Submitted:
05 June 2024
Posted:
05 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Data Extraction and Analysis
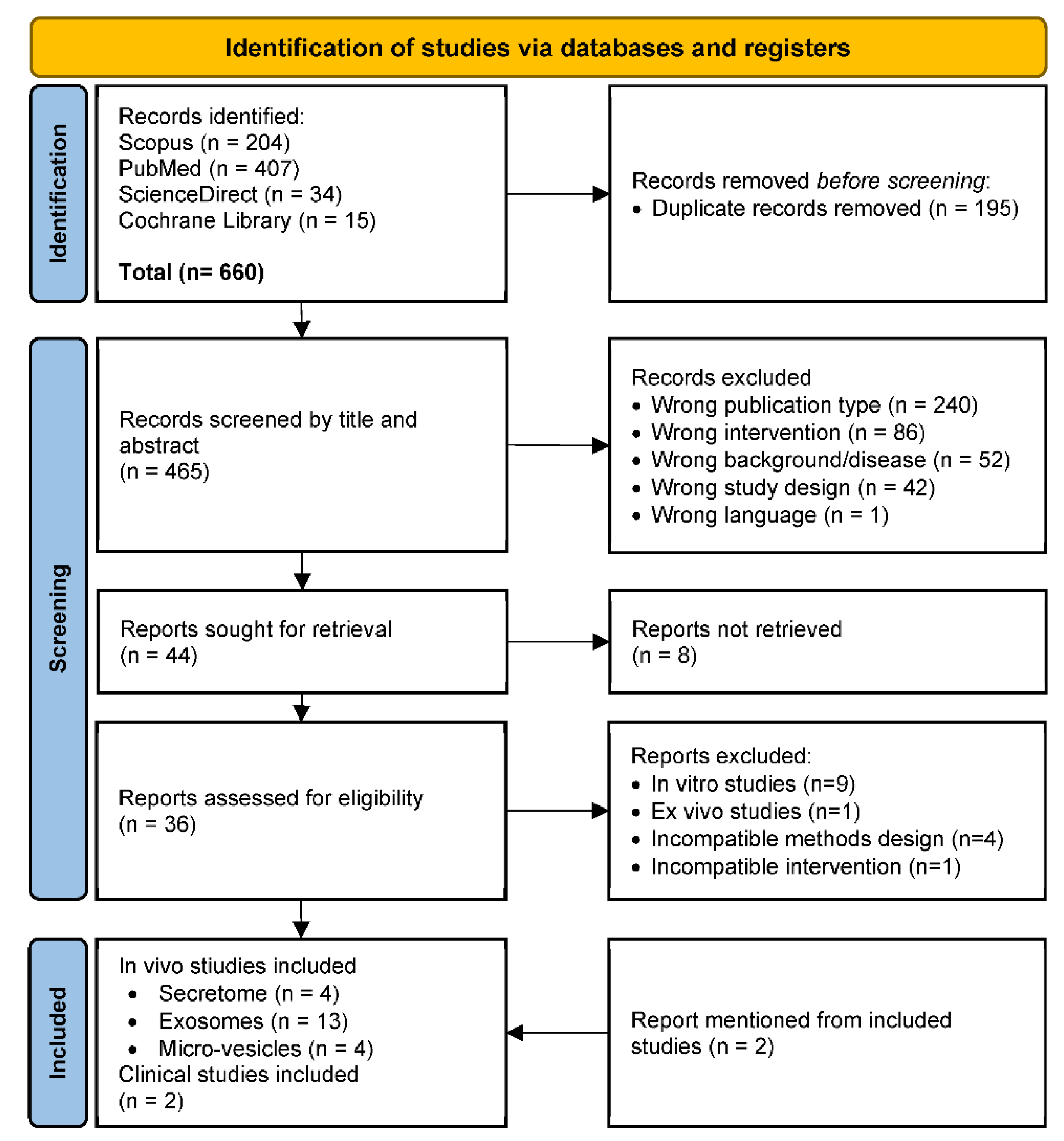
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
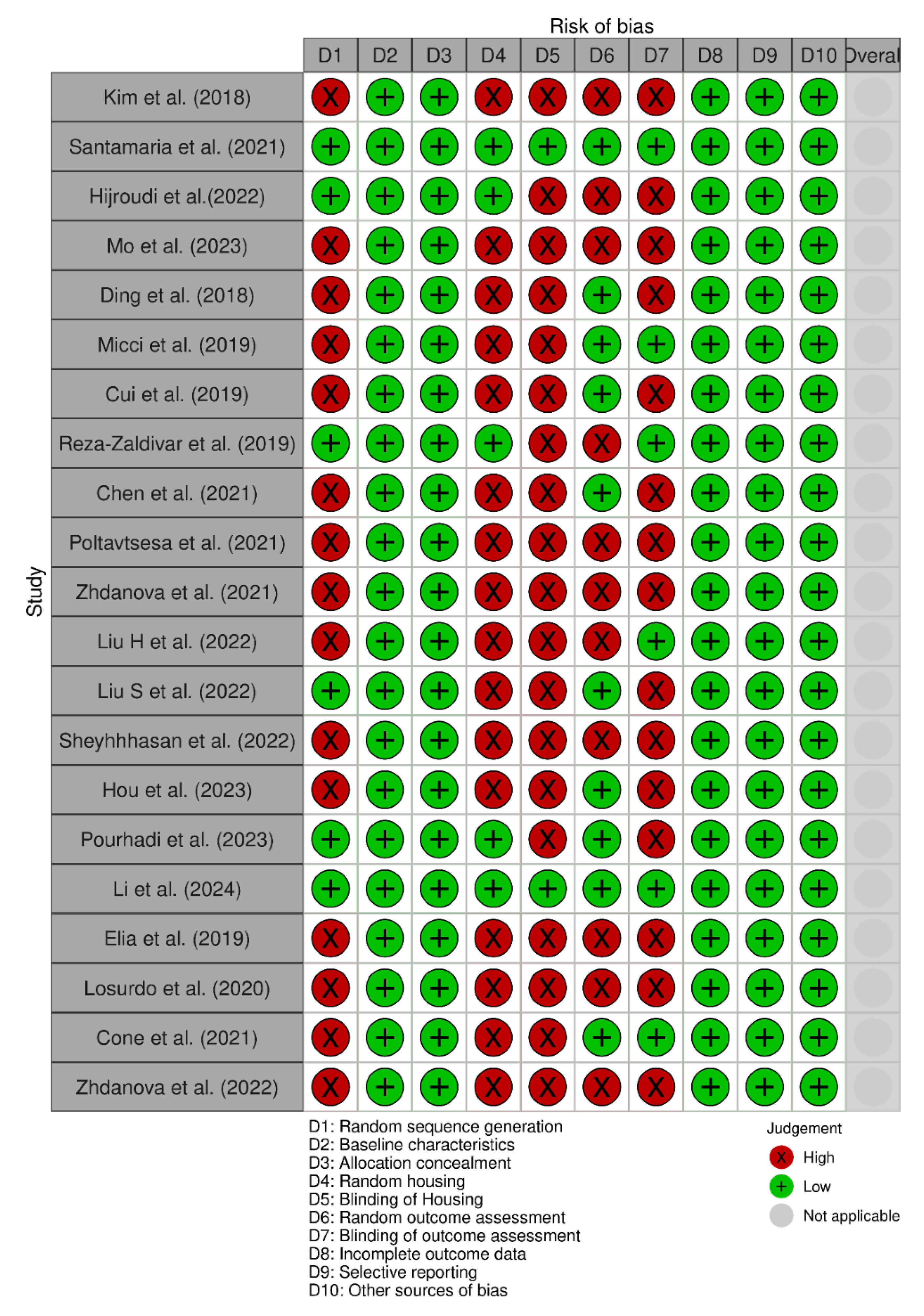
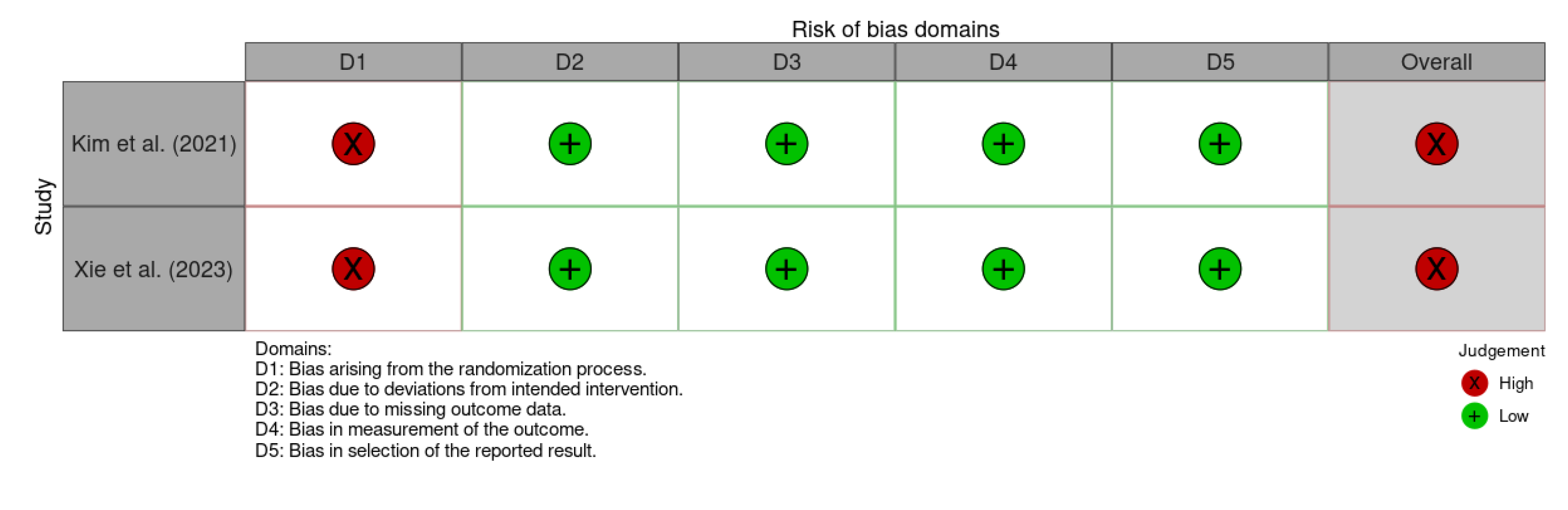
3.2. Risk of Bias Assessment
3.3. Characteristics of Animal Studies
3.4. Characteristics of Clinical Trials
3.5. Data Analysis of In Vivo Study Results
3.6. Safety and Efficacy of MSCs for AD based on Clinical Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Competing Interests
References
- Qiu C, Kivipelto M, von Strauss E. Epidemiology of Alzheimer’s disease: occurrence, determinants, and strategies toward intervention. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2009, 11, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 2. Lanctôt KL, Hahn-Pedersen JH, Eichinger CS, Freeman C, Clark A, Tarazona LRS, et al. Burden of Illness in People with Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review of Epidemiology, Comorbidities and Mortality. The Journal of Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease.
- 3. Mayeux R, Stern Y. Epidemiology of Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
- Dharmarajan TS, Gunturu SG. Alzheimer’s disease: a healthcare burden of epidemic proportion. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2009, 2, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- 5. Alzheimer’s Association. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s and Dementia.
- Rasmussen J, Langerman H. Alzheimer’s Disease - Why We Need Early Diagnosis. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2019, 9, 123–130. [Google Scholar]
- Passeri E, Elkhoury K, Morsink M, Broersen K, Linder M, Tamayol A, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease: Treatment Strategies and Their Limitations. Vol. 23, International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022.
- Hickman RA, Faustin A, Wisniewski T. Alzheimer Disease and Its Growing Epidemic: Risk Factors, Biomarkers, and the Urgent Need for Therapeutics. Neurol Clin. 2016, 34, 941–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zemek F, Drtinova L, Nepovimova E, Sepsova V, Korabecny J, Klimes J, et al. Outcomes of Alzheimer’s disease therapy with acetylcholinesterase inhibitors and memantine. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2014, 13, 759–774. [Google Scholar]
- Hoy, SM. Lecanemab: first approval. Drugs. 2023, 83, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dyck CH, Swanson CJ, Aisen P, Bateman RJ, Chen C, Gee M, et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N Engl J Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly T, Epelbaum S. The accelerated approval of Aducanumab invites a rethink of the current model of drug development for Alzheimer’s disease. AJOB Neurosci. 2023, 14, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong SY, Suh CH, Shim WH, Lim JS, Lee JH, Kim SJ. Incidence of Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities in Patients With Alzheimer Disease Treated With Anti-β-Amyloid Immunotherapy: A Meta-analysis. Neurology. 2022, 99, e2092–101. [Google Scholar]
- Villain N, Planche V, Levy R. High-clearance anti-amyloid immunotherapies in Alzheimer’s disease. Part 1: Meta-analysis and review of efficacy and safety data, and medico-economical aspects. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2022, 178, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiss AB, Muhieddine D, Jacob B, Mesbah M, Pinkhasov A, Gomolin IH, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment: The Search for a Breakthrough. Vol. 59, Medicina. 2023.
- Elia CA, Losurdo M, Malosio ML, Coco S. Extracellular Vesicles from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Pleiotropic Effects on Amyloid-β, Inflammation, and Regeneration: A Spark of Hope for Alzheimer’s Disease from Tiny Structures? Bioessays. 2019, 41, e1800199.
- Rostagno, AA. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Vol. 24, International journal of molecular sciences. Switzerland;
- Tiwari S, Atluri V, Kaushik A, Yndart A, Nair M. Alzheimer’s disease: pathogenesis, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019, 14, 5541–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan L, Mao C, Hu X, Zhang S, Yang Z, Hu Z, et al. New Insights Into the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease [Internet]. Vol. 10, Frontiers in Neurology. 2020. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2019. 0131.
- Guo T, Zhang D, Zeng Y, Huang TY, Xu H, Zhao Y. Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurodegener [Internet]. 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo CC, Chiang AWT, Baghdassarian HM, Lewis NE. Dysregulation of the secretory pathway connects Alzheimer’s disease genetics to aggregate formation. Cell Syst [Internet]. 2021, 12, 873–884.e4, Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2405471221002088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasemi M, Roshandel E, Mohammadian M, Farhadihosseinabadi B, Akbarzadehlaleh P, Shamsasenjan K. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived secretome-based therapy for neurodegenerative diseases: overview of clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther [Internet]. 2023, 14, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 23. Műzes G, Sipos F. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Secretome: A Potential Therapeutic Option for Autoimmune and Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Diseases. Cells.
- Reza-Zaldivar EE, Hernández-Sapiéns MA, Gutiérrez-Mercado YK, Sandoval-Ávila S, Gomez-Pinedo U, Márquez-Aguirre AL, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote neurogenesis and cognitive function recovery in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2019, 14, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan F, Li X, Wang Z, Li J, Shahzad K, Zheng J. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther [Internet]. 2024, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 26. Hade MD, Suire CN, Suo Z. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Cells.
- Ghadami S, Dellinger K. The lipid composition of extracellular vesicles: applications in diagnostics and therapeutic delivery [Internet]. Vol. 10, Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences. 2023. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmolb.2023. 1198.
- Khan MI, Jeong ES, Khan MZ, Shin JH, Kim JD. Stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s pathogenesis by ameliorating neuroinflamation, and regulating the associated molecular pathways. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2023, 13, 15731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo M, Yin Z, Chen F, Lei P. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosome: a promising alternative in the therapy of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther [Internet]. 2020, 12, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu J, Wang X. Alzheimer’s Disease: From Pathogenesis to Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy - Bridging the Missing Link. Front Cell Neurosci. 2021, 15, 811852. [Google Scholar]
- 31. Tüshaus J, Müller SA, Kataka ES, Zaucha J, Sebastian Monasor L, Su M, et al. An optimized quantitative proteomics method establishes the cell type-resolved mouse brain secretome. EMBO J. 1056.
- Giovannelli L, Bari E, Jommi C, Tartara F, Armocida D, Garbossa D, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell secretome and extracellular vesicles for neurodegenerative diseases: Risk-benefit profile and next steps for the market access. Bioact Mater [Internet]. 2023, 29, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 33. Teixeira FG, Salgado AJ. Mesenchymal stem cells secretome: current trends and future challenges. Neural Regen Res [Internet]. [Internet]. 2020;15(1). Available from: https://journals.lww.com/nrronline/fulltext/2020/15010/mesenchymal_stem_cells_secretome__current_trends.22.aspx.
- Hooijmans CR, Rovers MM, De Vries RBM, Leenaars M, Ritskes-Hoitinga M, Langendam MW. SYRCLE’s risk of bias tool for animal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins JP, Savović J, Page MJ, Sterne JAC. Revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2) [Internet]. 2019. p. 1–24. Available from: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/current-version-of-rob-2.
- Kim HJ, Cho KR, Jang H, Lee NK, Jung YH, Kim JP, et al. Intracerebroventricular injection of human umbilical cord blood mesenchymal stem cells in patients with Alzheimer ’ s disease dementia : a phase I clinical trial. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Xie X, Song Q, Dai C, Cui S, Tang R, Li S, et al. Clinical safety and efficacy of allogenic human adipose mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosomes in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A phase I/II clinical trial. Gen Psychiatr. 2023, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kim DH, Lim H, Lee D, Choi SJ, Oh W, Yang YS, et al. Thrombospondin-1 secreted by human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells rescues neurons from synaptic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease model. Sci Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Santamaria G, Brandi E, Vitola P La, Grandi F, Ferrara G, Pischiutta F, et al. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell secretome repairs the brain of Alzheimer’s mice. Cell Death Differ [Internet]. 2021, 28, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hijroudi F, Rahbarghazi R, Sadigh-Eteghad S, Bahlakeh G, Hassanpour M, Shimia M, et al. Neural Stem Cells Secretome Increased Neurogenesis and Behavioral Performance and the Activation of Wnt-β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuromolecular Med. 2022, 24, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo H, Kim J, Kim JY, Kim JW, Han H, Choi SH, et al. Intranasal administration of induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cortical neural stem cell-secretome as a treatment option for Alzheimer’s disease. Transl Neurodegener [Internet]. 2023, 12, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding M, Shen Y, Wang P, Xie Z, Xu S, Zhu ZY, et al. Exosomes Isolated From Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Neuroinflammation and Reduce Amyloid-Beta Deposition by Modulating Microglial Activation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurochem Res [Internet]. 2018, 43, 2165–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micci MA, Krishnan B, Bishop E, Zhang WR, Guptarak J, Grant A, et al. Hippocampal stem cells promotes synaptic resistance to the dysfunctional impact of amyloid beta oligomers via secreted exosomes. Mol Neurodegener. 2019, 14, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- Cui GH, Guo HD, Li H, Zhai Y, Gong Z Bin, Wu J, et al. RVG-modified exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells rescue memory deficits by regulating inflammatory responses in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Immunity and Ageing. 2019, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chen YA, Lu CH, Ke CC, Chiu SJ, Jeng FS, Chang CW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate alzheimer’s disease pathology and improve cognitive deficits. Biomedicines. 2021, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Zhdanova DY, Poltavtseva RA, Svirshchevskaya E V. , Bobkova N V. Effect of Intranasal Administration of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Exosomes on Memory of Mice in Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2021, 170, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poltavtseva RA, Bobkova N V. , Zhdanova DY, Svirshchevskaya E V., Sukhikh GT. Alzheimer’s Type Neurodegeneration. Possible Correction of Memory Impairment with Intravenous Administration of Exosomes. Biochem (Mosc) Suppl Ser A Membr Cell Biol. 2021, 15, 306–318. [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Fan M, Xu JX, Yang LJ, Qi CC, Xia QR, et al. Exosomes derived from bone-marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviate cognitive decline in AD-like mice by improving BDNF-related neuropathology. J Neuroinflammation [Internet]. 2022, 19, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Jin M, Ji M, Zhang W, Liu A, Wang T. Hypoxic pretreatment of adipose-derived stem cell exosomes improved cognition by delivery of circ-Epc1 and shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization in an Alzheimer’s disease mice model. Aging. 2022, 14, 3070–3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhhasan M, Amini R, Soleimani Asl S, Saidijam M, Hashemi SM, Najafi R. Neuroprotective effects of coenzyme Q10-loaded exosomes obtained from adipose-derived stem cells in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy [Internet]. 2022, 152, 113224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou X, Jiang H, Liu T, Yan J, Zhang F, Zhang X, et al. Depletion of gut microbiota resistance in 5×FAD mice enhances the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy. 2023, 161, 1–22. [Google Scholar]
- 52. Pourhadi M, Zali H, Ghasemi R, Faizi M, Mojab F, Soufi Zomorrod M. Restoring Synaptic Function: How Intranasal Delivery of 3D-Cultured hUSSC Exosomes Improve Learning and Memory Deficits in Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol [Internet]. Available from. [CrossRef]
- Li B, Chen Y, Zhou Y, Feng X, Gu G, Han S, et al. Neural stem cell-derived exosomes promote mitochondrial biogenesis and restore abnormal protein distribution in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2024, 19, 1593–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losurdo M, Pedrazzoli M, D’Agostino C, Elia CA, Massenzio F, Lonati E, et al. Intranasal delivery of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles exerts immunomodulatory and neuroprotective effects in a 3xTg model of Alzheimer’s disease. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020, 9, 1068–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cone AS, Yuan X, Sun L, Duke LC, Vreones MP, Carrier AN, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles ameliorate Alzheimer’s disease-like phenotypes in a preclinical mouse model. Theranostics. 2021, 11, 8129–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhdanova D, Gomzikova M, Bobkova N, Starostina I, Kovalev V, Rizvanov A. Intranasal Administration of Microvesicles in the Brain of Mice with Induced Model of Alzheimer’s Type of Neurodegeneration. Bionanoscience [Internet]. 2022, 12, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 57. Pinho AG, Cibrão JR, Silva NA, Monteiro S, Salgado AJ. Cell Secretome: Basic Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities for CNS Disorders. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
- Garcia-Contreras M, Thakor AS. Extracellular vesicles in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathology to therapeutic approaches. Neural Regen Res. 2023, 18, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández AE, García E. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Alzheimer’s Disease. Stem Cells Int. 2021, 2021, 7834421. [Google Scholar]
- 60. Wang H, Huber CC, Li XP. Mesenchymal and Neural Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Treating Alzheimer’s Disease. Bioengineering (Basel).
- Polanco JC, Scicluna BJ, Hill AF, Götz J. Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from the Brains of rTg4510 Mice Seed Tau Protein Aggregation in a Threshold-dependent Manner. J Biol Chem. 2016, 291, 12445–12466.
- Lotfy A, AboQuella NM, Wang H. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si Z, Wang X. Stem Cell Therapies in Alzheimer’s Disease: Applications for Disease Modeling. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2021, 377, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemayel J, Chaker D, El Hachem G, Mhanna M, Salemeh R, Hanna C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived secretome and extracellular vesicles: perspective and challenges in cancer therapy and clinical applications. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023, 25, 2056–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Database | Search Strategy |
|---|---|
| Scopus | (“Alzheimer's Disease” OR “Alzheimer Dementia” OR “Senile Dementia” OR “Alzheimer Sclerosis” OR “Alzheimer Syndrome”) AND (Secretome OR Exosomes OR Microvesicles) AND (Neuroprotection OR “Neural Protection” OR “Neuronal Protection” OR Neuroregeneration OR “Neural Regeneration” OR “Neuronal Regeneration” OR Therapeutic OR Therapy OR Treatment) Filters (Limit-to): Document type “Articles”; Language "English" |
| PubMed and Cochrane Library | (“Alzheimer's Disease” OR “Alzheimer Dementia” OR “Senile Dementia” OR “Alzheimer Sclerosis” OR “Alzheimer Syndrome”) AND (Secretome OR Exosomes OR Microvesicles) AND (Neuroprotection OR “Neural Protection” OR “Neuronal Protection” OR Neuroregeneration OR “Neural Regeneration” OR “Neuronal Regeneration” OR Therapeutic OR Therapy OR Treatment) |
| ScienceDirect | ("Alzheimer's Disease" OR "Alzheimer Dementia") AND (Secretome OR Exosomes OR Microvesicles) AND (Therapeutic OR Therapy OR Treatment)Filters (Limit-to): Article type “Research article” |
| Author (Year) | Study type/ design | ID | Participant & Sample size | Age | Intervention |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kim et al. (2021) | Open-labelled Phase-I clinical trial | NCT03172117 | AD dementia patients (n = 9) | 50 -85 years | Intracerebroventricular injection of hUCB-derived MSCs (1.0 × 107 and 3.0 x 107 cells/2 mL) |
| Xie et al. (2023) | Open-labelled Phase-I/IIa clinical trial | NCT04388982 | Mild or moderate AD (n = 9 for safety analysis and n = 8 for efficacy analysis) | ≥50 years | intranasal administration of ahaMSCs- Exos (2×108, 4×108, 8×108 particles) |
| Reference | Safety | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Kim et al. (2021) |
|
N/R |
| Xie et al. (2023) | The trial reported no adverse events, indicating that the treatment was safe and well-tolerated. | Cognitive Function Improvement
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





