Submitted:
31 May 2024
Posted:
03 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
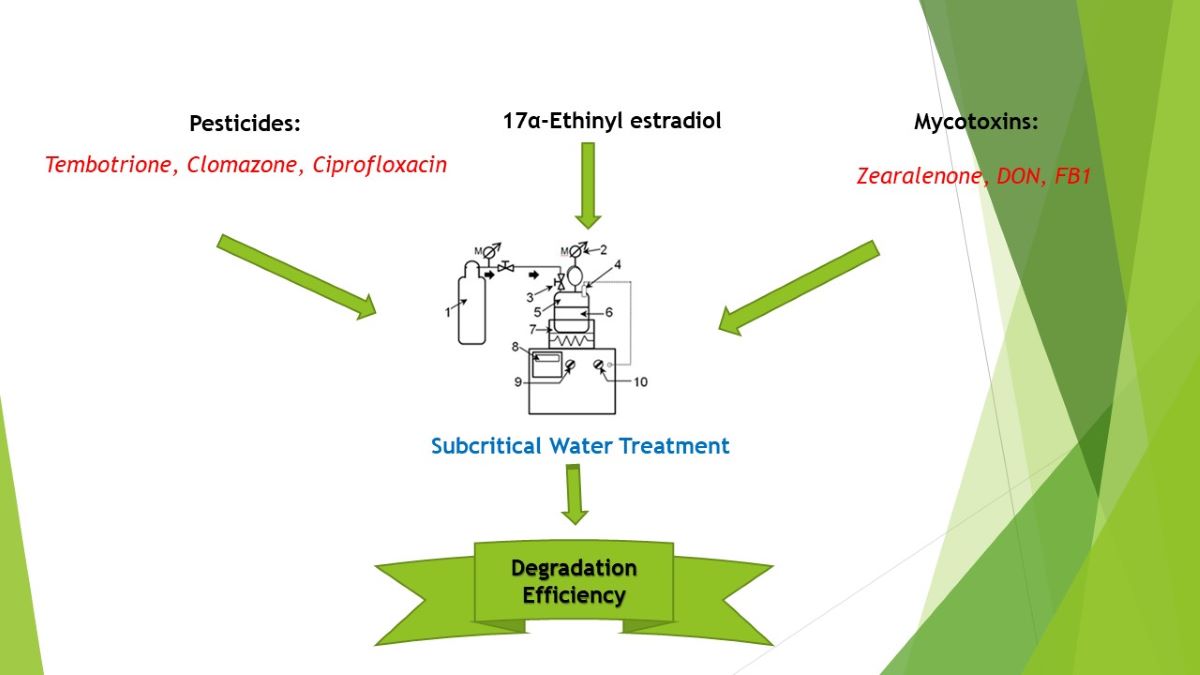
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
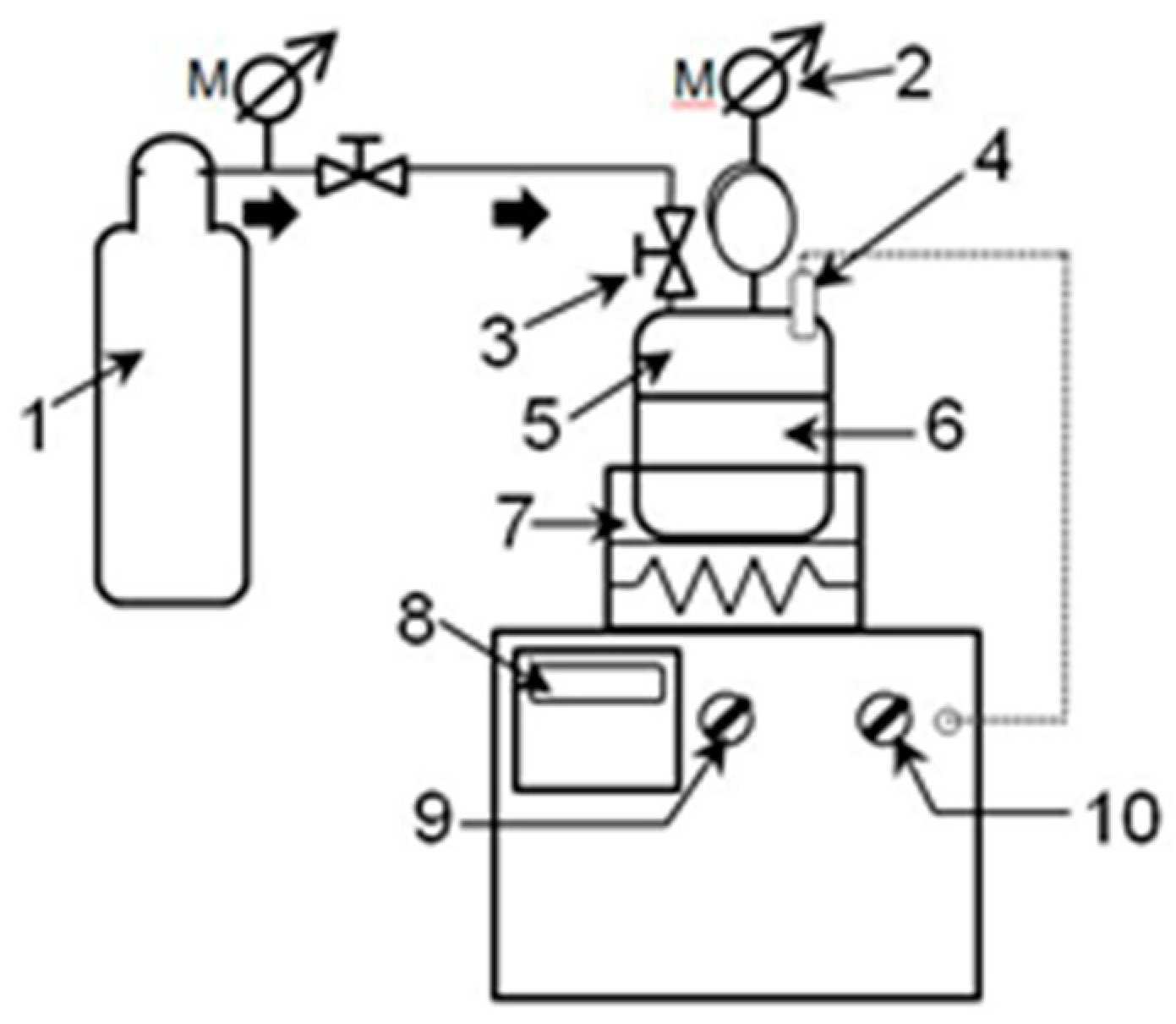
2.2. Subcritical water treatment
2.3. HPLC Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
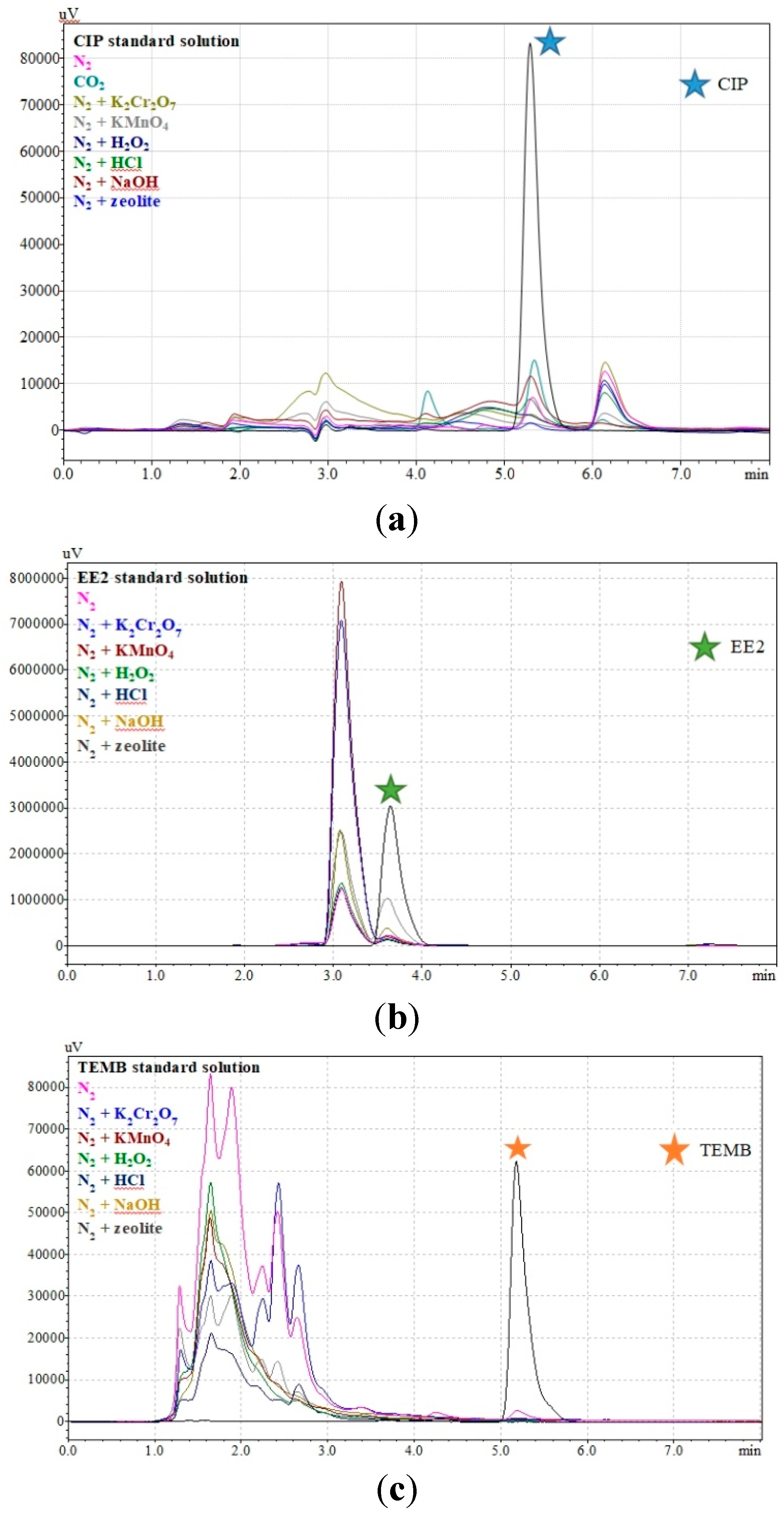
3.1. Decomposition of Herbicides and Pharmaceuticals in Subcritical Water
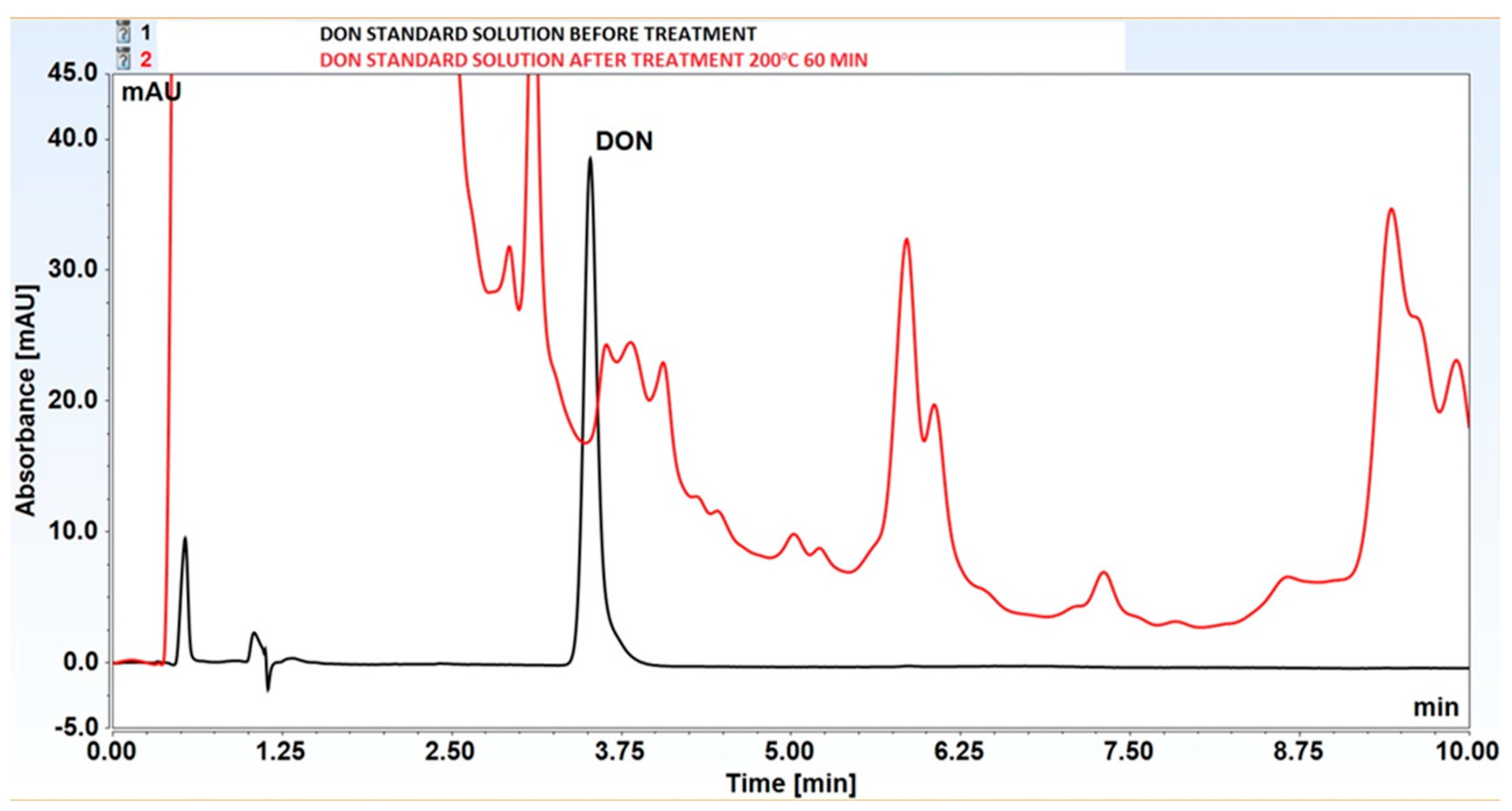
3.2. Decomposition of Selected Mycotoxins in Subcritical Water
4. Conclusions
CRedit Authorship Contribution Statement
Funding
Acknowledgments
Declaration of competing Interest
References
- Peters, R.W. Chelant extraction of heavy metals from contaminated soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 1999, 66(1-2), 151-210. [CrossRef]
- Soares, A. A.; Albergaria, J. T.; Fernandes Domingues, V.; da Conceição, M.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.; Delerue-Matos, C. Remediation of soils combining soil vapor extraction and bioremediation: benzene, Chemosphere, 2010, 80(8), 823-828 . [CrossRef]
- Švarc-Gajić, J. Remediation of environmental contamination by subcritical and supercritical water. In Environmental Remediation for Agri-Food Industry Using Nanotechnology and Sustainable Strategies. Putnik, P.; Šojić Merkulov D., Eds. Elsevier, 2024.ISBN: 9780443132988.
- Švarc-Gajić, J. Sampling and Sample Preparation in Analytical Chemistry. Nova Science Publishers, New York. 2011.
- Nazrul Islam, M.; Young-Tae, J.; Park, J.H. Remediation of PAHs contaminated soil by extraction using subcritical water, J. Ind. Engin. Chem. 2012, 18(5), 1689-1693 . [CrossRef]
- Chang, M. S.; J.; Shen, Y.; Yang, S. H.; Wu, G. J. Subcritical water extraction for the remediation of phthalate ester-contaminated soil, J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192(3), 1203-1209 . [CrossRef]
- Nazrul Islam, M.; Young-Tae, J.; Sun-Kook, J.; Park, J. H. Evaluation of subcritical water Extraction process for remediation of pesticide-contaminated soil. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2013, 224, 1652. [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, S.; Watanabe, K.; Nose, Morita, M. Remediation of soil contaminated with dioxins by subcritical water extraction. Chemosphere 2004, 54(1), 89-96. [CrossRef]
- Scheitlin, C. G.; Dasu, K.; Rosansky, S.; Espina Dejarme, L.; Siriwardena, D.; Thorn, J.; Mullins, L.; Haggerty, I.; Shqau, K.; Stowe, J. Application of supercritical water oxidation to effectively destroy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aqueous matrices. ACS EST Water 2023, 3(8), 2053–2062.
- Tavlarides, L. L.; Zhou, W.; Anitescu G. Supercritical fluid technology for remediation of pcb/pah-contaminated soils/sediments. Proceedings of the 2000 Conference on Hazardous Waste Research.
- Albahnasawi. A. Supercritical water oxidation: a breakthrough approach for remediation TNT-contaminated pink water, Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization, and Environmental Effects, 2023, 45(3), 9283-9296. [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Chen, Z.; Chu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Gao, T.; Duan, T.; Wang, M. Degradation, adsorption, and bioaccumulation of novel triketone HPPD herbicide tembotrione, Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2023, 30(28),72389-72397. [CrossRef]
- Rani, N.; Duhan, A.; Tomar, D.; Ultimate fate of herbicide tembotrione and its metabolite TCMBA in soil, Ecotoxicol. Environ. Safety 2020, 203, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wen, S.; Shi, T.; Li, W. X.; Pei, L.; Hua, R. Photocatalysis of the triketone herbicide tembotrione in water with bismuth oxychloride nanoplates: Reactive species, kinetics and pathways, J. Environ. Chem. Engin. 2022, 10(5), . [CrossRef]
- Van Scoy, A. R.; Tjeerdema, R. S. Environmental fate and toxicology of clomazone. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2014, 229, 35-49. [CrossRef]
- Tomco, P. L.; Holstege, D. M.; Zou, W.; Tjeerdema, R. S. Microbial degradation of clomazone under simulated California rice field conditions, J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58(6), 3674-80. https://doi: 10.1021/jf903957j. PMID: 20178392.
- Abramović, B. F.; Despotović, V. N.; Šojić, D.V.; Orčić, D. Z.; Csanádi, J.J.; Četojević-Simin, D. D. Photocatalytic degradation of the herbicide clomazone in natural water using TiO2: kinetics, mechanism, and toxicity of degradation products, Chemosphere, 2013, 93(1), 166-171 . [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.D.; Morehead, A.T.; Yang, Y. Degradation and extraction of organochlorine pollutants from environmental solids under subcritical water conditions, Molecules 2023, 28, 5445. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, J.; Zeng, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Xu, L.; Li, L. Complete degradation and detoxification of ciprofloxacin by a micro-/nanostructured biogenic Mn oxide composite from a highly active Mn2+ oxidizing Pseudomonas strain, Nanomaterials (Basel) 2021, 11(7), . [CrossRef]
- Borba, F. H.; Schmitz, A.; Pellenz, L.; Bueno, F.; Kasper, N.; Wenzel, B. M.; Baroni, S.; Dall’Oglio, I. C.; Módenes, A. N. Genotoxicity and by-products assessment in degradation and mineralization of ciprofloxacin by UV/H2O2 process, J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6(6), 6979-6988, . [CrossRef]
- Stavbar, S.; Knez Hrnčič, M.; Premzl, K.; Kolar, M.; Šostar Turk, S. Sub- and super-critical water oxidation of wastewater containing amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin, J. Supercrit. Fluids, 2017, 128, 73-78. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D. R.; Heid, M.R.; Ahmed, A. 17β-Estradiol and 17α-ethinyl estradiol exhibit immunologic and epigenetic regulatory effects in NZB/WF1 female mice, Endocrinology 2019, 160(1), 101-118, htps://doi: 10.1210/en.2018-00824.
- Nejedly, T.; Klimes, J. A model of natural degradation of 17-α-ethinylestradiol in surface water and identification of degradation products by GC-MS. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24(29), 23196-23206. [CrossRef]
- Reis, R.; Dhawle, R.; Du Pasquier, D.; Tindall, A. J.; Frontistis, Z.; Mantzavinos, D.; de Witte, P.; Cabooter, D. Electrochemical degradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol: Transformation products, degradation pathways and in vivo assessment of estrogenic activity, Environ. Inter. 2023, 176,. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. L.; Ravindran, S.; Swift, S.; Wright, L. J.; Singhal N. Catalytic oxidative degradation of 17α-ethinylestradiol by FeIII-TAML/H2O2: estrogenicities of the products of partial, and extensive oxidation. Water Res. 2012, 46(19), 6309-6318. [CrossRef]
- Mills, M.; Arias-Salazar, K.; Baynes, A.; Shen, L. Q.; Churchley, J.; Beresford N.; Gayathri, C.; Gil, R. R.; Kanda, R.; Jobling, S.; Collins, T. J. Removal of ecotoxicity of 17α-ethinylestradiol using TAML/peroxide water treatment, Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10511 . [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J. A.; Ma, Q.; Staveley, J. P.; Smolenski, J W. J.; Ericson J. Degradation and transformation of 17α-estradiol in water-sediment systems under controlled aerobic and anaerobic conditions, Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36(3), 621-629. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G. L.; Feng, J. Y. L.; Song, L.; Zhou, X. S. Zearalenone: A mycotoxin with different toxic effect in domestic and laboratory animals’ granulosa cells, Sec. Toxicogenomics 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.S. Mycotoxins, Toxicology. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Caballero, B.; Academic Press, 2023, pp. 4096-4108, ISBN 9780122270550, . [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lee, Y. W.; Jianhong Xu, I. S. Biodegradation of deoxynivalenol by a novel microbial consortium, Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, . [CrossRef]
- Borràs-Vallverdú, B.; Ramos, A. J.; Vicente Sanchis, S. M.; Rodríguez-Bencomo, J. J. Deoxynivalenol degradation in wheat kernels by exposition to ammonia vapours: A tentative strategy for detoxification, Food Control, 2020, 118, htps://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107444.
- Chao, S.; Jia, J.; Wub, S.; Sun, X. Saturated aqueous ozone degradation of deoxynivalenol and its application in contaminated grains, Food Control 2016, 69, htps://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.04.041.
- Krstović, S.; Krulj, J.; Jakšić, S.; Bočarov-Stančić, A.; Jajić, I. Ozone as decontaminating agent for ground corn containing deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, and ochratoxin, A. Cereal Chem. 2021, 98, 135-143. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, Y.; Liu L.; Chen, L. Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, C. Zearalenone degradation by dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma: The kinetics and mechanism., Foods. 2022, 11(10), 1494. https://doi: 10.3390/foods11101494.
- Gbashi, S., Madala, N. E., Adebo, O.A., Piater, L., Phoku, J. Z., Njobeh, P. B. Subcritical water extraction and its prospects for aflatoxins extraction in biological materials. In Aflatoxin-Control, Analysis, Detection and Health Risks. Bola Abdulra'uf L. (ed), 2017. http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.68706.
- Chen, J.; Wei, Z.; Wang, Y.; Long, M.; Wu, W.; Kuca, K. Fumonisin B1: mechanisms of toxicity and biological detoxification progress in animals, Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 149, . [CrossRef]
- Steyn, P. S. Mycotoxins in cereals. In ICC Handbook of 21st Century Cereal Science and Technology; Shewry, P.R.; Koksel H.; Taylor, J. R. N. Eds; Elsevier, 2023, pp 111-112. ISBN 978-0-323-95295-8. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, A,; Liu, N.; Chen, S.; Zhao, X.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Zhou, C.; Wang, J. Biodegradation of mycotoxin fumonisin B1 by a novel bacterial consortium SAAS79, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103,7129–7140. [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Hua, H.; Nimal Selvaraj, J.; Guiuan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Y. Degradation of fumonisin B1 by cinnamon essential oil, Food Control 2014, 38, 37-40, . [CrossRef]
- Jevtić, I.; Jakšić, S.; Četojević-Simin, D.; Uzelac, M.; Abramović, B. UV-induction of photolytic and photocatalytic degradation of fumonisins in water: reaction kinetics and toxicity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28(38), 53917-53925. [CrossRef]
- Švarc-Gajić, J.; Rodrigues, F.; Moreira, M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; Morais, S.; Doresh, O.; Silva, A.M.; Bassani, A.; Dzedik, V.; Spigno, G. Chemical composition and bioactivity of oilseed cake extracts obtained by subcritical and modified subcritical water. Bioresour. Bioproces. 2022 . [CrossRef]
- Švarc-Gajić, J.; Brezo-Borjan, T.; Gosselink, R. J. A.; Slaghek, T. M.; Šojić-Merkulov, D.; Ivetić, T.; Bognár, S.; Stojanović, Z. Optimization and potentials of Kraft lignin hydrolysates obtained by subcritical water at moderate temperatures, Processes 2022, 10, 2022, 2049. [CrossRef]
| Degradation efficiency (%) | ||||
| Conditions | TEMB | CLO | CIP | EE2 |
| N2 | 96.54±0.2* | 52.58±0.1 | 93.04±0.3 | 91.28±0.3 |
| CO2 | 100.00±0.2 | 61.17±0.1 | 81.98±0.3 | 70.96±0.2 |
| K2Cr2O7 | 99.67±0.1 | 19.62±0.7 | 100.00±0.1 | 97.74±0.3 |
| KMnO4 | 99.68±0.2 | 35.42±0.6 | 100.00±0.1 | 98.65±0.2 |
| H2O2 | 100.00±0.1 | 89.51±0.4 | 100.00±0.1 | 93.49±0.3 |
| HCl | 98.59±0.2 | 49.51±0.5 | 97.59±0.1 | 94.89±0.3 |
| NaOH | 100.00±0.1 | 51.92±0.5 | 94.53±0.3 | 87.18±0.2 |
| Zeolite | 98.50±0.2 | 38.95±0.6 | 98.96±0.2 | 62.89±0.3 |
| Degradation efficiency (%) | ||||
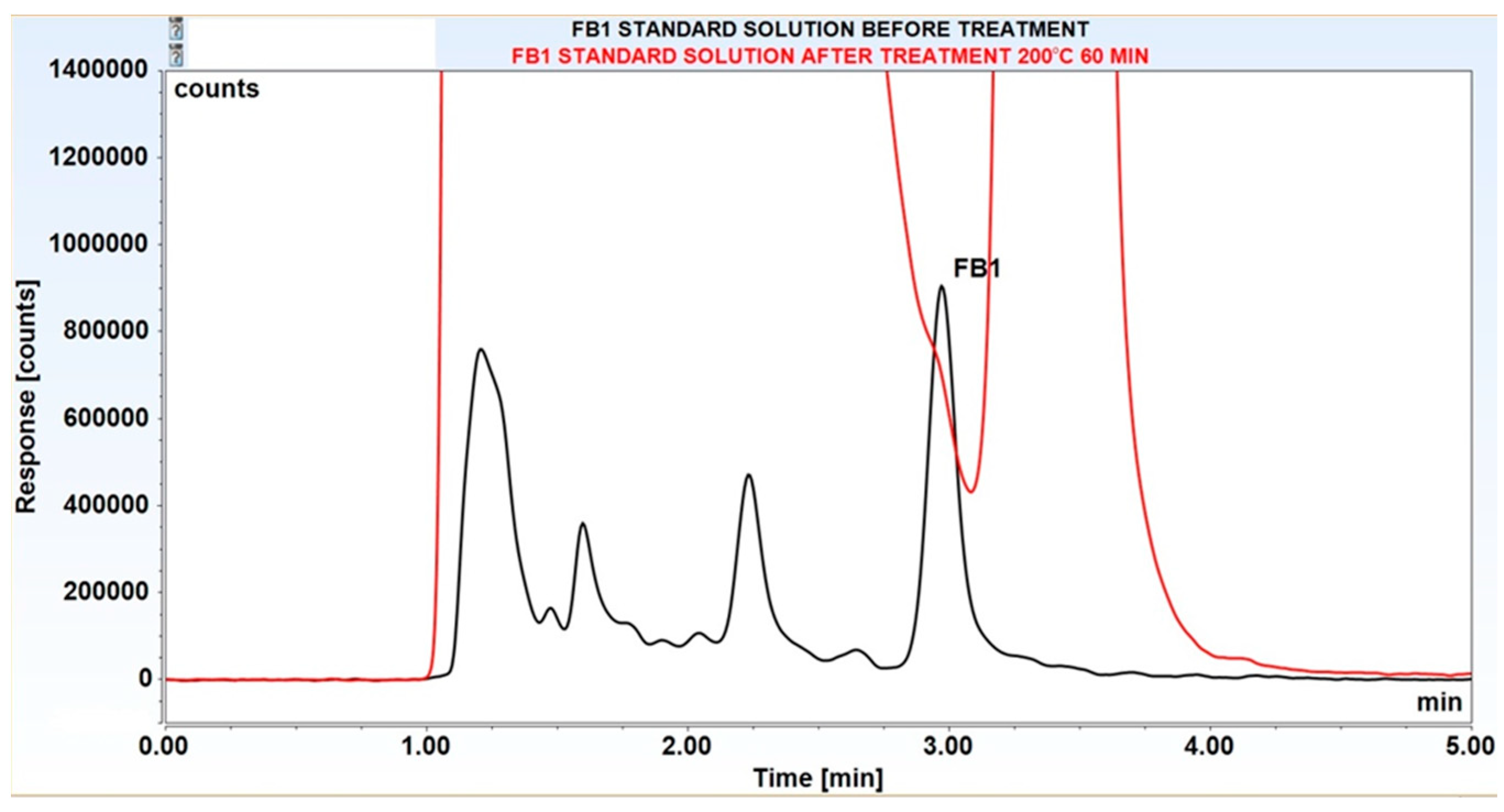
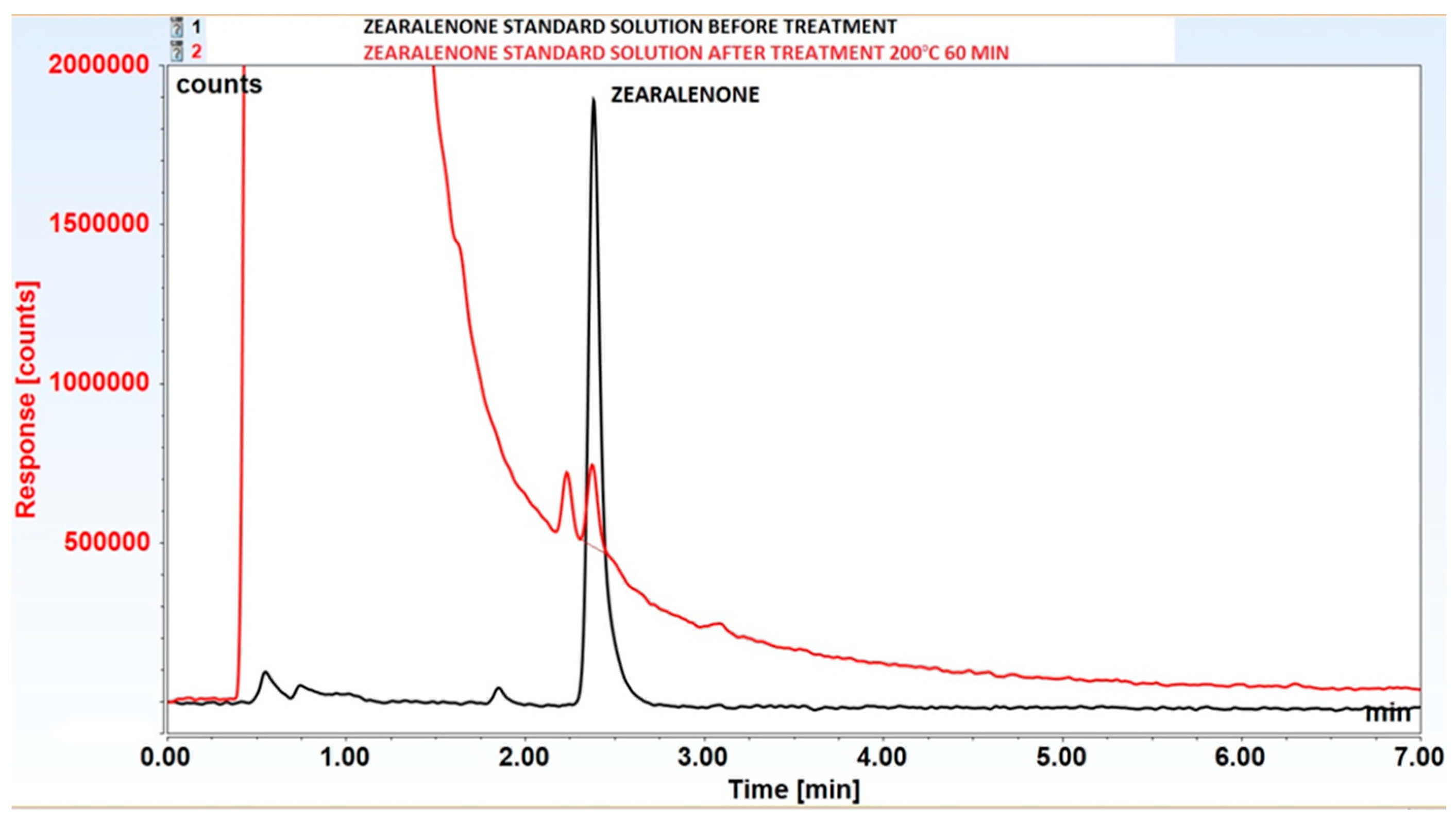
| Temperature (°C) | Time (min) | Zearalenone | DON | FB1 |
| 200°C | 60 | 90±0.5* | 100±0.1 | 100±0.2 |
| 200°C | 100 | 100±0.2 | n.a.** | n.a. |
| 230°C | 60 | 100±0.2 | n.a. | n.a. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





