1. Introduction
The transition towards Renewable Energy Sources (RES) is crucial for addressing climate change and achieving zero carbon emissions. Among renewable technologies, photovoltaic (PV) systems have emerged as a leading solution due to their ability to convert solar energy into electricity [
1]. PV power generation is associated with emissions solely during the production of its components. Once installed, PV panels harness solar irradiation to generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases. Over their estimated lifespan of 25 years, PV panels are designed to yield more energy than consumed during their production [
2]. In 2022, the PV industry celebrated a significant milestone, surpassing a total global capacity of 1 terawatt (TW), reaching 1,183 gigawatts (GWs) of PV installations. Over half of this capacity was added in the last four years alone. The year 2022 also saw a record-setting annual growth, with 236 GW of new PV capacity installed worldwide, a 35% increase from the previous years [
3].
Three primary factors influence the performance of a PV plant: the efficiency of the PV panels, the conversion efficiency of the converters, and the effectiveness of the Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithm. Enhancing the efficiency of the PV panels and the converter is a complex task that relies on the current state of technology and may necessitate the use of superior components, potentially elevating the system cost significantly. However, optimizing the MPPT by implementing new control algorithms is a more feasible approach. This improvement is cost-effective and can be readily applied to existing plants through a control algorithm update, promptly boosting the efficiency of PV power generation and reducing costs. However, the efficiency of MPPT algorithms is significantly affected by Partial Shading Conditions (PSCs), which can occur due to clouds, dust, snow, nearby buildings, trees, the aging effect of the panels [
4], and other obstructions. This creates non-uniform irradiance on the PV panels, leading to multiple Local Maximum Power Points (LMPPs) on the Power-Voltage (P-V) curve, posing a challenge for MPPT techniques in finding the Global Maximum Power Point (GMPP). Traditional techniques like Perturb & Observe (P&O) and Incremental Conductance (IC) have been foundational in the development of MPPT methodologies. However, their performance under PSC is often limited by the inability to consistently identify the GMPP, leading to suboptimal power extraction from PV arrays [
5,
6]. Recent advancements in MPPT technologies have introduced several algorithms to address the complexities introduced by PSCs, including Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC) [
7,
8], Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) [
9,
10], Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) [
11,
12,
13], and Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) [
14,
15,
16,
17]. While the discussed MPPT algorithms are well-documented in the literature, there is a noticeable lack of diversity in ANN approaches, with many studies following similar methodologies or hybrids. This research investigates a novel ANN approach, aiming to find simpler and more effective ways to implement ANN MPPT algorithms that perform well under PSCs and can be utilized in real-world applications.
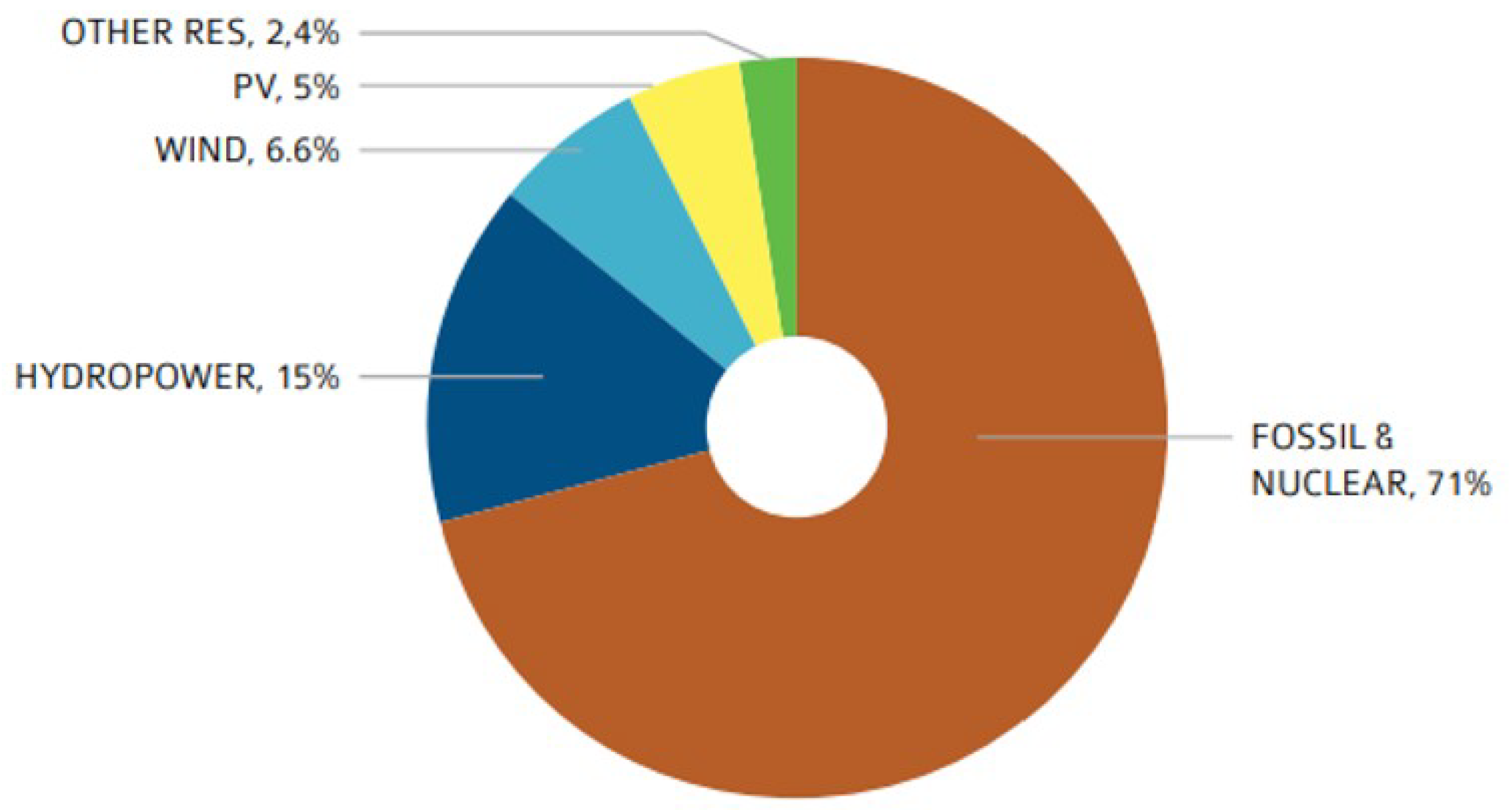
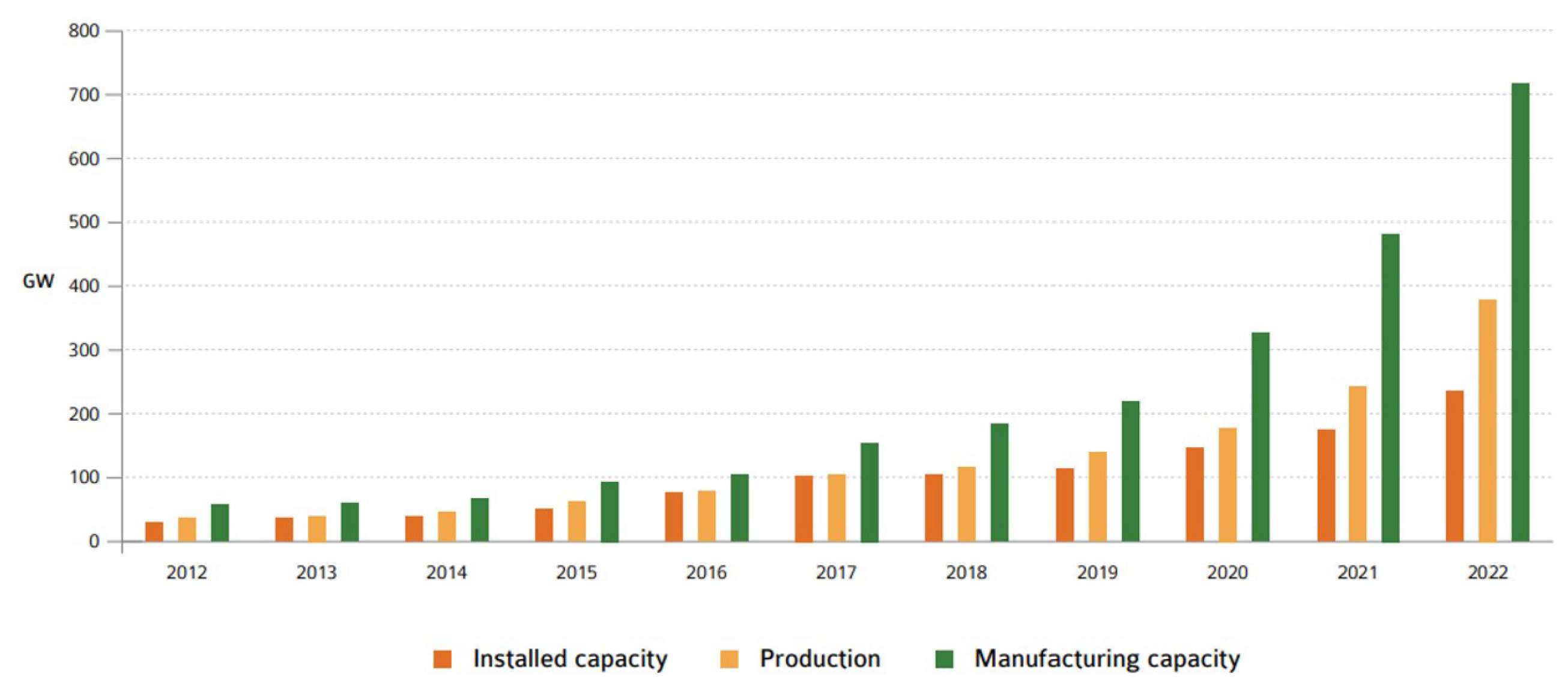
The motivation behind this research stems from the increasing prevalence of PV systems in the global energy mix as depicted in
Figure 1, with its growing trend shown in
Figure 2, and the need for more resilient and efficient MPPT strategies to cope with variable environmental conditions exacerbated by climate change. The exploration of ANNs in this context is not merely an academic pursuit but a step towards advancing a technology that stands at the forefront of innovation. By understanding and contrasting the capabilities and limitations of these MPPT algorithms, this research aims to contribute to the evolution of PV system efficiency and reliability, harnessing the allure of AI and ML to illuminate a path towards a sustainable future.
By exploring the strengths and weaknesses of each MPPT technique, this study seeks to contribute to the ongoing efforts to enhance the reliability and performance of PV systems, paving the way for broader adoption of solar energy as a cornerstone of sustainable development. As the field of PVs continues to evolve with the introduction of new materials (perovskite, thin-film [
3], GaAs [
18] and innovative applications (building-integrated PV, agrivoltaics and floating PV [
3]), the significance of effective MPPT techniques becomes even more pronounced. These developments not only offer the potential for higher efficiency solar cells but also expand the versatility of PV systems in various environmental conditions and architectural designs. Therefore, understanding the implications of partial shading and optimizing MPPT algorithms are crucial steps towards maximizing the potential of solar energy in the pursuit of a cleaner, more sustainable future.
This research significantly advances the body of knowledge in renewable energy technology with a focus on optimizing PV systems under PSCs. The study provides a comprehensive comparative analysis of six different MPPT techniques using the MATLAB/Simulink environment. Through detailed simulations of various partial shading scenarios, it elucidates the performance, efficiency, and reliability of both traditional and advanced MPPT methods, including P&O, IC, FLC, GWO, PSO, and ANN.
The structure of the paper is as follows:
Section 2 discusses the PV system modeling, detailing the equivalent circuit models and the impact of partial shading.
Section 3 describes the simulation models and scenarios developed for the study.
Section 4 provides an overview of the MPPT algorithms evaluated, including their operational principles and implementation.
Section 5 presents the results and discussion, focusing on the performance analysis of each MPPT algorithm under various conditions.
Section 6 concludes the study with a summary of findings and suggestions for future research.
4. MPPT Algorithms Development. Modelling Techniques and Performance
This section provides an overview of the MPPT algorithms evaluated in this study, including the traditional P&O and IC, as well as advanced algorithms such as FLC, GWO, PSO, and ANN.
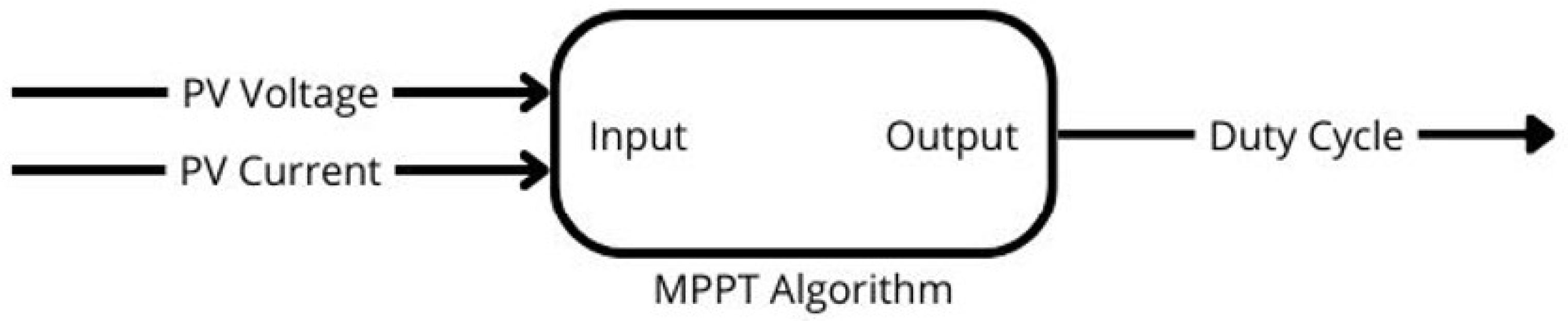
Figure 17 shows a block diagram of the inputs and outputs of the algorithms, which are implemented using MATLAB function blocks to operationalize their respective MPPT methods.
4.1. Perturb & Observe (P&O)
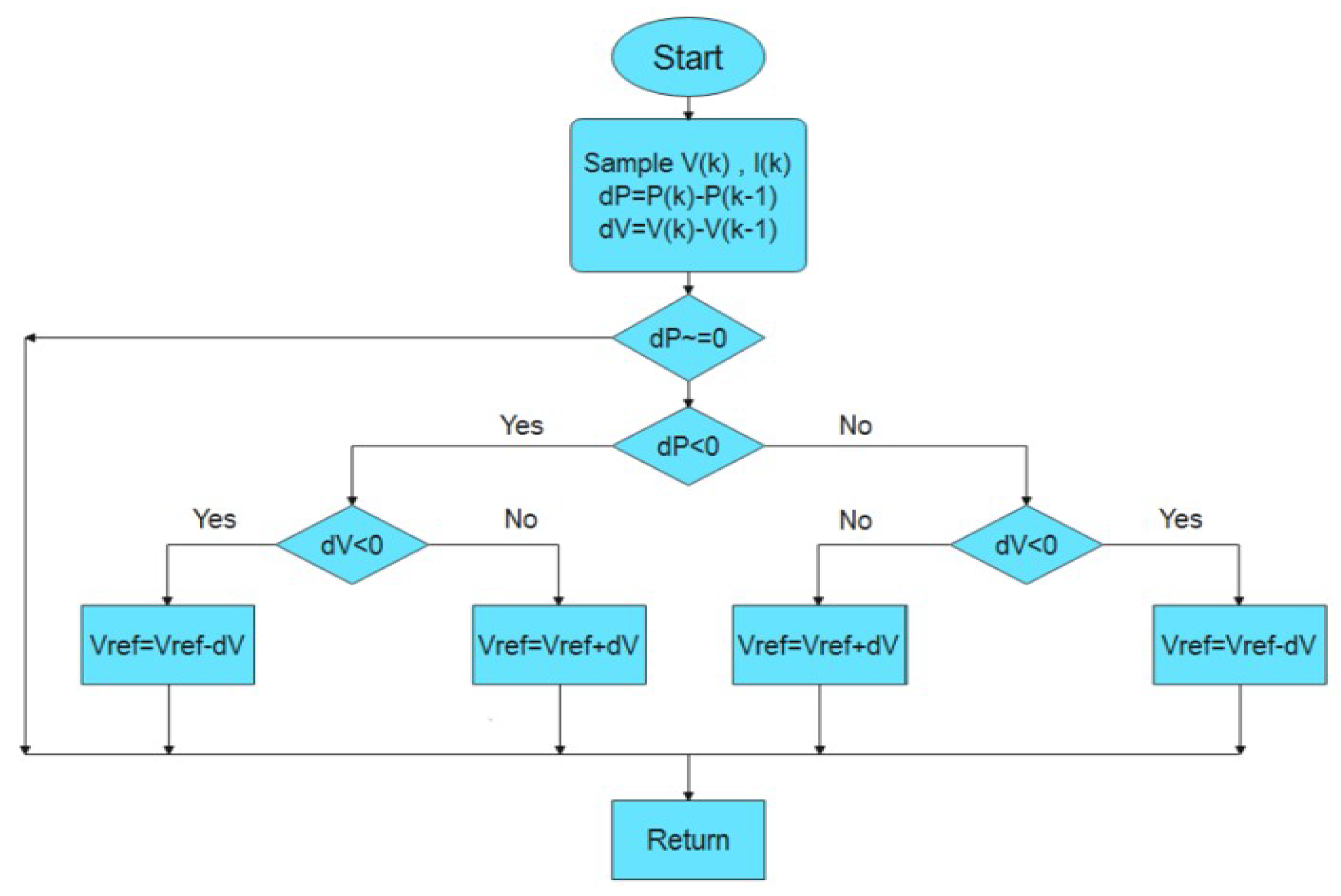
The P&O MPPT algorithm operates by periodically perturbing (adjusting) the operating voltage of the PVs and observing the resulting change in power output to track the MPP. The main principle behind the P&O algorithm is that, if an increase in the PV voltage leads to an increase in power, the operating point is moving towards the MPP. Conversely, if an increase in voltage leads to a decrease in power, the operating point is moving away from the MPP. The algorithm starts by measuring the current and voltage of the PVs to calculate the initial power. It then perturbs the voltage by a small increment and measures the new power output. By comparing the new power output with the previous power output, the algorithm determines the direction of the perturbation. If the new power is greater than the previous power, the perturbation continues in the same direction. If the new power is less than the previous power, the direction of the perturbation is reversed. This process is repeated continuously. The algorithm keeps adjusting the voltage in small steps and observing the changes in power output, thereby dynamically tracking the MPP. The perturbation can be either an increase or a decrease in voltage, and the size of the perturbation step can affect the algorithms responsiveness and stability. One of the main advantages of the P&O algorithm is its simplicity and ease of implementation. However, it can oscillate around the MPP under steady-state conditions and may struggle with rapid changes in environmental conditions. This is because the algorithm might continue perturbing even after reaching the MPP, causing the operating point to fluctuate around the optimal value. Despite these limitations, it is widely used due to its straightforward implementation and effectiveness in many scenarios.
The algorithm was implemented using a “MATLAB Function” block, with inputs and outputs as shown in
Figure 17. This block operationalized the P&O method through embedded MATLAB code, following the structure of the P&O algorithm illustrated in
Figure 18.
4.2. Incremental Conductance (IC)
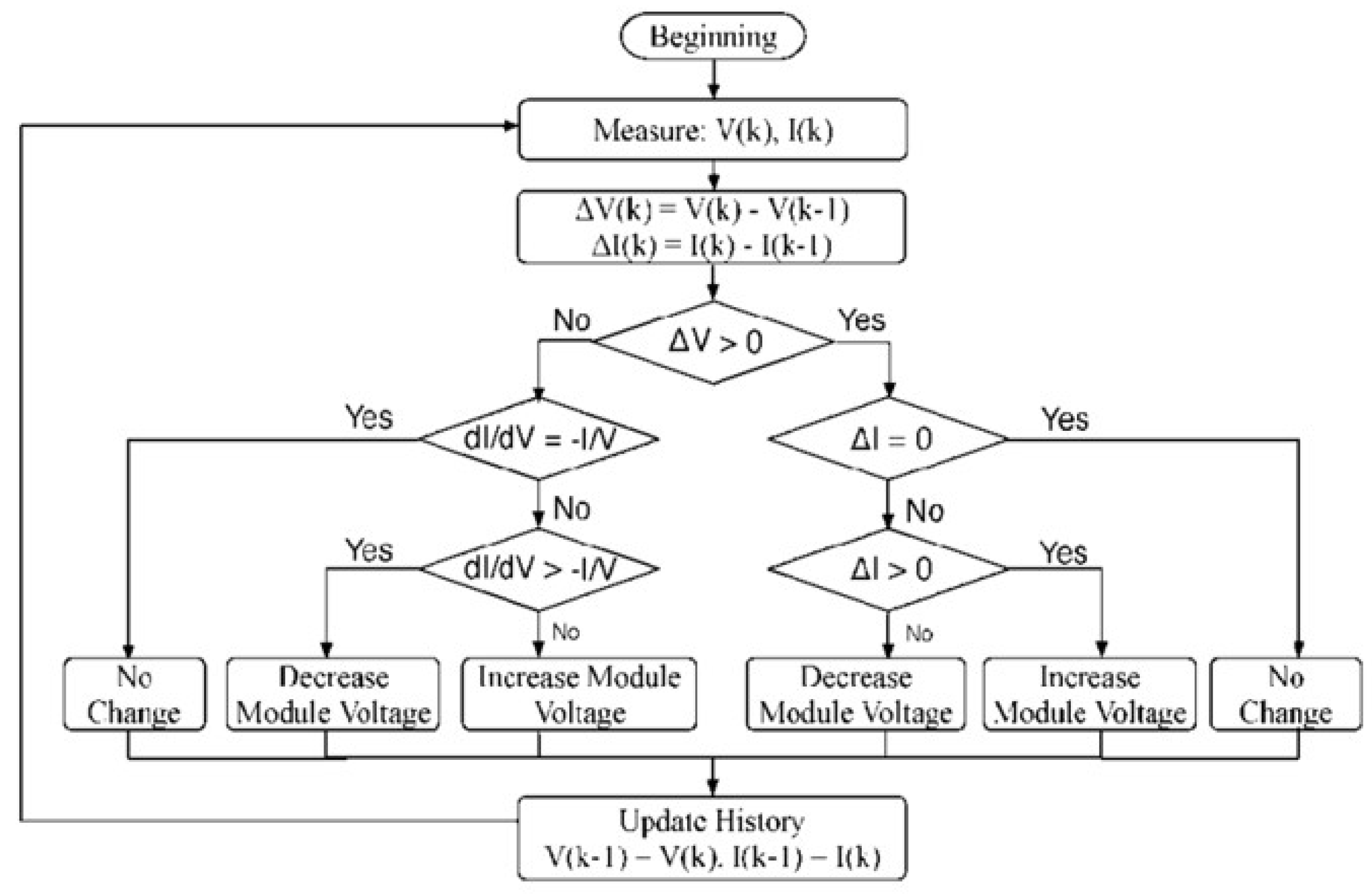
The core principle of the IC algorithm is based on the fact that the derivative of the power with respect to the voltage () is zero at the MPP, positive on the left of the MPP, and negative on the right. The algorithm uses this principle to track the MPP by measuring the instantaneous conductance () and the incremental conductance () of the PVs. The IC algorithm begins by measuring the PV’s current () and voltage (). It then calculates the incremental changes in current () and voltage () from their previous values. Using these measurements, the algorithm computes the instantaneous conductance () and the incremental conductance (). At each iteration, the algorithm evaluates the condition of the PVs to determine whether it is operating at, to the left of, or to the right of the MPP. If equals , the operating point is at the MPP, and no adjustment to the duty cycle is needed. If is greater than , the operating point is to the left of the MPP, indicating that the voltage should be increased to reach the MPP. Conversely, if is less than , the operating point is to the right of the MPP, indicating that the voltage should be decreased. Based on these evaluations, the algorithm adjusts the duty cycle of the boost converter accordingly. If the operating point is to the left of the MPP, the algorithm increases the duty cycle, which decreases the voltage and increases the current. If the operating point is to the right of the MPP, the algorithm decreases the duty cycle, which increases the voltage and decreases the current. The IC algorithm continues this process iteratively, constantly measuring the current and voltage, recalculating the conductance values, and adjusting the duty cycle to maintain operation at or near the MPP. This method allows the PV system to adapt dynamically to changes in environmental conditions, such as variations in irradiance and temperature, ensuring optimal power extraction from the PV array.
The algorithm was implemented using a "MATLAB Function" block, with inputs and outputs depicted in
Figure 17. This block operationalized the IC method through embedded MATLAB code, adhering to the structure of the IC algorithm illustrated in
Figure 19.
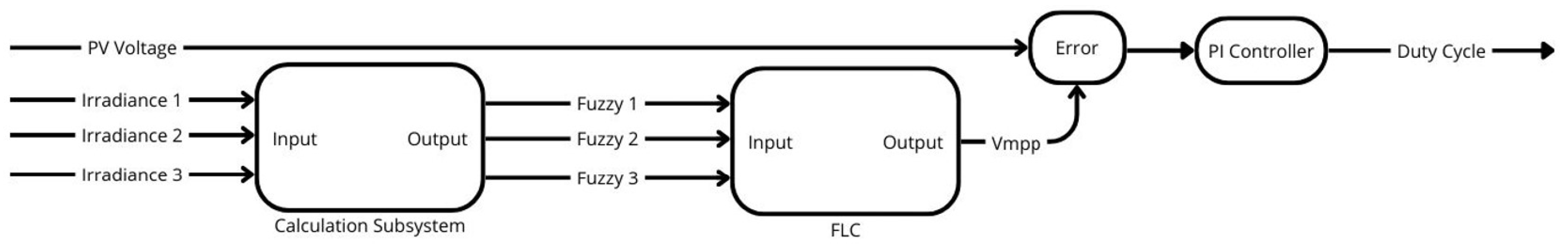
4.3. Fuzzy Logic Controller (FLC)
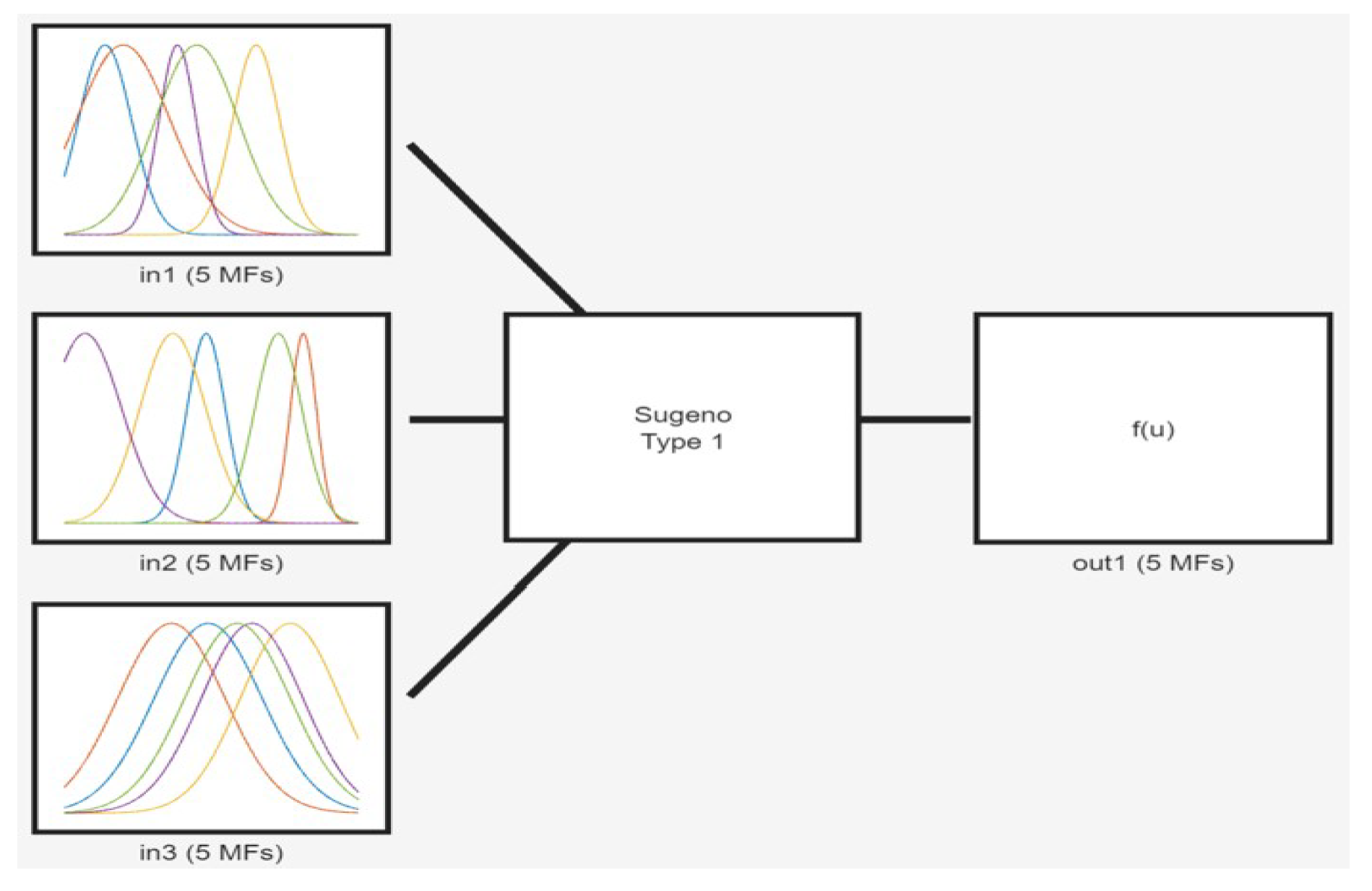
Figure 20 shows a block diagram of the FLC MPPT used in the simulation model. The core functionality of the model revolves around the FLC, which utilizes a Type-1 Sugeno Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) with Gaussian membership functions, adept at managing the non-linearity and uncertainty inherent in PV systems subject to PSC. The FLC operates by encoding expert knowledge into a set of "if-then" rules, where each input variable is associated with Gaussian functions characterized by their means and spreads. These functions are chosen for their smooth and continuous properties, which allow for effective handling of the gradual transitions in variable states. The (FIS) system is illustrated in
Figure 21.
In the simulation model, the solar irradiance values are processed through a calculation system. Here, they input irradiance values are normalized and scaled to generate a "FuzzyIn" signal. This signal feeds into the FLC, where it undergoes several processing stages: fuzzification, where the degree of truth for each input variable is determined against the Gaussian functions; rule-based inference, applying the "prod" and "probor" methods for conjunctions and disjunctions; and defuzzification, which integrates the outputs of all active rules through a weighted average method to produce a duty cycle value for the boost converter.
The fuzzy rules, specified in
Table 5, dictate the systems response to different scenarios, ensuring accurate tracking of the MPPT. Inputs are first fuzzified, then processed through the rule-based inference engine, with outputs aggregated and defuzzified to yield a precise duty cycle. This duty cycle subsequently drives the PWM signal controlling the MOSFET in the boost converter, effectively modulating the energy conversion to maintain optimal efficiency and align the PV output with the MPP.
4.4. Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO)
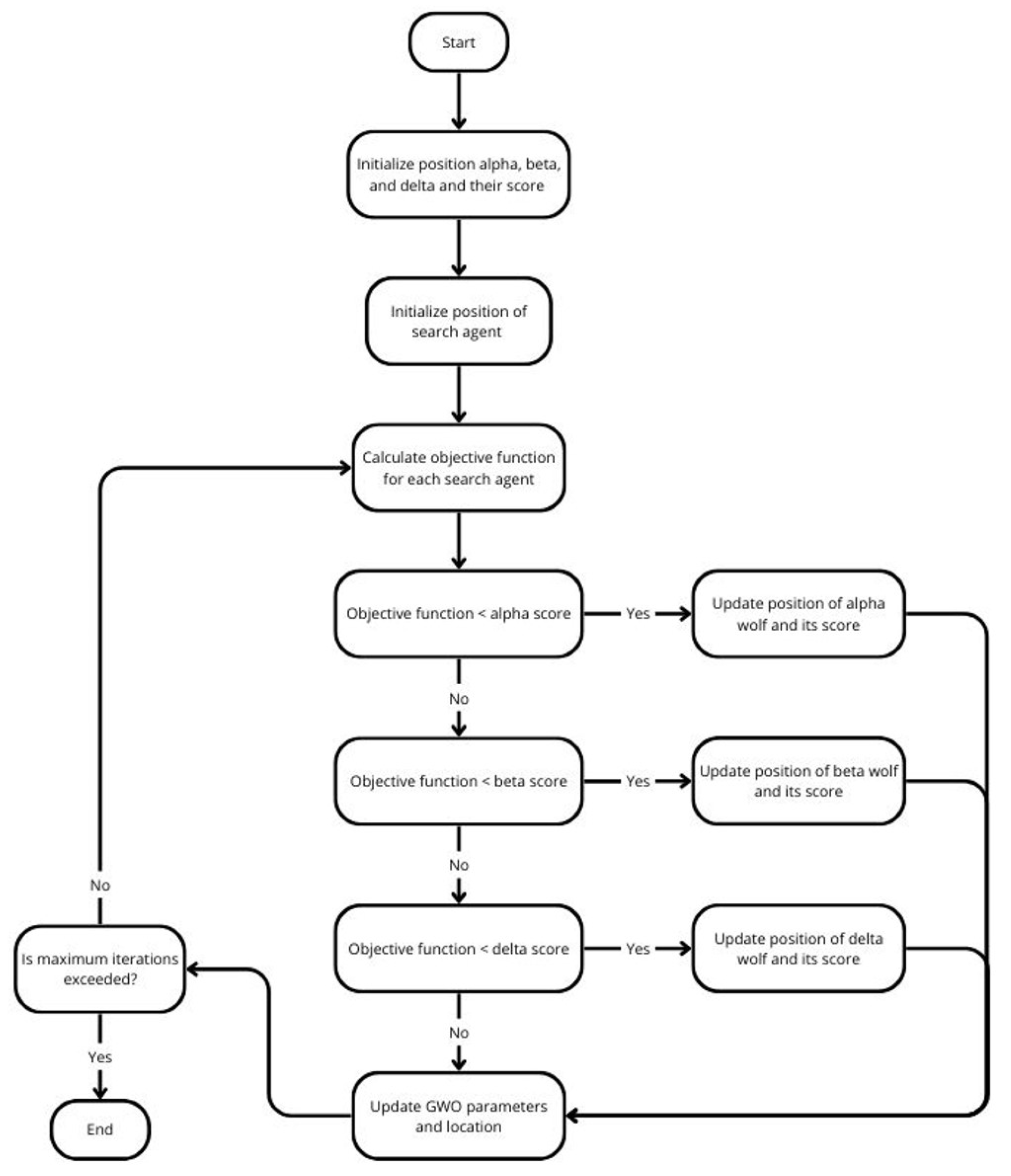
The GWO MPPT algorithm works by mimicking the social hierarchy and hunting behavior of grey wolves in nature to find the optimal duty cycle for a boost converter in the PV system. The goal of the algorithm is to maximize the power output from the PVs by continuously adjusting the duty cycle to operate at the MPP. The GWO algorithm starts by initializing a population of solutions, called grey wolves, which represent different possible duty cycle values. These wolves are divided into three categories: alpha, beta, and delta, corresponding to the best, second-best, and third-best solutions, respectively. The remaining wolves are considered omega and follow the top three wolves in the hierarchy. In each iteration of the algorithm, the positions of the wolves are updated based on the positions of the alpha, beta, and delta wolves. This process involves calculating the distances between each wolf and the alpha, beta, and delta wolves and then updating their positions using specific equations that simulate the encircling, hunting, and attacking strategies observed in grey wolves. The fitness of each wolf is evaluated based on the power output of the PV, which is calculated as the product of the PV voltage and current (). The algorithm compares the power output for each duty cycle value and updates the positions of the alpha, beta, and delta wolves if better solutions are found. This process of position updating and fitness evaluation continues iteratively until a stopping criterion is met, such as reaching a maximum number of iterations or achieving a convergence threshold. The position of the alpha wolf at the end of the iterations represents the optimal duty cycle for the boost converter. The optimal duty cycle is then sent to the PWM generator which adjusts the duty cycle of the boost converter accordingly. By doing so, the GWO MPPT algorithm ensures that the PV operates at or near its MPP, continuously adapting to changes in environmental conditions such as irradiance and temperature.
The GWO algorithm was implemented using a "MATLAB Function" block, as in
Figure 17. This block operationalized the method through embedded MATLAB code, following the structure illustrated in
Figure 22.
4.5. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
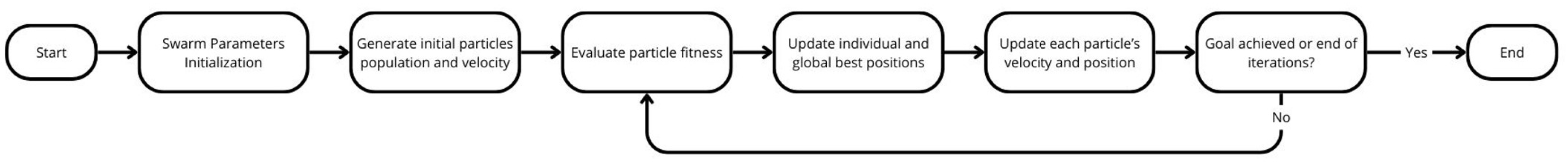
The PSO MPPT algorithm is a technique that mimics the social behavior of birds flocking or fish schooling to find the optimal solution in a search space. In the context of this PV system, the PSO algorithm aims to find the optimal duty cycle for the boost converter to ensure that the PVs operates at its MPP. The algorithm begins by initializing a swarm of particles, where each particle represents a potential solution, which in this case is a possible duty cycle for the boost converter. These particles are distributed randomly across the search space. Each particle has a position, which corresponds to a duty cycle value, and a velocity, which determines the direction and magnitude of the particles movement through the search space. At each iteration, the particles update their positions and velocities based on two primary factors: their personal best position and the global best position. The personal best position is the highest power output a particle has achieved so far, while the global best position is the highest power output achieved by any particle in the swarm. The particles adjust their velocities by considering their current velocity, the distance to their personal best position, and the distance to the global best position. The influence of these distances is moderated by random coefficients, which introduce a stochastic element to the algorithm, helping the particles explore the search space more thoroughly. Once the velocities are updated, the particles move to new positions in the search space. The power output at these new positions is evaluated by calculating the product of the PV voltage and current. If a particles new position yields a higher power output than its previous best position, the personal best is updated. Similarly, if any particle achieves a power output higher than the current global best, the global best is updated. This process of updating velocities, moving particles, and evaluating power outputs continues iteratively. Over time, the swarm of particles converges towards the optimal duty cycle that maximizes the power output of the PVs. The particle at the global best position represents the optimal duty cycle, which is then used to control the boost converter. The PSO algorithm is particularly effective because it combines exploration and exploitation. The particles explore the search space to find the global optimum, and they exploit the best solutions found by guiding the swarm towards these solutions. This balance helps the PSO algorithm avoid local maxima and ensures that it finds the true MPP.
The PSO algorithm was implemented using a "MATLAB Function" block, with inputs and outputs as shown in
Figure 17. This block utilized embedded MATLAB code to operationalize the PSO method, adhering to the structure illustrated in
Figure 23.
4.6. Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs)
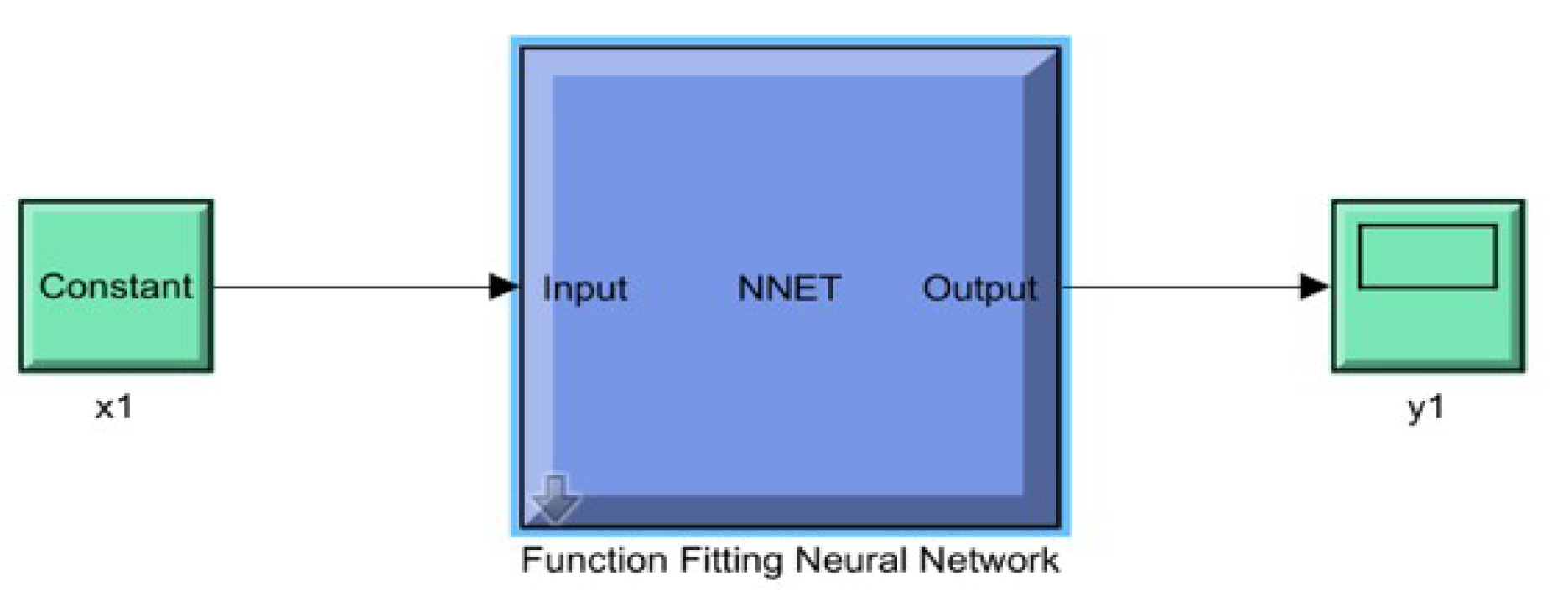
Two ANN MPPT’s were developed, each with a different approach. After the successful training of each ANN, the optimized model was exported into the Simulink environment as depicted in
Figure 24. This was accomplished by creating a dedicated Simulink block that encapsulates the functionality of the ANN. Named the “Function Fitting Neural Network”, this block clearly delineates inputs and outputs, providing a streamlined interface for simulation tasks.
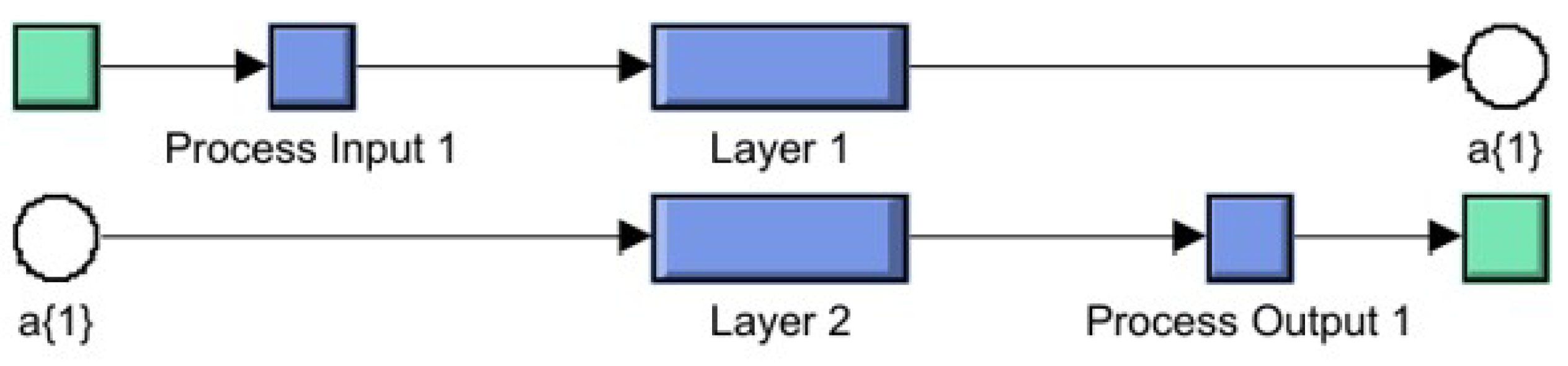
Delving deeper into the structure of this ANN block,
Figure 25 outlines the sequential arrangement of its processing elements. The “Process Input 1” block first conditions the input data, preparing it for processing through the neural layers. The data then passes through “Layer 1”, which consists of neurons equipped with sigmoid activation functions to introduce necessary non-linearity for effective pattern recognition. Following this, “Layer 2” acts as the output layer, applying a linear transformation to produce the final predictions.
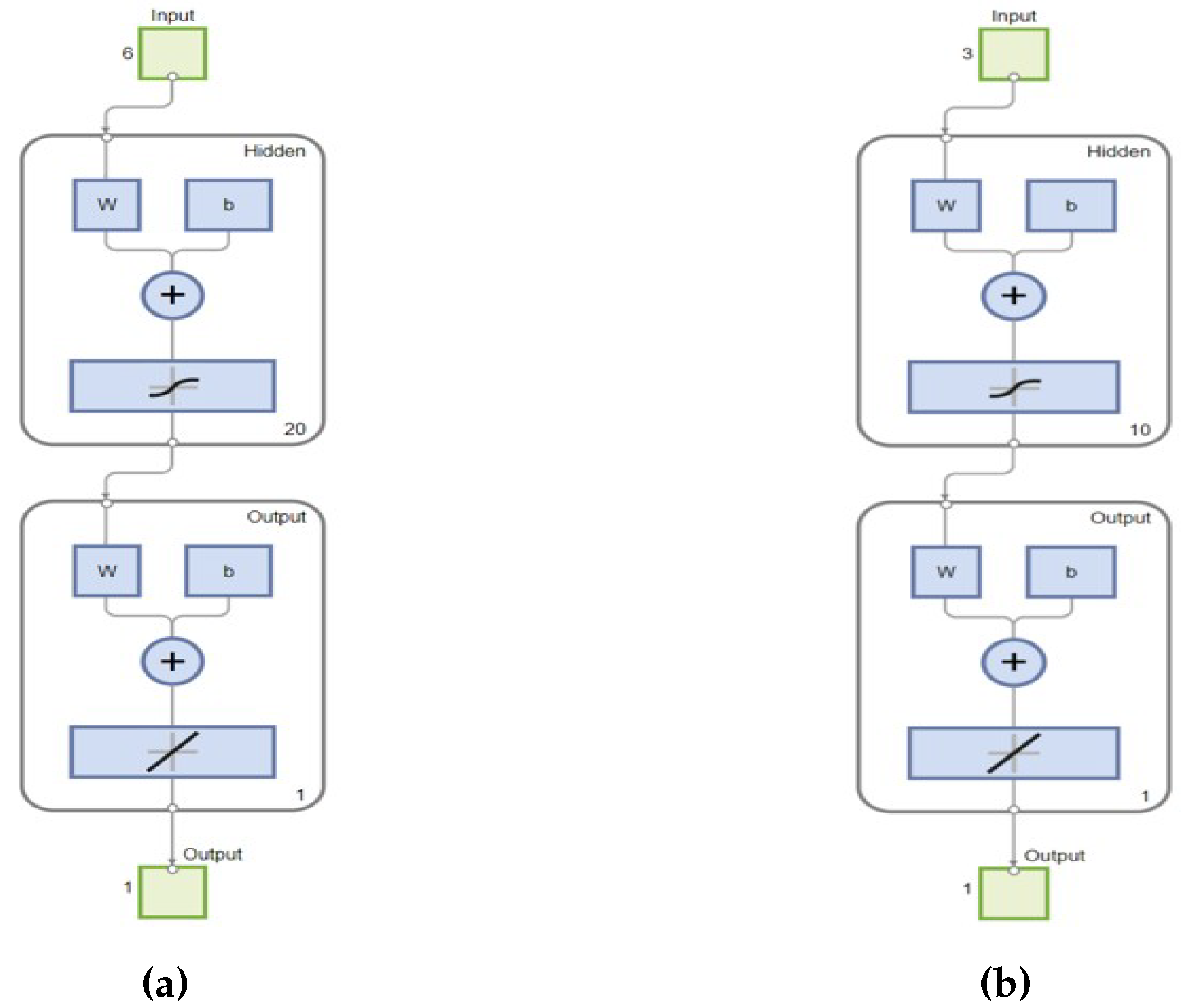
Figure 26 shows the structures of ANN(1)
(a) and ANN(2)
(b), both employing a two-layer feedforward network with sigmoidal activation functions in the hidden layers and a linear function in the output neuron, suitable for regression tasks. The ANN development, training, validation, and testing processes were conducted using MATLAB’s Deep Learning Toolbox, with the dataset split into 70% for training, 15% for validation, and 15% for testing, ensuring comprehensive evaluation of the models’ performance. Both networks were trained using the Levenberg-Marquardt backpropagation algorithm, known for its effectiveness in minimizing the Mean Squared Error (MSE) by precisely adjusting the weights (w) and biases (b) across the network, enhancing the models’ ability to predict continuous voltage values accurately.
ANN(1) features a twenty-neuron hidden layer, which allows the network to capture nonlinear relationships between the inputs and the output more effectively. ANN(2) on the other hand, processes three solar irradiance inputs through a ten-neuron hidden layer, each computing a weighted sum followed by a sigmoid activation function. The output layer consists of a single neuron for continuous voltage prediction.
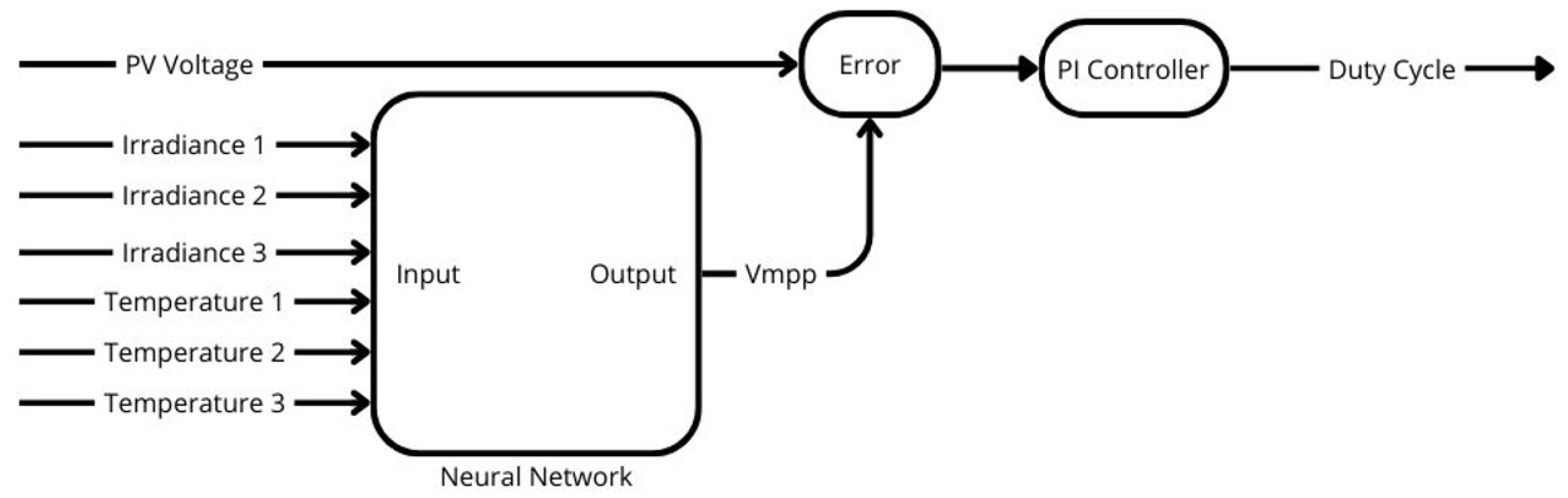
The ANN(1) model was designed to predict the maximum voltage output of the PV system. Using historical real-world data, the network is trained to estimate this maximum voltage based on the irradiance and temperature of each PV module. Consequently, the neural network has six inputs: the irradiance and temperature for each PV as shown in the block diagram depicted in
Figure 27
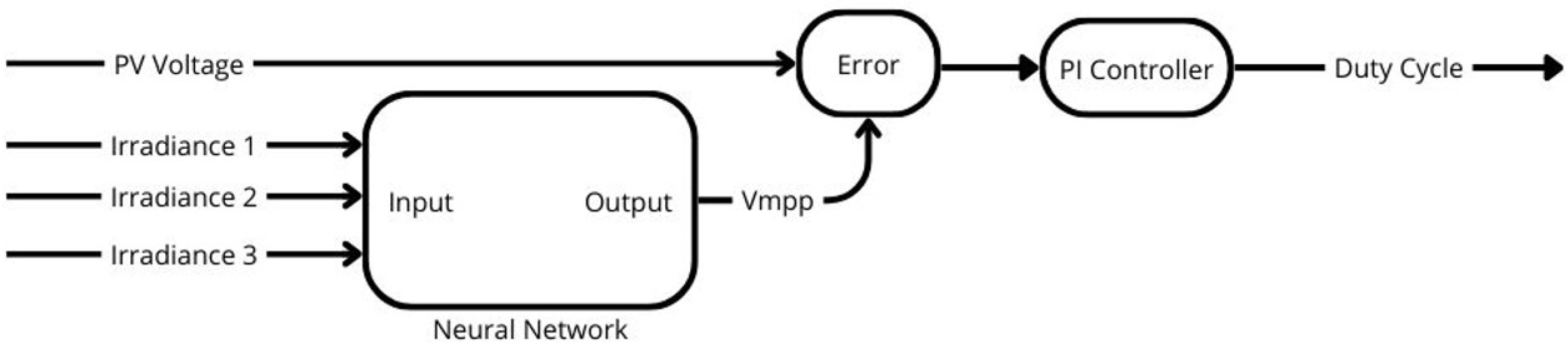
The ANN(2) MPPT model illustrated in
Figure 28 was designed to predict the maximum voltage output from the PV system based on variable solar irradiance inputs and was specifically trained for PSCs. In this ANN, the inputs are the irradiance values from each of the PVs, and the output is the maximum voltage level of the PV system. This approach is not commonly found in the literature and will be investigated in this study as an possibly simpler ANN algorithm than using real historical data for training.
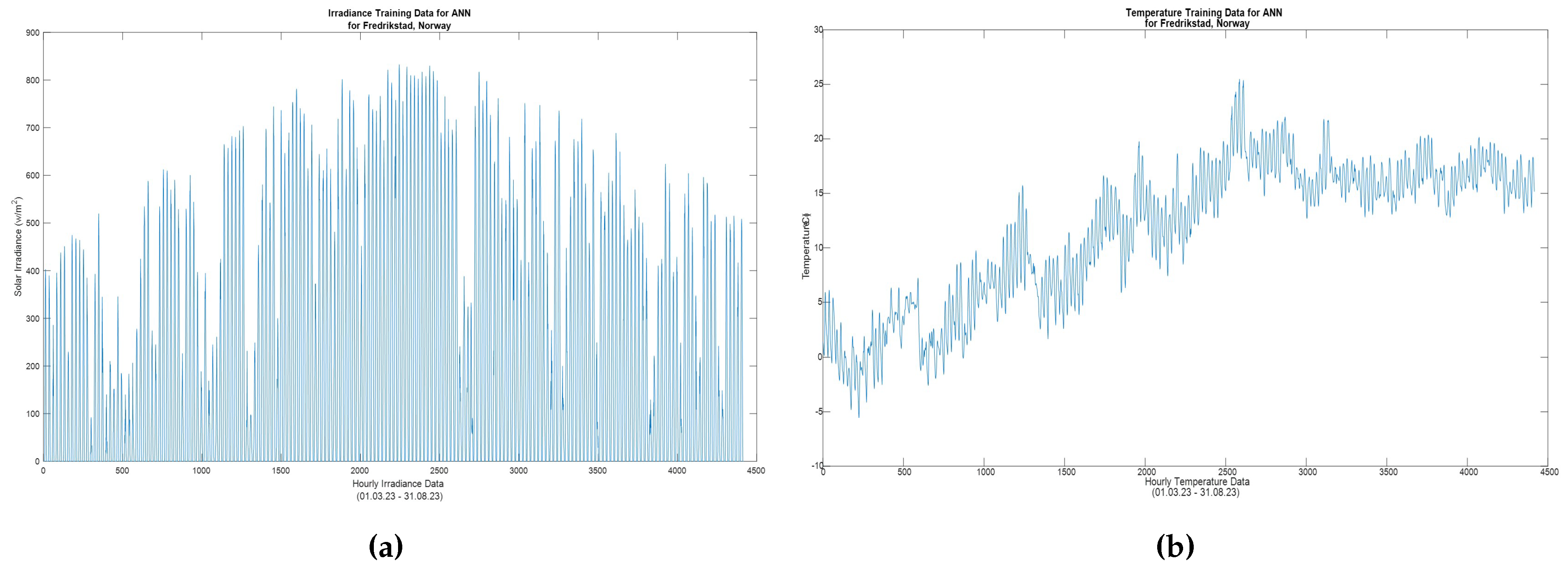
Figure 29 shows the real-world solar irradiance
(a) and temperature data
(b), (obtained from NASA Power [
22]) which were used for training the ANN(1) MPPT. This data is presumably structured in a way that each entry corresponds to hourly observations from Fredrikstad, Norway, covering the period from March to August 2023.
To create the dataset for training the ANN(2) to handle MPPT under PSCs, 1000 samples were generated, simulating various irradiance levels (0 to 1000 W/m
2) on three PV panels. The voltage at the maximum power point (V
mpp) was calculated for each set of irradiance values. The minimum irradiance value among the panels determined the overall performance, with V
mpp scaled proportionally. For instance, half sunlight (500 W/m
2) resulted in half of the maximum V
mpp (42.8 V). This method ensured the dataset accurately reflected varying conditions for effective MPPT management under PSCs. A snippet of the training data is shown in
Table 6.
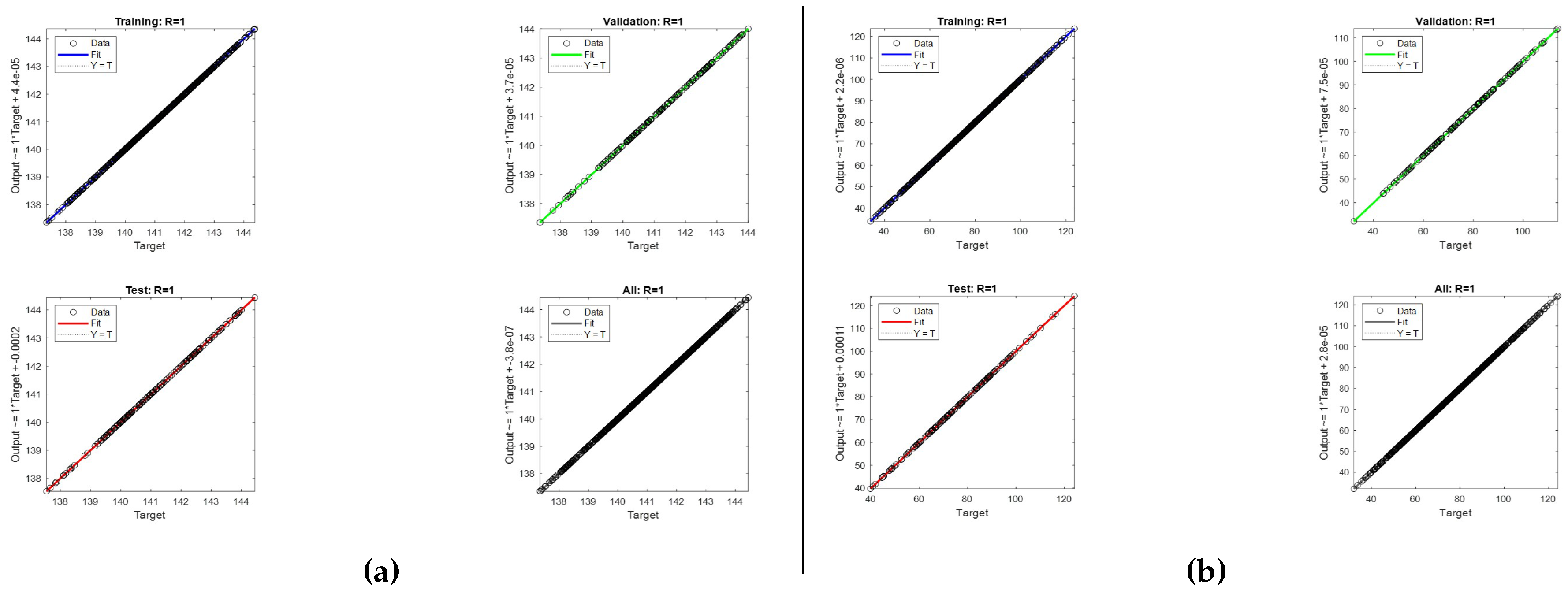
Figure 30 presents the regression plots for ANN(1)
(a) and ANN(2)
(b), demonstrating a strong fit between the models’ predictions and actual target values for both ANNs. In both cases, the training dataset (top left) aligns closely with the Y = T line, indicating excellent model fit and no significant bias. The validation dataset (top right) also aligns well with the Y = T line, suggesting good generalization capabilities. For the test datasets (bottom left), both ANN(1) and ANN(2) show slight deviations at the higher end but maintain a strong correlation overall. The combined performance plots (bottom right) for both ANNs confirm their robustness and high accuracy across training, validation, and test datasets, indicating their reliable predictive performance under various conditions.
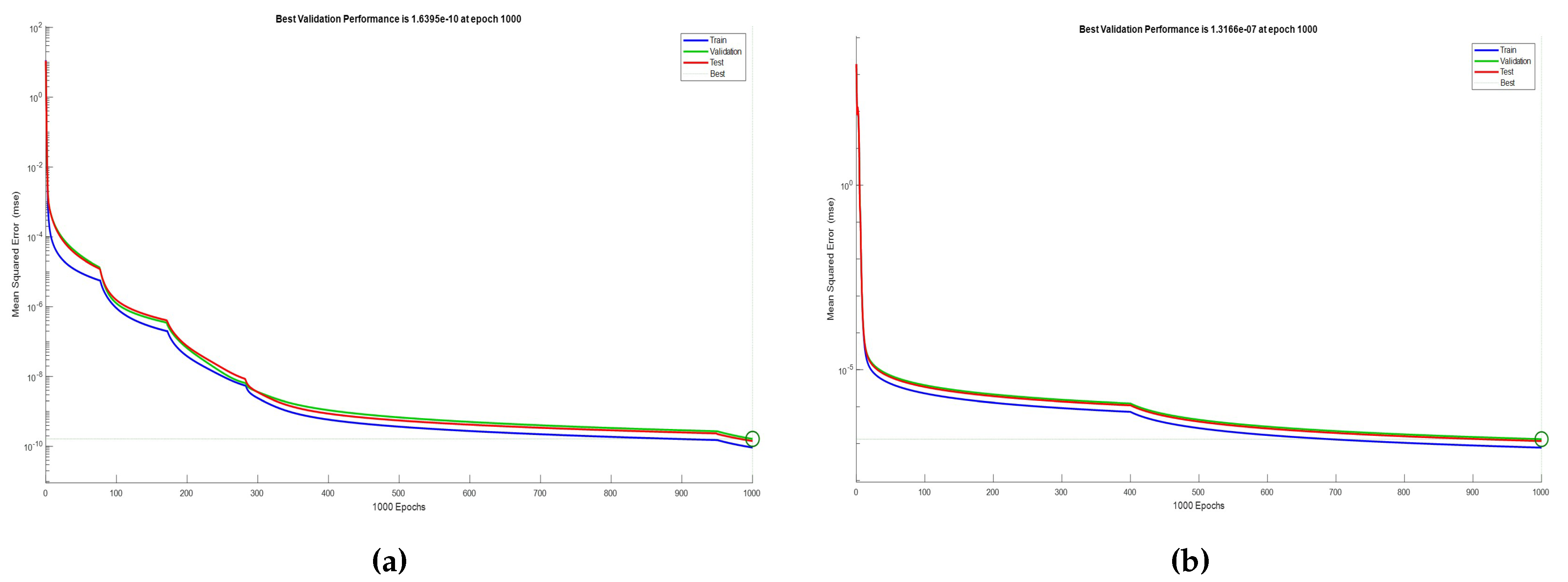
Figure 31 shows the performance plots for ANN(1)
(a) and ANN(2)
(b) during training, with MSE for training (blue), validation (green), and test (red) datasets plotted over epochs. Both ANNs demonstrate a sharp decline in MSE within the first 100 epochs, indicating rapid learning. By around 600 epochs, the MSE stabilizes, indicating optimal learning. For ANN(1), the MSE stabilizes around 600 epochs, and the close tracking of the validation and test lines with the training line suggests good generalization and robustness, with no significant overfitting. For ANN(2), as the epochs increase, the MSE converges, suggesting stabilization around the optimal solution. The final MSE values for ANN(2) are very low, showing high accuracy. The validation and test lines closely track the training line, indicating good generalization and a low risk of overfitting. The best validation performance (1.3166e-07) occurs at epoch 1000, with no significant improvement beyond this point. Both models demonstrate excellent learning speed, accuracy, and generalization capabilities, with no signs of overfitting.
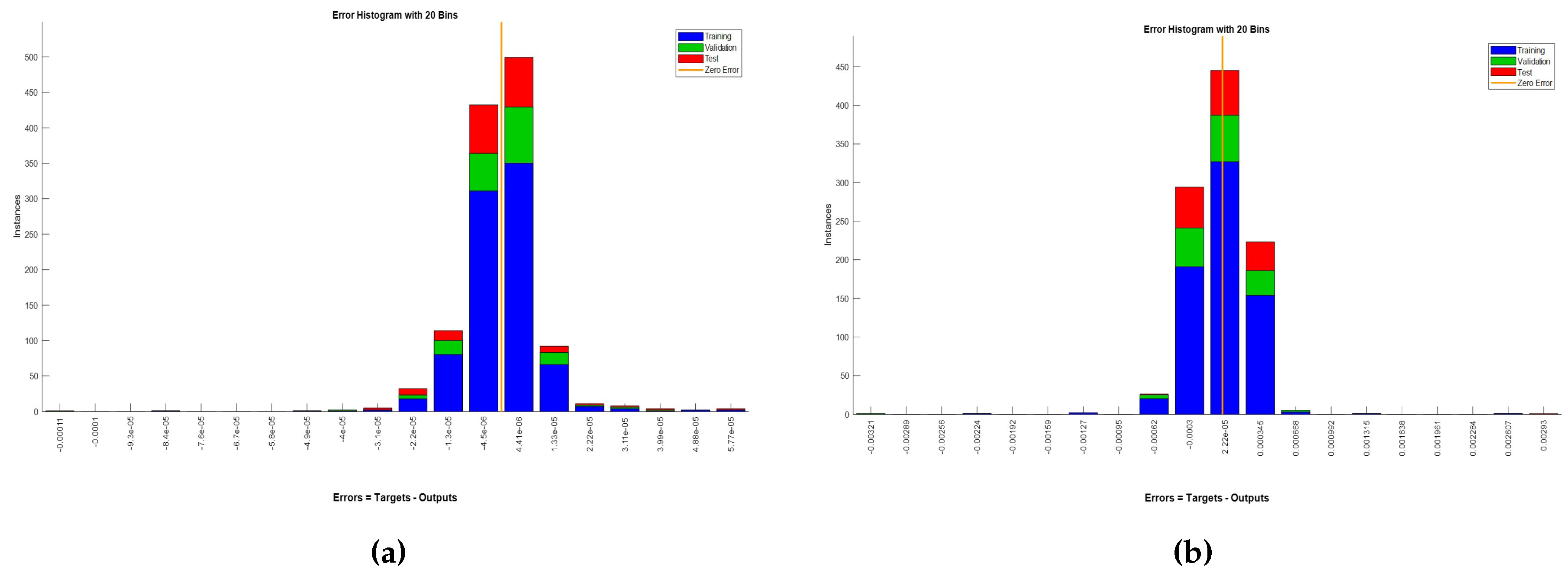
Figure 32 presents the error histogram plots for ANN(1)
(a) and ANN(2)
(b). For both ANNs, the majority of prediction errors are centered around the "Zero Error" line, indicating high accuracy and precision in the models’ predictions. For ANN(1), the errors for the training data (blue) cluster around zero, confirming a good fit. Validation and test errors (green and red) follow a similar pattern, suggesting good generalization. The close alignment of validation and test errors with the training errors indicates that the model is not overfitting. The uniform error distribution across datasets, with most errors near zero, demonstrates the model’s robustness and consistent performance without significant bias. ANN(2) shows a large number of instances (errors) concentrated around the zero-error bin. This concentration suggests that the ANN predictions are very accurate for a significant portion of the dataset. The distribution of errors for ANN(2) also indicates that the model generalizes well and maintains high accuracy across different datasets. Both ANNs demonstrate robust performance with minimal prediction errors and consistent accuracy across training, validation, and test datasets.
6. Conclusions
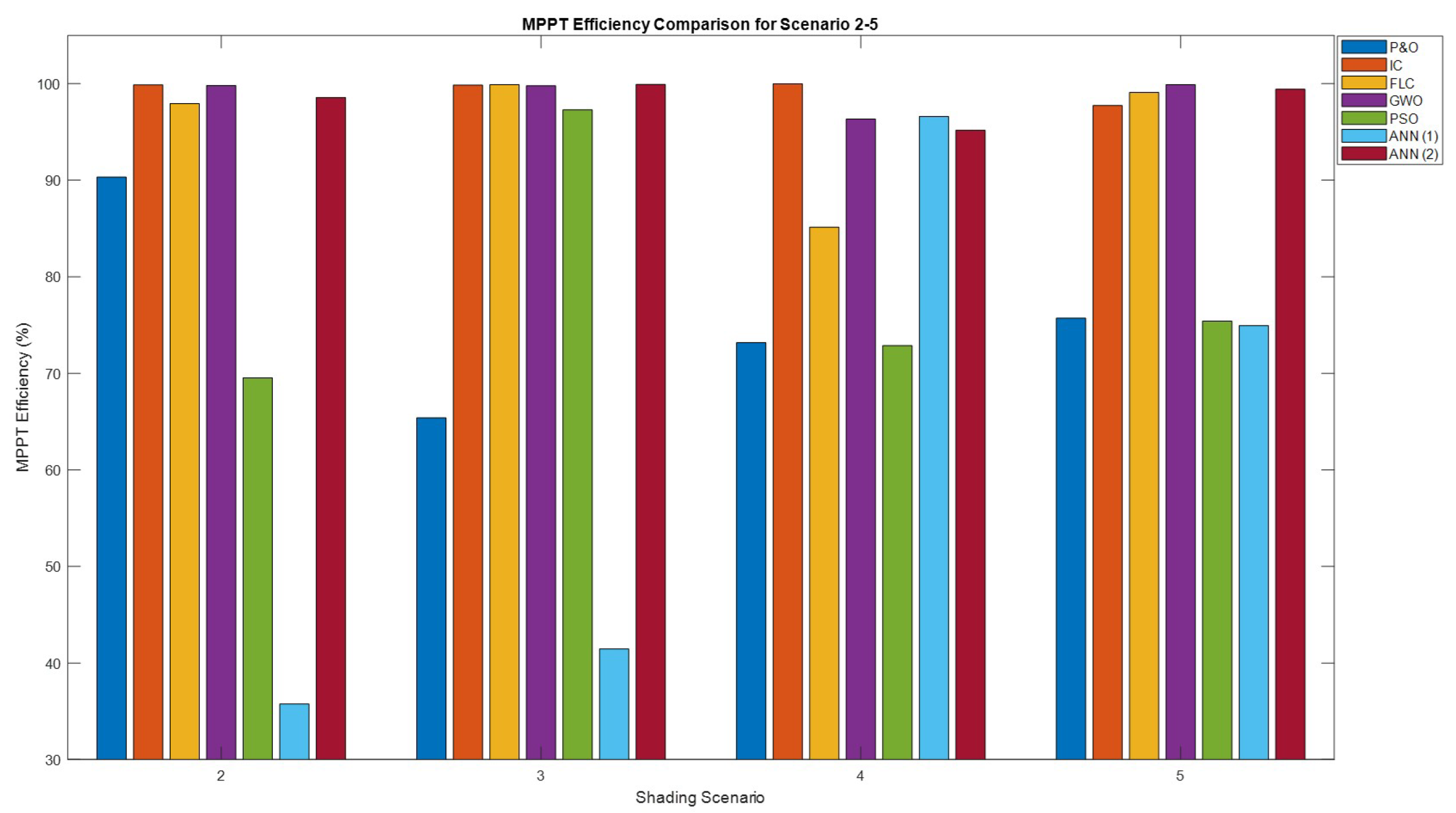
This paper presented a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of various Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithms under Partial Shading Conditions (PSCs) for photovoltaic (PV) systems. The study focused on traditional methods such as Perturb and Observe (P&O) and Incremental Conductance (IC), as well as advanced techniques including Fuzzy Logic Control (FLC), Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO), Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), and two Artificial Neural Network (ANN) models (ANN(1) and ANN(2)). The simulations were conducted in a controlled MATLAB/Simulink environment to ensure accurate and reliable comparisons. The findings indicate that while ANN(1) performed exceptionally well under uniform solar conditions, it struggled with PSCs due to its reliance on stable environmental inputs. On the other hand, ANN(2) demonstrated superior performance across various PSC scenarios, outperforming traditional and advanced MPPT techniques in terms of efficiency and convergence speed. Specifically, ANN(2) was on average 72% faster than P&O, 83% faster than IC, and 26% faster than PSO. ANN(2) also showed significant advantages over GWO and FLC in complex scenarios. The efficiency improvements were notable as well, with ANN(2) being on average 23.41% more efficient than P&O, 0.61% more efficient than IC, 4.28% more efficient than FLC, 1.68% more efficient than GWO, 24.61% more efficient than PSO, and 29.76% more efficient than ANN(1). These results underscore the potential of ANN-based approaches to enhance the performance and reliability of solar energy systems under dynamic shading conditions. The study also highlights the importance of integrating more adaptive and intelligent systems like AI and ML into PV optimization processes. The ANN(2) model, which used only irradiance as an input, simplified the MPPT process, reduced the complexity and potential cost of implementation while maintaining high performance. This makes it interesting to further investigate it as a practical solution for real-world PV systems, especially in environments with frequent and complex shading patterns with stable temperature environments.
Figure 1.
Global Energy Production 2022 [
3].
Figure 1.
Global Energy Production 2022 [
3].
Figure 2.
Yearly PV installation, module PV production and module production capacity 2012 - 2022 (GW) [
3].
Figure 2.
Yearly PV installation, module PV production and module production capacity 2012 - 2022 (GW) [
3].
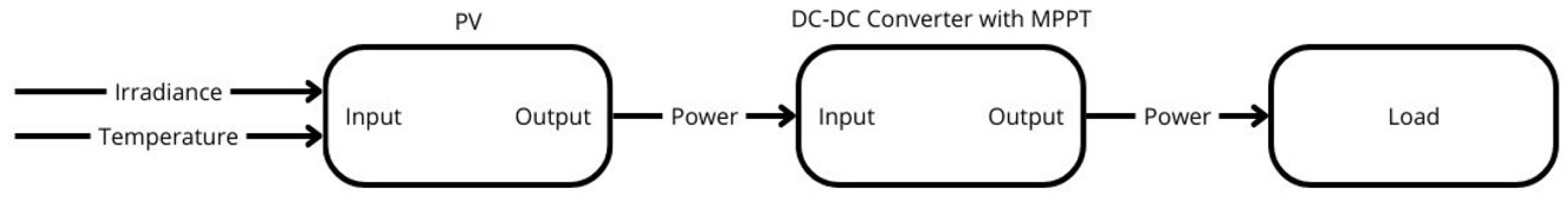
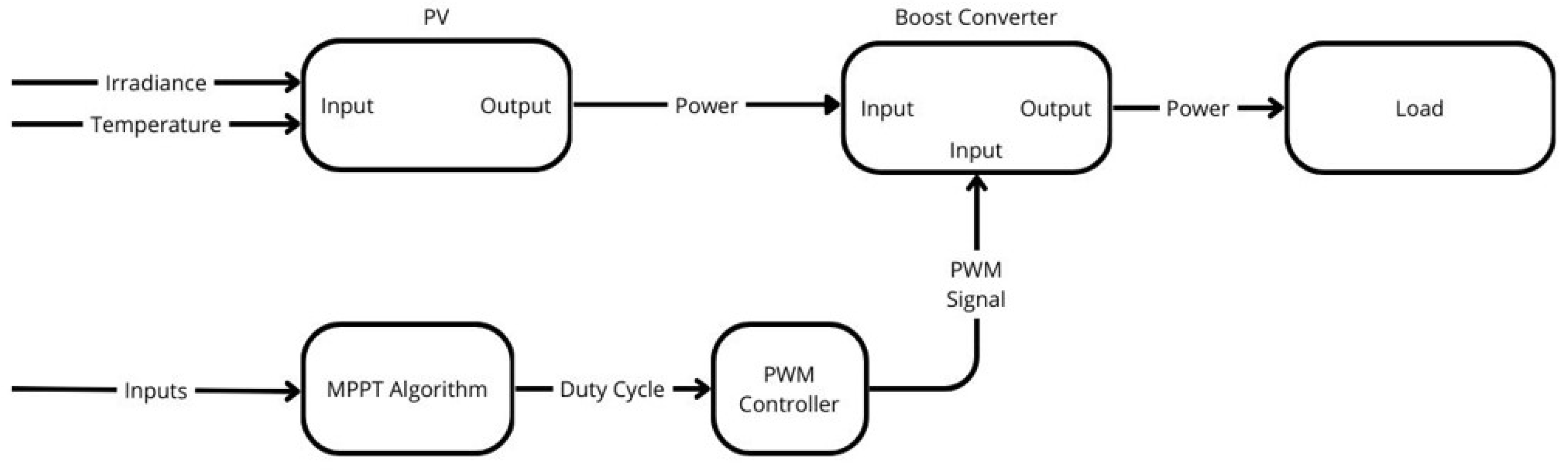
Figure 3.
Block diagram of the PV system components.
Figure 3.
Block diagram of the PV system components.
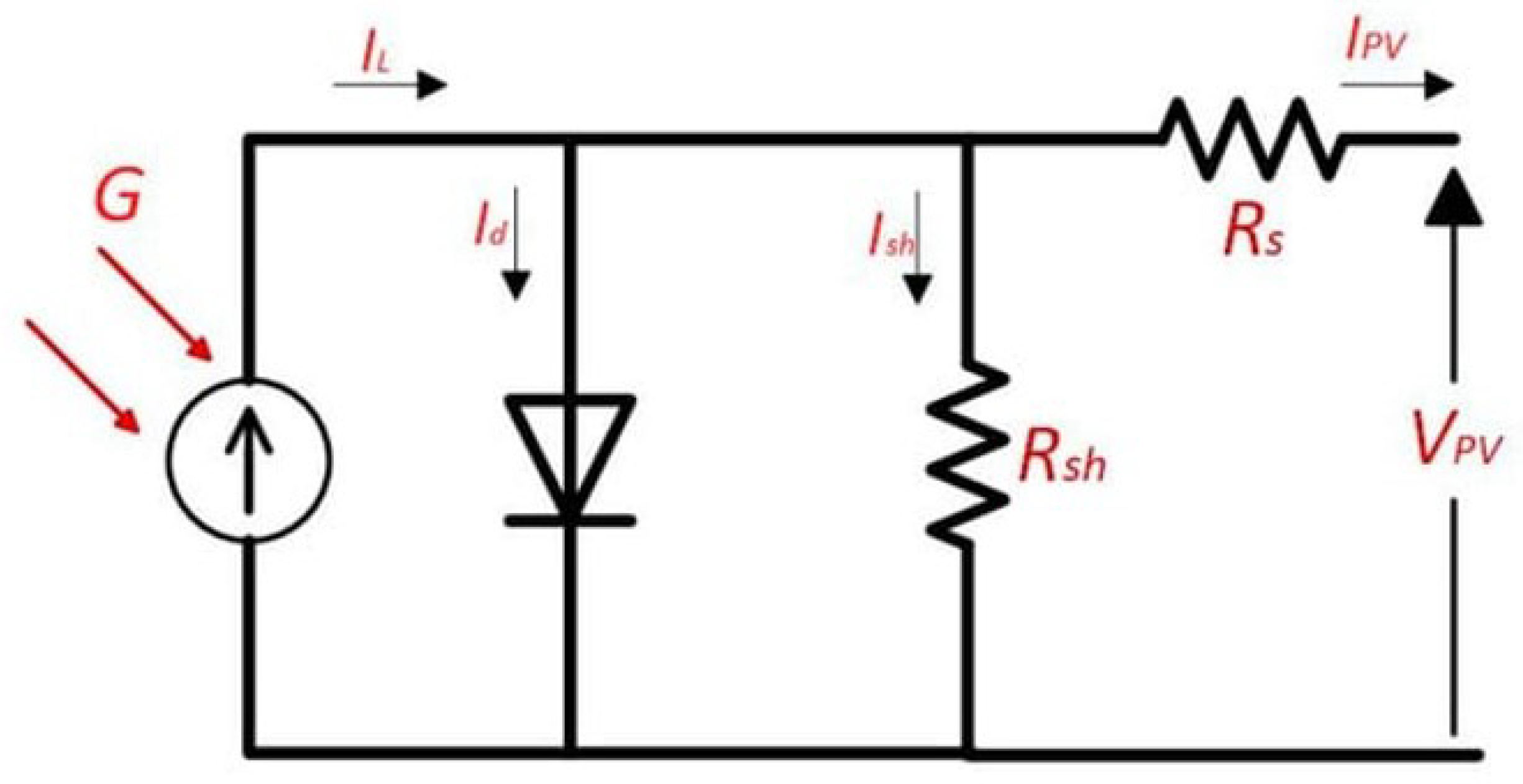
Figure 4.
Equivalent circuit of PV cell [
20].
Figure 4.
Equivalent circuit of PV cell [
20].
Figure 5.
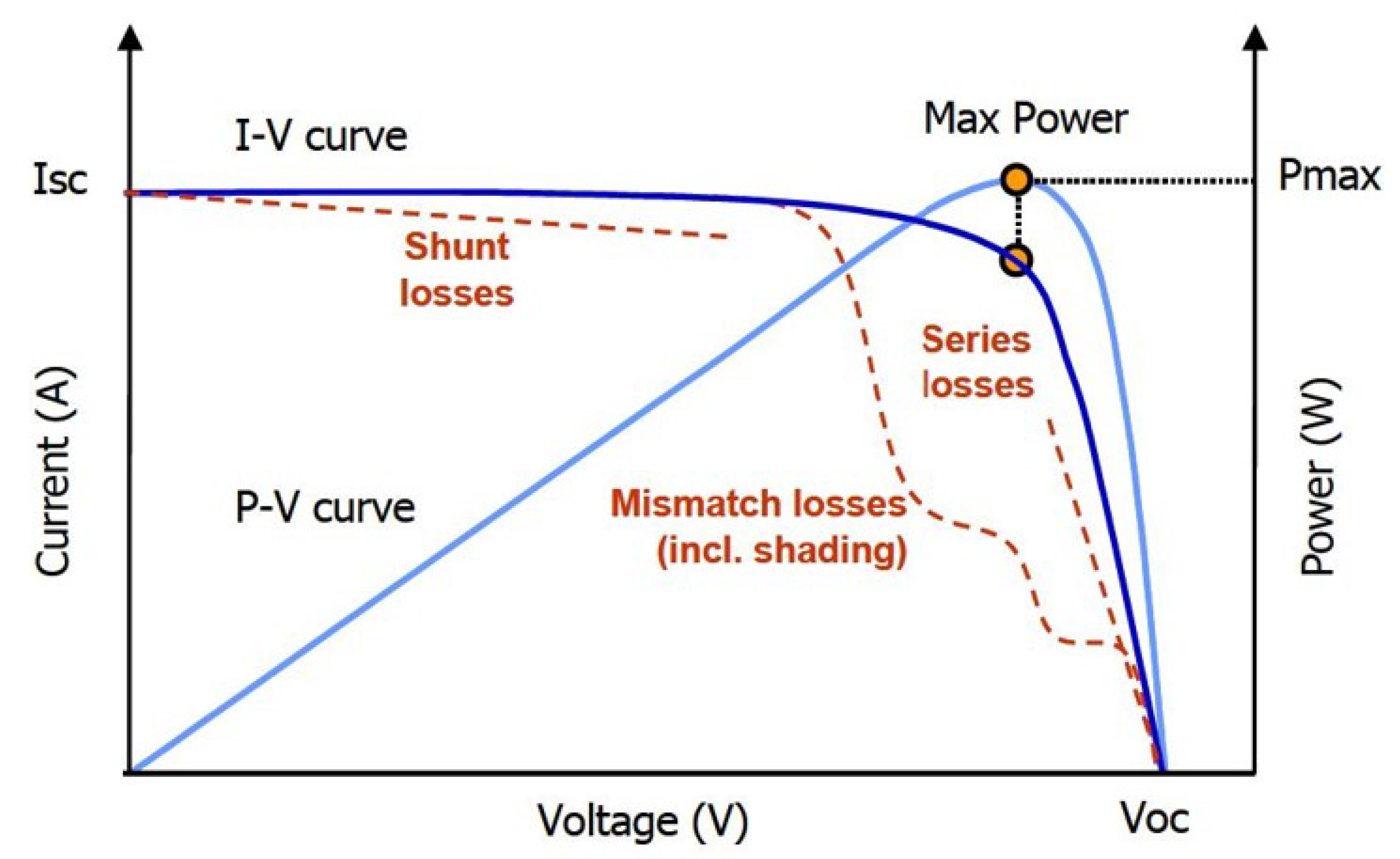
Performance Characteristics of a PV cell or module, represented by the Current-Voltage (I-V) curve and the Power-Voltage (P-V) curve.
Figure 5.
Performance Characteristics of a PV cell or module, represented by the Current-Voltage (I-V) curve and the Power-Voltage (P-V) curve.
Figure 6.
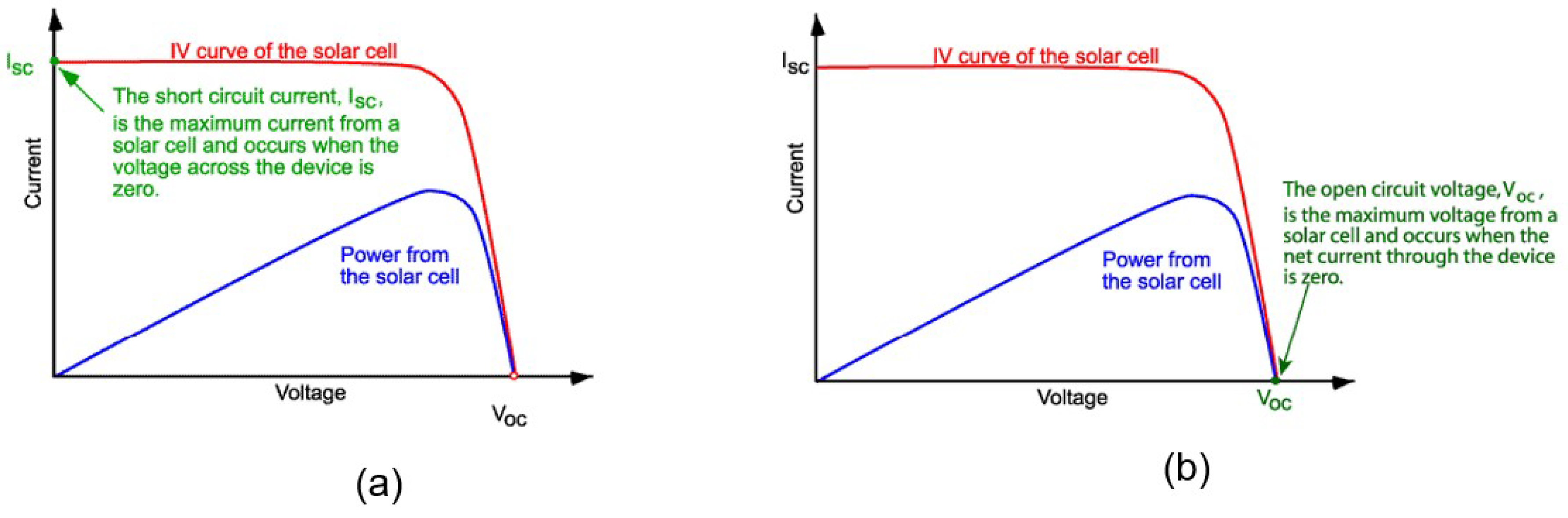
I-V curve of a PV cell where (a) is illustrating the short-circuit current, and (b) is showing the open-circuit voltage.
Figure 6.
I-V curve of a PV cell where (a) is illustrating the short-circuit current, and (b) is showing the open-circuit voltage.
Figure 7.
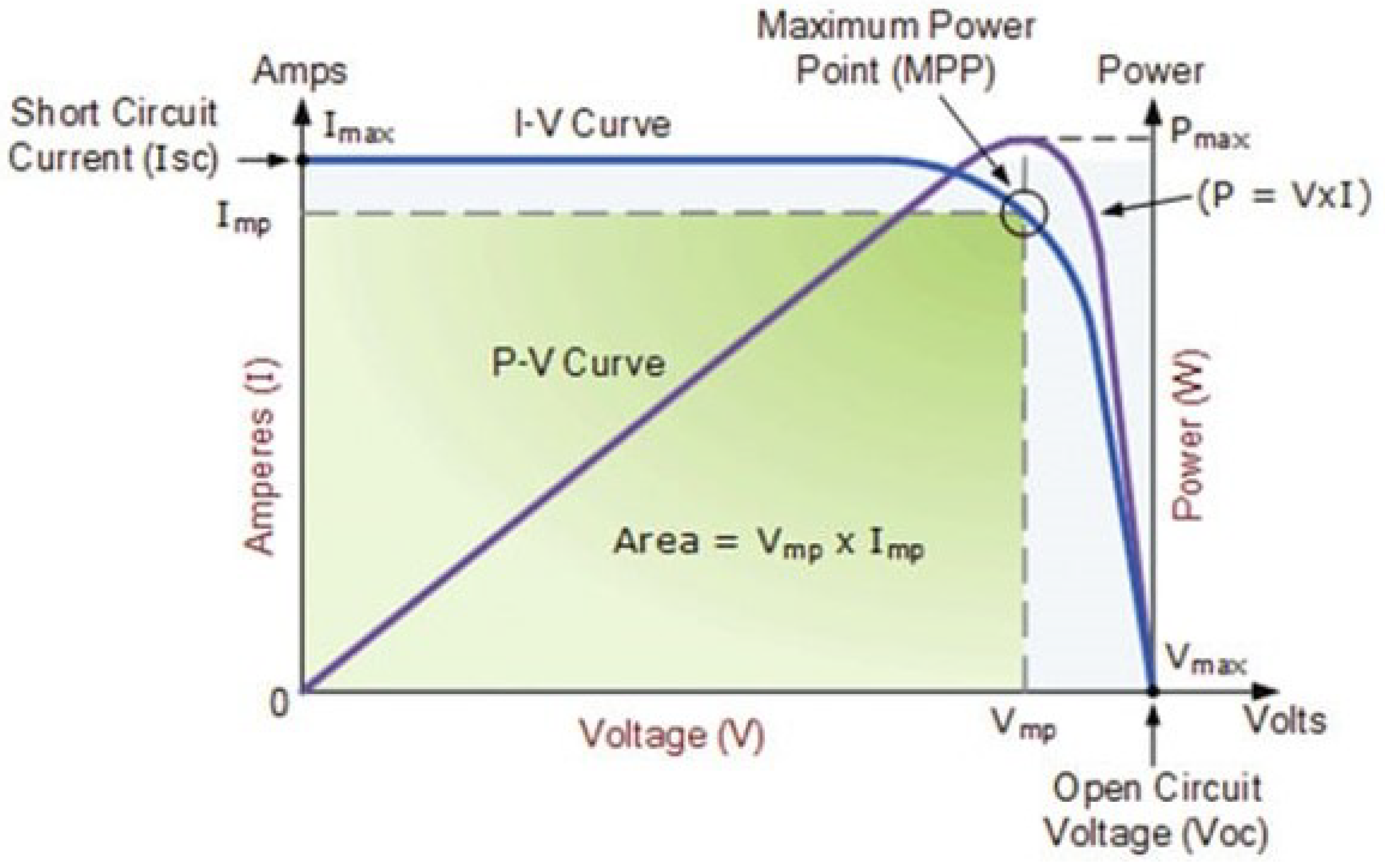
I-V curve, P-V curve, and MPP [
4].
Figure 7.
I-V curve, P-V curve, and MPP [
4].
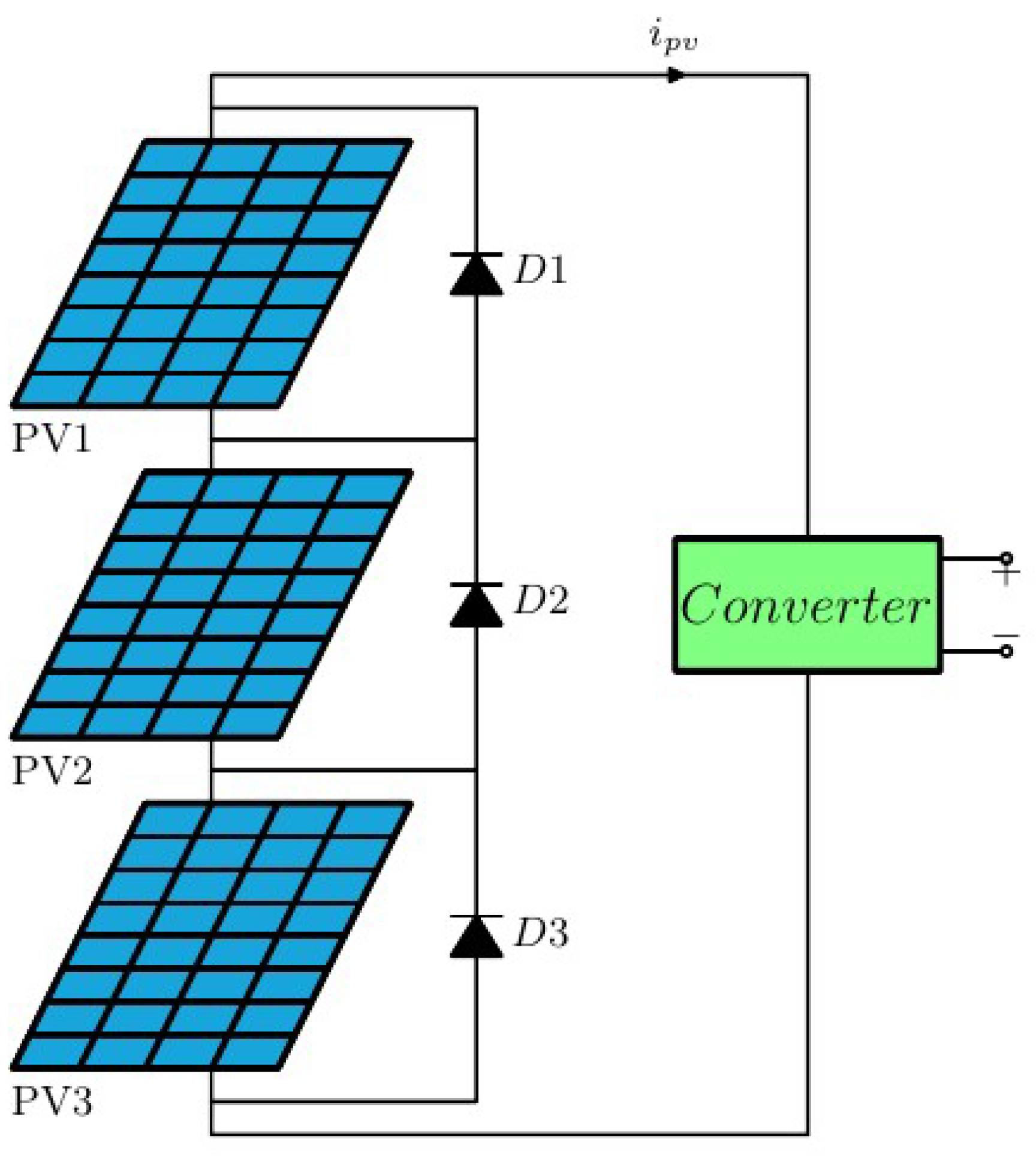
Figure 8.
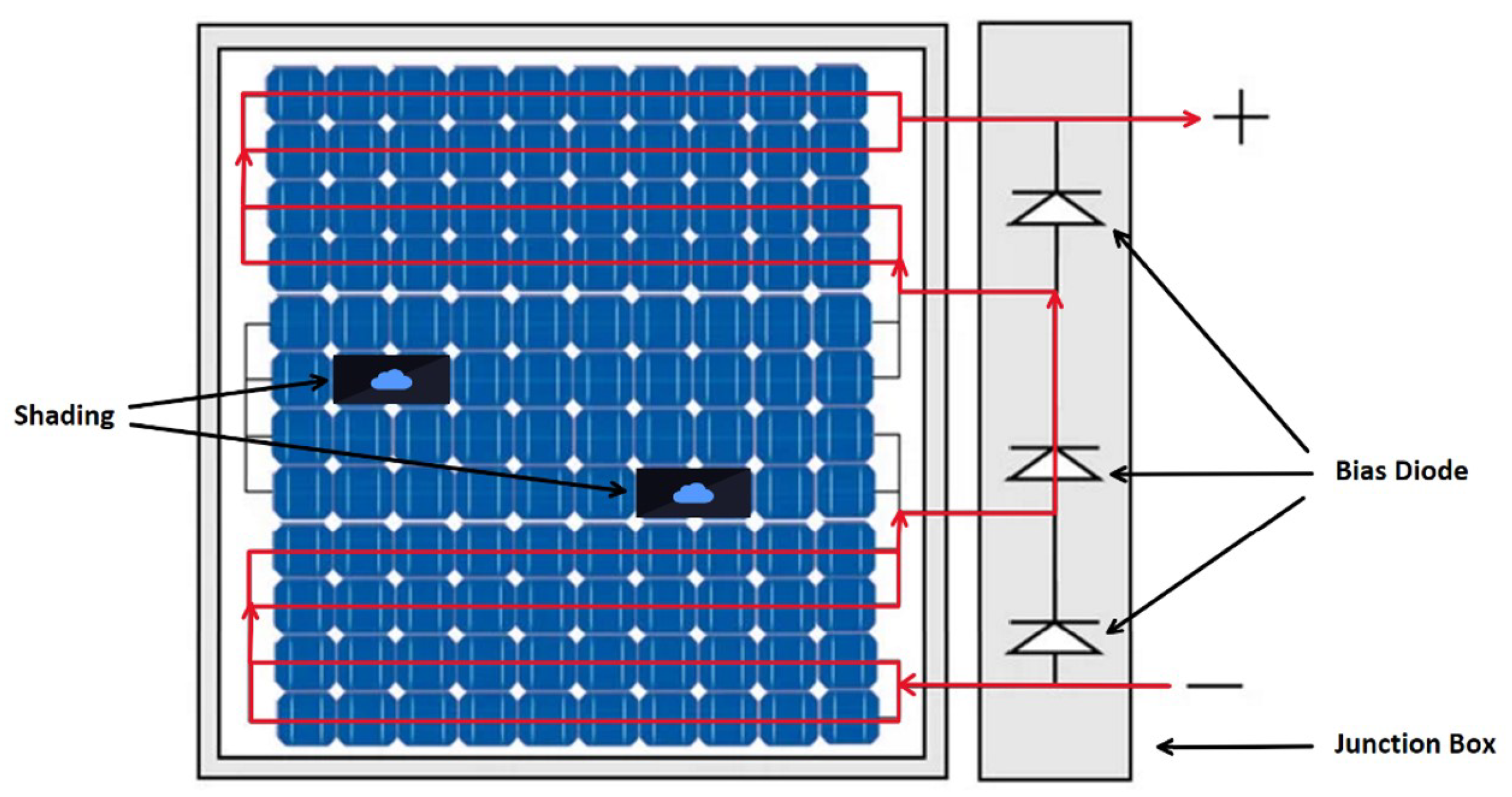
Illustration of three series PVs with bias diodes under PSC.
Figure 8.
Illustration of three series PVs with bias diodes under PSC.
Figure 9.
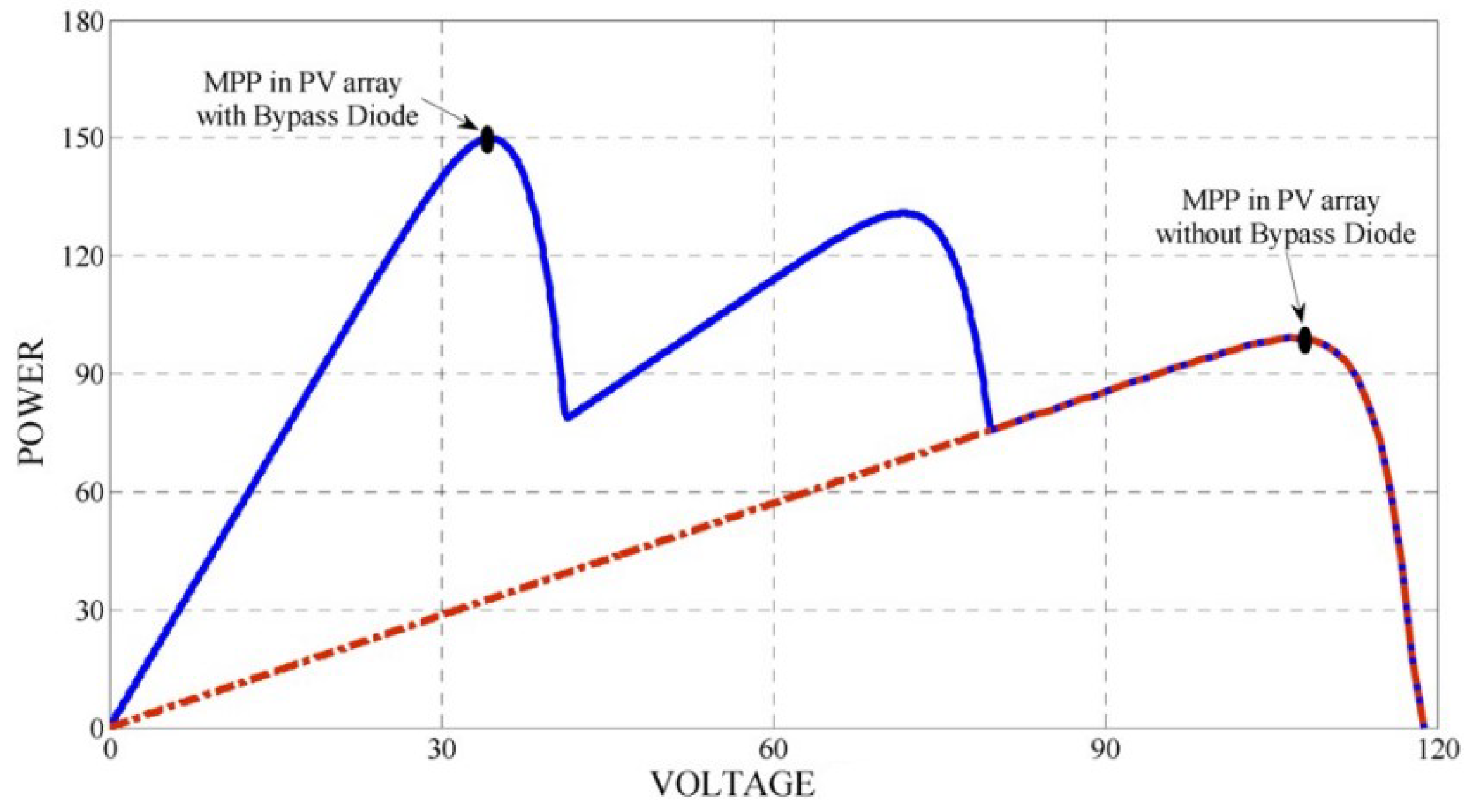
P-V curve for PV under PSC with LMPP and GMPP showing the effect of bias diode.
Figure 9.
P-V curve for PV under PSC with LMPP and GMPP showing the effect of bias diode.
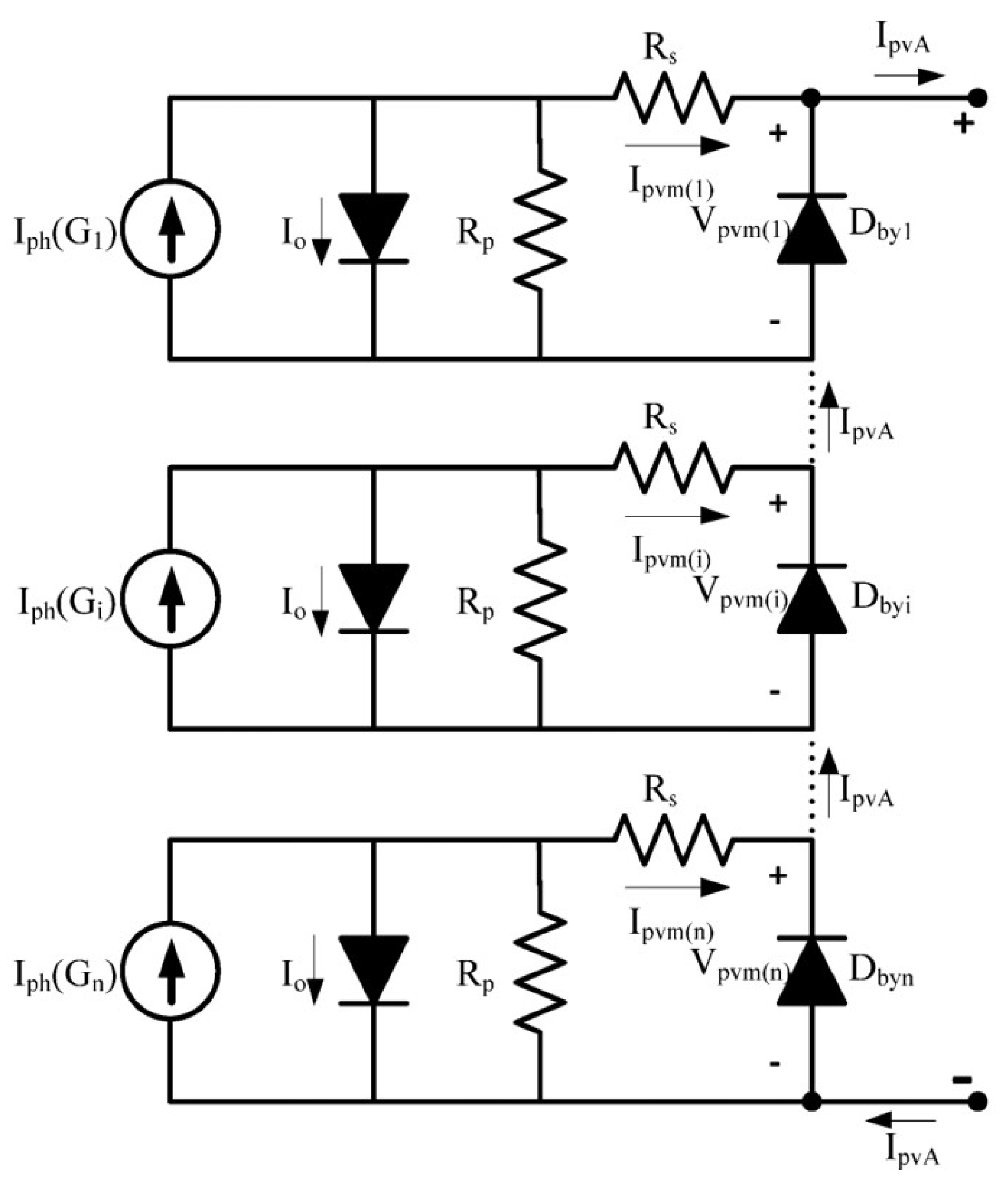
Figure 10.
Equivalent of three series connected PV with bias diodes.
Figure 10.
Equivalent of three series connected PV with bias diodes.
Figure 11.
Block diagram of the simulation model
Figure 11.
Block diagram of the simulation model
Figure 12.
Three Series Connected PVs with bias Diodes Connected to a Converter.
Figure 12.
Three Series Connected PVs with bias Diodes Connected to a Converter.
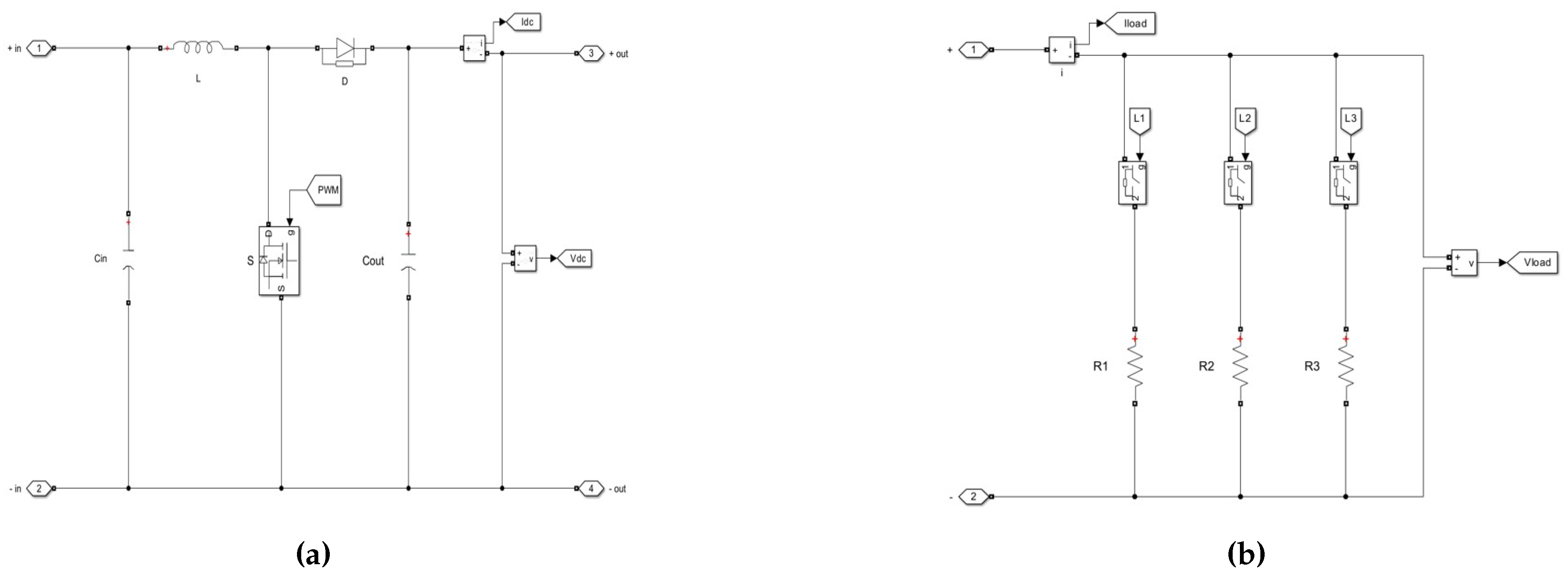
Figure 13.
Simulation model of the boost converter (a), and load (b).
Figure 13.
Simulation model of the boost converter (a), and load (b).
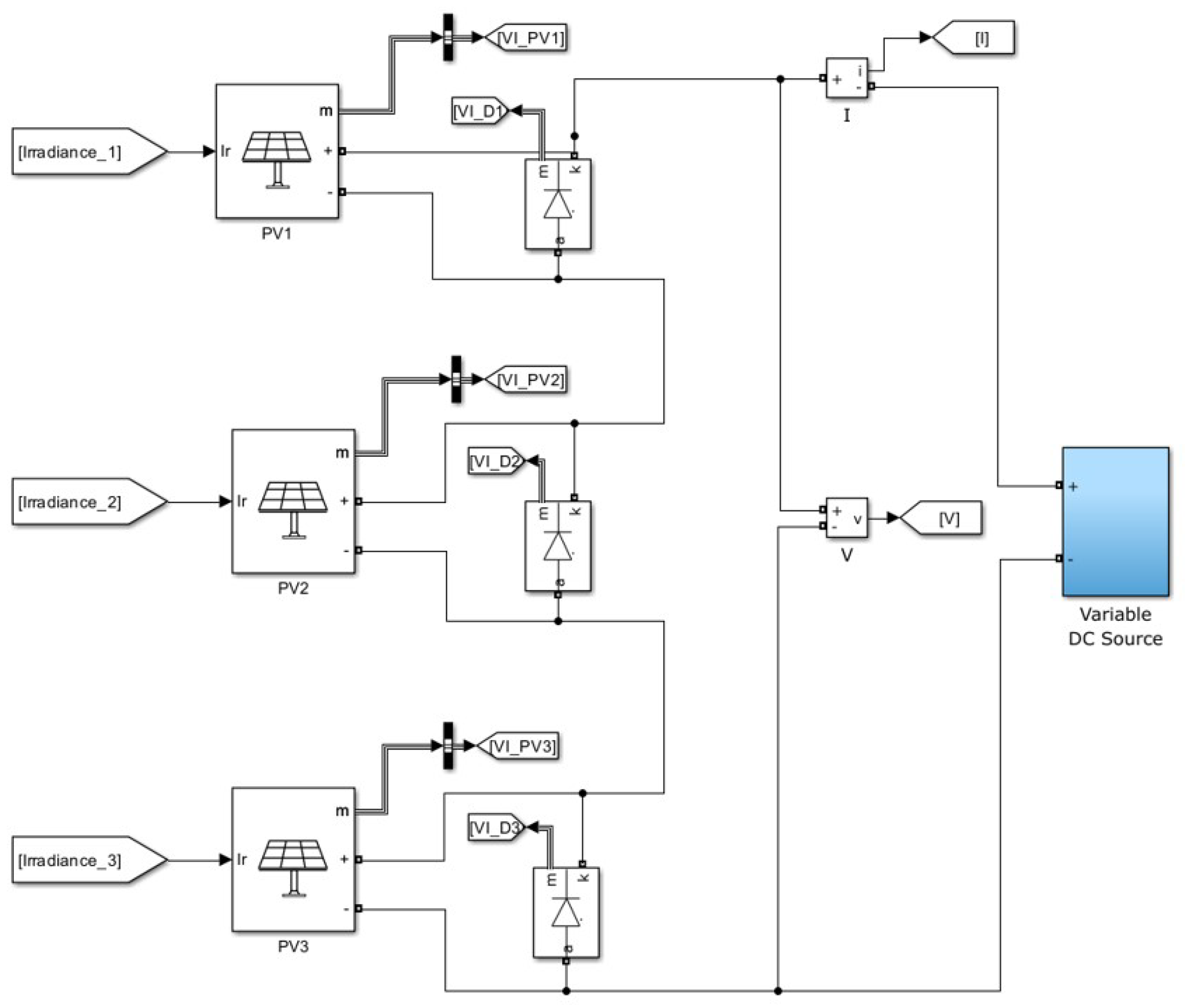
Figure 14.
Simulink Model used to obtain I-V and P-V characteristics to locate MPP.
Figure 14.
Simulink Model used to obtain I-V and P-V characteristics to locate MPP.
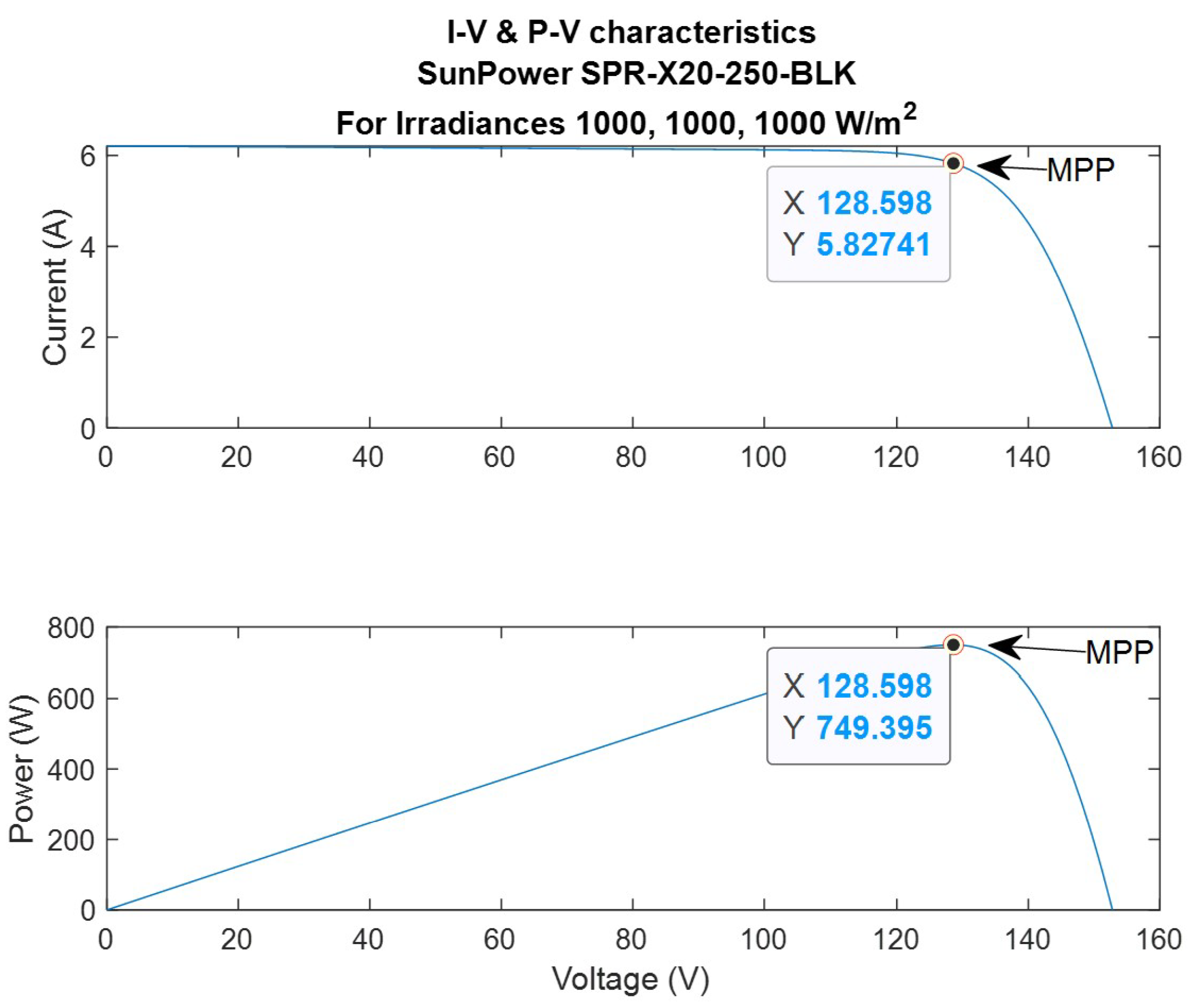
Figure 15.
I-V and P-V characteristics for the PV system illustrating the MPP under full solar irradiance.
Figure 15.
I-V and P-V characteristics for the PV system illustrating the MPP under full solar irradiance.
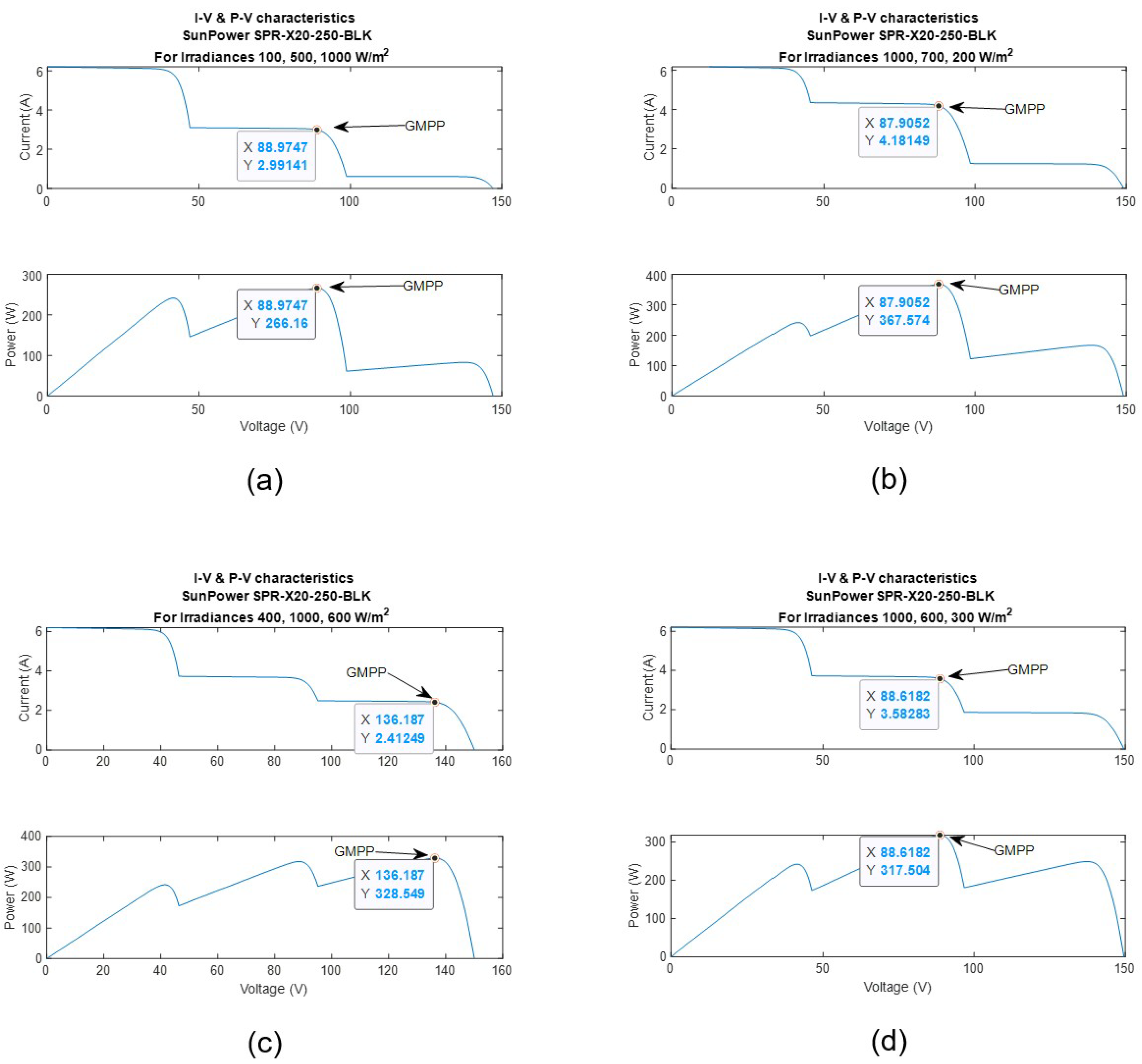
Figure 16.
I-V- and P-V characteristics illustrating the GMPP for the PV system under shading scenario 2 (a), 3 (b), 4 (c), and 5 (d).
Figure 16.
I-V- and P-V characteristics illustrating the GMPP for the PV system under shading scenario 2 (a), 3 (b), 4 (c), and 5 (d).
Figure 17.
Block diagram of the MPPT algorithms using MATLAB function blocks.
Figure 17.
Block diagram of the MPPT algorithms using MATLAB function blocks.
Figure 18.
Flowchart of the P&O algorithm.
Figure 18.
Flowchart of the P&O algorithm.
Figure 19.
Flowchart of the IC algorithm.
Figure 19.
Flowchart of the IC algorithm.
Figure 20.
Block diagram of the FLC algorithm
Figure 20.
Block diagram of the FLC algorithm
Figure 21.
Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) Plot.
Figure 21.
Fuzzy Inference System (FIS) Plot.
Figure 22.
Simplified flowchart of the GWO algorithm.
Figure 22.
Simplified flowchart of the GWO algorithm.
Figure 23.
Simplified flowchart of the PSO algorithm.
Figure 23.
Simplified flowchart of the PSO algorithm.
Figure 24.
Generated ANN Simulink block.
Figure 24.
Generated ANN Simulink block.
Figure 25.
Layers inside the ANN Simulink block.
Figure 25.
Layers inside the ANN Simulink block.
Figure 26.
The ANN structure of ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 26.
The ANN structure of ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 27.
Block diagram of the ANN(1) MPPT
Figure 27.
Block diagram of the ANN(1) MPPT
Figure 28.
Block diagram of the ANN(2) MPPT
Figure 28.
Block diagram of the ANN(2) MPPT
Figure 29.
Solar Irradiance (a) and Temperature (b) data used for training
Figure 29.
Solar Irradiance (a) and Temperature (b) data used for training
Figure 30.
Regression Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 30.
Regression Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 31.
Performance Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 31.
Performance Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 32.
Error Histogram Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 32.
Error Histogram Plots for ANN(1) (a), and ANN(2) (b).
Figure 33.
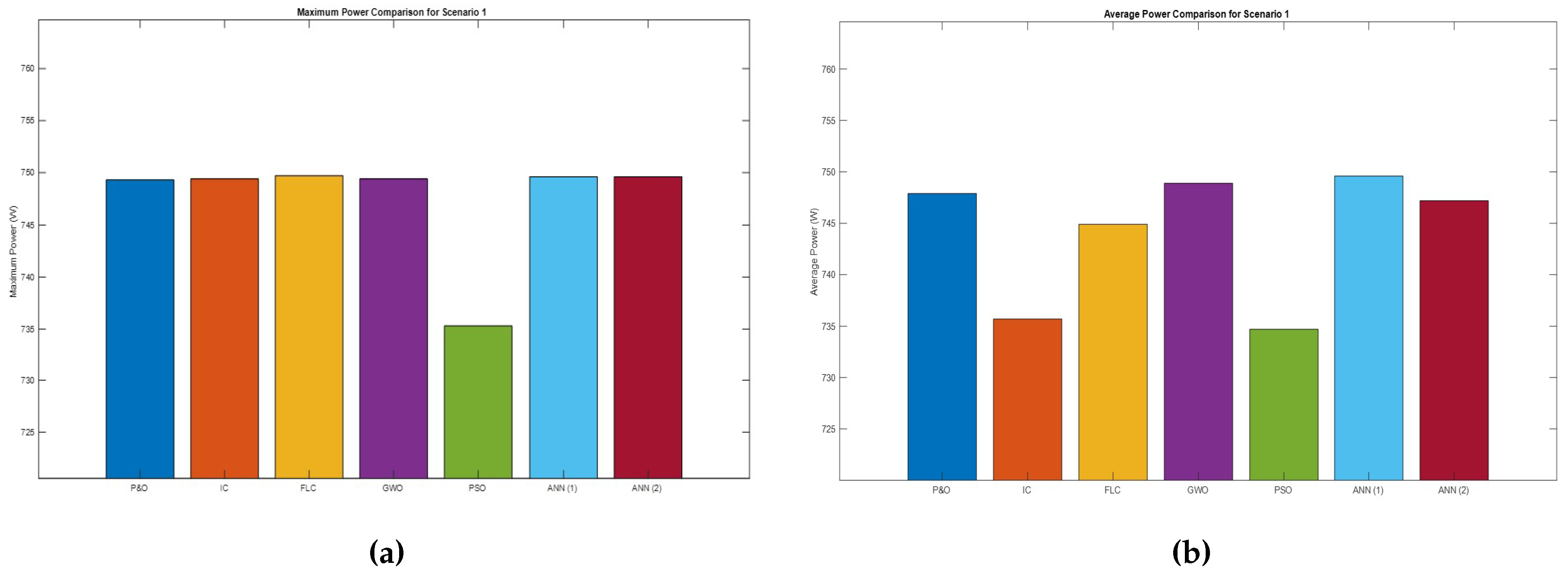
Comparison of the maximum (a) and the average (b) power for shading scenario 1.
Figure 33.
Comparison of the maximum (a) and the average (b) power for shading scenario 1.
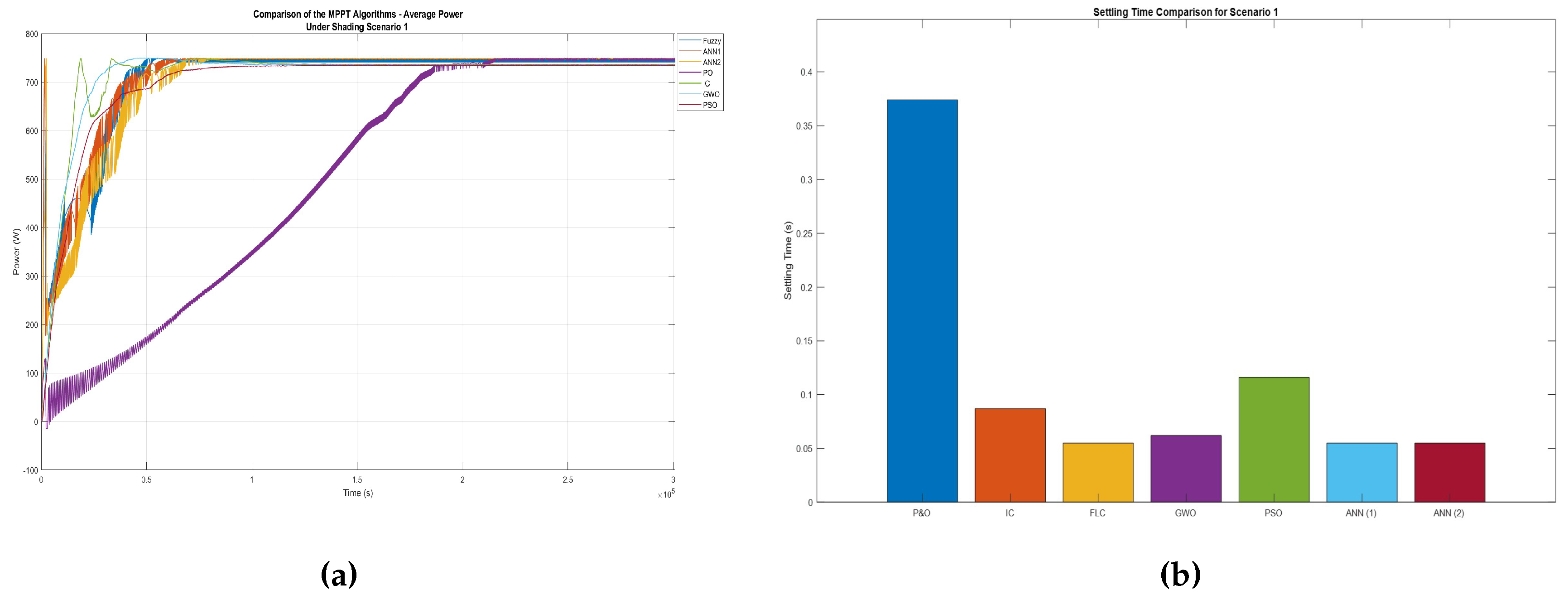
Figure 34.
Comparison of the average power (a) and the settling time (b) for shading scenario 1.
Figure 34.
Comparison of the average power (a) and the settling time (b) for shading scenario 1.
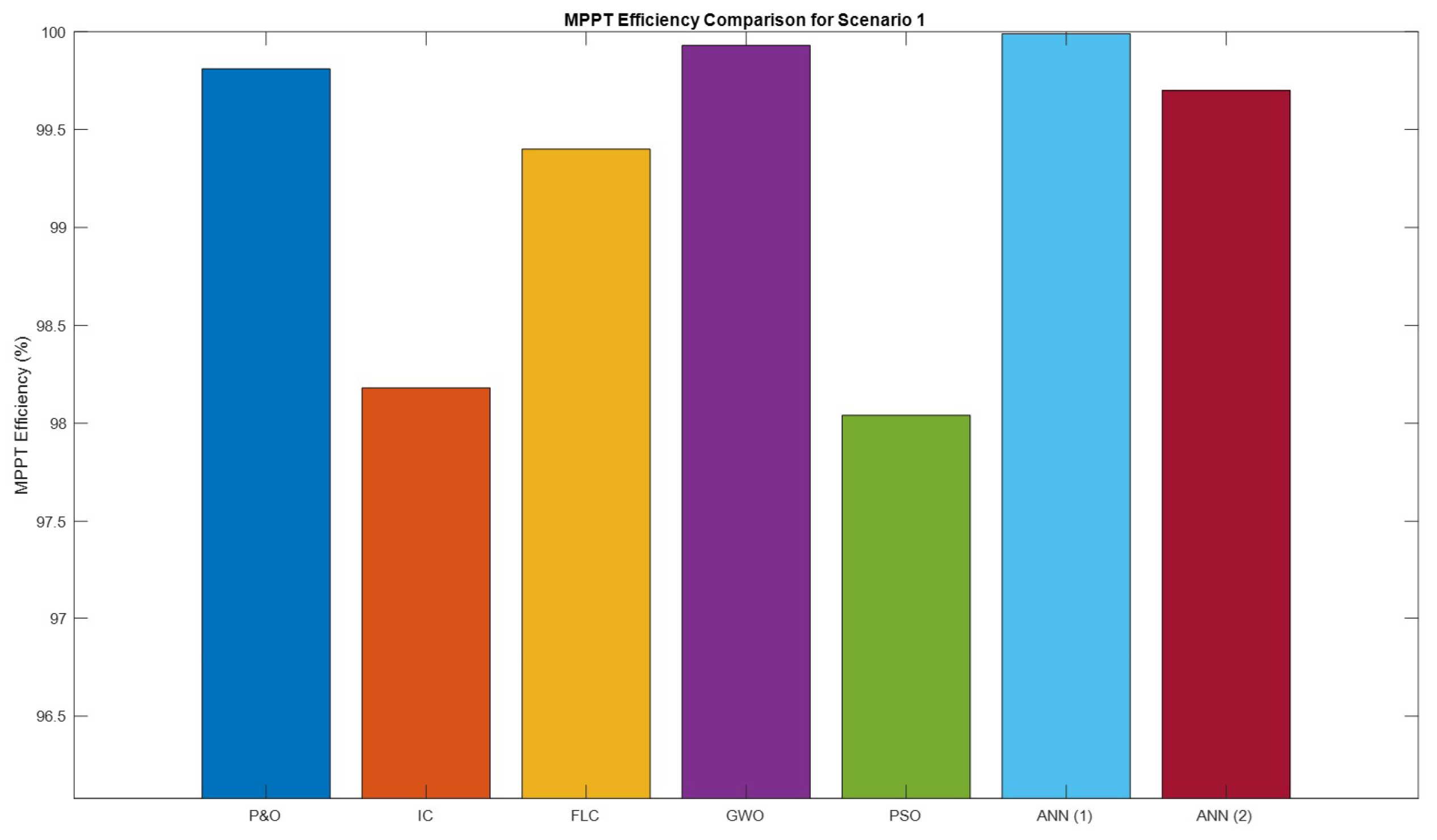
Figure 35.
Comparison of the MPPT efficiencies for shading scenario 1.
Figure 35.
Comparison of the MPPT efficiencies for shading scenario 1.
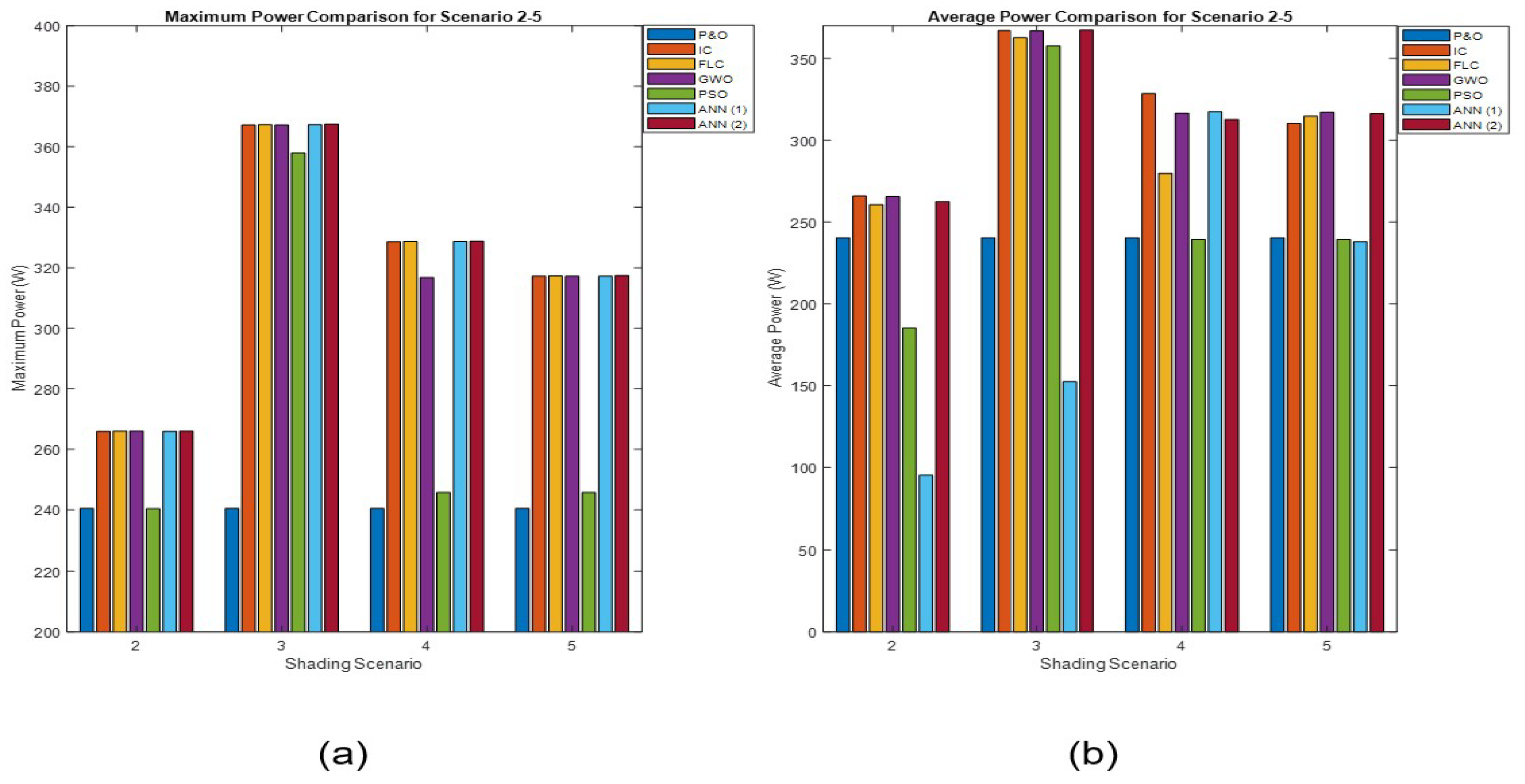
Figure 36.
Comparison of the maximum power (a) and the average power (b) for shading scenario 2-5.
Figure 36.
Comparison of the maximum power (a) and the average power (b) for shading scenario 2-5.
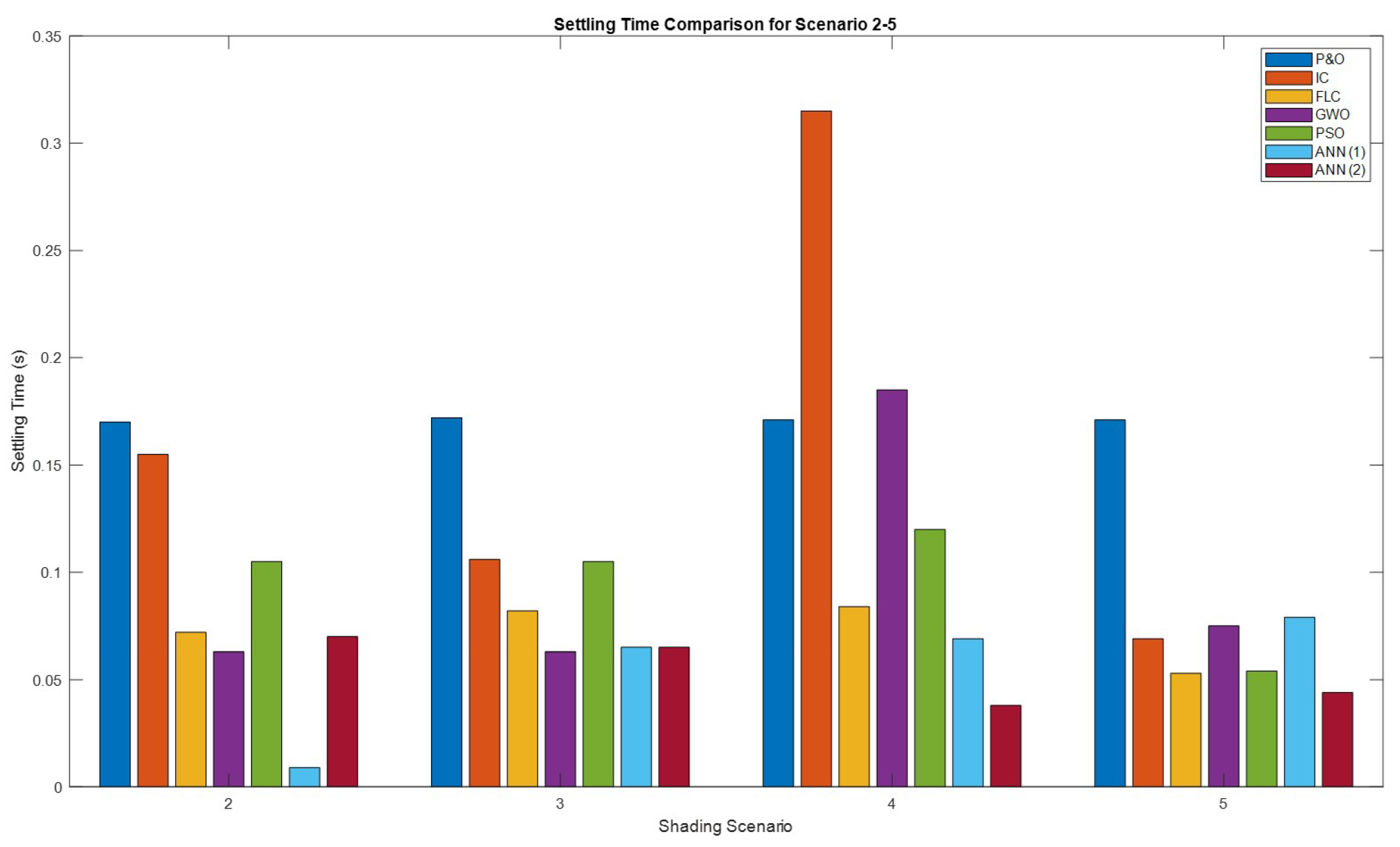
Figure 37.
Comparison of the settling time for shading scenario 2-5.
Figure 37.
Comparison of the settling time for shading scenario 2-5.
Figure 38.
Comparison of the MPPT efficiencies for shading scenario 2-5.
Figure 38.
Comparison of the MPPT efficiencies for shading scenario 2-5.
Table 1.
Module data for Sunpower SPR-X20-250-BLK.
Table 1.
Module data for Sunpower SPR-X20-250-BLK.
| Parameters |
Symbols |
Values |
| Maximum Power (W) |
PMPP
|
249.952 |
| Cells Per Module |
Ncell
|
72 |
| Open Circuit Voltage (V) |
VOC
|
50.93 |
| Short-Circuit Current (A) |
ISC
|
6.2 |
| Voltage at Maximum Power Point (V) |
VMP
|
42.8 |
| Current at Maximum Power Point (A) |
IMP
|
5.84 |
| Temperature Coefficient of VOC (%/C) |
KOC
|
-0.291 |
| Temperature Coefficient of ISC (%/C) |
KSC
|
0.013306 |
Table 2.
Model parameters for Sunpower SPR-X20-250-BLK.
Table 2.
Model parameters for Sunpower SPR-X20-250-BLK.
| Parameters |
Symbols |
Values |
| Light-Generated Current (A) |
IL
|
6.2119 |
| Diode Saturation Current (A) |
I0
|
1.3593e-11 |
| Diode Ideality Factor |
n |
1.0262 |
| Shunt Resistance () |
Rsh
|
420.5449 |
| Series Resistance () |
Rs
|
0.37748 |
Table 3.
Model parameters for Boost Converter and Load.
Table 3.
Model parameters for Boost Converter and Load.
| Parameters |
Symbols |
Values |
| Input Filter Capacitor (mF) |
|
1 |
| Output Filter Capacitor (µF) |
|
32.27 |
| Boost Inductor (mH) |
L |
1.1478 |
| Switching Frequency (kHz) |
|
5 |
| Resistive Load () |
R |
100 |
Table 4.
Solar Irradiance Scenarios.
Table 4.
Solar Irradiance Scenarios.
| Shading Scenario |
Irradiance 1 (W/m) |
Irradiance 2 (W/m) |
Irradiance 3 (W/m) |
| 1 |
1000 |
1000 |
1000 |
| 2 |
100 |
500 |
1000 |
| 3 |
1000 |
700 |
200 |
| 4 |
400 |
1000 |
600 |
| 5 |
1000 |
600 |
300 |
Table 5.
Rules Table.
| Rule Number |
Rule |
Weight |
Name |
| 1 |
If in1 is in1cluster1 and in2 is in2cluster1 and in3 is in3cluster1 then out1 is out1cluster1 |
1 |
rule1 |
| 2 |
If in1 is in1cluster2 and in2 is in2cluster2 and in3 is in3cluster2 then out1 is out1cluster2 |
1 |
rule2 |
| 3 |
If in1 is in1cluster3 and in2 is in2cluster3 and in3 is in3cluster3 then out1 is out1cluster3 |
1 |
rule3 |
| 4 |
If in1 is in1cluster4 and in2 is in2cluster4 and in3 is in3cluster4 then out1 is out1cluster4 |
1 |
rule4 |
| 5 |
If in1 is in1cluster5 and in2 is in2cluster5 and in3 is in3cluster5 then out1 is out1cluster5 |
1 |
rule5 |
Table 6.
Training data for the ANN(2) model.
Table 6.
Training data for the ANN(2) model.
| Irradiance Panel 1 (W/m) |
Irradiance Panel 2 (W/m) |
Irradiance Panel 3 (W/m) |
Maximum Voltage Output (V) |
| 723.4451 |
979.4541 |
258.5401 |
83.9496 |
| 264.0207 |
213.7384 |
271.5827 |
32.0705 |
| 393.8638 |
958.1213 |
721.5790 |
88.7485 |
| 818.9435 |
494.9419 |
589.5526 |
81.4671 |
| 622.9487 |
208.0732 |
82.3322 |
71.1911 |
| 942.3752 |
751.3258 |
933.0167 |
112.4235 |
| 543.0011 |
984.4322 |
510.6935 |
87.2318 |
| 895.8498 |
972.5006 |
117.2215 |
108.3409 |
| 559.1643 |
328.7496 |
600.5573 |
63.7066 |
| 983.3986 |
344.9982 |
985.2885 |
99.0257 |
| 967.8675 |
652.4311 |
687.5626 |
106.3631 |
| 463.3094 |
709.8439 |
329.9017 |
99.9889 |
| 908.7390 |
791.5343 |
403.4721 |
90.0403 |
| 878.0810 |
344.8405 |
883.5706 |
74.8037 |
| 386.5441 |
967.2057 |
412.3786 |
87.8199 |
| 699.4323 |
710.9914 |
366.9940 |
76.0735 |
| 258.1459 |
877.6753 |
89.5023 |
89.5043 |
| 869.3686 |
632.0528 |
215.4435 |
73.4818 |
Table 7.
Performance evaluation of the MPPT algorithms.
Table 7.
Performance evaluation of the MPPT algorithms.
| MPPT Algorithm |
Settling Time |
Response Time |
Efficiency |
| P&O |
Slow |
Moderate |
Low |
| IC |
Very Slow |
Moderate |
High |
| FLC |
Fast |
Fast |
High |
| GWO |
Fast |
Fast |
High |
| PSO |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Moderate |
| ANN(1) |
Fast |
Fast |
Variable |
| ANN(2) |
Fast |
Very Fast |
Very High |