Submitted:
04 June 2024
Posted:
05 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
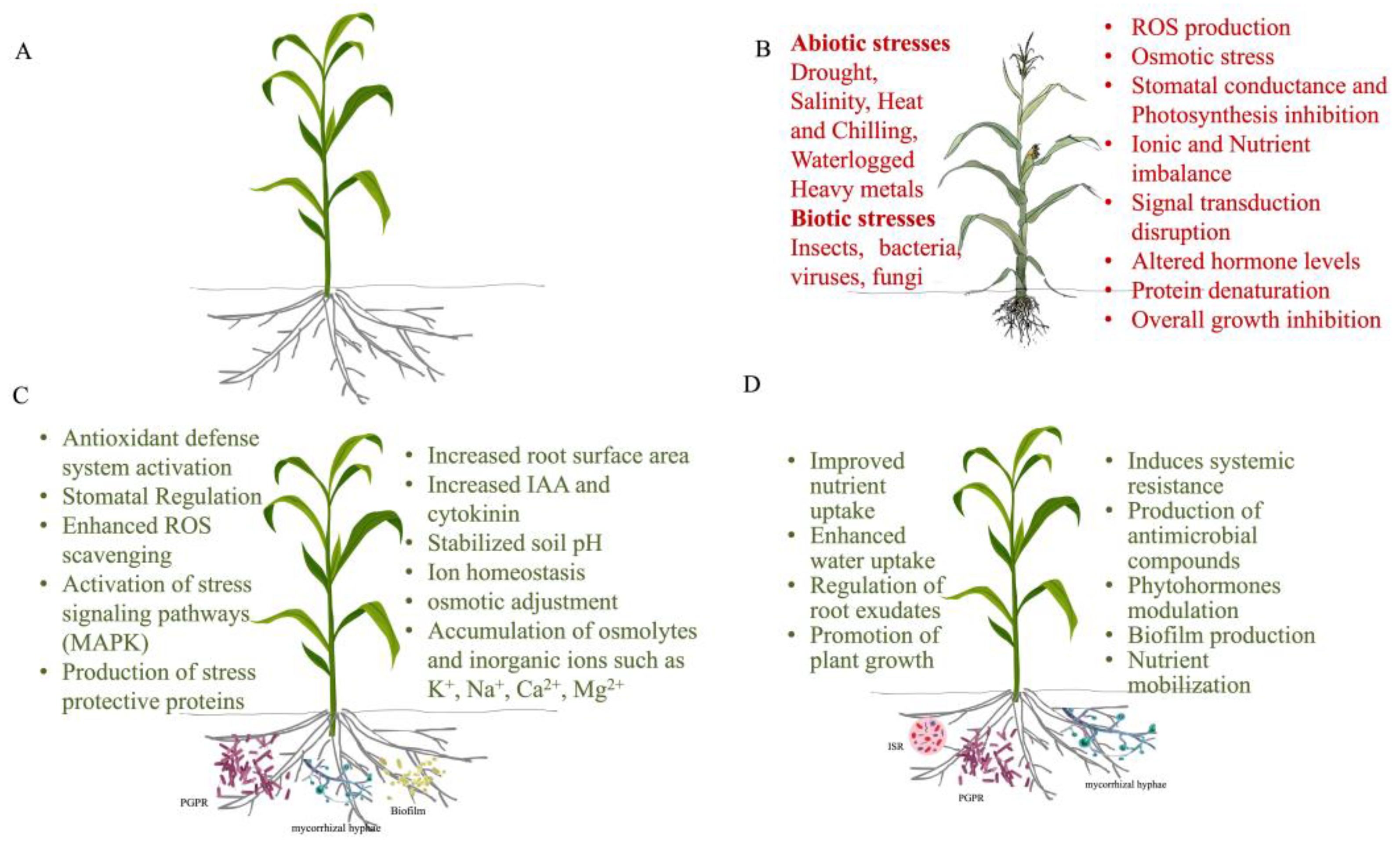
2. Abiotic Stresses and Their Impact on Crop Productivity
3. Biotic Stress and Crop Production
4. Mechanism of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Maize
4.1. Drought Stress
4.2. Maintaining Ion Homeostasis in Salinity Stress
4.3. Osmotic Adjustment
4.5. Polyamines and Their Roles in Biotic Stress in Maize
5. Beneficial Plant-Microbe Interactions in Maize
5.1. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis
5.2. Nitrogen-Fixing Symbiosis with Rhizobia
5.3. Agricultural Application of Stress-Tolerant Microbes
5.4. Microbe Mediated Induced Systemic Resistance (ISR) in Maize
| Host associated microbial strains | Effect/Mechanism of Stress tolerance | References |
| Microbial mediated beneficial drought stress tolerance | ||
|
Rhizobium (R. etli bv. Phaseoli, R. leguminosarum bv. Trifolii, Sinorhizobium sp |
Enhanced growth, increased plant height, improved grain yield |
[82] |
|
Herbaspirillum seopedicae Azospirillum sp |
Increased grain yield Higher N accumulation |
[83] |
| Piriformospora indica | Increased leaf area and SPAD value Increased root fresh and dry weight Decreased Malondialdehyde (MDA) accumulation Upregulation of antioxidants and drought related genes |
[85] |
| Pseudomonas putida | Forms viable biofilms around roots Increase soil holding capacity Improve soil structure |
[91] |
|
Pseudomonas aeruginosa Alcaligenes faecalis Proteus peneri |
Increase soil moisture content Enhances plant growth traits such as leaf area, shoot length, root length Downregulation of catalase, ascorbate peroxidase and glutathione peroxidase |
[92] |
|
Klebsiella variicola Pseudomonas fluorescens Raoultella planticola |
Increased levels of betaine, glycine and choline Improved plant growth |
[93] |
|
Burkholderia sp. Mitsuaria sp. |
Increased proline and phytohormone accumulation Higher antioxidant activity Decreased MDA content |
[94] |
| Megathyrsus maximus | Increased proline accumulation Decrease in MDA content Reduced glutathione reductase activity |
[95] |
|
Azospirillum brasilense Pseudomonas putida Sphingomonas |
Symcoms containing these microbes increases shoot dry weight, root dry weight and plant height | [96] |
| Azospirillum lipoferum | Increased proline, soluble sugar and amino acids accumulation Enhances shoot and root weight, root length |
[97,98] |
| Bacillus sp. | Increased proline accumulation Reduction in electrolyte leakage Decreased activity of antioxidants |
[99] |
|
Burkholderia phytofirmans Strain PsJN Enterobacter sp. FD17 |
Increased root and shoot biomass Higher chlorophyll content Increased leaf area and photosynthetic rate |
[100] |
| Rhizophagus irregularis | Increased hydraulic conductivity and water permeability coefficient Increased phosphorylation of Plasma membrane intrinsic proteins (PIPs) Increased photosynthetic activity |
[101] |
| B pumilus | Increased relative water content and osmotic potential Higher photosynthetic activity Increased ABA production |
[102] |
|
Azospirillum brasilense SP-7 Herbaspirillum seropedicae Z-152 |
Decreased expression of ZmVP14 | [103] |
| Microbial mediated beneficial saline stress tolerance | ||
| Bacillus sp. PM31 | Improved maize growth under salinity stress | [86] |
| Co-inoculation of Rhizophagus intraradices Massilia sp. RK4 |
Increased nutrient uptake Increased AMF root colonization Decreased leaf proline levels |
[104] |
|
Rhizobium sp. Pseudomonas sp. |
Enhanced proline production Decrease in electrolyte leakage Reduction in osmotic potential Selective K ions uptake |
[105] |
|
Pseudomonas fluorescens, P. syringae, P. chlororaphis Enterobacter aerogenes |
ACC-deaminase for increasing plant height, biomass, and cob yield Higher grain mass and straw yield Increased P and K uptake Higher K+/Na+ ratio |
[106] |
| Glomus mosseae | Enhanced soluble sugars accumulation Increased total organic acids, acetic acid, malic acid, oxalic acid, fumaric acid and citric acid accumulation Increased upregulation of osmoregulation process |
[107] |
| B. amyloliquefaciens SQR9 | Increased chlorophyll content Enhanced soluble sugar content Decreased level of Na+ Upregulation of RBCS, RBCL, H+-PPase, HKT1, NHX1, NHX2 and NHX3 |
[108] |
| Kocuria rhizophila Y1 | Increased photosynthetic capacity and relative water content Increased antioxidant levels Decreased level of Na+ |
[109] |
| Azotobacter chroococcum | Increased K+/Na+ ratio Higher chlorophyll content Increased proline concentration |
[91] |
| Microbial mediated beneficial heat stress tolerance | ||
|
Bacillus sp. AH-08, AH-67, AH-16 Pseudomonas sp. SH-29 |
Upregulation of heat shock proteins (HSP) Increased total chlorophyll, catalase, and peroxidase Enhances plant height, leaf area, root & shoot fresh and dry weight Decreased concentration of MDA |
[110] |
|
Rhizophagus intraradices Funneliformis mosseae F. geosporum |
Increased quantum efficiency of PSII Higher photosynthetic rate Increased plant height, leaf width and cob number |
[111] |
| Glomus etunicatum | Increased water content and leaf water potential Increased photosynthetic activity Higher stomatal conductance |
[112] |
| Glomus sp. | Regulation of electron transport through PSII Increased plant height and leaf width |
[113] |
6. Challenges and Future Perspectives
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chávez-Arias, C.C.; Ligarreto-Moreno, G.A.; Ramírez-Godoy, A.; Restrepo-Díaz, H. Maize Responses Challenged by Drought, Elevated Daytime Temperature and Arthropod Herbivory Stresses: A Physiological, Biochemical and Molecular View. Front Plant Sci 2021, 12, 702841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyirenda, H.; Mwangomba, W.; Nyirenda, E.M. Delving into Possible Missing Links for Attainment of Food Security in Central Malawi: Farmers’ Perceptions and Long Term Dynamics in Maize (Zea Mays L.) Production. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asibi, A.E.; Chai, Q.; A. Coulter, J. Mechanisms of Nitrogen Use in Maize. Agronomy 2019, 9. [CrossRef]
- Gheith, E.M.S.; El-Badry, O.Z.; Lamlom, S.F.; Ali, H.M.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ghareeb, R.Y.; El-Sheikh, M.H.; Jebril, J.; Abdelsalam, N.R.; Kandil, E.E. Maize (Zea Mays L.) Productivity and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in Response to Nitrogen Application Levels and Time. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 941343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitah, M.; Malec, K.; Maitah, K. Influence of Precipitation and Temperature on Maize Production in the Czech Republic from 2002 to 2019. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 10467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AbdElgawad, H.; Zinta, G.; Hegab, M.M.; Pandey, R.; Asard, H.; Abuelsoud, W. High Salinity Induces Different Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Responses in Maize Seedlings Organs. Front Plant Sci 2016, 7, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachtman, D.; Liu, W. Molecular Pieces to the Puzzle of the Interaction between Potassium and Sodium Uptake in Plants. Trends Plant Sci 1999, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, S.; Jain, S.; Jain, V. Salinity Induced Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant System in Salt-Tolerant and Salt-Sensitive Cultivars of Rice (Oryza Sativa L.). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2011, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, A.O. Insect Pests of Maize: A Guide for Field Identification.; 1987.
- Widstrom, N.W. The Role of Insects and Other Plant Pests in Aflatoxin Contamination of Corn, Cotton, and Peanuts—A Review. Journal of Environmental Quality 1979, 8, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelake, R.M.; Pramanik, D.; Kim, J.-Y. Exploration of Plant-Microbe Interactions for Sustainable Agriculture in CRISPR Era. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochefort, A.; Simonin, M.; Marais, C.; Guillerm-Erckelboudt, A.-Y.; Barret, M.; Sarniguet, A. Transmission of Seed and Soil Microbiota to Seedling. mSystems 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harman, G.; Khadka, R.; Doni, F.; Uphoff, N. Benefits to Plant Health and Productivity From Enhancing Plant Microbial Symbionts. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vocciante, M.; Grifoni, M.; Fusini, D.; Petruzzelli, G.; Franchi, E. The Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) in Mitigating Plant’s Environmental Stresses. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilber-Rosenberg, I.; Rosenberg, E. Role of Microorganisms in the Evolution of Animals and Plants: The Hologenome Theory of Evolution. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2008, 32, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, J.; Singh, V.; Hewitt, K.; Kaundal, A. Exploration of the Rhizosphere Microbiome of Native Plant Ceanothus Velutinus – an Excellent Resource of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria. Front Plant Sci 2022, 13, 979069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesh, J.; Hewitt, K.; Devkota, A.R.; Wilson, T.; Kaundal, A. IAA-Producing Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria from Ceanothus Velutinus Enhance Cutting Propagation Efficiency and Arabidopsis Biomass. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Lee, B.-M. Effects of Climate Change and Drought Tolerance on Maize Growth. Plants (Basel) 2023, 12, 3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziyomo, C.; Bernardo, R. Drought Tolerance in Maize: Indirect Selection through Secondary Traits versus Genomewide Selection. Crop Science 2013, 53, 1269–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, H.A.; Men, S.; Hussain, S.; Chen, Y.; Ali, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Liao, C.; et al. Interactive Effects of Drought and Heat Stresses on Morpho-Physiological Attributes, Yield, Nutrient Uptake and Oxidative Status in Maize Hybrids. Sci Rep 2019, 9, 3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatfield, J. Increased Temperatures Have Dramatic Effects on Growth and Grain Yield of Three Maize Hybrids. Agricultural & Environmental Letters 2016, 1, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehlein, S.K.; Liu, P.; Webster, A.; Ribeiro, C.; Suzuki, M.; Wu, S.; Guan, J.-C.; Stewart, J.D.; Tracy, W.F.; Settles, A.M.; et al. Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Elevated Temperature on Zea Mays Endosperm Development during Grain Fill. The Plant Journal 2019, 99, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cakir, R. Effect of Water Stress at Different Development Stages on Vegetative and Reproductive Growth of Corn. Field Crops Research 2004, 89, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hütsch, B.W.; Faust, F.; Jung, S.; Schubert, S. Drought Stress during Maize Flowering May Cause Kernel Abortion by Inhibition of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Activity. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Maqbool, M.A.; Cengiz, R. Drought Stress in Maize (Zea Mays L.): Effects, Resistance Mechanism, Global Achievements and Biological Strategies for Improvement; 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-25442-5.
- Izaurralde, R.C.; Thomson, A.M.; Morgan, J.A.; Fay, P.A.; Polley, H.W.; Hatfield, J.L. Climate Impacts on Agriculture: Implications for Forage and Rangeland Production. Agronomy Journal 2011, 103, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabaldón-Leal, C.; Webber, H.; Otegui, M.E.; Slafer, G.A.; Ordóñez, R.A.; Gaiser, T.; Lorite, I.J.; Ruiz-Ramos, M.; Ewert, F. Modelling the Impact of Heat Stress on Maize Yield Formation. Field Crops Research 2016, 198, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, H.; Ren, H.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Ren, B.; Liu, P. Maize (Zea Mays L.) Responses to Heat Stress: Mechanisms That Disrupt the Development and Hormone Balance of Tassels and Pollen. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 2023, 209, 502–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Krause, M.; Sandhu, D.; Sekhon, R.S.; Kaundal, A. Salinity Stress Tolerance Prediction for Biomass-Related Traits in Maize (Zea Mays L.) Using Genome-Wide Markers. The Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, M.; Hussain, M.; Wakeel, A.; Siddique, K.H.M. Salt Stress in Maize: Effects, Resistance Mechanisms, and Management. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2015, 35, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Chao, L.; Zhou, M.; Hong, M.; Luo, L.; Wang, L.; Ying, W.; Jingwei, C.; Songjie, G.; Fashui, H. Oxidative Damages of Maize Seedlings Caused by Exposure to a Combination of Potassium Deficiency and Salt Stress. Plant Soil 2011, 340, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, C.; Ashraf, M.; Dikilitas, M.; Tuna, A.L. Alleviation of Salt Stress-Induced Adverse Effects on Maize Plants by Exogenous Application of Indoleacetic Acid (IAA) and Inorganic Nutrients - A Field Trial. Australian Journal of Crop Science 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Katerji, N.; van Hoorn, J.W.; Hamdy, A.; Karam, F.; Mastrorilli, M. Effect of Salinity on Water Stress, Growth, and Yield of Maize and Sunflower. Agricultural Water Management 1996, 30, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahzad, M.; Witzel, K.; Zörb, C.; Mühling, K.H. Growth-Related Changes in Subcellular Ion Patterns in Maize Leaves (Zea Mays L.) under Salt Stress. Journal of Agronomy and Crop Science 2012, 198, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeru, F.; Wambua, A.; Muge, E.; Haesaert, G.; Gettemans, J.; Misinzo, G. Major Biotic Stresses Affecting Maize Production in Kenya and Their Implications for Food Security. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodha, T.D.; Hembram, P.; Nitile Tep, J.B. Proteomics: A Successful Approach to Understand the Molecular Mechanism of Plant-Pathogen Interaction. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, F.; Yang, L.; Tai, F.; Hu, X.; Wang, W. “Omics” of Maize Stress Response for Sustainable Food Production: Opportunities and Challenges. OMICS 2014, 18, 714–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, M.; Ranamukhaarachchi, S.L.; Ahmad, S.; Nawaz, R.; Qayyum, M.M.N.; Razaq, A.; Faiz, F. Variability and Correlation of Selected Soil Attributes and Maize Yield Influenced by Tillage Systems in Mountainous Agroecosystem. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 2022, 77, 466–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Abbo, S. Genetics of Flowering Time in Chickpea and Its Bearing on Productivity in Semiarid Environments. Advances in Agronomy 2001, 72, 107–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Wright, G.; Siddique, K. Adaptation of Grain Legumes (Pulses) to Water-Limited Environments. Advances in Agronomy, Vol 71 2001, 71, 193–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Anwar, S.; Ashraf, M.Y.; Khaliq, B.; Sun, M.; Hussain, S.; Gao, Z.; Noor, H.; Alam, S. Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies to Improve Heat Tolerance in Rice. A Review. Plants 2019, 8, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleiman, M.F.; Al-Suhaibani, N.; Ali, N.; Akmal, M.; Alotaibi, M.; Refay, Y.; Dindaroglu, T.; Abdul-Wajid, H.H.; Battaglia, M.L. Drought Stress Impacts on Plants and Different Approaches to Alleviate Its Adverse Effects. Plants (Basel) 2021, 10, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, P.; Zou, Y.-N.; Wu, Q.-S.; Kuča, K. Effects of Mycorrhizal Fungi on Root-Hair Growth and Hormone Levels of Taproot and Lateral Roots in Trifoliate Orange under Drought Stress. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science 2019, 65, 1316–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A. Osmotic Adjustment Is a Prime Drought Stress Adaptive Engine in Support of Plant Production. Plant Cell Environ 2017, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamaoui, M.; Jemo, M.; Datla, R.; Bekkaoui, F. Heat and Drought Stresses in Crops and Approaches for Their Mitigation. Front. Chem. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandhu, D.; Kaundal, A. Dynamics of Salt Tolerance: Molecular Perspectives. In Biotechnologies of Crop Improvement, Volume 3: Genomic Approaches; Gosal, S.S., Wani, S.H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2018; pp. 25–40 ISBN 978-3-319-94746-4.
- Amin, I.; Rasool, S.; Mir, M.A.; Wani, W.; Masoodi, K.Z.; Ahmad, P. Ion Homeostasis for Salinity Tolerance in Plants: A Molecular Approach. Physiol Plant 2021, 171, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, S.; Kumar, A.; Benazir, I.; Kumar, G. Reassessing the Role of Ion Homeostasis for Improving Salinity Tolerance in Crop Plants. Physiologia Plantarum 2021, 171, 502–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Liang, X.; Zhang, M.; Lu, M.; Guo, Y.; Qin, F.; Jiang, C. The Classical SOS Pathway Confers Natural Variation of Salt Tolerance in Maize. New Phytologist 2022, 236, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Guo, Y. Elucidating the Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Plant Salt-Stress Responses. New Phytologist 2018, 217, 523–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Gui, C.; Nguvo, K.J.; Ma, L.; Wang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X. Beneficial Rhizobacterium Triggers Induced Systemic Resistance of Maize to Gibberella Stalk Rot via Calcium Signaling. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 2023, 36, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Horie, T.; Xue, S.; Leung, H.-Y.; Katsuhara, M.; Brodsky, D.E.; Wu, Y.; Schroeder, J.I. Differential Sodium and Potassium Transport Selectivities of the Rice OsHKT2;1 and OsHKT2;2 Transporters in Plant Cells. Plant Physiology 2009, 152, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivcak, M.; Brestic, M.; Sytar, O. Osmotic Adjustment and Plant Adaptation to Drought Stress. In Drought Stress Tolerance in Plants, Vol 1: Physiology and Biochemistry; Hossain, M.A., Wani, S.H., Bhattacharjee, S., Burritt, D.J., Tran, L.-S.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 105–143. ISBN 978-3-319-28899-4. [Google Scholar]
- Subbarao, G.V.; Nam, N.H.; Chauhan, Y.S.; Johansen, C. Osmotic Adjustment, Water Relations and Carbohydrate Remobilization in Pigeonpea under Water Deficits. Journal of Plant Physiology 2000, 157, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, U.K.; Islam, M.N.; Siddiqui, M.N.; Khan, M.A.R. Understanding the Roles of Osmolytes for Acclimatizing Plants to Changing Environment: A Review of Potential Mechanism. Plant Signal Behav 2021, 16, 1913306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yancey, P.H. Compatible and Counteracting Solutes: Protecting Cells from the Dead Sea to the Deep Sea. Science Progress 2004, 87, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Foolad, M.R. Roles of Glycine Betaine and Proline in Improving Plant Abiotic Stress Resistance. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2007, 59, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshiba, Y.; Kiyosue, T.; Nakashima, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Regulation of Levels of Proline as an Osmolyte in Plants under Water Stress. Plant Cell Physiol 1997, 38, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Prado, C.; Podazza, G.; Interdonato, R.; González, J.A.; Hilal, M.; Prado, F.E. Soluble Sugars—Metabolism, Sensing and Abiotic Stress. Plant Signal Behav 2009, 4, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.-F.; Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Dong, X.-Y.; Sun, Y. Molecular Basis for Polyol-Induced Protein Stability Revealed by Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J Chem Phys 2010, 132, 225103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Harish; Singh, R.K.; Verma, K.K.; Sharma, L.; Quiroz-Figueroa, F.R.; Meena, M.; Gour, V.S.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; et al. Recent Developments in Enzymatic Antioxidant Defence Mechanism in Plants with Special Reference to Abiotic Stress. Biology (Basel) 2021, 10, 267. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yang, A.; Yin, H.; Zhang, J. Influence of Water Stress on Endogenous Hormone Contents and Cell Damage of Maize Seedlings. J Integr Plant Biol 2008, 50, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.; Gunnerås, S.A.; Petersson, S.V.; Tarkowski, P.; Graham, N.; May, S.; Dolezal, K.; Sandberg, G.; Ljung, K. Cytokinin Regulation of Auxin Synthesis in Arabidopsis Involves a Homeostatic Feedback Loop Regulated via Auxin and Cytokinin Signal Transduction. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2956–2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.; Ori, N. Mechanisms of Cross Talk between Gibberellin and Other Hormones. Plant Physiol 2007, 144, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.R.; Qayyum, A.; Razzaq, A.; Ahmad, M.; Mahmood, I.; Sher, A. Role of Foliar Application of Salicylic Acid and L-Tryptophan in Drought Tolerance of Maize. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2012, 22, 768–772. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.-Y.; Wang, X.-F.; Wu, F.-Q.; Du, S.-Y.; Cao, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, X.-L.; Peng, C.-C.; Yu, X.-C.; Zhu, S.-Y.; et al. The Mg-Chelatase H Subunit Is an Abscisic Acid Receptor. Nature 2006, 443, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.M.B.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Defense in Plants under Abiotic Stress: Revisiting the Crucial Role of a Universal Defense Regulator. Antioxidants (Basel) 2020, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, H.-Y.; Shannon, L.M.; Tian, F.; Bradbury, P.J.; Chen, C.; Flint-Garcia, S.A.; McMullen, M.D.; Ware, D.; Buckler, E.S.; Doebley, J.F.; et al. ZmCCT and the Genetic Basis of Day-Length Adaptation Underlying the Postdomestication Spread of Maize. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2012, 109, E1913–E1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasso-Robles, F.I.; Jiménez-Bremont, J.F.; Becerra-Flora, A.; Juárez-Montiel, M.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Pieckenstain, F.L.; García De La Cruz, R.F.; Rodríguez-Kessler, M. Inhibition of Polyamine Oxidase Activity Affects Tumor Development during the Maize-Ustilago Maydis Interaction. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2016, 102, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Berberich, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Seo, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Kusano, T. Spermine Signalling in Tobacco: Activation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases by Spermine Is Mediated through Mitochondrial Dysfunction. Plant J 2003, 36, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herridge, D.F.; Peoples, M.B.; Boddey, R.M. Global Inputs of Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Agricultural Systems. Plant Soil 2008, 311, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoples, M.B.; Brockwell, J.; Herridge, D.F.; Rochester, I.J.; Alves, B.J.R.; Urquiaga, S.; Boddey, R.M.; Dakora, F.D.; Bhattarai, S.; Maskey, S.L.; et al. The Contributions of Nitrogen-Fixing Crop Legumes to the Productivity of Agricultural Systems. Symbiosis 2009, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, K.; Hayashi, H. Strigolactones: Chemical Signals for Fungal Symbionts and Parasitic Weeds in Plant Roots. Ann Bot 2006, 97, 925–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucido, A.; Andrade, F.; Basallo, O.; Eleiwa, A.; Marin-Sanguino, A.; Vilaprinyo, E.; Sorribas, A.; Alves, R. Modeling the Effects of Strigolactone Levels on Maize Root System Architecture. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.C.; Koch, K.E.; Suzuki, M.; Wu, S.; Latshaw, S.; Petruff, T.; Goulet, C.; Klee, H.J.; McCarty, D.R. Diverse Roles of Strigolactone Signaling in Maize Architecture and the Uncoupling of a Branching-Specific Subnetwork. Plant Physiol 2012, 160, 1303–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genre, A.; Chabaud, M.; Timmers, T.; Bonfante, P.; Barker, D.G. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Elicit a Novel Intracellular Apparatus in Medicago Truncatula Root Epidermal Cells before Infection. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 3489–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortier, E.; Mounier, A.; Kreplak, J.; Martin-Laurent, F.; Recorbet, G.; Lamotte, O. Evidence That a Common Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Network Alleviates Phosphate Shortage in Interconnected Walnut Sapling and Maize Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, D. The Role of Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis in Plant Abiotic Stress. Front Microbiol 2024, 14, 1323881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, J.; An, X.; Li, Z.; Neuhäuser, B.; Ludewig, U.; Wu, X.; Schulze, W.; Chen, F.; Feng, G.; Lambers, H.; et al. The Mycorrhiza-Specific Ammonium Transporter ZmAMT3;1 Mediates Mycorrhiza-Dependent Nitrogen Uptake in Maize Roots. The Plant Cell 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Meng, L.; Yin, T.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. Changes in Soil Rhizobia Diversity and Their Effects on the Symbiotic Efficiency of Soybean Intercropped with Maize. Agronomy 2023, 13, 997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, T.M.R.; Carlos, H.C.; Fabio, L.C.M.; Gustavo, V.M. Azospirillum Spp. Potential for Maize Growth and Yield. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 17, 574–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Ahmed, I.; Sheirdil, R.A. An Overview of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) for Sustainable Agriculture. In Crop Production for Agricultural Improvement; Ashraf, M., Öztürk, M., Ahmad, M.S.A., Aksoy, A., Eds.; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, 2012; pp. 557–579. ISBN 978-94-007-4115-7. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia de Salamone, I.E.; Döbereiner, J.; Urquiaga, S.; Boddey, R.M. Biological Nitrogen Fixation in Azospirillum Strain-Maize Genotype Associations as Evaluated by the 15N Isotope Dilution Technique. Biol Fertil Soils 1996, 23, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deynze, A.V.; Zamora, P.; Delaux, P.-M.; Heitmann, C.; Jayaraman, D.; Rajasekar, S.; Graham, D.; Maeda, J.; Gibson, D.; Schwartz, K.D.; et al. Nitrogen Fixation in a Landrace of Maize Is Supported by a Mucilage-Associated Diazotrophic Microbiota. PLOS Biology 2018, 16, e2006352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, W. Piriformospora Indica Confers Drought Tolerance on Zea Mays L. through Enhancement of Antioxidant Activity and Expression of Drought-Related Genes. The Crop Journal 2017, 5, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, B.; Hafeez, A.; Afridi, M.S.; Javed, M.A.; Sumaira; Suleman, F.; Nadeem, M.; Ali, S.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Elshikh, M.S.; et al. Bacterial-Mediated Salinity Stress Tolerance in Maize (Zea Mays L.): A Fortunate Way toward Sustainable Agriculture. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 20471–20487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryals, J.; Neuenschwander, U.; Willits, M.; Molina, A.; Steiner, H.; Hunt, M. Systemic Acquired Resistance. Plant Cell 1996, 8, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Gui, Y.; Li, Z.; Jiang, C.; Guo, J.; Niu, D. Induced Systemic Resistance for Improving Plant Immunity by Beneficial Microbes. Plants (Basel) 2022, 11, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, P.A.H.M.; Doornbos, R.F.; Zamioudis, C.; Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.J. Induced Systemic Resistance and the Rhizosphere Microbiome. Plant Pathol J 2013, 29, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravanakumar, K.; Fan, L.; Fu, K.; Yu, C.; Wang, M.; Xia, H.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, J. Cellulase from Trichoderma Harzianum Interacts with Roots and Triggers Induced Systemic Resistance to Foliar Disease in Maize. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 35543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Tapias, D.; Moreno-Galván, A.; Pardo-Díaz, S.; Obando, M.; Rivera, D.; Bonilla, R. Effect of Inoculation with Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria (PGPB) on Amelioration of Saline Stress in Maize (Zea Mays). Applied Soil Ecology 2012, 61, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, H.; Bano, A. Role of Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria and Their Exopolysaccharide in Drought Tolerance of Maize. Journal of Plant Interactions 2014, 9, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, W.; Tian, L.; Ruan, Z.; Zheng, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, L.; Cui, Z.; Zheng, P.; Li, Z.; Gao, M.; et al. Accumulation of Choline and Glycinebetaine and Drought Stress Tolerance Induced in Maize (Zea Mays) by Three Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Strains. Pakistan Journal of Botany 2015, 47, 581–586. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.-F.; Zhou, D.; Lapsansky, E.; Reardon, K.; Guo, J.; Andales, M.; Vivanco, J.; Manter, D. Mitsuaria Sp. and Burkholderia Sp. from Arabidopsis Rhizosphere Enhance Drought Tolerance in Arabidopsis Thaliana and Maize (Zea Mays L.). Plant and Soil 2017, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Galván, A.; Cortés-Patiño, S.; Romero-Perdomo, F.; Uribe-Vélez, D.; Bashan, Y.; Bonilla, R. Proline Accumulation and Glutathione Reductase Activity Induced by Drought-Tolerant Rhizobacteria as Potential Mechanisms to Alleviate Drought Stress in Guinea Grass. Applied Soil Ecology 2020, 147, 103367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Romero, D.; Baez, A.; Quintero-Hernández, V.; Castañeda-Lucio, M.; Fuentes-Ramírez, L.E.; Bustillos-Cristales, M. del R.; Rodríguez-Andrade, O.; Morales-García, Y.E.; Munive, A.; Muñoz-Rojas, J. Compatible Bacterial Mixture, Tolerant to Desiccation, Improves Maize Plant Growth. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0187913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bano, Q.; Ilyas, N.; Bano, A.; Zafar, N.; Akram, A.; Hassan, F.U. Effect of Azospirillum Innoculation on Maize (Zea Mays L.) Under Drought Stress. Pakistan Journal of Botany 45, 13–20.
- Cohen, A.; Travaglia, C.; Bottini, R.; Piccoli, P. Participation of Abscisic Acid and Gibberellins Produced by Endophytic Azospirillum in the Alleviation of Drought Effects in Maize. Botany 2009, 87, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardharajula, S.; Shaik, Z.A.; Grover, M.; Reddy, G.; Venkateswarlu, B. Drought-Tolerant Plant Growth Promoting Bacillus Spp.: Effect on Growth, Osmolytes, and Antioxidant Status of Maize under Drought Stress. Journal of Plant Interactions 2011, 6, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Mitter, B.; Reichenauer, T.G.; Wieczorek, K.; Sessitsch, A. Increased Drought Stress Resilience of Maize through Endophytic Colonization by Burkholderia Phytofirmans PsJN and Enterobacter Sp. FD17. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2014, 97, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, G.; Erice, G.; Ding, L.; Chaumont, F.; Aroca, R.; Ruiz-Lozano, J.M. The Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Symbiosis Regulates Aquaporins Activity and Improves Root Cell Water Permeability in Maize Plants Subjected to Water Stress. Plant, Cell & Environment 2019, 42, 2274–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, H.; Nosheen, A.; Naz, R.; Bano, A.; Keyani, R. L-Tryptophan-Assisted PGPR-Mediated Induction of Drought Tolerance in Maize (Zea Mays L.). Journal of Plant Interactions 2017, 12, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curá, J.A.; Franz, D.R.; Filosofía, J.E.; Balestrasse, K.B.; Burgueño, L.E. Inoculation with Azospirillum Sp. and Herbaspirillum Sp. Bacteria Increases the Tolerance of Maize to Drought Stress. Microorganisms 2017, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, R.; Kim, K.; Subramanian, P.; Senthilkumar, M.; Anandham, R.; Sa, T. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi and Associated Bacteria Isolated from Salt-Affected Soil Enhances the Tolerance of Maize to Salinity in Coastal Reclamation Soil. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2016, 231, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Fatima, M. Salt Tolerance in Zea Mays (L). Following Inoculation with Rhizobium and Pseudomonas. Biol Fertil Soils 2009, 45, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, S.M.; Zahir, Z.A.; Naveed, M.; Arshad, M. Rhizobacteria Containing ACC-Deaminase Confer Salt Tolerance in Maize Grown on Salt-Affected Fields. Can J Microbiol 2009, 55, 1302–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, M.; Tang, M.; Zhang, F.; Huang, Y. Influence of Arbuscular Mycorrhiza on Organic Solutes in Maize Leaves under Salt Stress. Mycorrhiza 2011, 21, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G.; Kimani, V.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, R. Induced Maize Salt Tolerance by Rhizosphere Inoculation of Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens SQR9. Physiologia Plantarum 2016, 158. n/a-n/a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Guan, C. A Novel PGPR Strain Kocuria Rhizophila Y1 Enhances Salt Stress Tolerance in Maize by Regulating Phytohormone Levels, Nutrient Acquisition, Redox Potential, Ion Homeostasis, Photosynthetic Capacity and Stress-Responsive Genes Expression. Environmental and Experimental Botany 2020, 174, 104023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Imtiaz, M.; Nawaz, M.S.; Mubeen, F.; Sarwar, Y.; Hayat, M.; Asif, M.; Naqvi, R.Z.; Ahmad, M.; Imran, A. Thermotolerant PGPR Consortium B3P Modulates Physio-Biochemical and Molecular Machinery for Enhanced Heat Tolerance in Maize during Early Vegetative Growth. Annals of Microbiology 2023, 73, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Agnihotri, R.; Sharma, M.P.; Reddy, V.R.; Jajoo, A. Effect of High-Temperature Stress on Plant Physiological Traits and Mycorrhizal Symbiosis in Maize Plants. Journal of Fungi 2021, 7, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Song, F.-B.; Xu, H.-W. Arbuscular Mycorrhizae Improves Low Temperature Stress in Maize via Alterations in Host Water Status and Photosynthesis. Plant and Soil 2010, 331, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, S.; Jajoo, A. Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi Protects Maize Plants from High Temperature Stress by Regulating Photosystem II Heterogeneity. Industrial Crops and Products 2020, 143, 111934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




