1. Introduction
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 80% of the world’s population relies on traditional medicine, including natural plant-based products, to meet their primary healthcare needs [
1]. This highlights the immense potential of plant-derived extracts as a rich source for the discovery of new drug candidates [
2].
Natural plant-based products, whether in their pure form or as standardized extracts, offer more than a thousand opportunities for the development of novel therapeutic agents [
3]. The widespread use of traditional medicine systems across the globe underscores the importance of further investigating the medicinal properties of these natural resources [
2].
Tapping into the vast repository of plant-derived compounds holds promise for addressing the pressing healthcare challenges faced worldwide. The increasing demand for alternative and complementary therapies, coupled with the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance, emphasizes the urgent need to explore the untapped potential of natural plant products for new drug discoveries. [
2].
For generations, the Ziziphus spina-christi, or Sidr tree as it is commonly referred to, has played a significant role in traditional healthcare systems in many parts of the world. Its use in traditional medicine has been well-documented, with the plant being recognized for its wide range of medicinal applications [
4]. As an evergreen species, the Ziziphus spina-christi is indigenous to the Saharo-Arabian and Irano-Turanian regions, where it has been deeply rooted in the cultural and traditional practices of the local communitie. The tree’s diverse array of therapeutic properties and its potential to contribute to human health have long been acknowledged and valued in these regions. [
5].
The antimicrobial properties of Ziziphus spina-christi have been a significant area of focus for researchers, as they seek to harness the plant’s natural capabilities to combat infectious diseases [
6]. The plant’s capacity to inhibit the growth and spread of various pathogenic microbes has generated significant interest within the scientific community, prompting further investigations into its mechanisms of action and potential therapeutic applications [
7].
The remarkable antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi is believed to be rooted in its rich phytochemical composition, which encompasses a diverse array of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, saponins, tannins, and triterpenes. These secondary metabolites have been extensively studied for their potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, rendering the plant a highly promising candidate for the development of natural, plant-derived antimicrobial agents [
7].
The phytochemical profile of Ziziphus spina-christi is a key factor in its antimicrobial efficacy. The presence of these diverse bioactive compounds, each with their unique mechanisms of action, contributes to the plant’s ability to inhibit the growth and proliferation of a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses [
7]. These secondary metabolites have been found to exhibit potent antimicrobial, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties, making the plant a promising candidate for the development of natural, plant-based antimicrobial agents [
8].
The rich tapestry of traditional knowledge surrounding the medicinal applications of Ziziphus spina-christi has provided important insights into the plant’s diverse therapeutic potential. The fact that it has been employed in traditional healthcare systems to address a variety of health concerns, such as skin infections, digestive issues, and respiratory conditions, suggests that the plant’s phytochemical constituents may possess a broad spectrum of biological activities [
9]. The escalating issue of antibiotic resistance, where microorganisms develop the ability to withstand the effects of commonly used antimicrobial drugs, has become a significant concern worldwide. This public health crisis underscores the pressing need to explore and develop new antimicrobial strategies that can effectively combat infectious diseases [
10].
The scientific exploration of medicinal plants, such as Ziziphus spina-christi, has evolved to encompass a comprehensive and interdisciplinary methodology. Researchers have recognized the need to combine various analytical tools and perspectives to gain a deeper understanding of the plant’s therapeutic properties and to unlock its full potential for drug development [
11]. In this context, the present study focuses on the biochemical properties and antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi.
The primary objective of this study is to evaluate the antimicrobial activity of the leaf extracts of Ziziphus spina-christi and to compare the biological activity of this plant. By adopting a comprehensive approach that integrates multiple analytical techniques, this research aims to provide a more in-depth understanding of the biochemical characteristics and antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Ziziphus spina-christi Leaves
The plant materials used in this study were collected directly from the field in various geographical locations within Sudan, including Khartoum state (Khartoum city, Nile Street, Al Mogran area), Blue Nile state (Al Damazin city), North Kordofan (Al Rahad city), and River Nile State (Al Hidiba city). The collected plant parts, specifically the leaves, were identified and authenticated by experts at the Medicinal and Aromatic Plant and Traditional Medicine Research Institute (MAPTMRI). Voucher specimens were deposited in the herbarium of the Department of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Medical Sciences and Technology, for future reference and verification.
2.2. Method
The procedure was carried out according to method described by Sukhdev et. al. [
12].
2.2.1. Extraction of the Plant
Z. spina-christi leaves were cleaned and dried at room temperature (about 30°C) for approximately 5 days for each area separately. After it had been dried completely, the leaves were ground to a course powder using mortar and pestle until fine coarse particle were form then ground again using a grounding mill. 34 grams of leaves powder were macerated by ethanol 96% in a conical flask separately for 3 days at room temperature. Extracts were first filtered through Whatman No. 4 filter paper. After filtration, the extracts were evaporated using rotatory evaporator and concentrated and allowed to dry for 2 days.
2.2.2. Preparation of Media
About 28 grams of Nutrient agar powder weighed, dissolved in 1 liter of distilled water and allowed to soak for 10 minutes. The medium was placed in water bath to dissolve, swirled to mix and sterilized by autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121°C. It was then cooled to 47°C, mixed well then poured into sterile Petri dishes.
2.2.3. Preparation of the Microorganisms
The bacterial strains used for screening of antimicrobial activity were two gram-positive (S. aureus and bacillus. sp) and two gram-negative (E. coli and pseudomonas. AR) and one fungus (candida albicans). All these microorganisms are standard microorganisms obtain from microbiology lab at the Aromatic and Medicinal Plant Institute- Research Center. [
12].
The percentage yield was calculated as follows:
%yield= (weight of extract obtained / weight of plant sample) x 100
3.1.1. Phytochemical Screening
Phytochemical screening is the process of tracing a plant’s secondary metabolites. The dry extract was dissolved in suitable solvents and subjected to various chemical tests to detect the presence of the main secondary metabolites.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Alkaloids
About 2 grams of the dried powdered drug were extracted with 20 ml of 1% HCl for 30minutes in boiling water bath, the suspension formed was filtrated then the acidic filter divided into 3 test tubes equally and test for alkaloids with the following tests.
3.2.2.1.1. Mayer’s Test
To a few ml of extract, two drops of Mayer’s reagent were added, and color change was observed. A white creamy color indicates a positive test.
3.2.2.1.1. Wagner’s Test
Wagner’s reagent was added in test tube containing few ml of extract. A precipitate with reddish brown color indicates the presence of alkaloids.
3.2.2.1.1. Dragendorff’s Test
Dragendroff’s reagent was added in test tube containing a few ml of extract. A precipitate with orange color indicates a positive test.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Flavonoids
Few drops of sodium hydroxide 20% solution were added to little quantity of the alcoholic extract, formation of yellow precipitate color indicates a positive result.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Sterols and Triterpenes
3.2.2.1.1. Salkowski Test
Two ml of the extract was mixed with two ml chloroform, followed by three ml of concentrated sulphuric acid were added carefully to the wall of the test tubes, and allowed to stand, appearance of reddish brown color interface indicate sterol presence, while golden yellow color is for triterpenes.
3.2.2.1.1. Liebermann-Burchard Test
Two ml of chloroform solution were added to the extract followed by Few drops of acetic anhydride were added and mixed well, 1 ml of concentrated sulphuric acid was added from the side of the test tube, and a deep red colour indicates presence of triterpenes and sterol’s.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Tannins
One gram of the powdered drug was extracted by boiling with 20 ml of distilled water for 10 minutes and it was filtrated.
3.2.2.1.1. Ferric Chloride Test
Few drops of 1% FeCl3 were added to 2 ml of the extract solution in test tube. Characteristic bluish, or greenish black color and a precipitate indicate a positive test.
3.2.2.1.1. Gelatin Test
About 5 ml of the extract were treated with few drops of the Gelatin-salt reagents. Formation of an immediate precipitate is taken as evidence for the presence of tannins.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Saponins
3.2.2.1.1. Frothing Test
About 1g of the dried powdered plant material was extracted by boiling with 10 ml distilled water for 10 minutes and it was filtered. After cooling, the extract was placed in a clean test tube. The tube was stoppered and vigorously shaken for about 30 seconds, then allowed to stand for 30 seconds, formation of honeycomb forth persisting for more than 30 minutes indicate the presence of saponins and classified for saponins content as follows: no froth=negative; froth less than 1 cm = weakly positive; froth 1cm = medium; froth 1.2 cm = high positive; and froth greater than 2 cm = strongly positive.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Cardiac Glycosides
3.2.2.1.1. Kedde’s test
About 2ml of the extract were evaporated to dryness in a Petri dish; few drops of ethanol,3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid ( kedd’s (A)) reagent was added and followed by few drops NaOH (kedd’s (B)) reagent was added. The presence of a red - pink color indicates positive result.
3.2.2.1.1. Keller Killiani’s Test
The extract was evaporated to dryness and about 2 ml of 5% FeCl3, glacial acetic acid were added and concentrated H2SO4 to be poured to the wall of the test tube to 2 ml of the extract. Positive tests are confirmed by the presence of a reddish-brown color at the junction of the two liquid layers with a green upper layer indicate the presence of cardiac glycoside.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Reducing Sugars
3.2.2.1.1. Fehling’s Test
Both Fehling’s reagents were mixed with equal volume, and a two ml of extract were added and heated for 2 minutes. A red – orange precipitate of cuprous oxide forms if reducing sugars are present.
3.2.2.1. Detection of Anthraquinone Glycosides
3.2.2.1.1. Ammonia Test
About 0.5 g of extract was boiled with 10 ml of 50% ethyl alcohol for 5 minutes, filtered and adjusted with hot alcohol to 20 ml and concentrated to 10 ml. The concentrate was extracted three times with 5 ml chloroform in a Separatory funnel and shaken then combined with 5 ml 10% ammonia solution. The ammonia layer was separated in a test tube and the color was observed.
3.2.3. Antimicrobial Activity
The culture media was sterilized by autoclave, and then poured in the petri-dishes, bacteria and fungi were transferred in a clean tube filled with 2ml of normal saline. A swap was emerged in the tube and moved slowly on the sterilized culture media.
3.2.4. Preparation of the Test Organisms
3.2.4.1. Preparation of the Microbial Suspensions
One ml aliquots of a 24 hours broth culture of the test organisms were aseptically distributed onto nutrient agar slopes and incubated at 37º C for 24 hours. The bacterial growth was harvested and washed off with 100 ml sterile normal saline, to produce a suspension containing about 108- 109 C.F.U/ ml. The suspension was stored in the refrigerator at 4° C till used.
The average number of viable organisms per ml of the stock suspension was determined by means of the surface viable counting technique [
13]. Serial dilutions of the stock suspension were made in sterile normal saline solution and 0.02 ml volumes of the appropriate dilution were transferred by micro pipette onto the surface of dried nutrient agar plates. The plates were allowed to stand for two hours at room temperature for the drops to dry and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours. After incubation, the number of developed colonies in each drop was counted. The average number of colonies per drop (0.02 ml) was multiplied by 50 and by the dilution factor to give the viable count of the stock suspension, expressed as the number of colonies forming units per ml suspension.
Each time a fresh stock suspension was prepared. All the above experimental conditions were maintained constant so that suspensions with very close viable counts would be obtained.
3.2.5. In Vitro Testing of Extracts for Antimicrobial Activity
3.2.5.1. Antimicrobial Activity:
The cup-plate agar diffusion method was adopted with some minor modifications to assess the antibacterial activity of the prepared extracts.
One ml of the standardized bacterial stock suspension 108 –109 C.F.U/ ml were thoroughly mixed with 100ml of molten sterile nutrient agar which was maintained at 45 ºC. 20ml aliquots of the inoculated nutrient agar were distributed into sterile Petri-dishes.
The agars was left to set and in each of these plates 4 cups (10 mm in diameter) were cut using a sterile-cork borer (No. 4) and agar discs were removed.
Alternate cups were filled with 0.1 ml sample of each of the oils dilutions in 10% DMSO using automatic microliter pipette, and allowed to diffuse at room temperature for two hours. The plates were then incubated in the upright position at 37 ºC for 18 hours.
After incubation the diameters of the resultant growth inhibition zones were measured for each extract [
14].
3. Results
4.1. Phytochemitry
4.1.1. Yield Percentage
The highest percentage of extractive yield showed in
Z. spina-christi leaves (Al Hidiba city - 8.288 %) followed by (Al Rahad city - 8.023 %), followed by (Khartoum city - 7.34 %) and the lowest percentage yield showed in (Al Damazin city - 6.87 %). Results are presented in
Table 1.
4.1.1. Qualitative Phytochemical Screening
The phytochemical screening of
Z. spina-christi Leaves ethanolic extracts from different areas of collection showed presence of flavomoids, triterpenes & steroles, tannins, saponins, cardiac glycosides and reducing sugar while alkaloids and anthraquinone were not detected. Results are presented in
Table 2.
The results proved that the four extracts were comparable in concentration of chemical composition, while saponin showed high foam formation in Al Hidiba city and Khartoum city. Saponins exhibit antimicrobial properties, guarding human body against fungi, bacteria and viruses. Flavonoids, a class of polyphenol secondary metabolites, are presented broadly in plants and diets. They are believed to have various bioactive effects including anti-viral, anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective, anti-diabetic, anti-cancer, anti-aging, etc. also; flavonoid rich plant extracts from different species have been reported to possess antibacterial activity. On the other hand, previous studies reported that Z. spina-christi leaf containing cardiac glycosides which are highly toxic compounds found in a number of plants and possess different therapeutic effects including antibacterial and antifungal activities. Z. spina-christi leaf considered as a one of richest source of tannins, tannins occur in crude drugs either as major active constituent used in the treatment of varicose ulcers, haemorrhoids, minor burns, frostbite, as well as inflammation and posses antimicrobial effect. These results comply with previous reports on the chemical constituents of Z. spina-christi plant except the presence of alkaloids.
Table 2.
Phytochemical screening of Z. spina-christi leaves of different areas of collection:.
Table 2.
Phytochemical screening of Z. spina-christi leaves of different areas of collection:.
| Test |
Specific test |
Result |
| Al Hidiba city |
Al-Rahad city |
Khartoum city |
Al-Damazin city |
| Alkaloids |
Mayer’s test |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
| Wagner’s test |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
| Dragendroff’s test |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
| Flavonoids |
Sodium hydroxide test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Sterols & Triterpenes |
Salkowski test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Liebermann-Burchard test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Tannins |
Ferric Chloride test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Gelatin test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Saponins |
Foam test |
++ve |
+ve |
++ve |
+ve |
| Glycosides |
Kedde’s test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Keller-Killiani’s test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| Reducing sugars |
Fehling’s test |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
+ve |
| AnthraquinoneGlycosides |
Ammonia test |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
-ve |
4.1. Antimicrobial Activity
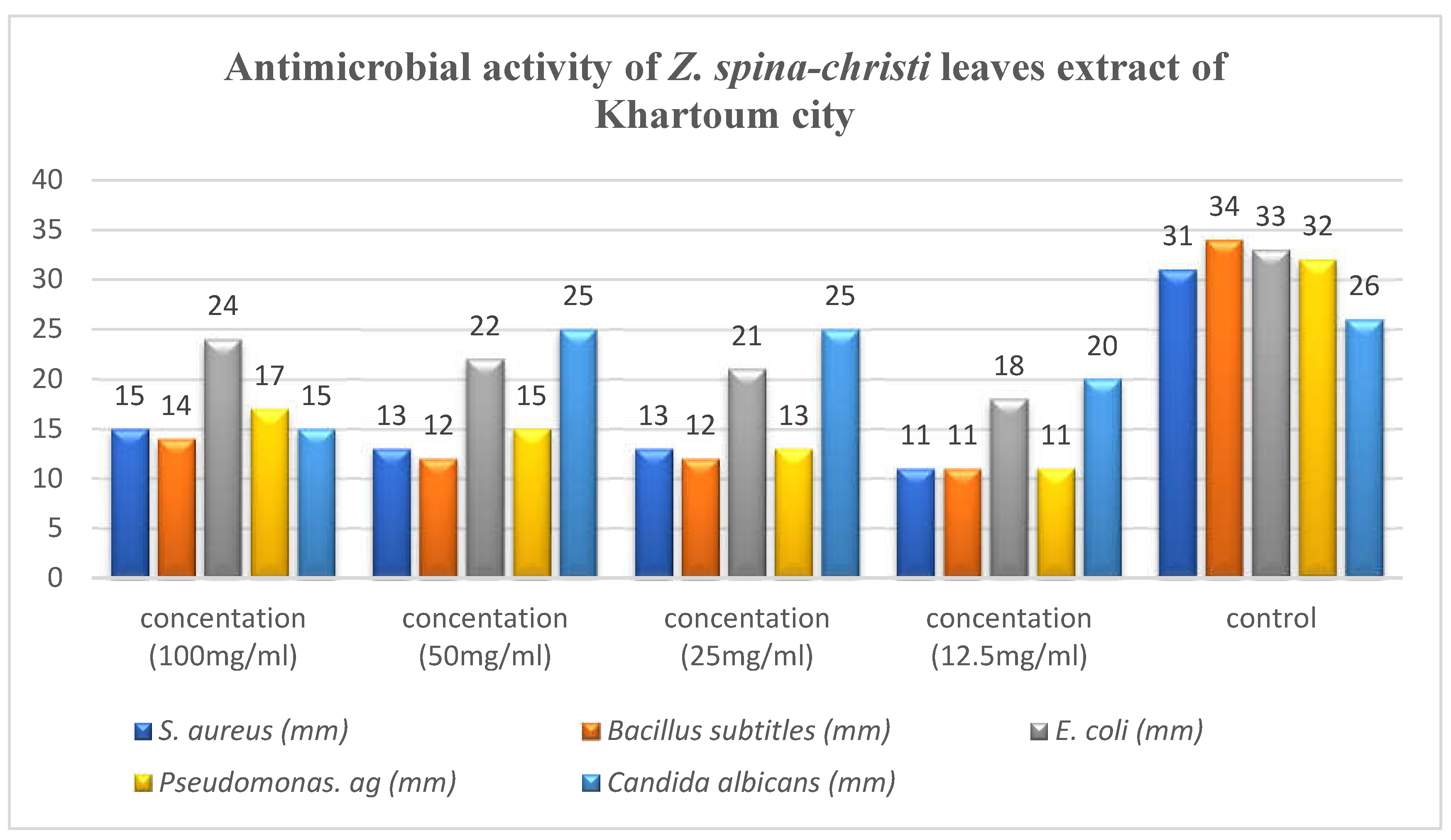
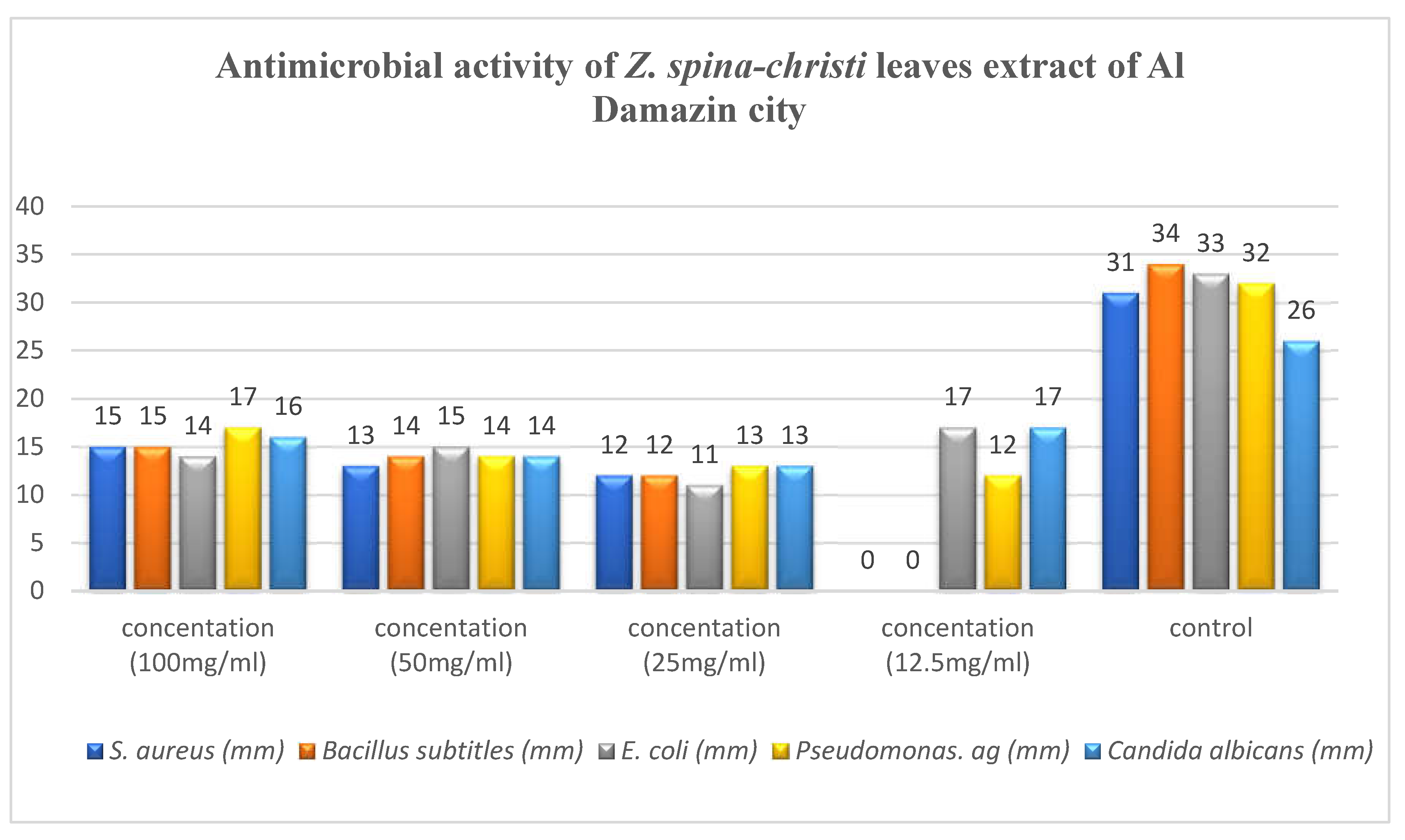
Antimicrobial activity of the ethanolic extracts of Z. spina-christi leaves collected from different areas, Al Hidiba city, Al Rahad city, Khartoum city and Al Damazin city were tested against two gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus and Bacillus subtitles), two gram-negative bacteria (E. coli and Pseudomona aeruginosa) and one fungi (Candida albicans).
All extracts showed activity against these microorganisms with some variation in activity ranging from 11 to 25 mm, results shown in
Table 3,
Table 4,
Table 5 and
Table 6.
Pseudomona aeruginosa and E. coli exhibited higher sensitivity against all extracts compared with S. aureus and Bacillus subtitles. All extracts showed high antifungal activity against C.albicans. In general, the extract of Khartoum city showed the highest antimicrobial activity, followed by the extract of Al Rahad city followed by the extract of Al Hidiba city and the least anti-microbial effect showed in the extract of Al Damazin city respectively.
Table 3.
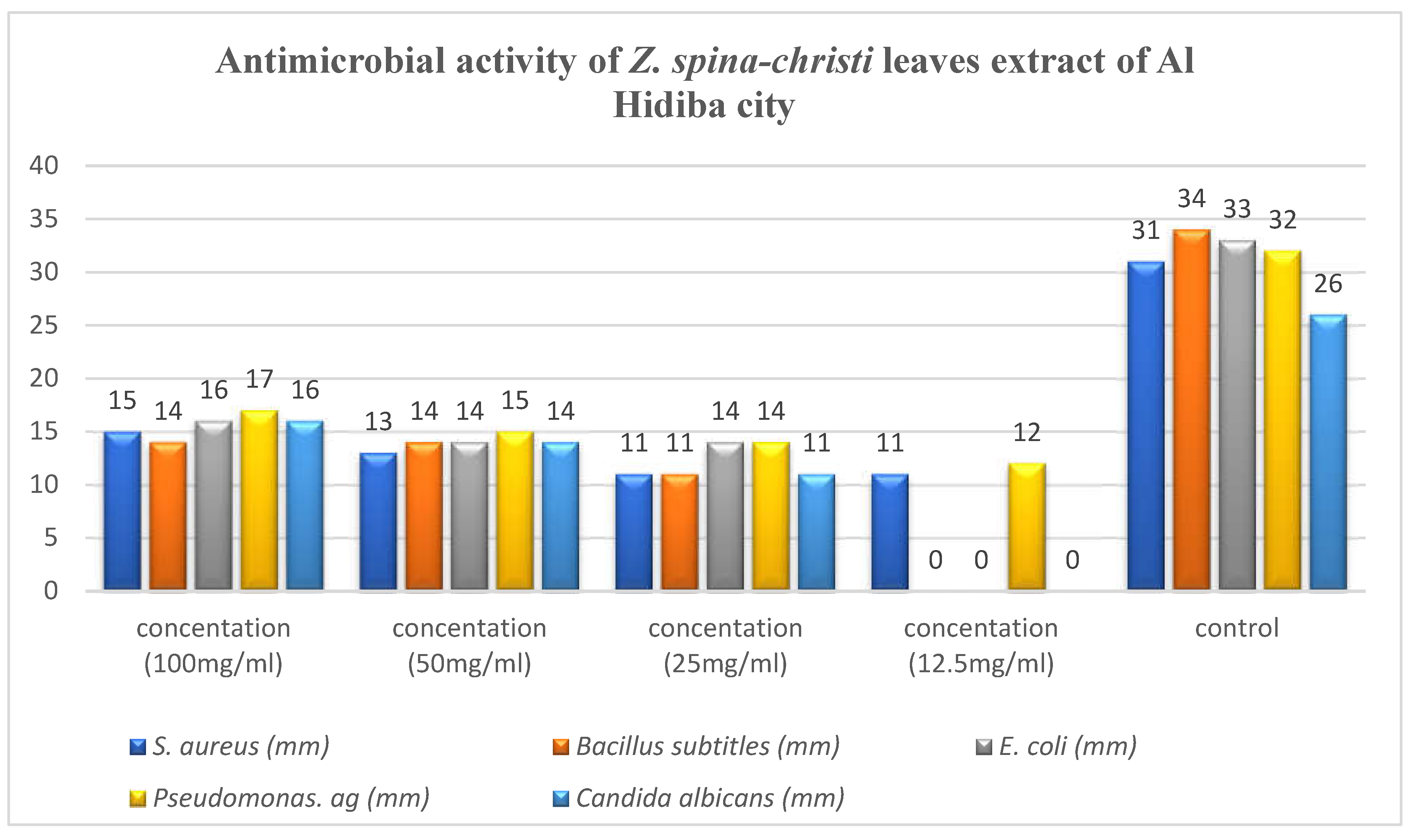
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Hidiba city:.
Table 3.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Hidiba city:.
| Extract |
D.I.Z* (mm) |
| Gram positive bacteria |
Gram negative bacteria |
Fungi |
Concentration
(mg/ml) |
S. aureus |
B. subtitles |
E. coli |
Ps. aeruginosa |
C. albicans |
| 100 |
15 |
14 |
16 |
17 |
16 |
| 50 |
13 |
14 |
14 |
15 |
14 |
| 25 |
11 |
11 |
14 |
14 |
11 |
| 12.5 |
11 |
- |
- |
12 |
- |
| Control |
Ciprofloxacin |
Clotrimazole |
| 31 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
26 |
The highest activity reveled against
pseudomonas aeruginosa was 17 mm at concentration of 100mg/ml, Ciprofloxacin and Clotrimazole showed higher activity than extract (
Figure 3).
Table 4.
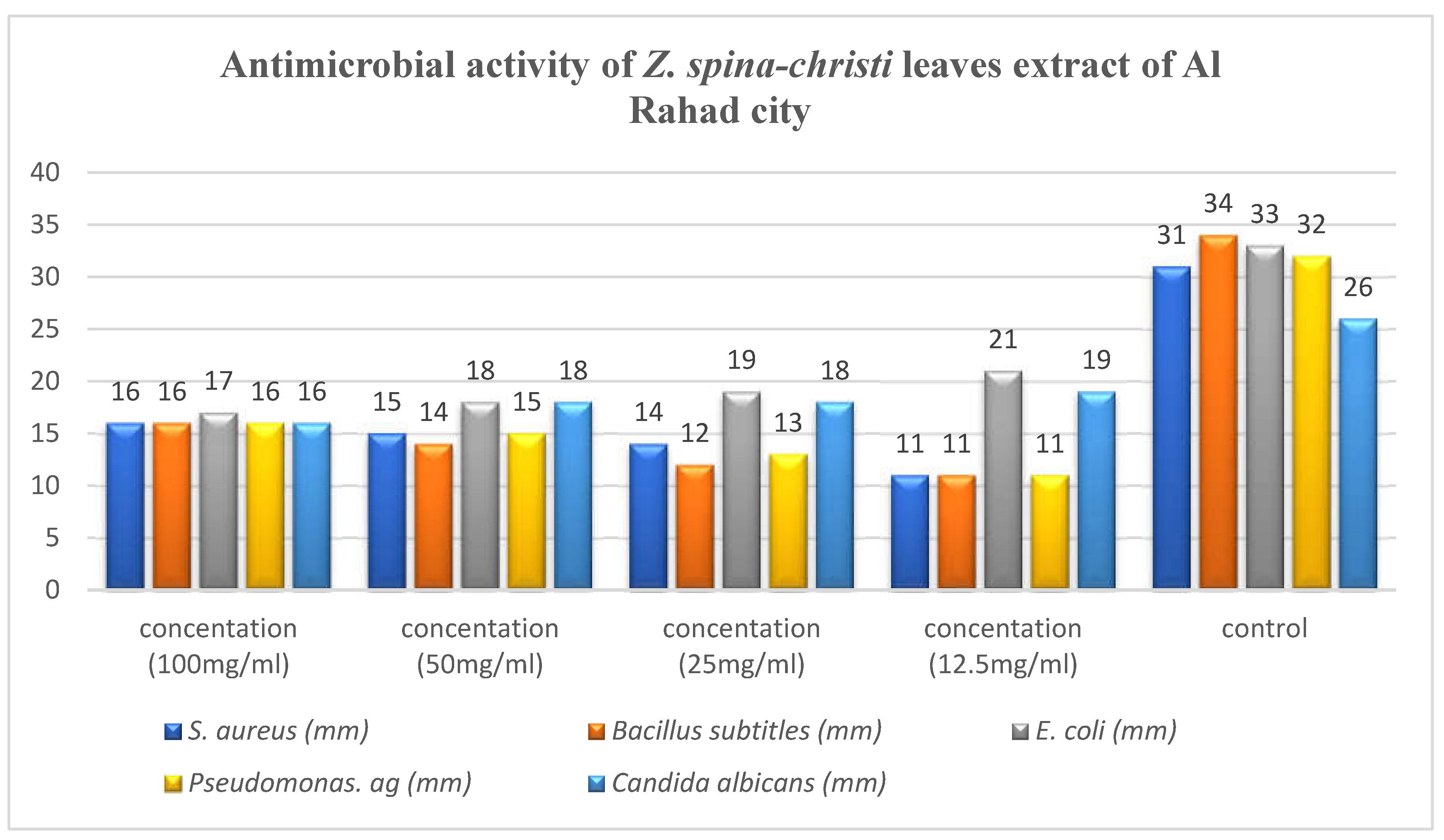
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Rahad city.
Table 4.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Rahad city.
Extract |
D.I.Z* (mm) |
| Gram positive bacteria |
Gram negative bacteria |
fungi |
Concentration
(mg/ml) |
S. aureus |
B. subtitles |
E. coli |
Ps. aeruginosa |
C. albicans |
| 100 |
16 |
16 |
17 |
16 |
16 |
| 50 |
15 |
14 |
18 |
15 |
18 |
| 25 |
14 |
12 |
19 |
13 |
18 |
| 12.5 |
11 |
11 |
21 |
11 |
19 |
| Control |
Ciprofloxacin |
Clotrimazole |
| 31 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
26 |
The highest activity showed against
E. coli was found to be 21 mm at concentration of 12.5 mg/ml, while the lowest activity reveled against
S.aureus, Bacillus sp and
pseudomonas sp. was found to be 11 mm at concentration of 12.5mg/ml (
Figure 4).
Table 5.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city.
Table 5.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city.
Extract |
D.I.Z* (mm) |
| Gram positive bacteria |
Gram negative bacteria |
fungi |
Concentration
(mg/ml) |
S. aureus |
B. subtitles |
E. coli |
Ps. aeruginosa |
C. albicans |
| 100 |
15 |
14 |
24 |
17 |
15 |
| 50 |
13 |
12 |
22 |
15 |
25 |
| 25 |
13 |
12 |
21 |
13 |
25 |
| 12.5 |
11 |
11 |
18 |
11 |
20 |
| Control |
Ciprofloxacin |
Clotrimazole |
| 31 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
26 |
The highest activity reveled against
Candida albicans and was found to be 25 mm at concentration of 50 mg/ml and concentration of 25mg/ml, while the lowest activity reveled against
S. aureus, Bacillus sp and
Ps. aeruginosa with inhibition zone of 11 mm at concentration of 12.5mg/ml (
Figure 5).
Table 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city.
Table 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city.
Extract |
D.I.Z* (mm) |
| Gram positive bacteria |
Gram negative bacteria |
fungi |
Concentration
(mg/ml) |
S. aureus |
B. subtitles |
E. coli |
Ps. aeruginosa |
C. albicans |
| 100 |
15 |
15 |
14 |
17 |
16 |
| 50 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
14 |
14 |
| 25 |
12 |
12 |
11 |
13 |
13 |
| 12.5 |
- |
- |
17 |
12 |
17 |
| Control |
Ciprofloxacin |
Clotrimazole |
| 31 |
34 |
33 |
32 |
26 |
Figure 5.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city.
Figure 5.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city.
Figure 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city.
Figure 6.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city.
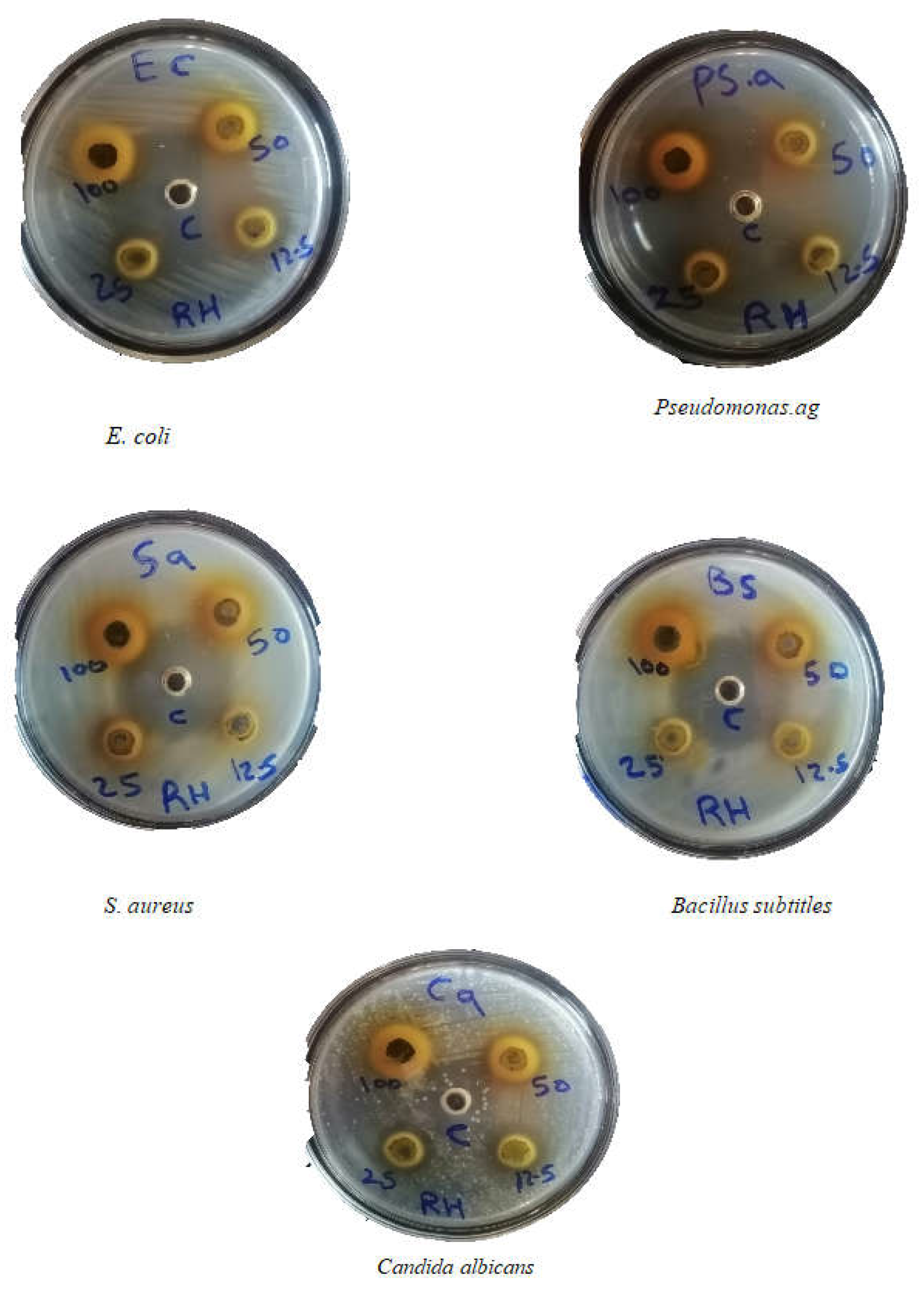
Figure 7.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city on different concentrations.
Figure 7.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Khartoum city on different concentrations.
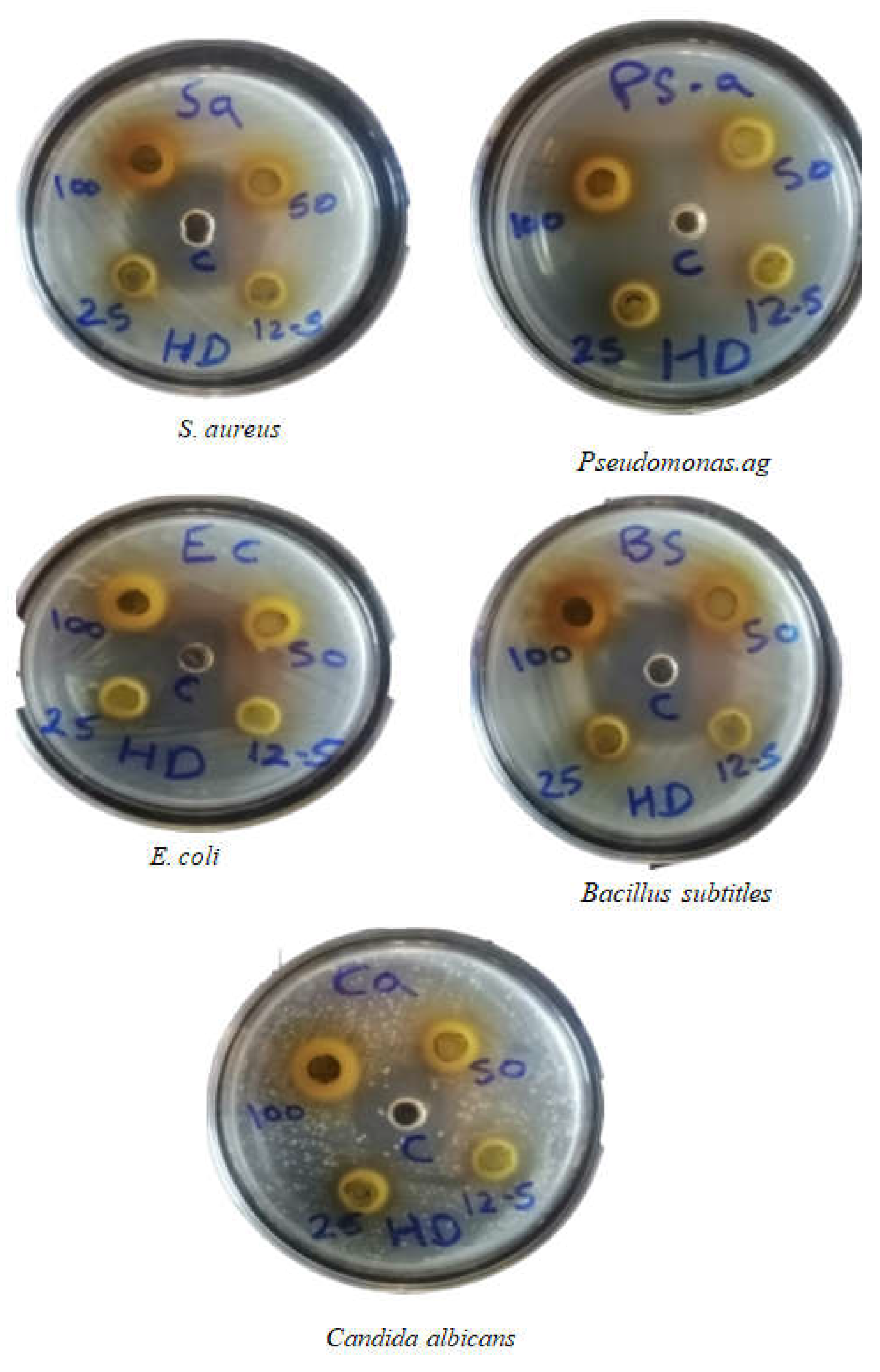
Figure 9.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city on different concentrations.
Figure 9.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Damazin city on different concentrations.
Figure 10.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Hidiba city on different concentrations.
Figure 10.
Antimicrobial activity of Z. spina-christi leaves extract of Al Hidiba city on different concentrations.
4. Discussion
The results of this study indicate that the leaves of Ziziphus spina-christi are a promising source of antimicrobial natural products. The phytochemical screening revealed the presence of a diverse array of secondary metabolites, including several classes of compounds known for their antimicrobial properties. For instance, flavonoids, tannins, and saponins have all been extensively studied for their ability to inhibit the growth of a wide range of pathogenic microorganisms [
15,
16]. Similarly, triterpenes and cardiac glycosides have also demonstrated potent antimicrobial activities in previous investigations [
17,
18].
Notably, the antimicrobial potency of the Z. spina-christi leaf extracts varied considerably depending on the geographic origin of the plant material [
19]. The extract from Khartoum city exhibited the strongest antimicrobial effects, suggesting that the chemical composition and concentration of bioactive compounds may be influenced by environmental factors such as soil characteristics, climate, and agricultural practices. This finding highlights the importance of exploring intraspecific variation when evaluating the medicinal potential of plant species [
20]. Identifying the specific phytochemicals responsible for the observed antimicrobial activities, as well as the underlying factors driving the observed geographical differences [
21], should be the focus of future research.
Given the global crisis posed by the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, the development of novel antimicrobial agents derived from natural sources is of paramount importance [
22]. The results of this study provide a strong scientific foundation for further investigating Z. spina-christi as a promising candidate for the discovery of plant-based antimicrobial compounds. The isolation and characterization of the bioactive constituents, coupled with in-depth mechanistic studies and optimization of extraction and formulation methods, could ultimately lead to the creation of innovative antimicrobial therapies [
23]. Such efforts may help alleviate the burden of drug-resistant infections and improve global public health outcomes [
24].
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study demonstrate the significant antimicrobial potential of Ziziphus spina-christi leaves, which contain a diverse array of phytochemicals with known antimicrobial properties. The observed variation in antimicrobial potency between extracts from different geographic regions underscores the importance of exploring intraspecific chemical diversity when evaluating the medicinal applications of plant species.
These results provide a strong scientific foundation for further research aimed at identifying the specific bioactive compounds responsible for the observed antimicrobial activities. Isolating and characterizing the active phytochemicals, coupled with in-depth mechanistic studies and optimization of extraction and formulation methods, could ultimately lead to the development of innovative plant-based antimicrobial agents.
Given the global crisis posed by the rise of antibiotic-resistant pathogens, the successful translation of these findings into effective antimicrobial therapies could have profound implications for public health. Harnessing the antimicrobial potential of Z. spina-christi may help alleviate the burden of drug-resistant infections and contribute to the ongoing efforts to combat the growing threat of antimicrobial resistance.
Overall, this study highlights the promise of Z. spina-christi as a valuable source of natural antimicrobial compounds and warrants further investigation to fully explore its medicinal applications. The continued exploration of medicinal plant species, such as Z. spina-christi, represents a vital strategy in the search for novel antimicrobial agents to address the global health crisis posed by drug-resistant pathogens.
Data Availability:
All data underlying the results are available as part of the article and no additional source data are required.
References
- Balkrishna, A., et al., Exploring the Safety, Efficacy, and Bioactivity of Herbal Medicines: Bridging Traditional Wisdom and Modern Science in Healthcare. Future Integrative Medicine, 2024. 3(1): p. 35-49. . [CrossRef]
- Bitwell, C., et al., A review of modern and conventional extraction techniques and their applications for extracting phytochemicals from plants. Scientific African, 2023. 19: p. e01585. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.H., et al., Phytochemicals: a new arsenal in drug discovery. International Journal of Medical Science and Dental Health, 2024. 10(01): p. 29-44. [CrossRef]
- Elhaj, Y.H., Exploring the Antimicrobial Activity of Ziziphus spina–christi: A Promising Natural Supply of Antimicrobial Agents. Egyptian Academic Journal of Biological Sciences, G. Microbiology, 2024. 16(1): p. 21-31. [CrossRef]
- Al-Shaibani, E.A., D.A.A. Al-Ameri, and M.A. Al-Hegami, The Effect of Zizyphus spina-christi Extracts on hyperglycemia induced by hyperlipidemic diet in Albino rats. Sana’a University Journal of Applied Sciences and Technology, 2024. 2(1): p. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Kaushal, P., D. Maity, and R. Awasthi, Nano-green: Harnessing the potential of plant extracts for sustainable antimicrobial metallic nanoparticles. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology, 2024: p. 105488. [CrossRef]
- El Megdar, S., et al., Biological Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Lavandula mairei Humbert: Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities. Current Microbiology, 2024. 81(6): p. 151. [CrossRef]
- Dawood, H.M., et al., Metabolomics and chemometrics approaches unravel the metabolic diversity and in-vitro antidiabetic potential of two Ziziphus species. Industrial Crops and Products, 2024. 212: p. 118288. [CrossRef]
- Qari, S.H., A. Alqethami, and A.T. Qumsani, Ethnomedicinal evaluation of medicinal plants used for therapies by men and women in rural and urban communities in Makkah district. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal, 2024. 32(1): p. 101881. [CrossRef]
- Chaughule, R.S. and R.S. Barve, Role of herbal medicines in the treatment of infectious diseases. Vegetos, 2024. 37(1): p. 41-51. [CrossRef]
- Khan, N., S.S. Dogra, and A. Saneja, The dawning era of oral thin films for nutraceutical delivery: From laboratory to clinic. Biotechnology Advances, 2024: p. 108362. [CrossRef]
- Handa, S., et al., Extraction technologies for medicinal and aromatic plants. International centre for science and hightechnology. Trieste, 2014: p. 74-80.
- Miles, A.A., S. Misra, and J. Irwin, The estimation of the bactericidal power of the blood. Epidemiology & Infection, 1938. 38(6): p. 732-749.. [CrossRef]
- Kagan, I.A. and M.D. Flythe, Thin-layer chromatographic (TLC) separations and bioassays of plant extracts to identify antimicrobial compounds. JoVE (Journal of Visualized Experiments), 2014(85): p. e51411. [CrossRef]
- Khattak, M., et al., Exploration of reducing and stabilizing phytoconstituents in Arisaema dracontium extract for the effective synthesis of Silver nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial and toxicological proprties. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2024: p. 106711. [CrossRef]
- Fik-Jaskółka, M., et al., Antimicrobial Metabolites of Caucasian Medicinal Plants as Alternatives to Antibiotics. Antibiotics, 2024. 13(6): p. 487. [CrossRef]
- Anbessa, B., et al., Ethnomedicine, antibacterial activity, antioxidant potential and phytochemical screening of selected medicinal plants in Dibatie district, Metekel zone, western Ethiopia. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies, 2024. 24. [CrossRef]
- Mishra, M.K., Phytochemical analysis and evaluation of antibacterial activity of various extracts from leaves, stems and roots of Thalictrum foliolosum. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2024. 10(1): p. 70. [CrossRef]
- Baghazadeh-Daryaii, L., G.-R. Sharifi-Sirchi, and D. Samsampoor, Morphological, phytochemical and genetic diversity of Ziziphus spina–Christi (L) Des. in South and Southeastern of Iran. Journal of applied research on medicinal and aromatic plants, 2017. 7: p. 99-107. [CrossRef]
- Campetella, G., et al., Contrasting patterns in leaf traits of Mediterranean shrub communities along an elevation gradient: Measurements matter. Plant Ecology, 2019. 220: p. 765-776. [CrossRef]
- Vaou, N., et al., Towards advances in medicinal plant antimicrobial activity: A review study on challenges and future perspectives. Microorganisms, 2021. 9(10): p. 2041. [CrossRef]
- MacNair, C.R., S.T. Rutherford, and M.-W. Tan, Alternative therapeutic strategies to treat antibiotic-resistant pathogens. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024. 22(5): p. 262-275. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q., et al., Active metabolites combination therapies: towards the next paradigm for more efficient and more scientific Chinese medicine. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2024. 15: p. 1392196. [CrossRef]
- Farhat, M., et al., Drug-resistant tuberculosis: a persistent global health concern. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2024: p. 1-19. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).