Introduction
Thalassemia is a group of autosomal recessive inherited blood disorders. It can be divided into 2 forms, Alpha and Beta-thalassemia. The cause of the blood defects is gene mutations leading to low levels and/or malfunctioning/absence of the hemoglobin α and β globin proteins, respectively. [
1] Based on the varying degrees of severity, Beta thalassemia exists in 3 phenotypic forms: thalassemia major, thalassemia intermedia, and thalassemia minor. Individuals with thalassemia major, also known as transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia, usually present within the first two years of life with severe anemia requiring red blood cell transfusions regularly. The level of Hb might be <7 g/dl and Hb F < 90%. Individuals with untreated or poorly transfused thalassemia major usually present with growth retardation, pallor, jaundice, poor musculature, hepatosplenomegaly, leg ulcers, development of masses from extramedullary hematopoiesis, and skeletal changes that result from the expansion of the bone marrow to compensate for the loss in RBCs. [
2]
Traditionally, β-thalassemia has been more common in the Mediterranean, Middle East, and Southeast Asia. Approximately 8.5% of UAE residents suffer from B-thalassemia, a significant health and financial problem. An estimated AED 1.2 million is reported as the cost of treatment for TDT patients aged 16 and under. As a result of the high prevalence of thalassemia carriers in the country, a marriage between two carriers poses a 25% risk of having a child with TDT. [
3]
The main treatment modalities for transfusion dependent thalassemia include regular blood transfusions, iron chelation therapy, and medications like luspatercept (Ribosyl) and hydroxyurea. [
4] Regular transfusion therapy commonly leads to iron overload-related complications including endocrine complications (growth retardation, failure of sexual maturation leading to infertility, diabetes mellitus, and insufficiency of the parathyroid, thyroid, pituitary, and adrenal glands), dilated myocardiopathy, liver fibrosis, and cirrhosis. Additionally, secondary viral infections are also relatively common. Furthermore, the search for a compatible donor proves to be another barrier. [
5]
The only potentially curative option for thalassemia major is allogeneic hematopoietic-cell transplantation, but owing to risks of graft rejection, graft-versus-host disease, and other treatment-related toxic effects, transplantation is mainly reserved for young children with an HLA-identical sibling donor. Therefore, gene therapy is currently being evaluated as a new option in patients with β-thalassemia. The aim of this narrative review is to analyze novel treatment options especially gene therapy for transfusion dependent beta thalassemia.
Materials and Methods
We conducted an extensive literature search in four major databases: PubMed, ProQuest, Scopus, and CINAHL. Articles published in English from January 2010 to December 2023 were included in the review. The search strategy was based on the following query: (Gene therapy OR Gene Editing OR Genetic Modification OR Gene Addition) AND (Beta Thalassemia Major OR Transfusion dependent thalassemia OR Cooley’s Anemia OR Mediterranean Anemia). In addition, Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms were utilized to refine the search: Gene Therapy OR Genetic Therapies AND Thalassemia Major (beta-Thalassemia Major).
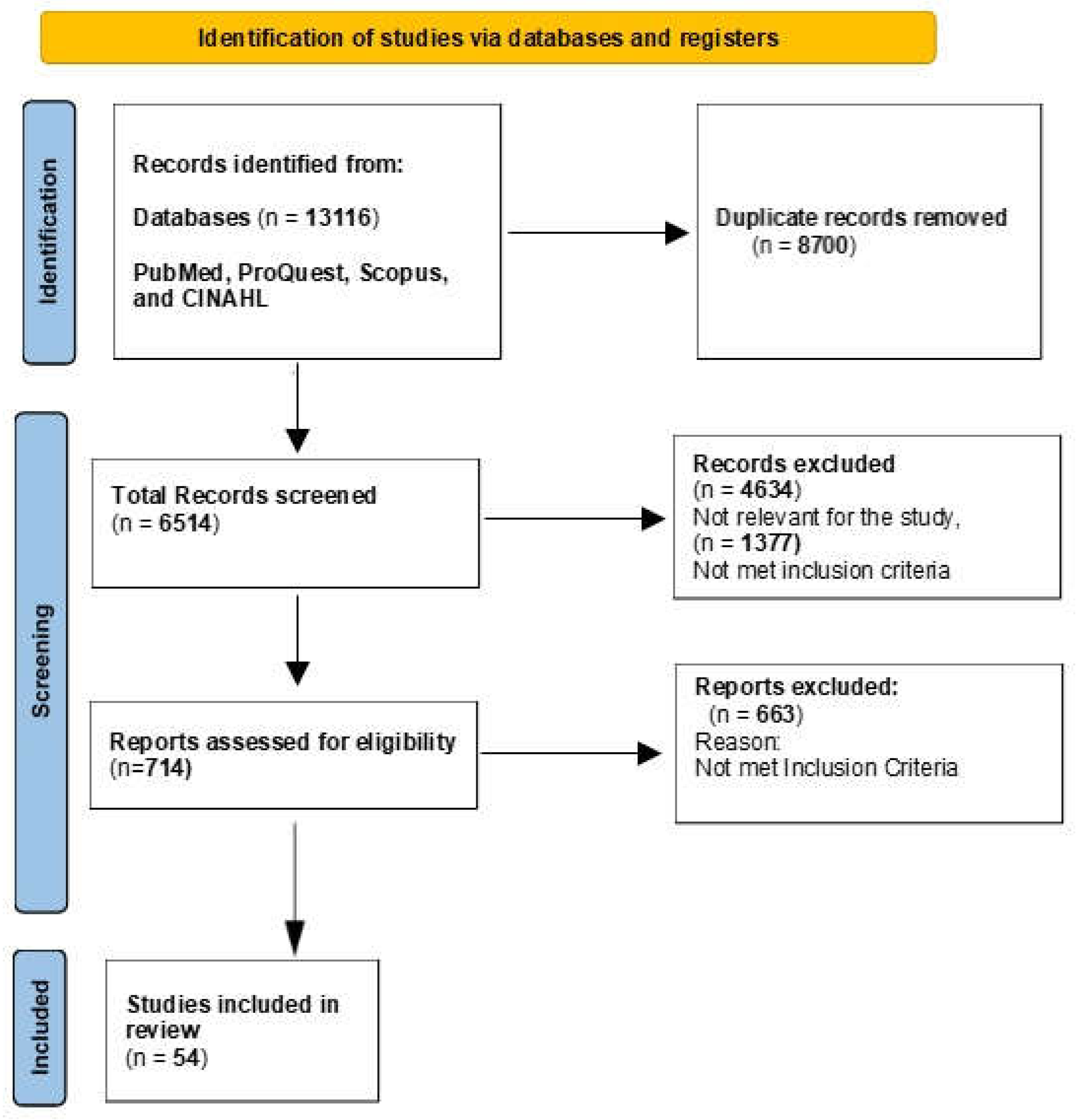
The initial search identified a total of 13,116 articles. Articles were included if they were published in English, focused on gene therapy or genetic modification techniques for beta thalassemia major and addressed transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia.
Articles were excluded if they were not directly related to gene therapy or genetic modification for beta thalassemia major, not published within the specified date range and reviews, editorials, or opinion pieces without original research data.
Data extraction was performed independently by seven authors to ensure accuracy and reduce bias. Discrepancies in data extraction were resolved through discussion among the authors until a consensus was reached.
Results
Out of total 13116 articles, 8700 duplicates, 4634 articles not met the inclusion criteria were excluded. Finally, 54 articles included in this narrative review. These studies examined various conventional therapies and gene therapy techniques aimed at treating transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia (
Figure 1).
Discussion
Treatment Modalities
The management of beta thalassemia major presents a nuanced interplay of established and evolving treatment strategies, each tailored to mitigate the complex manifestations of the disorder. Central to this paradigm are transfusion and chelation therapies, pioneering in anemia management and mitigating iron overload. Moreover, conventional treatment utilized splenectomy and hemoglobin F inducers to promote hemoglobin levels and effective erythropoiesis [
6]. However, the pursuit of curative interventions has led to the forefront of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, offering a potential respite for afflicted individuals, particularly in the pediatric population [
7]. Novel strategies aimed at reducing iron absorption have represented an area of interest. Apo-transferrin (apo-Tf), hepcidin agonists, JAK2 inhibitors, Tmprsso inhibitors, and activin receptor II (ActRII) ligand traps hold promise for improving iron overload management, averting splenomegaly and thrombosis, and decreasing the need for transfusions in individuals with ß-thalassemia [
6,
8]. With upcoming scientific advancements, expands to promising modalities such as gene therapy, heralding a new future in the therapeutic landscape of beta thalassemia major.
1. Conventional Therapy
1.1. Transfusion Therapy with Iron Chelation Therapy (ICT)
Patients diagnosed with β-thalassemia major (BTM) necessitate regular blood transfusions, complemented by appropriate iron chelation therapy (ICT), throughout their lifespan. These transfusions serve to address chronic anemia, prevent bone deformities, support normal growth and activity levels, and enhance overall quality of life (QoL) [
9,
10]. By providing fresh, normal red blood cells (RBCs), transfusions rectify anemia and suppress ineffective erythropoiesis, consequently averting hepatosplenomegaly and restricting bone marrow hyperplasia [
10,
11]. The advent of ICT has markedly improved life expectancy in BTM patients, attributed to heightened awareness among healthcare providers and patients, safer blood processing guidelines, enhanced techniques for iron overload assessment, and the availability of oral ICT options [
12,
13]. Notably, leukoreduced packed RBCs sourced from voluntary donors are preferred, with a minimum hemoglobin content of 40 g recommended [
9]. The decision to initiate transfusions hinges upon anemia presence, clinical symptoms, and comorbidities like organ dysfunction. Untreated BTM typically results in fatality before adolescence, while transfusion-supported patients can anticipate healthy longevity [
9,
10,
11]. However, transfusions carry risks such as acute (e.g., hemolytic reactions) and delayed adverse events (e.g., transfusion-transmitted infections, iron overload-related complications). To mitigate iron accumulation's detrimental effects, timely initiation of ICT, particularly oral agents like deferiprone and deferasirox, is imperative. Although ICT constitutes a significant portion of medical expenses, its judicious use significantly reduces the burden and costs associated with thalassemia complications and blood transfusions. [
9,
10,
14,
15,
16].
1.2. Splenectomy
In thalassemia major and intermedia, splenomegaly stemming from severe hemolysis can be mitigated through regular blood transfusions, yet hypersplenism may develop in children aged 5–10 years. In such cases, splenectomy becomes a consideration, especially when transfusion requirements exceed 200–220 ml RBCs/kg with 70% hematocrit or 250–275 ml/kg packed RBCs with 60% hematocrit annually [
17,
18,
19]. Despite the benefits, including decreased transfusion needs and improved hemoglobin levels, splenectomy poses risks, such as sepsis, venous thromboembolism, pulmonary hypertension, and leg ulcers [
10,
20]. Nevertheless, it remains an option for select patients facing complications like hypersplenism or worsening anemia not responsive to transfusion therapy. Thrombocytosis post-splenectomy necessitates vigilance and, if persistent, management with aspirin to mitigate thrombotic complications [
20]. Screening for accessory splenic tissue and ongoing assessment for transfusion requirements are imperative in managing splenectomies thalassemia patients [
20,
21,
22]. Moreover, Preoperative immunization against meningococcal and pneumococcal infections, followed by antimicrobial prophylaxis, aids in infection prevention, adding another layer of care [
10,
19].
1.3. Hemoglobin F Inducers
HbF inducers present a promising approach in thalassemia treatment by increasing γ-globin production, a β-like globin molecule capable of sequestering excess α-chains, thus countering the α/β-chain imbalance characteristic of the condition and enhancing effective erythropoiesis [
6]. Notably, hydroxyurea's mechanisms include γ-globin induction, inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase, and modulation of gene expressions related to apoptosis, cell cycle, and erythropoiesis [
24,
25]. Hydroxyurea (or hydroxycarbamide), extensively studied as an HbF inducer in β-thalassemia, has shown promising hematological improvements, with long-term safety deemed satisfactory. However, conflicting data primarily from single-arm trials or retrospective cohort studies warrants large-scale randomized controlled trials before widespread adoption in management. [
23]
While hydroxyurea is approved for reducing transfusion dependency in sickle cell disease, its efficacy in β-thalassemia remains uncertain [
27]. Guidelines suggest considering hydroxyurea for specific β-thalassemia patients, such as those who are alloimmunized or have specific genetic polymorphism. Although, close monitoring of response is crucial, with alternative treatments considered if necessary [
9,
26]. Other potential fetal Hb inducers, including 5-azacytidine and decitabine, have been explored, yet clinical evidence for their use remains limited [
10,
23,
28].
2. Novel Modalities
2.1. Gene Therapy
The main objective of gene therapy is to increase the synthesis of β- or ɣ-globin, thereby reducing the amounts of unattached α-globin chains, to reestablish the alpha/non-alpha globin ratio in RBCs. By doing so, RBC hemolysis and ineffective erythropoiesis is prevented, leading to prolonged RBC lifespan with functional haemoglobin-carrying erythrocytes. This results in the correction of anaemia and reduces the need for multiple transfusions [
29].
Autologous gene modification treatment requires several steps:
Extraction of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs): HSPCs, which can undergo self-renewal and multilineage differentiation, are found in the bone marrow. These cells express CD34 and are responsible for producing blood cells throughout a person's lifetime. Collection of the cells can be done either from the bone marrow or the peripheral blood [
30]. The conventional method of collecting autologous bone marrow is invasive and yields insufficient CD34+ HSPCs. Patients with B-thalassemia have an increased accumulation of erythroid precursors in their bone marrow, which can hinder the harvesting of an adequate dose of stem cells. Therefore, it is necessary to mobilize the stem cells [
31].
Mobilization and apheresis: Mobilization of cells from bone marrow to peripheral blood is carried out using the recommended combination of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) and plerixafor before collection by apheresis [
32]. A recent study shows that the combined use of G-CSF and plerixafor provides an adequate yield of stem cells. [
33]
Myeloablation: Myeloablation of the bone marrow is the next step and is performed to create enough space for the gene modified HSPCs to be reinserted, ensuring efficient engraftment. The recommended myeloablative agent is Busulfan since the dose can be tailored and modified for each patient depending on the response to the drug [
34].
Modified HSPCs infusion: The final step is the infusion of the cryopreserved genetically modified HSPCs, using 5% dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) solution, intravenously after it meets all the release criteria (sterility, viability, purity, and vector copy number [VCN] for gene-insertions), and minimum cell dose criteria (>2-3 × 10
6 CD34+/kg) [
34]. Gene therapy for TDT can be divided into two parts based on the method used, gene insertion and gene editing.
2.1.1. Gene Insertion
Gene insertion is a technique in which functional copies of genes, in this case, the β or ɣ-globin-producing genes, are introduced to the autologous HSPCs by using viral vectors, usually retro or lentiviruses, that carry the functional gene alongside its regulatory elements and insert it into the patient’s genome. The insertion of the vectors into the cells could either be in-vivo or ex-vivo. [
35]
Some of the risks associated with this approach are that the viral vector and insertion in an area near a proto-oncogene can stimulate uncontrolled proliferation leading to cancer development. For example, Hargrove et al. found that insertional dysregulation of cellular genes could be caused by lentiviral vectors. [
36] Hence, extensive preclinical testing is necessary and follow-up for these patients is required for 15 years to detect any adverse events.
Fortunately, this method of gene therapy is showing great promise. For example, Thompson et al. performed a clinical trial in which 22 patients with TDT received a functional copy of the β-globin gene using a lentiviral vector into autologous CD 34+ hematopoietic stem cells. The results showed that 15 out of the 22 patients (68%) achieved transfusion independence. Moreover, those patients also showed improved hemoglobin production and hematological parameters along with reduced iron overload. As for adverse effects, they were mild and resolved without sequelae. Finally, the author concluded that gene therapy has great potential to treat TDT, but further studies are warranted to confirm its long-term safety and efficacy. [
37]
Another study by Marktel et al. in which 3 adults and 6 children were treated with a different vector (GLOBE) showed significant hematopoietic recovery with reduced transfusion dependence in the adults along with complete discontinuation of transfusion in 3 out of 4 pediatric patients. The authors proposed that younger age is associated with a better outcome; Nonetheless, the trial is still in progress. [
38]
Another clinical trial is the Northstar-3 trial (HGB-212; NCT03207009) which is a phase 3 study assessing LentiGlobin gene therapy efficacy and safety in patients with TDT and either β
0 or β
+ IVS-I-110 mutations on both HBB alleles. 18 patients were included in the study of which 16 achieved transfusion dependence (89%) for at least 12 months after treatment and sustained hemoglobin levels with a median of 10.1 g/dL. Abdominal pain, leukopenia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, and pyrexia were some of the adverse events related to LentiGlobin therapy but overall the therapy was well-tolerated in the majority of participants. [
39].
2.1.2. Gene Editing
Gene editing is a novel technique that allows scientists to make precise and accurate modifications and edits in different sequences of the DNA and enables modifications to specific sites on the genome. This is different from gene insertion which is semi-random and lacks exactness.
The various types of targeted nucleases operate on a similar principle. First, they need to recognize a certain part of DNA and bind to it effectively and precisely. Secondly, certain regions of the DNA have to be “cut” or cleaved. The various methods can differ in how they bind to DNA, their nature, modularity of recognition, size of the recognition domain, and the resultant cleavage. [
40]
Some examples include meganucleases, zinc finger nuclease (ZFN), transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENS), and clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR) associated nuclease 9 (Cas9). An issue that could arise is unintended edits in other parts of the genome or what is known as “off-target” activity. [
41]
SOX 6 gene is a transcription factor that represses gamma-globin expression which in turn reduces gamma globin and increases synthesis of defective beta-globin in cases of thalassemia. Disruption of this gene has been shown to up-regulate gamma-globin expression in adult RBC cells and this could compensate for the loss of beta-globin in beta-thalassemia. Using this principle, a study performed by Laleh et al. used three different single-guide RNA CRISPR/cas9 to disrupt the SOX 6 gene in defective RBC cells in order to increase gamma-globin expression. The investigators suggest that this approach could be a potential approach for gamma-globin reactivation, but further studies are needed to know the degree of improvement that it might provide and its safety. [
42]
Recent genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified B-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma 11A (BCL11A) as a key regulator of fetal hemoglobin (HbF) expression that represses HbF and controls its transition to HbA. This finding has significant implications, as inactivation of BCL11A has been shown to induce the reactivation of fetal globin expression in human cells. [
43]
The following trials: CLIMB THAL-111 [
44] and CLIMB SCD-121 [
45] used CTX001 which is an autologous cellular drug that contains CRISPR Cas9 ribonucleoprotein targeting BCL11A erythroid-specific enhancer region to disrupt it and produce more gamma-globin. 2 patients were included in this study- one with TDT every year for 2 years and the other with SCD along with a history of two or more severe vaso-occlusive episodes per year. After receiving myeloablative therapy using busulfan, both patients were infused with CTX001 and were followed for 21 months.
The first patient with TDT showed significant improvement after only 18 months in which her hemoglobin increased from 9.0 to 14.1 g/dL (93% fetal hemoglobin) and became transfusion dependent. The only serious adverse events were pneumonia and veno-occlusive liver disease which resolved.
The second patient with SCD also showed an improvement in her hemoglobin levels 15 months after the intervention, from 7.2 to 12.0 g/dL, and had no new vaso-occlusive episodes. The major adverse event was sepsis which was resolved.
This clinical trial has shown optimistic results regarding the use of CTX001 gene therapy in the editing of BCL11A. Also, it showed that CTX001 results in stable engraftment, high levels of fetal hemoglobin expression, and the elimination of vaso-occlusive episodes or the need for transfusion. Even so, the long-term effect of CTX001 remains unknown, and the ability to generalize the findings to other TDT or SCD patients is not clear, these initial results show great promise for the future of gene editing [
46]
Emerging data from the CLIMB THAL-111 and CLIMBSCD-121 trials, presented at the American Society for Gene & Cell Therapy Annual Meeting, indicate that a single dose of the investigational gene therapy achieved transfusion independence in 95% of beta-thalassemia patients. [
47]
2.1.3. Zynteglo
Betibeglogene autotemcel (beti-cel), Zynteglo by Bluebird Bio-Inc), is the only autologous hematopoietic stem cell-based (HSC) gene therapy approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in August of 2022. It is a curative therapy, as an intravenous infusion, indicated for adult and paediatric patients suffering from transfusion-dependent B-thalassemia [
48]. The basis of the therapy is to introduce functional copies of the beta gene in-order to produce functional adult Hb. The suspension consists of the patient’s own mobilised CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells that are transduced ex-vivo with the BB305 lentiviral vector. The vector encodes for the β-globin (βA-T87Q) gene. Prior to administration of the infusion, myeloablative conditioning is required [
49].
The transplanted gene aims to correct the imbalance of the haemoglobin chains, normalise adult haemoglobin levels, and thereby eliminate the need for frequent blood transfusions. A 2022 phase-3 open label trial, evaluating the efficacy and safety of beti-cel, reported that 20 of the 23 patients achieved transfusion independence. For the patients who did not show transfusion independence, it was observed that there was a reduction of 30% and 26% in transfusion frequency [
50]. A study assessed the health-related quality of life (HRQoL) of patients who had undergone the phase-3 trial. It reported improvement in all domains of HRQoL (physical, psychological, social, environmental) in the patients who received Zynteglo [
51].
The most common adverse effects were found to be GIT disturbances (vomiting; nausea; diarrhoea, abdominal pain; constipation; low appetite); fever, mucositis, febrile neutropenia, musculoskeletal pain, cough, pigmentation disorder, headache, rash, itch, hair loss and nose bleeds. Serious adverse reactions (< 3%) included fever, thrombocytopenia, liver venoocclusive disease, febrile neutropenia, neutropenia, stomatitis. No fatalities were reported [
52]. The conditioning agents used may be the reason for the side effects observed [
53]. Considering that Zynteglo has not been studied in pregnant and lactating female patients and the risks surrounding myeloablative conditioning, the therapy is not indicated in pregnancy and lactation. Patients are advised to use an effective contraceptive method for at least 6 months after receiving Zynteglo as the effect on contraception is not sufficiently studied. Similarly, the effect on fertility has insufficient data, thus patients may take necessary precautions, if appropriate. Although indicated for the pediatric and adult population, safety and efficacy of the treatment is not established in children less than 4-year-olds and in older adults. Health-care professionals involved in the treatment are advised to monitor patients for possible hypersensitivity reactions, thrombocytopenia, bleeding, and failure of neutrophil engraftment. Annual screening for hematological malignancies is also recommended [
52].
While Zynteglo is certainly a ground-breaking advancement in the world of gene therapy, there are concerns related to the affordability of the therapy because of its high cost of around 2.8 million US dollars [
54]. This major drawback was the reason for its withdrawal from the European market after receiving approval from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in 2019 [
55]. Nonetheless, the one-time beti-cel therapy has been found to be cost-effective as compared to the standard of care in a study conducted in the United States [
56].
Conclusion
The treatment options available for β-Thalassemia major are limited and associated with a wide range of complications. The main therapy to maintain healthy levels of hemoglobin is blood transfusion. The maximum range of RBCs that can be transfused without giving a spike increase in volume of blood is only 15–20 ml/kg. While well-treated patients commonly reach adulthood, their life-expectancy is greatly diminished due to complications of iron overload. Regular blood transfusions result in accumulation of iron within the reticuloendothelial system as the iron excretory mechanisms of the body are compromised. The deposited iron harms endocrine glands, blood vessels, enhances the risk of liver carcinoma, cirrhosis and can lead to diabetes and infertility. Prolong blood transfusion products may also pave the way for pathologic hepatitis. Finding a compatible blood donor is a significant barrier in itself. Other solutions include bone marrow transplant, iron chelation therapy and splenectomy, each coming with their own set of challenges
Gene therapy is an innovative solution. On 19 August, Betibeglogene autotemcel (ZYNTEGLO), a one time cell-based gene therapy was officially FDA approved. It is a potentially curative treatment to correct the globin chain imbalance, thus potentially improving production of normal hemoglobin, erythropoiesis and chronic anemia. Treatment with beti-cel is expected to result in a significant clinical benefit and lower the patient’s high lifetime expenses. These advantages stem from increased life-expectancy, higher quality of life, reduced complications, and the avoidance of chelation treatment and ongoing transfusions.
Although cutting edge, it is high in cost- limiting availability. With its list of unlikely adverse effects came the biggest adverse effect: A 2.1 million-dollar price tag per person. This is only the cost of the medication; the price of hospitalization etc. remains separate. Establishing durability of treatment, incidence of risks associated with the therapy, use in special populations, and cost-effectiveness requires long-term follow-up and research.
Declaration of Interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of this article.
References
- Genetic Counseling and Testing for Hereditary Hemochromatosis. In Hereditary Hemochromatosis; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US), 2018; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK545151/.
- Rund, D.; Rachmilewitz, E. Beta-Thalassemia. N Engl J Med 2005, 353, 1135–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Cohen, A.; Porter, J.; Taher, A.; Viprakasit, V. Guidelines for the management of transfusion dependent thalassaemia (TDT). Thalassemia International Federation 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucharoen, S.; Weatherall, D.J. The Hemoglobin E Thalassemias. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, A.; Musallam, K.; Inati, A.; Weatherall, D.J. The Overlooked Genetic Blood Disorder: Beta Thalassemia Intermedia. JAMA 2021, 326, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Salah, N.; Bou-Fakhredin, R.; Mellouli, F.; Taher, A.T. Revisiting beta thalassemia intermedia: past, present, and future prospects. Hematology 2017, 22, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattamis, A.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; Aydinok, Y. Thalassaemia. Lancet 2022, 399, 2310–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adly, A.A.; Ismail, E.A. Management of Children With β-Thalassemia Intermedia: Overview, Recent Advances, and Treatment Challenges. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 2018, 40, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.T.; Sayani, F.; Trompeter, S.; Drasar, E.; Piga, A. Challenges of blood transfusions in β-thalassemia. Blood Rev 2019, 37, 100588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Cohen, A.; Porter, J.; Taher, A.; Viprakasit, V. (Eds.) Guidelines for the Management of Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia (TDT), 3rd ed. Thalassaemia International Federation: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichinsky, E.; Levine, L.; Bhatia, S.; et al. Standards of Care Guidelines for Thalassemia. Children's Hospital and Research Center: Oakland, CA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, B.A.; Porter, J.B. Results of long term iron chelation treatment with deferoxamine. In Iron Chelation Therapy; Hershko, C., Konijn, A.M., Link, G., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Boston, MA, 2002; pp. 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabutti, V.; Piga, A. Results of long-term iron-chelating therapy. Acta Haematol. 1996, 95, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardumian, A.; Telfer, P.; Constantinou, G.; et al. Standards for the Clinical Care of Children and Adults with Thalassaemia in the UK. United Kingdom Thalassaemia Society: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ladis, V.; Chouliaras, G.; Berdoukas, V.; et al. Relation of chelation regimes to cardiac mortality and morbidity in patients with thalassaemia major: an observational study from a large Greek Unit. Eur J Haematol 2010, 85, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Rugolotto, S.; De Stefano, P.; et al. Survival and complications in patients with thalassemia major treated with transfusion and deferoxamine. Haematologica 2004, 89, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.; Mumtaz, S.; Shakir, H.A.; et al. Current status of beta-thalassemia and its treatment strategies. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecorari, L.; Savelli, A.; Cuna, C.D.; Fracchia, S.; Borgna-Pignatti, C. The role of splenectomy in thalassemia major. An update. Acta Pediatr Mediterr 2008, 24, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M.; Sekimoto, M.; Takiguchi, S.; et al. High incidence of thrombosis of the portal venous system after laparoscopic splenectomy: a prospective study with contrast-enhanced CT scan. Ann Surg. 2005, 241, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, R.H.; Shah, A.R.; Ahmad, J.; Karnik, A.; Rai, N. Post splenectomy outcome in β-thalassemia. Indian J Pediatr. 2015, 82, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.N.; Tahereb, G.M.; Ahmad, T.; et al. Correlation of splenectomy with portal vein thrombosis in beta-thalassemia major. J Pak Med Assoc. 2011, 61, 760–762. [Google Scholar]
- Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Carnelli, V.; Caruso, V.; et al. Thromboembolic events in beta thalassemia major: an Italian multicenter study. Acta Haematol. 1998, 99, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musallam, K.M.; Taher, A.T.; Cappellini, M.D.; Sankaran, V.G. Clinical experience with fetal hemoglobin induction therapy in patients with β-thalassemia. Blood. 2013, 121, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finotti, A.; Breda, L.; Lederer, C.W.; et al. Recent trends in the gene therapy of β-thalassemia. J Blood Med. 2015, 6, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, B.S.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Makala, L.H. Cell signaling pathways involved in drug-mediated fetal hemoglobin induction: Strategies to treat sickle cell disease. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2015, 240, 1050–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Porter, J.B.; Viprakasit, V.; Taher, A.T. A paradigm shift on beta-thalassaemia treatment: How will we manage this old disease with new therapies? Blood Rev. 2018, 32, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, W.C.; Ho, J.J.; Loh, C.K.; Viprakasit, V. Hydroxyurea for reducing blood transfusion in non-transfusion dependent beta thalassaemias. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.; Vichinsky, E.; Musallam, K.; Cappellini, M.D.; Viprakasit, V. Guidelines for the Management of Non Transfusion Dependent Thalassaemia (NTDT). Thalassaemia International Federation: Nicosia, Cyprus, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Soni, S. Gene Therapies for Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassemia. Indian Pediatr. 2021, 58, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhushan, B.; Khanna, V.K.; Dubey, A.; et al. Emerging trends in gene therapy for β-thalassemia: A systematic review. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 1028–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origa, R.; Galanello, R.; Ganz, T.; et al. Liver iron concentrations and urinary hepcidin in β-thalassemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origa, R.; Galanello, R.; Ganz, T.; et al. Liver iron concentrations and urinary hepcidin in β-thalassemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.A.; O'Sullivan, C.; Jarritt, P.H.; Porter, J.B. Value of sequential monitoring of left ventricular ejection fraction in the management of thalassemia major. Blood Cells Mol Dis 2004, 33, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Von Andrian, U.H.; Massberg, S. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells: their mobilization and homing to bone marrow and peripheral tissue. Immunol Res. 2009, 44, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S. Gene therapies for transfusion dependent β-thalassemia: Current status and critical criteria for success. Am J Hematol. 2020, 95, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrove, P.W.; Kepes, S.; Hanawa, H.; et al. Globin Lentiviral Vector Insertions Can Perturb the Expression of Endogenous Genes in β-thalassemic Hematopoietic Cells. Mol Ther. 2008, 16, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.A.; Walters, M.C.; Kwiatkowski, J.; et al. Gene Therapy in Patients with Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2018, 378, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marktel, S.; Scaramuzza, S.; Cicalese, M.P.; et al. Intrabone hematopoietic stem cell gene therapy for adult and pediatric patients affected by transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia. Nat Med. 2019, 25, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, A.; Locatelli, F.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; et al. Northstar-3: interim results from a phase 3 study evaluating Lentiglobin gene therapy in patients with transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia and either a β0 or IVS-I-110 mutation at both alleles of the HBB gene. Blood 2019, 134 (Suppl. 1), 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoban, M.D.; Bauer, D.E. A genome editing primer for the hematologist. Blood. 2016, 127, 2525–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tee, L.Y.; Wang, X.; Huang, Q.; Yang, S. Off-target Effects in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Engineering. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariati, L.; Rohani, F.; Heidari Hafshejani, N.; et al. Disruption of SOX6 gene using CRISPR/Cas9 technology for gamma-globin reactivation: An approach towards gene therapy of β-thalassemia. J Cell Biochem. 2018, 119, 9357–9363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoudi, K.; Yannaki, E.; Psatha, N. Precision Editing as a Therapeutic Approach for β-Hemoglobinopathies. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 9527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gene therapy for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia and sickle cell disease. ClinicalTrials.gov. Identifier: NCT03655678.
- Lentiglobin gene therapy for β-thalassemia. ClinicalTrials.gov. Identifier: NCT03745287.
- Frangoul, H.; Altshuler, D.; Cappellini, M.D.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing for Sickle Cell Disease and β-Thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amorosi, D. Gene therapy a potential 'functional cure' for sickle cell disease, beta thalassemia. Hematol Oncol Today. 2023, 24, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Zynteglo (betibeglogene autotemcel) package insert, U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/vaccines-blood-biologics/zynteglo.
- Thompson, A.A.; Walters, M.C.; Kwiatkowski, J.; et al. Gene Therapy in Patients with Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2018, 378, 1479–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, S.; Salpeter, S.R.; Kaplan, R.M.; et al. The impact of gene therapy for transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Hematol. 2021, 96, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellini, M.D.; Cohen, A.R.; Porter, J.B.; et al. Improvement in Health-Related Quality of Life and Well-being in Patients with Transfusion-Dependent β-Thalassemia (TDT) Treated with Betibeglogene Autotemcel (LentiGlobin for β-Thalassemia, beti-cel): Northstar-2 and Northstar-3 Studies. Blood. 2021, 138 (Suppl. 1), 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zynteglo (betibeglogene autotemcel) package information, U.S. Food and Drug Administration website. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/160991/download.
- Arya, Y.A.; Sahi, P.K. Cell-Based Gene Therapy for β-Thalassemia. Indian Pediatr. 2023, 60, 313–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluebird Bio announces U.S. commercial infrastructure to enable Zynteglo. Bluebird Bio website. Available online: https://investor.bluebirdbio.com/news-releases/news-release-details/bluebird-bio-announces-us-commercial-infrastructure-enable.
- Zynteglo. European Medicines Agency website. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/medicines/human/EPAR/zynteglo.
- Locatelli, F.; Thompson, A.A.; Kwiatkowski, J.L.; et al. Betibeglogene Autotemcel Gene Therapy for Non–β0/β0 Genotype β-Thalassemia. N Engl J Med. 2021, 384, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).