1. Introduction
The Naringenin, a dominant flavanon in nature, exhibits a broad array of biological and pharmacological activities. The existing body of evidence suggests that naringenin has the ability to modulate acute and chronic inflammatory responses, positioning it as a promising candidate for therapeutic applications. Recent studies have indeed affirmed the effectiveness of naringenin in managing several inflammation-associated diseases including sepsis, acute hepatitis, fibrosis, and cancer [
1,
2,
3]. Moreover, naringenin has emerged as a significant agent in regulating lipid protein metabolism, offering potential utility in the management of diseases such as diabetes, arteriosclerosis, and insulin resistance, topics extensively covered in previous reviews [
4].
Recent research indicates potential pre and post-infection effects of naringenin [
5]. Similar to other natural compounds, naringenin demonstrates promising outcomes in vitro but reveals limited results in in vivo viral infection models. Nonetheless, both in vitro and in vivo anti-inflammatory potentials of naringenin have been emphasized, including in various animal models addressing respiratory syndromes. From this standpoint, we highlight the mechanisms where naringenin could assume a critical anti-inflammatory role in COVID-19.
A variety of substances including vitamins D, E, and B12, omega-3, and flavonoids have demonstrated the potential to exhibit antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, possibly influencing the course of COVID-19. Notably, Naringenin (NAR), a crucial natural flavonoid present in citrus fruits, especially in grapefruit (43.5mg/100mL) and oranges (2.13mg/100mL)(19), showcases analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antitumor, and antiviral effects [
6]. It was observed that the intake of 8mL/kg of orange juice can amplify the NAR concentration, reaching levels ranging from 0 to 300 µg/L four hours post-consumption [
7,
8,
9,
10]).
Concerning weight management, naringenin, extracted from several citrus varieties (Sinetrol-XPur), of which 20% is naringenin, has displayed vitality and support for individuals with a BMI in the range of 26 to 29.9 kg/m2[100]. Notable improvements in primary overweight-related endpoints were observed 12 weeks post-initiation, including reductions in waist and hip fat, abdominal fat, and total weight. In addition, there was a marked decrease in both polygon and staging markers [
11,
12,
13]. Stohs and colleagues have reported the use of naringin as a supplementary agent (600mg) in weight management efforts. The lion’s share of recent research trends pertaining to NARINGRIN mainly focus on the fields of medicine, life sciences, and food science, with emphasis on processes, anti-inflammatory actions, and conclusion phases. Nevertheless, studies in the emerging sector are generally minimal, and notably, investigations into the effects of naringenin on human dermal fibroblasts are virtually absent. Therefore, this study intends to showcase the cytoprotective effects of naringenin on ultraviolet rays-affected human dermal fibroblasts, spotlighting the roles of key wrinkle response mediators such as NFκB activity, COX2, TNFα, IL6, and IL8. Through this, the current research aims to investigate the potential of utilizing naringenin as an effective preventive agent in cosmetic formulations.
When cells are treated with LPS, a known initiator of ROS generation, it triggers a variety of intracellular activation mechanisms, leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines and fetal factors. The inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), a crucial enzyme in generating NO (nitric oxide), functions independently from cellular Ca
2+ notifications and is predominantly found in macrophages, vascular smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, and hepatocytes. This enzyme is activated by various stimuli such as LPS and TNF-α in a wide array of cells including myocardial cells, leading to substantial production and secretion of NO. This activation unfortunately gives rise to a plethora of small peroxides and cyclones, which is a result of excessive generative activity disruptions, consequently inducing adverse effects stemming from the oxidative destruction of cells [
14,
15,
16,
17].
The regulation of the NF-κB system stands as a central factor in addressing the myriad skin problems common in today’s society, representing ancient signaling pathways that control metabolic processes. This mechanism, governed by opposing regulatory processes, seeks to suppress inflammatory cells in mammals. The primary focus currently lies within the sphere of functional cosmetics and the emerging inner beauty industry, although its current state of efficacy remains somewhat inadequate. Hence, this research undertook the task of investigating the interplay between naringenin - known for its anti-aging, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidative properties - and the NF-κB pathway.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Sample Preparation
In this study, human dermal fibroblasts (HDFs) were purchased from Lonza Switzerland and cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Hyclone, USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Hyclone), 1% penicillin/streptomycin (100 IU/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin; Invitrogen, USA) and cultured at 37 ° C and 5% CO2. Naringenin (Sigma-Aldrich, USA) was used to dissolve the purified powder (> 99%) in a suitable concentration in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma-Aldrich). Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a cell stimulating agent, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. For the experiment, the solution was dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO; Sigma-Aldrich) at a proper concentration. HDFs (1 × 106 cells / well) were incubated in a 60mm cell culture dish for 24 h. An appropriate concentration of naringenin was added to the culture medium. Lipopolyscharide was co-treated at a constant concentration for 24 h and analyzed 3 h later. The significance of PCR was validated using a melting curve. The gene expressions were compared for analysis by normalizing the β-actin expression.
2.2. Assessment of Cell Viability
The WST-1 Cell Proliferation Assay System utilizes a mechanism involving the transformation of tetrazolium salts (WST-1) into a color-yielding substance called formazan by mitochondrial dehydrogenase within cells. This process is employed to quantitatively gauge cell proliferation or survival abilities. During this experimental procedure, HDFs (3×103 cells/well) were cultured at a volume of 100 μL per well in a 96-well plate, which facilitates vigorous metabolic activities. Following an incubation period of 24 hours, these cells were simultaneously exposed to various agents including naringenin and LPS for an additional 24-hour period. After this, 10 μL of the EZ-Cytox cell viability assay kit reagent (ItsBio, Korea) was introduced to the incubated cells and allowed to incubate for an additional hour. The absorbance was then measured at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, USA). This procedure was replicated thrice to calculate the average cell survival rate along with the standard deviation.
2.3. qRT-PCR Analysis
Changes of gene expression caused by naringenin in the cells was quantitatively confirmed. qRT-PCR was performed by mixing 0.2 μM primers, 50 mM KCl, 20 mM Tris/HCl pH 8.4, 0.8 mM dNTP, 0.5 U Extaq DNA polymerase, 3 mM MgCl 2, and 1X SYBR green (Invitrogen). PCR was validated by melting curve. The melting curve confirmed the validity of PCR. Expression of each gene was standardized and compared. The primers used in this experiment are shown in
Table 1
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
PGE2 (Cayman chemical, USA; competitive) were evaluated using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit according to the instruction manual for the HDF culture medium. Prostaglandin E2, monoclonal antibody were immobilized on plastic cell culture dish wells. One hundred microliters of each culture medium was dispensed (at room temperature for 2 h). After washing five times each with a single washing buffer, 100 μL horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated antibody was added for 1 h at room temperature, and 100 μL of tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) was added and incubated for 30 min in a dark room. The absorbance was measured at 405–420 nm (PGE2)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All experiments were performed independently three times, and the results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Student’s t test was used to analyze all findings, with a p value of 0.05, 0.01, or 0.001 below considered as statistically significant (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Cytotoxicity
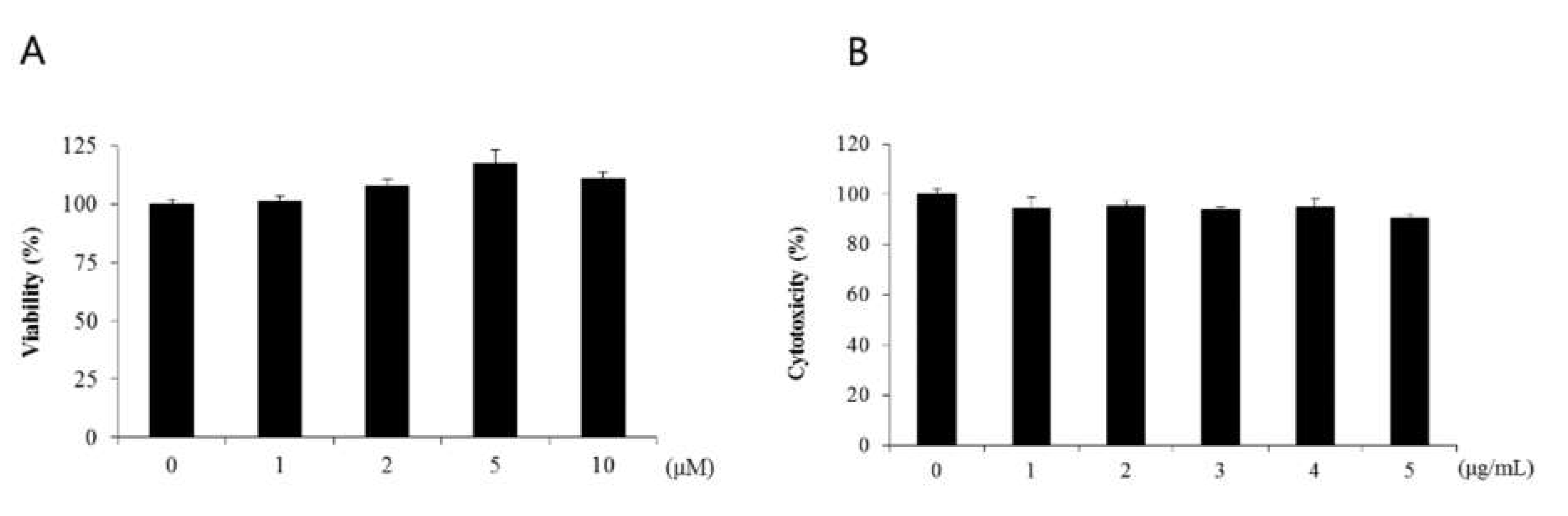
Lipopolysaccharide acts as an endotoxin in cells, activating signals such as MAPK, NF-κB, and IRF-3 and promoting excessive secretion of inflammatory cytokines (Lu et al. 2008). Lipopolysaccharide induced nuclear factor-кB activity through IκB phosphorylation and its degradation. In this study, WST-1 assay was performed to determine the cytotoxicity of naringenin in human dermal fibroblasts. Human dermal fibroblasts were treated with untreated control group and naringenin-treated group at 1-, 2-, 5-, and 10-μM dose levels, each respectively, for 24 h. Cell viability of untreated control group was set as 100%, and up to 1-μM dose level, the survival rate was shown to be 100% or more. When naringenin was treated at 1-, 2-, 5-, and 10-μM dose levels, the cell viability levels of 101%, 107%, 117%, and 110% did not decrease, confirming almost no toxicity (Figure 1a). To confirm the changes in the survival rate of cells, HDFs was treated with LPS at 1-, 2-, 3-, 4-, and 5-μg dose levels, respectively, and the survival rate was 94% at 1 μg/mL (Figure 1b).
Figure 3–1.
No toxicity towards HDFs was observed with the application of naringenin. The cell viability was assessed at different concentrations of LPS (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 μg) applied to HDFs. It was ascertained that the survival rate was 94% at a concentration of 1 μg/mL, which led to the selection of 1 μM as the optimum concentration for further usage.
Figure 3–1.
No toxicity towards HDFs was observed with the application of naringenin. The cell viability was assessed at different concentrations of LPS (1, 2, 3, 4, 5 μg) applied to HDFs. It was ascertained that the survival rate was 94% at a concentration of 1 μg/mL, which led to the selection of 1 μM as the optimum concentration for further usage.
3.2. The Impact of Naringenin on HDFs Inflammation Suppression Induced by LPS
1. Changes in NF-κB Expression
Within the NF-κB signaling pathway, LPS activates NF-κB through phosphorylation. This activation triggers a relocation to the nucleus, stimulating the transcription of inflammatory cytokines and mediators which might induce various diseases [
18,
19]
The NF-κB luciferase assay demonstrated that cellular spacing expanded to a level of 3.0 when treated with LPS. However, subsequent treatment with naringenin at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM resulted in a reduction to levels 2 and 1.4, respectively, illustrating a dose-dependent decrease facilitated by naringenin (Figure 2-1).
3.3. Changes in the Expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8
NF-κB activation effects on HDFs treated simultaneously with LPS and naringenin.
NF-κB reporter NIH-3T3 stable cells were cultured for an additional 24 hours after the cellular treatment at optimum conditions Right after adding it to the Luciferin, luminous intensity was measured using a luminometer. The luminous intensity of luciferin was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner. Results came back with averages of three independent experiments showing error bars with standard deviation. (*** p<0.001)
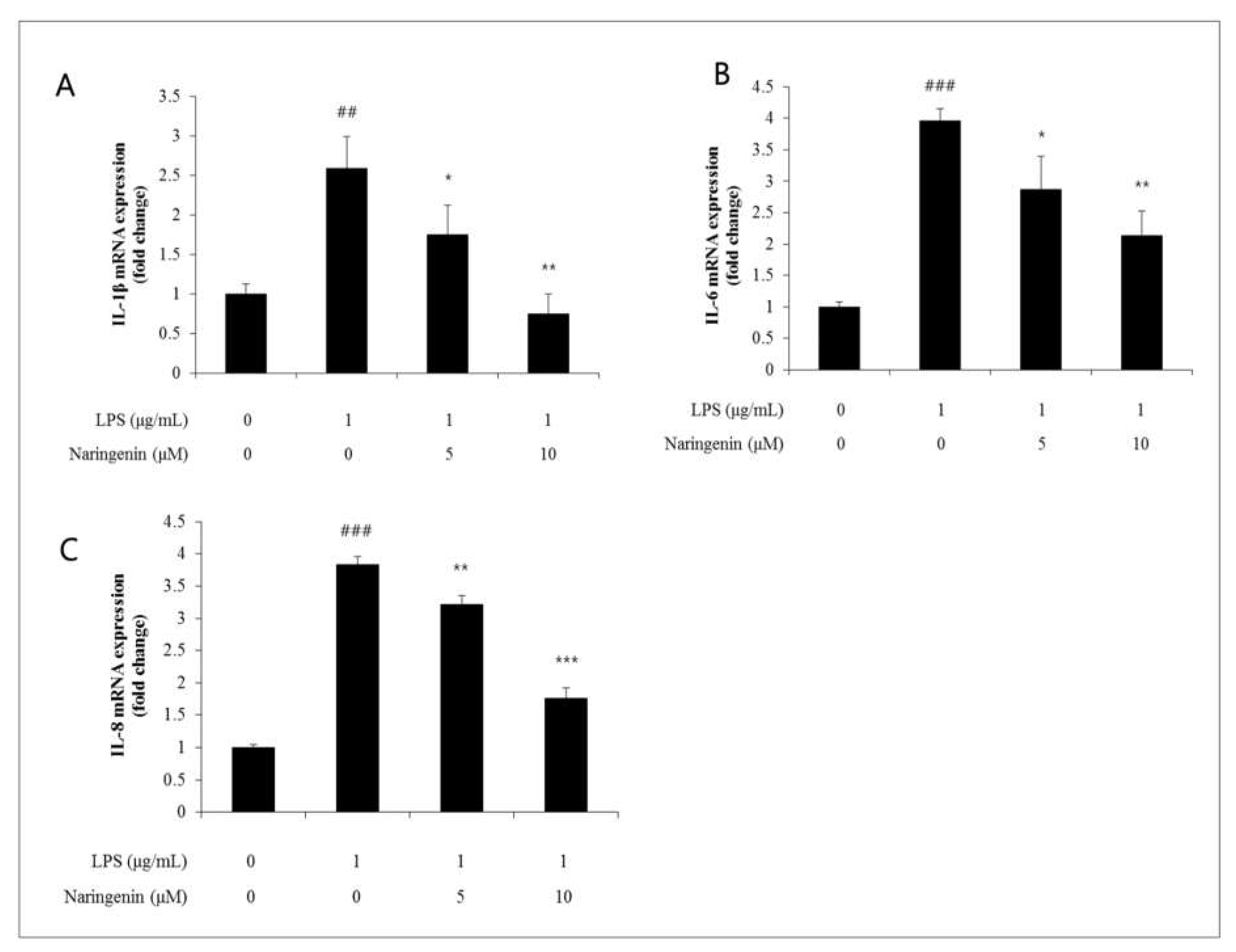
During the onset of inflammation, IL-1β serves as a significant cytokine that initiates febrile reactions by stimulating various systems, including the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis. This cytokine plays a vital role in activating the immune, neuroendocrine, and neuroimmune systems [
20]. Likewise, IL-6 is noted as a cytokine synthesized by a variety of cells such as T lymphocytes, B lymphocytes, neuroglial cells, mast cells, macrophages, endothelial cells, and fibroblasts. It is involved in initiating diverse inflammatory diseases, triggering acute phase reactions, and promoting lymphocyte proliferation. IL-8, another inflammatory cytokine, functions as a chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, and T cells. Belonging to the chemokine superfamily, it is secreted in response to stimuli like LPS or leukotrienes, facilitating neutrophil infiltration at the sites of inflammation. Furthermore, IL-8 exerts potent chemoattractive actions on neutrophils, eosinophils, and T-lymphocytes, enhancing the expression of adhesion molecules and encouraging the release of lysozyme and reactive oxygen species, thus actively participating in neutrophil activation. Moreover, the release of IL-6 and IL-8 can lead to skin conditions such as contact dermatitis and atopic dermatitis, potentially intensifying acute responses to various stimuli. This study examined the effects of naringenin on the dermal tissues, particularly focusing on the fluctuations in the expression levels of the IL-1β gene, utilizing qRT-PCR techniques. When LPS was applied in the presence of naringenin, the intercellular spacing amplified to 2.6 levels. This increase was moderated to 1.8 and 0.8 levels respectively when treated with 5 and 10 μM concentrations of naringenin, displaying a dose-dependent decline (Figure 3-8). Furthermore, the influence of naringenin on dermal tissues was analyzed by observing alterations in IL-6 gene expression through qRT-PCR methods. After the administration of LPS alongside naringenin, the intercellular space expanded to 3.9 levels, which then decreased to 2.8 and 2.1 levels with the application of 5 and 10 μM concentrations of naringenin, indicating a dose-dependent reduction. In a similar vein, the impact of naringenin on dermal tissues was evaluated by monitoring shifts in IL-8 gene expression using qRT-PCR techniques. Following the introduction of LPS with naringenin, the intercellular distance broadened to 3.8 levels, which later contracted to 3.2 and 1.8 levels upon treatment with 5 and 10 μM concentrations of naringenin, thereby verifying a dose-dependent decrease.
Figure 3–3.
(A) IL-1β, a representative cytokine that acts in the early stages of inflammation, increased by LPS, was reduced to 1.8 and 0.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations. (B) IL-8 increased by LPS also decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations, and (C) IL-8 increased by LPS also decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations. When treated separately, it decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels.
Figure 3–3.
(A) IL-1β, a representative cytokine that acts in the early stages of inflammation, increased by LPS, was reduced to 1.8 and 0.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations. (B) IL-8 increased by LPS also decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations, and (C) IL-8 increased by LPS also decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels when treated with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations. When treated separately, it decreased to 3.2 and 1.8 levels.
4. Changes in the Expression of COX2, PGE2
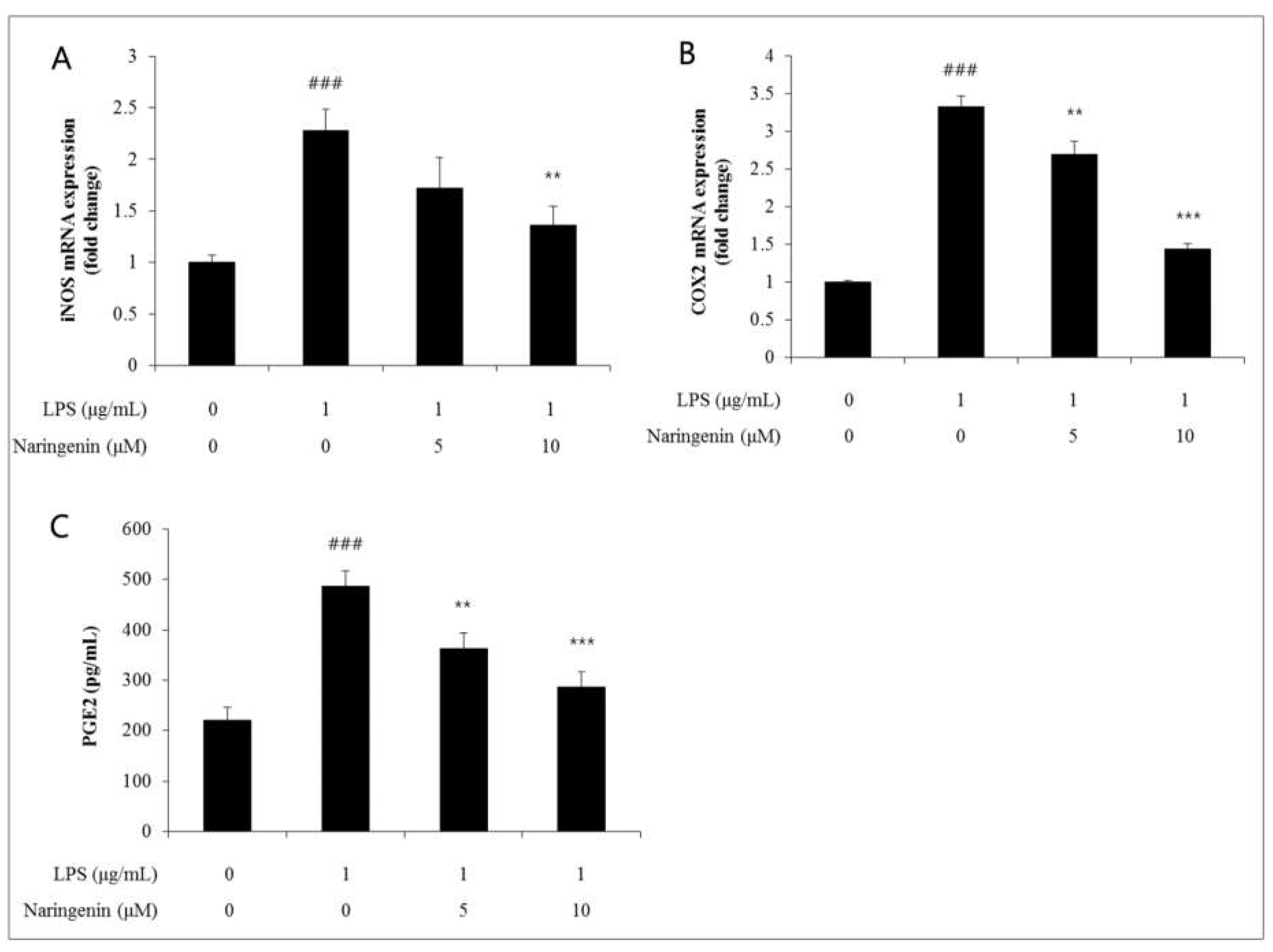
The inflammatory mediator, cyclooxygenase (COX), serves as a catalyst in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). This enzyme is classified into two subsets: COX1 and COX2. Particularly, COX2 is induced within inflammatory cells in response to inflammatory stimuli, and the PGE2 generated by COX2 acts as a pivotal inflammatory agent involved in processes such as pain sensation and fever initiation. Moreover, it actively participates in inflammatory responses, immune reactions, and promotes angiogenesis, thereby having a profound association with the onset of cancer. PGE2 is recognized as a significant inflammatory molecule, deeply involved in the pathogenesis of various diseases, undergoing synthesis from arachidonic acid through the action of COX2. This study examined the influence of naringenin on dermal tissue by evaluating the alterations in COX2 gene expression using qRT-PCR techniques.
This research conducted an analysis of the shifts in COX2 gene expression 24 hours after treating Human Dermal Fibroblasts (HDFs) with varying concentrations of naringenin, followed by a 3-hour LPS treatment. When naringenin was used for the LPS treatment, the intercellular space expanded up to 3.3 μM. This space then contracted to levels 2.7 and 1.4 when naringenin was applied at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM, respectively, thereby confirming a naringenin dosage-dependent decrease (Figure 3-3). Similarly, the effect of naringenin on dermal tissue was observed concerning the alterations in PGE2 gene expression, utilizing the ELISA assay technique. The cell gap escalated to 487 levels after LPS treatment along with naringenin. This gap reduced to 363 and 287 levels upon administering naringenin at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM, respectively, thus verifying a decline that is dependent on the naringenin concentration.
NF-κB activation effects on HDFs treated simultaneously with LPS and naringenin.
NF-κB reporter NIH-3T3 stable cells were cultured for an additional 24 hours after the cellular treatment at optimum conditions Right after adding it to the Luciferin, luminous intensity was measured using a luminometer. The luminous intensity of luciferin was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner. Results came back with averages of three independent experiments showing error bars with standard deviation. (*** p<0.001).
Figure 4–1.
(A)In the NADPH oxidase assay, when naringenin was treated at 5 and 10 μM concentrations, it decreased to 2.0 and 1.3 levels, and iNOS increased by LPS decreased to 1.7 and 1.4 levels when naringenin was treated at 5 and 10 μM concentrations.(B)The COX2 gene expression was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner(B). (C)The PGE2 gene expression was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner. Results came back with averages of three independent experiments showing error bars with standard deviation. (** p<0.01).
Figure 4–1.
(A)In the NADPH oxidase assay, when naringenin was treated at 5 and 10 μM concentrations, it decreased to 2.0 and 1.3 levels, and iNOS increased by LPS decreased to 1.7 and 1.4 levels when naringenin was treated at 5 and 10 μM concentrations.(B)The COX2 gene expression was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner(B). (C)The PGE2 gene expression was decreased by naringenin in a dose-dependent manner. Results came back with averages of three independent experiments showing error bars with standard deviation. (** p<0.01).
4. Discussion & Conclusions
In recent times, the escalation of air pollution, particularly from particulate matter, has been identified as a significant contributor to the onset of various ailments, including respiratory diseases. This predicament is exacerbated in our locale due to the supplementary pollutants emitted from factories and automobiles, which have a detrimental effect on the health of our community. It is widely acknowledged that the conventional aging process is dictated by genetic determinants and unfolds gradually over time, a phenomenon referred to as intrinsic skin aging. Accordingly, it is evident that the recent influx of particulate matter originating from China not only exacerbates atopic dermatitis and accelerates skin aging but also increases the likelihood of heightened sensations of skin irritation and itchiness, particularly among individuals with sensitive skin.
When it comes to treating dermatitis, steroids are commonly prescribed. However, their protracted use can lead to adverse side effects such as skin atrophy and vascular dilation. Recently, there has been a surge in interest in nanoparticle-based therapies for atopic dermatitis, with a particular focus on essential oils. These oils are notable for their small molecular size which facilitates easy absorption, and they possess moisturizing, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial properties, thereby intensifying research efforts to explore their efficacy in alleviating atopic dermatitis [
18,
19,
20].
Therefore, this study further implies the significant role of NF-κB activation in initiating and intensifying aging, by focusing on the relationship between the secretion of proteins associated with aging-related secretory phenotypes and aging itself (Rovillain et al., 2011). Hence, the research embarked on an exploration centered on the gene expressions of inflammatory agents, which are core components of SASP, including NF-κB subordinate genes IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, COX2, and PGE2. Through the inhibition of the gene expression of these primary SASP components via blocking the NF-κB pathway using naringenin, this study aims to ascertain its potential as an effective anti-inflammatory agent in vitro, setting the stage for further investigations into its prospects as an ingredient in anti-aging cosmetic products.
Firstly, the study conducted an extensive analysis of the impact of naringenin on cellular aging treatment and psychological suppression alleviation, utilizing bio-markers for a thorough investigation. During the LPS treatment, as depicted in the NF-κB luciferase analysis, the intercellular gap expanded to a 3.0 level. However, this gap reduced to levels of 2.0 and 1.4 when treated with naringenin concentrations of 5 and 10 μM, respectively. Significantly, the cytokine which initially amplified IL-1β due to LPS, exhibited reduced levels of 1.8 and 0.8 when administered with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM concentrations. Concurrently, IL-6 and IL-8 levels, elevated due to LPS, were registered at 2.8, 2.1, and are anticipated to be 3.2, 1.8 levels, respectively, when handled with the same naringenin concentrations. Meanwhile, the LPS-induced surge in COX2 was noted at 2.7 and 1.4 levels upon administering 5 and 10 μM of naringenin, respectively. Furthermore, a marked presence was noted for PGE2, registering levels of 363 and 287 under similar conditions.
Secondly, the study noted the antioxidative suppression effects of naringenin and NAC in inhibiting the formation of antimicrobial oxidative substances triggered by LPS. Aside from the untreated cases, which maintained a 100% rate, the total ROS quantity increased to a level of 2.1 following LPS treatment. Conversely, it was documented at 1.7 and 1.2 levels when naringenin was applied at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM. It is projected to stabilize at a level of 1.0 upon the administration of 10 mM of NAC. Experimental data suggest that at a lower concentration of 10 μM, naringenin enhances the ability of skin cells to disperse ROS more effectively compared to the control group treated with 10 mM of NAC, thus fostering an antioxidative suppression phenomenon. The NADPH oxidase analysis demonstrated levels of 2.0 and 1.3 when managed with naringenin at 5 and 10 μM, and the increase in iNOS due to LPS manifested at levels of 1.7 and 1.4 under similar circumstances. In opposition to the established views regarding LPS and the removal of free iron (Fe2+), the analysis revealed maintenance levels of 0.7 and 0.9 when treated with naringenin at concentrations of 5 and 10 μM.
References
- Stohs, S.J.; Preuss, H.G.; Keith, S.C.; Keith, P.L.; Miller, H.; Kaats, G.R. Effects of p-synephrine alone and in combination with selected bioflavonoids on resting metabolism, blood pressure, heart rate and self-reported mood changes. Int. J. Med Sci. 2011, 8, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Pers pect Biol. Pinho-Ribeiro FA, Zarpen AC, Mizokami SS, Borghi SM, Bordignon J, Silva RL, et al. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The citrus flavonone naringenin reduces lipopolysaccharideinduced inflammatory pain and leukocyte recruitment by inhibiting NFκB activation. J Nutr Biochem., 2016, 33, 8–14. [CrossRef]
- Lyu SY, Park WB, "Production of cytokine and NO by RAW 264.7 macrophages and PBMC in vitro incubation with flavonoids", 『Arch Pharm Res』, 28: 573-581, 2005.
- Hirai S, Kim YI, Goto T, Kang MS, Yoshimura M, Obata A, Yu R,Kawada, "Inhibitory effect of naringenin chacolone on inflammatory changes in the interaction between adipocytes and macrophages", 『Life Sci』, 81: 1272-79, 2007.
- Karuppagounder V, Arumugam S, Thandavarayan RA, "Naringenin ameliorates daunorubicin induced nephrotoxicity by mitigating AT1R, ERK1/2-NFҡB P65 mediated inflammation", 『j.intimp』, 28: 154-9, 2015.
- Després, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, K.G.M.M.; Zimmet, P.; Shaw, J. Metabolic syndrome—a new world-wide definition. A consensus statement from the International Diabetes Federation. Diabet Med 2006, 23, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, RP. Side effects of calcium channel blockers. Hypertension 1988, 11, II42–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnier, M.; Brunner, H.R. Angiotensin II receptor antagonists. Lancet 2000, 355, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sowers JR, Epstein M. Diabetes mellitus and associated hypertension, vascular disease, and nephropathy. Hypertension 1995, 26:869–79.
- Estaquio, C.; Castetbon, K.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Bertrais, S.; Deschamps, V.; Dauchet, L.; Péneau, S.; Galan, P.; Hercberg, S. The French National Nu- trition and Health Program Score is associated with nutritional status and risk of major chronic diseases. J Nutr 2008, 138, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Serdula, M.; Janket, S.-J.; Cook, N.R.; Sesso, H.D.; Willett, W.C.; Manson, J.E.; Buring, J.E. A prospective study of fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of type 2 diabetes in women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, K.; Appel, C. Polyphenols as dietary supplements: A double- edged sword. Nutrition and Dietary Supplements 2010, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripoli, E.; Guardia, M.L.; Giammanco, S.; Majo, D.D.; Giammanco, M. Cit- rus flavonoids: molecular structure, biological activity and nutritional properties: a review. Food Chem 2007, 104, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhr, U.; Kummert, A.L. The fate of naringin in humans: a key to grape- fruit juice-drug interactions? Clin Pharmacol Ther 1995, 58, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ameer, B.; Weintraub, R.A. Drug interactions with grapefruit juice. Clin Pharmacokinet 1997, 33, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.G. Fruit juice inhibition of uptake transport: a new type of food–drug interaction. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2010, 70, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.G.; Dresser, G.K.; Leake, B.F.; Kim, R.B. Naringin is a major and selective clinical inhibitor of organic anion-transporting polypeptide 1A2 (OATP1A2) in grapefruit juice. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007, 81, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresser, G.K.; Bailey, D.; Leake, B.; Schwarz, U.; Dawson, P.; Freeman, D.; Kim, R. Fruit juices inhibit organic anion transporting polypeptide– mediated drug uptake to decrease the oral availability of fexofenadine. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002, 71, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trombetta, D.; Cimino, F.; Cristani, M.; Mandalari, G.; Saija, A.; Ginestra, G.; Speciale, A.; Chirafisi, J.; Bisignano, G.; Waldron, K.; et al. In vitro protec- tive effects of two extracts from bergamot peels on human endothelial cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a). J Agric Food Chem 2010, 58, 8430–8436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-J.; Jung, U.J.; Cho, S.-J.; Jung, H.-K.; Shim, S.; Choi, M.-S. Citrus un- shiu peel extract ameliorates hyperglycemia and hepatic steatosis by altering inflammation and hepatic glucose- and lipid-regulating en- zymes in db/db mice. J Nutr Biochem 2013, 24, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.I.; Shin, H.S.; Kim, H.M.; Hong, Y.S.; Yoon, S.A.; Kang, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, M.H.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, S.J. Immature Citrus sunki peel extract exhibits antiobesity effects by beta-oxidation and lipolysis in high-fat diet-induced obese mice. Biol Pharm Bull 2012, 35, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramful D, Tarnus E, Rondeau P, Robert Da Silva C, Bahorun T, Bourdon E. Citrus fruit extracts reduce advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and H2O2-induced oxidative stress in human adipocytes. J Agric Food Chem 2010.
- Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Sheard, J.; Ying, Y. The effects of grapefruit on weight and insulin resistance: relationship to the metabolic syndrome. J Med Food 2006, 9, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Lists of primers.
Table 1.
Lists of primers.
| Gene |
Forward primer |
Forward primer |
| IL-6 |
TAACAGTTCCTGCATGGGCGGC |
AGGACAGGCACAAACACGCACC |
| IL-8 |
CTCTCTTGGCAGCCTTCCCTC |
AATCACTCTCAGTTCTTTG |
| IL-1β |
GATCCACACTCTCCAGCTGCA |
CAACCAACAAGTGATATTCTCCATG |
| COX2 |
CGCGGATCCGCGGTGAGAACCGTTTAC |
GCGAGGAAGCGGAAGAGTCTAGAGTCGACC |
| iNOS |
GCGTTACTCCACCAACAATGGCAA |
ATAGAGGATGAGCTGAGCATTCCA |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).