1. Introduction
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL), is the most frequent cancer on children under 15 years old, with a high incidence between 2 and 5 years. The treatment for this disease has made important progress, which is why the concept of being mortal had changed, now is considered curable. The methotrexate is an important component on the treatment protocols of these patients. It has been proposed that the function of enzymes and transporters involved in the pathway of MTX, may be altered by genetic polymorphisms substantially influence the kinetics and response to therapy with high dose of MTX.
High-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX) plays an significant part in the therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) in many treatment procedures around the world. However, there is a large variability in the pharmacokinetics and toxicity of the drug. [
1] Polymorphisms in the MTX pathway genes influence the kinetics and response to high-dose MTX therapy in childhood ALL.
Acute leukemias are the most common group of cancer in children; where acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) represents the 80 %. Although the etiology is uncertain, there are predisposing factors; as genetic, viral and environmental factors. The clinical manifestations in occasions are produced by the existence of malignant cells in the bone marrow; such as anemia, thrombocytopenia and leukopenia [
1].
The diagnosis is made by morphological, cytogenetic and molecular analysis of the bone marrow aspirate. The treatment takes an average of two years. The expectation of cure for children with ALL has improved exponentially thanks to new drugs and in recent years to a treatment adapted to the risk of patients. Currently, the percentage of cure of patients with ALL is 75 % [
2].
Many studies have been carried out on methotrexate and its application in the treatment of ALL: the researchers of [
3] investigated the influence of the polymorphisms C677T and A1298C on the gene of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) on the toxicity induced by MTX during the treatment of children with ALL.
Performing a regression analysis in patients with ALL, it was found that the ALL subtype was the strongest predictor of MTXPG accumulation, which shows that the genetic variation acquired in the ALL cells themselves had a stronger influence on the accumulation of MTXPG [
4]. Children with ALL who received high doses of MTX in tests, multiple common polymorphisms in SLCO1B1 were associated with MTX clearance [
5,
6,
7].
Authors on [
8,
9,
10] found that variants of the SLC19A1, SLC22A8, MTR and MTHFD1 genes were shown to be associated with the development of acute toxicity after HD-MTX treatment.
Results on [
11,
12,
13] show evidence for the contribution pharmacogenetics to the toxicity of high-dose MTX and plasma MTX concentrations 48 hours after treatment in patients with ALL or non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The influence of MTHFR C677T on MTX-related toxicities and plasma levels were confirmed.
Authors on [
14,
15] found that the TT genotype of the MTHFR gene is associated with an increase in MTX toxicity and the relapse rate. They consider the dose adjustment of MTX in the treatment protocols, depending on the genotype of the patient.
The studies on [
16] identified that the 677TT genotype of the MTHFR gene is associated with decreased clearance of MTX and that genetic polymorphisms in the folate pathway and SLC19A1 were associated with MTX toxicity.
Five variants in four genes (MTHFR, ABCB1, ABCC2, and TYMS) were shown to be associated with toxicity, they also found a statistically significant association between MTHFR rs1801133 and anemia, in the consolidation phase [
17].
By investigating key genes involved in the MTX pathway, authors on [
18] detect genetic polymorphisms associated with MTX pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and outcome. The strongest association was observed between the SLCO1B1 rs4149056 SNP and MTX pharmacokinetic parameters such as, clearance
, and
.
The aim of the study on [
19] was to analyze the influence of genetic polymorphisms in RFC1 (reduced folate carrier), MS (methionine synthase) and MTRR (methionine synthase reductase) on the occurrence of adverse effects from MTX therapy, such as hematological disorders, hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Polymorphisms in genes coding drug-metabolizing enzymes may cause individual differences in the effectiveness and toxicity of many medications including cytostatics.
In ALL [
20], too many stem cells become a type of white blood cell called lymphocyte. These lymphocytes are also called lymphoblasts or leukemic cells. There are three types of lymphocytes: 1)
B lymphocytes: produce antibodies to help fight infections, 2)
Lymphocytes: T Help B lymphocytes generate antibodies that help fight infection. 3)
Natural aggressor cells: attack cancer cells or viruses.
The factors that increase the risk of contracting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you are going to get cancer; And not having a risk factor does not mean that you are not going to get cancer. Possible risk factors for ALL include the following aspects :Having a brother with leukemia, Being exposed to X-rays before birth, Being exposed to radiation, Having had previous treatment with chemotherapy or other medications that weaken the immune system, Having certain genetic disorders such as Down syndrome, The possible signs of childhood ALL include fever and bruising [
21].
MTX is antimetabolic that has anti-proliferative and immunosuppressive activity by competitively inhibiting the enzyme di-hydrofolate reductase (DFR), a key enzyme in the metabolism of folic acid that regulates the amount of intracellular folate available for the synthesis of proteins and acids. nucleic It prevents the formation of tetrahydrofolate necessary for the synthesis of nucleic acids. It catalyzes the reduction of 5,10 methylene tetrahydrofolate to 5 methyl tetrahydrofolate, a form in which endogenous folate circulates, which is the donor of methyl groups necessary for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine during protein synthesis. This mainly affects cells that are in the phase of the cell cycle [
1].
Mucositis is caused by the rapid proliferation of epithelial cells, causing the oropharynx and gastrointestinal tract to be particularly vulnerable to treatment with MTX. The combination of intensive chemotherapy and radiotherapy increases the damage of this drug to the level of the mucous membranes. Many factors are involved in the pathophysiology of mucositis, beginning with damage to connective tissue and blood vessels in the submucosa. This is followed by the release of proinflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species that exacerbate vascular damage and turn the process into a vicious circle that leads to tissue destruction. Bacterial colonization of ulcers increases tissue damage by the inflammation that is generated to control the infection.
MTX poisoning can be avoided in the following way: it should not be administered in patients with renal, hepatic or both deficiency; also those with a pleural effusion or ascites, to avoid plasma concentrations of MTX, these being of predictive value for such toxicity. In addition to constant monitoring to reverse the undesirable effects of the medication.
The article is organized as follows:
Section 2 describes the methodology used for the development of the project, in turn it is divided into subsections that describe the Identification of the problem, the determination of the necessary requirements, the needs analysis, the design of the system, as well as the development and documentation.
Section 3 describes the results obtained from the design and training of the proposed neural network, and is also divided into subsections that present the graphical interface for data recording, the methotrexate validation neural network, as well as the performance results. In
Section 4, the discussion to the research project is addressed. Finally,
Section 5 presents the conclusions of the work.
2. Methodology
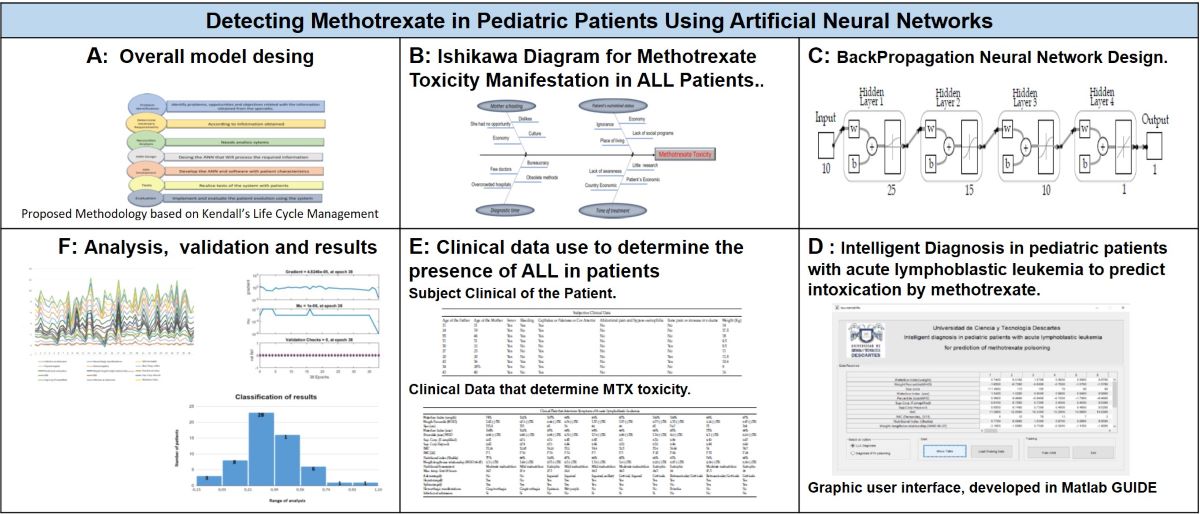
This section present the used methodology for the project development, the analysis is based on the Kendall System Analysis and Design which proposes seven phases, which for our analysis are presented on
Figure 1. The seven phases will be described below.
2.1. Problem Identification
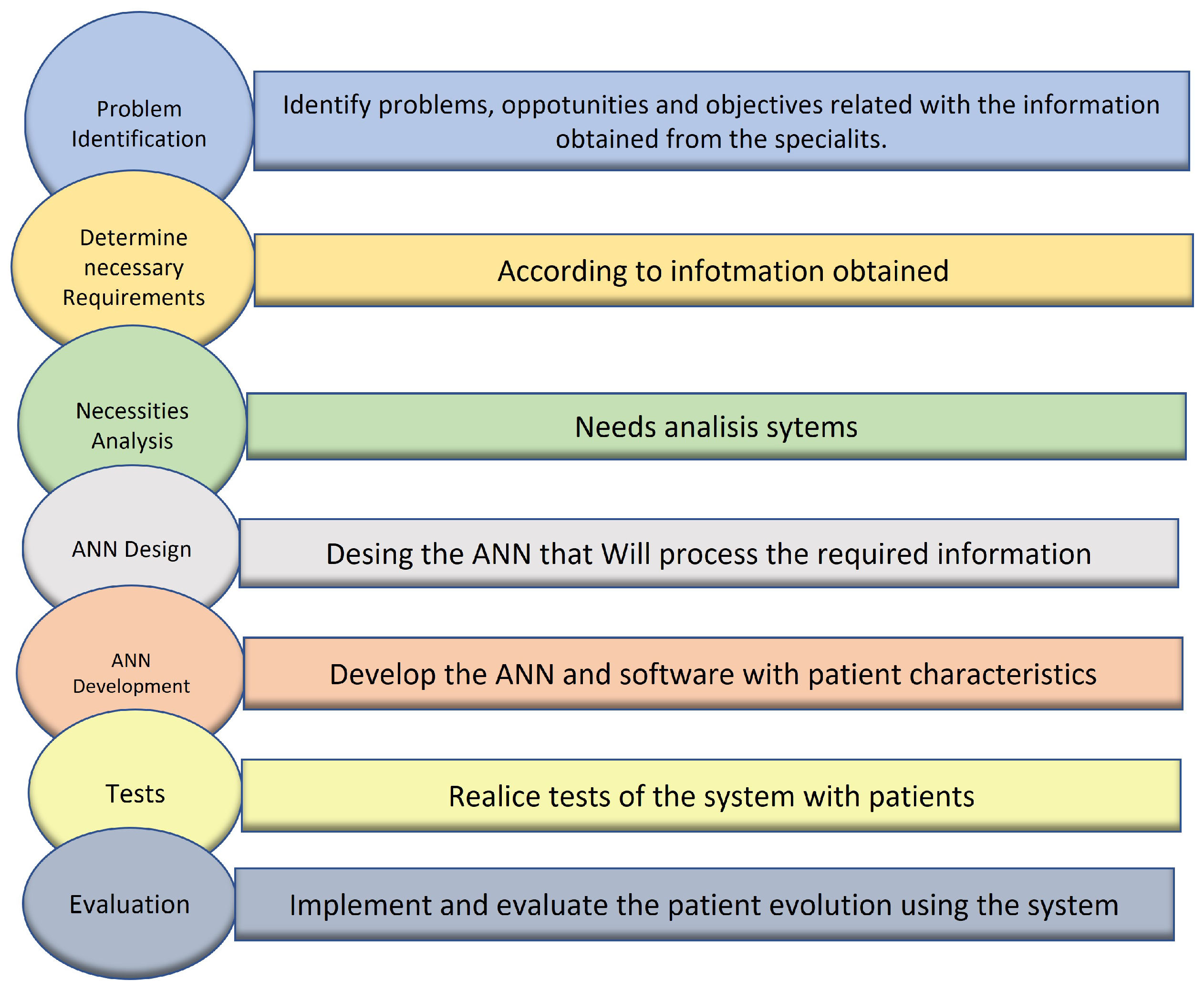
In order to understand the problem´s cause, an analysis through the Ishikawa Diagram (
Figure 2), in which the possible causes of Methotrexate Toxicity Manifestation in Patients with ALL are determined.
2.2. Determine Necessary Requirements
The needs and requirements of the system are determined these were provided by personal of the Regional Center of high specialty of the Hospital of Pediatric Specialties of Tuxtla Gutiérrez. A list of the required patient information is presented;
Table 1 shows the sociodemographic data of the patient admitted to the pediatric hospital,
Table 2 presents the subjective clinical data that oncologists use to determine the presence of ALL in patients, at last
Table 3 shows the objective clinical data that allows to determine the presence of ALL, as well as the manifestation of symptoms for Methotrexate intoxication.
2.3. Necessities Analysis
On this phase the recollected information was concentrated, for analysis. In order to realize the design and training of the network, it was necessary to separate the data that possess specific information. A normalization method was used for all the collected data (
Table 1,
Table 2,
Table 3) to design and train the Neuronal Network.
Table 4 presents the data used: the “Clinical Data Objectives” since to determine the presence of each type of symptomatology, a laboratory study was necessary.
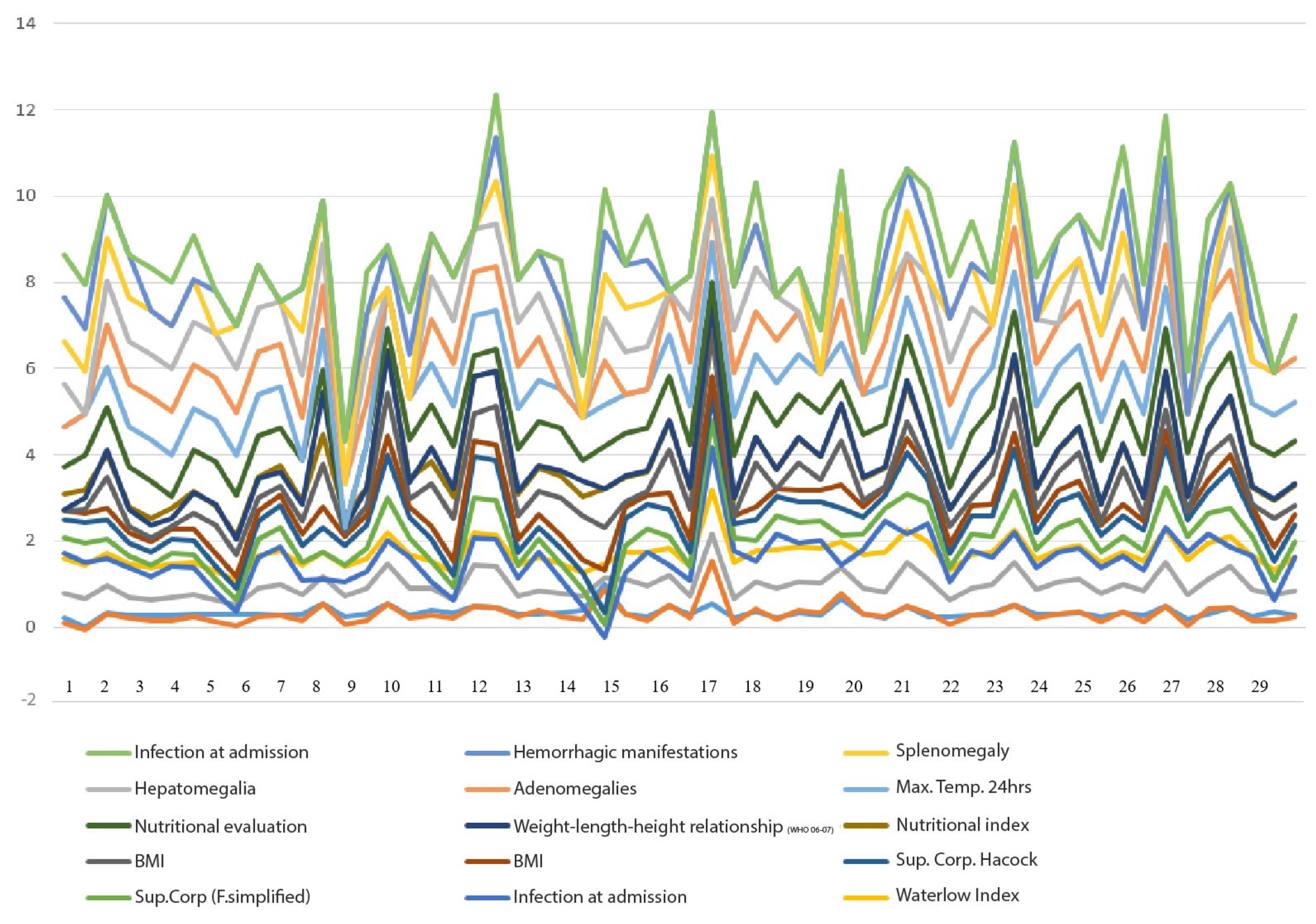
Figure 3 shows the graphs of the patients’ behavior, depending on the amount and the gravity of the symptoms presented.
2.4. System Design
To collect the personal and clinical data of patients, see
Figure 3, admitted to the Tuxtla Gutiérrez Pediatric Hospital, a movil application was designed.
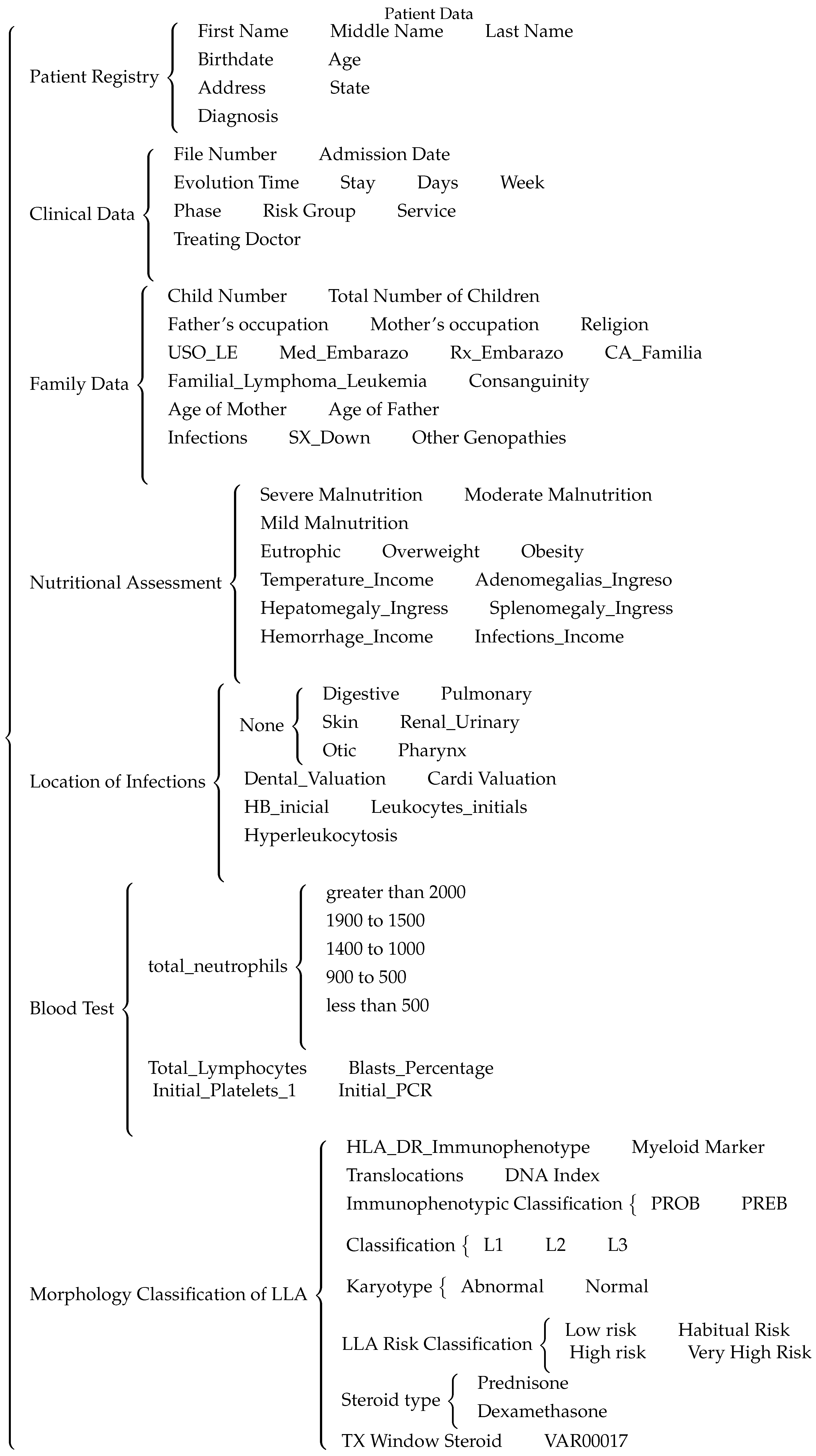
The diagram presented in
Figure 4 shows the different patient data recollected, which are: patient’s registry, clinical data, family data, nutritional values, location of infections, blood analysis and the morphological classification and risk factor of the patient’s ALL.
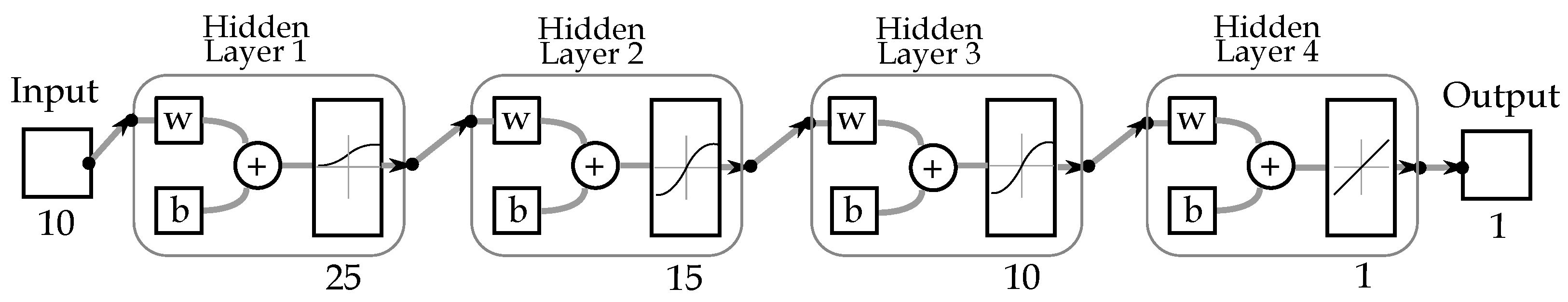
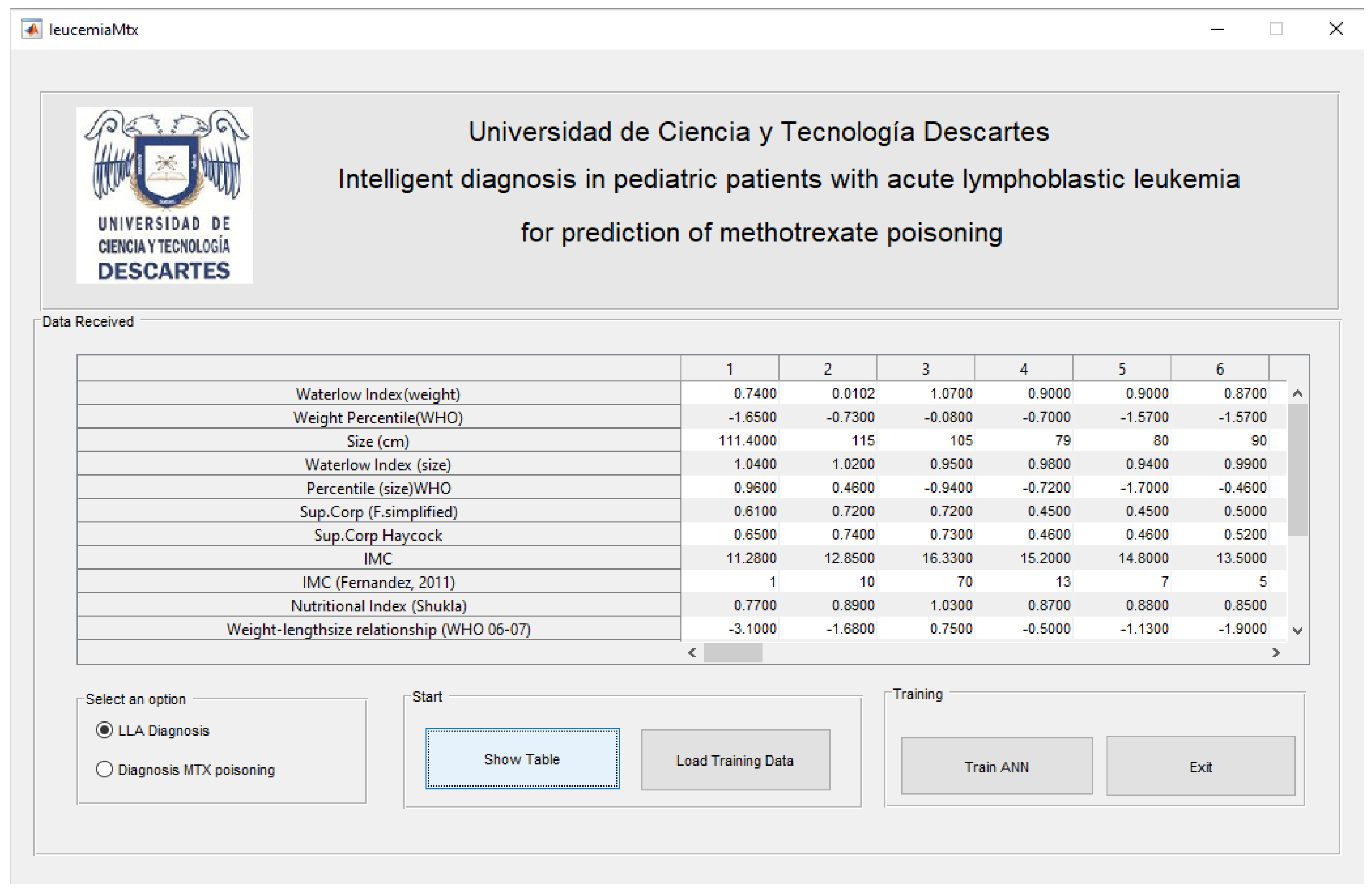
Figure 5 depicts the implemented neural architecture, the network comprises 25 neurons in the initial hidden layer (input layer), 15 and 10 neurons in the subsequent hidden layers, and a single neuron in the output layer (result of data processing). For data collection, we developed a Graphic interface was developed in order to collect the patient data, and train the network, this interface is shown on
Figure 6.
2.5. Development and Documentation
With the patient characteristics, it is possible to know their ALL condition, as well as diagnose the risk of poisoning due to the supply of methotrexate according to the criteria established by the World Health Organization (WHO), and in this case provide a safe alternative for diagnosing ALL; in which traditional methods have not had the desired results. For the Diagnostic System, a Graphical User Interface (GUIDE) programmed in Matlab is used and shown in
Figure 6.
3. Results
This section presents the results of the design and training of the proposed neural network, as well as the tests performed on the graphical interface for the registration of the patient’s personal and clinical data. The analysis of the tests is also presented.
3.1. Graphical Interface for Data Registration
The graphic user interface, developed in Matlab GUIDE (
Figure 6), is divided into four sections. In the first section, the data received is displayed. In the second section, the user can select either the option for the diagnosis of ALL or the option for the diagnosis of intoxication. The third section shows both the data received and the training data. Finally, the fourth section presents the training of the neural network and provides the option to exit the system. It is crucial to highlight that the graphical user interface (GUI) receives the data transmitted by a website and stored in an Excel file.
3.2. Neuronal Methotrexate Validation Network
The previously described BackPropagation Neural Network design comprises 10 input data, four hidden layers of 25, 15, 10 and 1 neurons, respectively (
Figure 5). Once the network had been designed, the mean square error was calculated in order to evaluate its performance. A portion of the neural network training code, which was designed in accordance with the aforementioned specifications, is presented herein:
- (1)
t=xlsread(’baseDatosRnafinal.xlsx’,’Hoja8’,’A3:BG1’);
- (2)
msgbox("Data has been loaded correctly");
- (3)
net=newff(minmax(p),[25,15,10,1], ’logsig’,’tansig’,’tansig’,’purelin’,’trainlm’);
- (4)
net.trainparam.show=10;
- (5)
net.trainparam.lr=0.05;
- (6)
net.trainparam.epochs=50;
- (7)
net.trainparam.goal=1e-5;
- (8)
net=train(net,p,t);
- (9)
net=init(net);
- (10)
net, tr=train(net,p,t);
- (11)
a=sim(net,p);
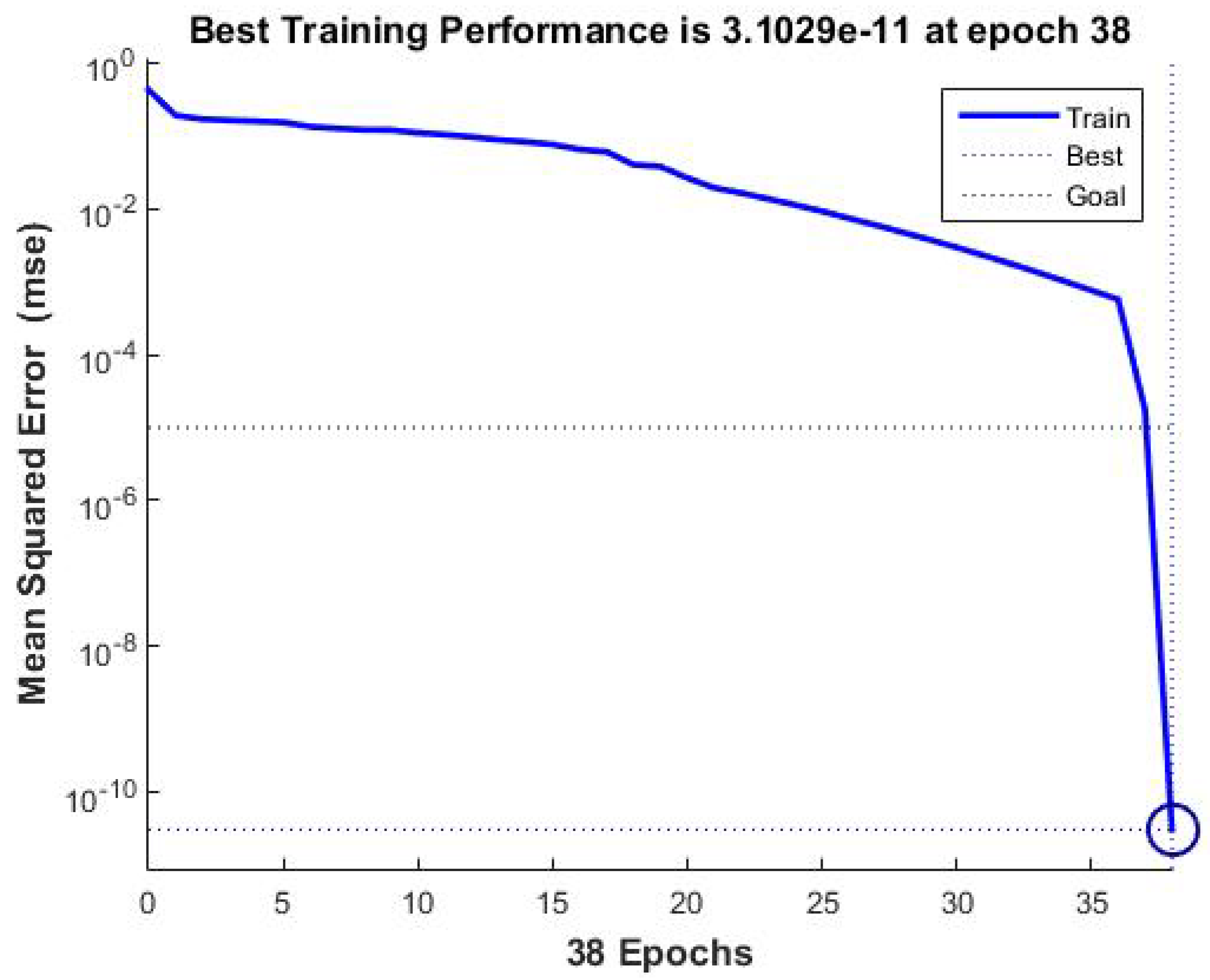
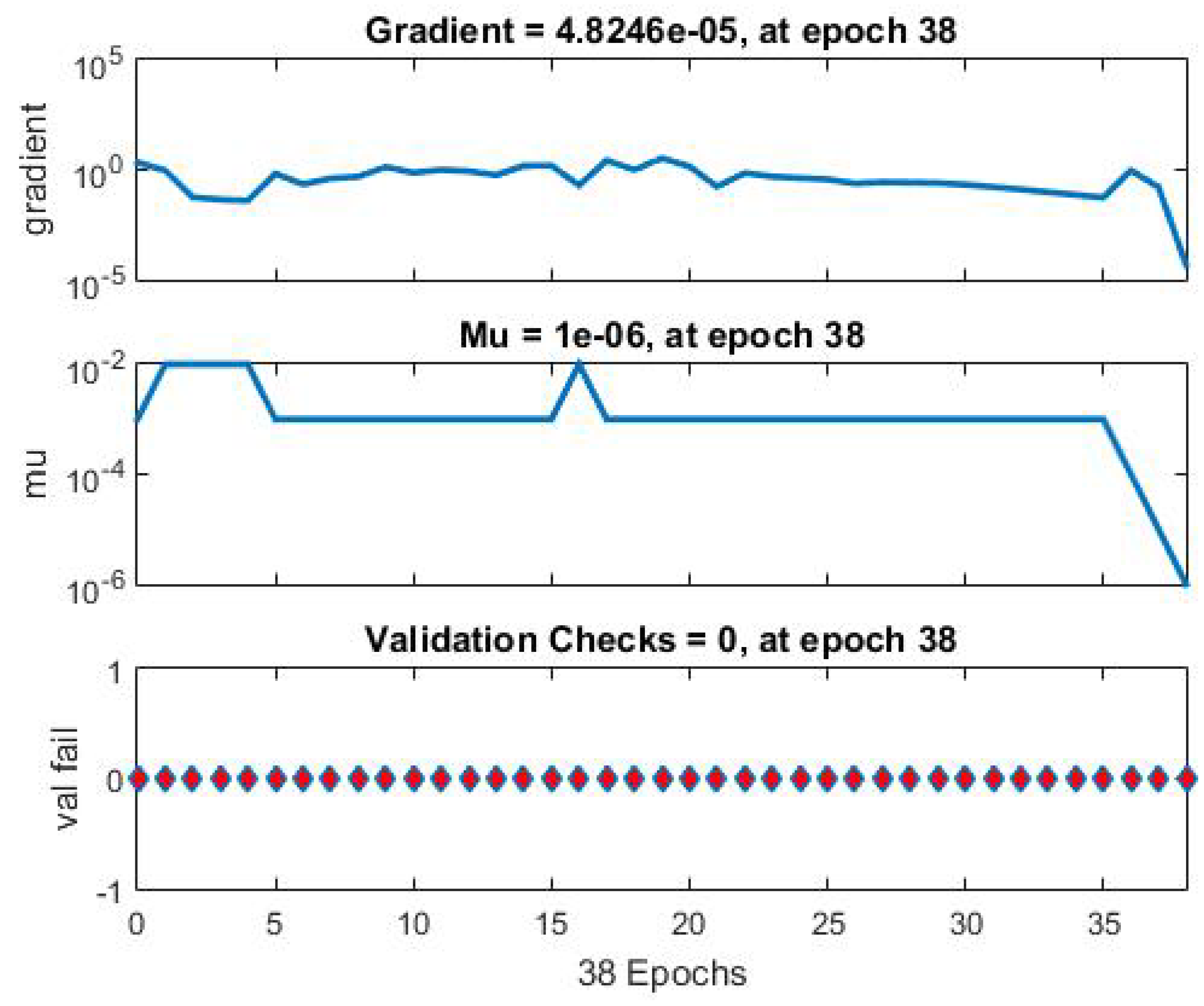
The mean square error was reduced to
after 38 iterations, indicating that the propagation error was effectively eliminated with each iteration. Please refer to
Figure 1 for further details.
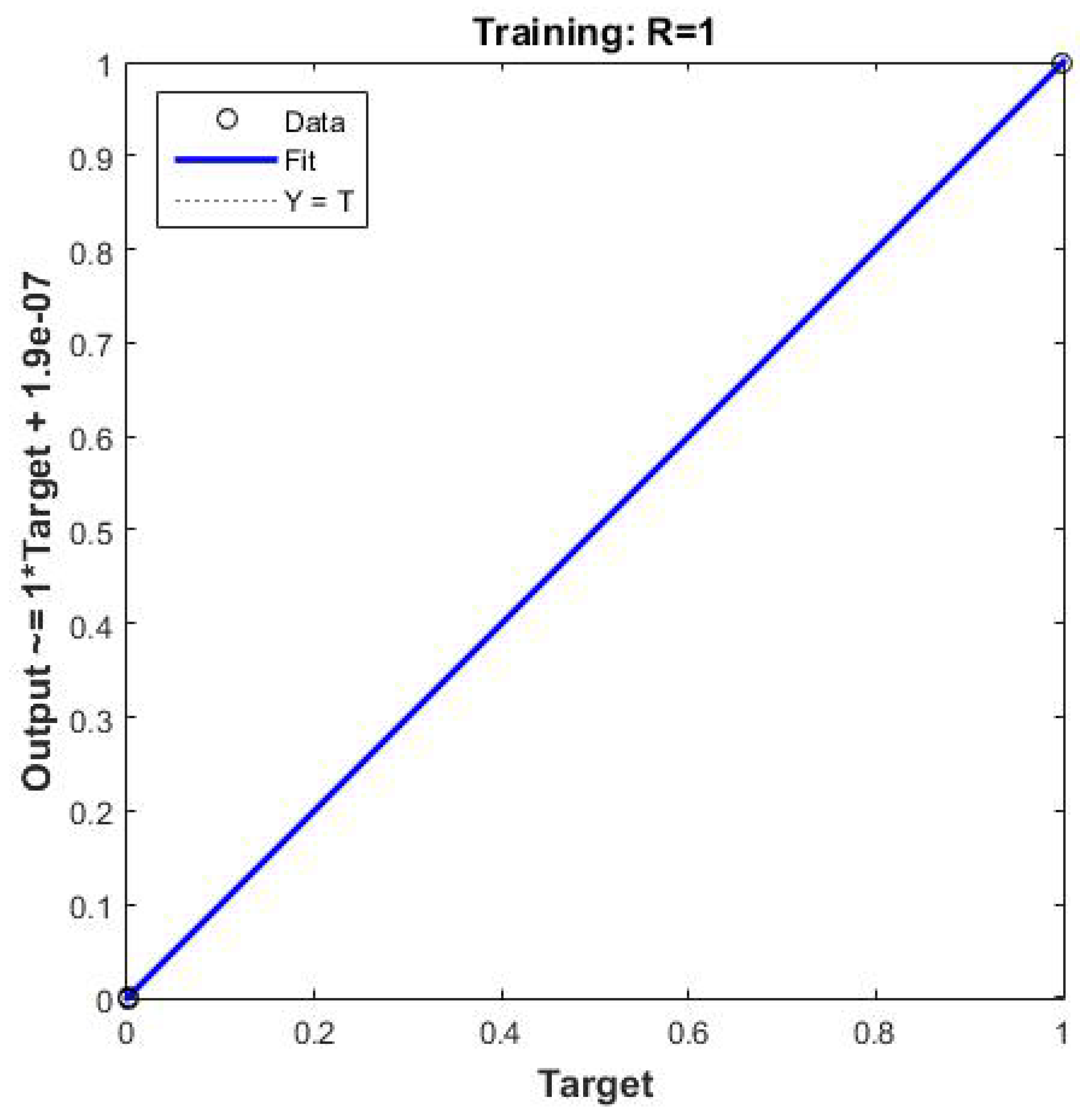
Figure 7,
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 present the mean square error, the learning curve, and the linear regression curve, respectively. The latter indicates the amount of data that moves away from the input data. All data are included in the line of linear regression, indicating that no data loss occurs during the training process.
3.3. Performance Results
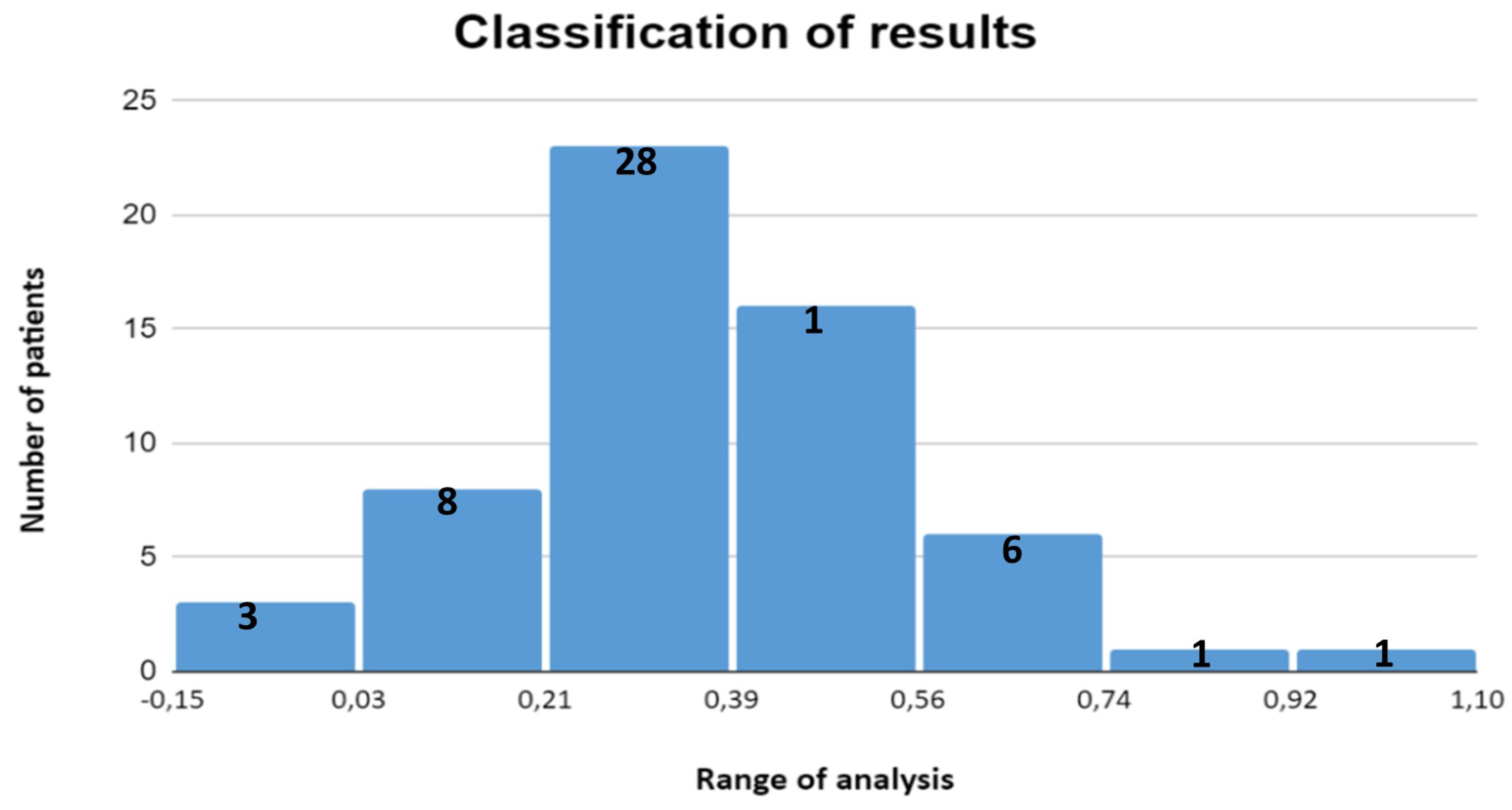
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is a disease that primarily affects children under the age of 15. In this study, a graphical user interface (GUI) was developed to collect data from the patient and his or her family environment, providing a comprehensive view of the patient. The design and implementation of artificial neural network algorithms with supervised training enabled the determination of the levels of toxicity associated with the administration of methotrexate in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia at the Hospital de Alta Especialidad Pediátrica del Estado de Chiapas. In addition, statistical patterns established by the World Health Organization and criteria defined by hospital medical specialists were used. The resulting data are presented in
Figure 10. This allowed for an accurate evaluation of symptoms according to the morphological and risk classification of the disease in each patient. This classification will allow physicians to make decisions regarding necessary safety measures during the first 48 hours following methotrexate administration, which promises to significantly improve treatment follow-up, prevent common complications such as mucositis, and ultimately contribute to increasing patients’ life expectancy. The ability to accurately identify methotrexate levels in patients using this tool can also reduce the costs associated with treatment monitoring by optimizing the management of medical resources and minimizing the need for unnecessary interventions.
4. Discussion
It is possible to create a graphical user interface for data collection of patients under 15 years, this allows to have a complete picture of the current situation of the patient
The development and training of the neural network that contains the information of hospital admissions of the patients, as well as their family data, which allows to determine the toxicity levels in the methotrexate supply, in patients with ALL less than 15 years old as observed in the Learning Curve of
Figure 7, with statistical patterns help World Health Organization or by the doctors themselves. The patient A difference in the pathophysiology of MTX neurotoxicity that is complex, because by inhibiting DFR it increases adenosine and homocysteine. Adenosine dilates cerebral blood vessels, delays the release of neurotransmitters in the pre-synaptic junctions, modifies the response after the synaptic and slows the neuronal discharges manifested by headache, anorexia, vomiting, nausea, arterial hypertension, poisonous, vertigo, aphasia , agitation, lethargy, seizures, sensory depression, and coma. This neurotoxicity is usually associated with an MTX-induced neurotoxicity or renal failure that leads to a poor like this sample as show by [
22].
5. Conclusions
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia is a conditions suffered by children under 15 years old, which treatment has presented substantial progress, to improve the life of children suffering from this disease .
It was possible to design a graphical user interface to collect patients data and family to have a complete vision of the patient’s current situation.
The development and training of the neuronal network allow determining the levels of toxicity by Methotrexate supply in patients with ALL with the help of statistical patterns established by the World Health Organization or by the physicians themselves, allowing access to the symptoms characteristics depending on the morphological and risk classification of the ALL suffered by the patient.
Once this classification is available, it will help the doctor decide the safety measures that must be taken within of the first 48 hours after Methotrexate supply.
This development will help improve the treatment monitoring and prevent frequent complications such as mucositis, as well as increase the life expectancy of patients. It will help reduce costs in the treatment follow-up by identifying the levels of methotrexate in patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; methodology, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; software, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; validation, M.S.A., O.T.J.A., B.R.J.I., G.R.J.A., V.I.J.M. and F.A.G.; formal analysis, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; investigation,M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; resources, M.S.A.; data curation, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; writing—original draft preparation, M.S.A., O.T.J.A. and B.R.J.I.; writing—review and editing, M.S.A., O.T.J.A., B.R.J.I., G.R.J.A., V.I.J.M. and F.A.G.; visualization, M.S.A., O.T.J.A., B.R.J.I., G.R.J.A., V.I.J.M. and F.A.G.; supervision, M.S.A.; project administration, M.S.A.; funding acquisition, M.S.A., O.T.J.A., B.R.J.I., G.R.J.A., V.I.J.M. and F.A.G.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was funded by the authors and some of the institutions where the authors themselves are employed.
Institutional Review Board Statement
"The necessity for ethical review and approval was waived for this study due to the fact that patients had consented to the use of their data and had provided verbal consent to this use. The direct interaction with patients is not a responsibility of our department."
Informed Consent Statement
“Informed verbal consent has been obtained from patients for publication of this article. The direct interaction with patients is not a responsibility of our department.”
Data Availability Statement
“No public involvement in any aspect of this research.”
Acknowledgments
We are infinitely grateful to the patients, patients’ relatives, administrators, researchers, doctors, nurses, technicians and all the direct and indirect actors to carry out this wonderful study, God bless them all and those who are not for the advancement in this life we will always remember them with much love. We extend our gratitude to Dr. Néstor Rodolfo García Chong for his invaluable contributions to the creation of the DataSet, as well as to our former PhD student in Technology Development, Jorge Iván Bermúdez Rodríguez. Life is a paradigm in which the individual may exist in one moment and not in another. It hurts my soul to know that each patient suffers and his family, I ask God for comfort and refuge in his arms.
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflicts of interest.”
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ALL |
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| MTX |
Methotrexate |
| HD-MTX |
High-dose methotrexate |
| C677T |
polymorphisms |
| A129C |
polymorphisms |
| MTHFR |
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase |
| MTXPG |
methotrexate polyglutamates |
| SLCO1B1, SLC19A1, SLC22A8 and MTHFD1 |
genes were shown to be associated with the |
| |
development of acute toxicity after |
| |
HD-MTX treatment |
| MTHFR C677T |
common changes of MTHFR |
| MTHFR, ABCB1, ABCC2, and TYMS |
variants in four genes (MTHFR, ABCB1, ABCC2, and |
| |
TYMS) were shown to be associated with toxicity, |
| |
they also found a statistically significant association |
| |
between MTHFR rs1801133 and anemia, |
| |
in the consolidation phase |
| MTHFR rs1801133 |
Frequency of the c677t polymorphism |
| SLCO1B1 rs4149056 |
polymorphisms |
|
MTX pharmacokinetic parameters |
| RFC1 |
Reduce Folate Carrier |
| MTRR |
Methionine Synthase Reductase |
| DFR |
Enzyme di-hydrofolate reductase |
| ANN |
Artificial Neural Network |
| Matlab GUIDE |
Matlab Graphical User Interface |
| GUIDE |
Graphical User Interface |
| WHO |
World Health Organization (WHO) |
| GUI |
Graphical User Interface |
References
- Jaime-Fagundo, J.C.; Forrellat-Barrios, M.; Arencibia-Núñez, A. Urgencias hematológicas. III. Toxicidad por metotrexato. Revista Cubana de Hematología, Inmunología y Hemoterapia 2012, 28, 246–252. [Google Scholar]
- Lavadenz Pérez, R.S.; et al. Identificación de alteraciones biocelulares en la mucosa oral en pacientes con leucemia linfoblástica aguda post tratamiento poliquimioterápico en el Instituto de Oncohematologia Paolo Belli mediante estudios citológicos. PhD thesis.
- Mandal, P.; Samaddar, S.; Chandra, J.; Parakh, N.; Goel, M. Adverse effects with intravenous methotrexate in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: a retrospective study. Indian Journal of Hematology and Blood Transfusion 2020, 36, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Francia, R.; Crisci, S.; De Monaco, A.; Cafiero, C.; Re, A.; Iaccarino, G.; De Filippi, R.; Frigeri, F.; Corazzelli, G.; Micera, A.; et al. Response and toxicity to cytarabine therapy in leukemia and lymphoma: from dose puzzle to pharmacogenomic biomarkers. Cancers 2021, 13, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpa, V.; Kalinderi, K.; Fidani, L.; Tragiannidis, A. Association of microRNA Polymorphisms with Toxicities Induced by Methotrexate in Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Hematology Reports 2023, 15, 634–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, A. Childhood leukaemia: an update. Paediatrics and Child Health 2016, 26, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y., S. O.Z.Q.e.a. Leukemia incidence trends at the global, regional, and national level between 1990 and 2017. Exp Hematol Oncol 9, 14. [CrossRef]
- Zazuli, Z.; Irham, L.M.; Adikusuma, W.; Sari, N.M. Identification of Potential Treatments for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia through Integrated Genomic Network Analysis. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Henz, P., P. A.G.L.e.a. Population Pharmacokinetic Model of Methotrexate in Brazilian Pediatric Patients with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Pharm Res 2023, 40, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csordas, K.; Lautner-Csorba, O.; Semsei, A.F.; Harnos, A.; Hegyi, M.; Erdelyi, D.J.; Eipel, O.T.; Szalai, C.; Kovacs, G.T. Associations of novel genetic variations in the folate-related and ARID5B genes with the pharmacokinetics and toxicity of high-dose methotrexate in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. British journal of haematology 2017, 166, 410–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan Liao, Jing Nie, X. J.X.J.Y.Z.W.Q.X.H.S.H.P.S.D.Y.S.F.Y.Z.J.L.J.M.; Tang, Y.M. The effect of the plasma methotrexate concentration during high-dose methotrexate therapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia & Lymphoma 2024, 65, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Wu, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, C.; Liu, X.; Hao, F.; Hu, C. Association between high-dose methotrexate-induced toxicity and polymorphisms within methotrexate pathway genes in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min Zhan, Yiqi Sun, F. Z.H.W.Z.C.L.Y.; Li, X. Population pharmacokinetics of methotrexate in paediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and malignant lymphoma. Xenobiotica 2022, 52, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y., H. H.D.L.e.a. Effects of gene polymorphisms on delayed MTX clearance, toxicity, and metabolomic changes after HD-MTX treatment in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Eur J Pediatr. [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, R., K. H.S.J.e.a. Evaluation of cytogenetic and molecular markers with MTX-mediated toxicity in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sheikh, A., Y. A.A.D.e.a. Effects of thymidylate synthase polymorphisms on toxicities associated with high-dose methotrexate in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. [CrossRef]
- Zgheib, N.K.; Akra-Ismail, M.; Aridi, C.; Mahfouz, R.; Abboud, M.R.; Solh, H.; Muwakkit, S.A. Genetic polymorphisms in candidate genes predict increased toxicity with methotrexate therapy in Lebanese children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Pharmacogenetics and genomics 2014, 24, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, S.; Zolk, O.; Renner, B.; Paulides, M.; Zimmermann, M.; Möricke, A.; Stanulla, M.; Schrappe, M.; Langer, T. Germline genetic variations in methotrexate candidate genes are associated with pharmacokinetics, toxicity, and outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2013, 121, 5145–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzielska, E.; Węcławek-Tompol, J.; Matkowska-Kocjan, A.; Chybicka, A. The influence of genetic RFC1, MS and MTHFR polymorphisms on the risk of acute lymphoblastic leukemia relapse in children and the adverse effects of methotrexate. Adv Clin Exp Med 2013, 22, 579–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohar, A.; Frías-Mendivil, M.; Suchil-Bernal, L.; Mora-Macías, T.; Garza, J.G. Descriptive epidemiology of cancer at the Instituto Nacional de Cancerología of Mexico. salud pública de méxico 1997, 39, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, B.; Sánchez, C.; Torres, L.; Sánchez, V. Relevancia de la morfología a través del tiempo en el diagnóstico de la leucemia linfoide aguda. Rev. colomb. cancerol 2006, 10, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Faganel Kotnik, B., G. I.B.G.P.e.a. Association of genetic polymorphism in the folate metabolic pathway with methotrexate pharmacokinetics and toxicity in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and malignant lymphoma. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2011, 67, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).