1. Introduction
Polypharmacy, the administration of multiple drugs to treat complex diseases, is a common therapeutic approach [
1]. However, it introduces the risk of drug-drug interactions (DDIs), which can alter the pharmacological effects of medications [
2,
3]. Studies indicate that DDIs contribute to approximately 30% of reported adverse drug events (ADEs), leading to increased incidence rates, mortality, and occasionally, the withdrawal of drugs from the market. This results in significant medical costs due to the stringent demands of drug development [
4]. Therefore, the accurate identification and understanding of DDIs are essential for guiding polypharmacy prescriptions by clinicians and patients, as well as for informing drug development efforts in pharmaceutical companies. Despite the availability of
in-vitro experiments and clinical trials to identify DDIs, the systematic screening of potential DDI candidates from a vast array of drugs remains challenging, time-consuming, and resource-intensive.
Accurate prediction and understanding of drug-drug interactions (DDIs) are pivotal for healthcare and pharmaceutical sectors due to their substantial impact on adverse drug events (ADEs) and associated costs. Despite the abundance of biomedical data, there exists a pressing need for computational methods to effectively navigate the extensive landscape of potential DDIs. While repositories such as DrugBank offer comprehensive repositories of documented DDIs, they represent only a fraction of the myriad of possible drug combinations. Consequently, numerous computational approaches have emerged in recent years to address this gap [
5].
In recent years, there has been a significant surge in the availability of scientific literature, electronic medical records, adverse event reports, drug labels, and related data sources [
6]. Researchers have actively pursued methods to extract information about drug-drug interactions (DDIs) from diverse textual sources and medical records using advanced natural language processing (NLP) techniques [
7]. Additionally, efforts have been made to infer potential DDIs through similarity-based approaches, leveraging known interactions [
4,
6,
7]. Moreover, various computational techniques including machine learning [
8], network modeling [
6], and knowledge graphs [
2] have been applied to predict DDIs. However, many of these computational methods predominantly focus on identifying the occurrence of a DDI given a specific drug pair.
In recent years, there has been a significant surge in efforts to deepen our understanding of drug-drug interactions (DDIs) through the development of advanced multi-type DDI prediction methodologies. These methodologies aim to provide more comprehensive insights beyond simple predictions of DDI occurrences [
7]. A crucial development in this field was the establishment of a gold standard DDI dataset sourced from DrugBank. This dataset encompasses 192,284 DDIs associated with 86 DDI types across 191,878 drug pairs [
5]. It served as the foundation for multi-type DDI prediction tasks, formulated as multi-label classification challenges.
A noteworthy approach is the Deep-DDI method, which introduced deep neural networks (DNNs) to harness structural information from chemical compounds for each drug pair. Subsequent advancements have focused on enhancing prediction accuracy by incorporating diverse biological information, such as drug targets and enzymes, to characterize drug pairs. Additionally, these methods integrate structural information obtained from autoencoders or the encoder module of transformers to learn low-dimensional latent features, in conjunction with DNN algorithms for classification [
8,
9,
10].
In recent research endeavors, numerous methods have emerged aiming to enhance the prediction accuracy and depth of understanding of drug-drug interactions (DDIs). One notable approach involves representing the feature vector of a drug through a similarity profile, which assesses the structural likeness of a given drug against others in the dataset. Moreover, recent advancements include the utilization of few-shot learning techniques, as demonstrated by Deng
et al. [
11], to improve prediction performance for rare types of DDIs with limited samples [
12,
13]. Additionally, the CSMDDI method introduced by Liu
et al. [
14] generates embedding representations of drugs and DDI types, followed by learning a mapping function to predict multi-type DDIs [
15]. Another notable contribution is the deep MDDI model proposed by Feng
et al. [
16], which integrates an encoder utilizing deep relational graph convolutional networks and a tensor-like decoder to capture topological features and predict multi-label DDI types. Furthermore, Yang
et al. [
17] developed a substructure-aware graph neural network, employing a message-passing neural network with a novel substructure attention mechanism and a substructure-substructure interaction module for DDI prediction. These methodologies collectively contribute to advancing the field of DDI prediction and hold promise for improving drug safety and efficacy.
Some early approaches, such as those by Vilar
et al. [
18] and Lu
et al. [
19], focused solely on known DDIs, while newer similarity-based methods, like those by Vilar
et al. [
18] and Zhang
et al. [
20], utilized drug similarities to predict potential DDIs. Ensemble methods, introduced by Gottlieb
et al. [
21] and Zhang
et al. [
20], combined various drug similarity measures to improve prediction accuracy. Additionally, machine learning models like Dependency-based Convolutional Neural Network (DCNN) by Liu
et al. and Deep DDI by Ryu
et al. utilized text mining and deep learning techniques to predict DDIs based on drug structures and names [
22]. A novel approach in this field is network pharmacology, exemplified by methods like NIMS proposed by Li
et al. [
14], which constructs disease-specific biological networks to identify synergistic drug interactions based on therapeutic targets. This approach has shown promise, as demonstrated by Guo
et al. [
23], who used synergistic modules in a differential gene interaction network to effectively inhibit Inflammation-Induced Tumorigenesis (IIT) [
24].
In our pursuit of enhancing drug-drug interaction (DDI) prediction accuracy, we adopt a comprehensive approach that integrates similarity selection, fusion, and neural network techniques. This methodology aims to elevate the precision of DDI prediction, thus contributing to advancements in drug discovery and healthcare. Our similarity selection process draws from a heuristic method proposed by Olayan
et al. [
25], originally designed for drug-target interaction prediction, allowing us to focus on high-information subsets of the data. Additionally, we leverage Similarity Network Fusion (SNF), a well-established technique in biological research, to amalgamate diverse data types and bolster prediction accuracy.
Our method, termed DNN, combines a neural network model with techniques for similarity selection and fusion to enhance the precision of DDI prediction through nonlinear analysis and feature extraction. DNN operates through a structured process: initially, it aggregates information on diverse drug similarities, including chemical, target-based, and Gene Ontology similarities, sourced from multiple datasets. Subsequently, a heuristic process proposed by Olayan
et al. [
25] is applied to identify the most informative and least redundant subset of similarity types. This refined subset is then integrated using the Similarity Network Fusion (SNF) method. Following this, the amalgamated similarity matrix, alongside interaction data, serves as the input for training the neural network. Our assessment of DNN against three prominent machine learning classifiers—Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Adaptive Gradient Boosting (AdaBoost), and Light Gradient-Boosting Machine (LGBM)—across three benchmark datasets involved stratified five-fold cross-validation [
26]. Additionally, case studies conducted on various drugs underscore DNN's efficacy in predicting unknown DDIs. These findings validate the robustness and efficiency of DNN as an approach for precise DDI prediction [
27,
28,
29].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Datasets
In our investigation, we utilize two datasets with varying sample scales. The first dataset, referred to as Dataset1, is a benchmark dataset assembled by Deng
et al. [
11]. It encompasses 445,390 drugs and 209,904 pairwise DDIs across 20 distinct DDI types. Each drug entry in Dataset1 is characterized by four fundamental types of features extracted from DrugBank [
30], namely chemical substructures, targets, pathways, and enzymes.
Conversely, Dataset2, sourced from the research conducted by Lin
et al. [
31], comprises 222,695 drugs with 209,904 pairwise DDIs spanning the same 20 DDI types as Dataset1. However, Dataset2 offers a more extensive array of features for each drug entry. These features encompass various aspects such as QTc-prolonging activities, serum concentration, absorption, neural activity, stimulatory activities, hyperglycemic and hyponatremic activities, arrhythmia, adverse effects, metabolism, bronchoconstrictory and bronchodilatory activities, toxicity, central nervous system depressant activities, excretion, myopathy, therapeutic efficacy, myelosuppression, vasoconstricting and vasodilatory activities, potassium, calcium, and sodium concentration, as well as hypertensive and hypotensive activities, sedative activities, and miscellaneous interactions.
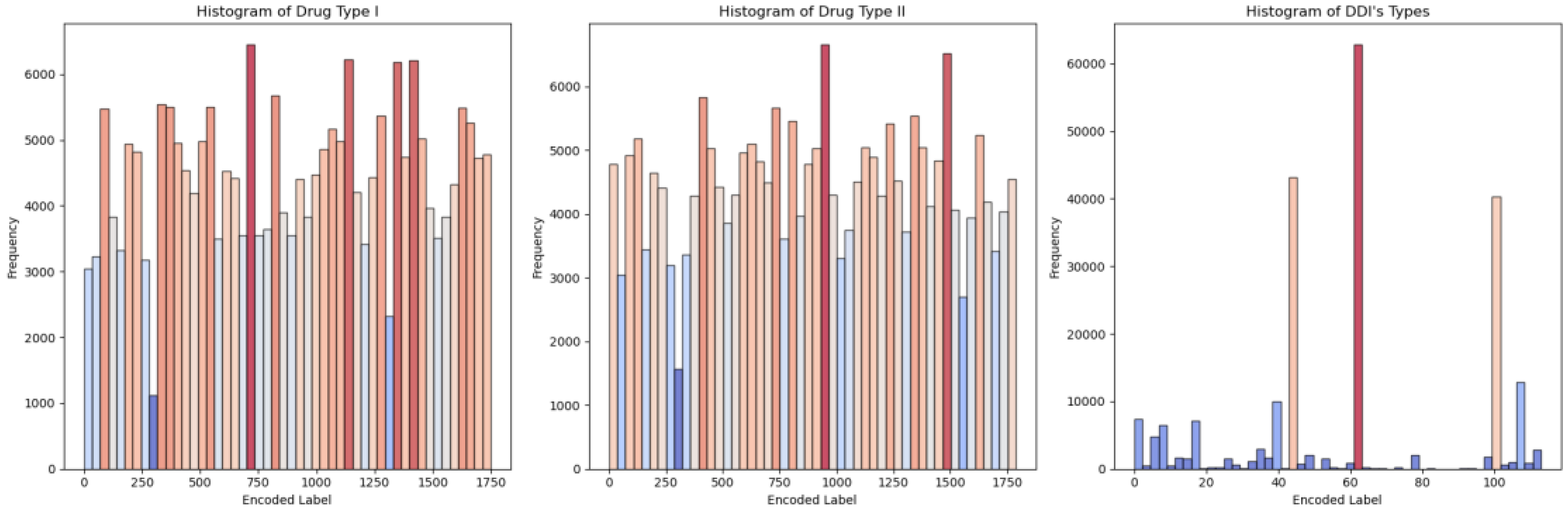
For situations involving multiple drugs, we assign a unique identifier to each situation as a DDI type and aggregate them based on features extracted from other datasets. This enables the application of machine learning classifier models. To delve into the specifics of DDI types,
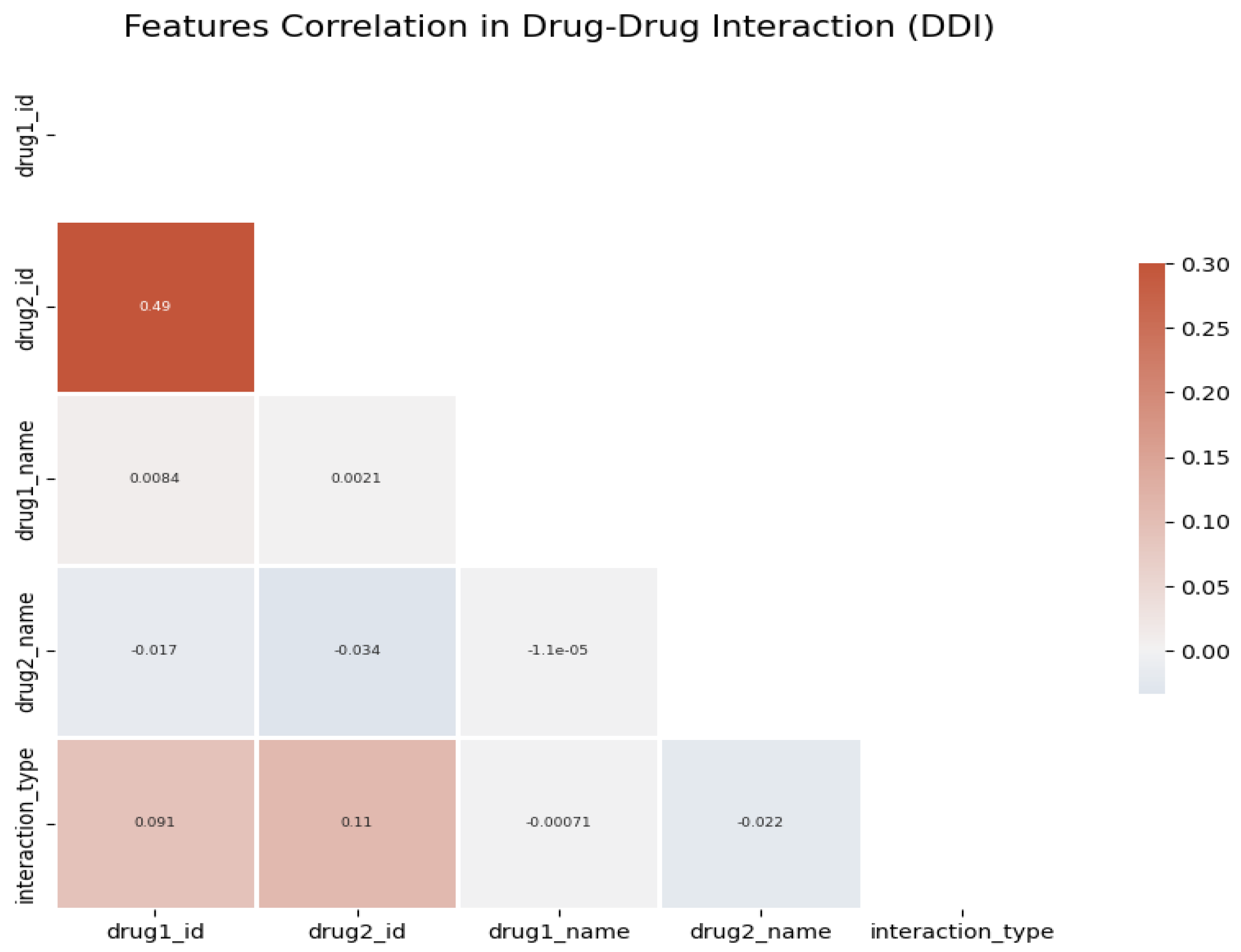
Figure 1 illustrates the correlation between different drug types in multidrug interactions, as shown in
Figure 2, highlighting a range of highly and less correlated DDI types. To enhance precision in subsequent models, we introduce an innovative approach by combining positively correlated (
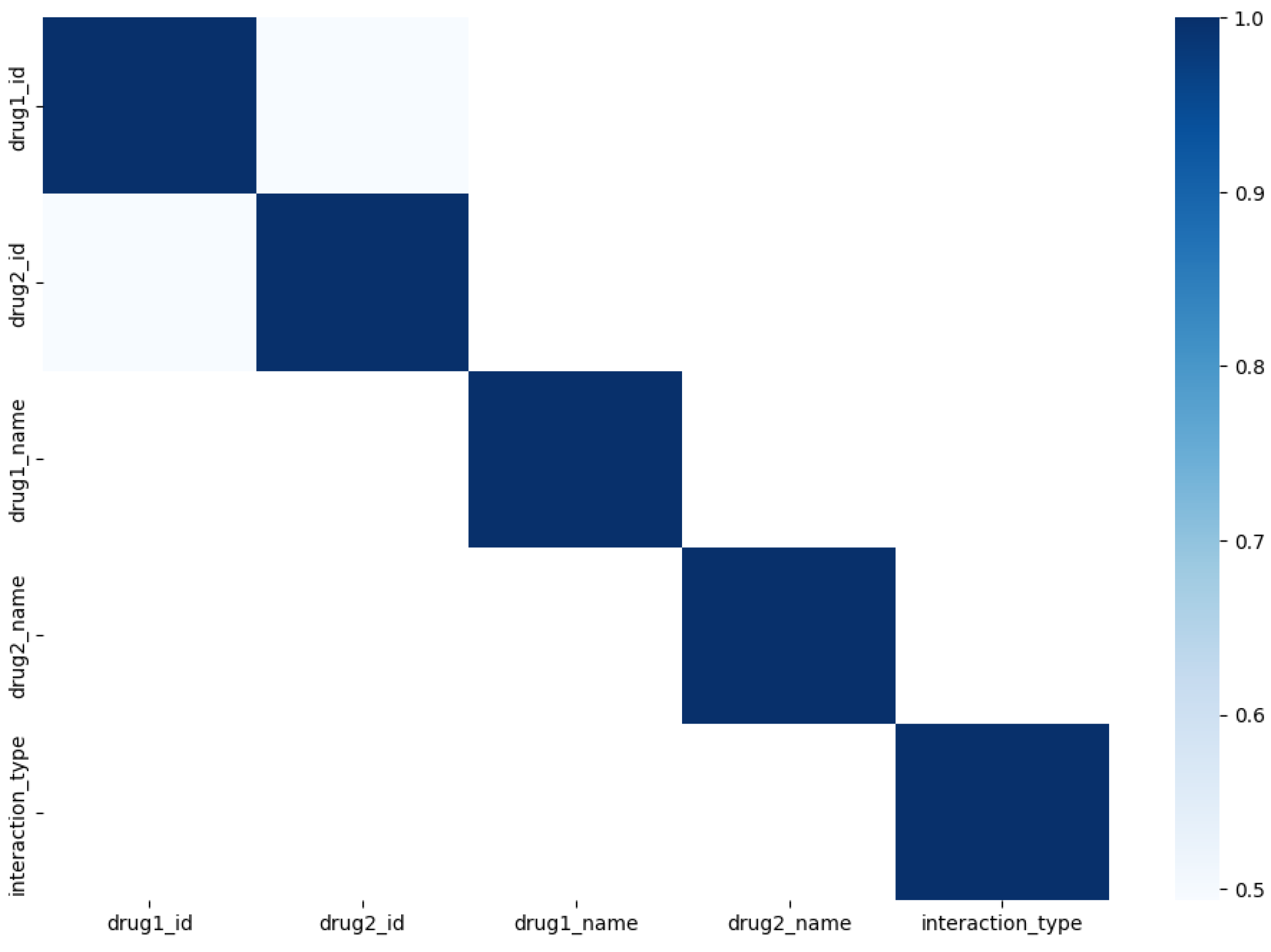
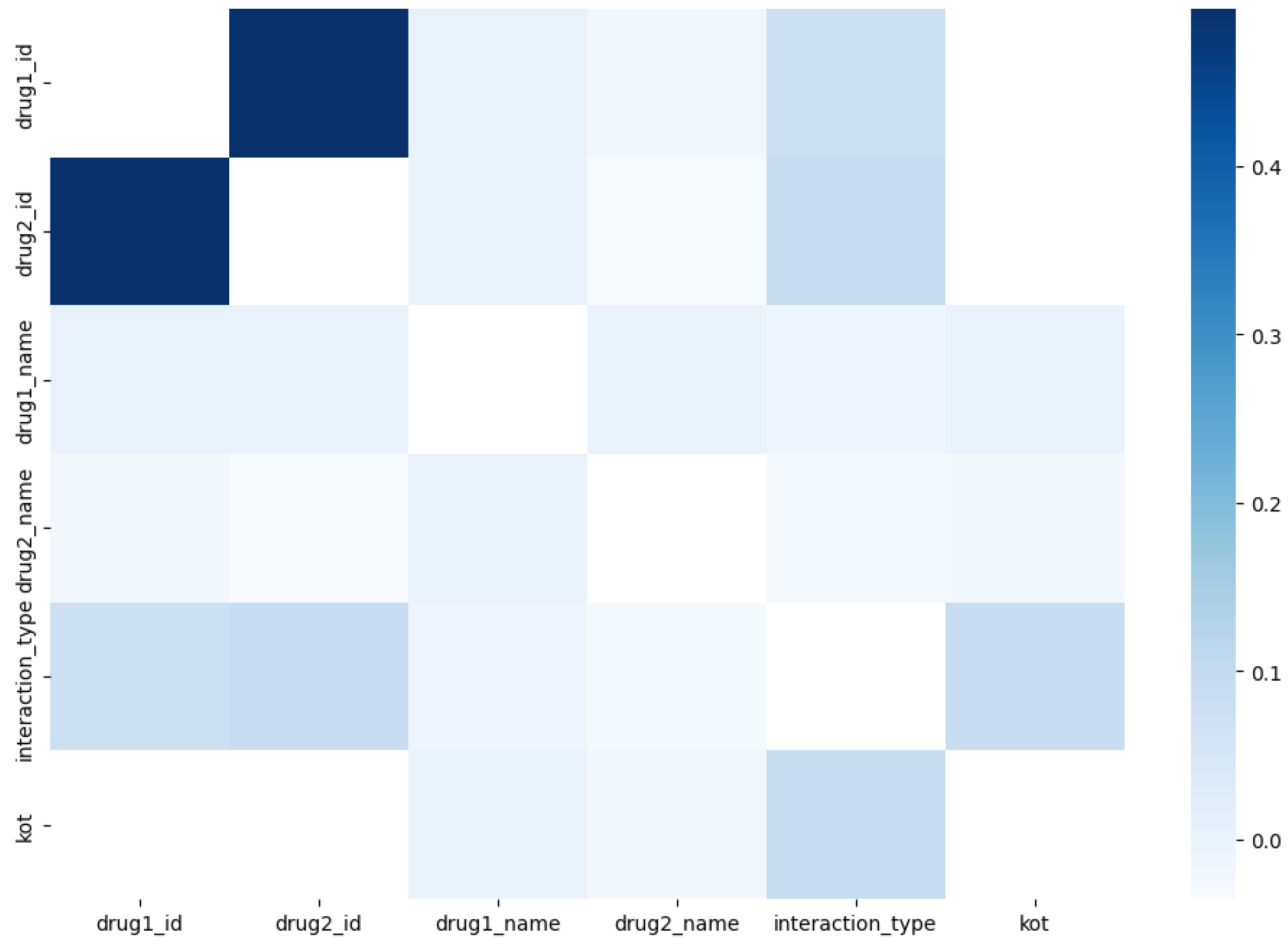
Figure 3) and negatively correlated (
Figure 4) DDI types. This combination enriches the feature set, facilitating more efficient feature representation.
In the DDI dataset, the five most frequently occurring drugs in the "Drug I " column are Fluvoxamine, Venlafaxine, Phenytoin, Ziprasidone, and Cyclosporine. Similarly, in the "Drug II" column, the top five drugs by frequency are Curcumin, Pitolisant, Rucaparib, Stiripentol, and Apalutamide. Regarding the interaction types represented in the "DDI’s types" column, the top five in terms of frequency are 'risk or severity of adverse effects', 'metabolism', 'serum concentration', 'therapeutic efficacy', and 'hypotensive activities'. These are provided valuable insights into the most prevalent drugs and interaction types present in the dataset, which can inform further analysis and modeling efforts in the study of DDI.
2.2. Dataset Splitting
For each dataset, we carefully selected a metric and devised a splitting pattern that best suits its unique characteristics. Given the diverse nature of our dataset's input parameters, which include both categorical factors like material and process types, as well as sub-categorical processes, along with numerical inputs, we performed scaling. Moreover, to ensure consistency, we normalized the output classes - DDI’s types. The normalization process follows the equation:
Where,
is the scaled value,
is the original value,
is the minimum value in the dataset, and
is the maximum value in the dataset.
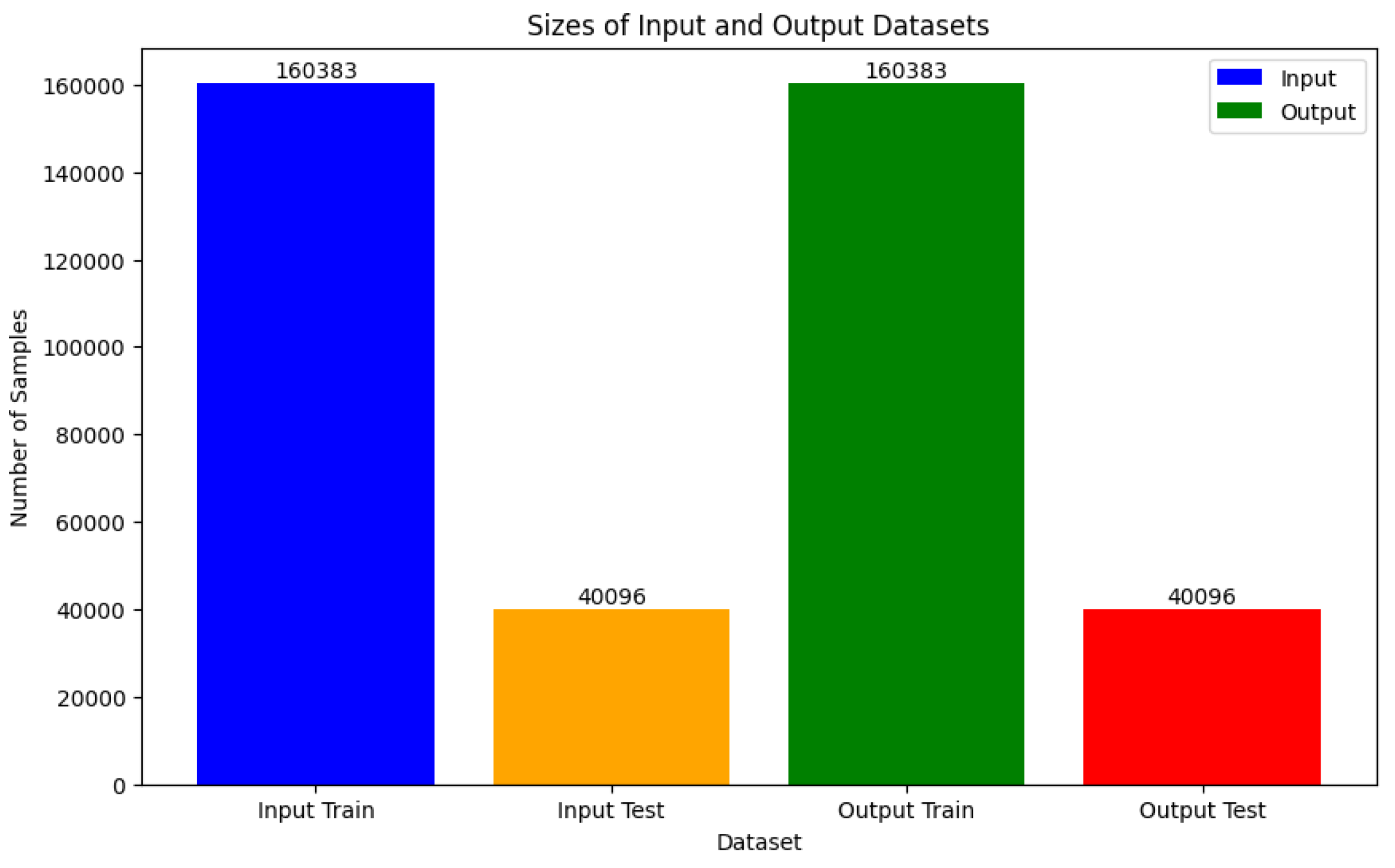
In machine learning, it's imperative to split datasets into training and test subsets to gauge model performance on unseen data. Consequently, we divided our dataset into training and testing sets. The models were trained using the training data, while the test data remained separate for evaluating model performance. This division was executed post scaling of the datasets, as depicted in
Figure 5.
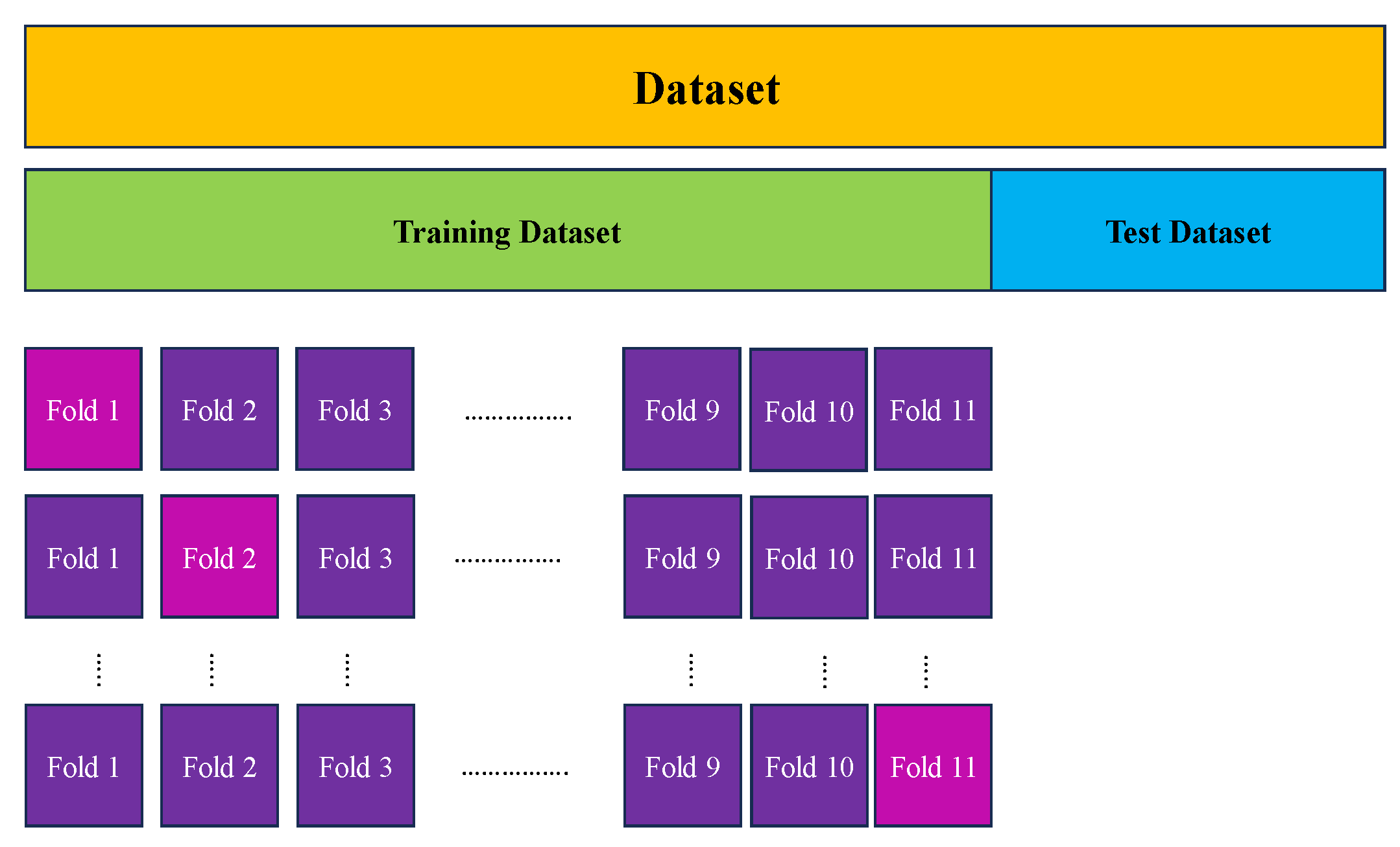
To ensure a comprehensive evaluation of our model's performance and enhance its reliability, we integrated k-fold cross-validation into our methodology. This widely-adopted technique involves dividing the dataset into k equally-sized folds or subsets. The model is then trained on k-1 folds and validated on the remaining fold. This iterative process is repeated k times, with each fold serving as the validation set exactly once.
In addition to k-fold cross-validation, we implemented supplementary measures to validate the robustness of our model. These measures encompassed bootstrap resampling techniques and sensitivity analyses to assess the stability of our findings under diverse conditions. Such comprehensive validation approaches are crucial for establishing the credibility and generalizability of our predictive models in real-world scenarios.
The primary objective of employing cross-validation is to mitigate overfitting, wherein the model becomes excessively tailored to the training data, leading to poor generalization to unseen data. By evaluating the model across multiple validation sets, cross-validation provides a more accurate estimate of its ability to generalize. However, it's important to acknowledge that this approach may introduce increased variability in model testing, particularly when assessing against individual data points. Outliers within these data points can significantly impact testing variability.
Furthermore, k-fold cross-validation can be computationally intensive due to its iteration over the dataset's size. To address this concern and minimize overfitting, we selected k=11, as it demonstrated highly effective performance with minimal errors and overfitting, as illustrated in
Figure 6.
2.3. ML Models
In the context of classifying DDI types in multidrug interactions, the importance of time and cost considerations is paramount, as highlighted in the introduction. Achieving precise outcomes while minimizing expenses, without resorting to clinical tests, underscores the significance of exploring machine learning (ML) models as feasible alternatives to conventional experimental and numerical methods. This study delves into the performance of various ML models using pre-segmented datasets, focusing on non-linear algorithms. Below, we provide a brief overview of these models, followed by an in-depth discussion on effective metric methodologies in the subsequent section. The results and discussions section will then unveil the outcomes of these models, followed by a comparative analysis in the metrics section to discern their respective efficiencies.
2.3.1. Non-Linear Classification Algorithm
In situations where classes cannot be distinctly separated by a linear boundary, the utilization of non-linear classifiers becomes imperative in machine learning models. These classifiers excel in addressing intricate classification challenges by discerning complex patterns and relationships within the data. Unlike linear models, non-linear classifiers demonstrate superior performance when dealing with complex datasets. Here, we introduce the most prevalent models applied to our DDI type classes, including tree-based algorithms and Neural Networks (NNs) algorithms, offering insights into the capabilities of non-linear algorithms.
2.3.1.1. Gradient Boosting Trees (GBT)
Gradient Boosting Trees (GBT) stands out as a robust tree-based algorithm that iteratively enhances a loss function by incorporating decision trees into the ensemble. With each iteration, a new tree is trained to forecast the residuals, representing the disparities between the actual and predicted values, of the prior trees. These forecasts are merged to derive the ultimate prediction. GBT demonstrates proficiency in managing intricate data relationships and is esteemed for its ability to yield remarkably precise predictions. It particularly thrives in scenarios where conventional machine learning algorithms encounter difficulties, such as navigating through noisy or high-dimensional datasets.
2.3.1.1.1. Extreme Gradient Boosting Machine (XGBM)
Extreme Gradient Boosting Machine (XGBoost) stands out as a refined version of the gradient boosting algorithm, celebrated for its exceptional speed and effectiveness. Crafted to enhance the gradient boosting process, XGBoost incorporates features such as parallel computing, regularization, and tree pruning, all aimed at boosting accuracy and efficiency.
2.3.1.1.2. Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM)
The Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LGBM) mirrors XGBoost as a gradient boosting framework, esteemed for its speed, efficiency, and scalability. Particularly adept at managing large-scale datasets, LGBM has garnered widespread acclaim across diverse machine learning endeavors due to its stellar performance. Noteworthy for its swift training pace and efficacy, LGBM owes its attributes to its leaf-wise tree growth strategy and optimizations like Gradient-Based One-Side Sampling (GOSS) and Exclusive Feature Bundling (EFB). In contrast, XGBoost defaults to a depth-wise tree growth strategy, potentially leading to slower performance, especially with extensive datasets.
2.3.1.1.3. Adaptive Gradient Boosting Machine (AdaBoost)
AdaBoost, an abbreviation for Adaptive Boosting, stands as an ensemble learning technique crafting a robust classifier by amalgamating numerous weak classifiers. It operates by iteratively training a sequence of weak learners on weighted iterations of the training dataset. With each iteration, the algorithm prioritizes instances previously misclassified, thereby adaptively refining its strategy to enhance overall performance.
AdaBoost assigns a weight
to each weak learner
, where
represents the iteration number. The final prediction
is then obtained by summing the weighted predictions of all weak learners:
Here,
denotes the total number of weak learners. The sign function ensures that the final prediction is either +1 or -1, depending on the overall weighted sum of the weak learners' predictions.
2.3.1.2. Neural Networks (NNs)
Neural Networks (NNs) are versatile machine learning algorithms capable of handling a wide range of tasks, including regression and classification [
32]. These networks are composed of individual neurons that process input data through both linear and nonlinear transformations. Through iterative backpropagation, the outputs generated by these neurons are refined, with adjustments made to the weights and biases to optimize the model's performance.
2.3.1.2.1. Deep Neural Networks (DNN)
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are characterized by their layered architecture, featuring interconnected neurons. Typically, these networks comprise an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Neurons within the network process input data via weighted connections and activation functions to produce output. DNNs are widely utilized across various machine learning tasks, including classification, regression, and pattern recognition, owing to their ability to capture complex data relationships. The behavior of a node in a DNN is governed by the following general equation:
Where,
is the output of the
-th node in the layer,
is the activation function applied element-wise,
is the weight connecting the
-th input to the
-th node,
is the
-th input to the node,
is the
-th bias term for the node, and
is the number of inputs to the node.
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
To assess the performance of our machine learning models on new data, we implemented 11-fold cross-validation after randomizing our datasets. This method involves dividing the data into 11 subsets and conducting 11 rounds of training and validation, where each subset serves as the validation set once while the rest act as the training set. The overall accuracy of our models is then determined by averaging the accuracies obtained across all eleven iterations.
Our dataset focuses on a classification task aimed at identifying DDI’s types in multidrug impact. We employed various evaluation metrics, including accuracy, precision (micro, macro, and weighted), recall (micro, macro, and weighted), and F1 score (micro, macro, and weighted). These metrics offer comprehensive insights into the model's performance, considering factors such as class imbalance and overall effectiveness across all classes. Additionally, to visualize the learning progress of our models, we utilize learning curves. These curves depict how specific metrics, such as accuracy or loss, change throughout the model training process, providing insights into the model's performance over successive iterations.
3. Results and Discussion
In our classification task, the use of machine learning (ML) is crucial for predicting outcomes in large datasets efficiently, yielding precise results in less time and without the expenses associated with clinical investigations. To focus our classification efforts, we initially select the five most important classes of Drug-Drug Interactions (DDIs). These classes are pivotal in DDI research, and handling the high-volume datasets requires robust CPU or GPU systems.
The first dataset comprises Drug I, including ‘Fluvoxamine’, ‘Venlafaxine’, ‘Phenytoin’, ‘Ziprasidone’, ‘Cyclosporine’, ‘Pentobarbital’, ‘Bortezomib’, ‘Citalopram’, ‘Ticlopidine’, ‘Isradipine’, ‘Diltiazem’, ‘Sildenafil’, ‘Ranolazine’, ‘Clozapine’, ‘Indinavir’. The second dataset, Drug II, consists of ‘Curcumin’, ‘Pitolisant’, ‘Rucaparib’, ‘Stiripentol’, ‘Apalutamide’, ‘Vemurafenib’, ‘Lumacaftor’, ‘Ceritinib’, ‘Isavuconazole’, ‘Acetyl sulfisoxazole’, ‘Dabrafenib’, ‘Cobicistat’, ‘Asenapine’, ‘Lorpiprazole’, ‘Fosphenytoin’. These fifteen classes encompass ‘risk or severity of adverse effects’, ‘metabolism’, ‘serum concentration’, ‘therapeutic efficacy’, ‘hypotensive activities’, ‘QTc-prolonging activities’, ‘antihypertensive activities’, ‘central nervous system depressant (CNS depressant) activities’, ‘anticoagulant activities’, ‘vasoconstricting activities’, ‘hypoglycemic activities’, ‘risk or severity of hypotension’, ‘sedative activities’, ‘hypokalemic activities’, ‘absorption’. We utilize DNN, XGBoost, LGBM, and AdaBoost models to investigate and classify these classes, as depicted in
Figure 1.
In our study, datasets were gathered from diverse sources, prioritizing specific features and parameters deemed crucial for our investigation. These datasets were consolidated into five columns, each representing an identifier associated with a set of DDI-related attributes, such as side effects and drug types, along with the types of DDIs. In our SQL database, sourcing datasets based on meaningful correlations and relevant features proved challenging. Despite efforts to collect data from reliable sources and recent studies, the complexity of feature correlations posed a significant obstacle. This complexity extends to machine learning models, making it challenging to optimize weights and biases for each node or branch in tree-based models.
Navigating the challenges of overfitting and underfitting adds complexity to our analysis. To mitigate these issues and ensure the reliability of our results, we employ various techniques such as comparing training-validation datasets, testing metrics like confusion matrices, and analyzing learning curves. These approaches offer insights into the efficiency of our model across a logical range of overfitting scenarios.
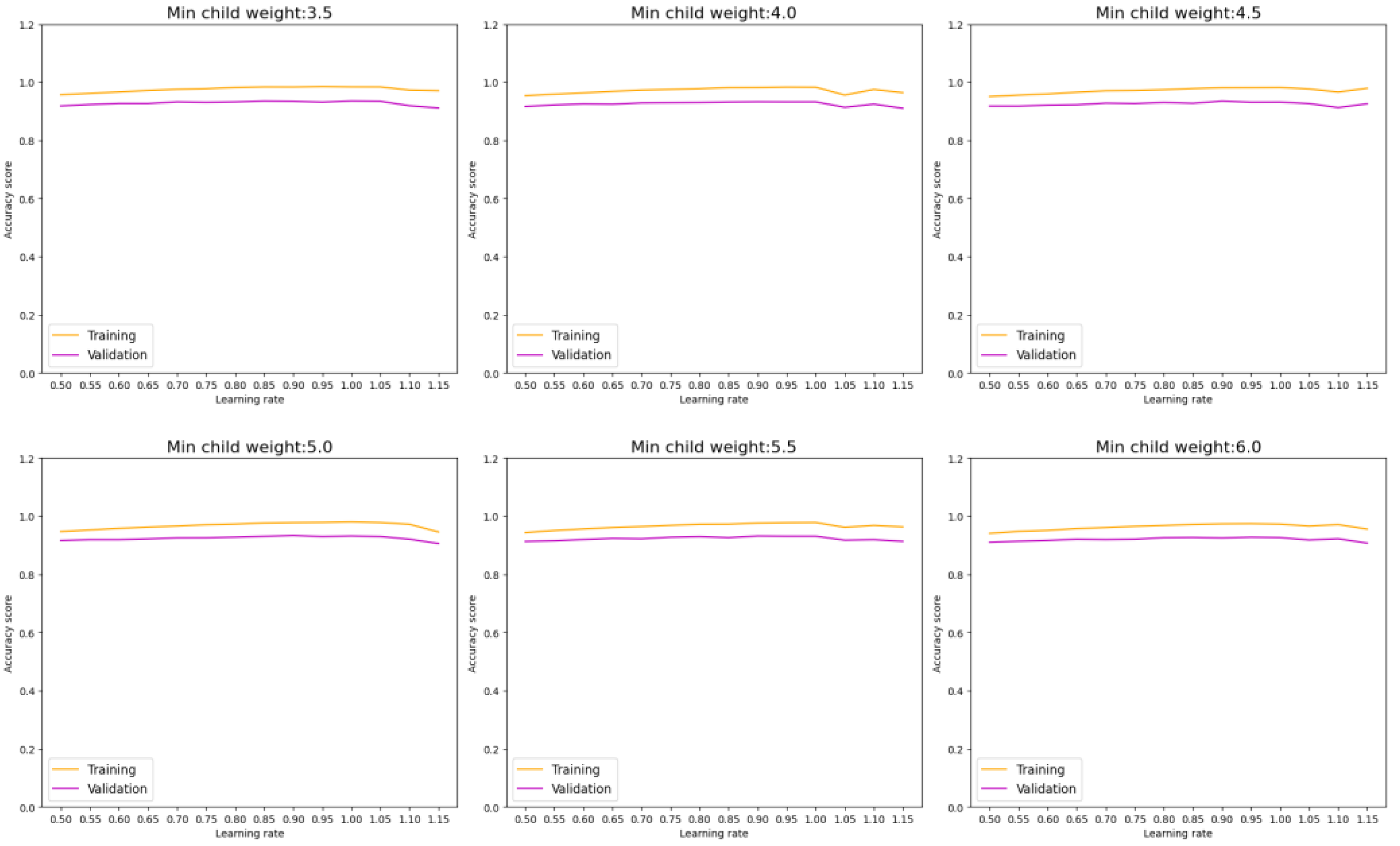
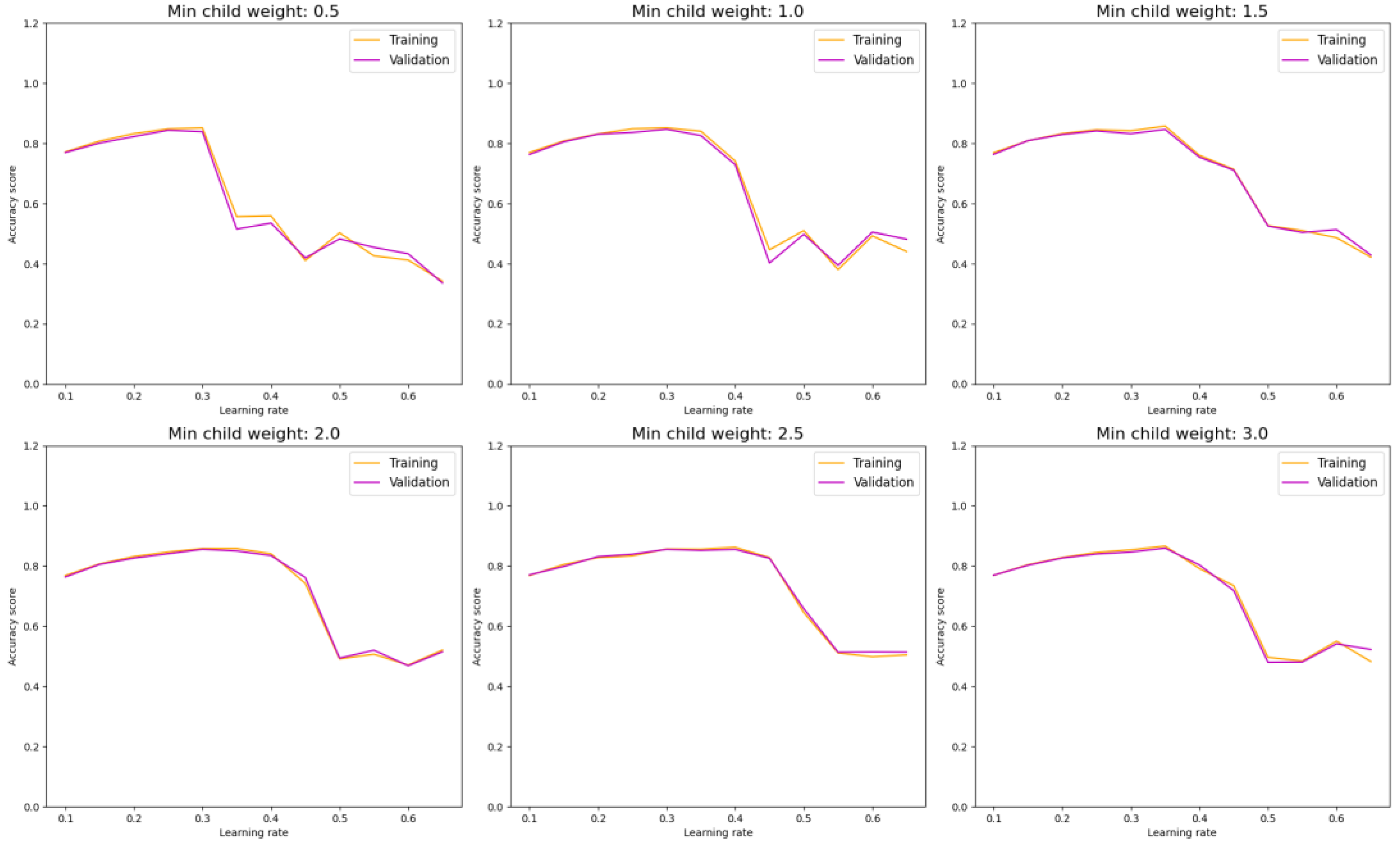
In scrutinizing the performance of our model in classifying DDI types, we begin with an assessment of the XGBoost model. By exploring different combinations of hyperparameters such as learning rate and min child weight, we can monitor both model performance and overfitting tendencies.
Figure 7 illustrates that a higher min child weight beyond 6 does not significantly enhance accuracy. Additionally, a learning rate within the range of 0.95 demonstrates optimal performance for the XGBoost model.
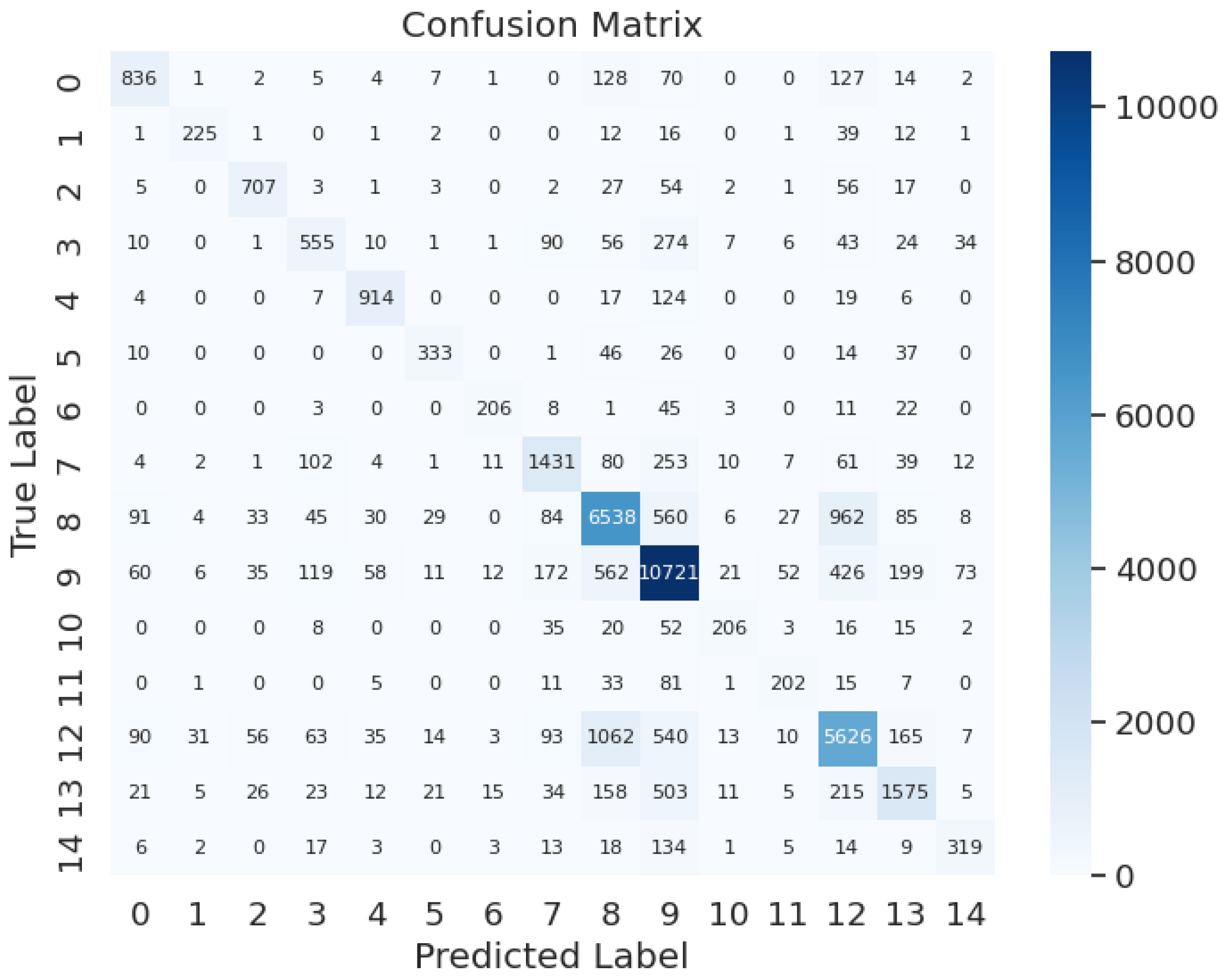
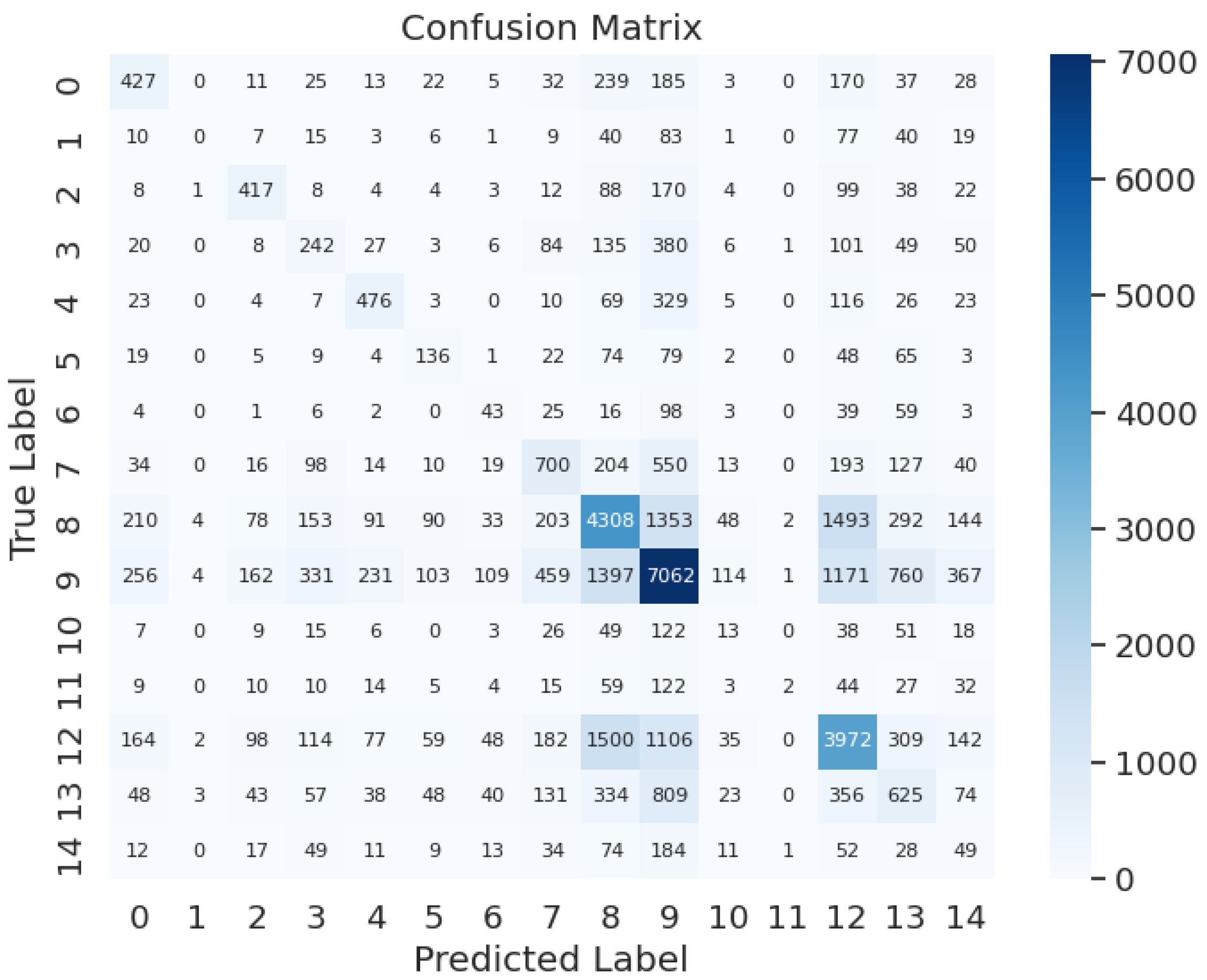
The evaluation process continues with testing and assessing each group of labels using confusion matrices. Labeling risk or severity of adverse effects as label 0, metabolism as label 1, serum concentration as label 2, therapeutic efficacy as label 3, hypotensive activities as label 4, QTc-prolonging activities as label 5, antihypertensive activities as label 6, central nervous system depressant (CNS depressant) activities as label 7, anticoagulant activities as label 8, vasoconstricting activities as label 9, hypoglycemic activities as label 10, risk or severity of hypotension as label 11, sedative activities as label 12, hypokalemic activities as label 13, absorption as label 14, as depicted in
Figure 8, the model achieves an accuracy of 85.8%, precision of 98%, recall of 95%, and an F1-score of 96%. This demonstrates the model's high performance, effectively balancing overfitting concerns without encountering underfitting issues, essential for real-world DDI recognition testing.
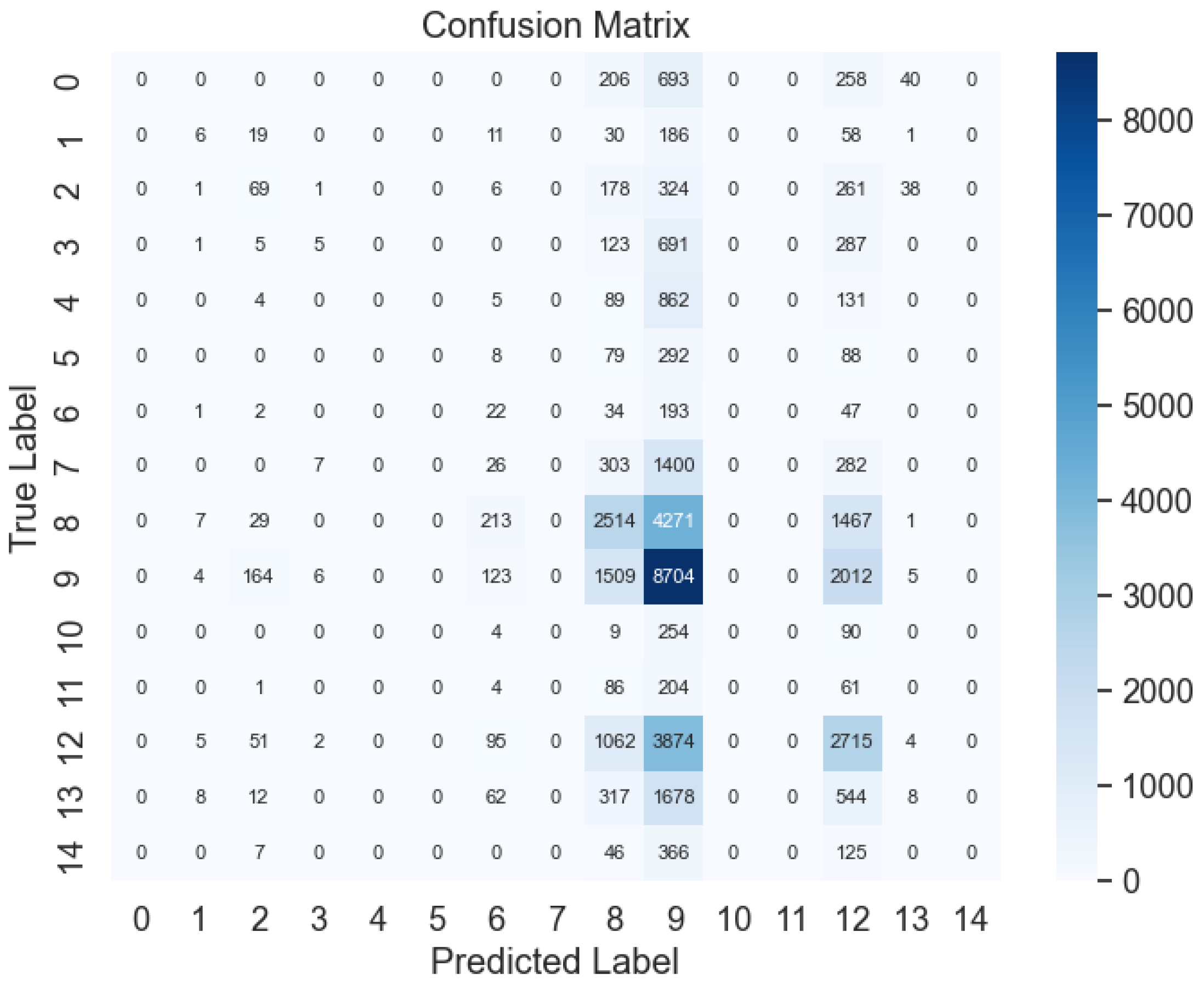
Figure 9 showcases the LGBM model's performance. Optimizing parameters such as a higher min child weight and learning rate efficiently enhances model accuracy, reducing the disparity between training and validation curves and indicating decreased overfitting. Test evaluations confirm the model's effectiveness, with metrics including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score all attaining 86%, as demonstrated in the confusion matrix in
Figure 10, for the situation when 0.3 as learning rate and min child weight as 2. It also shows that for a more than an optimum point forementioned, model performance adversely moved down. The key point for this monitoring procedure is to avoid overfitting as the gap between the training and validation is so neglectable.
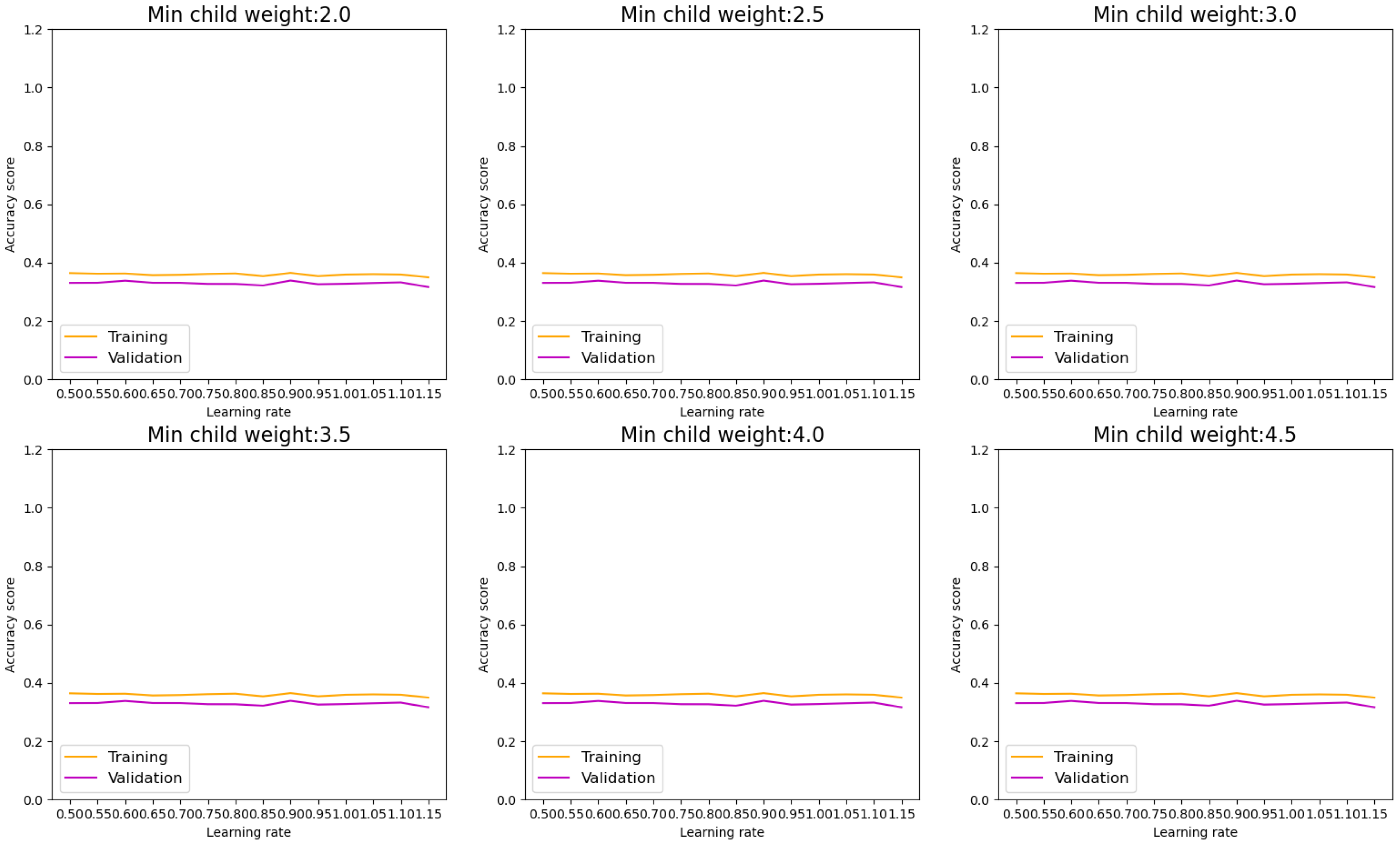
Advancing to the examination of AdaBoost in
Figure 11, alterations in parameters, such as elevating the min child weight and learning rate, do not notably augment model performance across all samples. Nevertheless, exceeding this threshold, additional increments in samples do not result in significant enhancements, indicating diminishing returns. The evaluation metrics, depicted in the confusion matrix in
Figure 12, validate the model's adeptness in classifying DDI types, with notable test evaluations affirming its effectiveness. Metrics encompassing accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score all reach 46%.
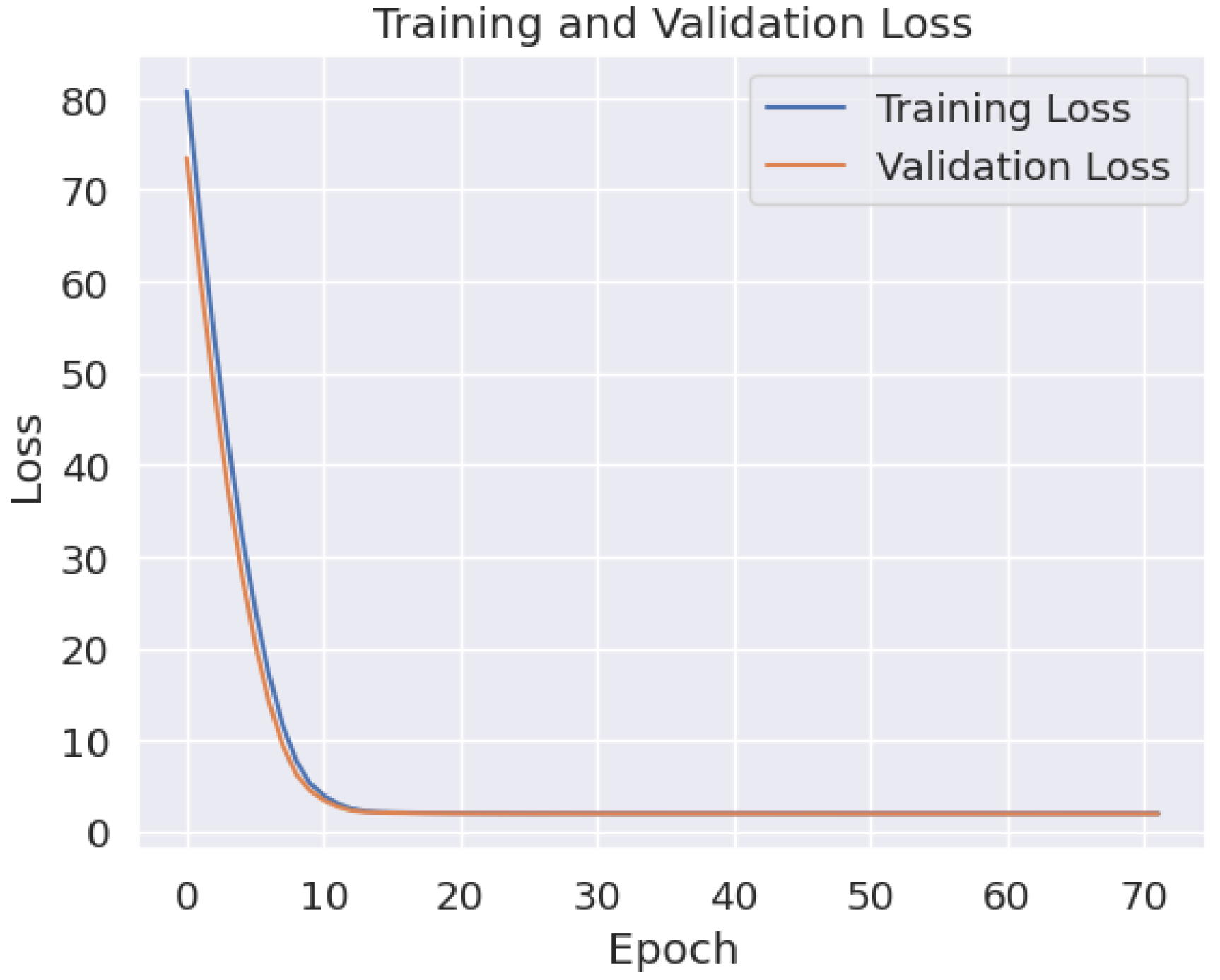
Considering the complex features inherent in DDI classification, deep neural networks (DNNs) offer efficient solutions and can effectively address overfitting concerns. In our algorithm, incorporating four hidden layers, regularization (l1 and l2) for monitoring overfitting, and dropout mechanisms, along with batch normalization to handle batch size during model fitting, yield promising results.
Figure 13 depicts the training and validation plot, indicating robust performance with minimal overfitting, evidenced by a logical gap between the two curves and their consistent movement within well-defined performance categories. The confusion matrix results in
Figure 14 further validate this performance, with accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score metrics all registering at 94.6%.
This study highlights the efficacy of DNNs in handling intricate datasets and correlations, surpassing traditional ML models. It paves the way for deeper exploration into DDI recognition, with the goal of minimizing testing expenses while improving precision. For additional insights into the performance of ML models,
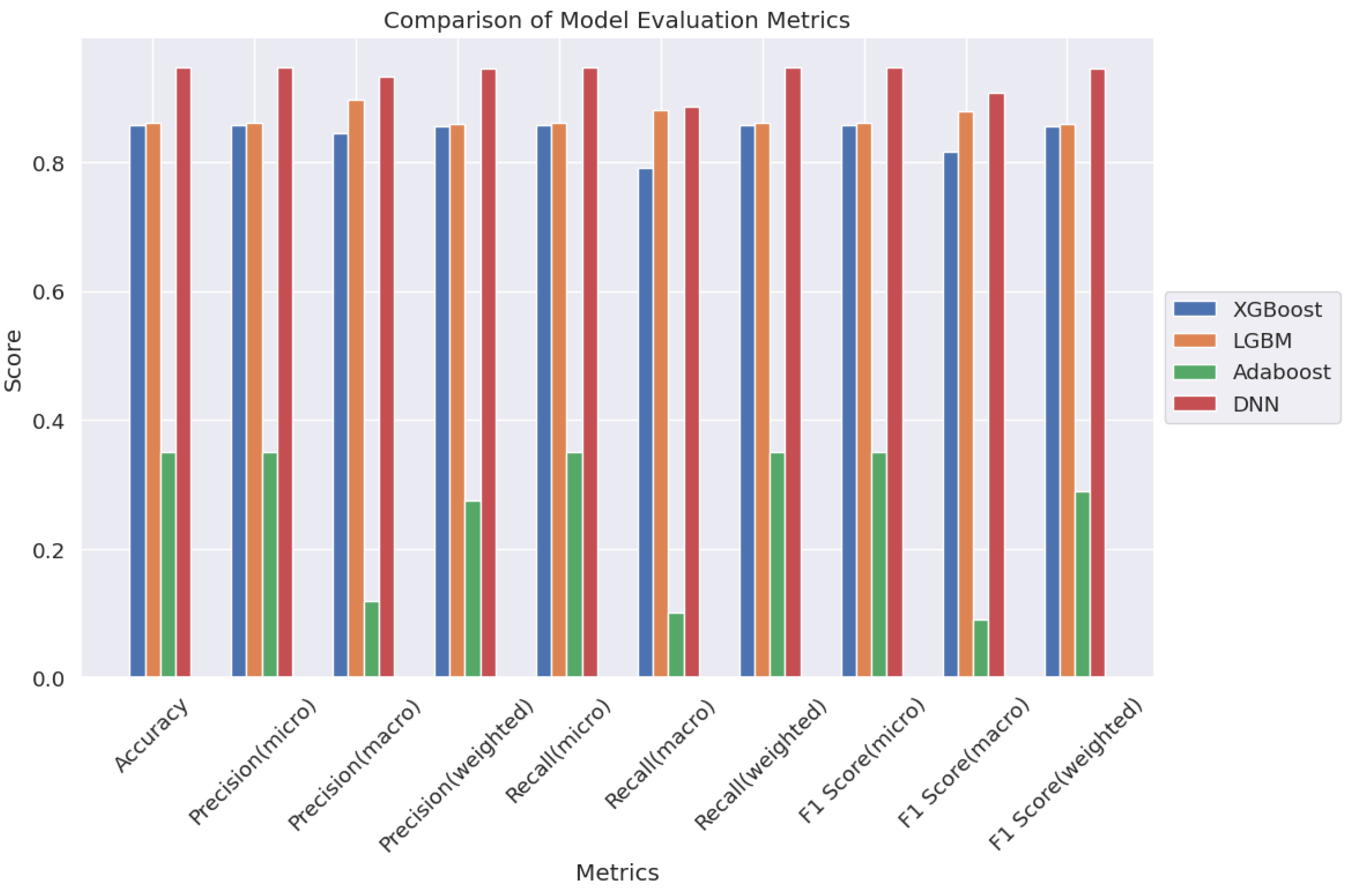
Figure 15 presents a comparative plot of all models utilized for DDI type classification.
4. Conclusions
We propose a novel approach for predicting multi-type drug-drug interactions (DDIs) using supervised contrastive learning and three-level loss functions. Through rigorous validation, we demonstrate the effectiveness of these techniques and their superiority over existing methods. Case studies further validate our model's ability to identify previously unknown DDIs, highlighting its practical significance in drug discovery and healthcare.
The prediction of DDIs holds significant implications for drug discovery, offering insights into risk reduction and interaction mechanisms. By integrating diverse drug data and harnessing multi-source information for prediction, our model surpasses current methodologies in terms of performance. Statistical analysis underscores the substantial performance enhancements achieved by our approach, indicating its potential for DDI prediction.
Key findings from our investigation include:
Deep neural networks (DNNs) outperform traditional machine learning (ML) models, exhibiting consistently higher accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score metrics (94.6%) compared to XGBoost, LGBM, and AdaBoost models. This underscores the pivotal role of ML, particularly DNNs, in DDI classification tasks.
Optimization of ML, particularly DNN, results in highly precise predictions, with correlation metrics exceeding 50% and remaining below 40%, a level of precision not attained by other ML models. This method had an important effect on improvement of the model performance.
To address overfitting concerns, we employ various techniques such as learning curves, confusion matrices, and training-validation plots, alongside k-fold cross-validation (k=11), ensuring robust model performance across different datasets.
Extensive dataset collection, comprising over 5 million entries for each drug type and DDI type, facilitates comprehensive testing and validation, enabling thorough monitoring of overfitting and underfitting issues.
Comparative analysis of ML models, including tree-based models and DNNs, offers valuable insights into the impact of multidrug side effects, highlighting the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of ML in DDI analysis.
Monitoring ML model performance with two hyperparameters as learning rate and min child weight made an easier way to tune parameters for a higher performance and lower overfitting.
In conclusion, our study underscores the promise of advanced ML techniques, particularly DNNs, in enhancing DDI prediction accuracy and efficiency. By leveraging diverse data sources and innovative modeling approaches, we contribute to the advancement of DDI research and drug discovery processes.