Submitted:
07 June 2024
Posted:
10 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
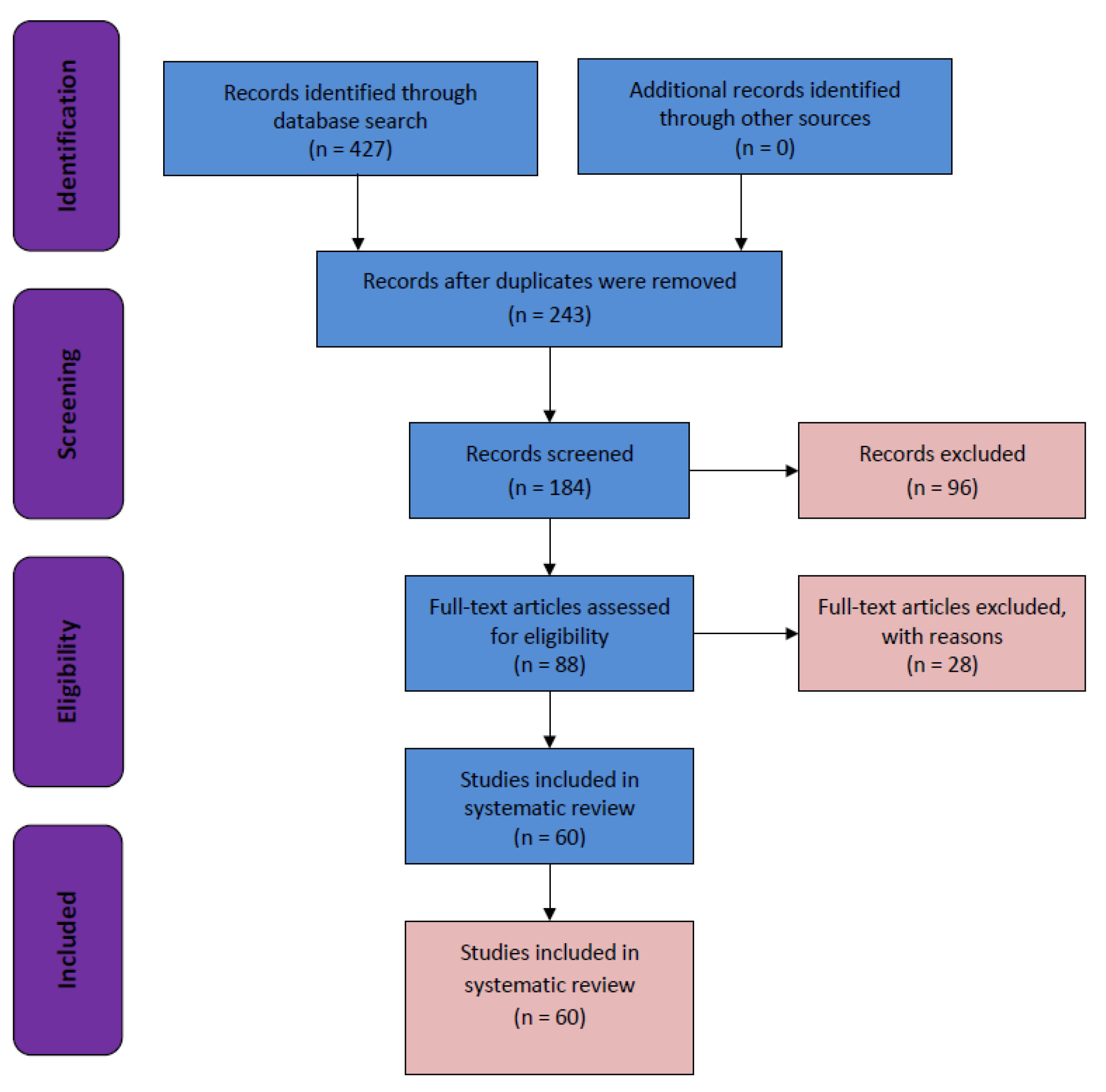
Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
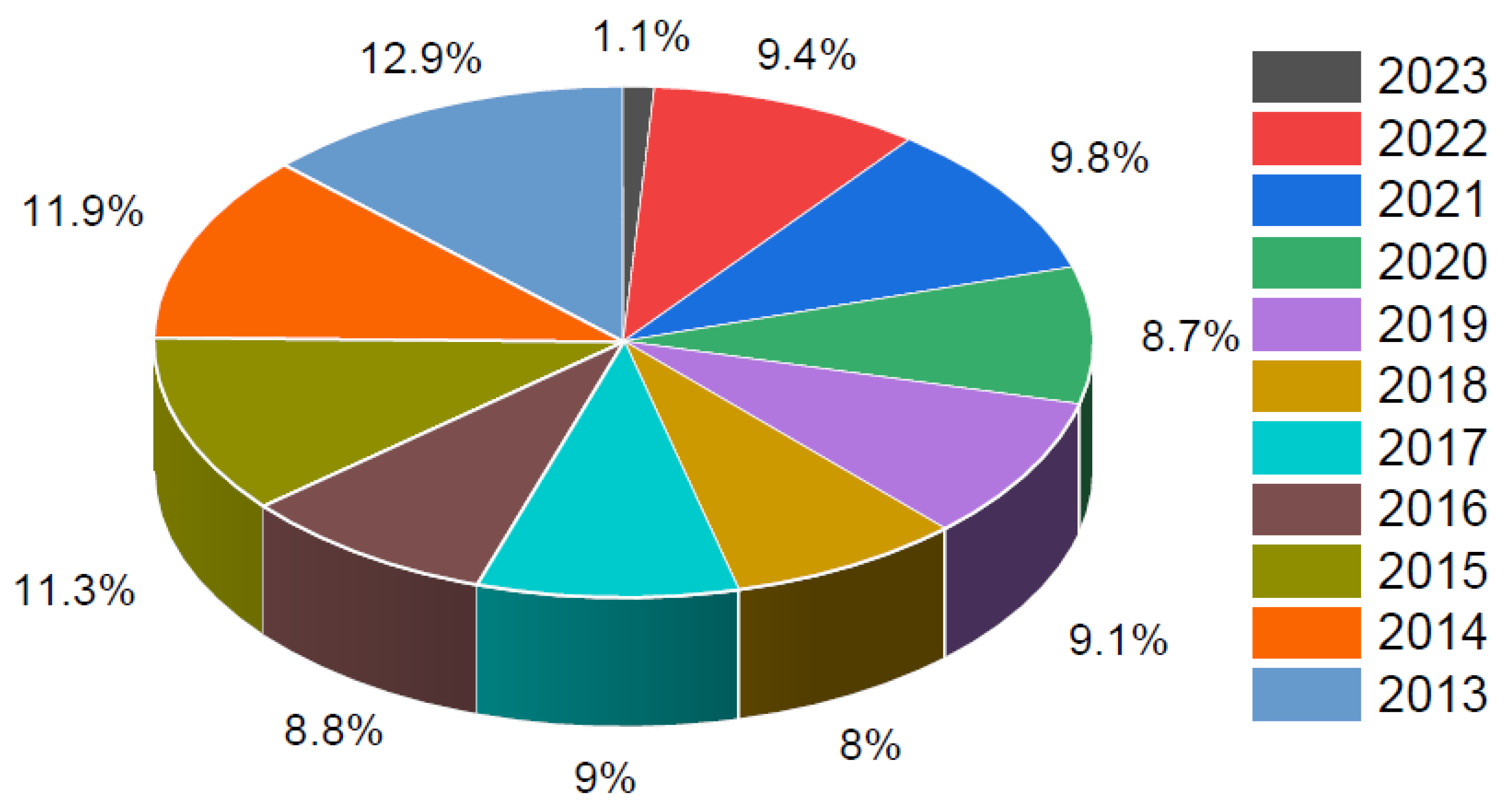
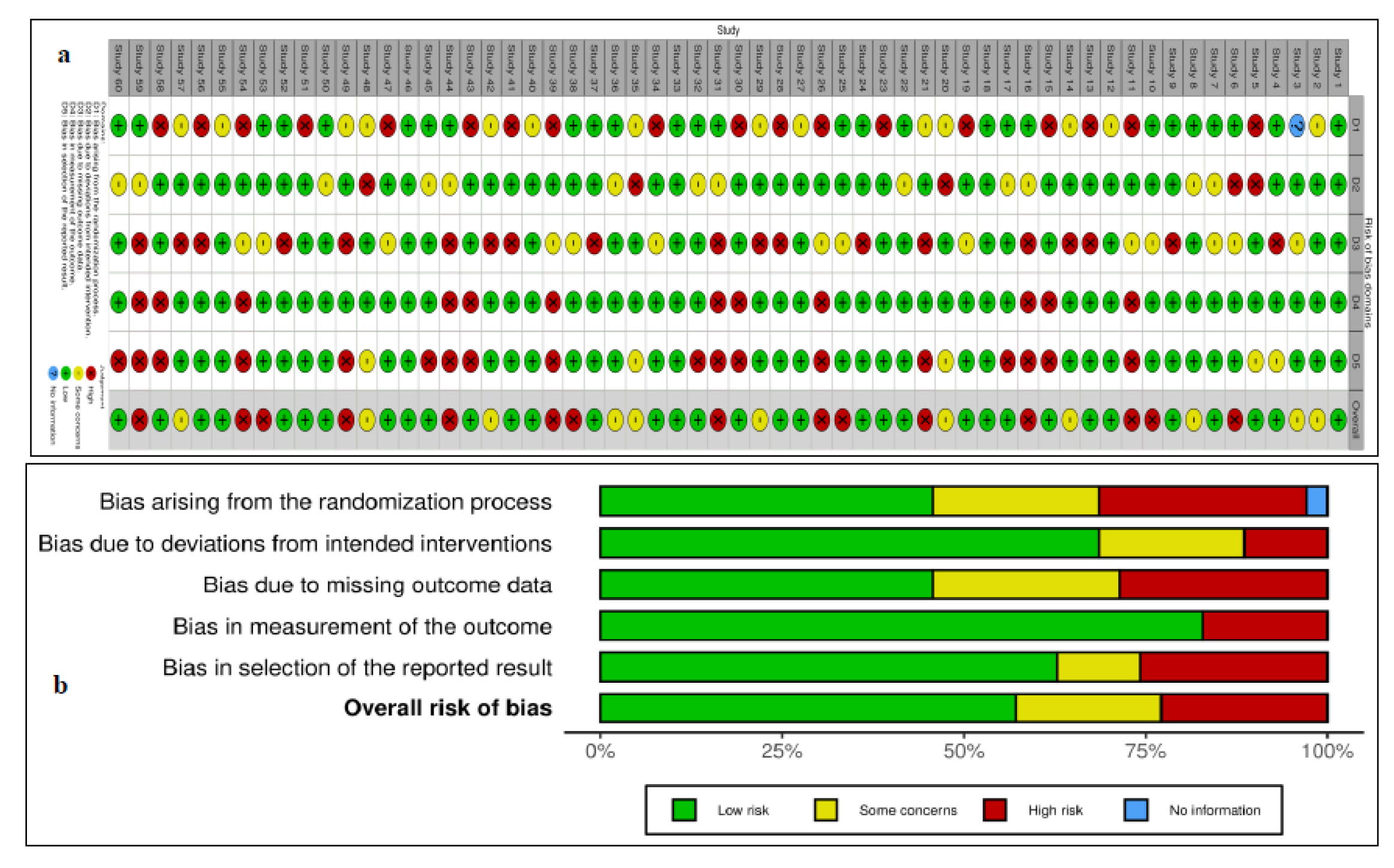
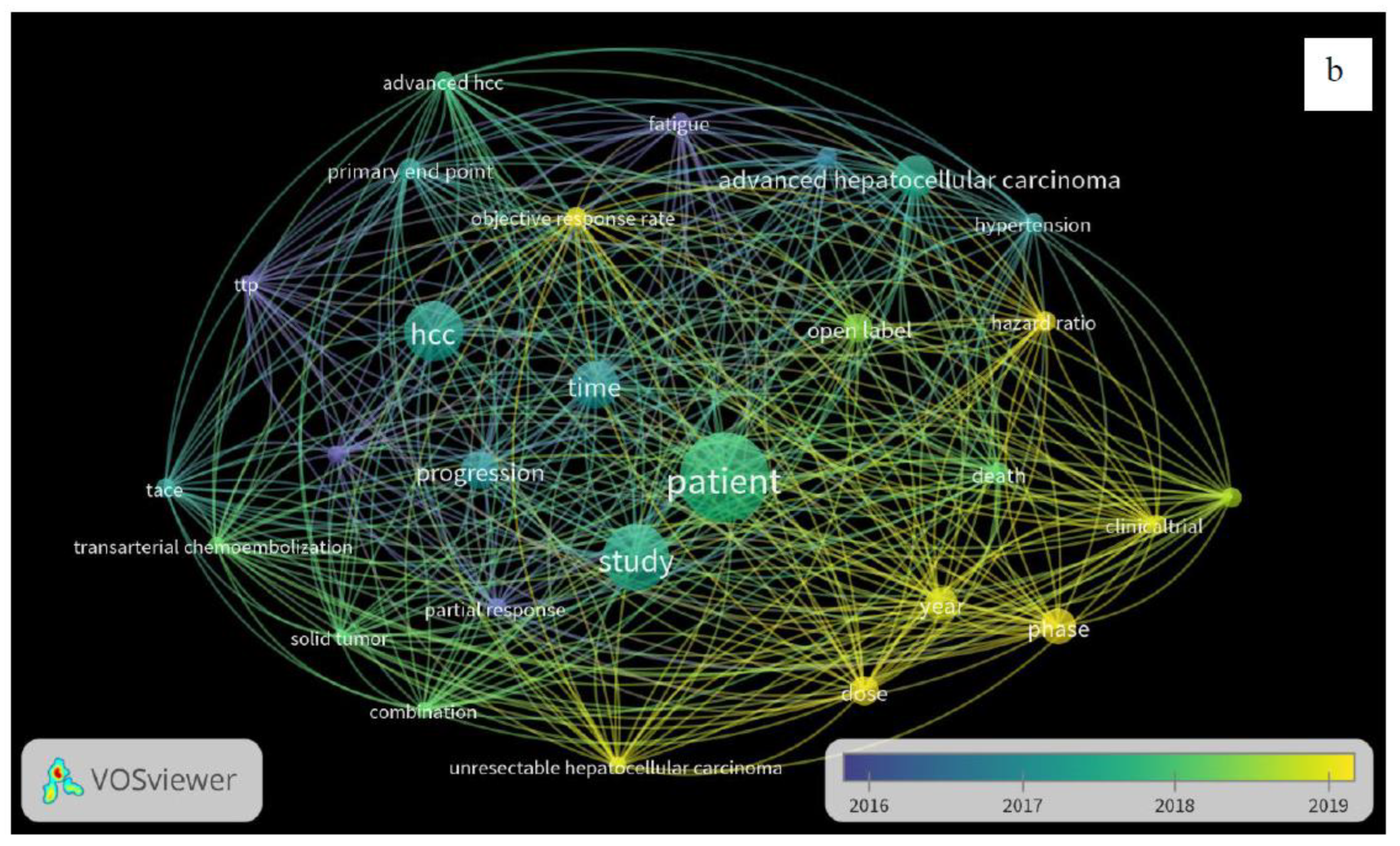
3. Results
| Author names | Year | Drugs used | Phase | No. of participants (n) | Design | Dosage | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Finn et al. | 2020 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab v/s Sorafenib |
III | 501 | Open-label RCT | Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Bevacizumab = 15 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[33] |
| Kudo M et al. | 2018 | Lenvatinib v/s Sorafenib | III | 468 | Open-label RCT | Lenvatinib = 12 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[34] |
| Cheng AN et al. | 2021 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab v/s Sorafenib |
III | 501 | Open-label RCT | Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Bevacizumab = 15 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[35] |
| El-Khoueiry AB et al. | 2017 | Nivolumab | I/II | 262 | Open-label, on-comparative, dose escalation and expansion trial | 1–10 mg | [36] |
| Abou-Alfa GK et al. | 2018 | Cabozantinib | III | 707 | Double-blind, RCT | 60 mg | [37] |
| Yau T et al. | 2020 | Nivolumab + ipilimumab | I/II | 148 | Open-label, Multicohort | Nivolumab = 3 mg Ipilimumab = 1 mg | [38] |
| Kelley RK et al. | 2021 | Tremelimumab + Durvalumab | I/II | 332 | Open-label RCT | Tremelimumab = 300 mg Durvalumab = 1,500 mg |
[39] |
| Lee JH et al. | 2015 | Autologous CIK cells | III | 230 | Open-label RCT | 6.4 × 109 | [40] |
| Bruix J et al. | 2015 | Sorafenib | III | 900 | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | 577 mg | [41] |
| Yau T et al. | 2019 | Nivolumab | I/II | 267 | Open-label RCT | 3 mg | [42] |
| Kelley RK et al. | 2022 | Cabozantinib + atezolizumab V/S sorafenib |
III | 837 | Open-label RCT | Cabozantinib = 40 mg Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg | [43] |
| Yau T et al. | 2020 | Nivolumab | III | 743 | Open-label RCT | 240 mg | [44] |
| Galle PR et al. | 2021 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab v/s Sorafenib |
III | 501 | Open-label RCT | Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Bevacizumab = 15 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[45] |
| Zhu AX et al. | 2019 | Ramucirumab | III | 197 | Open-label RCT | 8 mg | [46] |
| Lencioni R et al. | 2016 | Transarterial chemoembolization with doxorubicin-eluting beads (DC Bead®; DEB-TACE) + Sorafenib | II | 307 | Open-label RCT | DEB-TACE = 150 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[47] |
| Vogel A et al. | 2021 | Lenvatinib v/s Sorafenib |
III | 954 | Randomized, open-label, non-inferiority | Lenvatinib = 12 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[48] |
| Finn RS et al. | 2019 | Pembrolizumab | III | 413 | Randomized, double-blind | 200 mg | [49] |
| Lee MS et al. | 2020 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab | Ib | 104 | Open-label RCT | Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Bevacizumab = 15 mg |
[50] |
| Cheon J et al. | 2022 | Atezolizumab + Bevacizumab | III | 138 | Retrospective | Atezolizumab = 1200 mg Bevacizumab = 15 mg |
[51] |
| Park JW et al. | 2019 | Sorafenib | III | 339 | Open-label RCT | Sorafenib = 600 mg | [52] |
| Choi NR et al. | 2022 | Lenvatinib+ Sorafenib | 206 | Open-label RCT | Lenvatinib = 12 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[53] | |
| Cheon J et al. | 2020 | Lenvatinib | III | 67 | Retrospective | Lenvatinib = 12 mg | [54] |
| Yoon SM et al. | 2018 | Sorafenib | - | 99 | Open-label RCT | Sorafenib = 400 mg | [55] |
| Hong JY et al. | 2022 | Pembrolizumab | II | 55 | Open-label RCT | 200 mg | [56] |
| Chow PKH et al. | 2018 | Sorafenib | III | 360 | Open-label RCT | 800 mg | [57] |
| Ryoo BY et al. | 2021 | Enzalutamide | II | 165 | Randomized, Double-blind | 160 mg | [58] |
| Ryoo BY et al. | 2021 | Tepotinib v/s Sorafenib | Ib/II | 117 | Open-label RCT | Tepotinib = 1200 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[59] |
| Cheng AL et al | 2015 | Tigatuzumab + sorafenib | II | 163 | Open-label RCT | Tigatuzumab = 6 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[60] |
| Cainap C et al. | 2015 | Linifanib v/s Sorafenib | III | 1035 | Open-label RCT | Linifanib = 17.5 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[61] |
| Zhu AX et al. | 2015 | Sorafenib + Erlotinib | III | 720 | Open-label RCT | Erlotinib = 150 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[62] |
| Tak WY et al. | Sorafenib +Resminostat v/s Sorafenib |
I/II | 179 | Open-label RCT | Sorafenib + resminostat = 3+400 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[63] | |
| Johnson PJ et al. | 2013 | Brivanib v/s Sorafenib | III | 1150 | Open-label RCT | Brivanib = 800 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[64] |
| Zhu AX et al. | 2015 | Ramucirumab | III | 283 | Randomized, double-blind | 8 mg | [65] |
| Lim HY et al. | 2014 | Refametinib + Sorafenib | II | 95 | Open-label RCT | Refametinib= 50 mg Sorafenib= 600 mg |
[66] |
| Chung YH et al. | 2017 | Ramucirumab | III | 565 | Open-label RCT | 8 mg | [67] |
| Qin S et al. | 2020 | Camrelizumab | II | 220 | Open-label RCT | 3 mg | [68] |
| Qin S et al. | 2021 | Apatinib | III | 400 | Randomized, double-blind | 750 mg | [69] |
| Llovet JM et al. | 2022 | Lenvatinib + Pembrolizumab | III | 950 | Randomized, double-blind | Lenvatinib= 12 mg Pembrolizumab = 400 mg |
[70] |
| Ding X et al. | 2021 | Lenvatinib v/s Sorafenib | III | 64 | Open-label RCT | Lenvatinib= 12 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[71] |
| Peng Z et al. | 2022 | Lenvatinib | III | 338 | Open-label RCT | Lenvatinib= 12 mg | [72] |
| He M et al. | 2019 | Sorafenib v/s Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin+ Sorafenib |
II | 818 | Open-label RCT | Sorafenib = 400 mg Oxaliplatin= 85 mg Leucovorin = 400 mg Fluorouracil = 400 mg |
[73] |
| Qin S et al. | 2019 | Tislelizumab v/s Sorafenib | III | 640 | Open-label RCT | Tislelizumab = 200 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[74] |
| Mei K et al. | 2021 | Camrelizumab + Apatinib | Ib/II | 28 | Open-label RCT | Camrelizumab = 3 mg Apatinib = 500 mg |
[75] |
| Kia Y et al. | 2022 | Camrelizumab + Apatinib | II | 20 | Open-label RCT | Camrelizumab = 200 mg Apatinib = 250 mg |
[76] |
| Xu J et al. | 2021 | Camrelizumab + Apatinib | II | 120 | Open-label | Camrelizumab = 200 mg Apatinib = 250 mg |
[77] |
| Qin S et al. | 2021 | Donafenib v/s Sorafenib | II/III | 668 | Open-label RCT | Donafenib = 200 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[78] |
| Lyu N et al. | 2022 | Oxaliplatin+ Leucovorin +Fluorouracil v/s Sorafenib |
III | 262 | Open-label RCT | Oxaliplatin = 130 mg Leucovorin = 200 mg Fluorouracil = 400 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[79] |
| Ren Z et al. | 2021 | Sintilimab + bevacizumab v/s Sorafenib |
II/III | 595 | Open-label RCT | Sintilimab = 200 mg bevacizumab = 15 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[80] |
| Li QJ et al. | 2022 | Oxaliplatin + Leucovorin + Fluorouracil v/s Epirubicin + Lobaplatin |
III | 315 | Open-label RCT | Oxaliplatin = 130 mg Leucovorin = 400 mg Fluorouracil = 400 mg Epirubicin = 50 mg Lobaplatin = 50 mg |
[81] |
| Kang YK et al. | 2015 | Axitinib | II | 202 | Double-blind RCT | Axitinib = 5 mg | [82] |
| Llovet JM et al. | 2013 | Brivanib | III | 395 | Double-blind RCT | Brivanib = 800 mg | [83] |
| Yau TCC et al. | 2017 | Foretinib | I/II | 32 | Single-arm | Foretinib = 60 mg | [84] |
| Zhu AX et al. | 2014 | Everolimus | I | 546 | Open-label RCT | Everolimus = 7.5 mg | [85] |
| Kelley RK et al. | 2020 | Cabozantinib | II | 331 | Open-label RCT | Cabozantinib = 60 mg | [86] |
| Verset G et al. | 2022 | Pembrolizumab | II | 51 | Open-label RCT | Pembrolizumab = 200 mg | [87] |
| Abou-Alfa GK et al. | 2018 | Cabozantinib | III | 707 | Double-blind RCT | Cabozantinib = 60 mg | [88] |
| Tai WM et al. | 2016 | Selumetinib +Sorafenib | Ib | 27 | Open-label RCT | Selumetinib= 75 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg | [89] |
| Toh HC et al. | 2013 | Linifanib | II | 44 | Single-arm, open-label | Linifanib = 0.25 mg | [90] |
| Lim HY et al. | 2018 | Refametinib v/s Refametinib + Sorafenib |
II | 1318 | Open-label RCT | Refametinib = 50 mg Sorafenib = 400 mg |
[91] |
| Chow PK et al. | 2014 | Sorafenib | II | 29 | Open-label RCT | Sorafenib = 400 mg | [92] |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusion
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Llovet, J.M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Pikarsky, E.; Sangro, B.; Schwartz, M.; Sherman, M.; Gores, G. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villanueva, A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Gao, Q. Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, T.; Kiyosawa, K. Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2007, 37, S95–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, et al. BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ MERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumour progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 2004;64:7099–109.
- Petrick, J.L.; Florio, A.A.; Znaor, A.; Ruggieri, D.; Laversanne, M.; Alvarez, C.S.; Ferlay, J.; Valery, P.C.; Bray, F.; McGlynn, K.A. International trends in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, 1978–2012. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 147, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.K.; Chun, H.G. Status of hepatocellular carcinoma in South Korea. 2, 39. [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm SM, Adnane L, Newell P, et al. Preclinical overview of sorafenib, a multikinase inhibitor that targets both Raf and VEGF and PDGF receptor tyrosine kinase signalling. Mol Cancer Ther 2008;7:3129–40.
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervello, M.; McCubrey, J.A.; Cusimano, A.; Lampiasi, N.; Azzolina, A.; Montalto, G. Targeted therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: novel agents on the horizon. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 236–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samant, R.S.; Shevde, L.A. Recent Advances in Anti-Angiogenic Therapy of Cancer. Oncotarget 2011, 2, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmani, M.; Davis, E.M.; Crabtree, T.R.; Habibi, J.R.; Nguyen, T.K.; Dent, P.; Grant, S. The Kinase Inhibitor Sorafenib Induces Cell Death through a Process Involving Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 5499–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.-T.; Cheng, A.-L.; Shiau, C.-W.; Huang, H.-P.; Huang, J.-W.; Chen, P.-J.; Chen, K.-F. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is a major kinase-independent target of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, P.; Arienti, C.; Amadori, D.; Fabbri, F.; Carloni, S.; Tesei, A.; Vannini, I.; Silvestrini, R.; Zoli, W. Role of RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, p-STAT-3 and Mcl-1 in sorafenib activity in human pancreatic cancer cell lines. J. Cell. Physiol. 2009, 220, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervello, M.; Bachvarov, D.; Lampiasi, N.; Cusimano, A.; Azzolina, A.; McCubrey, J.A.; Montalto, G. Molecular mechanisms of sorafenib action in liver cancer cells. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2008, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iavarone, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Piscaglia, F.; Zavaglia, C.; Grieco, A.; Villa, E.; Cammà, C.; Colombo, M. ; on behalf of the SOFIA (SOraFenib Italian Assessment) study group Field-practice study of sorafenib therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective multicenter study in Italy. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; De Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, F.; Yang, J.; Fan, H.; Xie, Q.; Jiang, K.; Gong, J.; Gao, B.; Yang, Q.; Lei, Z. Risk of Adverse Events in Cancer Patients Receiving Nivolumab With Ipilimumab: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 877434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butte, M.J.; Keir, M.E.; Phamduy, T.B.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J. Programmed Death-1 Ligand 1 Interacts Specifically with the B7-1 Costimulatory Molecule to Inhibit T Cell Responses. Immunity 2007, 27, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Riella, L.V.; Chock, S.; Liu, T.; Zhao, X.; Yuan, X.; Paterson, A.M.; Watanabe, T.; Vanguri, V.; Yagita, H.; et al. The Novel Costimulatory Programmed Death Ligand 1/B7.1 Pathway Is Functional in Inhibiting Alloimmune Responses In Vivo. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem A, Shah H. Atezolizumab. [Updated 2022 ]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK567758/.
- Roviello, G.; Bachelot, T.; Hudis, C.A.; Curigliano, G.; Reynolds, A.R.; Petrioli, R.; Generali, D. The role of bevacizumab in solid tumours: A literature based meta-analysis of randomised trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casak, S.J.; Donoghue, M.; Fashoyin-Aje, L.; Jiang, X.; Rodriguez, L.; Shen, Y.-L.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhao, H.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Atezolizumab Plus Bevacizumab for the Treatment of Patients with Advanced Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 27, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.-W.; Park, J.-W.; Nam, B.-H.; Yu, A.; Woo, S.M.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, S.H.; Koh, Y.H.; Kim, H.B.; Park, S.J.; et al. Clinical outcomes of a cohort series of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis B virus-endemic area. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow PK, Gandhi M. Phase III multicenter open-label randomized controlled trial of selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) versus sorafenib in locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: the SIRveNIB study. J Clin Oncol 2017;35 15_Suppl:4002.
- Vilgrain, V.; Pereira, H.; Assenat, E.; Guiu, B.; Ilonca, A.D.; Pageaux, G.-P.; Sibert, A.; Bouattour, M.; Lebtahi, R.; Allaham, W.; et al. Efficacy and safety of selective internal radiotherapy with yttrium-90 resin microspheres compared with sorafenib in locally advanced and inoperable hepatocellular carcinoma (SARAH): an open-label randomised controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1624–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Liver Cancer Association; National Cancer Center; Practice Guideline Revision Committee. 2018 Korean Liver Cancer Association–National Cancer Center Korea Practice Guidelines for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Liver 2019, 13, 227–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; et al. Updated efficacy and safety data from IMbrave150: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab vs. sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2021, 76, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H., 3rd; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): an open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Kang, Y.-K.; Kim, T.-Y.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Santoro, A.; Sangro, B.; Melero, I.; Kudo, M.; Hou, M.-M.; Matilla, A.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Previously Treated With Sorafenib: The CheckMate 040 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, e204564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, R.K.; Sangro, B.; Harris, W.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Kang, Y.-K.; Qin, S.; Tai, D.W.-M.; Lim, H.Y.; Yau, T.; et al. Safety, Efficacy, and Pharmacodynamics of Tremelimumab Plus Durvalumab for Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Randomized Expansion of a Phase I/II Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Lim, Y.-S.; Yeon, J.E.; Song, T.-J.; Yu, S.J.; Gwak, G.-Y.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.W.; et al. Adjuvant Immunotherapy With Autologous Cytokine-Induced Killer Cells for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruix, J.; Takayama, T.; Mazzaferro, V.; Chau, G.-Y.; Yang, J.; Kudo, M.; Cai, J.; Poon, R.T.; Han, K.-H.; Tak, W.Y.; et al. Adjuvant sorafenib for hepatocellular carcinoma after resection or ablation (STORM): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Kang, Y.-K.; Hou, M.-M.; Numata, K.; Yeo, W.; Chopra, A.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Sorafenib-experienced Asian cohort analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, R.K.; Rimassa, L.; Cheng, A.-L.; Kaseb, A.; Qin, S.; Zhu, A.X.; Chan, S.L.; Melkadze, T.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Breder, V.; et al. Cabozantinib plus atezolizumab versus sorafenib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (COSMIC-312): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 995–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Park, J.-W.; Finn, R.S.; Cheng, A.-L.; Mathurin, P.; Edeline, J.; Kudo, M.; Harding, J.J.; Merle, P.; Rosmorduc, O.; et al. Nivolumab versus sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 459): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 23, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Zhu, A.X.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sorafenib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (IMbrave150): an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kang, Y.-K.; Yen, C.-J.; Finn, R.S.; Galle, P.R.; Llovet, J.M.; Assenat, E.; Brandi, G.; Pracht, M.; Lim, H.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab after sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and increased α-fetoprotein concentrations (REACH-2): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M.; Han, G.; Tak, W.Y.; Yang, J.; Guglielmi, A.; Paik, S.W.; Reig, M.; Kim, D.Y.; Chau, G.-Y.; et al. Sorafenib or placebo plus TACE with doxorubicin-eluting beads for intermediate stage HCC: The SPACE trial. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, A.; Qin, S.; Kudo, M.; Su, Y.; Hudgens, S.; Yamashita, T.; Yoon, J.-H.; Fartoux, L.; Simon, K.; López, C.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib for first-line treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: patient-reported outcomes from a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.S.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Hsu, C.-H.; Numata, K.; Stein, S.; Verret, W.; Hack, S.P.; Spahn, J.; Liu, B.; Abdullah, H.; et al. Atezolizumab with or without bevacizumab in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (GO30140): an open-label, multicentre, phase 1b study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 808–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, J.; Yoo, C.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Lee, M.A.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, I.; Oh, S.; Hwang, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in Korean patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2021, 42, 674–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-W.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, D.Y.; Bae, S.-H.; Paik, S.W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, H.Y.; Lee, H.C.; Han, S.Y.; Cheong, J.Y.; et al. Sorafenib with or without concurrent transarterial chemoembolization in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The phase III STAH trial. J. Hepatol. 2018, 70, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, N.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Hong, J.H.; Hur, M.H.; Cho, H.; Park, M.K.; Kim, J.; Bin Lee, Y.; Cho, E.J.; Lee, J.-H.; et al. Comparison of the outcomes between sorafenib and lenvatinib as the first-line systemic treatment for HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022, 22, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheon, J.; Chon, H.J.; Bang, Y.; Park, N.H.; Shin, J.W.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, J.; Yoo, C.; Ryoo, B.-Y. Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Lenvatinib in Korean Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Analysis. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 613–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.M.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.H.; Shin, J.H.; An, J.; Lee, H.C.; Lim, Y.-S. Efficacy and Safety of Transarterial Chemoembolization Plus External Beam Radiotherapy vs Sorafenib in Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Macroscopic Vascular Invasion: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hong, J.Y.; Cho, H.J.; Sa, J.K.; Liu, X.; Ha, S.Y.; Lee, T.; Kim, H.; Kang, W.; Sinn, D.H.; Gwak, G.-Y.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma patients with high circulating cytotoxic T cells and intra-tumoral immune signature benefit from pembrolizumab: results from a single-arm phase 2 trial. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, P.K.; Gandhi, M.; Tan, S.-B.; Khin, M.W.; Khasbazar, A.; Ong, J.; Choo, S.P.; Cheow, P.C.; Chotipanich, C.; Lim, K.; et al. SIRveNIB: Selective Internal Radiation Therapy Versus Sorafenib in Asia-Pacific Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1913–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryoo, B.-Y.; Palmer, D.H.; Park, S.R.; Rimassa, L.; Sarker, D.; Daniele, B.; Steinberg, J.; López, B.; Lim, H.Y. Efficacy and Safety Results from a Phase 2, Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Enzalutamide Versus Placebo in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Drug Investig. 2021, 41, 795–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; He, A.R.; Lim, H.Y.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Hung, C.-H.; Sheen, I.-S.; Izumi, N.; Austin, T.; Wang, Q.; et al. Safety and efficacy of tigatuzumab plus sorafenib as first-line therapy in subjects with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase 2 randomized study. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cainap, C.; Qin, S.; Huang, W.-T.; Chung, I.J.; Pan, H.; Cheng, Y.; Kudo, M.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, P.-J.; Toh, H.-C.; et al. Linifanib Versus Sorafenib in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results of a Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Rosmorduc, O.; Evans, T.J.; Ross, P.J.; Santoro, A.; Carrilho, F.J.; Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. SEARCH: A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of Sorafenib Plus Erlotinib in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, W.Y.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Lim, H.Y.; Kim, D.-Y.; Okusaka, T.; Ikeda, M.; Hidaka, H.; Yeon, J.-E.; Mizukoshi, E.; Morimoto, M.; et al. Phase I/II study of first-line combination therapy with sorafenib plus resminostat, an oral HDAC inhibitor, versus sorafenib monotherapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in east Asian patients. Investig. New Drugs 2018, 36, 1072–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.J.; Qin, S.; Park, J.-W.; Poon, R.T.; Raoul, J.-L.; Philip, P.A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Hu, T.-H.; Heo, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Brivanib Versus Sorafenib As First-Line Therapy in Patients With Unresectable, Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Results From the Randomized Phase III BRISK-FL Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Park, J.O.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Poon, R.; Pastorelli, D.; Blanc, J.-F.; Chung, H.C.; Baron, A.D.; Pfiffer, T.E.F.; et al. Ramucirumab versus placebo as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib (REACH): a randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.Y.; Heo, J.; Choi, H.J.; Lin, C.-Y.; Yoon, J.-H.; Hsu, C.; Rau, K.-M.; Poon, R.T.; Yeo, W.; Park, J.-W.; et al. A Phase II Study of the Efficacy and Safety of the Combination Therapy of the MEK Inhibitor Refametinib (BAY 86-9766) Plus Sorafenib for Asian Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 5976–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, I.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M.; Borg, C.; Malfertheiner, P.; Seitz, J.F.; Park, J.O.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Kudo, M.; Poon, R.; et al. Ramucirumab as second-line treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma following first-line therapy with sorafenib: Patient-focused outcome results from the randomised phase III REACH study. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 81, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Ren, Z.; Meng, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chai, X.; Xiong, J.; Bai, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, H.; Fang, W.; et al. Camrelizumab in patients with previously treated advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a multicentre, open-label, parallel-group, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Li, Q.; Gu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, A.; Chen, X.; Zhou, C.; Ren, Z.; et al. Apatinib as second-line or later therapy in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (AHELP): a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 6, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Vogel, A.; Madoff, D.C.; Finn, R.S.; Ogasawara, S.; Ren, Z.; Mody, K.; Li, J.J.; Siegel, A.B.; Dubrovsky, L.; et al. Randomized Phase 3 LEAP-012 Study: Transarterial Chemoembolization With or Without Lenvatinib Plus Pembrolizumab for Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma Not Amenable to Curative Treatment. Cardiovasc. Interv. Radiol. 2022, 45, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Sun, W.; Li, W.; Shen, Y.; Guo, X.; Teng, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, L.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study. Cancer 2021, 127, 3782–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Fan, W.; Zhu, B.; Wang, G.; Sun, J.; Xiao, C.; Huang, F.; Tang, R.; Cheng, Y.; Huang, Z.; et al. Lenvatinib Combined With Transarterial Chemoembolization as First-Line Treatment for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Phase III, Randomized Clinical Trial (LAUNCH). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Li, Q.; Zou, R.; Shen, J.; Fang, W.; Tan, G.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Wei, W.; et al. Sorafenib Plus Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin vs Sorafenib Alone for Hepatocellular Carcinoma With Portal Vein Invasion: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 953–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Finn, R.S.; Kudo, M.; Meyer, T.; Vogel, A.; Ducreux, M.; Macarulla, T.M.; Tomasello, G.; Boisserie, F.; Hou, J.; et al. RATIONALE 301 study: tislelizumab versus sorafenib as first-line treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Futur. Oncol. 2019, 15, 1811–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, K.; Qin, S.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zou, J. Camrelizumab in combination with apatinib in second-line or above therapy for advanced primary liver cancer: cohort A report in a multicenter phase Ib/II trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Tang, W.; Qian, X.; Li, X.; Cheng, F.; Wang, K.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Song, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab plus apatinib during the perioperative period in resectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, open label, phase II clinical trial. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Shen, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Wu, J.; Shao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Yin, T.; et al. Camrelizumab in Combination with Apatinib in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma (RESCUE): A Nonrandomized, Open-label, Phase II Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.; Bi, F.; Gu, S.; Bai, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Z.; Ying, J.; Lu, Y.; Meng, Z.; Pan, H.; et al. Donafenib Versus Sorafenib in First-Line Treatment of Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized, Open-Label, Parallel-Controlled Phase II-III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, N.; Wang, X.; Li, J.-B.; Lai, J.-F.; Chen, Q.-F.; Li, S.-L.; Deng, H.-J.; He, M.; Mu, L.-W.; Zhao, M. Arterial Chemotherapy of Oxaliplatin Plus Fluorouracil Versus Sorafenib in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Biomolecular Exploratory, Randomized, Phase III Trial (FOHAIC-1). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 468–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Xu, A.; Cang, S.; Du, C.; Li, Q.; Lu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guo, Y.; et al. Sintilimab plus a bevacizumab biosimilar (IBI305) versus sorafenib in unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma (ORIENT-32): a randomised, open-label, phase 2–3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.-J.; He, M.-K.; Chen, H.-W.; Fang, W.-Q.; Zhou, Y.-M.; Xu, L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Guo, Y.; Guo, R.-P.; et al. Hepatic Arterial Infusion of Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin Versus Transarterial Chemoembolization for Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Randomized Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-K.; Yau, T.; Park, J.-W.; Lim, H.Y.; Lee, T.-Y.; Obi, S.; Chan, S.L.; Qin, S.; Kim, R.D.; Casey, M.; et al. Randomized phase II study of axitinib versus placebo plus best supportive care in second-line treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2457–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Decaens, T.; Raoul, J.-L.; Boucher, E.; Kudo, M.; Chang, C.; Kang, Y.-K.; Assenat, E.; Lim, H.-Y.; Boige, V.; et al. Brivanib in Patients With Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Who Were Intolerant to Sorafenib or for Whom Sorafenib Failed: Results From the Randomized Phase III BRISK-PS Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 3509–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.C.; Lencioni, R.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Chao, Y.; Yen, C.-J.; Lausoontornsiri, W.; Chen, P.-J.; Sanpajit, T.; Camp, A.; Cox, D.S.; et al. A Phase I/II Multicenter Study of Single-Agent Foretinib as First-Line Therapy in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, A.X.; Kudo, M.; Assenat, E.; Cattan, S.; Kang, Y.-K.; Lim, H.Y.; Poon, R.T.P.; Blanc, J.-F.; Vogel, A.; Chen, C.-L.; et al. Effect of Everolimus on Survival in Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma After Failure of Sorafenib. JAMA 2014, 312, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, R.K.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Merle, P.; Park, J.-W.; Bolondi, L.; Chan, S.L.; Lim, H.Y.; Baron, A.D.; Parnis, F.; Knox, J.; et al. Second-line cabozantinib after sorafenib treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a subgroup analysis of the phase 3 CELESTIAL trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verset, G.; Borbath, I.; Karwal, M.; Verslype, C.; Van Vlierberghe, H.; Kardosh, A.; Zagonel, V.; Stal, P.; Sarker, D.; Palmer, D.H.; et al. Pembrolizumab Monotherapy for Previously Untreated Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Data from the Open-Label, Phase II KEYNOTE-224 Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2547–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Meyer, T.; Cheng, A.-L.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Rimassa, L.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; Cicin, I.; Merle, P.; Chen, Y.; Park, J.-W.; et al. Cabozantinib in Patients with Advanced and Progressing Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, W.M.; Yong, W.P.; Lim, C.; Low, L.S.; Tham, C.K.; Koh, T.S.; Ng, Q.S.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, L.Z.; Hartano, S.; et al. A phase Ib study of selumetinib (AZD6244, ARRY-142886) in combination with sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, H.C.; Chen, P.-J.; Carr, B.I.; Knox, J.J.; Gill, S.; Ansell, P.; McKeegan, E.M.; Dowell, B.; Pedersen, M.; Qin, Q.; et al. Phase 2 trial of linifanib (ABT-869) in patients with unresectable or metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2012, 119, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.Y.; Merle, P.; Weiss, K.H.; Yau, T.; Ross, P.; Mazzaferro, V.; Blanc, J.-F.; Ma, Y.T.; Yen, C.J.; Kocsis, J.; et al. Phase II Studies with Refametinib or Refametinib plus Sorafenib in Patients with RAS-Mutated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4650–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, P.K.H.; Poon, D.Y.H.; Khin, M.-W.; Singh, H.; Han, H.-S.; Goh, A.S.W.; Choo, S.-P.; Lai, H.-K.; Lo, R.H.G.; Tay, K.-H.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Sequential Radioembolization-Sorafenib Therapy for Inoperable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e90909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





