1. Introduction
There is ongoing interest in the coronary microvasculature: The coronary vasa vasorum for their role in atherosclerotic processes, and the distal myocardium perfusing microvasculature as its dysfunction is of clinical importance [
1,
2]. Growing use of microvascular dysfunction testing and new clinical tools like contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), Superb microvascular imaging (SMI), and technical advancement in clinically used computed tomography stress the need for a better understanding of the coronary microvasculature as part of the entire coronary vascular tree [
3].
Micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) is a powerful non-destructive imaging technique and has been used to achieve high-resolution three-dimensional scans of iodine-stained arteries with good plaque morphology differentiation [
4,
5]. This method requires the dissection of the artery from the specimen, thereby taking it out of its microvascular context. Scanning entire hearts poses difficulties regarding movement due to tissue relaxation and dehydration, leading to blurred images [
6].
We developed an iodine-enhanced high-resolution Micro-CT method to examine the coronary microvasculature in intact human hearts. The contrasting technique used is a variation of the well-described technique with Iodine potassium iodide (IKI, Lugol's solution) [
7]. Our approach aligns with the growing need for advanced imaging techniques to facilitate a deeper understanding of micro- and macrovascular pathology in the context of cardiovascular diseases.
2. Materials and Methods
Human hearts were procured through the Anatomy Bequest Program at the University of Minnesota or from LifeSource, Inc. (St Paul, MN). The procedures are covered by the research protocol reviewed and approved by the Human Subjects Committee Internal Review Board at the University of Minnesota.
We selected hearts from the Visible Heart Library that were known to have coronary artery disease and had a high likelihood of a chronically occluded artery. When the hearts were initially received, the fresh organs were pressure-perfusion fixed with a 10% formalin solution for blood clearance, as previously described [
8].
For selective contrast injection, coronary ostia were visualized using an endoscopic camera (OLYMPUS iPLEX NX, IV9435N) through the aorta. Venogram catheters (Medtronic, Attain 6125-18) with an occluding balloon at the distal end were inserted and blocked with 1.5ml air to prevent back-flow and enable antegrade injection.
To mitigate tissue movement, we placed the heart into a sealed polyethylene bag except for exiting catheters. The heart was put into a 13x13x19cm radiolucent container (cardboard/Styrofoam). Next, polyurethane foam (insulation foam) was injected into the box to fix the heart three-dimensionally (
Supplementary Figure S1).
Iodine-potassium-iodide (IKI) as aqueous solution was used as a diffusible radiopaque contrast agent (Lugol's solution, Potassium Iodide 6.3%, Iodine 4.1%, Carolina Biological Supply Company, 87-2797). Repeatedly, 15ml undiluted solution was manually injected with slow and steady pressure. After each injection, micro-CT scans with a low number of projections (360) were performed to verify distribution and contrast in the region of interest. Once sufficient tissue penetration was reached, the coronary arteries were flushed with regular saline solution to improve lumen contours.
Imaging was conducted using a North Star Imaging X3000 Micro-CT scanner (Rogers, Minnesota). Initial low-radiation scans at 360 rad over 6 minutes helped center the hearts to focus on the vessels of interest and optimize contrast distribution. Subsequently, high-resolution scans at 3600 rad, taking 60 minutes, were performed (
Table 1). The distance to the radiation source was chosen so that the specimen would not come in contact with the X-ray emitter.
Images were reconstructed using NSI efx-CT software (North Star Imaging, Rogers, MN, USA) and then exported in DICONDE, TIFF, or JPEG format. All Image volumes were then loaded into MIMICS (26.0, Materialise, Plymouth, MI, USA) for greyscale-threshold-based segmentation and further analysis. Variable photon attenuation line profiles were generated from cross-sectional cuts through the artery wall, analogous to previous reports [
4].
Following staining and scanning, the hearts were carefully unpacked, using acetone to soften hard to remove parts of polyurethane foam. The hearts were then taken out of their polyethylene bags and rinsed in water for 2-4 weeks, after which they underwent micro-CT scanning again to confirm contrast clearance before being returned to formalin.
3. Results
3.1. Imaging Outcomes
Sufficient contrast and equal diffusion were reached with 80 – 180 ml of the IKI solution. Cumulative scan and reconstruction times from initial injection until the desired image quality and artery position were reached took 9-12 hours over two days.
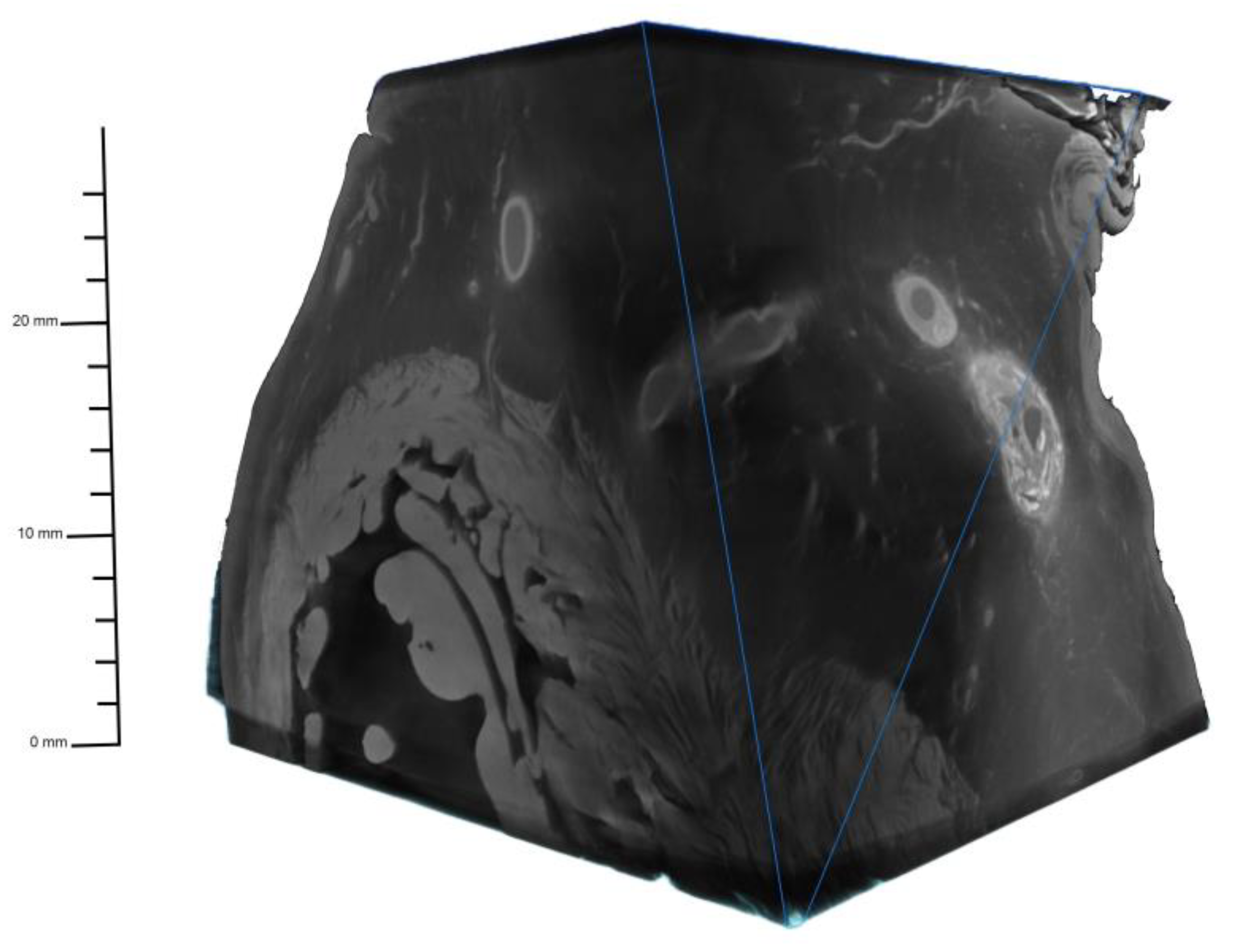
The micro-CT scans effectively visualized the coronary artery, the vessel wall, and the surrounding microvasculature in great detail without motion blurring (
Figure 1).
Maximum voxel resolutions between 20 and 35 micrometers were reached. Extensive calcified plaques presented with beam hardening artifacts (
Figure 2).
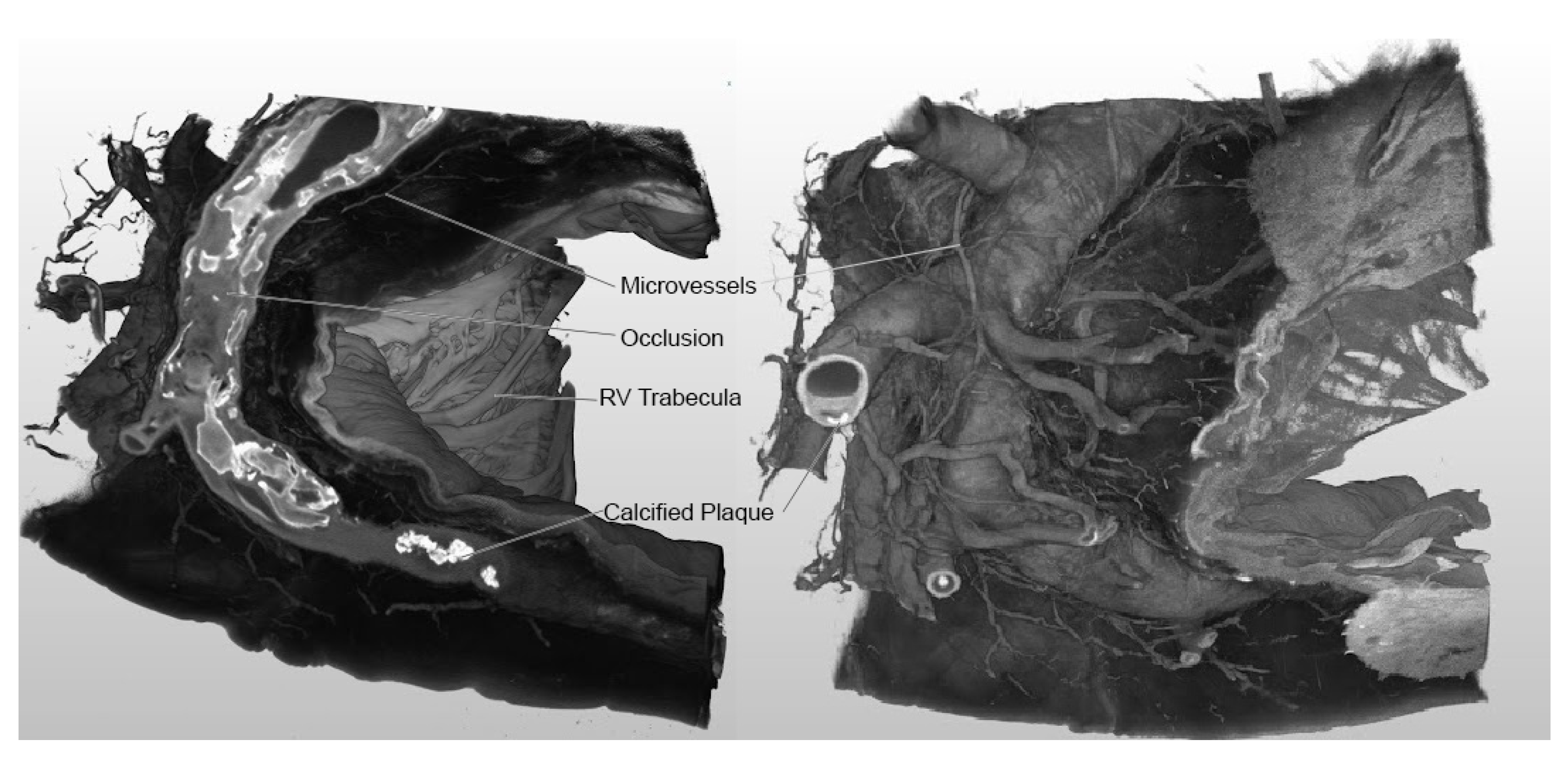
Both 2D images and 3D, density-level threshold-based, non-segmented reconstructions showcased the intricate network of vessels, highlighting areas of stenosis and occlusion (Supplementary Video 1,
Figure 3)
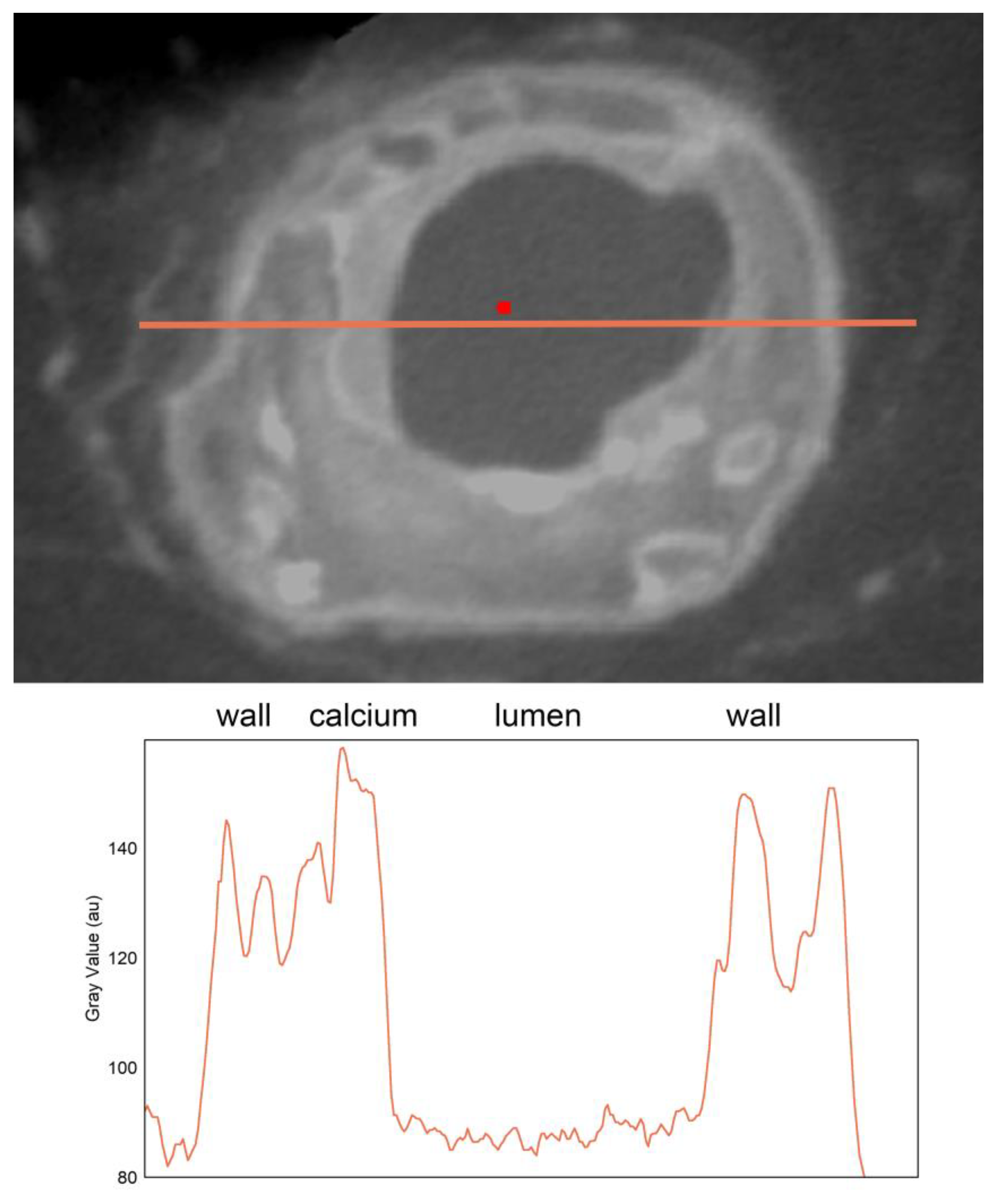
3.2. Individual Line Profiles
Cross-sectional vessel wall line profiles for iodine diffusion contrast staining with IKI showed line profiles comparable to those published by Self et al. [
4]. There was a consistent increase in signal density at the adventitia and more continuous values throughout the media. Intensity peaks in lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaque and calcium deposition in the atherosclerotic vessel were consistently seen (
Figure 2, Supplementary Video 2).
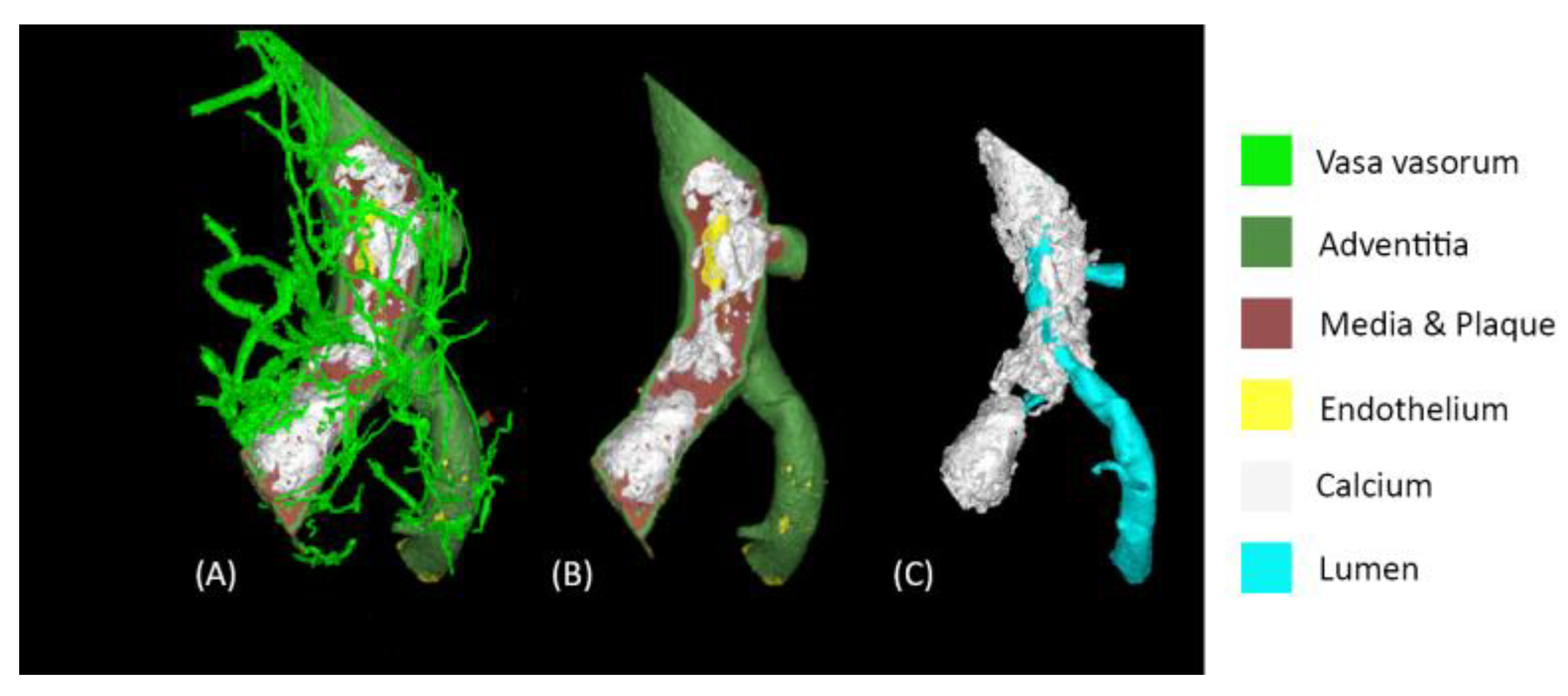
3.3. Vessel Segmentation
The contrast solution enhanced the artery's layers (intima, adventitia) and the vasa vasorum (
Figure 4). As the principal vessel and the surrounding vasculature were contrasted, segmentation of collaterals and myocardium-perfusing microvessels was also possible (Supplemental Video 1).
3.4. Post-Processing Observations
Repeat scanning after the washout period revealed that the hearts maintained their structural integrity throughout the process. The contrast agent, while providing visualization during scanning, was effectively cleared from the tissues after 2-4 weeks.
4. Discussion
We present a novel way of achieving contrasted high-resolution scans of the coronary vasculature without destroying the used specimen. Both specimen preparation and staining techniques are aimed at preserving the integrity and further usability of the formalin-fixed organs.
This is the first report describing the use of diffusion-enhanced micro-computed tomography in intact coronary vasculature.
Alternative vessel-contrasting procedures often have the contrasting agent stay within the vessels or can only be cleared with great difficulty.
The most widely used product to visualize microvasculature with micro-CT is the radiopaque, lead-containing, liquid, low-viscosity polymer MV-122(Microfil ®, Flow Tech, Inc, Carver, Massachusetts) [
2,
9,
10].
Most commonly, MV-122 is injected into the artery, which is then embedded in low-melting-point paraffin wax to reduce motion artifacts - both of which permanently alter the specimen [
10].
Low-viscosity barium-based contrast solutions (BaCl2/gelatin mixture) are an alternative to MV-122 [
11]. Yet, our experiments leading up to the development of the Lugol-based technique showed that barium-based solutions would not readily clear the specimen after scanning.
A similar method to our IKI-based technique is iodine-enhanced micro-CT using Iohexol. Just as IKI, Iohexol lends contrast not only to the vessel but also to the surrounding tissues. This results in more detail regarding the vessel wall and plaque composition than the mere lumenogram of the other methods [
4,
12,
13].
The Lugol's solution used in our study resulted in comparable images at a lower cost, as Iohexol can be up to 30 times the price of commercially available Lugol's. With almost 200 years of use in medicine, Lugols solution is ubiquitous and affordable, whereas the availability of iodinated intravenous contrast solutions has recently been unreliable [
14,
15]. Previously reported need for high concentrations or long staining times of certain specimens did not apply to staining the cardiac vasculature via intraarterial injection. However, total organ immersion would require more volume [
16]. In comparison to Iohexol 250mg/l, which has a viscosity of approximately 5 mPa*s at 25 degrees Celsius, Lugol's solution has a lower estimated viscosity of 1 mPa*s, which enables it to penetrate the microvasculature more readily [
17,
18].
As the iodine and potassium iodide concentrations can vary significantly between manufacturers, and some manufacturers do not disclose the exact contents, some researchers prefer custom-mixed solutions, which gives complete control over the respective concentrations [
7,
16].
Being able to discriminate the lumen, the arterial wall layers, as well as the vasa vasorum allows for both 3-D reconstruction of channels open to blood flow for further work like image-based computational fluid dynamics (CFD) analysis to characterize the hemodynamics, simulate local endothelial shear stress, as well as quantification of vasa vasorum densities to contribute to the better understanding of atherogenesis and what makes coronary plaques vulnerable [
2,
10,
19,
20].
Having a non-dissected vascular tree additionally allows for the collateral vessel network to be appreciated in the context of the whole heart. This is of importance as collaterals in chronic total coronary occlusions stem from the contralateral coronary artery in roughly 70% of right occlusions and 50% of left coronary artery occlusions [
21]. Any dissection of the coronary tree would, therefore impede research of this vascular network. Thus far, there has not been a micro-CT three-dimensional reconstruction of the human coronary collateral network in chronically occluded arteries.
Lastly, this method enables exploration of the presence or absence of continuous intralesional microchannels in true chronic total occlusions and their three-dimensional path. Previous work on this is limited to cross-sectional pathology/HE slices or rabbit animal models of the femoral artery [
22].
Limitations:
Having the structure of interest (coronary artery) not dissected from the heart poses challenges to reaching high-resolution images. Scanning the right coronary artery will, in most cases, result in better-contrasted images, since it is more likely to be embedded in pericardial fat, which is less dense than myocardium. Generally, better resolution is achieved the closer the object is to the tube—the size of the heart and the packing box pose limits here. To reach high-resolution images non-conventional techniques like Sub-Pixel processing and Limited Angle Tomography can be used to achieve even better imaging results.
Beam hardening artifacts caused by coronary calcium can pose issues during three-dimensional segmentation, leading to under-estimation of calcified plaque volumes (inside of calcified plaque may become indistinguishable from soft plaque). This problem can be improved by refining the technique using copper filters, hardening the radiation beam, or taking a native vessel scan before contrast injection or after contrast clearance, as this artifact is not as pronounced in non-contrasted tissues.
Lastly, the technique presented here can be very time-consuming, which could limit adoption.
5. Conclusions
The results of this study demonstrate the feasibility and effectiveness of this staining and packing technique to achieve high-resolution micro-CT images for detailed analysis of coronary microvasculature in intact human hearts. This provides the tools to obtain a new understanding of the coronary microvascular architecture and its alterations in the context of coronary artery disease.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: Preprints.org, Supplemental Video 1, Supplemental Video 2, Supplemental Methods
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R.. and P.I.; methodology, J.R..; validation, J.R..; formal analysis, J.R..; investigation, J.R..; resources, J.R.. and P.I.; data curation, J.R..; writing—original draft preparation, J.R..; writing—review and editing, J.R.. and P.I.; visualization, J.R..; supervision, P.I.; project administration, J.R. ; funding acquisition, P.I.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors on request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank John Brigham for his patience and assistance in working with the Micro-CT and Neal Duong for his support in developing the Iodine-based tissue staining.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in regard to this publication.
References
- Camici, P.G.; d'Amati, G.; Rimoldi, O. Coronary microvascular dysfunction: Mechanisms and functional assessment. Nature Reviews Cardiology 2015, 12, 48–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gössl, M.; Versari, D.; Lerman, L.O.; Chade, A.R.; Beighley, P.E.; Erbel, R.; et al. Low vasa vasorum densities correlate with inflammation and subintimal thickening: Potential role in location—Determination of atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 2009, 206, 362–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantella LE, Liblik K, Johri AM. Vascular imaging of atherosclerosis: Strengths and weaknesses. Atherosclerosis 2021, 319, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Self, T.S.; Ginn-Hedman, A.M.; Kaulfus, C.N.; Newell-Fugate, A.E.; Weeks, B.R.; Heaps, C.L. Iodine-enhanced micro-computed tomography of atherosclerotic plaque morphology complements conventional histology. Atherosclerosis 2020, 313, 43–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keklikoglou, K.; Arvanitidis, C.; Chatzigeorgiou, G.; Chatzinikolaou, E.; Karagiannidis, E.; Koletsa, T.; et al. Micro-CT for Biological and Biomedical Studies: A Comparison of Imaging Techniques. Journal of Imaging 2021, 7, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- du Plessis, A.; Broeckhoven, C.; Guelpa, A.; le Roux, S.G. Laboratory x-ray micro-computed tomography: A user guideline for biological samples. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metscher, B.D. MicroCT for comparative morphology: Simple staining methods allow high-contrast 3D imaging of diverse non-mineralized animal tissues. BMC Physiol 2009, 9, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quill, J.L.; Hill, A.J.; Laske, T.G.; Alfieri, O.; Iaizzo, P.A. Mitral leaflet anatomy revisited. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009, 137, 1077–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, A.C.; Beeuwkes, R.; Lainey, L.L.; Silverman, K.J. Hypothesis: Vasa Vasorum and Neovascularization of Human Coronary Arteries. New England Journal of Medicine 1984, 310, 175–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gössl, M.; Rosol, M.; Malyar, N.M.; Fitzpatrick, L.A.; Beighley, P.E.; Zamir, M.; et al. Functional anatomy and hemodynamic characteristics of vasa vasorum in the walls of porcine coronary arteries. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol 2003, 272, 526–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.H.; Herman, A.M.; Stephenson, J.M.; Wu, T.; Bahadur, A.N.; Burns, A.R.; et al. Development of barium-based low viscosity contrast agents for micro CT vascular casting: Application to 3D visualization of the adult mouse cerebrovasculature. J Neurosci Res 2020, 98, 312–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginn-Hedman, A.-M.; Self, T.S.; Jessen, S.L.; Heaps, C.L.; Weeks, B.R.; Clubb, F.J. Diffusible contrast-enhanced micro-CT improves visualization of stented vessels. Cardiovascular Pathology 2022, 60, 107428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, T.S.; Ginn-Hedman, A.-M.; Newell-Fugate, A.E.; Weeks, B.R.; Heaps, C.L. Iodine-based contrast staining improves micro-computed tomography of atherosclerotic coronary arteries. MethodsX 2021, 8, 101297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottardi, W. Iodine and disinfection: Theoretical study on mode of action, efficiency, stability, and analytical aspects in the aqueous system. Arch Pharm (Weinheim) 1999, 332, 151–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeppel, D.R.; Boehm, I.B. Shortage of iodinated contrast media: Status and possible chances - A systematic review. Eur J Radiol 2023, 164, 110853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gignac, P.M.; Kley, N.J.; Clarke, J.A.; Colbert, M.W.; Morhardt, A.C.; Cerio, D.; et al. Diffusible iodine-based contrast-enhanced computed tomography (diceCT): An emerging tool for rapid, high-resolution, 3-D imaging of metazoan soft tissues. J Anat 2016, 228, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smedby, Ö. Viscosity of Some Contemporary Contrast Media before and after Mixing with Whole Blood. Acta Radiologica 1992, 33, 600–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kestin, J.; Sokolov, M.; Wakeham, W.A. Viscosity of liquid water in the range −8 °C to 150 °C. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data 1978, 7, 941–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, D.; Pinilla-Echeverri, N.; Coskun, A.U.; Pu, Z.; Kajander, O.A.; Rupert, D.; et al. The role of endothelial shear stress, shear stress gradient, and plaque topography in plaque erosion. Atherosclerosis 2023, 376, 11–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Wakatsuki, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Fukuda, D.; Kawabata, Y.; Matsuura, T.; et al. Atherosclerotic Coronary Plaque Is Associated With Adventitial Vasa Vasorum and Local Inflammation in Adjacent Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Fresh Cadavers. Circ J 2020, 84, 769–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEntegart, M.B.; Badar, A.A.; Ahmad, F.A.; Shaukat, A.; MacPherson, M.; Irving, J.; et al. The collateral circulation of coronary chronic total occlusions. EuroIntervention 2016, 11, e1596–e603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munce, N.R.; Strauss, B.H.; Qi, X.; Weisbrod, M.J.; Anderson, K.J.; Leung, G.; et al. Intravascular and Extravascular Microvessel Formation in Chronic Total Occlusions. JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging 2010, 3, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).