Submitted:
30 May 2024
Posted:
30 May 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
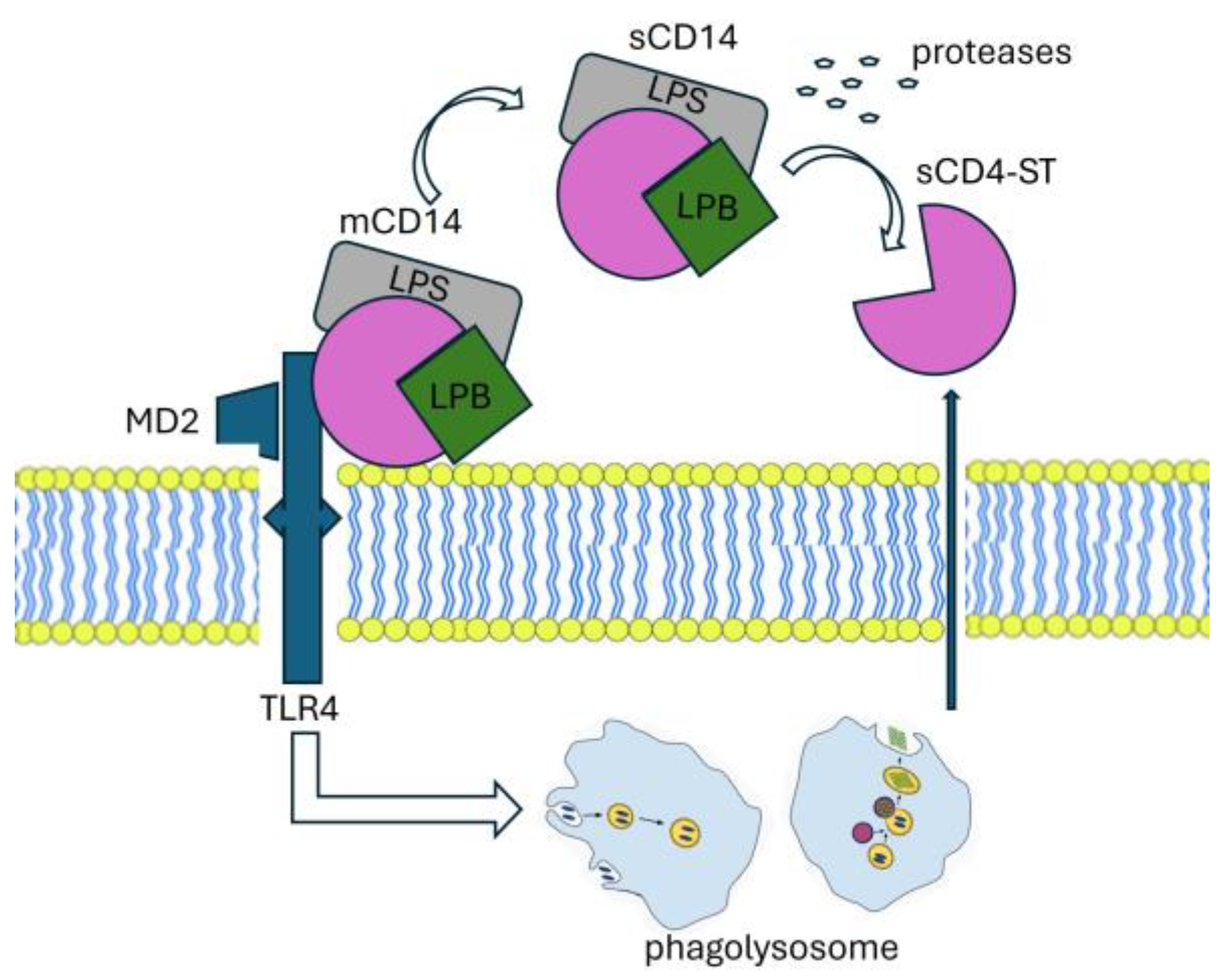
2.1.1. Immunobiology of Presepsin
2.1.2. Diagnostic Utility of Presepsin
2.1.3. Prognostic Value of Presepsin
2.1.4. Therapeutic Implications
3.1. Presepsin and COVID-19
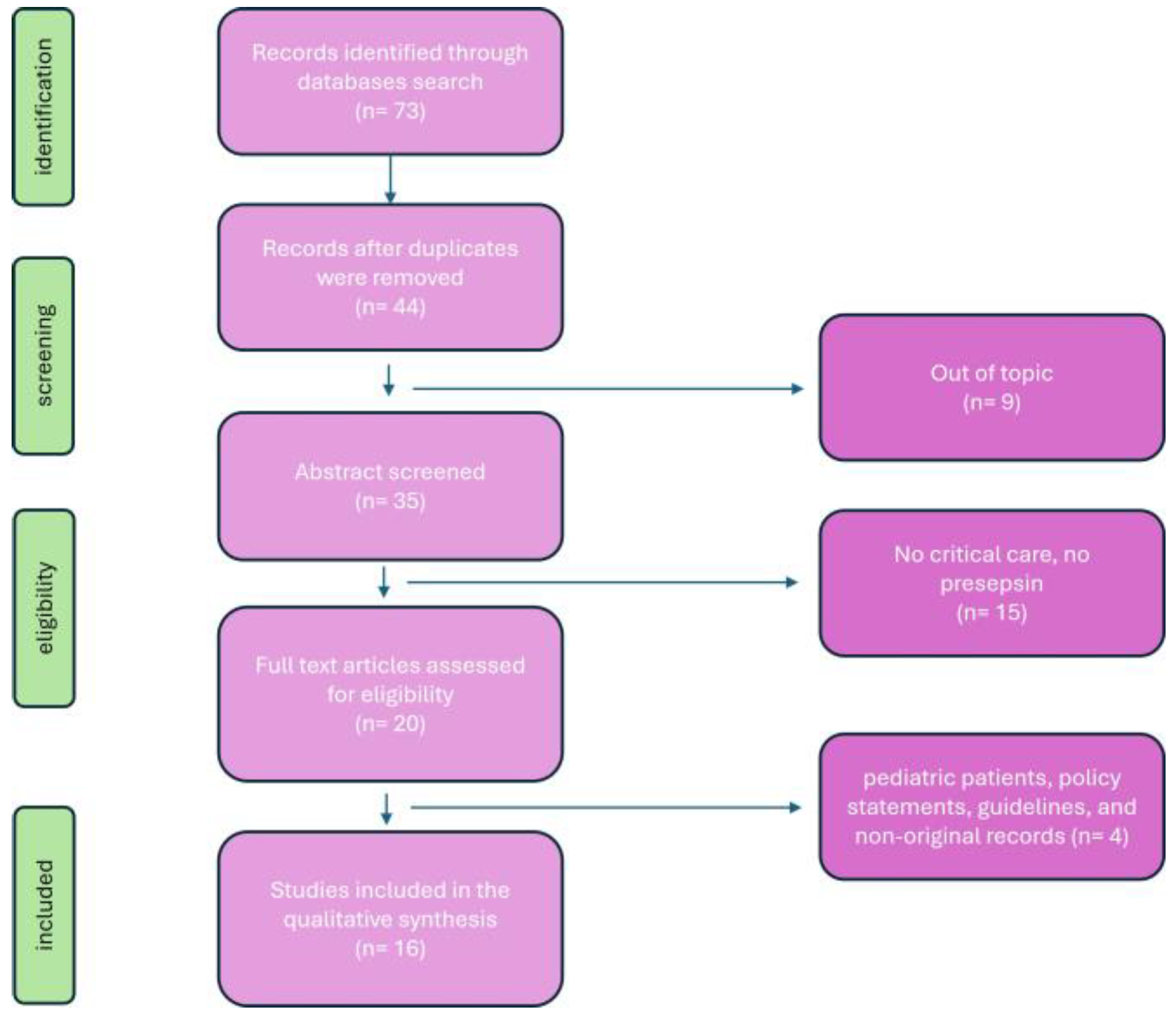
| Study | Patients |
Design | Main Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Masson et al [45] |
100 ICU patients; severe sepsis or septic shock |
Multicenter RTC |
PSP, measured at day 1, was higher in non-survivors than in survivors. The evolution of PSP levels over time was significantly different in survivors compared to non-survivors; PSP concentrations on day 2 and day 7 post-admission were independently correlated with 28 days and 90 days post-admission mortality. |
| Endo et al [37] | 103 ICU patients; sepsis or septic shock | Multicenter prospective study | PSP decreased on days 3 and 7 after ICU admission in survivors. PSP was more closely associated with SOFA and APACHE scores than PCT. |
| Endo et al [35] | 207 ICU patients; suspected sepsis | Multicenter prospective study | PSP does not differ between patients with Gram-positive vs Gram-negative bacterial infections. The sensitivity for discrimination of bacterial and nonbacterial infectious diseases of blood culture was 35.4 % vs PSP was 91.9 %. |
| Godnic et al [33] | 47 ICU patients | Comparative study three groups: SIRS, sepsis, septic shock |
bacterial infection showed statistical significance in PSP, CRP not in PCT. The severity of diagnosed SIRS was significantly associated only with PCT. Values of PCT were the only ones to predict SIRS severity and could distinguish between sepsis and severe sepsis or septic shock. |
| Liu et al [69] | 859 hospitalized patients; SIRS | Single-center prospective observational study | PSP increased with sepsis severity. PSP demonstrated effectiveness in predicting sepsis (sensitivity and specificity 84.6% and 62.5%). PSP in septic were higher in non-survivors than in survivors at 28 days. |
| Sargentini et al [30] |
21 ICU patients | Single-center, prospective observational study | ROC for the sepsis diagnosis was 0.945 PCT vs 0.756 for PSP. While PSP could effectively distinguish between septic and non-septic patients in the ICU, its performance was inferior compared to PCT. |
| Sargentini et al [38] |
64 ICU patients | Single-center prospective observational study | PSP levels remained elevated in recurrent septic patients, while PCT levels normalized during the transient remission phase. The presence of persistently high PSP levels may serve as an indicator for clinicians to consider continuation of antibiotic therapy in patients with sepsis. |
| Carpio et al [39] | 246 patients included | Single-center, prospective observational study. SIRS and/or sepsis vs healthy | PSP were significantly different in patients with SIRS, sepsis, severe sepsis, and septic shock and showed strong association with 30-day mortality. Combination of PSP with MEDS score improved the performance for outcome prediction. PSP values in the course of the disease were statistically different between non-survivors and survivors. |
| Klouche et al [42] | 144 ICU patients | Observational prospective study | PSP and PCT were significantly higher in septic than in non-septic patients. The prognostic value of PSP in stratifying short-term mortality risk in patients with pneumonia has been confirmed. In the patients admitted for acute respiratory failure, the accuracy of PSP to diagnose sCAP was significantly better than PCT. |
| Zaho et al [44] |
225 ARDS patients | Multicenter prospective cohort trial sepsis-related ARDS vs non-sepsis-related ARDS | PSP was found to be an independent predictor of in-hospital mortality in sepsis-related ARDS. Patients with sepsis-related ARDS had higher PSP levels than patients with non-sepsis-related ARDS. ROC PSP (0.81) was significantly greater than that of PCT (0.62). Among patients with sepsis-related ARDS, PSP levels were significantly higher in non-survivors than in survivors. |
| Xiao et al [46] | 656 patients | Multicenter prospective cohort trial |
PSP to guide antibiotic therapy-> not adversely affect 28-day and 90-day survival rates. Patients in the PSP group also had significantly more days without antibiotics than those in the control group. |
| Brodska et al [48] |
60 ICU patients | Single-center observational prospective | PSP did not correlate with SOFA on day 1. PSP did not demonstrate superior performance compared to traditional biomarkers such as PCT, CRP, and lactate in predicting mortality among critically ill patients with sepsis and SIRS. |
| Koh et al [49] | 153 patient’s septic and septic shock | Retrospective cohort survival vs non-survival |
PSP values elevated in non-survivor vs survivor group. PSP levels exceeding 1176 pg/ml exhibited a sensitivity of 66.7% and specificity of 61.1% in predicting in-hospital mortality. |
| Yu et al [53] |
109 patients | Monocentric observational prospective Survival vs non survival |
PSP levels in the survival group decreased persistently, while they rose gradually in the non-survival group. |
| Masson et al [45] | 997 patients; severe sepsis/septic shock | Multicenter randomized trial | PSP concentration at admission was associated with SOFA score. PSP levels tended to decrease in patients with negative blood cultures and in those with positive blood cultures and appropriate antibiotic therapy, while raised in patients with positive microbiology and inappropriate antibiotic therapy. |
| Kondo et al [36] |
3012 patients |
Meta-analysis |
no differences in both pooled sensitivities and specificities between PCT and PSP (0.80 vs 0.84, and 0.75 vs 0.73). Both biomarkers proved to be valuable for the early diagnosis of sepsis and the reduction of mortality in critically ill adults. |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, H.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Y.-W. Clinical Microbiology in Detection and Identification of Emerging Microbial Pathogens: Past, Present and Future. Emerg Microbes Infect 11, 2579–2589. [CrossRef]
- Dellinger, R.P.; Rhodes, A.; Evans, L.; Alhazzani, W.; Beale, R.; Jaeschke, R.; Machado, F.R.; Masur, H.; Osborn, T.; Parker, M.M.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign. Crit Care Med 2023, 51, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peri, A.M.; Stewart, A.; Hume, A.; Irwin, A.; Harris, P.N.A. New Microbiological Techniques for the Diagnosis of Bacterial Infections and Sepsis in ICU Including Point of Care. Curr Infect Dis Rep 2021, 23, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burillo, A.; Bouza, E. Use of Rapid Diagnostic Techniques in ICU Patients with Infections. BMC Infect Dis 2014, 14, 593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilmann, E.; Gregoriano, C.; Schuetz, P. Biomarkers of Infection: Are They Useful in the ICU? Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2019, 40, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marazzi, M.G.; Randelli, F.; Brioschi, M.; Drago, L.; Romanò, C.L.; Banfi, G.; Massaccesi, L.; Crapanzano, C.; Morelli, F.; Corsi Romanelli, M.M.; et al. Presepsin: A Potential Biomarker of PJI? A Comparative Analysis with Known and New Infection Biomarkers. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 2018, 31, 394632017749356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliu-Bejta, A.; Atelj, A.; Kurshumliu, M.; Dreshaj, S.; Baršić, B. Presepsin Values as Markers of Severity of Sepsis. Int J Infect Dis 2020, 95, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 Trafficking and Its Influence on LPS-Induced pro-Inflammatory Signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funda, D.P.; Tučková, L.; Farré, M.A.; Iwase, T.; Moro, I.; Tlaskalová-Hogenová, H. CD14 Is Expressed and Released as Soluble CD14 by Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells In Vitro: Lipopolysaccharide Activation of Epithelial Cells Revisited. Infect Immun 2001, 69, 3772–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galliera, E.; Massaccesi, L.; Vecchi, E. de; Banfi, G.; Romanelli, M.M.C. Clinical Application of Presepsin as Diagnostic Biomarker of Infection: Overview and Updates. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM) 2020, 58, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegame, A.; Kondo, A.; Kitaguchi, K.; Sasa, K.; Miyoshi, M. Presepsin Production in Monocyte/Macrophage-Mediated Phagocytosis of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 5978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddaloni, C.; De Rose, D.U.; Santisi, A.; Martini, L.; Caoci, S.; Bersani, I.; Ronchetti, M.P.; Auriti, C. The Emerging Role of Presepsin (P-SEP) in the Diagnosis of Sepsis in the Critically Ill Infant: A Literature Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, S.; Caironi, P.; Spanuth, E.; Thomae, R.; Panigada, M.; Sangiorgi, G.; Fumagalli, R.; Mauri, T.; Isgrò, S.; Fanizza, C.; et al. Presepsin (Soluble CD14 Subtype) and Procalcitonin Levels for Mortality Prediction in Sepsis: Data from the Albumin Italian Outcome Sepsis Trial. Crit Care 2014, 18, R6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Hu, L.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F.; He, T. Accuracy of Presepsin in Sepsis Diagnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0133057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekhuizen, H.; Blokland, I.; Corsèl-van Tilburg, A.J.; Koning, F.; van Furth, R. CD14 Contributes to the Adherence of Human Monocytes to Cytokine-Stimulated Endothelial Cells. J Immunol 1991, 147, 3761–3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.D.; Ramos, R.A.; Tobias, P.S.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Mathison, J.C. CD14, a Receptor for Complexes of Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS Binding Protein. Science 1990, 249, 1431–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidzadeh, K.; Christensen, S.M.; Dalby, E.; Chandrasekaran, P.; Mosser, D.M. Macrophages and the Recovery from Acute and Chronic Inflammation. Annu Rev Physiol 2017, 79, 567–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megha, KB.; Joseph, X.; Akhil, V.; Mohanan, PV. Cascade of Immune Mechanism and Consequences of Inflammatory Disorders. Phytomedicine 2021, 91, 153712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, A. Cascade System Activation in Shock. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand Suppl 1993, 98, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, U.; Krüger, C.; Westermann, J.; Lukowsky, A.; Ehlers, M.; Schütt, C. An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for the Quantification of Solubilized CD14 in Biological Fluids. J Immunol Methods 1992, 155, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, E.A.; Miller, D.S.; Jahr, T.G.; Sundan, A.; Bazil, V.; Espevik, T.; Finlay, B.B.; Wright, S.D. Soluble CD14 Participates in the Response of Cells to Lipopolysaccharide. J Exp Med 1992, 176, 1665–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchens, R.L.; Thompson, P.A.; Viriyakosol, S.; O’Keefe, G.E.; Munford, R.S. Plasma CD14 Decreases Monocyte Responses to LPS by Transferring Cell-Bound LPS to Plasma Lipoproteins. J Clin Invest 2001, 108, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunialti, M.K.C.; Martins, P.S.; Barbosa de Carvalho, H.; Machado, F.R.; Barbosa, L.M.; Salomao, R. TLR2, TLR4, CD14, CD11B, and CD11C Expressions on Monocytes Surface and Cytokine Production in Patients with Sepsis, Severe Sepsis, and Septic Shock. Shock 2006, 25, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, K.; Naitou, K.; Hirose, J.; Takahashi, T.; Furusako, S. Presepsin (sCD14-ST): Development and Evaluation of One-Step ELISA with a New Standard That Is Similar to the Form of Presepsin in Septic Patients. Clin Chem Lab Med 2011, 49, 937–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, M.; Inoue, Y.; Nishioka, M.; Ikegame, A.; Nakao, T.; Kishi, S.; Doi, T.; Nagai, K. Clinical Evaluation of Presepsin Considering Renal Function. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0215791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragoş, D.; Ghenu, M.I.; Timofte, D.; Balcangiu-Stroescu, A.-E.; Ionescu, D.; Manea, M.M. The Cutoff Value of Presepsin for Diagnosing Sepsis Increases with Kidney Dysfunction, a Cross-Sectional Observational Study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2023, 102, e32620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Ruan, W.-Q.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.-X.; Li, Q. Validity of Presepsin for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Sepsis in Elderly Patients Admitted to the Intensive Care Unit. Minerva Anestesiol 2020, 86, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capossela, L.; Margiotta, G.; Ferretti, S.; Curatola, A.; Bertolaso, C.; Pansini, V.; Di Sarno, L.; Gatto, A. Presepsin as a Diagnostic Marker of Sepsis in Children and Adolescents: A Short Critical Update. Acta Biomed 2023, 94, e2023062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marascio, N.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Romeo, F.; Cicino, C.; Trecarichi, E.M.; Quirino, A.; Torti, C.; Matera, G.; Russo, A. The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Clinical Outcome of Septic Patients: State of the Art and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24, 9307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargentini, V.; Ceccarelli, G.; D’Alessandro, M.; Collepardo, D.; Morelli, A.; D’Egidio, A.; Mariotti, S.; Nicoletti, A.M.; Evangelista, B.; D’Ettorre, G.; et al. Presepsin as a Potential Marker for Bacterial Infection Relapse in Critical Care Patients. A Preliminary Study. Clin Chem Lab Med 2015, 53, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.-L.; Wang, G.-X.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.-M.; Zhou, J.; Yu, H.; Xie, M.-R.; Li, C.-S. Dynamic Blood Presepsin Levels Are Associated with Severity and Outcome of Acute Pancreatitis: A Prospective Cohort Study. World J Gastroenterol 2022, 28, 5203–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, F.T.; Ali, M.A.M.; Elnakeeb, M.M.; Bendary, H.N.M. Presepsin Is an Early Monitoring Biomarker for Predicting Clinical Outcome in Patients with Sepsis. Clin Chim Acta 2016, 460, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godnic, M.; Stubljar, D.; Skvarc, M.; Jukic, T. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of sCD14-ST--Presepsin for Patients Admitted to Hospital Intensive Care Unit (ICU). Wien Klin Wochenschr 2015, 127, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Chen, Y.-X.; Yin, Q.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Li, C.-S. Diagnostic Value and Prognostic Evaluation of Presepsin for Sepsis in an Emergency Department. Crit Care 2013, 17, R244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, G.; Shozushima, T.; Ishikura, H.; Murai, A.; Nishida, T.; Irie, Y.; Miura, M.; Iguchi, H.; et al. Usefulness of Presepsin in the Diagnosis of Sepsis in a Multicenter Prospective Study. J Infect Chemother 2012, 18, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Umemura, Y.; Hayashida, K.; Hara, Y.; Aihara, M.; Yamakawa, K. Diagnostic Value of Procalcitonin and Presepsin for Sepsis in Critically Ill Adult Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Intensive Care 2019, 7, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Takahashi, G.; Shozushima, T.; Ishikura, H.; Murai, A.; Nishida, T.; Irie, Y.; Miura, M.; Iguchi, H.; et al. Presepsin as a Powerful Monitoring Tool for the Prognosis and Treatment of Sepsis: A Multicenter Prospective Study. J Infect Chemother 2014, 20, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sargentini, V.; Collepardo, D.; D Alessandro, M.; Petralito, G.; Ceccarelli, G.; Alessandri, F.; Piciocchi, A.; Angeloni, A.; Venditti, M.; Bachetoni, A. Role of Biomarkers in Adult Sepsis and Their Application for a Good Laboratory Practice: A Pilot Study. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 2017, 31, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carpio, R.; Zapata, J.; Spanuth, E.; Hess, G. Utility of Presepsin (sCD14-ST) as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker of Sepsis in the Emergency Department. Clin Chim Acta 2015, 450, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilotto, A.; Rengo, F.; Marchionni, N.; Sancarlo, D.; Fontana, A.; Panza, F.; Ferrucci, L. ; FIRI-SIGG Study Group Comparing the Prognostic Accuracy for All-Cause Mortality of Frailty Instruments: A Multicentre 1-Year Follow-up in Hospitalized Older Patients. PLoS One 2012, 7, e29090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilotto, A.; Dini, S.; Daragjati, J.; Miolo, M.; Mion, M.M.; Fontana, A.; Storto, M.L.; Zaninotto, M.; Cella, A.; Carraro, P.; et al. Combined Use of the Multidimensional Prognostic Index (MPI) and Procalcitonin Serum Levels in Predicting 1-Month Mortality Risk in Older Patients Hospitalized with Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP): A Prospective Study. Aging Clin Exp Res 2018, 30, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouche, K.; Cristol, J.P.; Devin, J.; Gilles, V.; Kuster, N.; Larcher, R.; Amigues, L.; Corne, P.; Jonquet, O.; Dupuy, A.M. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Soluble CD14 Subtype (Presepsin) for Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia in ICU Patients. Ann Intensive Care 2016, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, B.; Djuric, O.; Denic, L.; Isakovic, A.; Doklestić, K.; Stankovic, S.; Vidičević, S.; Palibrk, I.; Samardzic, J.; Bumbasirevic, V. Prognostic Value of Soluble CD14-ST (Presepsin) in Diagnosis of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia and Sepsis in Trauma Patients. Vojnosanitetski pregled 2017, 75, 27–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tan, Y.; Wang, L.; Shi, Y. Discriminatory Ability and Prognostic Evaluation of Presepsin for Sepsis-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 9114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, S.; Caironi, P.; Fanizza, C.; Thomae, R.; Bernasconi, R.; Noto, A.; Oggioni, R.; Pasetti, G.S.; Romero, M.; Tognoni, G.; et al. Circulating Presepsin (Soluble CD14 Subtype) as a Marker of Host Response in Patients with Severe Sepsis or Septic Shock: Data from the Multicenter, Randomized ALBIOS Trial. Intensive Care Med 2015, 41, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Tan, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J.; Duan, M.; Zhi, D.; Tang, Z.; Hang, C.; et al. Potential Value of Presepsin Guidance in Shortening Antibiotic Therapy in Septic Patients: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Trial. Shock 2022, 57, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enguix-Armada, A.; Escobar-Conesa, R.; García-De La Torre, A.; De La Torre-Prados, M.V. Usefulness of Several Biomarkers in the Management of Septic Patients: C-Reactive Protein, Procalcitonin, Presepsin and Mid-Regional pro-Adrenomedullin. Clin Chem Lab Med 2016, 54, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodska, H.; Valenta, J.; Pelinkova, K.; Stach, Z.; Sachl, R.; Balik, M.; Zima, T.; Drabek, T. Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Presepsin vs. Established Biomarkers in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis or Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome. Clin Chem Lab Med 2018, 56, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, D.H.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, S.-I. Usefulness of Presepsin in Predicting the Prognosis of Patients with Sepsis or Septic Shock: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Yeungnam Univ J Med 2021, 38, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, J.; Rhee, C.; Klompas, M. A Critical Analysis of the Literature on Time-to-Antibiotics in Suspected Sepsis. J Infect Dis 2020, 222, S110–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortegiani, A.; Antonelli, M.; Falcone, M.; Giarratano, A.; Girardis, M.; Leone, M.; Pea, F.; Stefani, S.; Viaggi, B.; Viale, P. Rationale and Clinical Application of Antimicrobial Stewardship Principles in the Intensive Care Unit: A Multidisciplinary Statement. J Anesth Analg Crit Care 2023, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antimicrobial Resistance: Risk Associated with Antibiotic Overuse and Initiatives to Reduce the Problem. Ther Adv Drug Saf 2014, 5, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Qi, Z.; Hang, C.; Fang, Y.; Shao, R.; Li, C. Evaluating the Value of Dynamic Procalcitonin and Presepsin Measurements for Patients with Severe Sepsis. Am J Emerg Med 2017, 35, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aikebaier, S. COVID-19, New Challenges to Human Safety: A Global Review. Front Public Health 2024, 12, 1371238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaninotto, M.; Mion, M.M.; Cosma, C.; Rinaldi, D.; Plebani, M. Presepsin in Risk Stratification of SARS-CoV-2 Patients. Clin Chim Acta 2020, 507, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirpençe, Ö.; Doğan, H.O.; Erşan, S.; Şahin, M.; Şahin, H.; Bakır, M. Presepsin Levels of Patients with Crimean-Congo Hemorrhagic Fever. Jpn J Infect Dis 2016, 69, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karacaer, C.; Sert, H.; Demirci, T.; Varım, C.; Kaya, G.; Genc, A.B.; Ergenc, D.C.H.; Ergenc, Z.; Yaylacı, S.; Nalbant, A.; et al. The Significance of a Novel Inflammatory Biomarker, Presepsin, in Predicting Disease Prognosis in Patients with COVID-19. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2022, 26, 8612–8619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, A.; Nukui, Y.; Kameda, T.; Saito, R.; Koda, Y.; Ichimura, N.; Tohda, S.; Ohkawa, R. Variation in Presepsin and Thrombomodulin Levels for Predicting COVID-19 Mortality. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 21493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assal, H.H.; Abdelrahman, S.M.; Abdelbasset, M.A.; Abdelaziz, M.; Sabry, I.M.; Shaban, M.M. Presepsin as a Novel Biomarker in Predicting In-Hospital Mortality in Patients With COVID-19 Pneumonia. Int J Infect Dis 2022, 118, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocyigit, A.; Sogut, O.; Durmus, E.; Kanimdan, E.; Guler, E.M.; Kaplan, O.; Yenigun, V.B.; Eren, C.; Ozman, Z.; Yasar, O. Circulating Furin, IL-6, and Presepsin Levels and Disease Severity in SARS-CoV-2-Infected Patients. Sci Prog 2021, 104, 368504211026119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F.; Henry, B.M. Presepsin Value Predicts the Risk of Developing Severe/Critical COVID-19 Illness: Results of a Pooled Analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med 2022, 60, e1–e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.; Perna, B.; Maritati, M.; Remelli, F.; Trevisan, C.; Spampinato, M.D.; Costanzini, A.; Volpato, S.; Contini, C.; De Giorgio, R. Presepsin Levels and COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin Exp Med 2023, 23, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aquila, P.; Raimondo, P.; Orso, D.; De Luca, P.; Pozzessere, P.; Parisi, C.V.; Bove, T.; Vetrugno, L.; Grasso, S.; Procacci, V. A Simple Prognostic Score Based on Troponin and Presepsin for COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department: A Single-Center Pilot Study. Acta Biomed 2021, 92, e2021233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, S.; Ikeda, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Nishida, K.; Yamada, K.; Horie, S.; Shimada, Y.; Miki, H.; Goto, H.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Predictive Prognostic Biomarkers in Patients with COVID-19 Infection. Mol Med Rep 2023, 27, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.; Hur, M.; Kim, H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W.; Nam, M. Prognostic Utility of Procalcitonin, Presepsin, and the VACO Index for Predicting 30-Day Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Ann Lab Med 2022, 42, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.H.; Jo, S.J.; Lee, J.; Lim, J. Usefulness of Monocyte Distribution Width and Presepsin for Early Assessment of Disease Severity in COVID-19 Patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022, 101, e29592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakawa, N.; Matsuyama, S.; Matsuoka, M.; Kitamura, I.; Miyashita, K.; Kitagawa, Y.; Imai, K.; Ogawa, K.; Maeda, T.; Saito, Y.; et al. Serum Stratifin and Presepsin as Candidate Biomarkers for Early Detection of COVID-19 Disease Progression. J Pharmacol Sci 2022, 150, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikura, H.; Maruyama, J.; Nakashio, M.; Hoshino, K.; Morimoto, S.; Izutani, Y.; Noake, J.; Yamagaito, T.; Yoshida, M.; Kitamura, T.; et al. Daily Combined Measurement of Platelet Count and Presepsin Concentration Can Predict In-Hospital Death of Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19). Int J Hematol 2023, 117, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yin, Q.; Chen, Y.-X.; Zhao, Y.-Z.; Li, C.-S. Role of Presepsin (sCD14-ST) and the CURB65 Scoring System in Predicting Severity and Outcome of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in an Emergency Department. Respir Med 2014, 108, 1204–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





