1. Introduction
Photoreceptor cells do not regenerate in the mammalian retina and therefore the loss of these highly specialized neurons results in irreversible visual deficits. In humans, the dysfunction and death of rod and cone photoreceptors underlies many untreatable forms of blindness, notably including degenerative diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and retinitis pigmentosa (RP) [
1,
2,
3]. Despite recent success treating AMD-associated choroidal neovascularization [
4], the lack of a method to prevent photoreceptor loss continues to hinder efforts to address diseases of this type. Multiple groups have endeavored to solve this problem either through cell replacement or delivery of neurotrophic factors to the diseased microenvironment, and a number of cell-based therapeutic programs have begun clinical testing [
5]. Of these, efforts utilizing subretinal transplantation of pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) into patients with AMD have attracted particular attention. This approach aims to promote photoreceptor survival and function through replacement of diseased RPE underlying the macular region of the retina [
6,
7,
8,
9,
10,
11, NCT01691261; NCT02286089; NCT02590692]. Alternatively, multipotent neural progenitor cells derived from brain or neural retinal tissue have been placed under the macula in either AMD [
12, NCT01632527] or RP [
13, NCT02464436] patients, respectively. Other groups have taken the relatively simpler approach of injecting various cell types of extra-neural origin, most typically bone marrow-derived (e.g., mesenchymal cells or CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors) into the vitreous cavity [
14,
15], or beneath the retina [NCT00458575; NCT01226628], with the goal of eliciting a neurotrophic response.
Clinically, cell-based strategies continue to face challenges, including potential side effects related to product delivery such as perforation and focal detachment of a frail, degenerating retina, achieving meaningful levels of donor cell integration and cell replacement, or sustained delivery of neurotrophic agents. Uncertainties also surround the use of non-ocular donor cells in the eye, including concerns over safety [
15] and whether a reliable benefit can be achieved [
16]. What has not been explored is intravitreal delivery of neural cell types for neuroprotection rather than cell replacement. Such an approach could combine the biological advantages of a homologous cell type with an expedient, less invasive delivery method. Here we show that allogeneic retinal progenitor cells (RPCs) induce photoreceptor rescue when transplanted to the vitreous cavity of the dystrophic Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) rat. These initial findings are then extended to human RPCs using the same model, thus providing preclinical proof-of-concept for the application of this approach in patients with photoreceptor degeneration.
2. Results
Prior work has shown that neural progenitor cells survive as allografts in the rodent eye, specifically within the vitreous, retina, and subretinal space, without the need for immune suppression [
17,
18,
19]. Our initial goal was to establish an allogeneic animal model using the RCS rat in which a defect in the MerTK gene results in photoreceptor degeneration [
20]. Using an RPC line of rat origin, it was first confirmed that the cells expressed the endogenous E1A reporter gene in culture (
Fig 1A), along with the non-specific RPC-associated markers nestin, sox2, vimentin, and Ki-67 (
Fig 1B-E). Analysis using qPCR revealed the expression of multiple cytokines that might exert a neurotrophic influence (
Fig 1F) on photoreceptor cells. Following injection into the vitreous cavity, the dissociated cells displayed a strong tendency to aggregate and the resulting grafts were readily visualized histologically. Clusters of transplanted RPCs were most frequently located near the peripheral retina, adjacent to the injection site. Alternatively, grafted cells were found more centrally within the vitreous or, in some cases, adhering to the vitreal surface of the retina or posterior of the lens. Definitive integration of donor cells into the host neural retina was not observed. After survival times of 6-8 weeks, functional testing demonstrated a positive treatment effect for cells when compared to sham or untreated controls. This was shown first via optomotor testing (
Fig 1G) and then via electroretinography (
Fig 1H). Subsequent histological analysis revealed significant partial rescue of the outer nuclear layer (ONL) of approximately 4 rows of photoreceptor nuclei in RPC-treated eyes (Fig1 JK), as opposed to 1-2 rows in sham-treated (
Fig 1J) and a single broken row in untreated controls (
Fig 1I). Additional evidence of anatomical preservation came from examination of the outer plexiform layer (OPL), where photoreceptor cell bodies make synaptic contact with second order neurons. Cell-treated eyes showed improved OPL thickness compared to controls (Fig1L-Q) and this finding was evident before ONL preservation became apparent.
The above support for the use of intravitreal RPCs as an allogeneic cell-based treatment for photoreceptor degeneration motivated the development of analogous human RPCs (hRPCs), suitable for use in clinical trials. These hRPCs were derived by the authors under GMP-compatible conditions at the University of California, Davis. In culture, the cells adhered to fibronectin-coated flasks while exhibiting the characteristic morphology (
Fig 2A). Immunocytochemistry confirmed expression of the known RPC markers nestin, vimentin, sox2, and Ki-67 (
Fig 2B-E), consistent with the rat cells above, as well as SSEA-1 (CD15) and GD2 ganglioside (
Fig 2F,G), as previously reported for human RPCs[
21]. Microarray analysis showed that the global transcriptome of cultured hRPCs clearly segregated from fetal retinal tissue (i.e., source material), autologous fibroblasts, and an allogeneic retinoblastoma cell line (
Fig 2H). qPRC confirmed that RPCs could also be distinguished from these other cells based on differential expression of selected genes (
Fig 2I). Flow cytometry was used to evaluate expression of selected surface and cytoplasmic markers. Specifically, the cells were shown to co-express nestin and sox2, as well as class I but not class II MHC antigens (
Fig 2J). Because transfer to the microenvironment of the vitreous cavity may result in phenotypic changes in donor cells, growth factor withdrawal was used to examine the baseline propensity towards cellular differentiation in culture. This resulted in differentiation of RPCs along either glial or neuronal lineages, with the former evidenced by elevated expression of GFAP (
Fig 2K) in a subset of cells. Low passage cells maintained a normal karyotype (
Fig 2L), confirmed with FISH (
Fig 2M), and did not express elevated levels of telomerase, consistent with their status as non-immortal progenitor cells (
Fig 2N).
We next tested the efficacy of human cells in the RCS rat model. Human-to-rat xenografts (hRPCs) were viable for brief periods (<2 weeks) in the vitreous cavity without immune modulation (
Fig 3A), however, the use of an immunosuppressive regimen was necessary to evaluate potential therapeutic effect at longer time points [
22]. With immune suppression, hRPCs survived out to the P90 endpoint (approx. 68 days post-transplantation). Donor cells typically formed spherical cellular aggregates in the vitreous (
Fig 3A,C), although they could also be found adhering to surrounding structures, including the retina and posterior lens capsule (
Fig 3B,D). Cells within the grafts expressed the retinal progenitor-associated markers nestin, vimentin and Ki-67, or neuronal or glial lineage markers such as DCX, NeuN, recoverin, or GFAP, indicative of ongoing differentiation (
Fig 3B-D). Host RCS retinas showed an hRPC-associated treatment effect, with increased survival of both rods and cones (
Fig 3E,F) and quantified as increased number of nuclear profiles present in the outer nuclear layer (ONL) of hRPC-treated versus sham (P>0.05) (
Fig 3G). The visually-mediated optomotor response (OR), as measured in awake, unrestrained RCS rats showed evidence of improved spatial resolution over control animals, both untreated and sham (
Fig 3H). Cell-treated eyes also showed improved ERG responses over a variety of stimulus conditions and range of in-life time points (
Fig 3I-K).
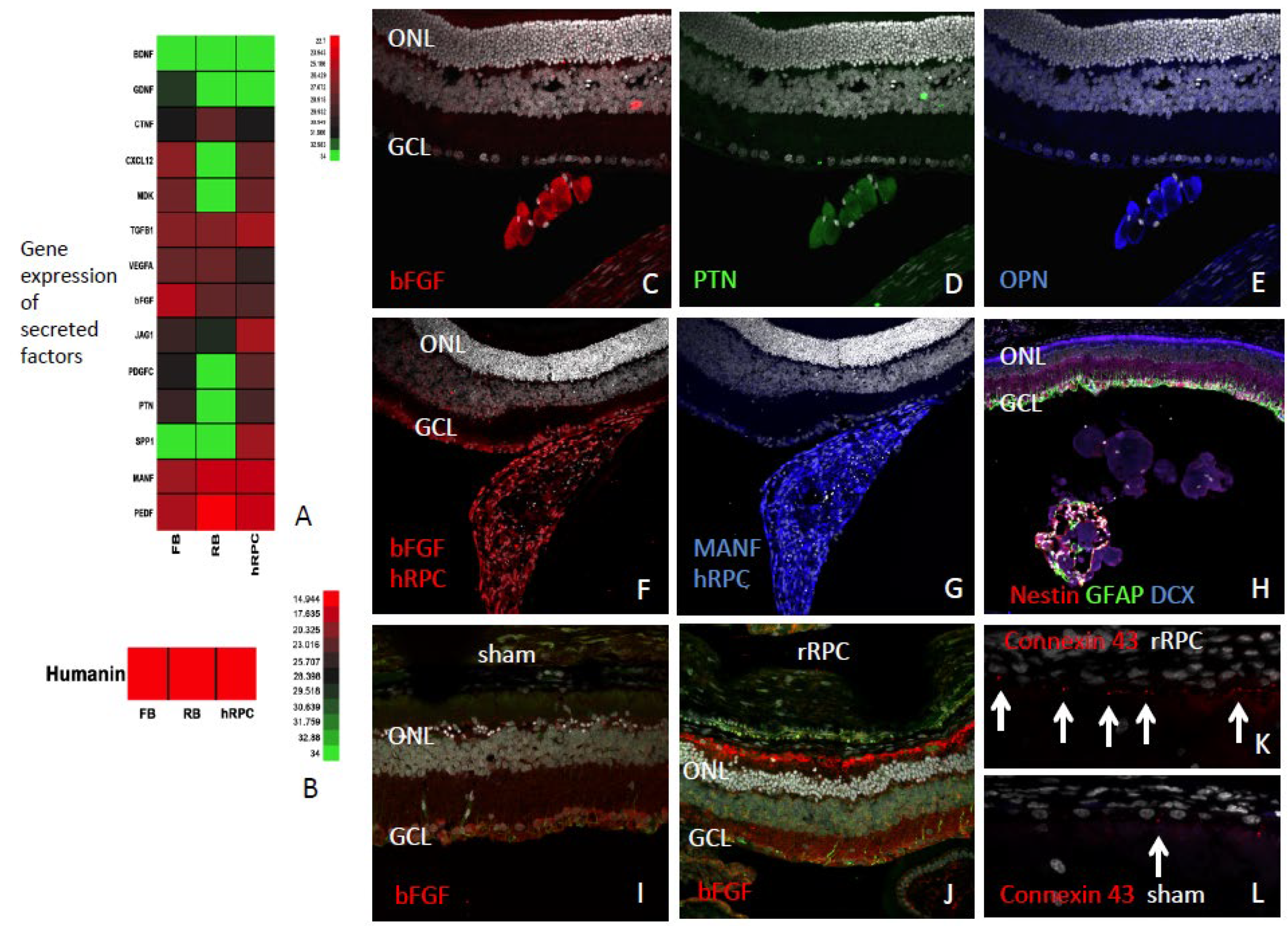
To better understand RPC-associated treatment effects, factors produced by the cells were investigated, as well as host cellular responses. Compared to retinoblastoma cells or fibroblasts, one factor preferentially expressed by RPCs was osteopontin (OPN), also known as SPP1 (
Fig 4A). Other factors expressed at high levels were PEDF, MANF, JAG1, and TGF beta1. Additional factors expressed by hRPCs included pleiotrophin (PTN), platelet derived growth factor-C (PDGFC), basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), midkine (MDK) and CXCL12. The established neurotrophic factors BDNF and GDNF did not appear to be expressed by hRPCs in culture, whereas the novel cytoprotective candidate humanin was (
Fig 4B). Following transplantation to the eye, hRPCs maintained expression of factors, including bFGF, PTN, OPN, and MANF as demonstrated by IHC (
Fig 4C-G). Donor cells were labeled with either immature or lineage markers, indicative of progressive differentiation within the grafts (
Fig 4H).
Examination of host retinas revealed a variety of treatment-related responses among local cell types. Labeling for bFGF was localized to photoreceptors and, more specifically, appeared to correspond to the region of outer segments (
Fig 4I,J). The loss of connexin 43 by RPE cells, associated with the dytrophic process, was less pronounced in RPC-treated eyes (
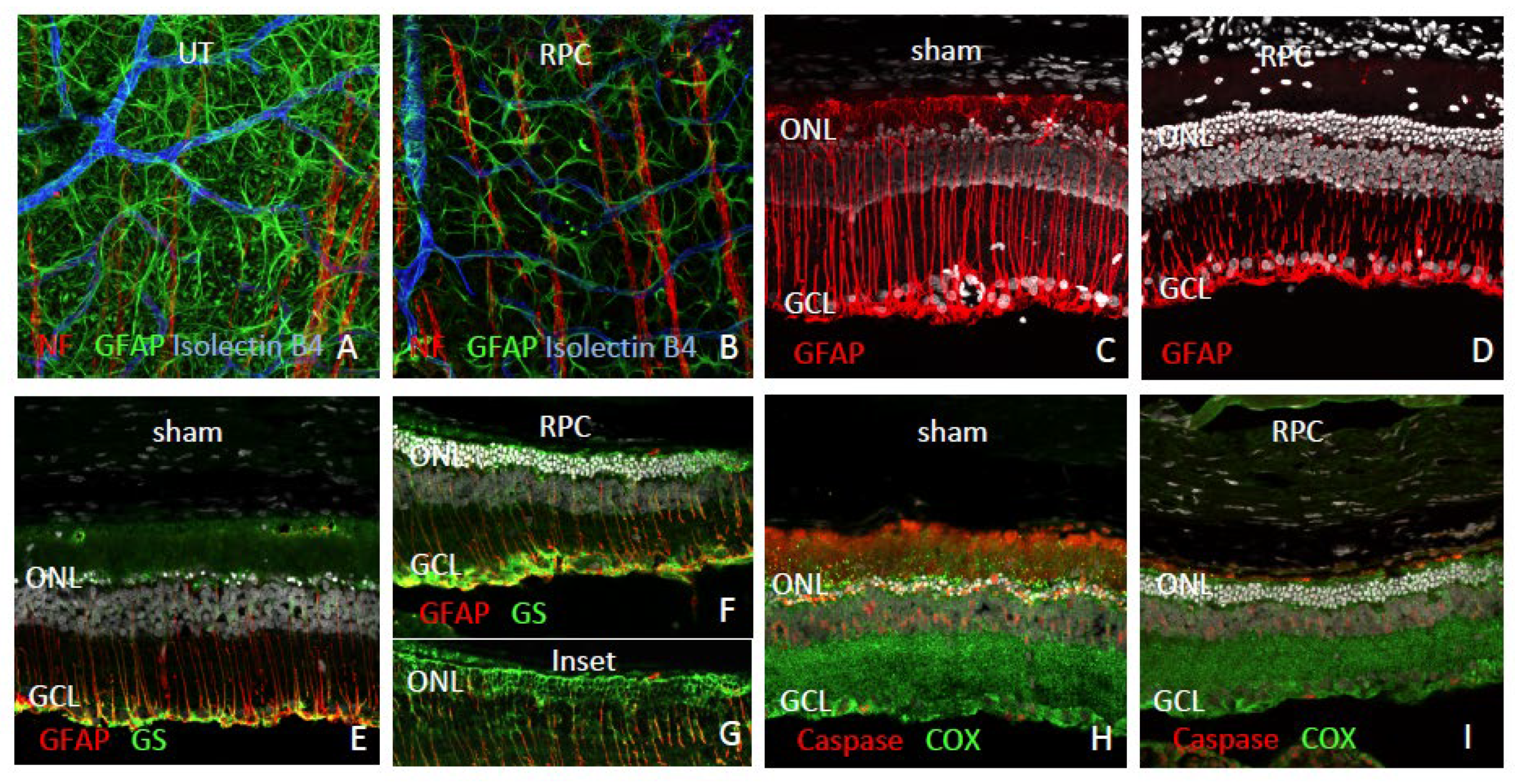
Fig 4K,L). The characteristic upregulation of GFAP by hypertrophic Mueller cells and astrocytes in the degenerating RCS retina, was also reduced in RPC-treated eyes, as viewed en face via wholemounts (
Fig 5A,B) or via cross-sections (
Fig 5C-G). Compartmentalization of molecular response within Mueller cells was particularly evident for glutamine synthetase, with heavy labeling restricted to the outer retina adjacent to photoreceptor cell bodies (ONL) in RPC-treated eyes (
Fig 5D-G). Caspase, a marker of apoptosis, was diminished in RPC-treated retinas and elevated in shams (
Fig 5H,I), along with regional alterations in cytochrome oxidase expression suggesting changing metabolic activity in response to altered function demands.
3. Discussion
Here we show that intravitreal transplantation of unmodified retinal progenitor cells results in photoreceptor preservation and amelioration of functional deficits associated with a rod-cone dystrophy, as assessed by multiple measures. The RPC-based treatment effect was first demonstrated by transplanting allogeneic rat cells and then replicated using the analogous human cells, paving the way for translation of this approach to the clinic. The transplanted cells were well tolerated in the vitreous cavity, with or without systemic immune suppression (for xenogeneic and allogeneic models, respectively), and survived for a prolonged period, either as free-floating clusters in the vitreous cavity or adhering non-invasively to surrounding intraocular structures.
These results differ from previous studies in that immature retinal cells were used to implement a neuroprotective strategy rather than replace host photoreceptor cells. Consequently, a relatively simple intravitreal placement was sufficient to achieve therapeutic efficacy. This is notable for a number of reasons. First, most prior work in the RCS rat has focused on subretinal implantation of cells, particularly RPE cells, with the goal of local cell replacement. Subretinal injection, however, is itself associated with a notable sham effect in the RCS rat [
23]. The use of sham controls is therefore critical in this model [
24], but false positives due to sham effect remain a concern when interpreting rescue data following any subretinal intervention. In contrast, the sham effect associated with intravitreal injection is marginal in comparison. Furthermore, intravitreal injection is less technically demanding than subretinal placement, thereby facilitating clinical implementation of this approach.
Intravitreal RPC grafts remained avascular and no angiogenic response was observed in the host eyes. RPCs were well tolerated as allografts, whereas immune suppression was required for sustained survival of human-to-rat xenografts despite concerns this might diminish functional responses in RCS eyes [
22]. We have observed previously that introduction of RPCs induces a host microglial/macrophage response, that this reaction is graft-directed but relatively mild, and that it subsides over time and is not associated with disruption of host retinal architecture [
25]. Here we confirm that the RPC treatment effect was evident in both allograft and xenograft models, regardless of immune modulation. The retinas of host animals showed preservation of not only the outer nuclear layer (ONL) but also the adjacent outer plexiform layer (OPL), where photoreceptor cells synapse onto second order neurons. Preservation of the OPL appears to provide a relatively early anatomic marker of efficacy. An early functional indication of efficacy was relative preservation of ERG response in RPC-treated animals. RPCs are endogenous to the retina and thus might be expected to exhibit an enhanced safety profile over ectopic cell types, particularly those associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition and myofibroblastic transformation. Cells assuming such contractile properties are associated with retinal traction, retinal detachment, and proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR). In contrast, intravitreal RPCs were not observed to exert tractional forces on the retina in this study.
The photoreceptor rescue associated with non-integrated, intravitreal RPCs is consistent with a diffusible trophic effect and in fact the cells elaborate a range of factors with potential neurotrophic activity. Basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) is known to have trophic effects in the RCS retina [
26]. Osteopontin (OPN) has previously been linked to macrophage chemotaxis [
27], as well as retinal ganglion cell [
28] and photoreceptor rescue [
29], in addition to its non-ocular role as a bone-associated extracellular protein. Midkine family member pleiotrophin is known to be expressed by neural cells [
30], as is midkine itself, and the latter has been associated with photoreceptor rescue [
31]. Additional factors expressed by hRPCs include MANF [
32], PEDF [
33], and humanin [
34].
In addition to preservation of photoreceptor cells, including features of the outer segment and synaptic layers, response to RPC treatment was also seen in the non-neuronal cells of the retina. Such responses included relative normalization of morphology and gene expression levels, as seen with connexin 43 in RPE and GFAP in Mueller cells and astrocytes.
Viewed as a delivery system, a cell-based approach has the potential for sustained release, as well as the potential for modulated expression of multiple factors based on interaction with the diseased tissue [
2]. From a clinical standpoint, intravitreal delivery lends itself to re-dosing of patients in a way that subretinal delivery does not.
Taken together, the advantages exhibited by this combination of cell type and delivery method serve to facilitate clinical administration. The proof-of-principle data, together with formal toxicology studies and clinical protocol, contributed to opening an IND with the FDA and initial clinical trials in late stage retinitis pigmentosa (RP) have been undertaken (NCT02320812; NCT03073733). It will therefore soon be possible to evaluate findings from the animal studies presented here in light of data obtained from patients with RP.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
Rat RPCs (R28) were purchased from Kerafast (Boston, MA) cultured in DMEM (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) supplemented with 10% FBS, 1% MEM non-essential amino acids, 1% MEM vitamins, 1% GlutaMax-I (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD) as described in the product sheet.
Human RPCs were originally derived from fetal tissue and cryopreserved at low passage number. Cells were later thawed as needed and cultured on fibronectin coated flasks in Advanced DMEM/F12 suppled with 1x GlutaMax-I CTS, 1% N2 supplement CTS, 20ng/ml EGF, 20ng/ml FGF-basic CTS (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD) for 2 days for all experiments with medium changed one day after thawing. Medium was collected 2 days after cells thawed (one day after medium changed) with exact hours of growing and number of cells in the flask recorded for secreted protein amount calculation in ELISA assays.
Cells used for transplantation were harvested with TrypLE (Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD) and formulated in BSS PLUS Irrigating solution (Alcon Laboratories, Fort Worth, TX) to the desired concentration right before transplantation. Cell number and viability were re-assessed after completing surgery. The cell number was consistently within 20% of the final dosing concentration and the viability was >85% after transplantation.
Approval for use of human cells was obtained from human stem cell research oversight (hSCRO) committee, and proposed use was reviewed by Institutional Review Board (IRB).
4.2. RNA Extraction
Total RNA was extracted from cells or retinas and processed using either an RNeasy Mini Kit or an AllPrep DNA/RNA/Protein Mini Kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) following the manufacturer’s instructions. DNase I was added in process to eliminate traces of genomic DNA. RNA was quantified via spectrophotometer (ND-1000; NanoDrop Technologies Inc., Wilmington, DE) for optical density (OD) absorption ratio OD260 nm/OD280 nm 2.00–2.10, OD260 nm/OD230 nm 2.00–2.20.
4.3. Microarray Analysis
Results from microarray chips were normalized using the sketch-quantile method (Expression Console™ ver.1.1 software, Affymetrix). Microarray analysis was performed in JMP Genomics (SAS Americas, Cary, NC) using a one-way ANOVA, and statistical significance was established by setting the False Discovery rate threshold to α<0.05[
35]. Principal component analysis (PCA) plots were generated in JMP Genomics as part of the analysis. Individual gene expression changes were considered functionally significant for fold change >|±2-fold| and α<0.05.
4.4. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction Assay
Two micrograms of total RNA was reverse transcribed with an Omniscript RT kit (Qiagen, Valencia, CA) and 10 µM random primers (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Real-time PCR was performed using a ViiA 7 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). 2x TaqMan Gene Expression Master Mix and TaqMan® Gene Expression Assays (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA) were used for qPCR reaction and each reaction was performed in triplicate. Graphs were plotted, and analysis was performed with the ΔΔCt method (QuantStudio™ Real-Time PCR Software and DataAssist 3.01, Applied Biosystems) or JMP Genomic software (SAS Americas, Cary, NC). All data points are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). TaqMan Gene Expression assays used in this study are listed in
Table 1.
4.5. Immunocytochemistry
Cells were plated and grown on four-well chamber slides for 48 hours, then fixed for 20 min in 4% paraformaldehyde, and washed three times with DPBS, followed by permeabilizing and blocking with blocking buffer (0.3% Triton X-100 and 5% donkey serum) for 1 hour at room temperature, followed by another DPBS wash. Primary antibodies was prepared in antibody buffer (0.3% Triton X-100 and 1% donkey serum) and incubated with cells overnight at 4oC. After washing with DPBS, cells were incubated with anti-mouse Alex Fluor 546 secondary antibody (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Carlsbad, CA) for 1 hour at room temperature in dark, followed by several DPBS washings. The chamber slides was mounted with VECTASHIELD antifade mounting medium with DAPI (Vector laboratories, Burlingame, CA) and images were acquired with a Nikon Ti microscope, NIS-elements viewer and analyzed by Image J software. ImageJ is a free Java-based image processing platform developed by the National Institute of Health (
http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/). Antibody controls were processed identically, except that incubation with primary antibody was eliminated. Primary antibodies used in this study are: Adenovirus type 2 E1A (M73, Abcam, Cambridge, MA), Ki-67 (B56), Nestin (25/NESTIN), Sox2 (030-678) (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA), Vimentin (V9, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO), GD2 (14.G2a, Millipore, Temecula, CA). Percentage positive profiles were calculated by counting those profiles expressing specific immunoreactivity divided by the cells identified by DAPI staining in 10-11 randomly selected fields.
4.6. FACS
hRPCs were trypsinized to single cell suspension 48 hours after thawing, with medium changed 24 hours after thawing. For Sox2, Ki67, Nestin and GFAP staining, cells were fixed with fixation buffer and permeabilized with PERM Buffer III (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA) before staining. Following centrifugation and supernatant removal, antibodies were added to the cells and incubated in the dark for 30-60min. After several washes, cells were analyzed on BD FACSAria II flow cytometer and the data plotted using FlowJo software (FlowJo, LLC, Ashland, OR). Unstained and isotype stained controls were included in all samples. The antibodies used were anti-Nestin (25/NESTIN), anti-Sox2 (030-678), anti-Ki-67 (B56), anti-GFAP (1B4), anti-Human HLA-ABC (G46-2.6) an anti-Human HLA-DR, DP, DQ (Tu39) and their corresponding isotype controls (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
4.7. ELISA
Media collected 2 days after hRPC thawing (1 day after medium changed) was used to measure hRPC OPN and FGF-basic secretion. OPN and FGF-basic levels were measured by Human Osteopontin OPN Quantikine ELISA kit and Human FGF basic Quantikine ELISA kit (R&D systems, Minneapolis, MN) following manufacturer’s instructions. OD450 and OD540 were detected on BioTek Synergy HT microplate reader (Winooski, VT). To create a standard curve, CurveExpert software (Hyams Development) was used to generate a best fit curve through the standard points. All samples were performed in triplicate.
4.8. Animals
Dystrophic Royal College of Surgeons (RCS) rats (rdy+ p+) were used for this study. All animals were pigmented with the brown-eyed, dark-hooded RCS phenotype. The rats were bred in a colony at the University of California, Irvine, and maintained under a 12 hr light/dark cycle (maximum 7.7 lux at cage level) and fed a Teklad irradiated standard diet, Harlan #292. Animals were housed and handled in adherence with guidelines set forth by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of California, Irvine. To mimic the baseline conditions under which rats are evaluated following treatment with xenografted cell therapeutics, selected litters of RCS rats received daily dexamethasone injections (1.6 mg/kg i.p.) for a period of 2 weeks starting at the age of weaning (P21) and were also maintained on cyclosporine-A (Bedford Labs) administered in the drinking water (210 mg/l) from weaning age until the time of euthanasia. All procedures were carried out in accordance with the ARVO Statement for the Use of Animals in Ophthalmic and Vision Research.
4.9. Transplantation
Animals were anesthetized via IP injection of ketamine (30mg/kg) and dexmedetomidine (0.1 mg/kg). A 2 µl aqueous solution of either vehicle (balanced salt solution: BSS PLUS) or cell suspension containing low/medium/high/extra high dose of hRPC was injected into the vitreous cavity at age P21-P22. After surgery, atipamezole (1.0 mg/kg) was given IP. Animals were returned to cage with soft food.
4.10. Optomotor response (OR) threshold
Visual acuity was measured based on spatial frequency discrimination, tested at P45, P60 and P90 using an Optomotry testing apparatus (Cerebral Mechanics). Using testing protocol established by Douglas, et al.[
36], rats were placed inside the Optomotry apparatus and their response was measure for both the clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Acuity was quantified by increasing the spatial frequency of the grating using a staircase progression until the reflexive head movements ceased, thereby obtaining a maximum threshold.
4.11. Electroretinography (ERG)
Animals were evaluated by full-field electroretinography (ERG) using a Ganzfeld stimulator at three different time points: P45, P60, and P90. All animals were dark adapted overnight (>12 h) and all testing was done under a dim red light. Before the test, each animal’s eye was dilated with 1 drop each of topical Tropicamide 1% ophthalmic solution (Bausch & Lomb) and Phenylephrine 2.5% ophthalmic solution (Akorn), and animals were then anesthetized by intraperitoneal injection using a combination of Ketamine 70 mg/kg (Mylan Institutional Galway) and Xylazine 3.5 mg/kg (Akorn or equivalent). Animals were placed on a heated platform (37°C) to maintain a constant body temperature during the ERG test. ERGs were recorded from both eyes simultaneously using gold wire loops placed on each cornea, with a drop of methylcellulose applied to the corneal surface. A stainless steel needle electrode (Rhythmlink) was placed subdermally at the base of the tail as ground, and stainless steel needle electrode was placed subdermally in the ventral midline of the chin as the reference. Measurements were performed using an Espion e3 recording unit coupled to the ColorDome Ganzfeld LED stimulator (Diagnosys LLC). The protocol included scotopic flash light intensities of 0.5 and 5 cds/m2, a photopic flash light intensity of 50 cds/m2 after 10 min of light adaptation, and 30 Hz photopic flicker at an intensity of 25 cds/m2 (background of 30 cds/m2).
4.12. Histology
The terminal endpoint was age P90-P100, i.e., Day 69-79 post injection. Rats were humanely euthanized by CO2 asphyxiation. Eyes were enucleated and fixed either in Davidson's solution for paraffin embedding process or in 0.1M cacodylate buffered 4% paraformaldehyde for cryo-embedding process for 48 hours at 4oC, then embedded either in paraffin (Polysciences) or in O.C.T. Compound (Fisher), respectively. For each eye, sagittal sections of 5 μm-thickness (paraffin embedded samples) or 10 μm-thickness (O.C.T. embedded-samples) were cut from nasal to lateral side of the glove and every 5th slides were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). All stained slides were examined under Nikon SMZ25 stereomicroscope (Nikon, Japan) and selected slides from the peri-optic nerve area were imaged using a Nikon Eclipse Ti-inverted research microscope (Nikon, Japan) for morphological evaluation of retinal architecture and outer nuclear layer (ONL) thickness.
4.13. IHC
For hRPC-treated eyes, human-specific marker (STEM121) was used to evaluate donor cell survival and engraftment. Specific markers including the neural progenitor marker nestin, proliferation markers Ki-67 or PNCA, neural lineage markers such as DCX or MAP2 or recoverin or opsin, and glial lineage marker GFAP can be used for evaluation of cell fate of surviving donor cells. The markers Isolectin B4 and Iba1 were used to evaluate host immune response to the grafted cells.
4.14. Statistics
ERG and OR results were analyzed in JMP (SAS Americas, Cary, NC) using a Student’s T-test.
Microarray analysis was performed in JMP Genomics (SAS Americas, Cary, NC) using a one-way ANOVA and setting the False Discovery rate to α<0.05[
35].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F., H.K.; Methodology, J.Y., G.L., S.F., H.K.; Formal analysis, J.Y., G.L.; Investigation, J.Y., C.H., S.M., G.L., W.C., N.T.; Supervision, S.F., H.K.; Writing – original draft preparation, S.F., H.K.; writing – review and editing, S.F. H.K.
Figure 1.
Allogeneic RPCs ameliorate degeneration in RCS rats. (a-e) Rat-derived RPCs labeled for E1A reporter gene (red) (a), nestin (b), sox2 (c), Ki-67 (d), and vimentin (e) (DAPI = blue). (f) Relative expression by rRPCs of selected genes of interest, including cytokines, as compared to allogeneic fibroblasts. (g-h) Functional performance of rRPC- versus sham- and untreated eyes in dark-eyed dystrophic RCS recipients as assessed via optomotor (g) and ERG (h) testing (cell = rRPC; UT = untreated). (i-k) Assessment of photoreceptor cell loss via relative attenuation of the outer nuclear layer (ONL), comparing untreated (i), sham (j), and rRPC-treated (k) retinas at 3 months of age. (l-n) Relative integrity of the outer plexiform layer (OPL) of non-dystrophic wildtype rats (l) as compared to sham (m) and rRPC-treated (n) dystrophic RCS rats, assessed at an earlier time point (P35) and therefore exhibiting greater preservation of the ONL. Synaptophysin (green) and CtbP2 (red) label structures within the OPL, while cone sheaths are labeled with peanut agglutinin (blue); DAPI (white). (o-q) Cropped versions of above images (l-n) with only synaptophysin (green) and CtbP2 (red) labeling to better visualize differences in OPL preservation between conditions. Scale bar = 50 µm.
Figure 1.
Allogeneic RPCs ameliorate degeneration in RCS rats. (a-e) Rat-derived RPCs labeled for E1A reporter gene (red) (a), nestin (b), sox2 (c), Ki-67 (d), and vimentin (e) (DAPI = blue). (f) Relative expression by rRPCs of selected genes of interest, including cytokines, as compared to allogeneic fibroblasts. (g-h) Functional performance of rRPC- versus sham- and untreated eyes in dark-eyed dystrophic RCS recipients as assessed via optomotor (g) and ERG (h) testing (cell = rRPC; UT = untreated). (i-k) Assessment of photoreceptor cell loss via relative attenuation of the outer nuclear layer (ONL), comparing untreated (i), sham (j), and rRPC-treated (k) retinas at 3 months of age. (l-n) Relative integrity of the outer plexiform layer (OPL) of non-dystrophic wildtype rats (l) as compared to sham (m) and rRPC-treated (n) dystrophic RCS rats, assessed at an earlier time point (P35) and therefore exhibiting greater preservation of the ONL. Synaptophysin (green) and CtbP2 (red) label structures within the OPL, while cone sheaths are labeled with peanut agglutinin (blue); DAPI (white). (o-q) Cropped versions of above images (l-n) with only synaptophysin (green) and CtbP2 (red) labeling to better visualize differences in OPL preservation between conditions. Scale bar = 50 µm.
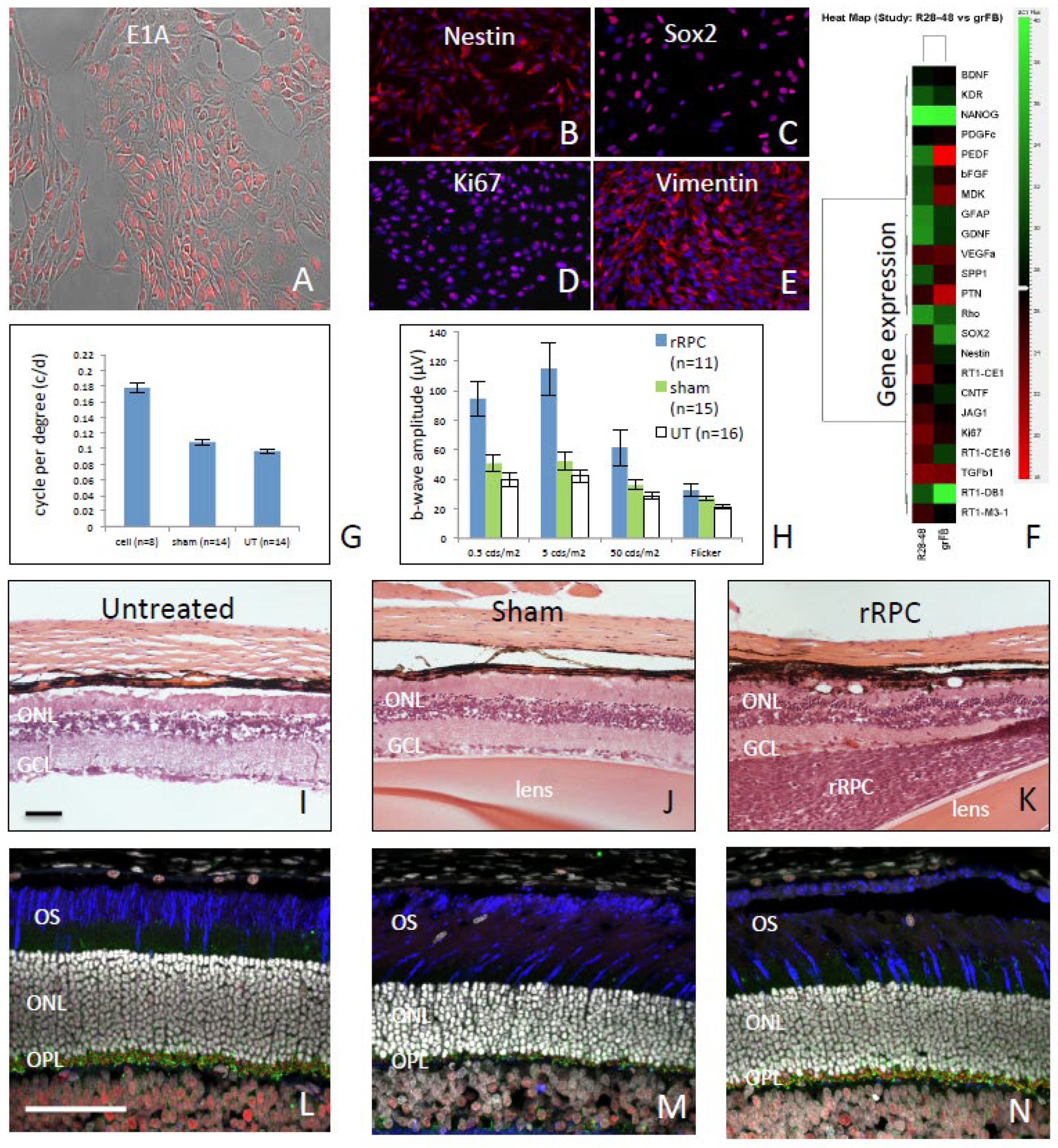
Figure 2.
Characteristics of human RPCs in culture. (a-g) Grown as an adherent monolayer and viewed in phase contrast (a), labeled for Nestin (b), Vimentin (c), Sox2 (d), Ki-67 (e), SSEA-1/CD-15 (f), and GD2 ganglioside (g); counter-labeled with DAPI (blue). (h) Principal component analysis of the global transcriptome obtained via microarray shows clustering of replicate samples and separation between hRPCs, human fibroblasts (FB), retinoblastoma cells (RB), and fetal retinal tissue. (i) Expression by hRPCs of selected genes of interest, as compared to syngeneic fibroblasts and an allogeneic retinoblastoma cell line. (j) Flow cytometric analysis comparing expression of MHC class I (vertical axis) versus class II (horizontal) in upper right scatter plot and co-expression of nestin (vertical) and sox2 (horizontal) in lower right scatter plot; with appropriate isotype controls in upper left and lower left plots, respectively. (k) Differentiation of hRPCs via growth factor withdrawal (blue bars) induces expression of glial-associated markers CRALBP and GFAP, as well as neuronal markers MAP2 and Recoverin, within the cultured population, versus undifferentiated controls (green bars). (l-n) Cultured hRPCs have a normal 46, XX karyotype without chromosomal abnormalities (l), as confirmed by FISH (m), and are negative for telomerase activity, as are syngeneic fibroblasts but not retinoblastoma cells (n). (o-r) Analysis of human RPCs across cell manufacturing lots. Comparison of gene expression levels of 5 different lots (GMP1-5) manufactured for clinical use, using qPCR (o-q). Also tested were syngeneic human fibroblasts (FB) and a retinoblastoma line (RB). (r) Cells from one of the lots (GMP5) were differentiated via growth factor withdrawal (SMnoGF) and evaluated for changes in expression of the markers MAP2 and GFAP relative to undifferentiated controls (SM). Scale bars = 50 µm; * = P < 0.05.
Figure 2.
Characteristics of human RPCs in culture. (a-g) Grown as an adherent monolayer and viewed in phase contrast (a), labeled for Nestin (b), Vimentin (c), Sox2 (d), Ki-67 (e), SSEA-1/CD-15 (f), and GD2 ganglioside (g); counter-labeled with DAPI (blue). (h) Principal component analysis of the global transcriptome obtained via microarray shows clustering of replicate samples and separation between hRPCs, human fibroblasts (FB), retinoblastoma cells (RB), and fetal retinal tissue. (i) Expression by hRPCs of selected genes of interest, as compared to syngeneic fibroblasts and an allogeneic retinoblastoma cell line. (j) Flow cytometric analysis comparing expression of MHC class I (vertical axis) versus class II (horizontal) in upper right scatter plot and co-expression of nestin (vertical) and sox2 (horizontal) in lower right scatter plot; with appropriate isotype controls in upper left and lower left plots, respectively. (k) Differentiation of hRPCs via growth factor withdrawal (blue bars) induces expression of glial-associated markers CRALBP and GFAP, as well as neuronal markers MAP2 and Recoverin, within the cultured population, versus undifferentiated controls (green bars). (l-n) Cultured hRPCs have a normal 46, XX karyotype without chromosomal abnormalities (l), as confirmed by FISH (m), and are negative for telomerase activity, as are syngeneic fibroblasts but not retinoblastoma cells (n). (o-r) Analysis of human RPCs across cell manufacturing lots. Comparison of gene expression levels of 5 different lots (GMP1-5) manufactured for clinical use, using qPCR (o-q). Also tested were syngeneic human fibroblasts (FB) and a retinoblastoma line (RB). (r) Cells from one of the lots (GMP5) were differentiated via growth factor withdrawal (SMnoGF) and evaluated for changes in expression of the markers MAP2 and GFAP relative to undifferentiated controls (SM). Scale bars = 50 µm; * = P < 0.05.
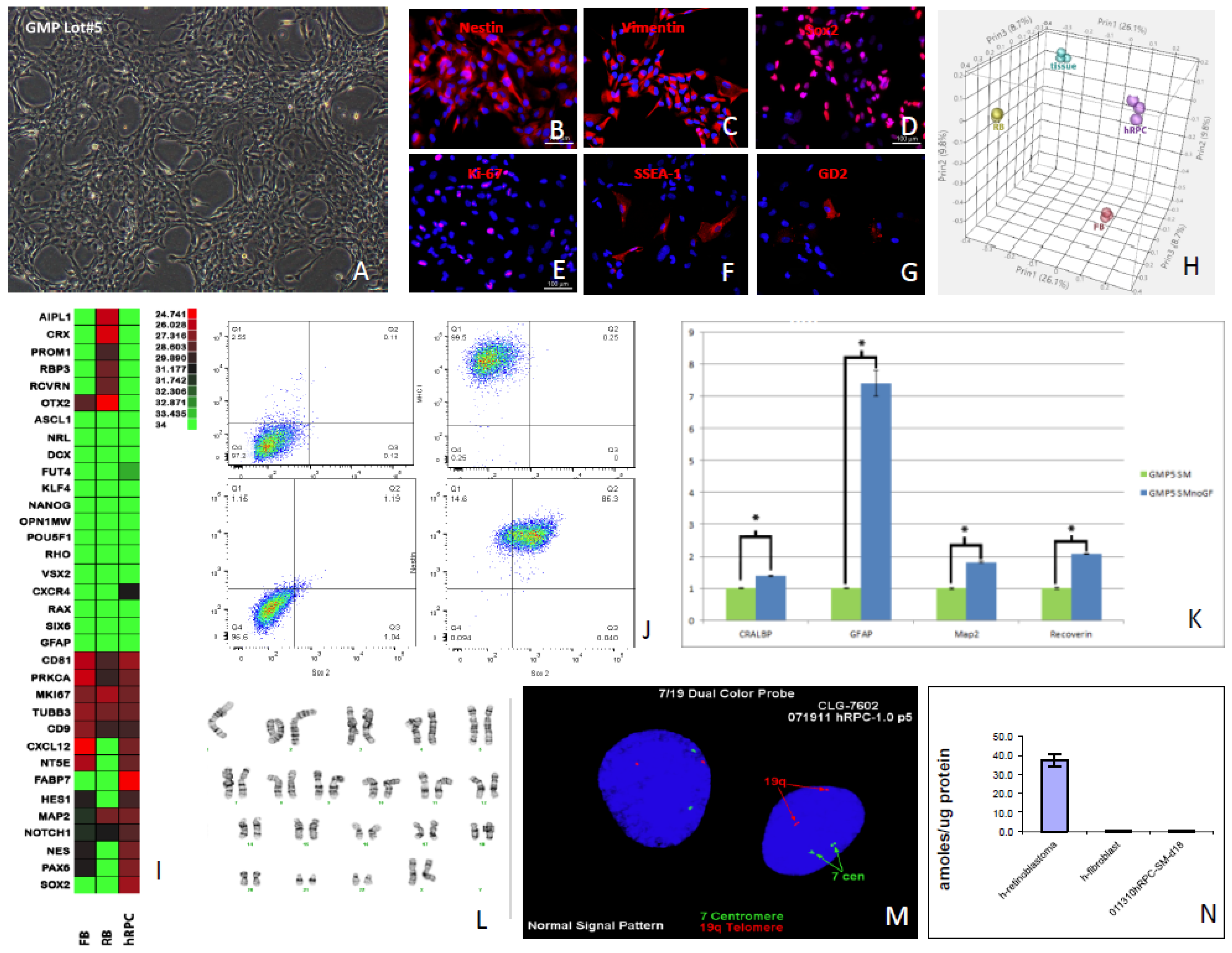
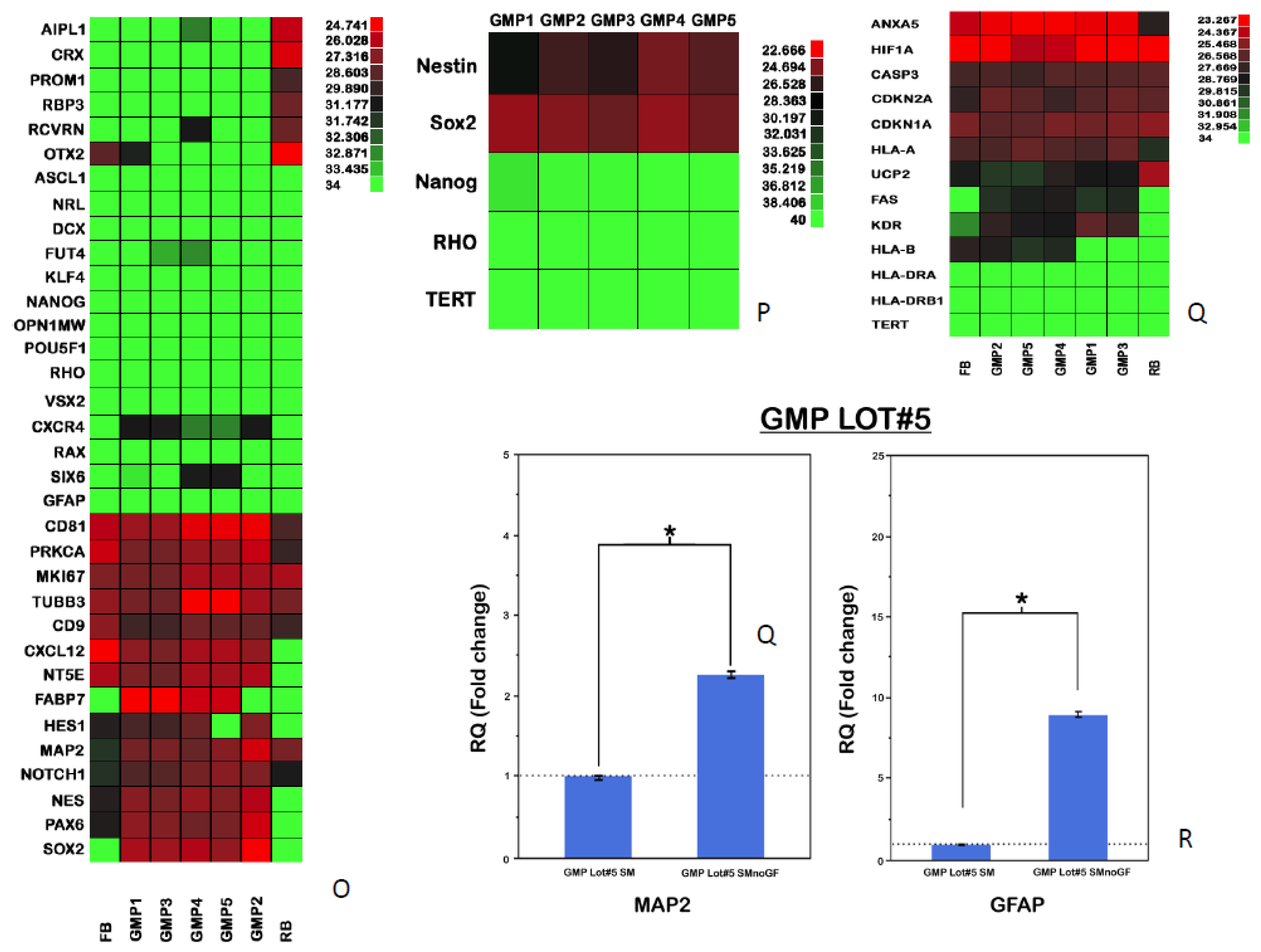
Figure 3.
Transplanted hRPCs ameliorate retinal degeneration in RCS rats. (a-d) Section of rat eye showing human donor cells (red) clustering post-injection to form aggregates in the posterior vitreous cavity (a,c), with occasional adhesion to inner retinal surface but absence of intraretinal hRPC migration. An alternate location for transplanted cells was the posterior lens capsule (b,d). Donor cells were labeled for Ki-67 (b), Nestin (d), Vimentin (c), DCX (b,d), GFAP (a,c), NeuN (c), and Recoverin (d). (e,f) Wholemounts viewed en face at photoreceptor level using confocal microscopy and computer-generated montages showing rhodopsin (red) and middle wavelength cone opsin (green) expressing profiles in hRPC- (e) and untreated (f) eyes. (g) Analysis of ONL cell counts from retinal cross sections of hRPC- and sham-treated retinas. (h) Optomotor responses (cycles per degree) comparing sensitivity of hRPC-treated eyes to sham- and untreated controls. (i-k) ERG responses in hRPC-treated eyes (45k cell dose) compared to sham- and untreated controls across three in-life time points (P45, P60, P90). Scale bar = 50 µm.
Figure 3.
Transplanted hRPCs ameliorate retinal degeneration in RCS rats. (a-d) Section of rat eye showing human donor cells (red) clustering post-injection to form aggregates in the posterior vitreous cavity (a,c), with occasional adhesion to inner retinal surface but absence of intraretinal hRPC migration. An alternate location for transplanted cells was the posterior lens capsule (b,d). Donor cells were labeled for Ki-67 (b), Nestin (d), Vimentin (c), DCX (b,d), GFAP (a,c), NeuN (c), and Recoverin (d). (e,f) Wholemounts viewed en face at photoreceptor level using confocal microscopy and computer-generated montages showing rhodopsin (red) and middle wavelength cone opsin (green) expressing profiles in hRPC- (e) and untreated (f) eyes. (g) Analysis of ONL cell counts from retinal cross sections of hRPC- and sham-treated retinas. (h) Optomotor responses (cycles per degree) comparing sensitivity of hRPC-treated eyes to sham- and untreated controls. (i-k) ERG responses in hRPC-treated eyes (45k cell dose) compared to sham- and untreated controls across three in-life time points (P45, P60, P90). Scale bar = 50 µm.
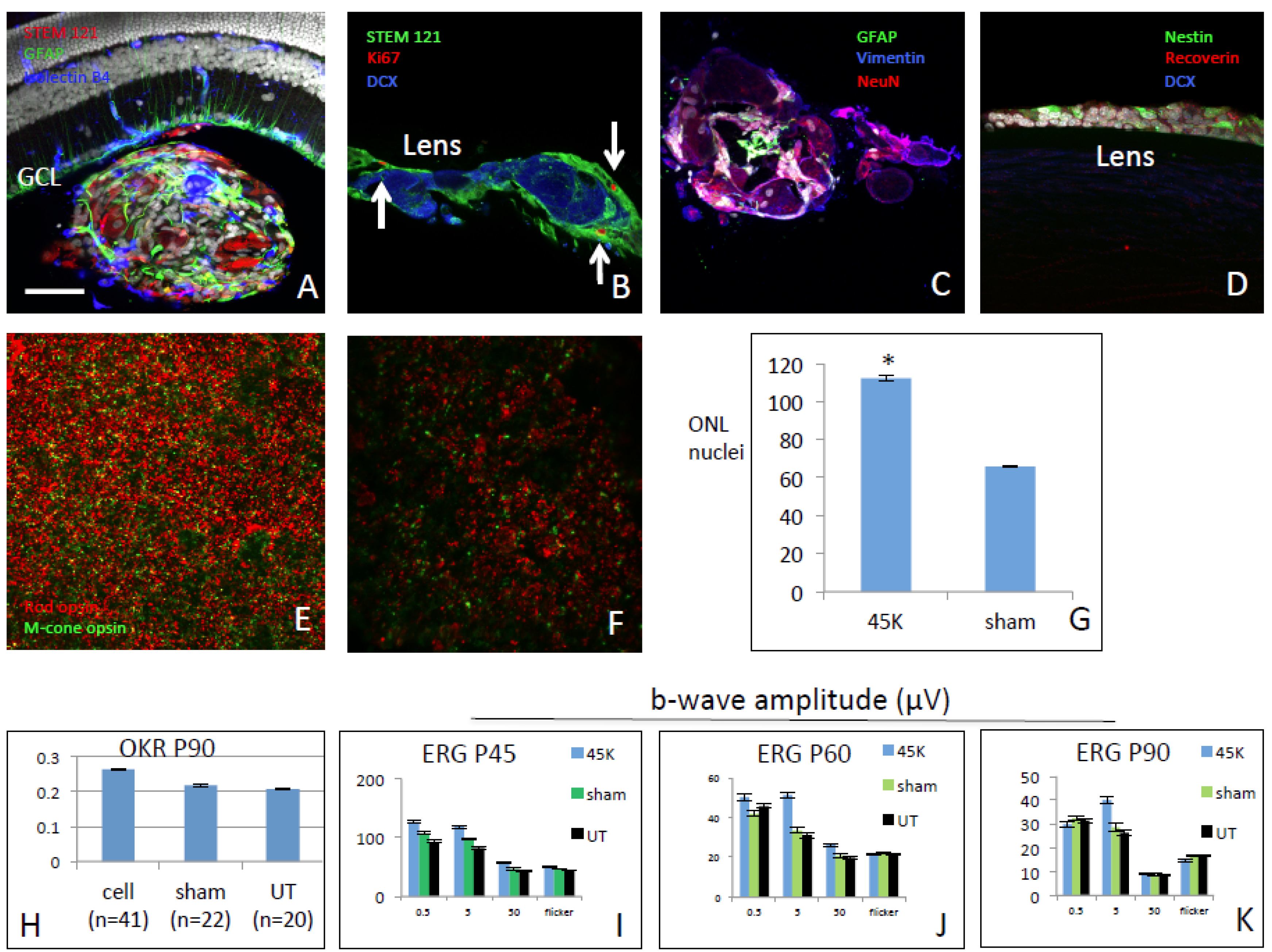
Figure 4.
Expression of cytokines and modulation of retinal cell types by RPCs. (a,b) Relative expression of selected cytokines by cultured hRPCs, measured by qPCR, as compared to retinoblastoma cells (RB) and fibroblasts (FB). (c-e) Co-expression of candidate cytokines bFGF (c), PTN (d), and OPN (e) within an intravitreal hRPC graft (at P32) and co-expression of bFGF (f) and MANF (g) by another hRPC graft (at P28), assessed using immunohistochemistry. (h) Expression pattern of Nestin, GFAP, and DCX within an intravitreal hRPC graft at a later timepoint (P90). (i-j) Relative expression of bFGF in sham (i) and rRPC-treated dystrophic RCS retinas (P90), showing relative labelling within the region of rod outer segments. (k-l) Relative expression of Connexin 43 in sham (k) and rRPC-treated (l) dystrophic RCS eyes (P35), seen as fine punctate labeling in the region of the RPE layer (arrows).
Figure 4.
Expression of cytokines and modulation of retinal cell types by RPCs. (a,b) Relative expression of selected cytokines by cultured hRPCs, measured by qPCR, as compared to retinoblastoma cells (RB) and fibroblasts (FB). (c-e) Co-expression of candidate cytokines bFGF (c), PTN (d), and OPN (e) within an intravitreal hRPC graft (at P32) and co-expression of bFGF (f) and MANF (g) by another hRPC graft (at P28), assessed using immunohistochemistry. (h) Expression pattern of Nestin, GFAP, and DCX within an intravitreal hRPC graft at a later timepoint (P90). (i-j) Relative expression of bFGF in sham (i) and rRPC-treated dystrophic RCS retinas (P90), showing relative labelling within the region of rod outer segments. (k-l) Relative expression of Connexin 43 in sham (k) and rRPC-treated (l) dystrophic RCS eyes (P35), seen as fine punctate labeling in the region of the RPE layer (arrows).
Figure 5.
Glial activation patterns in intravitreal RPC-treated dystrophic RCS retinas (at P90). (a,b) Retinal wholemounts: GFAP (green), Isolectin B4 (blue), Neurofilament (red) in untreated (a) and hRPC-treated (b) eyes. (c,i) Retinal cross-sections: GFAP (red), DAPI (white) in sham (c) and rRPC-treated eyes (d). Glutamine synthetase (GS, green), GFAP (red), and DAPI (white) in sham (e) and rRPC-treated eyes (f,g). GS labeling better visualized without DAPI (g). Caspase 3 (red), cytochrome oxidase (COX, green) and DAPI (white) labeling in sham (h) and rRPC-treated (i) eyes.
Figure 5.
Glial activation patterns in intravitreal RPC-treated dystrophic RCS retinas (at P90). (a,b) Retinal wholemounts: GFAP (green), Isolectin B4 (blue), Neurofilament (red) in untreated (a) and hRPC-treated (b) eyes. (c,i) Retinal cross-sections: GFAP (red), DAPI (white) in sham (c) and rRPC-treated eyes (d). Glutamine synthetase (GS, green), GFAP (red), and DAPI (white) in sham (e) and rRPC-treated eyes (f,g). GS labeling better visualized without DAPI (g). Caspase 3 (red), cytochrome oxidase (COX, green) and DAPI (white) labeling in sham (h) and rRPC-treated (i) eyes.
Table 1.
TaqMan Gene Expression Assay used in real-time PCR.
Table 1.
TaqMan Gene Expression Assay used in real-time PCR.
| Gene |
Assay ID |
| Human GAPDH |
Hs99999905_m1 |
| Human NANOG |
Hs02387400_g1 |
| Human Nestin |
Hs00707120_s1 |
| Human RHO |
Hs00892431_m1 |
| Human SOX2 |
Hs01053049_s1 |
| Human SPP1 |
Hs00959010_m1 |
| Human TERT |
Hs00972656_m1 |
| Rat CNTF |
Rn00755092_m1 |
| Rat bFGF |
Rn00570809_m1 |
| Rat GAPDH |
Rn01775763_g1 |
| Rat GDNF |
Rn01402432_m1 |
| Rat GFAP |
Rn01253033_m1 |
| Rat JAG1 |
Rn00569647_m1 |
| Rat KDR |
Rn00564986_m1 |
| Rat MDK |
Rn00675549_g1 |
| Rat Ki67 |
Rn01451446_m1 |
| Rat NANOG |
Rn01462825_m1 |
| Rat Nestin |
Rn01455599-g1 |
| Rat PDGFc |
Rn00579958_m1 |
| Rat PTN |
Rn00567035_m1 |
| Rat Rho |
Rn00583728_m1 |
| Rat RT1-CE1 |
Rn04222416_gH |
| Rat RT1-CE16 |
Rn04222422_gH |
| Rat RT1-Db1 |
Rn01429350_m1 |
| Rat RT1-M3-1 |
Rn00575896_g1 |
| Rat PEDF |
Rn00709999_m1 |
| Rat Sox2 |
Rn01286286_g1 |
| Rat SPP1 |
Rn00681031_m1 |
| Rat TGFb1 |
Rn00572010_m1 |
| Rat VEGFa |
Rn01511602_m1 |