1. Introduction
The youth tourism market represents a key segment for tourism businesses (Frost & Shanka, 1999). Students constitute 20% of all international travelers. Generally, students and young independent travelers travel more frequently and for longer durations than most older tourists and those who purchase package holidays do (Keeley, 2001). The student tourism market is crucial because students will someday become the main consumers and form the foundation of the tourist market (Uysal, 2022). The behavioral tendencies of younger generations have led to the development of new approaches to tourism (Cavagaro & Staffieri, 2015). Furthermore, the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to implementation of restrictions, regulations, and efforts toward avoiding infection, has fundamentally altered travel behavior (Țicău & Shahrazad, 2022). Fernández et al. (2022) found that the number of international tourists decreased by 72% over the first 10 months of 2020. The pandemic consumption habits (Carracero et al., 2021), and tourists began to engage in domestic travel (Longwoods International, 2020). The travel behavior of university and college students changed after COVID-19 and are continuing to evolve (e.g. Olszewski-Strzyzowski et al., 2022; Țicău & Shahrazad, 2022; Yu, 2023). However, research in their preferences regarding accommodation during domestic travel remains sparse and warrants further exploration. Considering the tremendous potential of this travel market segment, in addition to the current instability and dynamic competition, new strategies should be developed to ensure accommodations available to meet young domestic traveler’s expectations.
The relevant literature has mainly focused on international travel by students (e.g., Brochado, Rita & Gameiro, 2015; Nash, Thyne, & Davies, 2006; Reisinger & Mavondo, 2002). Accommodation costs account for the largest portion of student tourists’ travel budgets (Moisă, 2010). Research on young travelers often has made assumptions regarding such travelers’ accommodation budgets or classified such travelers, particularly millennial travelers, as backpackers (e.g., Dayour, Kimbu, & Park, 2017). Few studies have investigated market for domestic tourism among young adults, possibly because of the considerable differences in youth travel behaviors across cultures (Nagai, Benckendorff, & Tkaczynski, 2018; Reisinger & Mavondo, 2002). Researchers have reported that university students are a heterogeneous group and called for further investigations in a cross-country context (Bicikova, 2014; Xiao, So & Wang, 2015). The factors influencing young tourists’ domestic accommodation choices likely differ from those affecting their international accommodation choices. In addition, vaccination and isolation policies implemented in response to the COVID-19 pandemic has restrict overseas travel, which has increased the appeal of domestic travel (e.g., Chansuk et al., 2022). Thus, an empirical case study investigating the accommodation preferences of student domestic travelers would enrich the tourism literature.
Another research issue worthy of attention is various analytical methods to gauge guests’ accommodation preferences. To examine the rationale underlying accommodation choice and the concerns regarding such choices, researchers typically collected tourist data by conducting Likert-scale surveys. Tourists differ in terms of their rating of accommodation options, and their evaluations are subjective. That is, two tourists may assign the same rating to an accommodation choice-related attribute even though the extent of their preference for the attribute may differ. In addition, researchers often evaluated such data by employing descriptive statistical techniques, ANOVA/t-test or exploratory factor analysis to identify collective characteristics (Spoerr, 2021). Further, the complex processes such as multiple regression and structural equation modeling have been employed to develop preference functions (e.g., Ye et al., 2022).
For addressing the above-mentioned research gaps, RIDIT analysis may be considered as a straightforward tool though few studies have applied this approach to examine the tourism sector, and understanding of how prospective tourists think is limited. According to Bhattacharya and Kumar (2017), RIDIT analysis can be used to perform service quality gap analysis or service quality benchmarking in the hospitality, tourism, and travel sectors. Thus, RIDIT analysis is suitable to evaluate the preferences of young tourists related to accommodation service attributes, and it may become a key analytical tool yielding empirical findings in this research domain.
Thus, the present study aims to identify and rank the attributes related to the domestic tourism accommodation choices of young tourists. University students were recruited as the sample in the subsequent analysis. Specifically, our research objective is to rank the service attributes related to domestic accommodation choices by priority, thereby facilitating the development of plans for maximizing the satisfaction of young tourists. Except the RIDIT analysis regarding the priority of the accommodation service attributes based on previous lodging experiences of young tourists, we also compare the analytical results with those obtained through other statistical methods. The research findings may help lodge managers, particularly hostel, to identify key areas of improvement and maximize their service quality.
The remainder of this article is organized as follows. First, we review the literature and briefly introduce the concept of RIDIT analysis. Next, we present the results of our RIDIT analysis and other statistical methods. Finally, we conclude by discussing the implications and application of our findings as well as future research directions.
2. Literature Review
2.1. University Student Segment in Youth Travel Market
Richards (2011) reported that although young tourists typically spend less per day than older tourists do, they stay for longer in a given place, resulting in young tourists spending more in total. Moreover, the expenditure of young tourists frequently directly benefits local businesses, and these tourists are more likely to visit the same destinations multiple times. Richards (2011) observed that young people contribute lifetime value to destinations through their ongoing travel activities. He further noted that youth travel is influential by daily spending levels, accommodation price categories, the duration of stays and that is associated with more extensive travel, a preference for local services, and a higher likelihood of attracting other travelers and returning later in life.
Youth tourism is a rapidly developing segment of international tourism. In 2022, Generation Z, which includes university students aged between 19 and 25 years, was predicted to eventually become the main consumer of tourism products (Uysal, 2022). The student tourism segment is frequently included within the broader youth travel market in tourism research. However, Seekings (1998) specifically analyzed this tourism segment and identified age, education level, and purpose of travel as crucial variables for segmenting the markets of backpackers and students. Pearce and Son (2004) discovered that, compared to backpackers, international English language student travelers are more likely to travel in large groups, opt for hotels or motels, and prefer city-based travel activities.
Nagai, Benckendorff and Tkaczynski (2018) revealed overlap in the characteristics of working holiday makers (WHMs), students, and backpackers. Many backpackers possess working holiday visas, and some backpackers are international students with student visas or other travelers holding short-term visas. Researchers often categorize WHMs as a subset of backpackers (Bui et al., 2013; Ho, Lin & Huang, 2014). Backpackers frequently opt for accommodations such as hostels or backpacker-specific lodging, and WHMs and backpacker have similar characteristics, such as a preference for budget accommodations (Tan et al., 2009).
Given the heterogeneity in the travel motivations and preferences among student travelers, some researchers have recommended further investigation of this market segment to gain a deeper understanding of it. Bicikova (2014) provided empirical evidence regarding the heterogeneity of students’ travel preferences, demonstrating that age and gender, among other variables, significantly influence their tourist behavior. Considerable differences have been observed in the travel behavior between international and domestic students, and nationality and cultural background should be considered during segmentation of the student travel market. Xiao, So and Wang (2015) argued that student travelers should be studied as a discrete market segment because they substantially differ from the youth market in terms of their motivations, travel patterns, and preferences. These authors advocated for differentiated marketing strategies tailored to the distinct preferences of domestic and international student travelers.
Because of the aforementioned factors, reviewing the literature on young tourists who prefer WHM, backpacker, or hostel accommodations can be valuable. Because an increased amount of attention has been given to exploring peer-to-peer (P2P) accommodation and its attraction for young tourists (Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016), this study reviewed the literature on this topic. In addition, this study addressed the changes in accommodation choices and the factors influencing tourists’ preferences and selections after the COVID-19 pandemic.
2.2. Pre-COVID-19 Pandemic Accommodation Choices of Young Tourists
2.2.1. Traditional Accommodation Choices
Heung and Leong (2006) found that university students in Hong Kong tend to stay in hostels while traveling rather than in hotels or motels. This may be because in hostels, students are able to prepare their own meals in the hostel kitchens and engage in social interactions that may lead to friendships. Cooking in these kitchens is generally less costly than dining out is, and therefore, it can reduce overall travel costs if consistently practiced throughout the trip.
Moisă (2010) reports that the accommodation budgets of young tourists accounted for 18% of their travel expenses and is ranked by them as the second most influencing factor. Young tourists also form the core of the backpacker population. A study indicates that the three factors with the most influence on accommodation choices are price, location and ratings and reviews; the other factors are cleanliness, staff friendliness, facilities, atmosphere, and safety (Somlai, 2015). In another study evaluating the overall quality of a hostel, surveyed backpackers rate social atmosphere as the most influential service dimension out of six service quality dimensions (i.e., social atmosphere, location and city connections, staff, cleanliness, security, and facilities) (Brochado et al., 2015).
Researchers have discovered that general tourists evaluate and select hotel accommodations by considering factors such as cleanliness, location, reputation, price, value, staff service attributes (e.g., friendliness and helpfulness), room comfort, brand reputation and security (Chu & Choi, 2000; Lockyer, 2005; Sohrabi et al., 2012). For non-hotel accommodation choices, the unique experiences are prioritized over practical attributes. Stringer (1981) discovers that travelers who stayed at British bed and breakfast lodgings (B&Bs) are primarily attracted by both the B&B experience and the lower prices of such lodgings relative to other accommodation choices. A B&B atmosphere has a positive influence on customer experience and customer value (Chen, 2015). The attractive attributes of B&Bs include an environment that is conductive for socialization, learning, relaxation; high accessibility; novelty; and physical utility (Chen et al., (2013). Travelers who have stayed in boutique accommodations have reported enjoying the unique character, cozy atmosphere, and customized services of these accommodations as well as the personal interactions with their hosts (McIntosh & Siggs, 2005). Wang (2007) reports that homestay guests enjoy the low cost and the interpersonal and authentic experiences provided by homestay accommodations. Travelers participating in couchsurfing and home swaps also report similar factors (Andriotis & Agiomirgianakis, 2014; Bialski, 2011).
Research on university student travel accommodation has been sparse. One study on the topic by Alsawafi and Almuhrzi (2022) identified reputation and quality as the primary factors influencing Arab college students’ accommodation choices during travel.
2.2.2. Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Accommodation Choices
With the increasing popularity of P2) accommodation platforms, understanding the perspectives and preferences of young tourists is crucial because of their varied tastes and preferences in the product market and the tourism sector (Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016). Millennials have considerable purchasing power and are, thus, a key target segment of P2P accommodation platforms (Amaro, Andreu & Huang, 2019). Research has demonstrated that Airbnb appeals more to younger demographics than to older ones (e.g., Guttentag, 2015; Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016). Travelers seek various benefits including value for money and authentic accommodation experiences. Factors that influence the choice of Airbnb accommodations include cost, unique local experiences, cultural exchange, social interaction with hosts and local residents, and insider tips on local attractions (Cheng, 2016; Guttentag, 2015; Poon & Huang, 2017; Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016). Other highly influencing factors include household amenities, home coziness, and large spacious areas (Johnson & Neuhofer, 2017). Sustainability-related dimensions, such as reducing the environmental, social and economic effects of accommodation consumption, may be a factor influencing travelers’ selection of Airbnb accommodation (Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016). Notably, the location of an accommodation is a critical factor. Tussyadiah and Zach (2017) reveal that travelers prefer quiet neighborhoods that are located within walking distance of local restaurants and are a short bus ride away from the city center. P2P platforms tend to focus on the discussions of neighborhoods and local businesses, whereas hotels tend to stress their proximity to attractions (Belarmino et al., 2017).
Several salient P2P accommodation features, such as opportunities for meaningful social encounters, contribute to the main characteristics that differentiate Airbnb from traditional accommodation services (Cheng, 2016). When hosts are available at accommodations, guests can experience a community-focused and social atmosphere and form authentic connections with locals (Prayag & Ozanne, 2018). Mody et al. (2017) identify several dimensions in which Airbnb accommodations are superior to hotels; they include localness, communities, personalization, escapism, aesthetics, and entertainment. Tussyadiah and Zach (2017) report that P2P accommodations create more conditions for building relationships with hosts and local areas, whereas hotels provide better functional services and accessibility, such as airport shuttle services, in-room services, breakfast options and free parking. Similarly, Belarmino et al., (2017) discover that conversations with hosts is a key service attribute of P2P accommodations, and that hotel room amenities (e.g., food, beverages, and scent) are the predominant themes discussed in guest reviews. Varma et al. (2016) conclude that Airbnb guests regard P2P accommodations as an alternative to traditional accommodations.
Although utilitarian, hedonic and social values are key concerns that influence the selection of P2P accommodations (Fan et al., 2022; Mohsin & Lengler, 2021), perceived risk has a strong negative influence on customer satisfaction and even customer purchase intention (Huang et al., 2019; Mohsin & Lengler, 2021). Relative to users of P2P accommodations, non-users perceive higher risks associated with using P2P accommodations and exhibits lower purchase intentions with respect to booking P2P accommodations (Huang et al., 2019). Young tourists from different generation cohorts may also differ in terms of P2P accommodation choices. Fan et al. (2022) indicate that the Generation Z cohort place more emphasis on sustainability and the value of social interactions relative to Millennials. These findings provide insights into the accommodation preferences of young university students.
In summary, P2P and traditional accommodations share several fundamental attributes, even though most studies have indicated that P2P accommodations are attractive because of their low pricing and diverse options (Wang & Nicolau, 2017). Except for host profiles, few differences have been identified in the factors influencing tourists to select Airbnb or traditional accommodations such as B&Bs (Chen et al., 2013). Nevertheless, the present study aims to identify the factors that influence young tourists choosing domestic accommodations.
2.3. Post-COVID-19 Pandemic Students' Travel Behavior and Accommodation
The tourism market changed considerably after the pandemic. According to Longwoods International (2020), tourists shifted from a preference for international travel to that of domestic tourism, that is, tourism in which individuals travel within their own country. Domestic tourism offers a sense of increased safety and comfort because tourists are closer to home throughout their trip. According to the report of World Tourism Organization (2020), domestic tourism opportunities have expanded: by 2020, the market reached six times that of the international market in terms of tourist numbers. Several studies have focused on post-pandemic domestic travel behaviors (e.g., Li, Nguyen, & Coca-Stefaniak, 2021). Sohn et al. (2021) discovered that the pandemic led to Korean tourists’ developing a stronger preference for short-haul destinations because of social distancing requirements in the country. Balińska and Olejniczak (2021) found that Polish tourists altered their tourism behavior by avoiding crowded spots and abstaining from international travel to comply with hygiene requirements in the area. Yu (2023) observed that many Chinese citizens have integrated travel into their daily lives, that is, have developed a preference for engaging in local leisure activities, which may have reduced the frequency with which they engage in long-distance travel. In summary, tourist behaviors and motivations have changed because of the pandemic in terms of, for example, destination choice, use of tourist services, travel frequency, measures of preserving health, and sense of travel safety (Olszewski-Strzyzowski, Pasek, & Lipowski, 2022).
Studies have indicated that student tourists’ behaviors have also changed because of the COVID-19 pandemic. Kusumaningrum and Wachyuni (2020) found that after the pandemic, the most common type of Millennial Indonesian tourist became the explorer type, followed by the drifter type. In addition, they determined that young tourists mainly had physical or physiological motives for traveling and that interpersonal motives were also crucial to them. Furthermore, the researchers found that the Millennial Indonesian tourists primarily chose natural destinations. Uysal (2022) reported that travelers from Generation Z differed from those from Generation X and Generation Y and revealed a transformation from traditional tourist behavior to modern tourist behavior in the post-COVID 19 pandemic. Olszewski-Strzyzowski, Pasek, and Lipowski (2022) indicated that the travel motives of university students and their engagement in tourism activities changed after the pandemic. A survey among Romanian university students highlighted that vacation expenses were a critical concern for such travelers because the students generally had low monthly incomes (Țicău & Shahrazad, 2022). Yu (2023) found that college students were more cautious and more likely to prioritize safety and affordability after the pandemic, indicating that security and affordability should highlight as the main attributes of travel products.
Various characteristics were found to cease to be advantages of P2P accommodations, particularly in the post COVID-19 era. Gassmann et al. (2019) identify price as a predominant factor for selecting P2P accommodation. However, price is not significant contributing factor for consumer loyalty toward Airbnb (Kim & Kim, 2020). In addition, social interactions do not play a key role in influencing the P2P accommodation choices of consumers (Farmaki & Stergiou, 2019; Ye et al., 2022). This may be related to health and safety concerns and the reduction of interpersonal interactions. Similarly, authentic experiences and social benefits are crucial for enhancing consumers’ commitment to Airbnb (Kim & Kim, 2020). However, Santos et al. (2022) describe that Airbnb users are the least focused on experiencing local culture, interacting with other guests, and living like a local.
2.4. Statistical Methods Used in Related Studies
Spoerr (2021) summarized the analytical methods used to categorize the hotel attributes. To face various accommodation attributes, exploratory factor analysis (EFA) has been used frequently to examine the structure of the interrelationships among a large set of the variables to define some common underlying dimensions. Indeed, many researchers applied EFA to reduce the number of accommodation attributes and identify the underlying constructs (e.g., Brochado, Rita, & Gameiro, 2015; Del Chiappa, Pung & Atzeni, 2022; Dilek & Fennell, 2018; Spoerr, 2021). However, it is inevitable to lose some important information by grouping variables. Some parametric tests, for example, t-test or ANOVA may be conducted further for each factor to investigate the differences based on the respondents’ characteristics. Furthermore, the test procedure should meet the requirement which is under a compulsory distribution.
Other complex analytical approaches also have been applied to identify specific accommodation attributes such as hierarchical regression model (e.g., Shanka & Taylor, 2003), conjoint analysis (e.g., Rhee & Yang, 2015), confirmatory factor analysis (Amat-Lefort, Marimon, & Mas-Machuca, 2023) and structural equation modeling (Wilkins, Merrilees, & Herington, 2007). Ye et al. (2022) employ multiple linear regression based on the ordinary least square method to determine whether tourists preferred hotel or P2P accommodations. They construct a relative preference model that considers multiple value attributes and personal traits. Although the complexities of statistical techniques have shed insights into the research issue, using a powerful but easy analytical method makes it challenging to draw conclusions about the importance of individual accommodation attributes.
3. RIDIT Analysis
Scales are commonly adapted to collect data in consumer studies. Clason and Dormody (1994) report that data collected through Likert-scale surveys usually involve the use of ordinal form or interval scales; this strategy assumes that the latent variables reflect the attitudes and opinions of respondents. Consumers usually fill out a questionnaire with scale items based on their experiences, thoughts, and preferences. Each scale item is rated and assigned a numerical value that is represented by a verbal category. Two consumers may rate an item as 5 on a 7-point scale; however, their perception of the meaning of the rating may differ. Relatedly, Pouplard, Qannari, and Simon (1997) indicates that variations exist between consumers, and that such biases influence data quality because of the subjectivity of Likert-scale results. Nonetheless, this method of data collection is frequently employed in consumer and social science research. Clason and Dormody (1994) report that descriptive statistics (frequency, means, and standard deviations), exploratory factor analysis, and multivariate analysis are commonly employed to analyze Likert-scale data; however, they argued that these statistical techniques cannot adequately rank scale item results in an ascending or descending order.
In contrast to other statistical methods that assume a parametric distribution, Bross (1958) reports that the RIDIT technique for analyzing and ranking categorical data. In addition to no requirement for the assumption of the sampling distributions, Fleiss, Levin and Paik (2003) claim that the RIDIT technique produces scores that are relative to an identified distribution. Wu (2007) indicates that RIDIT analyses can be used to rank Likert-scale item results in an ascending or descending order by priority and to investigate the relationships among scale items in terms of significance level.
RIDIT scores can be derived through mathematical methods. Bhattacharya and Kumar (2017) demonstrate that RIDIT analysis can be performed using a straightforward format in Microsoft EXCEL software without the need for complex computation. On the basis of the descriptions provided by Jansen (1984), the basic concept of RIDIT analysis is as follows. Ordinal data are converted to a probability scale through a procedure similar to that for a Wilcoxon rank-sum test. The mean statistics obtained through RIDIT analyses and Wilcoxon rank-sum test are directly connected. The hypothesis that no significant differences exist between mean RIDIT statistics across all scales of responses by using the χ2 statistic can be tested (Fleiss, Levin & Paik, 2013). Similar test between any group and the reference group was defined by them.
According to Pouplard, Qannari and Simon (1997), with a reference distribution function, it is easy to perform the calculations of the RIDIT values which are related to the cumulative distribution function associated with the probability function. Statistically, the mean RIDIT value is 0.5. On average, the items rated by respondents as being more important (i.e., scores of 4 or 5) tend to exhibit RIDIT > 0.5, whereas those rated as being less important (i.e., scores of 1 or 2) tend to exhibit a RIDIT value < 0.5. Accordingly, a higher RIDIT value for a given item generally indicates that the item is more prioritized by a given sample. Priority rankings can be generated because the items with the highest RIDIT values are most prioritized items. Jansen (1984) state that RIDIT analysis can be applied to samples of all sizes; furthermore, it can be easily applied to identify high levels of variance or homogeneity in a given response data set.
For the applications of RIDIT analysis in the field of travel and tourism, Bhattacharya and Kumar (2017) suggest that RIDIT analysis can be applied across numerous fields (e.g., tourism management) to statistically analyze tourist preferences. In this study, it is well suited to rank the preference of young tourists for accommodation attributes without making any assumption regarding the sample distribution.
4. Research Methods
4.1. Questionnaire Design
For achieving our research objective and for data collection, we developed a questionnaire comprising two parts. The first part included questions for evaluating travel characteristics, and the second part comprised 18 questions for assessing accommodation attributes. The measurement items of questionnaire were mainly adapted from the instruments used in other studies (e.g., Nash, Thyne, & Davies, 2006; Somlai, 2015). Respondents rated attributes (including facilities and specific features) that influenced their accommodation choices on a Likert scale (see
Figure 1 for a description of the attributes), with endpoints rating from 1 (
not at all important) to 5 (
extremely important), thereby indicating how influential each accommodation attribute was from their perspective. To ensure clarity and readability, the 18 items of the second part of the questionnaire were pre-tested in a sample of 30 people. A criterion was established to eliminate question items with average scores of 3.0 and standard deviation values > 1.5. On the basis of the pre-test result, all 18 items were retained.
4.2. Data Collection
In the present study, a traditional paper-based survey was conducted to collect data. Because of practical considerations and budget constraints, all participants were recruited from a university in central Taiwan with which the authors were affiliated as an employee or student. Approval for and assistance with data collection were obtained from faculty colleagues, and data collection was conducted in the classroom setting. After consenting to participate, the respondents were informed about the objectives and procedures of our research. After incomplete questionnaire responses were excluded, a total of 296 valid responses were included in the subsequent analyses.
Table 1 presents the descriptions and distributions of all relevant respondent variables.
5. Results and Discussion
In the present study, RIDIT analysis was performed as per the steps outlined by Wu (2007). Bhattacharya and Kumar (2017) demonstrate how Microsoft Excel functions can be used to calculate RIDIT values. In the Kruskal–Wallis test, the calculated W value was 1273.56, which was significantly higher than the χ2 value (18–1) of 27.59; this result indicated that the responses regarding the attributes varied statistically among the respondents. This test is nonparametric and based on rank data. However, it does not require the data to exhibit a normal distribution. In the present study, this test was used to identify significant differences in the results for accommodation attributes across five categories of scores. The overall ranking of the attribute results is presented in
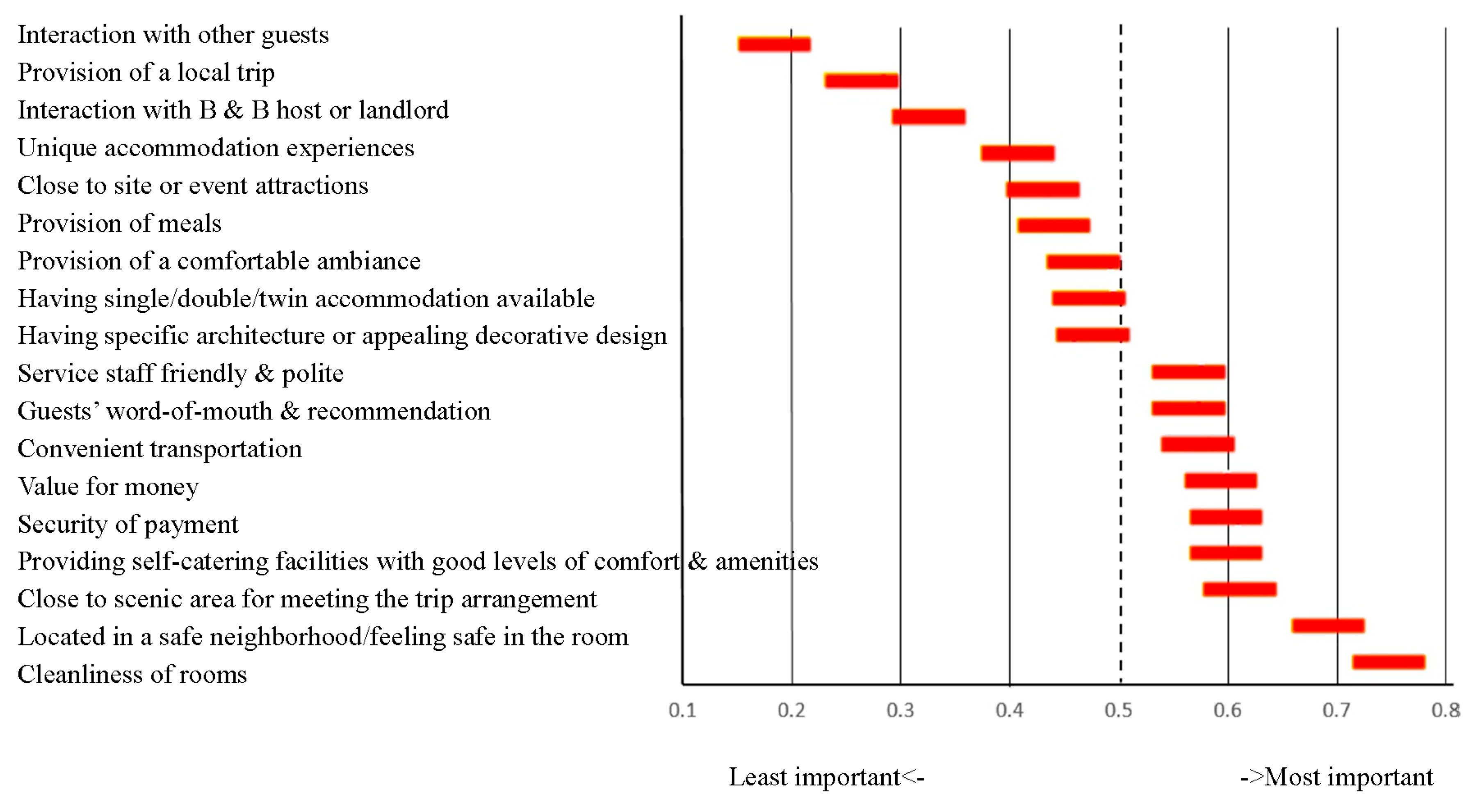
Table 2. Among the examined attributes (
Figure 1), “Cleanliness of rooms” was the most prioritized attribute by the respondents, followed by “Located in a safe neighborhood/feeling safe in the room,” and “Close to scenic area for meeting the trip requirement.” The least prioritized attribute was “Interaction with other guests.” These RIDIT results highlight the relative importance of each attribute to the respondents.
Figure 1.
Distributions of factors important to accommodation choice by university students (RIDIT analysis).
Figure 1.
Distributions of factors important to accommodation choice by university students (RIDIT analysis).
The most commonly used ranking technique involves the application of simple mean ranking, which allows for statistics such as mean and variance to be computed and for service attribute-related results to be compared.
Table 3 provides a comparison of the means and RIDIT results of all examined attributes. Notably, the two methods differ in terms of the rankings of the key service attributes. For instance, when simple mean ranking was employed, “Cleanliness of rooms,” “Close to scenic area for meeting the trip requirement,” “Security of payment,” and “Guests’ word-of-mouth & recommendation” were perceived to be less important by the respondents. In addition, when simple mean ranking was employed, it appears that “Having specific architecture or appealing decorative design,” “Provision of meals,” “Having single/double/twin accommodation available,” and “Close to site or event attractions” were perceived as being important by the respondents; however, the corresponding RIDIT values were low. The discrepancy between the rankings of service attributes conducted through these two methods can be explained by the high sensitivity of the attribute scoring process to small changes in data (e.g., the presence of outliers), which was due to the assignment of equally spaced scores (Bhattacharya & Kumar, 2017).
The RIDIT analysis results (including ranking results) were also compared with those obtained through exploratory factor analysis (EFA), which is commonly used technique. To identify the mechanisms underlying the variance in the service attribute results, we performed principal component analysis with orthogonal varimax rotation.
Table 4 lists the results of the EFA. Regarding adequacy and global significance, the results of the Bartlett test of sphericity and the Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin test were significant (0.845). Five factors corresponding the 18 items were extracted, and these factors accounted for 58.5% of the explained variance. A careful analysis of each factor indicated that providing appropriate labels for each factor was challenging because of the varying nature of these attributes. Furthermore, when the attributes were grouped under a given factor (e.g., Factor 2, Factor 4, and Factor 5), they tended to exhibit low or high priority rankings. In addition, the most prioritized attributes in the RIDIT analysis results, namely “Cleanliness of rooms” and “Located in a safe neighborhood/feeling safe in the room” corresponded to Factor 3, which explained only 6.5% of the variance. Although EFA involves grouping a number of service attributes into a small subset, the reduced scales are challenging to implement, and the subset is difficult to use because of its hypothetical nature (Bhattacharya & Kumar, 2017). Furthermore, EFA is highly sensitive to variable selection, and different samples may generate different results. Thus, compared with EFA, RIDIT analysis leads to different answers. The present study illustrates that RIDIT analysis may be a more effective method for ranking items in an ascending or descending order.
6. Conclusions and Implications
Our research results reveal that RIDIT analysis is a straightforward method for ranking service attributes measured on a Likert scale. Our research findings are similar to those of Nash, Thyne and Davies (2006), who report that a sample of backpackers gave high rankings to the attributes “cleanliness of rooms,” “value for money,” and “the presence of self-catering facilities.” However, the rankings of the factors by priority are different between the two studies. The service attributes identified in the present study reflect the characteristics, expectations, and needs of post-millennial tourists when choosing domestic accommodations. On the other hand, despite a different sample, the similar results were found between Spoerr’s (2021) and our studies. For Airbnb accommodations, Sthapit, Björk and Jiménez Barreto (2021) indicate that young travelers emphasize the promised quality of accommodations and the actual conditions. In view of the study of Chiang and Huang (2022), bathroom quality was the top hotel attribute that tourists were found to rate negatively among online reviews of Taipei’s economy hotel, reflecting the importance of room cleanliness to Taiwanese travelers.
Likewise, Del Chiappa, Pung and Atzeni’s study (2022) indicates that accommodation first key factor is sanitization and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) after Covid-19. The findings of Ye et al. (2022) are similar to our findings on the preferences of domestic tourists for four accommodation attributes (i.e., economy, convenience, familiarity, and coziness) after the COVID-19 pandemic. In addition, the respondents in the present study indicated that they preferred accommodations that were located close to scenic areas and had convenient transportation options because of their limited travel budget and lack of a car. Our results also indicated that the respondents strongly preferred self-catering facilities and that service staff did not significantly influence their choice of domestic accommodation.
A notable finding of the present study is that social interactions with hosts or other guests were the least important attribute for domestic young tourists when selecting accommodations These findings contradict those of other studies on Airbnb accommodations or on young international travelers (e.g., Guttentag, 2015; Tussyadiah & Pesonen, 2016). However, our finding is similar to that of Ye et al. (2022); that is, social interactions are not a key factor influencing the P2P accommodation choices of consumers. Moreover, our findings echo those of Santos et al. (2022), who report that Airbnb users are the least concerned about experiencing local culture, interacting with other guests, and living like a local. These findings suggest that domestic travelers are not focused on make new friends because most of them have travel companions and do not feel the need to meet new people. In summary, the considerations for selecting domestic accommodations may differ from those for selecting overseas accommodations. Because youth are highly familiar with their local environment, they may place more emphasis on the quality of basic lodging services when they are traveling domestically. Therefore, lodging managers should improve service efficiency, quality, and performance. To this end, understanding the service attributes prioritized by travelers may help these managers to develop plans for improvements and to identify areas requiring improvement. These adjustments can also improve their overall organizational efficiency.
With young travelers turning to domestic tourism during the post-COVID 19 era, precise techniques and effective positioning strategies can be applied to adapt to the dynamic and competitive accommodation market. Various scholars have discussed the application of artificial intelligence (AI) to hotel operation and management (e.g., Lukanova & Ilieva, 2019). This research trend aligns with the considerable development of AI technology, which has led to the development of robot-run hotels that provide the advantages of high efficiency, low labor cost and novelty. Zhang and Qi (2019) discover that the factors associated with education, attitude and income level strongly influenced the intention of travelers to stay in robot-run hotels. Young travelers may derive the most enjoyment from automated services in hotels and may acquire positive experiences during the consumption process.
The present study differs from previous studies in that it employed RIDIT analysis to identify the attributes prioritized by young tourists with respect to their accommodation choices, what might be important for guests and what certain guests perceive as important. Our findings clarify how RIDIT analysis can be applied to study opinions and preferences of prospective tourists, which are useful to hoteliers, as providing clear indications on how to improve certain quality aspects to meet guests’ requirements. A major advantage of RIDIT analysis is that it can measure the importance of attribute items on a Likert scale without the need for assuming a specific distribution (usually a normal distribution) and can test whether data points conform to a distribution assumption. Another advantage of RIDIT analysis is that it allows researchers to conduct hypothesis testing based on Kruskall-Wallis test. Therefore, researchers can apply RIDIT analysis to identify the rank-wise positions of the preferences of tourists whenever required.
A major limitation of the present study is that the findings cannot be generalized because the study sample pertains to a specific geographical area. Future studies should confirm our findings through other samples and expand the geographical scope of their research to achieve more comprehensive conclusions. A second limitation is that the factors identified in the present study were not have been classified by accommodation type, and that several crucial factors may have been neglected because of infrastructural restrictions. Future studies should conduct more extensive literature reviews to identify other key factors of service attributes that significantly influence accommodation choices. Another limitation pertains to the sample domain selected for the present study. Future studies should explore other significant factor and identify their influence among other youth segments with varying socio-economic and demographic characteristics.
Author Contributions
Chin-Pei Li, writing-original draft, investigation, and data curation; Chaang-Iuan Ho, conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition and writing-reviewing and editing; Shu-Han Huang, software, validation, and formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Disclosure statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Science and Technology Council, Taiwan, R.O.C. (Grant No. MOST 109-2410-H-324-008).
Data Availability Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Exploring the Key Attributes Influencing University Students’ Domestic Accommodation Choice
A RIDIT analysis.
References
- Alsawafi, A. M. & Almuhrzi, H. (2022). The college student travel market: exploring the key factors influencing higher education Arab students’ travel decisions. International Journal of Leisure and Tourism Marketing, 7(3), 235-250. [CrossRef]
- Amaro, S., Andreu, L., & Huang, S. (2019). Millennials’ intentions to book on Airbnb, Current Issues in Tourism, 22(18), 2284-2298. [CrossRef]
- Amat-Lefort, N., Marimon, F. & Mas-Machuca, M. (2023) Guest and host perspectives of service quality and satisfaction in digital home-sharing platforms. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 24(6), 859-884. [CrossRef]
- Avdimiotis, S., & Poulaki, I. (2019). Airbnb impact and regulation issues through destination life cycle concept. International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research, 13(4), 458-472. [CrossRef]
- Balińska, A. & Olejniczak, W. (2021). Experiences of Polish tourists traveling for leisure purposes during the COVID-19 pandemic. Sustainability, 13(21), 11919. [CrossRef]
- Belarmino, A., Whalen, E., Koh, Y., & Bowen, J. T. (2017). Comparing guests’ key attributes of peer-to-peer accommodations and hotels: Mixed-methods approach. Current Issues in Tourism, 22(1), 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S. & Kumar, R. V. (2017). Modeling tourists’ opinions using RIDIT analysis. In P. Vasant and Kalaivanthan, M. (Eds.), Handbook of research on holistic optimization techniques in the hospitality, tourism, and travel industry. Hershey, PA: IGI Global, Business Science Reference.
- Bialski, P. (2011). Technologies of hospitality: How planned encounters develop between strangers. Hospitality & Society, 1(3), 245-260. [CrossRef]
- Bicikova, K. (2014). Understanding student travel behavior: A segmentation analysis of British university students. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 31(7), 854-867. [CrossRef]
- Bolton, R. N., Parasuraman, A., Hoefnagels, A., Migchels, N., Kabadayi, S., Gruber, T., Komarova, Y., Solnet, D., & Aksoy, L. (2013). Understanding Generation Y and their use of social media: A review and research agenda. Journal of Service Management, 24(3), 245–267. [CrossRef]
- Brochado, A., Rita, P., & Gameiro, C. (2015). Exploring backpackers’ perceptions of the hostel service quality. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 27(8), 1839-1855. [CrossRef]
- Bross, I. D. J. (1958) How to use Ridit analysis. Biometrics, 14, 18-37.
- Bui, H. T., Wilkins, H. C., & Lee, Y.-S. (2013). The social identities of Japanese backpackers. Tourism, Culture & Communication, 13(3),147-159. [CrossRef]
- Carracedo, P., Puertas, R., & Marti, L. (2021). Research lines on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on business. A text mining analysis. Journal of Business Research, 132, 586–593. [CrossRef]
- Cavagnaro, E. & Staffieri, S. (2015). A study of students’ travellers values and needs in order to establish futures patterns and insights. Journal of Tourism Futures, 1(2), 94-107. [CrossRef]
- Chansuk, C., Arreeras, T., Chiangboon, C., Phonmakham, K., Chotikool, N., Buddee, R., Pumjampa, S., Yanasoi, T., & Arreeras, S. (2022). Using factor analyses to understand the post-pandemic travel behavior in domestic tourism through a questionnaire survey. Transportation Research Interdisciplinary Perspectives, 16, 100691. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. L. (2015). Impact of B&B atmosphere, customer experience, and customer value on customer voluntary performance: A survey in Taiwan. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 20(5), 541–562. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L. C., Lin S. P., & Kuo, C. M. (2013). Rural tourism: Marketing strategies for the bed and breakfast industry in Taiwan. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 32, 278-286. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M. (2016). Sharing economy: A review and agenda for future research. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 57, 60-70. [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.-F. & Huang, C.-W. (2022). Online reviews on online travel agency: Understanding tourists’ perceived attributes of Taipei’s economy hotels. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 23(4), 945-959. [CrossRef]
- Chu, R. K., & Choi, T. (2000). An importance-performance analysis of hotel selection factors in the Hong Kong hotel industry: A comparison of business and leisure travellers. Tourism Management, 21(4), 363-377. [CrossRef]
- Clason, D. L., & Dormody, T. J. (1994). Analyzing data measured by individual Liker-type items. Journal of Agriculturale Education, 35(4), 31-35. [CrossRef]
- Dayour, F., Kimbu, A. N., & Park, S. (2017). Backpackers: The need for reconceptualization. Annals of Tourism Research, 66, 191-193. [CrossRef]
- Del Chiappa, G., Pung, J. M. & Atzeni, M. (2022). Factors influencing choice of accommodation during Covid-19: A mixed-methods study of Italian consumers. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 23(4), 1037-1063. [CrossRef]
- Dilek, S. E., & Fennell, D. A. (2018). Discovering the hotel selection factors of vegetarians: The case of Turkey. Tourism Review, 73(4), 492–506. [CrossRef]
- Fan, A., Shin, H. W., Shi, J., & Wu, L. (2023). Young people share, but do so differently: An empirical comparison of peer-to-peer accommodation consumption between Millennials and Generation Z. Cornell Hospitality Quarterly, 64(3), 322-337. [CrossRef]
- Farmaki, A. & Stergiou, D. P. (2019). Escaping loneliness through Airbnb host-guest interactions. Tourism Management, 74, 331-333. [CrossRef]
- Fleiss, J. L., Levin, B., & Paik, M. C. (2013). Statistical inference for a single proportion. New York, USA: John Wiley & Sons. https://www.scirp.org/(S(czeh2tfqyw2orz553k1w0r45))/reference/ReferencesPapers. aspx?ReferenceID=2119421.
- Frost, F., & Shanka, T. (1999). Asian Australian student travel preferences: An empirical study. Asian Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 4(2), 19-26. [CrossRef]
- Gassmann, S.-E., Nunkoo, R., Tiberius, V., & Kraus, S. (2021). My home is your castle: forecasting the future of accommodation sharing. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 33(2), 467-489. [CrossRef]
- Guttentag, D. (2015). Airbnb: Disruptive innovation and the rise of an informal tourism accommodation sector. Current Issues in Tourism, 18(12), 1192-1217. [CrossRef]
- Heung, V. C. S. & Leong, J. S. L. (2006). Travel demand and behavior of university students in Hong Kong. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 11(1), 81-96. [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.-I., Lin, P.-Y., & Huang, S.-C. (2014). Exploring Taiwanses working holiday markers' motivations: An analysis of Means-End hierarchies. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 38(4), 463-486.
- Huang, D., Liu, X., Lai, D., & Li, Z. (2019). Users and non-users of P2P accommodation differences in perceived risks and behavioral intentions. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology, 10(3), 369-382. [CrossRef]
- Jansen, M. E. (1984). Ridit analysis, a review. Statistica Neerlandica, 8(3), 141–158.
- Johnson, A. G., & Neuhofer, B. (2017). Airbnb - an exploration of value co-creation experiences in Jamaica. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(9), 2361-2376. [CrossRef]
- Jun, S.-H. (2020). The effects of perceived risk, brand credibility and past experience on purchase intention in the Airbnb context. Sustainability, 12, 5212. [CrossRef]
- Keeley, P. (2001). The backpacker market in Britain. Insight, 12, B53–66.
- Kim, B. & Kim, D. (2020). Attracted to or locked in? Explaining consumer loyalty toward Airbnb. Sustainability, 12, 2814. [CrossRef]
- Kusumaningrum, D. A. & Wachyuni, S. S. (2020). The shifting trends in travelling after the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Tourism & Hospitality Review, 7(2), 31-40. [CrossRef]
- Li, J., Nguyen, T. H. H., & Coca-Stefaniak, J. A. (2021). Understanding post-pandemic travel behaviours – China’s Golden Week. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 49, 84–88. [CrossRef]
- Lockyer, T. (2005). The perceived importance of price as one hotel selection dimension. Tourism Management, 26 (4), 529-537. [CrossRef]
- Longwoods International. (2020). COVID-19 Travel Sentiment Study-Wave 7. Retrieved 6 October 2022 from https://longwoods-intl.com/news-press-release/covid-19-travel-sentiment-study-wave-7.
- Lukanova, G., & Ilieva, G. (2019). Robots, artificial intelligence, and service automation in hotels. In Ivanov, S. and Webster, C. (Ed.) Robots, Artificial Intelligence, and Service Automation in Travel, Tourism and Hospitality, Emerald Publishing Limited, Bingley, pp. 157-183.
- McIntosh, A. J., & Siggs, A. (2005). An exploration of the experiential nature of boutique accommodation. Journal of Travel Research, 44(1), 74-81. [CrossRef]
- Moisă, C. O. (2010). Aspects of the youth travel demand. Annales Universitatis Apulensis Series Oeconomica, 12(2), 575-582.
- Mody, M. A., Suess, C., & Lehto, X. (2017). The accommodation experience scape: A comparative assessment of hotels and Airbnb. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(9), 2377-2404.
- Mohsin, A. & Lengler, J. (2021). Airbnb hospitality: Exploring users and non-users’ perceptions and intentions. Sustainability, 13, 10884. [CrossRef]
- Nagai, H., Benckendorff, P., & Tkaczynski, A. (2018). Differentiating Asian working holiday makers from traditional backpackers on the basis of accommodation preferences. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 35, 66-74. [CrossRef]
- Nash, R., Thyne, M., & Davies, S. (2006). An investigation into customer satisfaction levels in the budget accommodation sector in Scotland: A case study of backpacker tourists and the Scottish Youth Hostels Association. Tourism Management, 27, 525-532. [CrossRef]
- Olszewski-Strzyzowski, D. J., Pasek, M., & Lipowski, M. (2022). Perspectives for tourism development in the post-pandemic period in the opinions of university students. Sustainability, 14, 16833. [CrossRef]
- Pearce, P. & Son, A. (2004) Youth tourism markets in Australia: comparing the travel behaviours of international English language students and backpackers. Tourism (Zagreb), 52(4), 341–350.
- Poon, K. Y., & Huang, W.-J. (2017). Past experience, traveler personality and tripographics on intention to use Airbnb. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 29(9), 2425-2443. [CrossRef]
- Pouplard, N., Qannari, E. M. & Simon, S. (1997). Use of ridits to analyse categorical data in preference studies. Food Quality and Preference, 8(5/6), 419-422. [CrossRef]
- Prayag, G & Ozanne, L.K. (2018). A systematic review of peer-to-peer (P2P) accommodation sharing research from 2010 to 2016: Progress and prospects from the multi-level perspective. Journal of Hospitality Marketing & Management, 27(6), 649-678. [CrossRef]
- Reisinger, Y., & Mavondo, F. (2002). Determinants of youth travel markets’ perceptions of tourism destinations. Tourism Analysis, 7, 55-66. [CrossRef]
- Rhee, H. T., & Yang, S. B. (2015). How does hotel attribute importance vary among different travelers? An exploratory case study based on a conjoint analysis. Electronic Markets, 25(3), 211–226. [CrossRef]
- Richards, G. (2011). An economic contribution that matters. In WYSE Travel Confederation/UNWTO (2011) The Power of Youth Travel, pp. 7-8.
- Santos, A. I. G. P., Perinotto, A. R. C., Soares, J. R. R., & Mondo, T. S. (2022). Feeling at home while traveling: An analysis of the experiences of Airbnb users. Tourism and Hospitality Management, 28(1), 167-192. [CrossRef]
- Seekings, J. (1998). The youth travel market. Travel and Tourism Analyst, 5, 37–55.
- Shanka, T. & Taylor, R. (2004). An investigation into the perceived importance of service and facility attributes to hotel satisfaction. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 4(3/4), 119-134. [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.-I., Alakshendra, A., Kim, H.-J., Kim, K.-H., & Kim, H.-D. (2021). Understanding the new characteristics and development strategies of coastal tourism for post-COVID-19: A case study in Korea. Sustainability, 13(13), 7408. [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, B., Vanani, I. R., Tahmasebipur, K., & Fazli, S. (2012). An exploratory analysis of hotel selection factors: A comprehensive survey of Tehran hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 31(1), 96-106. [CrossRef]
- Somlai, R. (2015). The influence of ratings on choosing accommodation. Sociology Study, 5(4), 282-290. [CrossRef]
- Spoerr, D. (2021). Factor analysis of hotel selection attributes and their significance for different groups of German leisure travelers. Journal of Quality Assurance in Hospitality & Tourism, 22(3), 312-335. [CrossRef]
- Sthapit, E., Björk, P., & Jiménez Barreto, J. (2021). Negative memorable experience: North American and British Airbnb guests’ perspectives. Tourism Review, 76(3), 639-653. [CrossRef]
- Stringer, P. F. (1981). Hosts and guests the bed-and-breakfast phenomenon. Annals of Tourism Research, 8(3), 357-376. [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y., Richardson, S., Lester, L., Bai, T., & Sun, L. (2009). Evaluation of Australia' s working holiday maker (WHM) program. Adelaide, Australia: National Institute of Labour Studies, Flinders University.
- Țicău, I. R. & Shahrazad, H. (2022). Changes in post-pandemic travelling behaviour. What are the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on students’ travelling interest? Cactus Tourism Journal, 4(1), 27-41.
- Tussyadiah, L. P., & Pesonen, J. (2016). Impacts of peer-to-peer accommodation use on travel patterns. Journal of Travel Research, 55(8), 1022-1040. [CrossRef]
- Tussyadiah, L. P., & Zach, F. (2017). Identifying salient attributes of peer-to-peer accommodation experience. Journal of Travel & Tourism Marketing, 34(5), 636-652.
- Uysal, D. (2022). Gen-Z’s consumption behaviours in post-pandemic tourism sector. TOLEHO, 4(1), 70-82.
- Varma, A., Jukic, N., Pestek, A., Shultz, C. J., & Nestorov, S. (2016). Airbnb: Exciting innovation or passing fad? Tourism Management Perspectives, 20, 228-237.
- Wang, Y. (2007). Customized authenticity begins at home. Annals of Tourism Research, 34(3), 789-804. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D., & Nicolau, J. L. (2017). Price determinants of sharing economy based accommodation rental: A study of listings from 33 cities on Airbnb.com. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 62, 120-131. [CrossRef]
- Wilkins, H., Merrilees, B., & Herington, C. (2007). Towards an understanding of total service quality in hotels. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 26(4), 840-853. [CrossRef]
- World Tourism Organization (2020). Understanding domestic tourism and seizing its opportunities. UNWTO briefing note – Tourism and COVID-19, issue 3. Understanding domestic tourism and seizing its opportunities. 10 (18111/ 9789284422111).
- Wu, C. H. (2007). On the application of grey relational analysis and RIDIT analysis to Likert scale surveys. International Mathematical Forum, 2(14), 675-687. [CrossRef]
- Ye, S., Lei, S. L., Zhao, X., & Law, R. (2023). Modeling tourists’ preference between hotels and peer-to-peer (P2P) sharing accommodation: a pre- and post-COVID-19 comparison. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 35(4), 1423-1447. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H., So, K. K. F, & Wang, Y. (2015). The university student travel market: Motivations and preferences for activities. Tourism Analysis, 20(4), 399-412. [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. (2023). Post-epidemic situation and suggestions for college students' tourism—Taking Guiyang City as an example. Tourism Management and Technology Economy, 6(6), 63-69. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y., & Qi, S. (2019). User experience study: The service expectation of hotel guests to the utilization of AI-based service robot in full-service hotels. In: Nah, F. F. H. and Siau, K. (eds) HCI in Business, Government and Organizations. eCommerce and Consumer Behavior. HCII 2019. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 11588. Springer, Cham.
Table 1.
Respondent profiles for travel and accommodation characteristics (N=296).
Table 1.
Respondent profiles for travel and accommodation characteristics (N=296).
| Variables |
% |
Variables |
% |
| Gender |
|
Accommodation choice for the recent trip |
| Male |
32.1% |
Hotel |
33.8% |
| Female |
67.9% |
B & B |
31.4% |
| Most recent trip1 |
Airbnb |
3% |
| 0.5 months or less |
40.9% |
Living in relative/friend’s home |
6.1% |
| 0.5-1 month |
13.5% |
No accommodation |
25.7% |
| 1-3 months |
16.6% |
Traveling companions for the recent trip |
| 3-6 months |
12.8% |
Alone |
1.7% |
| 6 months or more |
15.5% |
Family members |
34.5% |
| Number of days in the recent trip2 |
Relatives/Friends |
53.5% |
| 2-days-1-night |
35.5% |
Classmates |
6.1% |
| 3-days-2-night |
27.4% |
Others |
4.1% |
| 4-days-3-night |
5.7% |
Type of travel3 |
|
| 5 days or more |
3% |
Self-independent |
89.8% |
| 1-day |
28% |
Package by travel agency |
1.7% |
| Accommodation experiences |
Arrangement by travel agent |
2.0% |
| Hotel |
90.5% |
Incentive travel |
6.1% |
| B & B |
89.9% |
|
|
| Airbnb |
11.8% |
|
|
Table 2.
Calculation of the RIDIT values for the service attributes of accommodation choice with respect to their importance and prioritization.
Table 2.
Calculation of the RIDIT values for the service attributes of accommodation choice with respect to their importance and prioritization.
| |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
ρi |
Lower bound |
Upper
bound |
Priority ranking |
| Cleanliness of rooms (1) |
0 |
0 |
0.005 |
0.057 |
0.685 |
0.748 |
0.714 |
0.781 |
1 |
| Located in a safe neighborhood/feeling safe in the room (2) |
0 |
0 |
0.011 |
0.098 |
0.583 |
0.692 |
0.659 |
0.726 |
2 |
| Close to scenic area for meeting the trip requirements (3) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.014 |
0.183 |
0.413 |
0.611 |
0.577 |
0.644 |
3 |
| Providing self-catering facilities with good levels of comfort & amenities (4) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.019 |
0.180 |
0.399 |
0.598 |
0.565 |
0.632 |
4 |
| Security of payment (5) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.027 |
0.135 |
0.435 |
0.598 |
0.564 |
0.632 |
5 |
| The value derived for money spent (6) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.021 |
0.172 |
0.399 |
0.593 |
0.560 |
0.627 |
6 |
| Convenient transportation (7) |
0 |
0.002 |
0.021 |
0.158 |
0.391 |
0.572 |
0.538 |
0.605 |
7 |
| Guests’ word-of-mouth & recommendation (8) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.022 |
0.191 |
0.349 |
0.564 |
0.530 |
0.598 |
8 |
| Service staff friendly & polite (9) |
0 |
0.001 |
0.019 |
0.219 |
0.325 |
0.563 |
0.530 |
0.597 |
9 |
| Having specific architecture or appealing decorative design (10) |
0 |
0.002 |
0.045 |
0.197 |
0.231 |
0.475 |
0.442 |
0.509 |
10 |
| Having single/double/twin accommodation available (11) |
0 |
0.003 |
0.042 |
0.194 |
0.234 |
0.472 |
0.438 |
0.506 |
11 |
| Provision of a comfortable ambiance (12) |
0 |
0.002 |
0.047 |
0.186 |
0.231 |
0.467 |
0.433 |
0.500 |
12 |
| Provision of meals (13) |
0 |
0.002 |
0.050 |
0.212 |
0.176 |
0.440 |
0.406 |
0.473 |
13 |
| Close to site or event attractions (14) |
0 |
0.003 |
0.060 |
0.169 |
0.198 |
0.430 |
0.396 |
0.463 |
14 |
| Unique accommodation experiences (15) |
0 |
0.003 |
0.067 |
0.152 |
0.184 |
0.407 |
0.373 |
0.440 |
15 |
| Interaction with B & B host or landlord (16) |
0 |
0.007 |
0.074 |
0.136 |
0.107 |
0.325 |
0.291 |
0.359 |
16 |
| Provision of a local trip (17) |
0 |
0.010 |
0.081 |
0.109 |
0.063 |
0.263 |
0.230 |
0.297 |
17 |
| Interaction with other guests (18) |
0.001 |
0.015 |
0.068 |
0.064 |
0.036 |
0.183 |
0.150 |
0.217 |
18 |
Table 3.
Comparison of traditional means and RIDITs for service attributes.
Table 3.
Comparison of traditional means and RIDITs for service attributes.
| Attributes |
Mean |
SD |
RIDITs |
| |
|
| (1) |
3.828 |
.864 |
0.748 |
| (2) |
4.247 |
.748 |
0.692 |
| (3) |
3.696 |
.929 |
0.611 |
| (4) |
4.392 |
.719 |
0.598 |
| (5) |
3.784 |
.902 |
0.598 |
| (6) |
4.334 |
.759 |
0.593 |
| (7) |
4.236 |
.806 |
0.572 |
| (8) |
3.372 |
.959 |
0.564 |
| (9) |
3.922 |
.904 |
0.563 |
| (10) |
4.797 |
.527 |
0.475 |
| (11) |
4.351 |
.744 |
0.472 |
| (12) |
3.916 |
.877 |
0.467 |
| (13) |
4.628 |
.672 |
0.440 |
| (14) |
4.334 |
.827 |
0.430 |
| (15) |
3.956 |
.833 |
0.407 |
| (16) |
3.105 |
.956 |
0.325 |
| (17) |
2.642 |
1.022 |
0.263 |
| (18) |
4.226 |
.931 |
0.183 |
Table 4.
Factor analysis of the service attributes for the respondents’ accommodation choice.
Table 4.
Factor analysis of the service attributes for the respondents’ accommodation choice.
| Attributes |
Factors & the related loadings |
Mean |
SD |
| |
F1 |
F2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
| (9) |
.796 |
|
|
|
|
3.922 |
.904 |
| (15) |
.752 |
|
|
|
|
3.956 |
.833 |
| (12) |
.738 |
|
|
|
|
3.916 |
.877 |
| (11) |
.697 |
|
|
|
|
4.351 |
.744 |
| (17) |
|
.810 |
|
|
|
2.642 |
1.022 |
| (8) |
|
.761 |
|
|
|
3.372 |
.959 |
| (16) |
|
.709 |
|
|
|
3.105 |
.956 |
| (3) |
|
.518 |
|
|
|
3.696 |
.929 |
| (1) |
|
|
.738 |
|
|
3.828 |
.864 |
| (2) |
|
|
.662 |
|
|
4.247 |
.748 |
| (5) |
|
|
|
.782 |
|
3.784 |
.902 |
| (4) |
|
|
|
.768 |
|
4.392 |
.719 |
| (18) |
|
|
|
.617 |
|
4.226 |
.931 |
| (7) |
|
|
|
|
.711 |
4.236 |
.806 |
| (13) |
|
|
|
|
.652 |
4.628 |
.672 |
| (14) |
|
|
|
|
.631 |
4.334 |
.827 |
| (10) |
|
|
|
|
.620 |
4.797 |
.527 |
| (6) |
|
|
|
|
.600 |
4.334 |
.759 |
| Eigen values |
5.169 |
2.043 |
1.172 |
1.123 |
1.025 |
|
|
| Cronbach’s α |
0.754 |
0.720 |
0.514 |
0.613 |
0.697 |
|
|
| Variance explained (%) |
28.719 |
11.348 |
6.512 |
6.239 |
5.693 |
|
|
| Accumulated variance explained (%) |
28.719 |
40.067 |
46.579 |
52.818 |
58.511 |
|
|
| KMO |
0.845 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).