Submitted:
10 October 2024
Posted:
11 October 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substances
2.2. Animals and Diet
2.3. Body Weight and Body Composition
2.4. Vascular Reactivity Studies
2.5. The Langendorff Heart Studies
2.6. Analysis of Minerals in Rat Liver and Kidneys
2.6.1. Sample Preparation
2.6.2. Elements Measurements
2.6.3. Quality Assessment
2.7. Analysis of Minerals in Rat Blood
2.8. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Parameters
2.9. Data Analysis and Statistics
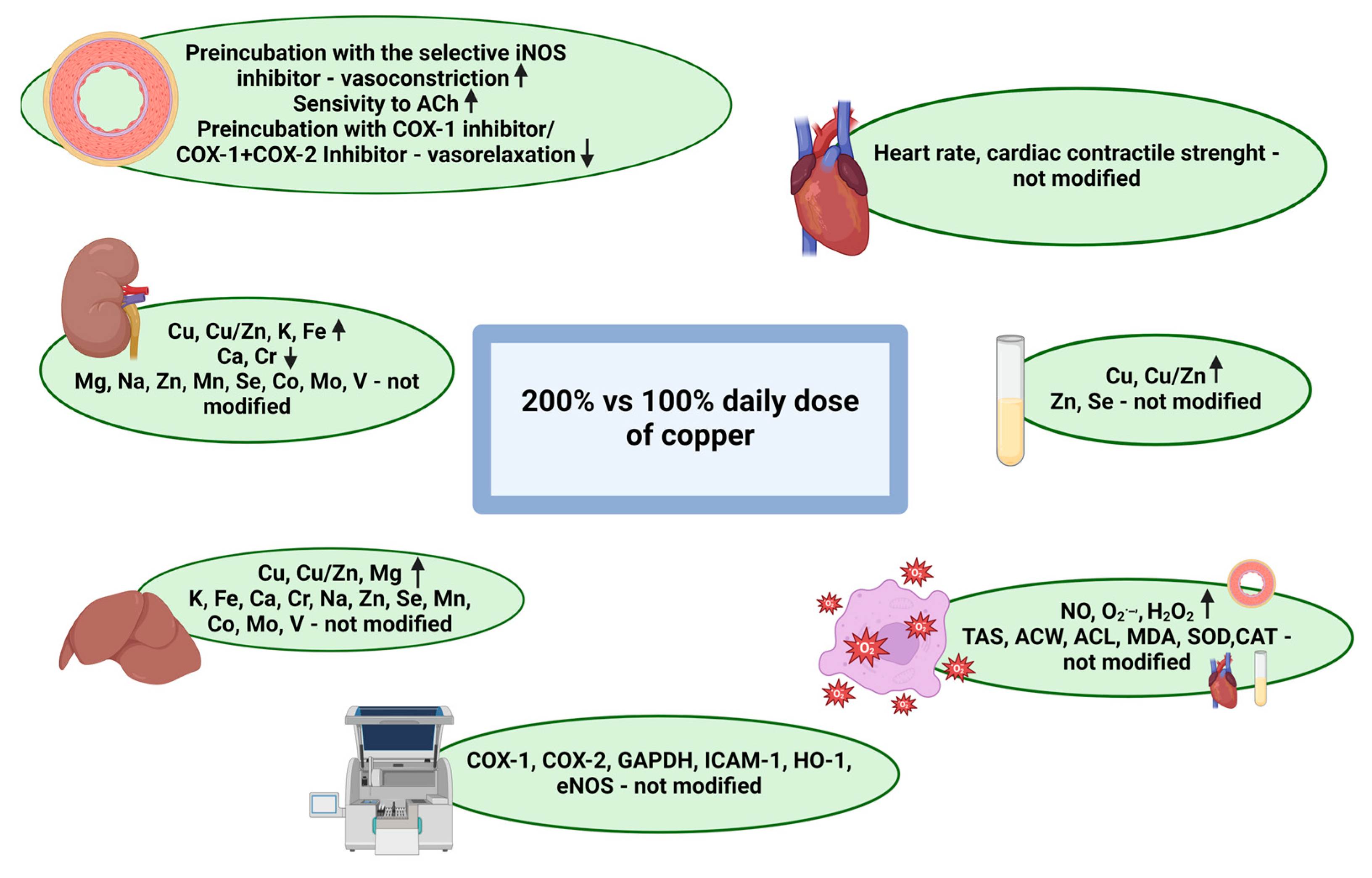
3. Results
3.1. Rat Characteristics
3.2. Minerals
3.2.1. Serum
3.2.2. Liver
3.2.3. Kidney
3.3. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Parameters
3.4. The Isolated Perfused Heart
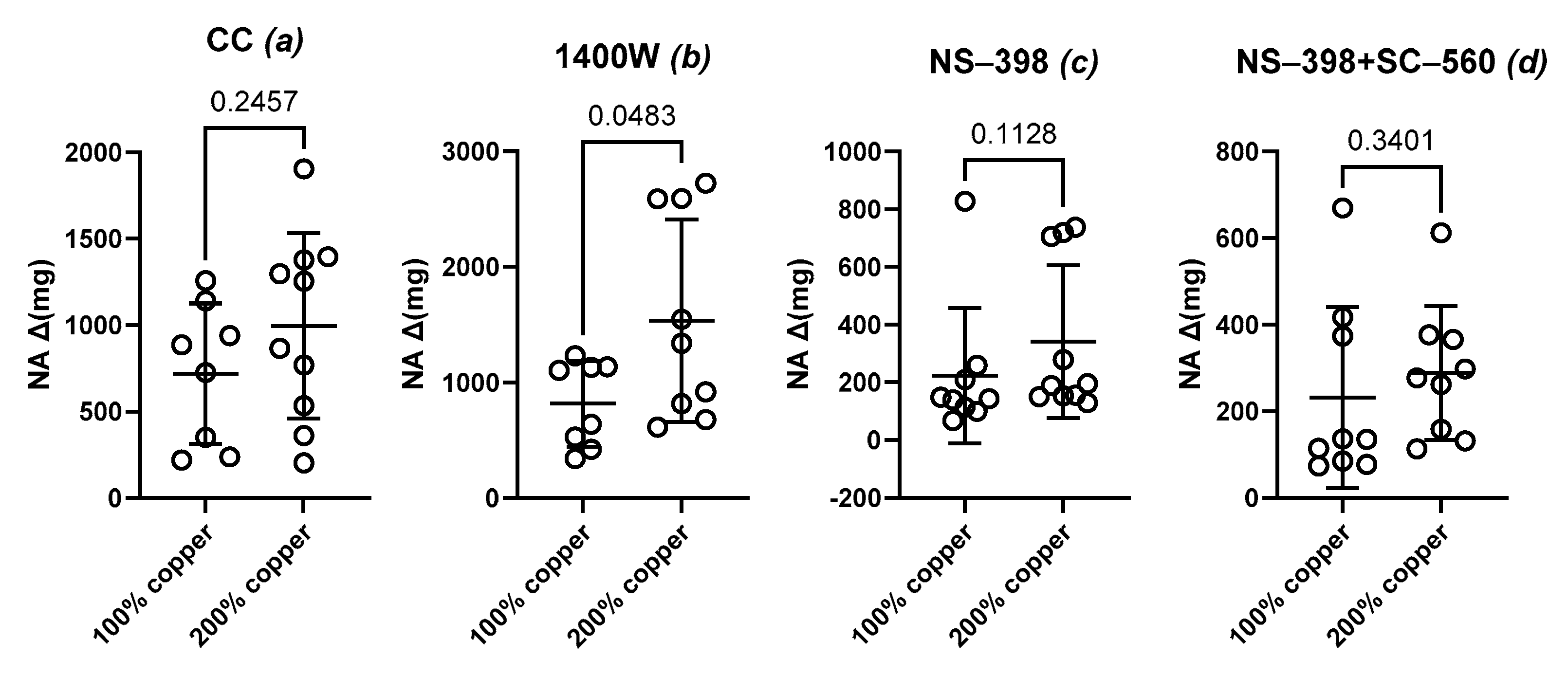
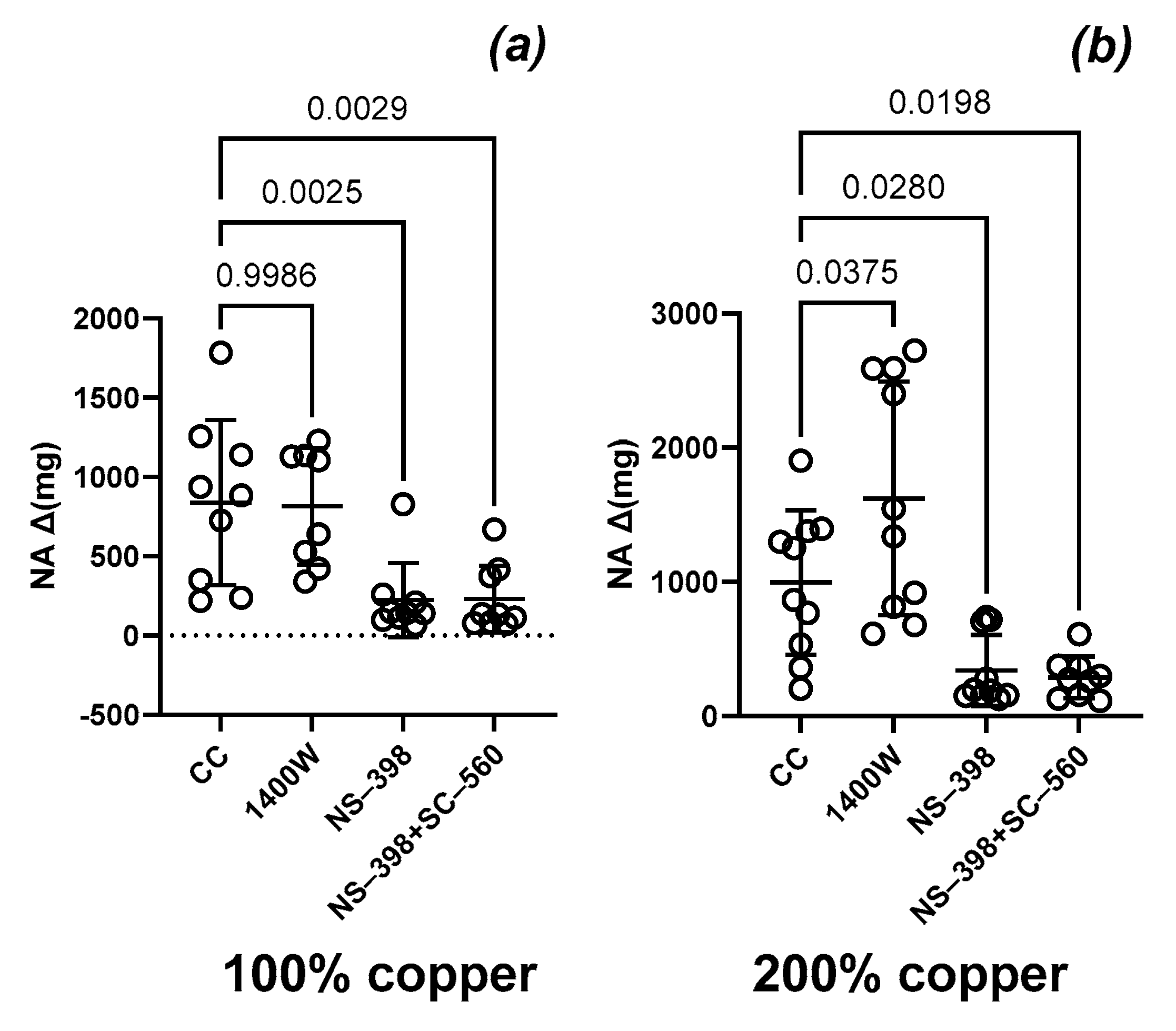
3.5. Vascular Contraction
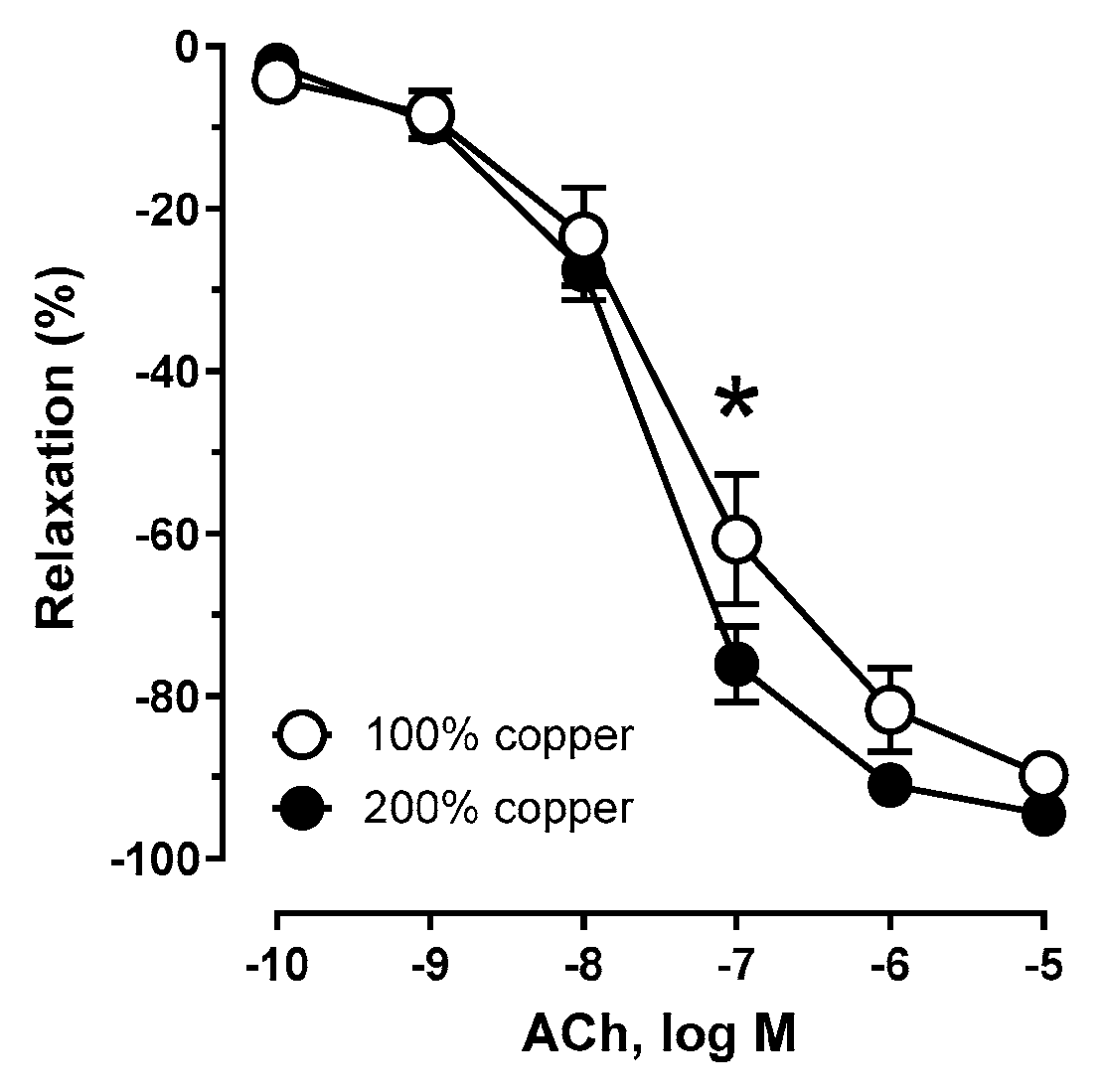
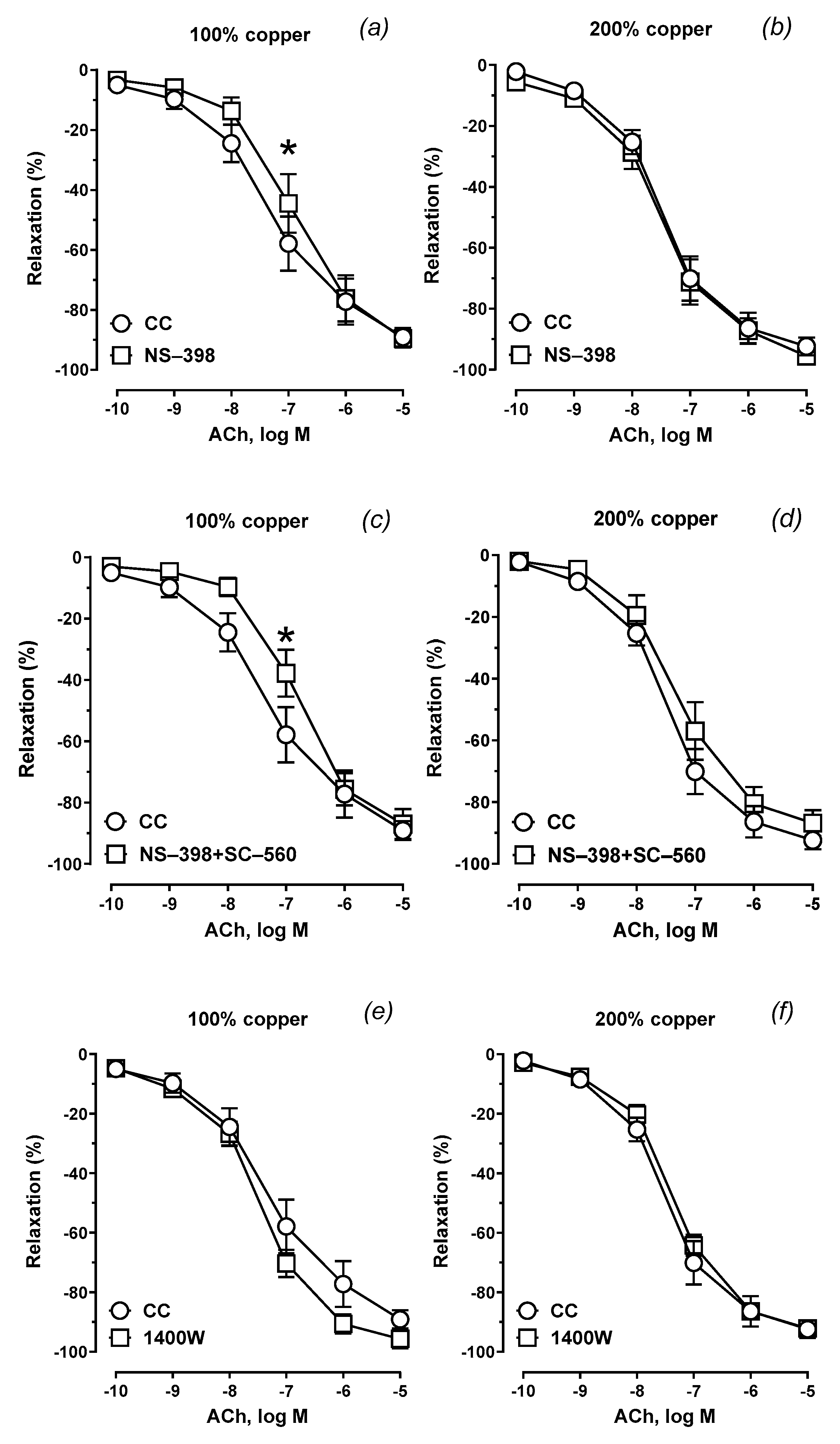
3.6. Vascular Relaxation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.; Min, J.; Wang, F. Copper homeostasis and cuproptosis in health and disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 378. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xiang, P.; Ha, J.H.; Wang, X.; Doguer, C.; Flores, S.R.L.; Kang, Y.J.; Collins, J.F. Copper supplementation reverses dietary iron overload-induced pathologies in mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 59, 56–63. [CrossRef]
- Hajam, Y.A.; Rani, R.; Ganie, S.Y.; Sheikh, T.A.; Javaid, D.; Qadri, S.S.; Pramodh, S.; Alsulimani, A.; Alkhanani, M.F.; Harakeh, S.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Human Pathology and Aging: Molecular Mechanisms and Perspectives. Cells 2022, 11, 552. [CrossRef]
- Kitala, K.; Tanski, D.; Godlewski, J.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Gromadziński, L.; Majewski, M. Copper and Zinc Particles as Regulators of Cardiovascular System Function—A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3040. [CrossRef]
- El-Ta’alu, A.; Ahmad, M.M. Age-Dependent Effects of Copper Toxicity on Connective Tissue Structural Stability in Wistar Rats Skin. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 37, 93–99. [CrossRef]
- Turnlund, J.R.; Reager, R.D.; Costa, F. Iron and copper absorption in young and elderly men. Nutr. Res. 1988, 8, 333–343. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.E.; Milne, D.B.; Lykken, G.I. Effects of age and sex on copper absorption, biological half-life, and status in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 56, 917–925. [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Gromadziński, L.; Cholewińska, E.; Ognik, K.; Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J. The Interaction of Dietary Pectin, Inulin, and Psyllium with Copper Nanoparticle Induced Changes to the Cardiovascular System. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3557. [CrossRef]
- Kitala-Tańska, K.; Socha, K.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Majewski, M. The Effect of an Elevated Dietary Copper Level on the Vascular Contractility and Oxidative Stress in Middle-Aged Rats. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1172. [CrossRef]
- Gordon, C.J.; Phillips, P.M.; Johnstone, A.F. A noninvasive method to study regulation of extracellular fluid volume in rats using nuclear magnetic resonance. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2016, 310, F426–F431. [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Krajewska-Włodarczyk, M.; Gromadziński, L.; Socha, K.; Cholewińska, E.; Ognik, K. The Role of 20-HETE, COX, Thromboxane Receptors, and Blood Plasma Antioxidant Status in Vascular Relaxation of Copper-Nanoparticle-Fed WKY Rats. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3793. [CrossRef]
- Kitala-Tańska, K. Summary of the Results. 2024. Available online: https://app.biorender.com/citation/66e2f1c5ea3e111ddbda34e8 (accessed on 21 September 2024).
- Wang, Y.C.; Hu, C.W.; Liu, M.Y.; Jiang, H.C.; Huo, R.; Dong, D.L. Copper induces vasorelaxation and antagonizes noradrenaline-induced vasoconstriction in rat mesenteric artery. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 32, 1247–1254. [CrossRef]
- Kunutsor, S.K.; Dey, R.S.; Laukkanen, J.A. Circulating Serum Copper Is Associated with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease, but Not Venous Thromboembolism: A Prospective Cohort Study. Pulse 2021, 9, 109–115. [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, J.; Liu, W.; Luo, Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, J.X. Copper overload induces apoptosis and impaired proliferation of T cell in zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 267, 106808. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, A.; Kaneto, H.; Miyatsuka, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Yamasaki, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Matsuoka, T.A.; Matsuhisa, M. Role of copper ion in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 699–706. [CrossRef]
- Ferns, G.A.; Lamb, D.J.; Taylor, A. The possible role of copper ions in atherogenesis: The Blue Janus. Atherosclerosis 1997, 133, 139–152. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Liu, X. Copper homeostasis and copper-induced cell death: Novel targeting for intervention in the pathogenesis of vascular aging. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115839. [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Liu, D.L.; Chua, Y.L.; Chen, C.; Lim, Y.L. Effects of micromolar concentrations of manganese, copper, and zinc on alpha1-adrenoceptor-mediating contraction in rat aorta. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2001, 82, 159–166. [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Persichini, T.; Dugo, L.; Colasanti, M.; Musci, G. Copper induces type II nitric oxide synthase in vivo. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1253–1262. [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y. The endothelial cyclooxygenase pathway: Insights from mouse arteries. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 780, 148–158. [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.R.; Cascio, M.B.; Sawa, A. GAPDH as a sensor of NO stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 502–509. [CrossRef]
- Couffinhal, T.; Duplàa, C.; Moreau, C.; Lamazière, J.M.; Bonnet, J. Regulation of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 225–234. [CrossRef]
- Habas, K.; Shang, L. Alterations in intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) in human endothelial cells. Tissue Cell. 2018, 54, 139–143. [CrossRef]
- Loboda, A.; Jazwa, A.; Grochot-Przeczek, A.; Rutkowski, A.J.; Cisowski, J.; Agarwal, A.; Jozkowicz, A.; Dulak, J. Heme oxygenase-1 and the vascular bed: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2008, 10, 1767–1812. [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.T.; DeMars, L.C. Increased heme oxygenase-1 expression during copper deficiency in rats results from increased mitochondrial generation of hydrogen peroxide. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1328–1333. [CrossRef]
- Borkowska-Sztachańska, M.; Thoene, M.; Socha, K.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Majewski, M.S. Decreased vascular contraction and changes in oxidative state in middle-aged Wistar rats after exposure to increased levels of dietary zinc. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2024, 491, 117049. [CrossRef]
- Incalza, M.A.; D’Oria, R.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Oxidative stress and reactive oxygen species in endothelial dysfunction associated with cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2018, 100, 1–19. [CrossRef]
- Karaaslan, F.; Demir, F.; Yılmaz, R.; Akıl, E. Total oxidant/antioxidant status, copper and zinc levels in acute ischemic stroke patients after mechanical thrombectomy. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2023, 229, 107718. [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wen, Y.; Lin, G.; Meng, C.; He, P.; Wang, F. Different Sources of Copper Effect on Intestinal Epithelial Cell: Toxicity, Oxidative Stress, and Metabolism. Metabolites 2020, 10, 11. [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, C.M.; Diniz, Y.S.; Faine, L.A.; Rodrigues, H.G.; Burneiko, R.C.M.; Ribas, B.O.; Novelli, E.L. Toxicity of copper intake: Lipid profile, oxidative stress and susceptibility to renal dysfunction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004, 42, 2053–2060. [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, M.; Boyacioglu, M.; Avcioglu, M.; Elmas, S. Changes Induced by Copper Toxicity in the Rat Liver and the Effects of Panax Ginseng on These Changes. Biol. Bull. Russ. Acad Sci. 2023, 50, S694–S707. [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wu, S.; Xu, X.; Tan, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Wang, F. Cope with copper: From molecular mechanisms of cuproptosis to copper-related kidney diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112075. [CrossRef]
- Malavolta, M.; Piacenza, F.; Basso, A.; Giacconi, R.; Costarelli, L.; Mocchegiani, E. Serum copper to zinc ratio: Relationship with aging and health status. Mech. Aging Dev. 2015, 151, 93–100. [CrossRef]
- Staniek, H. The Combined Effects of Cr(III) Supplementation and Iron Deficiency on the Copper and Zinc Status in Wistar Rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2019, 190, 414–424. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Doo, M.; Kim, B.H.; Ha, J.H. High Iron Consumption Modifies the Hepatic Transcriptome Related to Cholesterol Metabolism. J. Med. Food. 2024, 27, 895–900. [CrossRef]
- Draper, M.; Bester, M.J.; Van Rooy, M.J.; Oberholzer, H.M. Adverse neurological effects after exposure to copper, manganese, and mercury mixtures in a Spraque-Dawley rat model: An ultrastructural investigation. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 2023, 47, 509–528. [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.; Gromadziński, L.; Cholewińska, E.; Ognik, K.; Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J. Dietary Effects of Chromium Picolinate and Chromium Nanoparticles in Wistar Rats Fed with a High-Fat, Low-Fiber Diet: The Role of Fat Normalization. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5138. [CrossRef]
- Filetti, F.M.; Schereider, I.R.G.; Wiggers, G.A.; Miguel, M.; Vassallo, D.V.; Simões, M.R. Cardiovascular Harmful Effects of Recommended Daily Doses (13 μg/kg/day), Tolerable Upper Intake Doses (0.14 mg/kg/day) and Twice the Tolerable Doses (0.28 mg/kg/day) of Copper. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2023, 23, 218–229. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Kalita, J.; Misra, U.K.; Bora, H.K. A study of dose response and organ susceptibility of copper toxicity in a rat model. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 269–274. [CrossRef]
| Group Copper Content |
Control Conditions (CC) * | NS-398 ** | NS-398 + SC-560 *** | 1400 W **** | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | Emax (%) | pEC50 | AUC | Emax (%) | pEC50 | AUC | Emax (%) | pEC50 | AUC | Emax (%) | pEC50 | ||
| Group A 100% Cu |
Mean | 221.2 | 87.43 | 7.346 | 186.6 * | 87.84 | 6.948 | 172.8 * | 87.47 | 6.830 | 249.7 | 94.69 | 7.436 |
| SEM | 22.26 | 3.695 | 0.131 | 23.76 | 4.658 | 0.139 | 18.36 | 3.883 | 0.112 | 16.09 | 2.391 | 0.082 | |
| Group B 200% Cu |
Mean | 252.4 | 94.31 | 7.576 | 248.7 | 92.71 | 7.498 | 206.1 | 85.60 | 7.306 | 226.0 | 91.35 | 7.346 |
| SEM | 14.64 | 2.045 | 0.070 | 22.47 | 3.170 | 0.113 | 26.19 | 4.122 | 0.141 | 13.68 | 1.969 | 0.065 | |
| p | 0.035 | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





