1. Introduction
Turning is a highly dynamic process and its production performance is determined by various parameters such as cutter geometry, cutting conditions, chip formation, tool & work piece material, tool wear and so on. According to earlier studies, tool wear is the most important one amongst these parameters that affect the performance of production [
1,
2]. Thus, tool wear monitoring is vital to attain surface quality of the work piece and dimensional accuracy while turning. Indirect way of tool wear monitoring is based on acquiring the values of process variables measured (namely temperature, vibration, cutting force, acoustic emission, spinning-motor current, emitted sound and roughness of the surface) and the relationship among these values and tool wear [
1].
Monitoring based on sound is one of the technologies not investigated extensively for monitoring tool wear, although it has been widely used by turning operators in machining workshops for making decisions on tool condition [
1,
3]. The sound signal may be easily contaminated by the noises from motors, adjacent machines, nearby processes and conveyors. These contaminations could be removed by using the signal decomposition techniques namely, Wavelet decomposition (WD) and empirical mode decomposition (EMD) being used in signal processing techniques, discrete Wavelet transform (DWT) and Hilbert Huang transform (HHT), respectively.
The commonly used traditional data analysis methods, for example Fourier analysis, are all grounded on linear and stationary conventions, i.e., the signal to be processed should be temporarily stationary and linear; if not, the resulting Fourier spectrum will represent only little physical sense [
4]. In addition, it is signifying only the global not the required local properties of the original signal because of the use of convolutional integral for decomposing the signal in terms of sine and cosine functions [
5]. Short-Time Fourier Transform (STFT) is widely used technique, with limitations due to constant resolution in frequency and in time, where the resolution is defined by the width of the windowing function [
6]. Conversely, the Wavelet Transform (WT), one of the commonly used time-frequency analyzing methods can produce both frequency and time information of a signal at the same time by matching one dimensional signals to a multi-dimensional time vs frequency plane. Nevertheless, the wavelet transform is still having few unavoidable insufficiencies, including energy leakage, border distortion and the interference terms. These insufficiencies would produce numerous small unwanted spikes almost all over the frequency scales and make the end results very difficult to infer as well as confusing [
4,
7]. In order to sense tool condition, it is not sufficient to detect the exitance of a particular frequency in the original signal but it is required to localize the frequency with respect to time and its space [
8].
DWT is appropriate for localizing the time of frequency component of a signal, and has attracted substantial attention in the area of monitoring machine tool wear [
4,
7]. HHT is a new technique good for time-frequency analysis which can provide very good resolution in frequency and time simultaneously [
5]. HHT has been extensively used in the field of monitoring the condition of roll bearings [
9,
10]. Moreover, some researches have been carried out in the field of tool condition monitoring also using HHT [
10,
11]. In [
12], the authors have proposed an approach to detect flute breakage in end milling using HHT. The use of marginal Hilbert spectrum from HHT to corelate the tool wear in end-milling has been explored in [
13].
Even though HHT can offer a brilliant localization of the instantaneous frequencies in time, it has not received as much attention as DWT in the monitoring process of turning. One reason could be due to the fact that HHT is newer technique than the well-established DWT [
8]. This paper presents a comparative study on the decomposition of multi-component signals using HHT and DWT to highlight the superiority found in HHT for the analysis of tool-emitted sound signals obtained from turning processes.
2. Materials and Methods
It is a known fact that any nonlinear system is identified by its intra-wave frequency variations. To define these intra-wave frequency variations in the data, we need a procedure having posteriori defined basis, derived from data itself. Instantaneous frequency is the one normally revealing the intra-wave frequency modulation of any system. Hence the most physically meaningful way to describe nonlinear systems is in terms of their instantaneous frequency. Hilbert-Transform (HT) is the simple and easiest way to compute this instantaneous frequency [
5]. Hilbert Huang transform is a relatively new approach to signal processing which works very good for signals that are nonlinear and nonstationary as the definition of the basis is extracted from the original signal.
HHT is a process of decomposing any multi-component signal into many mono-component signals, so-called Intrinsic Mode Functions (IMF), and then locating its instantaneous frequencies [
5]. It is obtained from the principle of Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD) and the HT. First the captured nonlinear and nonstationary signal is decomposed into a group of IMFs by using EMD. Every IMF is an adaptive and near orthogonal representation of the decomposed signal. Because the IMF is almost mono-component the instantaneous frequencies found in each IMF can easily be determined.
2.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD)
Any signal (data) might have more than one different co-existing mode of oscillations at the same time, based on its complexity. Every oscillatory mode is represented by an IMF with the given below definitions [
5].
(a) Within a whole data set, the total count of zero-crossings and the total count of extrema must either same or differ maximum by one, and
(b) At any point on the whole data set, the mean value of the envelope formed by the local minima and the envelope formed by the local maxima is zero.
A special sifting process is implemented to remove every IMF from the given data set [
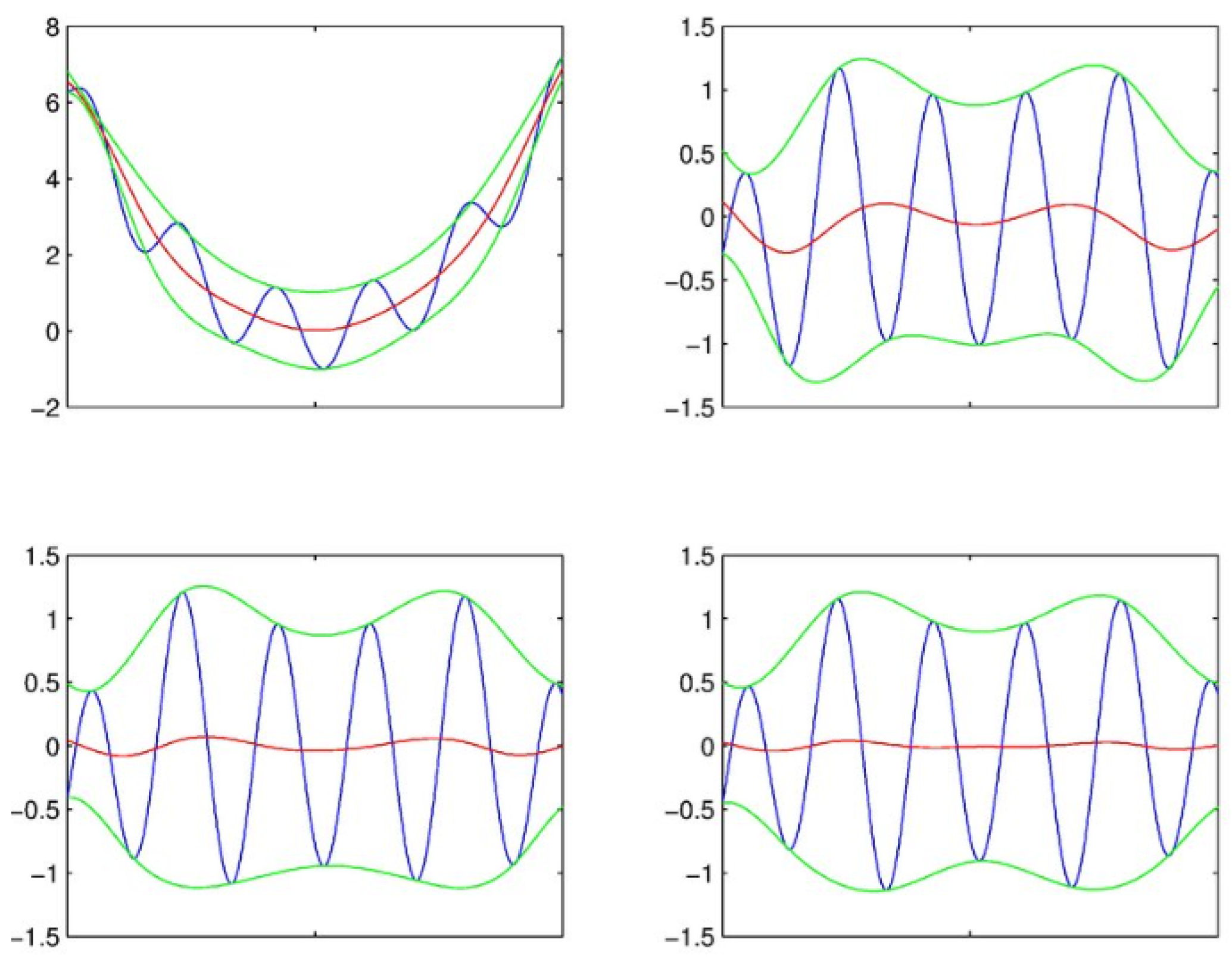
5]. The sifting process begins with identifying all the local minima, and then connecting all of the local minima by a cubic spline line. There by a lower envelope is formed to the data set. Then, by repeating the same procedure for the local maxima, an upper envelope is also formed to the data set. It is important that the lower and upper envelopes must cover all the data points between them. The lower and upper envelopes should cover all the data between them as shown in
Figure 1. Their mean is calculated as
m1(t), and the difference between the data and the mean is also calculated as
h1(t), using Equation (1).
This sifting process is repeated several times until the extracted signal becomes an IMF, satisfying the definitions mentioned above. The diagram at
Figure 1 shows a typical such four iterations until the mean becomes almost zero [
14]. It clearly shows the mean value of the envelope formed by the local minima and the envelope formed by the local maxima is zero. This difference
h1(t) is treated as data and the sifting process again applied on it.; then:
where
m11(t) is the mean of the lower and upper envelops of
h1(t). As shown in Equation (3),
h1k(t) is obtained by repeating this process up to
k times.
At end of each step in the processing, a checking is to be done on whether the number of extrema equals the number of zero crossings. The resultant time series will be the first IMF, and then it is marked as c1(t) = h1k(t).
Actually, the oscillations with height frequency found inside the original signal
x(t) are extracted in to the very first IMF component of the signal. And then this IMF is subtracted from the original signal and the result is called a residue
r1(t) as shown in Equation (4).
The residue
r1(t) is considered as if it was the original signal and this sifting process is again applied on it. The entire process of finding subsequent intrinsic modes
ci(t) is continued until the last intrinsic mode is found. The end residue is going to be either a constant or a monotonic function. The entire sifting process may be represented using Equation (5).
Hence a multi-component signal can be decomposed into n-empirical intrinsic mode functions (IMFs), plus a residue, rn(t) with the help of EMD.
Figure 1.
The sifting process of EMD showing four iterations [
14].
Figure 1.
The sifting process of EMD showing four iterations [
14].
2.2. Wavelet Decomposition (WD)
The idea of wavelet-based analysis was invented by Jean Morlet, an engineer from France, in 1982. The primary aim of wavelet transform (WT) is to get a more accurate illustration of both time and frequency content of a signal. Analyzing according to scale is the essential principle behind wavelets. Adopting a mathematically defined wavelet prototype function termed mother wavelet is the core process in wavelet analysis [
15].
The concept is almost similar to short time Fourier transform (STFT), except the windowing function width based on the central frequency. Therefore, for any given signal, the best bargains between time and frequency resolution can be attained automatically. Actually, “a wavelet is a kind of kernel function to be used in an integral transformation” [
15].
If
x(t) is a continuous signal, its wavelet transform, CWT can be obtained using the given below Equation (6).
where the
‘*’ denotes the complex conjugation.
Equation 7 represents the wavelet function defined by transforming and expanding a “mother” function.
where
ψ(t) is the basic or mother wavelet with the translation parameter
‘b’ and the dilation factor
‘a’.
The parameters
a and
b are frequently discretized for practical applications, which results the so called discrete wavelet transform (DWT). A wavelet function can be defined by discretizing
a=2j, and
b=k2j (
j, k ϵ Z) as shown in Equation (8).
The DWT can then be defined mathematically using the Equation (9).
where
Cj,k is given the name wavelet coefficient and it can be viewed, in general, as a time vs frequency map of that original continuous-signal
x(t).
Even though DWT is able to give complete and orthogonal representation of any signal, it is still considered as a priori approach because of the adaptation of mother wavelet in the decomposition process [
16,
17].
2.3. General Experimental Setup
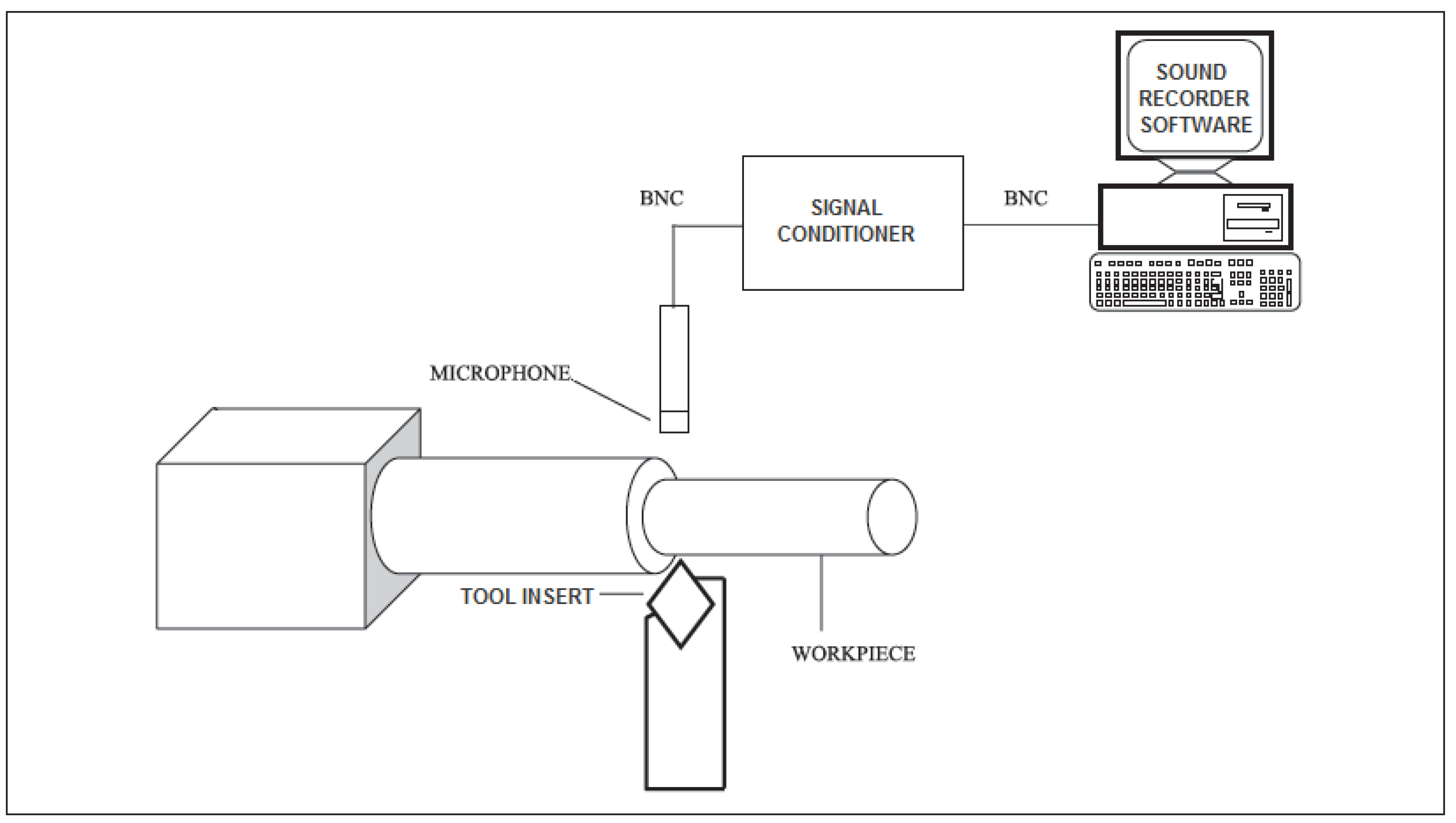
The experimental setup is shown in the form of a graphic diagram in
Figure 2. This experiment was conducted on a normal lathe, EME Turning machine. Some Carbide tool inserts of type NM6 were used to machine unalloyed mild steel AISI 1040. To obtain the tool-sound, produced because of the friction between the tool-bit tip and the work-piece surface, a PCB130D20 microphone is placed near tool insert tip. A specifically designed signal-conditioner is used to provide the appropriate voltage level for the PCP microphone. Hence the microphone is linked to a computer through this signal-conditioner. A special software, GoldWave, has been used to save the recorded sound by the microphone at the sampling-rate of 44.1KHz. Many experiments (machining) were conducted.
The experiment began with recording a free-run sound of the spindle rotating at the speed of 570 rev/min while keeping the tool insert not contacting with work-piece. Then the emitted sound while machining using a fresh tool (without any flank wear) was recorded, maintaining the same speed (570 rev/min), for 1mm depth of cut. This process of recording was repeated distinctly for slightly-worn tool having a flank wear of 0.2mm and severely-worn tool having a flank wear of 0.4mm. Throughout the experiment a constant feed rate set at 0.5 mm/rotation was uniformly maintained. The recording was done for 12 seconds. Each 12 seconds long signal was split into twelve one-second-long signals, to be used in the following signal decomposition process by WD and EMD. Each one second duration sound signals were digitized by using the Matlab waveread function.
3. Results and Discussion: Comparison of EMD and WD
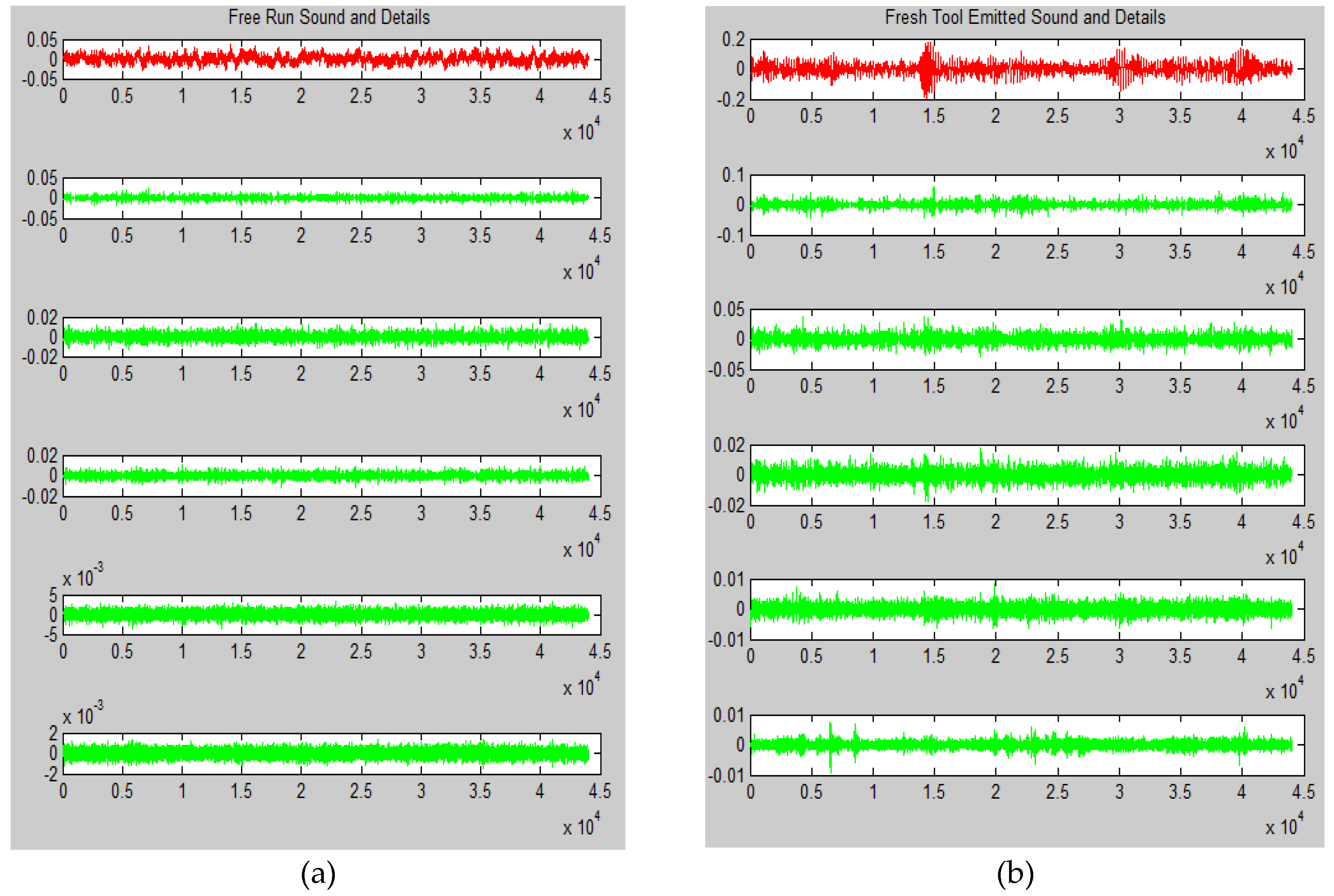
Figure 3a shows the result of the Wavelet decomposition applied on the sound signal captured when the tool insert is not in contact with work-piece, free-running sound.
Figure 3b shows the result of the Wavelet decomposition applied on the sound signal captured while machining using the fresh-tool (without flank wear). Similarly,
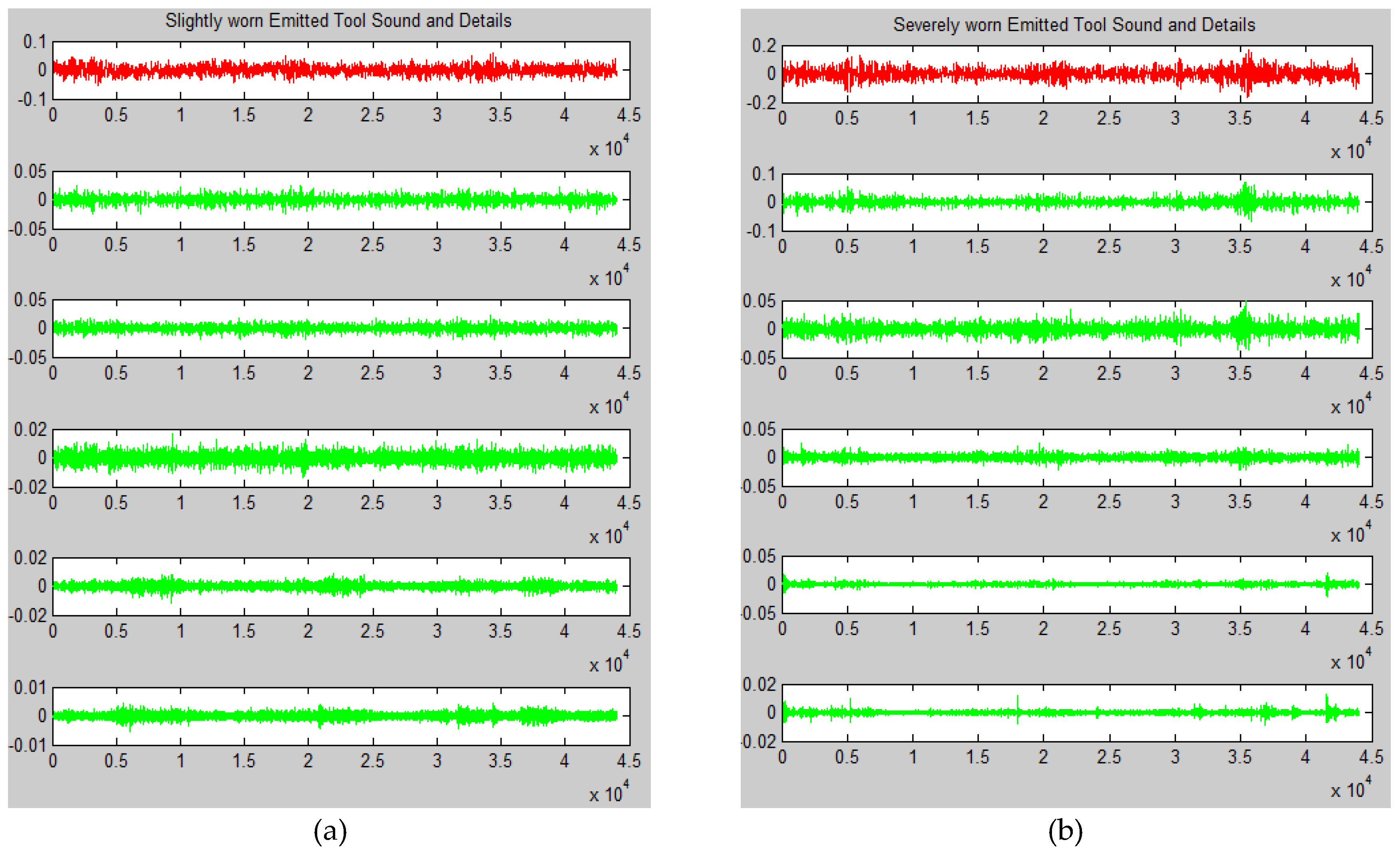
Figure 4a shows the result of the Wavelet decomposition of the sound signal captured while machining using the slightly-worn tool having a flank wear of 0.2mm. And
Figure 4b shows the result of the Wavelet decomposition of the sound signal captured while machining using the severely-worn tool, having a flank wear of 0.4mm.
This Wavelet decomposition is performed using the Matlab function, wavedec(X,N,’wname’), wher X is the tool sound signal to be decomposed, and N is the level which is set to 5. The parameter wname represents the mother wavelet and ‘db3’(‘Daubechies Extremal Phase Wavelet’ including ‘3 Vanishing Moments’) was selected. It is worth to note that the selection of mother wavelet (being ‘db3’) and the decomposition level, which is set to 5 are making the WD a priori approach.
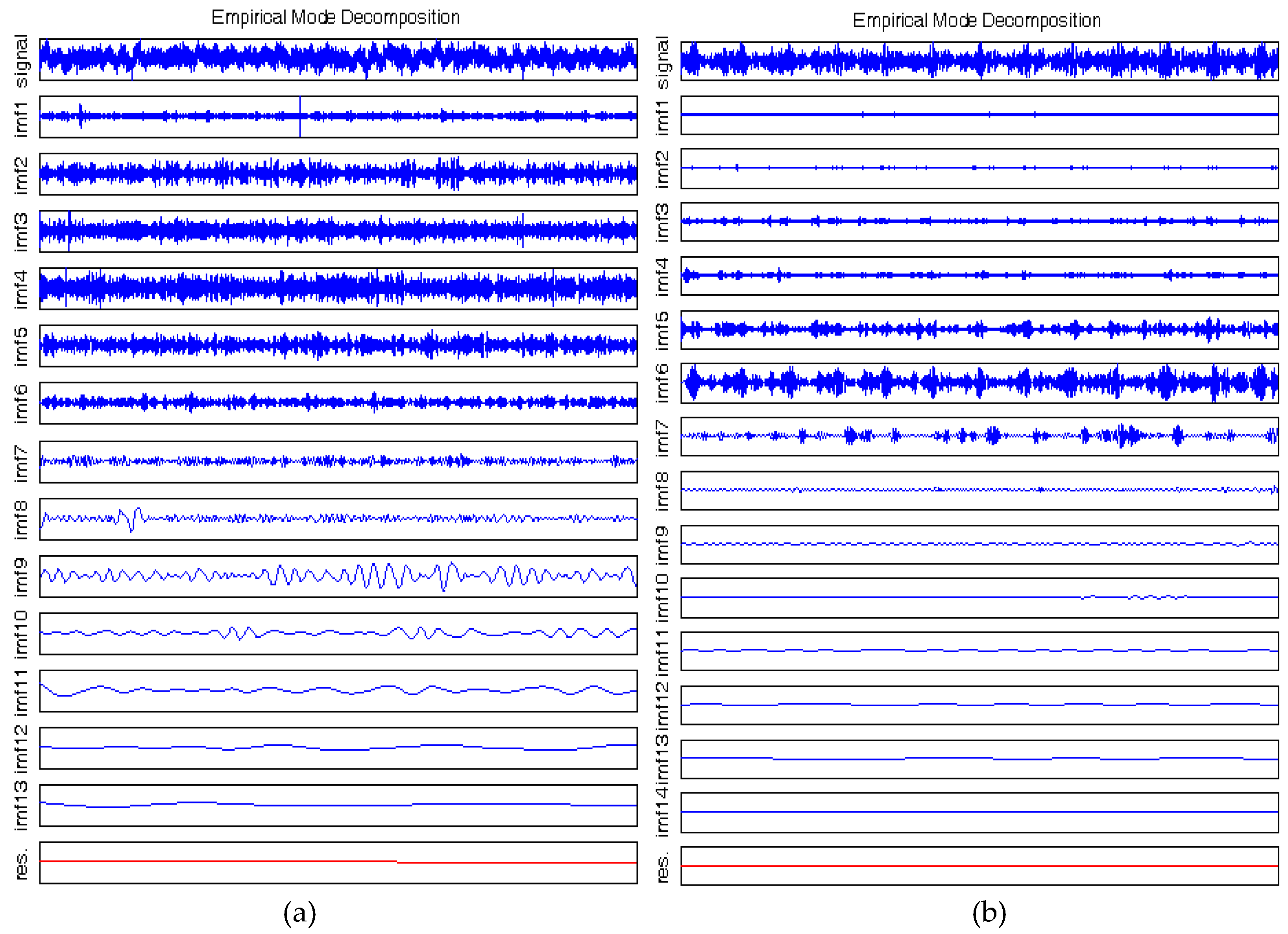
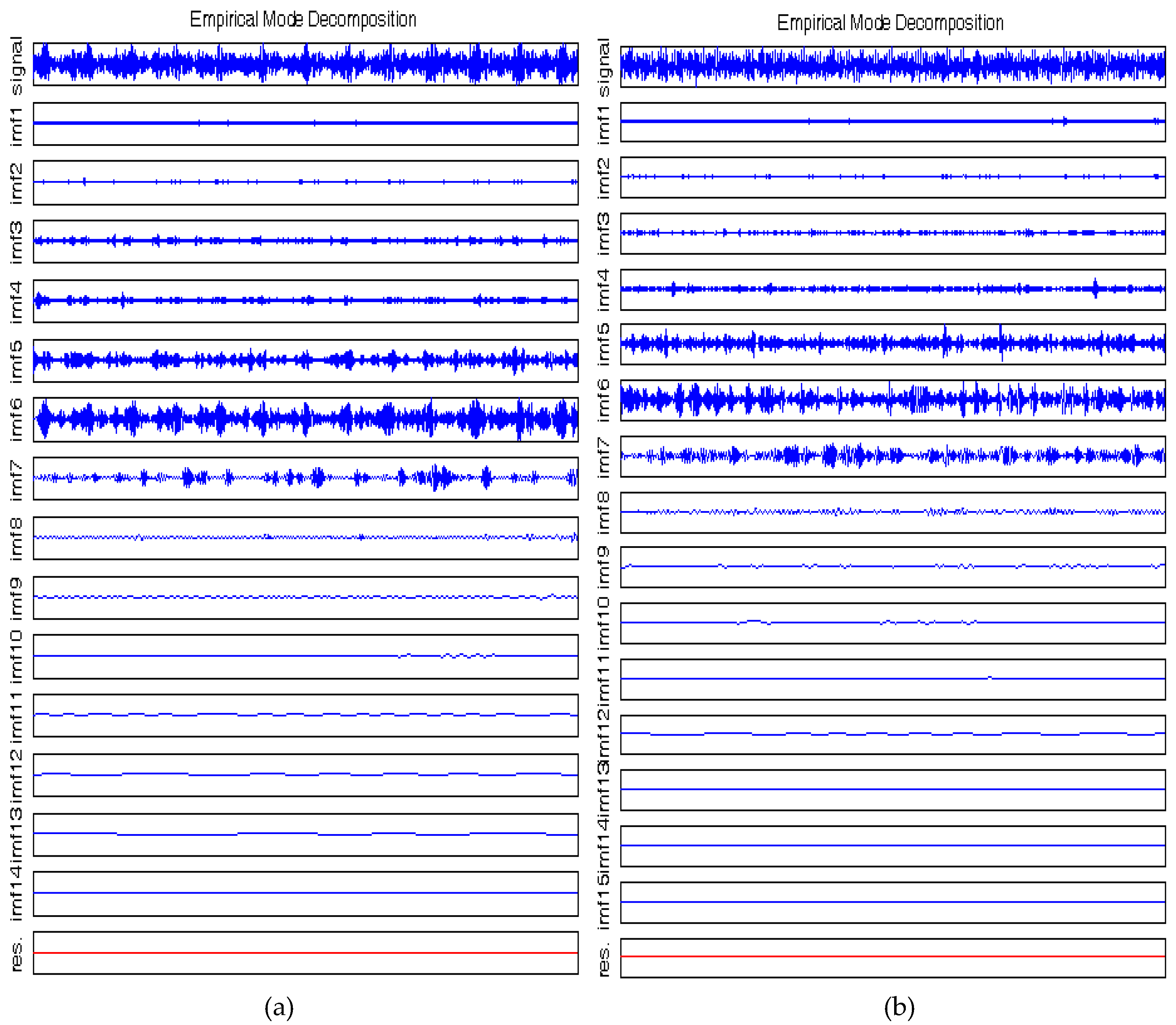
Figure 5a,b shows the result of Empirical Mode Decomposition on the sound signals captured during free-running and machining using fresh-tool respectively. Similarly
Figure 6a,b shows the result of the same decomposition on sound signals captured while machining with slightly and severely worn tools respectively. The important point here is the level of decomposition was not set to any initial value. Also, there is no specific basis selected, like mother wavelet in WD, as it is not required, and hence EMD is a posteriori approach. Now it is evident from the
Figure 5 and
Figure 6 that the level of decomposition has not been fixed in EMD, as the IMFs generated are different in numbers for free run (13 IMFs), slightly-worn (14 IMFs) and severely-worn (15 IMFs), tool sound signals. It is evident that the EMD is able to produce a variable number of components because it is a fully data-driven and adaptive method which can obtain the various oscillatory modes inside the original signal. This enabled EMD to overcome the inherent limitations of signal decomposition using wavelet approach, WD.
Wavelet analysis managed to extract only the coefficients throughout the decomposition process. Moreover, interpretation as amplitude and frequency should be done in a circuitous process [
17]. It could be possible by the way of using scaling concept, but still it drives again towards a priori approach. It is a well-known fact that the intra-wave frequency modulation is the signature of any nonlinear system. Hence the nonlinear system can only be efficiently described by approaches with posteriori defined basis extracted from signal.
Information found in the signal is not missing during the process of EMD. So, every individual information within the signal is getting reflected in conceivable different instantaneous frequencies and instantaneous amplitudes. These instantaneous frequencies and amplitudes could easily be extracted by applying Hilbert transform on each and every IMF. Therefore, we can conclude that the use of END method is more appropriate and efficient than wavelet decomposition method for decomposing emitted tool-sound signals used in our research.
The results produced in this research agree with the comparison found in [
18] using respiratory waveform. The authors of [
19] also documented in their conclusion that EMD overcomes the effect of the choice of mother wavelet in wavelet decomposition. They also mentioned that the reason is because of the adaptive sifting procedure used in EMD to identify the basis from same analyzed signal, a posterior approach. This is in contrast with the priori approach used in wavelet decomposition to choose the mother wavelet not from the signal being analyzed.
4. Conclusions
A comparison is made here to verify the performance of Wavelet Decomposition and Empirical Mode Decomposition methods in the process of decomposing tool sound signals obtained from turning process. This study enabled us to summarize their performance on various factors in the form of a table (
Table 1) which will be useful reference for researchers doing research related to decomposition of sound signal. EMD offers a complete, adaptive (because IMFs are data driven) and nearly orthogonal (because there is a residue) signal/data representation. WD also offers a complete and orthogonal (because signal is decomposed to form atomic functions) signal/data representation, however it is non-adaptive because the mother wavelet is chosen in advance (a priori approach). The instantaneous frequency can be determined with high precision by applying Hilbert transform on each IMFs. On the other hand, instantaneous frequency cannot be revealed by applying DWT on the atomic function, it can only be used to perceive the relative change in the frequency content of the original signal. Hence HHT is more suitable than DWT to analyze tool-emitted sound signals received from turning processes. However, implementation of HHT is computationally very expensive because of the much time consumed for the sifting process in the EMD. May be because of this shortcoming and the fact that HHT is younger than DWT, the use of HHT in tool condition monitoring has received slightly less attention among the research community. It is hoped that HHT will be an efficient and promising method in the near future, as the research is going on in reducing the time complexity of the sifting process in the EMD.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Azlina Nor; methodology, Emerson Raja Joseph; software, Thong Leng Lim; validation, Pushpa Rani Mariathangam, Bhuvaneswari Thangavel and Hossen J; formal analysis, Emerson Raja Joseph; investigation, Emerson Raja Joseph.; resources, Emerson Raja Joseph; data curation, Emerson Raja Joseph and Hossen J; writing—original draft preparation, Emerson Raja Joseph.; writing—review and editing, Pushpa Rani Mariathangam; visualization, Pushpa Rani Mariathangam and Bhuvaneswari Thangavel; supervision, Azlina Nor. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.” Please turn to the CRediT taxonomy for the term explanation. Authorship must be limited to those who have contributed substantially to the work reported.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The APC was funded by Multimedia University, Malaysia.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Recording our sincere thanks to Faculty of Engineering and Technology, MMU for allowing us to use the Mechanical lab for data collection.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Agari, S.R.; Lakshmikanthan, A.; Selvan, C.P.; Sekar, K.S.V. Improvement in the Machining Processes by Micro-Textured Tools during the Turning Process. Eng. Proc. 2024, 61, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, S.; Harti, J.I.; Jadhav, P.R.; Selvan, M.C.P.; Vijaysekar, K.S.; Venkatesh, B. Comparative Study on the Effect of Tool Wear on Turning Mild Steel and Stainless Steel with a Ceramic Tool Insert Using Taguchi Method. Eng. Proc. 2024, 61, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming-Chyuan Lu; Elijah Kannatey-Asibu, Jr. Flank Wear and Process Characteristic Effect on System Dynamics in Turning. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering 2004, 126(1), 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.K.; Chu, F.L. Application of the wavelet transform in machine condition monitoring and fault diagnostics: a review with bibliography. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2004, 18, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N. E.; Shen, Z.; Long, S. R.; Wu, M.; L., C.; Shih, H.; H., Zheng, Q.; N., Yen, N., C.; Tung, C.; and. Liu, H. The empirical mode decomposition and the Hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. Proceedings of Royal Society of London Series A: Mathematical Physical and Engineering Sciences 1998, 903-995.
- Hohyub Jeon; Yongchul Jung; Seongjoo Lee; Yunho Jung. Area-Efficient Short-Time Fourier Transform Processor for Time–Frequency Analysis of Non-Stationary Signals. Applied Sciences 2020, 10(20):7208. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.K.; Peter W.; Tse.; Chu F. L. A comparison study of improved Hilbert–Huang transform and wavelet transform: Application to fault diagnosis for rolling bearing. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2005, 19, 974-988.
- Živana B. Jakovljević. Comparative Analysis of Hilbert Huang and Discrete Wavelet Transform in Processing of Signals Obtained from the Cutting Process: An Intermittent Turning Example. FME Transactions 2013, 41, 342-348.
- Yan, R.; Gao, R.X. Hilbert-Huang transform based vibration signal analysis for machine health monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2006, 55, 2320–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- J. Emerson Raja; W.S. Lim; C. Venkataseshaiah; C. Senthilpari; S. Purushothaman. Need for Adaptive Signal Processing Technique for Tool Condition Monitoring in Turning Machines. Asian Journal of Scientific Research 2016, 9(1): 1-12. eISSN: 2077-2076, pISSN: 1992-1454. [CrossRef]
- J. E. Raja; M. N. E. Efzan; J. Hossen; P. Velrajkumar; V Sivaraman. CNN based tool wear classification using emitted AE signal with Empirical Mode Decomposition. Far East Journal of Electronics and Communications 2018, 18(7), 1015-1025. ISSN: 0973-700.
- Peng, Z.K.; Tse, P.W.; Chu, F.L. An improved Hilbert Huang transform and its application in vibration signal analysis. Journal of Sound and Vibration 2005, 286, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalvoda, T.; Hwang, Y.R. A cutter tool monitoring in machining process using Hilbert–Huang transform. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture 2010, 50, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts Stephen; McQuillan A.; Reece Steven; Aigrain S. Astrophysically robust systematics removal using variational inference: application to the first month of Kepler data. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 2013. 435. [CrossRef]
- Graps, A. An introduction to wavelets. IEEE Computational Science & Engineering 1995, 2(2), 50-61.
- Si, X.; Wang, J.; Dong, H.; Xi, J. Data-Driven Discovery of Anomaly-Sensitive Parameters from Uvula Wake Flows Using Wavelet Analyses and Poincaré Maps. Acoustics 2023, 5, 1046–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grobbelaar, M.; Phadikar, S.; Ghaderpour, E.; Struck, A.F.; Sinha, N.; Ghosh, R.; Ahmed, M.Z.I. A Survey on Denoising Techniques of Electroencephalogram Signals Using Wavelet Transform. Signals 2022, 3, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labate D.; Foresta F.L.; Occhiuto G.; Morabito, F.C.; Lay-Ekuakille A.; Vergallo P. Empirical Mode Decomposition vs. Wavelet Decomposition for the Extraction of Respiratory Signal From Single-Channel ECG: A Comparison. IEEE Sensors Journal 2013, 13(7), 2666-2674.
- Zivana Jakovljevic. Comparative Analysis of Hilbert Huang and Discrete Wavelet Transform in Processing of Signals Obtained from the Cutting Process: An Intermittent Turning Example. FME Transactions 2013, 41, 342-348.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).