Submitted:
29 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Prologue: How Tobamoviruses Went from a Threat to Crop Production to a Footnote in the History of Virology
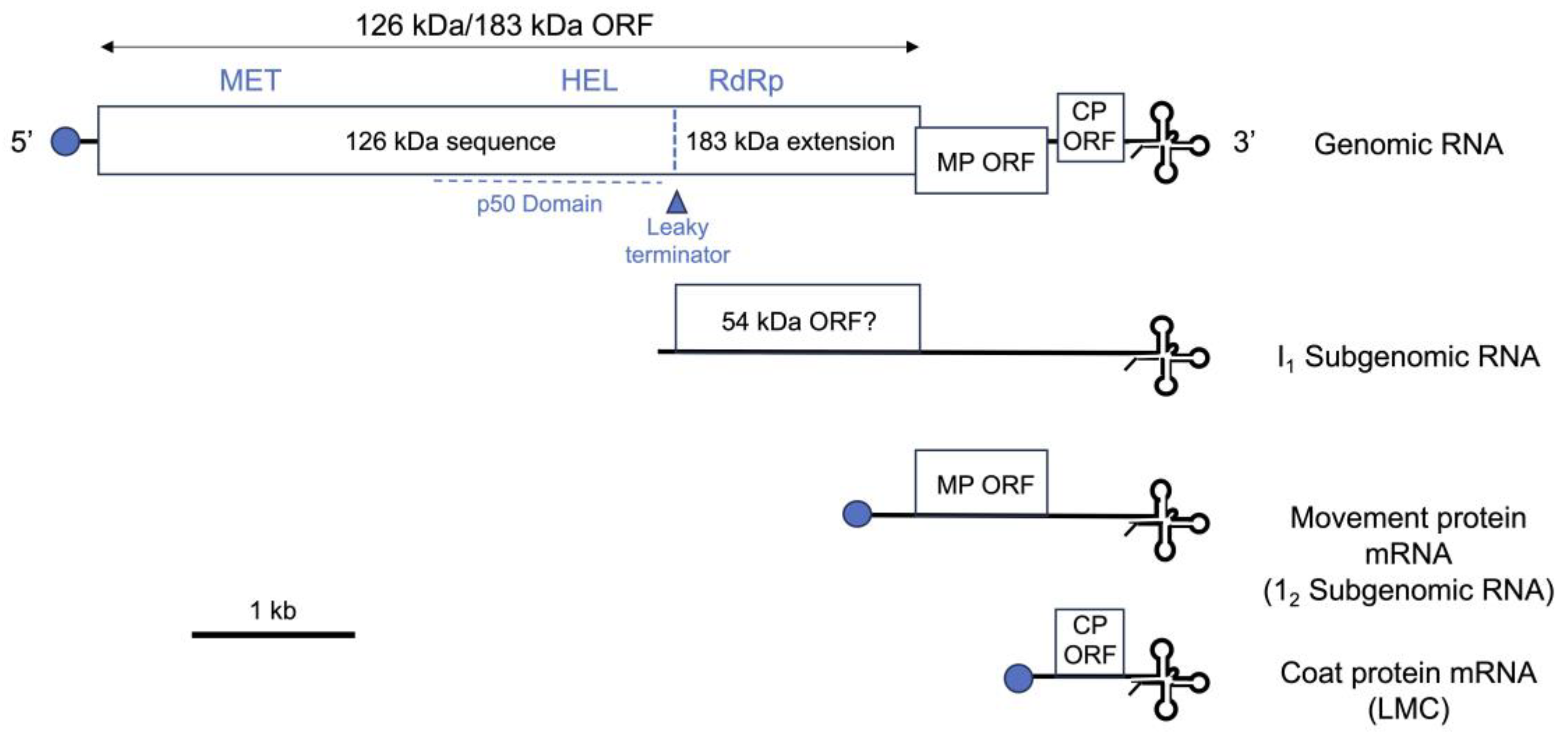
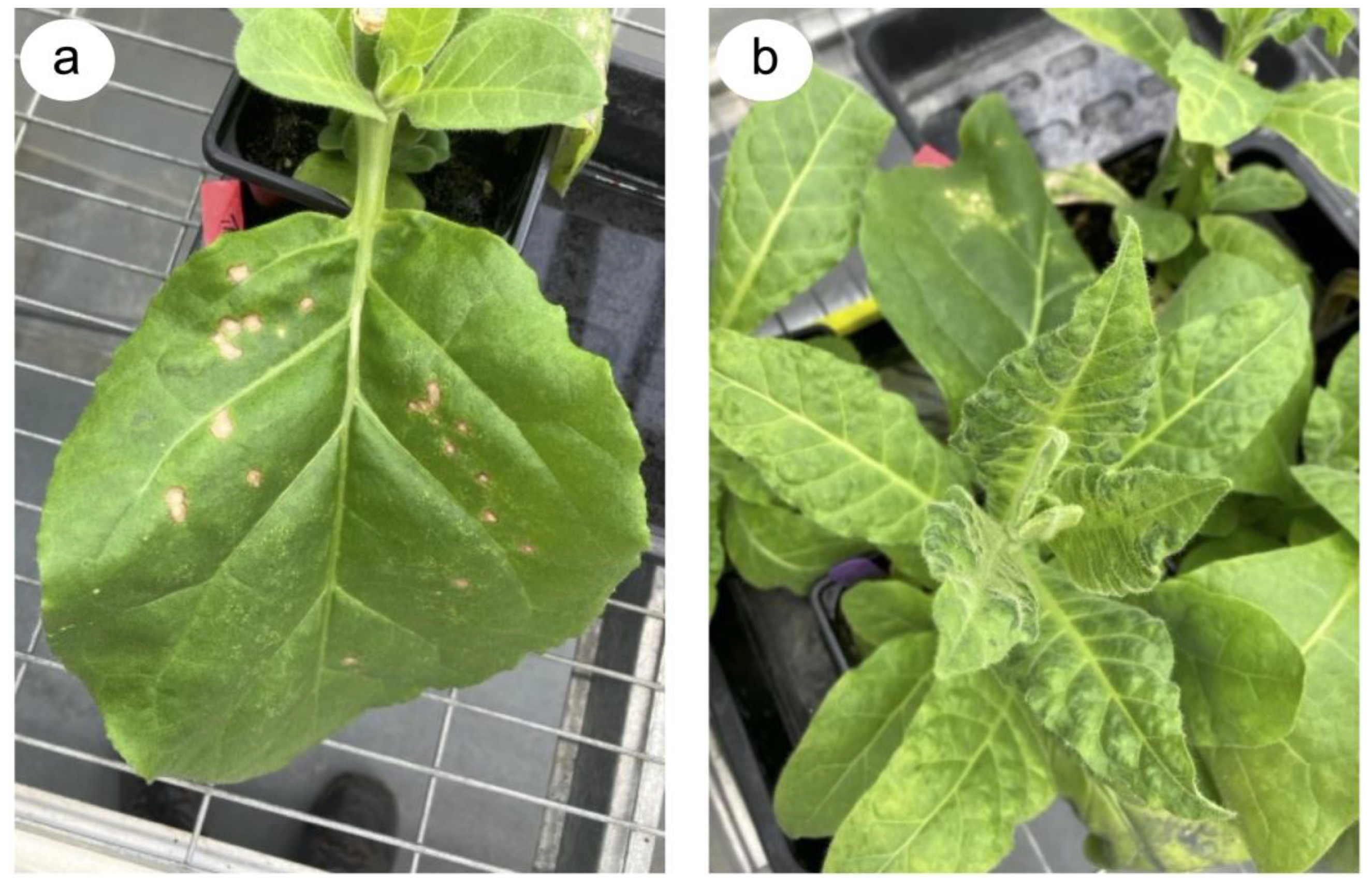
2. Why We Need Rapidly Deployable Approaches to Counter the Emergence of Resistance-Breaking and Other Emerging Tobamovirus Threats
3. A Potential Role for Cross-Protection in Protecting Crops against Emerging Tobamoviruses
4. Pathogen-Derived Resistance against Tobamoviruses
5. Using RNA Silencing to Engender Resistance against Tobamoviruses in Transgenic and in Non-Engineered Plants
6. Potential for Interspecies Transfer of R Genes, Rescue of ‘Broken’ Resistance and Creation of Novel Resistance Factors
7. Why There Is a Future for New (and Old) Methods for Protection and against Tobamoviruses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harrison, B.D.; Wilson, T.M.A. Milestones in the research on tobacco mosaic virus. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354(1383), 521-529. [CrossRef]
- Bos, L. Beijerinck's work on tobacco mosaic virus: historical context and legacy. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 1999, 354(1383), 675-685. [CrossRef]
- Scholthof, K.B. Tobacco mosaic virus: a model system for plant biology. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 13-34. [CrossRef]
- Broadbent, L. Epidemiology and control of tomato mosaic virus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1976 14, 75–96.
- Kenyon, L.; Kumar, S.; Tsai, W. S.; Hughes, J.D. Virus diseases of peppers (Capsicum spp.) and their control. Adv. Virus Res. 2014, 90, 297–354. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K., Kubota, K., Kano, A., Ishikawa, M. Tobamoviruses: old and new threats to tomato cultivation. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2023, 89, 305–321. [CrossRef]
- Ranawaka, B.; Hayashi, S.; Waterhouse, P.M.; de Felippes, F.F. Homo sapiens: The superspreader of plant viral diseases. Viruses 2020, 12, 1462. [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, R.; Rohde, M.J.; Richert-Pöggeler, K.R.; Ziebell, H. To be seen or not to be seen: Latent infection by tobamoviruses. Plants 2022, 11, 2166. [CrossRef]
- Zaitlin, M.; Palukaitis, P. Advances in understanding plant viruses and virus diseases. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2000, 38,117-143. [CrossRef]
- Lomonossoff, G.P. So what have plant viruses ever done for virology and molecular biology? Adv. Virus Res. 2018, 100, 145–162. [CrossRef]
- Lomonossoff, G.P.; Wege, C. TMV particles: The journey from fundamental studies to bionanotechnology applications. Adv. Virus Res., 2018, 102, 149–176. [CrossRef]
- Symonds, E.M.; Nguyen, K.H.; Harwood, V.J.; Breitbart, M. Pepper mild mottle virus: A plant pathogen with a greater purpose in (waste)water treatment development and public health management. Water Res., 2018, 144, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, I.M.; Lapidot, M.; Thomma, B. P. Emerging viral diseases of tomato crops. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2010, 23(5), 539–548. [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, I.M.; Lapidot, M. Major tomato viruses in the Mediterranean basin. Adv. Virus Res., 2012, 84, 31–66. [CrossRef]
- Turina, M.; Kormelink, R.; Resende, R.O. Resistance to Tospoviruses in vegetable crops: Epidemiological and molecular aspects. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2016, 54, 347-371. [CrossRef]
- Gilbertson, R.L.; Batuman, O.; Webster, C.G.; Adkins, S. Role of the insect supervectors Bemisia tabaci and Frankliniella occidentalis in the emergence and global spread of plant viruses. Annu. Rev. Virol., 2015, 2(1),67-93. [CrossRef]
- Ziebell, H.; Carr, J.P. Cross-protection: A century of mystery. Adv. Virus Res., 2010, 76, 211-264.
- Pelham, J. Resistance in tomato to tobacco mosaic virus. Euphytica, 1966, 15, 258-267.
- Ishibashi, K.; Naito, S.; Meshi, T.; Ishikawa, M. An inhibitory interaction between viral and cellular proteins underlies the resistance of tomato to nonadapted tobamoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2009, 106(21), 8778–8783. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Kezuka, Y.; Kobayashi, C.; Kato, M.; Inoue, T.; Nonaka, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Matsumura, H.; Katoh, E. Structural basis for the recognition-evasion arms race between Tomato mosaic virus and the resistance gene Tm-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2014, 111(33), E3486–E3495. [CrossRef]
- Pfitzner, A.J.P. Resistance to Tobacco mosaic virus and Tomato mosaic virus in tomato. In Natural Resistance Mechanisms of Plants to Viruses; G. Loebenstein, J.P. Carr, Eds. Springer, Netherlands, 2006; pp. 399-413.
- Moffett P. Mechanisms of recognition in dominant R gene mediated resistance. Adv. Virus Res. 2009, 75,1-33. [CrossRef]
- Palukaitis, P.; Yoon, J.Y. Defense signaling pathways in resistance to plant viruses: Crosstalk and finger pointing. Adv. Virus Res. 2024, 118,77-212. [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.P.; Murphy, A.M.; Tungadi, T.; Yoon, J.Y. Plant defense signals: Players and pawns in plant-virus-vector interactions. Plant Science, 2019, 279,87-95. [CrossRef]
- Dunigan, D.D.; Golemboski, D.B.; Zaitlin, M. Analysis of the N gene of Nicotiana. In Plant Resistance to Viruses. Ciba Foundation Symposium 133. Evered, D., Harnett, S., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons, Chichester UK, 1987; pp.120-135.
- Saito, T.; Meshi, T.; Takamatsu, N.; Okada, Y. Coat protein gene sequence of tobacco mosaic virus encodes a host response determinant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1987, 84(17), 6074–6077. [CrossRef]
- Knorr, D.A.; Dawson, W.O. A point mutation in the tobacco mosaic virus capsid protein gene induces hypersensitivity in Nicotiana sylvestris. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1988, 85(1), 170–174. [CrossRef]
- Culver, J.N.; Dawson. W.O. Tobacco mosaic virus elicitor coat protein genes produce a hypersensitive phenotype in transgenic Nicotiana sylvestris plants. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1991, 4,458-463.
- Scholthof, K.B. Spicing up the N gene: F. O. Holmes and Tobacco mosaic virus resistance in Capsicum and Nicotiana plants. Phytopathology, 2017, 107(2), 148–157. [CrossRef]
- Ojinaga, M.; Guirao, P.; Larregla, S. A survey of main pepper crop viruses in different cultivation systems for the selection of the most appropriate resistance genes in sensitive local cultivars in northern Spain. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2022, 11(6), 719. [CrossRef]
- Gilardi, P.; García-Luque, I.; Serra, M.T. The coat protein of tobamovirus acts as elicitor of both L2 and L4 gene-mediated resistance in Capsicum. J. Gen. Virol., 2004, 85(Pt 7), 2077–2085. [CrossRef]
- Tomita, R.; Sekine, K.T.; Mizumoto, H.; Sakamoto, M.; Murai, J.; Kiba, A.; Hikichi, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Kobayashi, K. Genetic basis for the hierarchical interaction between Tobamovirus spp. and L resistance gene alleles from different pepper species. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2011, 24(1), 108–117. [CrossRef]
- Poulicard, N.; Pagán, I.; González-Jara, P.; Mora, M. Á.; Hily, J. M.; Fraile, A.; Piñero, D.; García-Arenal, F. Repeated loss of the ability of a wild pepper disease resistance gene to function at high temperatures suggests that thermoresistance is a costly trait. New Phytologist, 2024, 241(2), 845–860. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, N.; Sharma, V.; Patel, P.; Sharma, P.N. Pepper mild mottle virus: a formidable foe of capsicum production—a review. Front. Virol., 2023, 3,1208853. [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Pérez, M. G.; García-Luque, I.; Fraile, A.; García-Arenal, F. Mutations that determine resistance breaking in a plant RNA virus have pleiotropic effects on its fitness that depend on the host environment and on the type, single or mixed, of infection. J. Virol., 2016, 90(20), 9128–9137. [CrossRef]
- Eldan, O.; Ofir, A.; Luria, N.; Klap, C.; Lachman, O.; Bakelman, E.; Belausov, E.; Smith, E.; Dombrovsky, A. Pepper plants harboring L resistance alleles showed tolerance toward manifestations of tomato brown rugose fruit virus disease. Plants, 2022, 11, 2378. [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.; Mansour, A.; Ciuffo, M.; Falk, B.W; Turina, M. A new tobamovirus infecting tomato crops in Jordan. Arch. Virol., 2016, 161, 503–506 (2016). [CrossRef]
- Luria, N.; Smith, E.; Reingold, V.; Bekelman, I.; Lapidot, M.; Levin, I.; et al. A new Israeli Tobamovirus isolate infects tomato plants harboring Tm-22 resistance genes. PLoS ONE, 2017, 12 (1), e0170429. [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.A.C. Global plant virus disease pandemics and epidemics. Plants (Basel), 2021, 10(2),233. [CrossRef]
- Zinger, A.; Lapidot, M.; Harel, A.; Doron-Faigenboim, A.; Gelbart, D.; Levin, I. Identification and mapping of tomato genome loci controlling tolerance and resistance to Tomato brown rugose fruit virus. Plants (Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 10(1),179. [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.M.; Abumuslem, M.; Turina, M.; Samarah, N.; Sulaiman, A.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Ata, Y. New weed hosts for tomato brown rugose fruit virus in wild mediterranean vegetation. Plants 2022, 11, 2287. [CrossRef]
- Salem, N.M.; Jewehan, A.; Aranda, M.A.; Fox A. Tomato brown rugose fruit virus pandemic. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2023, 61,137-164. [CrossRef]
- 43. Anon. Pest Alert: tomato brown rugose fruit virus (ToBRFV) European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization ISSN 0250-8052. 2020, Available online: https://pra.eppo.int/pra/e1e025c7-a704-46b8-90da-b26015bc6068 (accessed on 27 May 2024). [CrossRef]
- Fox, A.; Anderson, H.; Everett, M. Plant Pest Factsheet: Tomato brown rugose fruit virus. 2020, https://planthealthportal.defra.gov.uk/assets/factsheets/ToBRFV-factsheet-v4.pdf (accessed Feb 4, 2024).
- Hak, H.; Spiegelman, Z. The tomato brown rugose fruit virus movement protein overcomes Tm-22 resistance in tomato while attenuating viral transport. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2021, 34(9), 1024–1032. [CrossRef]
- Hak, H.; Raanan, H.; Schwarz, S.; Sherman, Y.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Spiegelman, Z. Activation of Tm-22 resistance is mediated by a conserved cysteine essential for tobacco mosaic virus movement. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2023, 24(8),838-848. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Griffiths, J.S.; Marchand, G.; Bernards, M.A.; Wang, A. Tomato brown rugose fruit virus: An emerging and rapidly spreading plant RNA virus that threatens tomato production worldwide. Mol. Plant Pathol., 2022, 23(9),1262-1277.
- Obregón, V.G.; Ibañez, J.M.; Lattar, T.E.; Juszczak, S.; Groth-Helms, D. (2023) First report of Tomato brown rugose fruit virus in tomato in Argentina. New Dis. Rep., 2023, 48, e12203. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, A.; Moffett, P. N and N'-mediated recognition confers resistance to tomato brown rugose fruit virus. microPubl. Biol., 2022, 10.17912/micropub.biology.000660. [CrossRef]
- Fidan, H.; Sarikaya, P.; Yildiz, K.; Topkaya, B.; Erkis, G.; Calis, O. Robust molecular detection of the new Tomato brown rugose fruit virus in infected tomato and pepper plants from Turkey. J. Integr. Agric., 2021, 20(8),2170–2179.
- Dombrovsky, A.; Tran-Nguyen, L.T.T.; Jones, R.A.C. Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus: Rapidly increasing global distribution, etiology, epidemiology, and management. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2017, 55,231–256. [CrossRef]
- Ainsworth GC. 1935. Mosaic disease of cucumber. Ann. Appl. Biol., 1935, 22,55–67.
- Kehoe, M.A.; Webster, C.; Wang, C.; Jones, R.A.C; Coutts, B.A. Occurrence of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus in Western Australia. Australasian Plant Pathol., 2022, 51(1),1-8.
- Polischuk, V.; Budzanivska, I.; Shevchenko, T.; Oliynik, S. Evidence for plant viruses in the region of Argentina Islands, Antarctica. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2007, 59,409–417, . [CrossRef]
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (U.S. DEPARTMENT OF AGRICULTURE). Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and watermelon green mottle mosaic virus. https://www.aphis.usda.gov/plant-pests-diseases/cgmmv (Accessed April 3 2024).
- Yoon, J.Y.; Choi, G.S.; Choi, S.K.; Hong, J.S.; Choi, J.K.; Kim, W.; Lee, G.P.; Ryu, K.H. Molecular and biological diversities of Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus from Cucurbitaceous crops in Korea. J. Phytopathol., 2008, 156,408-412. [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Li, R.; Shamimuzzaman, M.; Wu, Z.; Ling, K.S. Understanding the transmissibility of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus in watermelon seeds and seed health assays. Plant Dis. 2019, 103(6),1126-1131. [CrossRef]
- Pitman, T.L.; Vu, S.; Tian, T; Posis, K.; Falk, B.W. Genome and phylogenetic analysis of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus global isolates and validation of a highly sensitive RT-qPCR assay. Plant Dis., 2022, 106:6, 1713-1722.
- Darzia E.; Smith, E.; Shargil D.; Lachman, O.; Ganot, L.; Dombrovsky, A. The honeybee Apis mellifera contributes to Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus spread via pollination. Plant Pathol., 2018, 67, 244–251.
- Knapp, J.L.; Osborne, J. L. Cucurbits as a model system for crop pollination management. J. Pollination Ecol., 2019, 25, 89-102. [CrossRef]
- Groen, S.C.; Jiang, S.; Murphy, A.M.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Westwood, J.H.; Davey, M.P.; Bruce, T.J.A.; Caulfield, J.C.; Furzer, O.J.; Reed, A.; et al. Virus infection of plants alters pollinator preference: a payback for susceptible hosts? PLoS Pathog., 2016, 12, e1005790. [CrossRef]
- Mhlanga, N.M.; Murphy, A.M.; Wamonje, F.O.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Caulfield, J.C.; Glover, B.J.; Carr, J.P. An innate preference of bumblebees for volatile organic compounds emitted by Phaseolus vulgaris plants infected with three different viruses. Front. Ecol. Evol., 2021, 9, 626851. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, A.M.; Jiang, S.; Elderfield, J.A.D.; Pate, A.E.; Halliwell, C.; Glover, B.J.; Cunniffe, N.J.; Carr, J.P. Biased pollen transfer between virus-infected and non-infected plants by bumblebees favors the paternity of infected plants in cross-pollination. iScience, 2023, 26(3), 106116. [CrossRef]
- Tayal, M.; Wilson, C.; Cieniewicz, E. Bees and thrips carry virus-positive pollen in peach orchards in South Carolina, United States. J. Econ. Entomol., 2023, 116(4),1091-1101. [CrossRef]
- Glover, B.J.; Bunnewell, S.; Martin, C. Convergent evolution within the genus Solanum: the specialised anther cone develops through alternative pathways. Gene, 2004, 331, 1–7.
- 66. Cooley H, Vallejo-Marín M. Buzz-pollinated crops: A global review and meta-analysis of the effects of supplemental bee pollination in tomato. J. Econ. Entomol., 2021, 114(2),505-519. PMID: 33615362; PMCID: PMC8042731. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitzky, N.; Smith, E.; Lachman, O.; Luria, N.; Mizrahi, Y.; Bakelman H.; et al. The bumblebee Bombus terrestris carries a primary inoculum of Tomato brown rugose fruit virus contributing to disease spread in tomatoes. PLoS ONE, 2019, 14(1),e0210871. [CrossRef]
- Avni, B.; Gelbart, D.; Sufrin-Ringwald, T.; Zemach, H.; Belausov, E.; Kamenetsky-Goldstein, R.; Lapidot, M. ToBRFV infects the reproductive tissues of tomato plants but is not transmitted to the progenies by pollination. Cells, 2022, 11(18),2864. [CrossRef]
- Palukaitis, P.; Yoon, J.Y.; Choi, S.K.; Carr, J.P. Manipulation of induced resistance to viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol., 2017, 26,141-148.
- Zheng, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Plant immunity against Tobamoviruses. Viruses, 2024, 16(4),530. [CrossRef]
- Motoyoshi, F.; Nishiguchi, M. Control of virus diseases by attenuated virus strains, comparison between attenuated strains of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and tobacco mosaic virus. Gamma Field Symposia, 1988, 27, 91–109.
- Chen, H.; Ino, M.; Shimono, M.; Wagh, S. G.; Kobayashi, K.; Yaeno, T.; Yamaoka, N.; Bai, G.; Nishiguchi, M. A single amino acid substitution in the intervening region of 129K protein of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus resulted in attenuated symptoms. Phytopathology, 2020, 110(1),146-152. [CrossRef]
- Ziebell, H.; MacDiarmid, R. Prospects for engineering and improvement of cross-protective virus strains. Curr. Opin. Virol., 2017, 26,8-14.
- 74. Yoon ,J.Y.; Ahn, H.I.; Kim, M.; Tsuda, S.; Ryu, K.H. Pepper mild mottle virus pathogenicity determinants and cross protection effect of attenuated mutants in pepper. Virus Res., 2006, 118(1-2),23-30. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Huan, X.; Mu, X.; Zhu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Sun, X.; Tian, Y.; Gene, C.; Li, X. Engineering of the complementary mutation site in tobacco mosaic virus p126 to develop a stable attenuated mutant for cross-protection. Phytopathol. Res., 2024, 6, 27. [CrossRef]
- Botermans, M.; de Koning, P.P.M.; Oplaat, C.; Fowkes, A.R.; McGreig, S.; Skelton, A.; Adams, I.P.; Fox, A.; De Jonghe, K.; Demers, J.E.; Roenhorst, J.W.; Westenberg, M.; van de Vossenberg, B.T.L.H. Tomato brown rugose fruit virus Nextstrain build version 3: Rise of a novel clade. PhytoFrontiers, 2023, 3:2, 442-446.
- Matzrafi, M.; Abu-Nassar, J.; Klap, C.; Shtarkman, M.; Smith, E.; Dombrovsky, A. Solanum elaeagnifolium and S. rostratum as potential hosts of the tomato brown rugose fruit virus. PLoS ONE. 2023, 18(3), e0282441. [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, S.; Batuman, O. Co-infection of tomato brown rugose fruit virus and pepino mosaic virus in grocery tomatoes in South Florida: Prevalence and genomic diversity. Viruses, 2023, 15(12), 2305. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Leibman-Markus, M.; Weiss, D.; Spiegelman, Z.; Bar, M. Tobamovirus infection aggravates gray mold disease caused by Botrytis cinerea by manipulating the salicylic acid pathway in tomato. Front. Plant Sci., 2023, 14,1196456. [CrossRef]
- Tomitaka, Y.; Shimomoto, Y.; Ryang, B.S.; Hayashi, K.; Oki, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Sekine, K.T. Development and application of attenuated plant viruses as biological control agents in Japan. Viruses, 2024, 16(4),517. PMID: 38675860; PMCID: PMC11054975. [CrossRef]
- Sanford, J.C.; Johnson, S.A. The concept of parasite-derived resistance: deriving resistance genes from the parasite’s own genome. J. Theor. Biol., 1985, 113, 395-405.
- Beachy, R.N. Introduction: Transgenic resistance to plant viruses. Semin. Virol., 1993, 4,327-328.
- Powell-Abel, P.; Nelson, R.S.; De, B.; Hoffmann, N.; Rogers, S.G.; Fraley, R.T.; Beachy, R.N. Delay of disease development in transgenic plants that express the tobacco mosaic virus coat protein gene. Science, 1986, 232(4751),738–743. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, R. S.; Powell-Abel, P.; Beachy, R.N. Lesions and virus accumulation in inoculated transgenic tobacco plants expressing the coat protein gene of tobacco mosaic virus. Virology, 1987, 158(1), 126–132. [CrossRef]
- Shaw, J.G.; Plaskitt, K.A.; Wilson, T.M.A. Evidence that tobacco mosaic virus particles disassemble contranslationally in vivo. Virology, 1986, 148(2),326–336. [CrossRef]
- Register, J. C., 3rd; Beachy, R.N. (1988). Resistance to TMV in transgenic plants results from interference with an early event in infection. Virology, 1988, 166(2), 524–532. [CrossRef]
- Osbourn, J.K.; Watts, J.W.; Beachy, R.N.; Wilson, T.M.A. (1989). Evidence that nucleocapsid disassembly and a later step in virus replication are inhibited in transgenic tobacco protoplasts expressing TMV coat protein. Virology, 1989, 172(1), 370–373. [CrossRef]
- Palukaitis, P.; Zaitlin, M. Replicase-mediated resistance to plant virus disease. Adv. Virus Res., 1997, 48, 349–377. [CrossRef]
- Cillo, F.; Palukaitis, P. Transgenic resistance. Adv. Virus Res., 2014, 90, 35–146. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, E.J.; Stark, D.M.; Nelson, R.S.; Tumer, N.E.; Beachy, R.N. Transgenic plants that express the coat protein genes of tobacco mosaic virus or alfalfa mosaic virus interfere with disease development of some nonrelated viruses. Phytopathology 1989, 79,1284–1290.
- Park, S.M.; Lee, J.S.; Jegal, S.; Jeon, B.Y.; Jung, M.; Park, Y.S.; Han, S.L.; Shin, Y.S.; Her, N.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, M.Y.; Ryu, K. H.; Yang, S. G.; Harn, C.H. Transgenic watermelon rootstock resistant to CGMMV (cucumber green mottle mosaic virus) infection. Plant Cell Rep., 2005, 24(6),350-356. [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, D.; Slightom, J.L. Coat protein-mediated protection: an analysis of transgenic plants for resistance in a variety of crops. Semin. Virol., 1993, 4, 397-405.
- Jongedijk, E.; Huisman, M.J.; Cornelissen, B.J.C. Agronomic performance and field resistance of genetically modified, virus-resistant potato plants. Semin. Virol., 1993, 4, 407-416.
- Fuchs, M.; Provvidenti, R.; Slighthom, J.; Gonsalves, D. Evaluation of transgenic tomato plants expressing the coat protein gene of cucumber mosaic virus strain WL under field conditions. Plant Dis.,1996, 80,270-275.
- Golemboski, D.B.; Lomonossoff, G.P.; Zaitlin, M. Plants transformed with a tobacco mosaic virus nonstructural gene sequence are resistant to the virus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1990, 87, 6311–6315.
- Gal-On, A.; Wolf, D.; Antignus, Y.; Patlis, L.; Ryu, K. H.; Min, B. E.; Pearlsman, M.; Lachman, O.; Gaba, V.; Wang, Y.; Shiboleth, Y. M.; Yang, J.; Zelcer, A. Transgenic cucumbers harboring the 54-kDa putative gene of Cucumber fruit mottle mosaic tobamovirus are highly resistant to viral infection and protect non-transgenic scions from soil infection. Transgenic Res., 2005, 14(1),81-93. [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.P.; Beachy, R.N.; Klessig, D.F. Are the PR1 proteins of tobacco involved in genetically engineered resistance to TMV? Virology, 1989, 169,470-473.
- Palukaitis, P. The road to RNA silencing is paved with plant-virus interactions. Plant Pathol. J., 2011, 27(3),197-206.
- Lopez-Gomollon, S.; Baulcombe, D.C. Roles of RNA silencing in viral and non-viral plant immunity and in the crosstalk between disease resistance systems. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 645–662. [CrossRef]
- Lindbo, J.A.; Dougherty, W.G. Plant pathology and RNAi: a brief history. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2005, 43,191-204. [CrossRef]
- Lius, S.; Manshardt, R.M.; Fitch, M.M.; Slightom, J.L.; Sanford, J.C.; Gonsalves, D. Pathogen-derived resistance provides papaya with effective protection against papaya ringspot virus. Mol. Breeding, 1997, 3,161-168.
- Gonsalves, C.; Cai, W.; Tennant, P.; Gonsalves, D. Effective development of papaya ringspot virus resistant papaya with untranslatable coat protein gene using a modified microprojectile transformation method. Acta Hortic., 1998, 461, 311-314.
- Tenllado, F.; Barajas, D.; Vargas, M.; Atencio, FA; González-Jara, P.; Díaz-Ruíz, J.R. Transient expression of homologous hairpin RNA causes interference with plant virus infection and is overcome by a virus encoded suppressor of gene silencing. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2003,16(2),149-158. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.M.; An, D.R.; Zhao, J.; Huang, G.H.; He, Z.H.; Chen, J.Y. Transiently expressed short hairpin RNA targeting 126 kDa protein of tobacco mosaic virus interferes with virus infection. Acta Biochimica et Biophysica Sinica 38, 22 - 28 (2006).
- Hu, Q.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Líu, Y.; Zhou, X. Virus-derived transgenes expressing hairpin RNA give immunity to Tobacco mosaic virus and Cucumber mosaic virus. Virol. J., 2011, 8,41. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dubey, A.K.; Karmakar, R.; Kini, K.R.; Mathew, K.M.; Prakash, H.S. Inhibition of virus infection by transient expression of short hairpin RNA targeting the methyltransferase domain of Tobacco mosaic virus replicase. Phytoparasitica 2013, 41, 9–15. [CrossRef]
- Jones-Rhoades, M.W.; Bartel, D.P.; Bartel, B. MicroRNAs and their regulatory roles in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2006, 57, 19–53.
- Shivaprasad, P.V.; Chen, H.M.; Patel, K.; Bond, D.M.; Santos, B.A.C.M.; Baulcombe, D.C. A microRNA superfamily regulates nucleotide binding site-leucine-rich repeats and other mRNAs. Plant Cell, 2012, 24,859–874.
- Sunkar, R.; Li, Y.F.; Jagadeeswaran, G. Functions of microRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends Plant Sci., 2012, 17,196–203.
- Lin, S.S.; Henriques, R.; Wu, H.W.; Liu, Q.W.; Yeh, S.D.; Chua, N.H. Strategies and mechanisms of plant virus resistance. Plant Biotechnol. Rep., 2007, 1,125–134. [CrossRef]
- Gaafar, Y.Z.A.; Ziebell, H. Novel targets for engineering Physostegia chlorotic mottle and tomato brown rugose fruit virus-resistant tomatoes: in silico prediction of tomato microRNA targets. Peer J.,2020, 8, e10096 . [CrossRef]
- Tenllado, F.; Díaz-Ruíz, J.R. Double-stranded RNA-mediated interference with plant virus infection. J. Virol., 2001, 75(24),12288-12297. [CrossRef]
- Konakalla, N.C.; Kaldis, A.; Berbati, M.; Masarapu, H.; Voloudakis, A.E. Exogenous application of double-stranded RNA molecules from TMV p126 and CP genes confers resistance against TMV in tobacco. Planta, 2016, 244(4),961-969. [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Martín, J.; Ruiz, L.; Janssen, D.; Velasco, L. Exogenous application of dsRNA for the control of viruses in cucurbits. Front. Plant Sci., 2022, 13,895953. PMID: 35832223; PMCID: PMC9272007. [CrossRef]
- Niehl, A.; Soininen, M.; Poranen, M.M.; Heinlein, M. Synthetic biology approach for plant protection using dsRNA. Plant Biotechnol. J., 2018, 16, 1679-1687. [CrossRef]
- Uslu, V.V.; Wassenegger, M. Critical view on RNA silencing-mediated virus resistance using exogenously applied RNA. Curr. Opin. Virol., 2020, 42,18-24. [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Shen, L.; Li, Y.; Mei, Y.; Yang, W.; Li, C.; Cao, Y.; Chen, F.; Li, B.; Yang, J. Nanoparticle-dsRNA treatment of pollen and root systems of diseased plants effectively reduces the rate of tobacco mosaic virus in contemporary seeds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2023, 15(24), 29052-29063. [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M. D.; Hoak, J.M.; Ellis, B.W.; Brown, J.A.; Sit, T.L.; Wilkinson, C.A.; Reed, T.D.; Welbaum, G.E. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of individual flue-cured tobacco seeds and seedlings reveals seed transmission of tobacco mosaic virus. Phytopathology, 2020, 110(1),194-205. [CrossRef]
- Pospieszny, H.; Chirkove, S.; Atabekov, J. Induction of antiviral resistance in plants by chitosan. Plant Sci., 1991, 79, 63-68.
- Cook, A.B.; Peltier, R.; Hartlieb, M.; Whitfield, R.; Moriceau, G.; Burns, J.A.; Haddleton, D.M.; Perrier, S. Cationic and hydrolysable branched polymers by RAFT for complexation and controlled release of dsRNA. Polym. Chem., 2018, 9,4025-4035.
- Pugsley, C.E.; Isaac, R.E.; Warren, N.J;, Stacey, M.; Ferguson, C.T.J;, Cappelle, K.; Dominguez-Espinosa, R.; Cayre, O.J. Effective delivery and selective insecticidal activity of double-stranded RNA via complexation with diblock copolymer varies with polymer block composition. Pest Manag. Sci., 2024, 80,669-677. [CrossRef]
- Mitter, N.; Worrall, E.A.; Robinson, K.E.; Li, P.; Jain, R.G.; Taochy, C.; et al. Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses. Nat. Plants, 2017, 3,16207. [CrossRef]
- Worrall, E.A.; Bravo-Cazar, A.; Nilon, A.T.; Fletcher, S.J.; Robinson, K.E.; Carr, J.P.; Mitter, N. Exogenous application of RNAi-inducing double-stranded RNA inhibits aphid-mediated transmission of a plant virus. Front. Plant Sci., 2019, 10,265. [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.G.; Fletcher, S.J; Manzie, N.; Robinson, K.E.; Li, P.; Lu, E.; Brosnan, C.A.; Xu, Z.P.; Mitter, N. Foliar application of clay-delivered RNA interference for whitefly control. Nat. Plants, 2022, 8(5),535-548. [CrossRef]
- Uslu, V.V.; Bassler, A.; Krczal, G.; Wassenegger, M. High-pressure-sprayed double stranded RNA does not induce RNA interference of a reporter gene. Front. Plant Sci., 2020, 11, 534391. [CrossRef]
- Csillery, G.; Tobias, I.; Rusko, J. 1983. A new pepper strain of tomato mosaic virus. Acta Phytopathol. Acad, Sci. Hung., 1983, 18,195-200.
- Sanfaçon, H.; Cohen, J.V.; Elder, M.; Rochon, D.M.; French C.J. Characterization of Solanum dulcamara yellow fleck-ob: a tobamovirus that overcomes the N resistance gene. Phytopathology, 1993, 83,400-404.
- Padgett, H.S.; Watanabe, Y.; Beachy, R.N. Identification of the TMV replicase sequence that activates the N gene-mediated hypersensitive response. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1997, 10(6),709-15.
- Whitham, S.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P.; Choi, D.; Hehl, R.; Corr, C.; Baker, B. The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: Similarity to toll and the Interleukin-1 receptor. Cell, 1994, 78,1101–1115.
- Whitham, S.; McCormick, S.; Baker, B. The N gene of tobacco confers resistance to tobacco mosaic virus in transgenic tomato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1996, 93(16), 8776–8781. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Schiff, M.; Dinesh-Kumar, S.P. Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J., 2002, 31(6), 777–786. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.S.; Linger, L. R.; Wolff, M.F.; Wernsman, E.A. The negative influence of N-mediated TMV resistance on yield in tobacco: linkage drag versus pleiotropy. TAG. Theoretical and applied genetics. Theoretische und angewandte Genetik, 2007, 115(2),169–178. [CrossRef]
- Brčák, J.; Ulrychová, M; Čech, M. Infection of tobacco and some Chenopodium species by the cucumber virus 4 (and 3) and by its nucleic acid. Virology, 1961, 16,105-114.
- Farnham, G.; Baulcombe, D.C. Artificial evolution extends the spectrum of viruses that are targeted by a disease-resistance gene from potato. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006,103(49),18828-18833. [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.J.; Slootweg, E.J.; Goverse, A.; Baulcombe, D.C. Stepwise artificial evolution of a plant disease resistance gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2013, 110(52),21189-21194. [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, M.; Yoshida, T.; Matsuyama, M.; Kouzai, Y.; Kano, A.; Ishibashi, K. Tomato brown rugose fruit virus resistance generated by quadruple knockout of homologs of TOBAMOVIRUS MULTIPLICATION1 in tomato. Plant Physiol., 2022, 189(2), 679-686.
- Kravchik, M.; Shnaider, Y.; Abebie, B.; Shtarkman, M.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; et al. Knockout of SlTOM1 and SlTOM3 results in differential resistance to tobamovirus in tomato. Mol. Plant Path., 2022, 23,1278–1289. [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, J.; Brumin, M.; Wolf, D.; Leibman, D.; Klap, C.; Pearlsman, M.; Sherman, A;, Arazi, T.; Gal-On, A., Development of broad virus resistance in non-transgenic cucumber using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Mol. Plant Path., 2016, 17(7),1140-1153.
- Yamanaka, T.; Ohta, T.; Takahashi, M.; Meshi, T.; Schmidt, R.; Dean, C.; Naito, S.; Ishikawa, M. TOM1, an Arabidopsis gene required for efficient multiplication of a tobamovirus, encodes a putative transmembrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2000, 97:10107–10112.
- Yamanaka, T.; Imai, T.; Satoh, R.; Kawashima, A.; Takahashi, M.; Tomita, K.; Kubota, K.; Meshi, T.; Naito, S.; Ishikawa, M. Complete inhibition of tobamovirus multiplication by simultaneous mutations in two homologous host genes. J. Virol.,2002, 76,2491–2497.
- Nishikiori, M.; Mori, M.; Dohi, K.; Okamura, H.; Katoh, E.; Naito, S.; Meshi, T.; Ishikawa, M. A host small GTP-binding protein ARL8 plays crucial roles in tobamovirus RNA replication. PLoS Pathog., 2011, 7,e1002409.
- Ishikawa, M., Obata, F.; Kumagai, T.; Ohno, T. Isolation of mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana in which accumulation of tobacco mosaic virus coat protein is reduced to low levels. Mol. Gen. Genet., 1991, 230,33–38.
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Q. TOM1 family conservation within the plant kingdom for tobacco mosaic virus accumulation. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 24(11),1385-1399. [CrossRef]
- Ishibashi, K.; Nishikiori, M.; Ishikawa, M. Interactions between tobamovirus replication proteins and cellular factors: their impacts on virus multiplication. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 2010, 23(11),1413-1419. [CrossRef]
- Taylor, D.N.; Carr, J.P. The GCD10 subunit of yeast eIF-3 binds the methyltransferase-like domain of the 126 and 183 kDa replicase proteins of Tobacco mosaic virus in the yeast two-hybrid system. J.Gen. Virol., 2000, 81,1587-1591.
- Yamaji, Y.; Sakurai, K.; Hamada, K.; Komatsu, K.; Ozeki, J.; Yoshida, A.; Yoshii, A.; Shimizu, T.; Namba, S.; Hibi, T. Significance of eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A in Tobacco mosaic virus infection. Arch. Virol., 2010, 155,263-268.
- Padmanabhan, M.S.; Kramer, S.R.; Wang, X.; Culver, J.N. Tobacco mosaic virus replicase-auxin/indole acetic acid protein interactions: Reprogramming the auxin response pathway to enhance virus infection. J. Virol., 2008, 82,2477-2485.
- Dorokhov, Y. L.; Mäkinen, K.; Frolova, O.Y.; Merits, A.; Saarinen, J.; Kalkkinen, N.; Atabekov, J.G.; Saarma, M. A novel function for a ubiquitous plant enzyme pectin methylesterase: the host-cell receptor for the tobacco mosaic virus movement protein. FEBS Lett., 1999, 461(3),223-228. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.H.; Sheng, J.; Hind, G.; Handa, A.K.; Citovsky, V. Interaction between the tobacco mosaic virus movement protein and host cell pectin methylesterases is required for viral cell-to-cell movement. EMBO J., 2000, 19(5),913-20. [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Lazarowitz, S.G.; Citovsky, V. The plasmodesmal localization signal of TMV MP is recognized by plant synaptotagmin SYTA. mBio, 2018, 9(4),e01314-18. Published 2018 Jul 10. [CrossRef]
- Lartey, R.T.; Ghoshroy, S.; Citovsky, V. Identification of an Arabidopsis thaliana mutation (vsm1) that restricts systemic movement of tobamoviruses. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact., 1998, 11(7),706-709. [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Citovsky, V. The systemic movement of a tobamovirus is inhibited by a cadmium-ion-induced glycine-rich protein. Nat. Cell Biol., 2002, 4(7),478-486. [CrossRef]
- Ueki, S.; Citovsky, V. Identification of an interactor of cadmium ion-induced glycine-rich protein involved in regulation of callose levels in plant vasculature. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2005. 102(34).12089-94. [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.T.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, H.A.; Choi, D.; Kim, K.H. A simple method for screening of plant NBS-LRR genes that confer a hypersensitive response to plant viruses and its application for screening candidate pepper genes against Pepper mottle virus. J. Virol. Meth., 2014, 201,57-64. [CrossRef]
- Wylie, S.J.; Zhang, C.; Long, V.; Roossinck, M.J.; Koh, S.H.; Jones, M.G.; Iqbal, S.; Li, H. Differential responses to virus challenge of Australian species of Nicotiana, and comparative analysis of RDR1 gene sequences. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121787. [CrossRef]
- Bally, J.; Jung, H.; Mortimer, C.; Naim, F.; Philips, J.G.; Hellens, R.; Bombarely, A. Goodin, M. M.; Waterhouse, P.M. The rise and rise of Nicotiana benthamiana: A plant for all reasons. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol., 2018, 56, 405-426. [CrossRef]
- Anon. 2024. The Philippines bans some genetically modified foods. The Economist https://www.economist.com/asia/2024/05/02/the-philippines-bans-some-genetically-modified-foods (accessed May 17, 2024).
- McKie, R. 2024 ‘A catastrophe’: Greenpeace blocks planting of lifesaving golden rice. The Guardian https://www.theguardian.com/environment/article/2024/may/25/greenpeace-blocks-planting-of-lifesaving-golden-rice-philippines?CMP=share_btn_url (accessed May 25, 2024).
- Case C-528/16: Judgment of the Court (Grand Chamber) of 25 July 2018 https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=CELEX%3A62016CA0528 (accessed May 23 2024).
- Romeis, J.; Naranjo, S.E.; Meissle, M.; Shelton, M.E. Genetically engineered crops help support conservation biological control. Biol. Cont., 2019, 130,136–154. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




