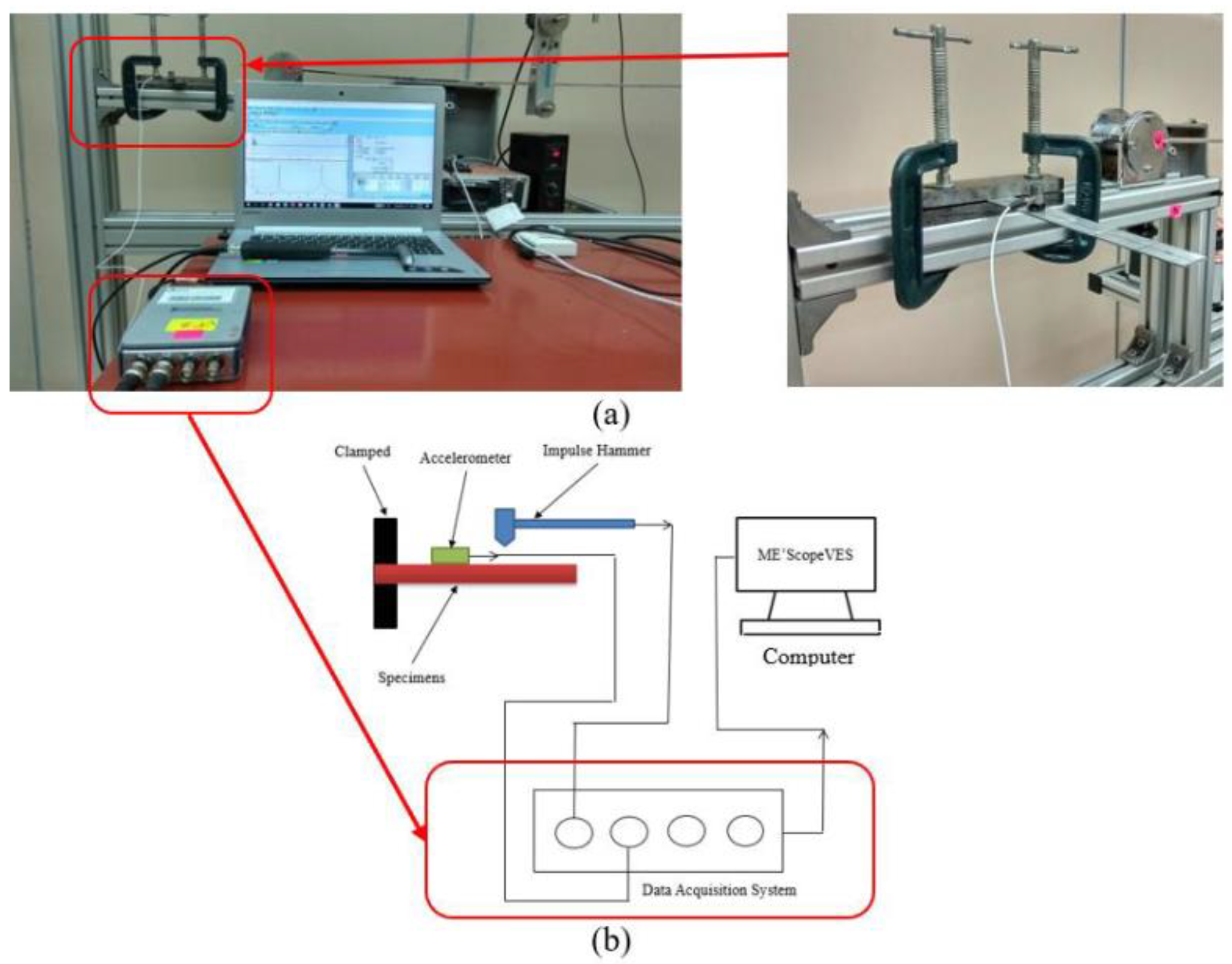
| Category | Test Type | Purpose | Technical Aspects | General Outcomes | Examples of the Testing Standards |
| Mechanical Properties Testing | Compression Strength | To determine a material's resistance to compression forces | Application of compressive force until failure | Maximum compression force the material can withstand | ASTM C39 [6]; BS EN 12390-3 [7]; EN 12390-3 [8] |
| Flexural Strength | To assess a material's ability to resist bending forces | Bending a specimen until it fractures or yields | Maximum stress at failure and the material's flexural modulus | ASTM C78 [9]; BS EN 12390-5 [10]; EN 12390-5 [11] | |
| Shear Strength | To evaluate the material's resistance to shear forces | Applying force parallel to the specimen's cross-section | Shear strength at yield or fracture | ASTM D732 [12]; BS 7991 [13]; EN ISO 1922 [14] | |
| Modulus of Elasticity Test | To determine a material's ability to deform elastically under stress | Subjecting the material to a known load and measuring deformation | Elastic modulus, indicating stiffness or rigidity | ASTM E111 [15]; BS EN ISO 527-1 [16]; EN ISO 527-1 [17] | |
| Hardness Test | To measure a material's resistance to deformation and scratching | Indenting the material with a specific force | Hardness value, indicating wear resistance and ductility | ASTM D785 [18]; BS EN ISO 2039-1 [19]; EN ISO 2039-1 [20] | |
| Impact Resistance Test | To determine the material's ability to withstand sudden impacts | Dropping a weight from a known height or swinging a pendulum | Energy absorbed before failure, indicating toughness | ASTM D256 [21]; BS EN ISO 179-1 [22]; EN ISO 179-1 [23] | |
| Creep Test | To measure time-dependent deformation under constant stress | Subjecting the material to a constant load at a temperature | Creep rate and time to failure, providing insights on long-term stability | ASTM C512 [24]; BS 1881-122 [25]; EN 13791 [26] | |
| Fatigue Test | To assess endurance under cyclic loading | Repeatedly applying a stress or strain cycle | Number of cycles to failure, indicating fatigue life | ASTM E466 [27]; BS 7270 [28]; EN 6072 [29] | |
| Chemical Properties Testing | Spectroscopy | Analyze material composition | Interaction of light with matter (absorption, emission, etc.) | Elemental and molecular composition | ASTM E1252 [30]; BS EN ISO 3696 [31]; EN ISO 3696 [32] |
| Chromatography | Separate and analyze components of a mixture | Mobile and stationary phases to separate substances | Identification and quantification of mixture components | ASTM D6581 [33]; BS EN 12341 [34]; EN 12341 [35] | |
| X-ray Fluorescence | Elemental analysis | Excitation of atoms in a sample by X-ray beam and measuring emitted radiation | Elemental composition | ASTM D4327 [36]; BS EN ISO 11885 [37]; EN ISO 11885 [38] | |
| pH Measurement | Determine acidity or alkalinity | Use of pH meters or indicators | pH value | ASTM E70 [39]; BS 3978 [40]; EN ISO 10523 [41] | |
| Thermal Properties Testing | Thermogravimetric Analysis | Measure changes in mass as a function of temperature | Controlled temperature program leading to material decomposition | Decomposition temperatures, mass loss | ASTM E1131 [42]; BS EN 8201 [43]; EN 8201 [44] |
| Differential Scanning Calorimetry | Measure heat flow associated with material transitions | Heat is applied and the difference in heat flow between the sample and reference is measured | Glass transition, crystallization, melting points | ASTM D3418 [45]; BS EN ISO 11357 [46]; EN ISO 11357 [47] | |
| Thermal Conductivity Test | Evaluate the material's ability to conduct heat | Steady-state or transient methods to measure heat flow | Thermal conductivity value | ASTM C518 [48]; BS EN 12667 [49]; EN 12667 [50] | |
| Thermal Expansion Test | Measure the material's dimensional change with the temperature | Material is heated and dimensional changes are recorded | Coefficient of thermal expansion | ASTM E831 [51]; BS EN ISO 11359 [52]; EN ISO 11359 [53] | |
| Hot Disk Thermal Constants Analyzer | Determine thermal conductivity, diffusivity, and specific heat | Transient plane source technique | Thermal properties | ASTM D7896 [54] | |
| Microstructural Properties Testing | Scanning Electron Microscopy | Examine surface morphology and composition | Electron beam scans the surface, generating various signals | High-resolution images, elemental analysis | ASTM ESEM [55]; BS 340-1 [56]; EN ISO 22309 [57] |
| X-ray Diffraction | Identify crystalline phases and orientation | X-rays diffracted by crystal lattice | Phase identification, crystal structure | ASTM D8 [58]; BS EN 13925 [59]; EN 13925 [60] | |
| Transmission Electron Microscopy | Visualize internal structure at atomic level | Electron beam transmitted through thin specimen | High-resolution internal structure | ASTM E2015 [61]; ISO 21432 [62]; ASTM E1621 [63] | |
| Atomic Force Microscopy | Image surfaces at atomic scale | Probe scans the surface with atomic-scale resolution | Surface topography | ASTM E2382 [64]; BS EN ISO 20903 [65]; EN ISO 20903 [66] | |
| Durability Properties Testing | Freeze-Thaw Testing | Evaluate durability against freeze-thaw cycles | Cyclic freezing and thawing of material samples | Resistance to freeze-thaw damage | ASTM C666 [67]; BS EN 1367-1 [68]; EN 1367-1 [69] |
| Sulfate Attack Testing | Assess resistance to sulfate exposure | Immersion in sulfate solution or exposure to sulfate-rich environment | Durability against sulfate attack | ASTM C1012 [70]; BS EN 13295 [71]; EN 13295 [72] | |
| Chemical Resistance Test | Determine the material's resistance to chemicals | Exposure to aggressive chemicals | Degree of resistance to chemical exposure | ASTM G31 [73]; ASTM C267 [74]; ISO 175 [75] | |
| Corrosion Testing | Assess susceptibility to corrosion | Exposure to a corrosive environment or application of electrical methods | Corrosion rate, type, and form | ASTM G48 [76]; ASTM G1 [77]; EN ISO 9227 [78] | |
| Chloride Penetration Testing | Evaluate resistance to chloride ingress | Application of an electrical field or ponding test | Depth of chloride penetration | ASTM C1202 [79]; BS EN 12390-8 [80]; EN 12390-8 [81] | |
| Carbonation Testing | Assess resistance to carbonation | Exposure to a CO2-rich environment | Depth of carbonation front | ASTM C1583 [82]; BS EN 13295 [83]; EN 13295 [84] | |
| Moisture Absorption Test | Measure the material's ability to absorb moisture | Weighing before and after moisture exposure | Percentage of moisture absorbed | ASTM C1585 [85]; BS 1881-124 [86]; EN 13791 [87] | |
| Salt Spray Test | Evaluate resistance to salt corrosion | Exposure to salt mist or fog | Corrosion resistance in saline environments | ASTM B117 [88]; BS EN ISO 9227 [89]; EN ISO 9227 [90] | |
| Physical Properties Testing | Porosity and Density Measurements | Determine porosity and density | Archimedes' principle, pycnometry, or mercury intrusion porosimetry | Porosity percentage, density | ASTM D792 [91]; BS EN 1936 [92]; EN 1936 [93] |
| Water Absorption Test | Assess the material's ability to absorb water | Immersion in water and measuring weight gain | Water absorption capacity | ASTM C1585 [85]; BS EN 13755 [94]; EN 13755 [95] | |
| Shrinkage Test | Measure the material's dimensional stability | Length measurements before and after drying or curing | Degree of shrinkage | ASTM C157 [96]; BS EN 12617-4 [97]; EN 12617-4 [98] | |
| Rheological Properties Testing | Viscosity Measurement | Determine fluid's resistance to flow | Rotational viscometers or capillary viscometers | Viscosity value | ASTM D445 [99]; BS EN ISO 3104 [100]; EN ISO 3104 [101] |
| Workability Tests | Evaluate concrete or mortar's ease of placement | Slump test, flow table test, or Vebe test | Workability index or value | ASTM C143 [102]; BS EN 12350-2 [103]; EN 12350-2 [104] | |
| Non-Destructive Testing | Ultrasonic Testing | Detect internal flaws or characterize materials | High-frequency sound waves are transmitted through material | Flaw detection, material thickness | ASTM E494 [105]; BS EN 583-2 [106]; EN 583-2 [107] |
| Radiography | Visualize internal features using X-rays or gamma rays | Penetrating radiation passes through material and is captured on film or sensor | Internal defects, weld quality | ASTM E1742 [108]; BS EN 444 [109]; EN 444 [110] | |
| Ground Penetrating Radar | Detect buried objects or changes in material properties | Radar pulses are sent into the ground and reflections from sub-surface structures are analyzed | Subsurface features, layer thickness | ASTM D6432 [111]; BS 5930 [112]; EN 1997-2 [113] | |
| Free Vibration Testing | Assess dynamic properties of structures | Natural frequencies, mode shapes, and damping ratios are determined through vibration analysis | Dynamic characteristics of structures | ASTM E289 [114]; BS EN ISO 7626-5 [115]; EN ISO 7626-5 [116] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





