1. Introduction
NSTEMI, UA and STEMI are the three presentations of acute coronary syndromes (ACS). Advancements in cardiac care units and revascularization techniques have improved patient outcomes in NSTEMI over the years, but NSTEMI still remains one of the leading causes of death in the United States. In patients presenting with NSTEMI, management can be either invasive (invasive coronary angiography without prior imaging) or conservative (initial stress or anatomic imaging followed with invasive angiography based on it). In general, trials show that an invasive strategy decreases the risk of MI but does not reduce the risk of death compared with selective angiography. The GRACE and TIMI risk scores are accurate scores with extensive validation data, but some experts perceive the routine use of these scores to be cumbersome. In trials that evaluated the effects of the routine use of risk scores, the impact of scores on processes of care was variable, and rates of death and MI were like usual care. Since patients with an acute coronary syndrome are at increased risk of death and nonfatal cardiac events, clinicians must assess prognosis on an individual basis to formulate plans for evaluation and treatment. The TIMI risk score for NSTEMI is a simple prognostication scheme that enables a clinician to categorize a patient’s risk of death and ischemic events at the critical initial evaluation. The TIMI score is calculated with one point each for age more than 65, presence of more than 3 risk factors for coronary artery disease, known coronary artery disease with more than 50% stenosis, two or more episodes of angina in the past 24 hours, elevated cardiac markers, ST changes and aspirin use in the past 7 days. In a retrospective review by Garcia et al. [
1], it was found that two-vessel disease was more likely found in patients with TIMI score 3 to 4 than in those with TIMI scores 0 to 2 and three-vessel or left main disease was more likely found in patients with TIMI score 3 to 4 than in patients with TIMI score 0 to 2), and in patients with TIMI score 5 to 7 than in patients with TIMI score 3 to 4 ( all the results had statistical significance).
Looking at the data from various clinical trials and meta-analyses, the timing of the revascularization strategy does play a critical role in determining outcomes of ACS admissions. IMACS was one of the largest clinical trials analyzing the outcomes of early versus delayed angiography and outcomes in NSTEMI patients [
2]: outcomes of the study proved an early intervention strategy (median: 14 hours since admission) was not superior to a delayed intervention strategy (median: 50 hours since admission) for prevention of in hospital death, myocardial infarction or stroke but had superior outcomes in preventing long term mortality and ischemic events.
2. Materials and Methods
Aim of the study is to analyze outcomes of NSTEMI (Age > 18) admissions across the United States. National Inpatient Sample (2019) was used for the analysis, STATA 18 was used to extract and analyze the data. ICD 10 codes were used for identifying patients admitted with NSTEMI (ICD 10 code 1214 was used). ICD10 PCS (y840) code was used to identify NSTEMI admissions who underwent heart catheterization during the admission. Population characteristics of NSTEMI admissions were done. The population characteristics of patients who died were analyzed and compared to the total NSTEMI admissions. Age, presence of CAD (> 50% stenosis), long standing aspirin use, > 3 risk factors for CAD and troponemia were used to calculate TIMI score for each of the NSTEMI admissions (ST changes in EKG and presence of 2 anginal episodes, the other factors involved in the TIMI score were not used in the estimation as NIS did not document these outcomes for the NSTEMI admissions). From the total pool of NSTEMI admissions, patients who had a calculated TIMI score >2 and did not undergo catheterization during the specific hospital admission were analyzed (NSTEMI patients with TIMI score > 2 and who died during the admission were excluded as absence of catheterization could be a bias due to mortality). Two Tailed p value < 0.005 was used as an indicator of statistical significance in the statistical tests used.
The admissions for NSTEMI admissions were compared in the baseline characteristics with NSTEMI admissions who died during the admission to evaluate for any healthcare or social disparities. From the NSTEMI admissions, subpopulation with calculated TIMI score (based on the age, CAD, aspirin use, risk factors for CAD and troponin elevation) > 2 were selected and the association of a high TIMI score with mortality during the admission were analyzed. Prevalence for mortality in the subpopulation with the high TIMI score who underwent heart catheterization during the admission was compared with the subpopulation that did not undergo heart catheterization. The social and health care factors of the subpopulation of NSTEMI admissions who did not undergo catheterization during the admission were analyzed. Lastly, the time to undergo catheterization during the admission (calculated in days with the admission day considered as day 0) and its association with mortality during the admission was studied. Chi square test was used for calculating associations among the categorical variables, while Mann-Whitney U test was used to compare the baseline characteristics. The correlation between time to catheterization and mortality were analyzed in the subpopulation of NSTEMI admissions with calculated TIMI score > 2, after accounting for age, sex, race and quarterly income.
3. Results
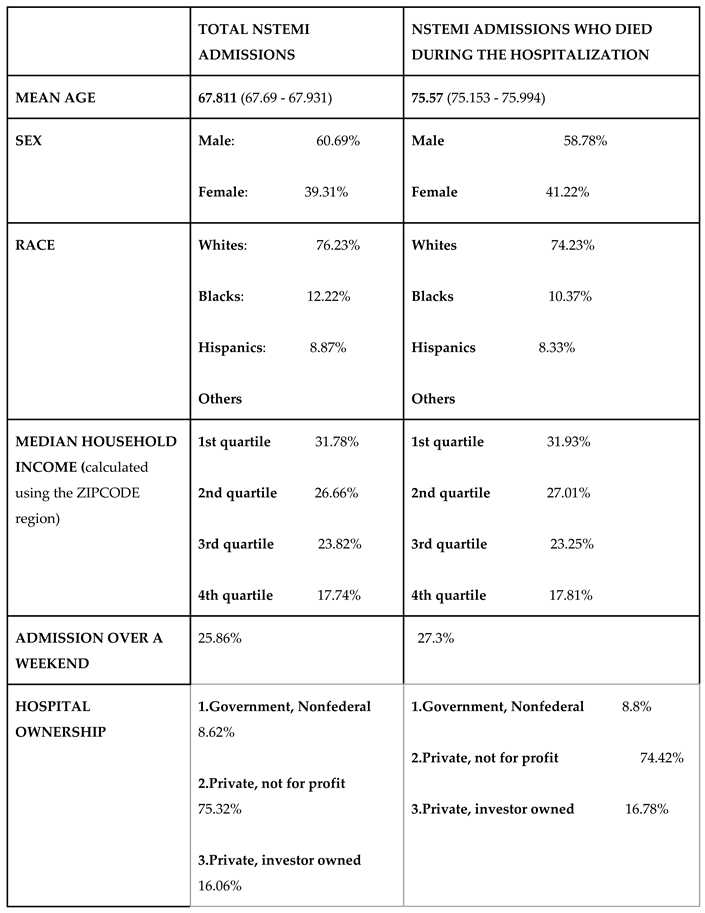
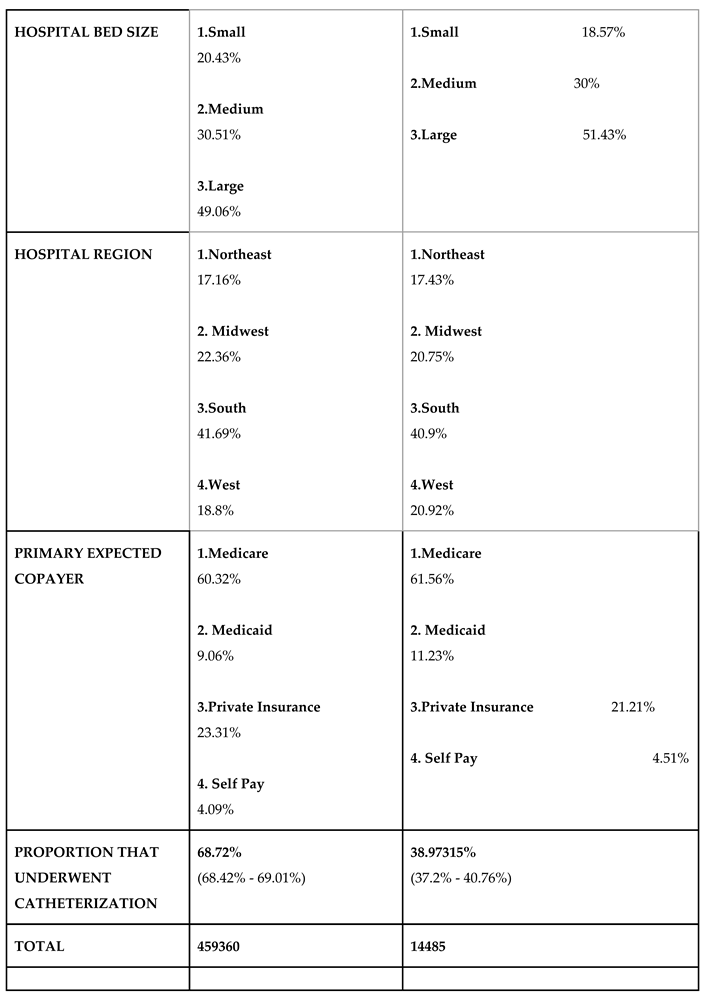
Using the national inpatient sample, 459360 admissions for NSTEMI were identified. Of this, 14485 died during the hospitalization.
Analyzing the population characteristics of NSTEMI admissions and comparing it with the social and healthcare characteristics of NSTEMI admissions (
Table 1) who died during the hospital stay, no social or healthcare disparities were found. The median household income of the patients, race, sex, primary expected copayer, region/ bed size/ location/ ownership of the admitted hospitals was same across both the groups. Percentages of the admissions over a weekend was also same across both the groups. The mean age of NSTEMI admissions who died was higher {75.57 (75.153 - 75.994) vs 67.811 (67.69 - 67.931)} compared to the mean age of all NSTEMI admissions. It was also noted that only 38.97315% (37.2% - 40.76%) of the patients who died during the NSTEMI admissions had a catheterization done during the admission, compared to 68.72% (68.42% - 69.01%) catheterization in the total NSTEMI admissions.
Total NSTEMI admissions were selected, of which the subpopulation with calculated TIMI score >=3 was selected (from the admission data, Age > 65, presence of more than 3 risk factors for CAD, presence of CAD, long term use of aspirin and troponin elevation were used in the calculation).
| TOTAL NSTEMI ADMISSIONS |
ASSOCIATION WITH MORTALITY DURING THE ADMISSIONS (ODDS RATIO) |
|
CALCULATED TIMI SCORE > 2
|
1.33119 (1.235877 - 1.43385)
p value 0.000 |
Among the NSTEMI admissions, the association with mortality during the admissions and calculated TIMI score > =3 was analyzed. In the logistic regression analysis, Age, sex, Race and median income were used in regression to account for confounding. A calculated TIMI score >=3 was associated with a statistically significant association with mortality during the admission.
| NSTEMI ADMISSIONS WITH TIMI SCORE > 2 |
PROPORTION DIED |
| SUBPOPULATION THAT UNDERWENT CATHETERIZATION DURING THE CURRENT ADMISSION |
2.4181%
(2.2502% - 2.5982%) |
| SUBPOPULATION THAT DID NOT UNDERGO CATHETERIZATION DURING THE CURRENT ADMISSION |
6.236%
(5.849% - 6.658%) |
Among the NSTEMI admissions with TIMI score >=3, those with and without the documented procedure of heart catheterization during the admissions were subdivided: proportion of mortality during the admissions was analyzed in both groups. Amongst the NSTEMI admissions with calculated TIMI score > =3, the subpopulation that underwent heart catheterization during the admission had a prevalence of mortality at 2.4181% (2.2502% - 2.5982%), while the prevalence of mortality in the subpopulation of admissions with calculated TIMI score >=3 that did not undergo catheterization was 6.236% (5.849% - 6.658% ). The prevalence of mortality in the subgroup that did not undergo catheterization during the admission was higher with statistical significance than the subgroup that did undergo catheterization during the admission.
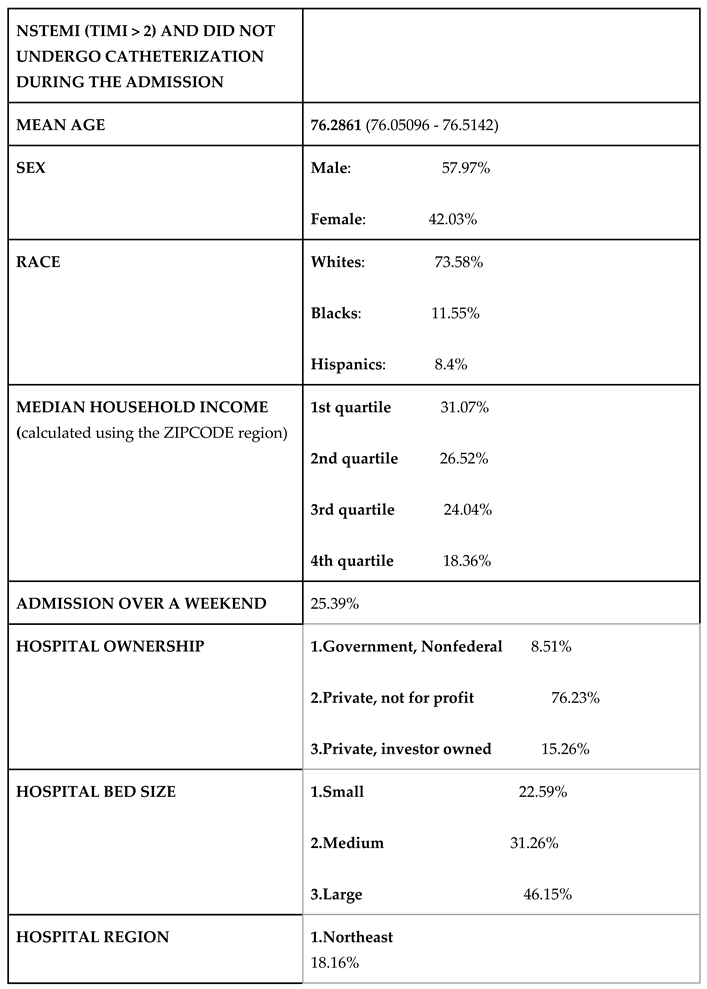
Population characteristics of NSTEMI admissions with calculated TIMI score >2 who did not undergo catheterization during the current admission. The subpopulation of NSTEMI admissions with a calculated TIMI score >=3, who did not undergo catheterization during the admission was subgrouped and analyzed for social and healthcare disparities (patients who died during the admission were excluded as mortality could be a confounding factor for not getting cath. No significant disparities in social or healthcare factors were found in this group compared to the total NSTEMI admission population. (Table 5). The primary expected copayer was Medicare in 83% of this population compared to Medicare being the primary copayer in 60% of the total NSTEMI admissions but the mean age of the subgroup was also higher compared to the total NSTEMI admissions (76.28 vs 67.81).
Analyzing the association between mortality during the admission in NSTEMI admissions (with TIMI score >=3) and documented time taken for catheterization (documented in days, considering the admission day and day 0). The analysis was done after accounting age, sex, race, quarterly income, coexisting diagnosis of CHF. Liner Regression analysis was done. The NSTEMI admissions were again subdivided based on the day of the admission they got the procedure done, namely into admissions that received heart catheterization on day 1, day 2, day 3 and on or after day 4 of the admissions: association of each of the groups with mortality during the admissions was analyzed. Time to catheterization (in days with admission day counted as day 0 had a positive correlation with mortality during the admission with a positive coefficient of regression: 0.002022 (standard error: 0.0003155, p value 0.000, 95% CI: 0.001402 - 0.0026411) in NSTEMI admissions with calculated TIMI score >=3. Calculating the association of in-hospital mortality during the admission and day on which heart catheterization was done (with admission day considered as day zero), admissions who had catheterization done on or beyond 4 days after the admission had an ODDs of association 2.56335 (2.314044 - 2.839516) with all-cause mortality. (
Table 6). NSTEMI admissions who underwent heart catheterization on day1, day 2 or day 3 did not have any significant association with mortality during the admission.
From the NSTEMI admission population, documented diagnoses that were associated with mortality during the admission were analyzed. Age documented at the admission, documented diagnosis of congestive heart failure, documented diagnosis of CKD had significant association with in-hospital mortality during the NSTEMI admissions. (
Table 7). Documented diagnosis of Diabetes, smoking, alcohol abuse or substance abuse did not have any significant association with in-hospital mortality among the NSTEMI admissions.
4. Discussion
While looking at the social and healthcare aspects associated with NSTEMI admissions (
Table 1), no discrepancies that stood out was seen. The only significant finding was an increase in crude mortality for NSTEMI admissions that did not underwent catheterization when compared to the admission that did undergo heart catheterization (38.97315% (37.2% - 40.76%) of the patients who died during the NSTEMI admissions had a catheterization done during the admission, compared to 68.72% (68.42% - 69.01%) catheterization in the total NSTEMI admissions). While analyzing the population characteristics of NSTEMI admissions with a TIMI score > 2 that did not undergo heart catheterization during the current admission, no notable discrepancies where seen when compared to the general NSTEMI admission characteristics. The primary expected copayer was Medicare in 83% of this population compared to Medicare being the primary copayer in 60% of the total NSTEMI admissions but the mean age of the subgroup was also higher compared to the total NSTEMI admissions (76.28 vs 67.81). Documented age at diagnosis, presence of co-existing diagnosis of congestive heart failure and CKD were associated with all-cause mortality in NSTEMI admissions, with statistical significance.
The heterogeneity of the presentations of patients admitted for NSTEMI confer a wide range of risk for death and ischemic events. These patients who lack indications for immediate intervention need to have early risk stratification performed. The TIMI risk score is a simple prognostic method of stratifying this risk and helps in therapeutic decision making. The Antman et al. study in 2000 first proposed the TIMI score based on seven different independent variables and predicts the outcomes of patients with unstable angina or an NSTEMI. A higher TIMI score is associated with an increased number of events at 14 days and has also been correlated with increasingly more severe angiographic coronary disease. In the TACTICS-TIMI 18 study, the outcomes were compared between patients who presented with UA or NSTEMI who underwent either early invasive treatment or conservative medical management. The trial found that patients with moderate to high-risk (TIMI score > 2) who underwent early invasive treatment showed a significant decrease in mortality and cardiac complications compared to those who were conservatively managed. Interestingly, there was no significant difference in outcomes in patients with low risk between the invasive and conservative management.
Our study was conducted to assess the outcomes of NSTEMI admissions using the TIMI score in the United States. It also evaluates the association of mortality in moderate to high-risk NSTEMI admissions (TIMI score > 2) in patients who did and did not undergo heart catheterization during the same hospitalization. Within the subgroup that received invasive intervention, those that were treated earlier (less than 4 days) had better outcomes. The superior prognosis with early revascularization is congruent with prior studies such as the RIDDLE-NSTEMI [
3] and ISAR-COOL [
4] trials. The TACTICS TIMI 18 trial [
5] found out that in UA and NSTEMI, and early invasive strategy with the concurrent use of Tirofiban was associated with better outcomes. FRISC II trial [
6] had similar findings which was supportive of early intervention strategies in UA/ NSTEMII. The unfavorable higher mortality in the delayed intervention groups were attributed to prolonged ischemic time leading to irreversible myocardial damage and subsequent necrosis. A 2022 prospective study in the United States included 113 patients who were admitted for a STEMI and found that lower total ischemic times were favorable with regards to mortality. Although there were several limitations to this study compared to our analysis, the findings strongly support that shorter total ischemic times (TIT) can be a good predictor of clinical outcomes. There is also minimal data in patients admitted for an NSTEMI on TIT; therefore, many considerations are extrapolated from data from trials investigating STEMI patients. The use of TIT has growing evidence to support the use of this factor as a quality indicator in combination with the well-established door-to-balloon (D2B) time.
The NIS database use has been rising due to the ease of access to many subjects and the generalizability of the data. However, there are several limitations when it comes to the use of this type of sample. One main limitation to consider is the lack of surrounding clinical content regarding confounding variables. It becomes more difficult to draw causal inferences from retrospective data due to drug information and inability to determine variables outside of the hospital or clinic. We have reported the demographics of the patients included in our study to provide objective data comparing the social disparities. For instance, the reason for a delay in heart catheterization for the patients admitted with an NSTEMI was not reported, whether it was acute renal injury, uncontrolled hypertension, etc. Another limitation of using NIS is the possibility of misclassification of information. The national data is based on claim codes that are easily susceptible to discrepancies with the actual diagnoses, such as recording codes for payment rather than the true clinical diagnosis. Specifically in our study, one limitation relates to the criteria of the TIMI risk score. The nature of the NIS database prohibited the inclusion of ST wave changes on electrocardiogram and severe anginal symptoms in the TIMI risk score calculation. If these factors were included, more patients would fit the moderate-risk (TIMI > 2) group; hence, our study may be under reporting the number of patients that would be included. However, those patients with either or both findings typically have other co-morbidities and would have been calculated with TIMI score > 2 nonetheless. Despite these limitations, further randomized controlled trials on this topic are warranted.
5. Conclusions
The findings of the current study strongly suggest that patients with moderate to high-risk NSTEMI admissions (TIMI score > 2) who undergo heart catheterization have better outcomes compared to those who do not. Furthermore, among the patients that undergo heart catheterization, those who receive early revascularization have favorable mortality rates compared to those who have a delay in treatment. Thus, attempts to decrease the TIT should be made to reduce overall mortality rates in patients admitted for NSTEMI.
Institutional Review Board Statement
retrospective analysis done using National In-patient sample.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable
Data Availability Statement
All the data used for analysis was used from HCUP national In patient sample which is the largest public healthcare database in the US.
Conflicts of Interest
Not applicable
References
- Correlation of TIMI risk score with angiographic severity and extent of coronary artery disease in patients with non–ST‐elevation ACS Santiago Garcia MD a, Mariana Canoniero MD a, Arley Peter MD a, Eduardo de Marchena MD a, Alexandre Ferreira MD a. [CrossRef]
- Early versus Delayed Invasive Intervention in Acute Coronary Syndromes Authors: Shamir R. Mehta, M.D., M.Sc., Christopher B. Granger, M.D., William E. Boden, M.D., Philippe Gabriel Steg, M.D., Jean-Pierre Bassand, M.D., David P. Faxon, M.D., Rizwan Afzal, M.Sc., for the TIMACS Investigators*Affiliations Published May 21, 2009N Engl J Med 2009;360:2165-2175. [CrossRef]
- Aleksandra Milosevic, Zorana Vasiljevic-Pokrajcic, Dejan Milasinovic, Jelena Marinkovic, Vladan Vukcevic, Branislav Stefanovic, Milika Asanin, Miodrag Dikic, Sanja Stankovic, Goran Stankovic: Immediate Versus Delayed Invasive Intervention for Non-STEMI Patients: The RIDDLE-NSTEMI Study: PMID: 26777321. [CrossRef]
- Neumann FJ, et al. Evaluation of Prolonged Antithrombotic Pretreatment (“Cooling-Off” Strategy) Before Intervention in Patients With Unstable Coronary Syndromes. JAMA 2003, 290, 1593–1599. [Google Scholar]
- Christopher P. Cannon, M.D., William S. Weintraub, M.D., Laura A. Demopoulos, M.D., Ralph Vicari, M.D., Martin J. Frey, M.D., Nasser Lakkis, M.D., Franz-Josef Neumann, M.D.,: Comparison of Early Invasive and Conservative Strategies in Patients with Unstable Coronary Syndromes Treated with the Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa Inhibitor Tirofiban: Published June 21, 2001N Engl J Med 2001;344:1879-1887. [CrossRef]
- Early invasive versus non-invasive treatment in patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome (FRISC-II): 15 year follow-up of a prospective, randomised, multicentre study: Wallentin et al. [CrossRef]
- Prof Lars Wallentin MD a b, Lars Lindhagen PhD b, Elisabet Ärnström MSc b, Steen Husted MD e, Magnus Janzon MD f g, Søren Paaske Johnsen MD h, Frederic Kontny MD i j, Tibor Kempf MD k, Prof Lars-Åke Levin PhD f g, Prof Bertil Lindahl MD a b, Mats Stridsberg MD c, Prof Elisabeth Ståhle MD d, Prof Per Venge MD c, Prof Kai C Wollert MD k, Prof Eva Swahn MD f, Bo Lagerqvist MD a b, FRISC-II study group.
Table 1.
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NSTEMI ADMISSIONS.
Table 1.
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE NSTEMI ADMISSIONS.
| TOTAL NSTEMI ADMISSIONS |
PROPORTION DIED |
| ADMISSIONS WITH CALCULATED TIMI SCORE > 2 |
3.61314%
(3.444% - 3.7926%) |
| Day of the admission when heart catheterization was done (NSTEMI Admissions with TIMI > 2) |
Association with mortality during the admissions (Odds ratio) |
| DAY 1 |
0.54325 |
| SDAY 2 |
0.50108 |
| DAY 3 |
0.44958 |
| DAY 4 AND BEYOND |
2.56335 (2.314044 - 2.839516)
p value 0.00 SE: 0.1338 |
| Documented Diagnosis in the NSTEMI admission cohort |
Association with all-cause mortality during the admission: Odds ratio |
p-value |
Confidence Interval
(95%) |
| Documented Age |
1.053836 |
0.000 |
1.050389 - 1.057294 |
| Congestive Heart Failure |
3.53566 |
0.000 |
3.2545 - 3.84108 |
| CKD |
2.470895 |
0.000 |
2.29387 - 2.661595 |
| Diabetes |
0.650759 |
0.000 |
0.591339 - 0.72789 |
| Alcohol abuse |
0.995608 |
0.974 |
0.80693- 1.23601 |
| Drug abuse |
0.48244 |
0.000 |
0.35357 - 0.6582 |
| Smoking |
0.450816 |
0.000 |
0.39584 - 0.51352 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).