Submitted:
12 June 2024
Posted:
13 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. System Model
3.1. Conventional Micro Cell Model
3.2. IRS-Assisted Micro Cell Model
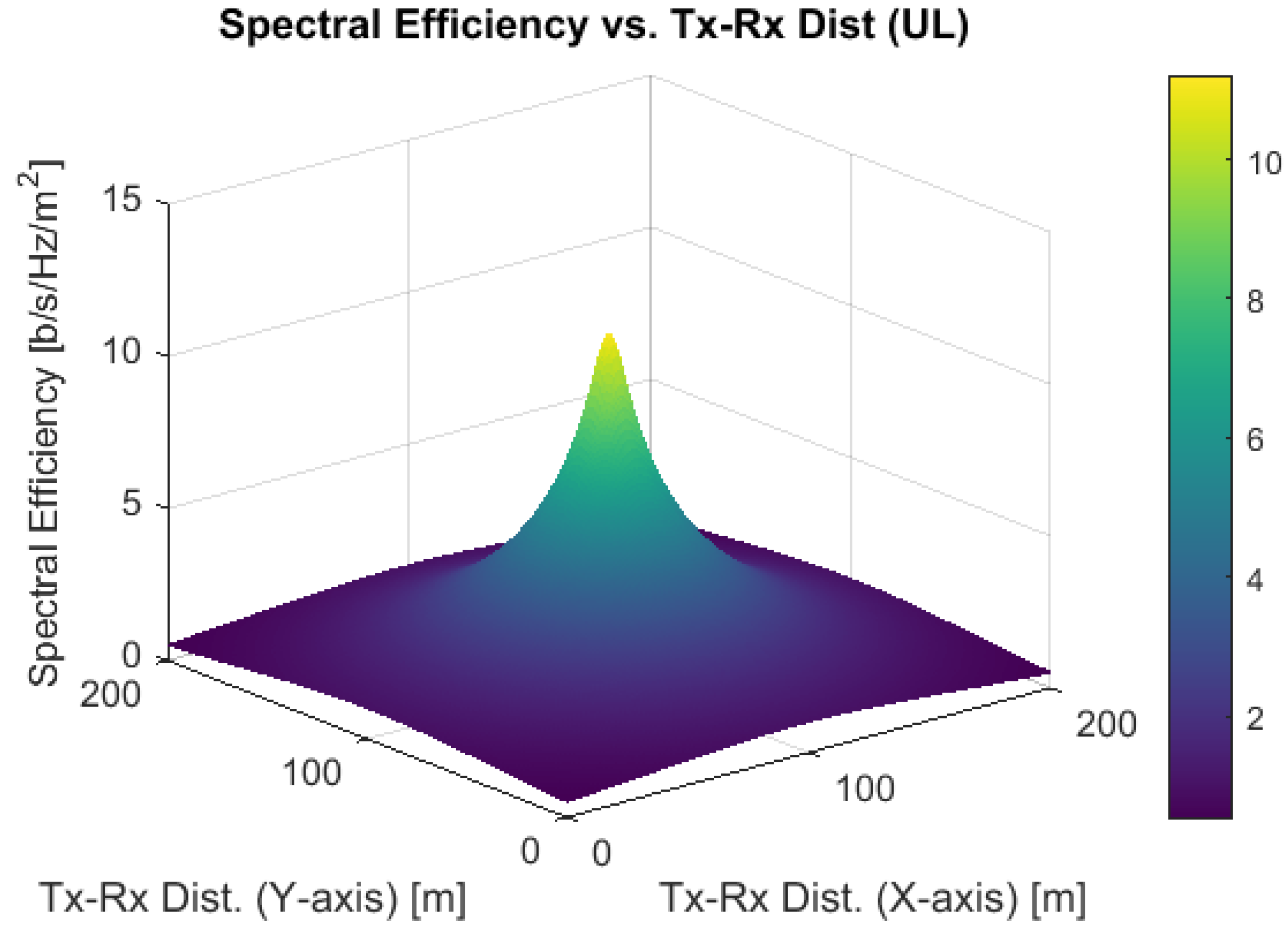
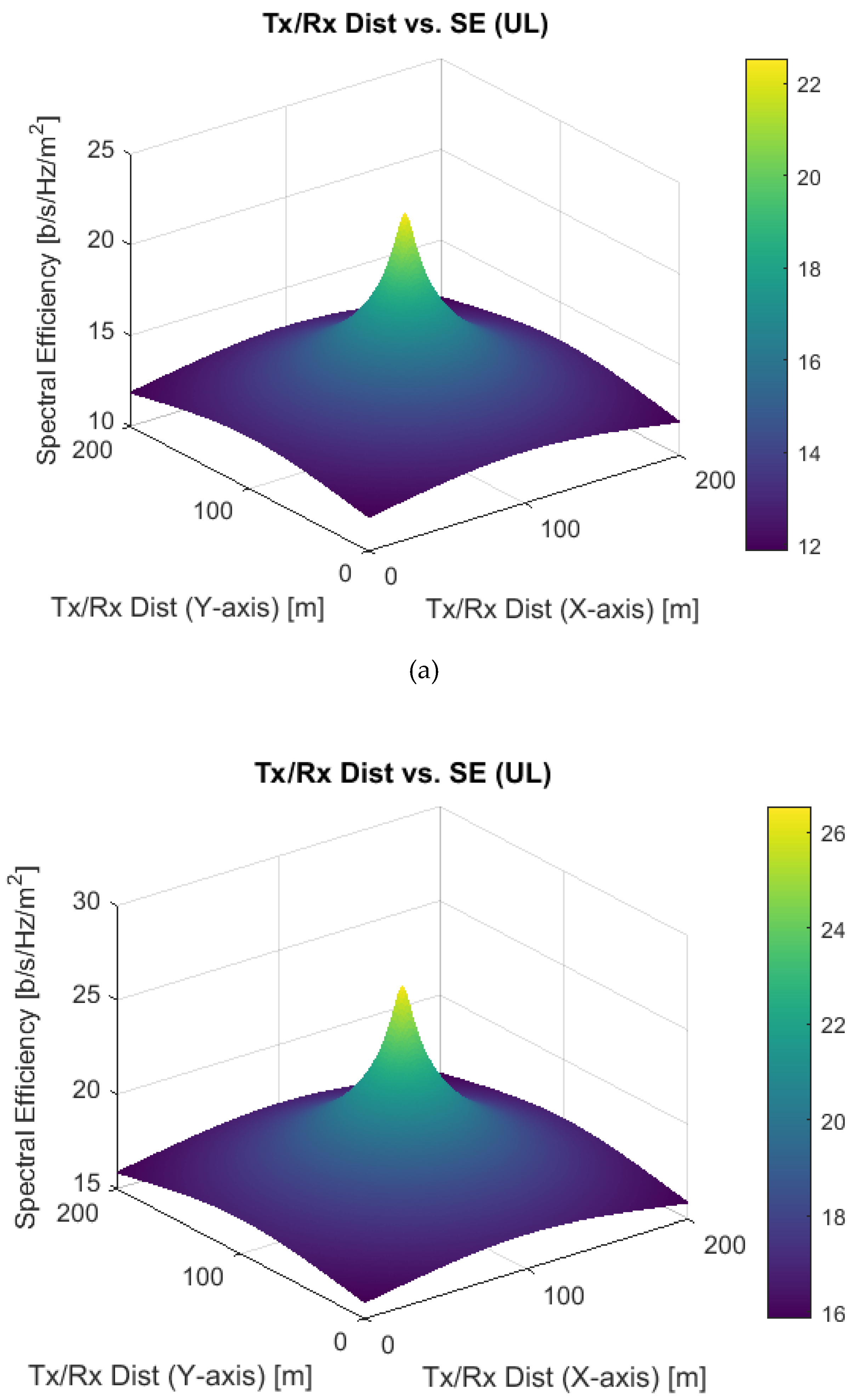
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusion
Declaration of Competing Interest
References
- Yazan Al-Alem, Yazan, Ahmed A. Kishk, and Raed M. Shubair. "Employing EBG in Wireless Inter-chip Communication Links: Design and Performance." In 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation and North American Radio Science Meeting, pp. 1303-1304. IEEE, 2020.
- Abdul Karim Gizzini, Marwa Chafii, Shahab Ehsanfar, and Raed M. Shubair. "Temporal Averaging LSTM-based Channel Estimation Scheme for IEEE 802.11 p Standard." arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.04829 (2021).
- Mohamed, I. AlHajri, Raed M. Shubair, and Marwa Chafii. "Indoor Localization Under Limited Measurements: A Cross-Environment Joint Semi-Supervised and Transfer Learning Approach." In 2021 IEEE 22nd International Workshop on Signal Processing Advances in Wireless Communications (SPAWC), pp. 266-270. IEEE, 2021.
- Yazan Al-Alem, Ahmed A. Kishk, and Raed Shubair. "Wireless chip to chip communication link budget enhancement using hard/soft surfaces." In 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), pp. 1013-1014. IEEE, 2018.
- Abdul Karim Gizzini, Marwa Chafii, Shahab Ehsanfar, and Raed M. Shubair. "Temporal Averaging LSTM-based Channel Estimation Scheme for IEEE 802.11 p Standard. arXiv:2106.04829 (2021).
- Mohamed, I. AlHajri, Nazar T. Ali, and Raed M. Shubair. "A cascaded machine learning approach for indoor classification and localization using adaptive feature selection." AI for Emerging Verticals: Human-robot computing, sensing and networking (2020): 205.
- Mikel Celaya-Echarri, Leyre Azpilicueta, Fidel Alejandro Rodríguez-Corbo, Peio Lopez-Iturri, Victoria Ramos, Mohammad Alibakhshikenari, Raed M. Shubair, and Francisco Falcone. "Towards Environmental RF-EMF Assessment of mmWave High-Node Density Complex Heterogeneous Environments." Sensors 21, no. 24 (2021): 8419. [CrossRef]
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, Josep M. Jornet, Asimina Kiourti, and Raj Mittra. "Graphene-Based Spiral Nanoantenna for Intrabody Communication at Terahertz." In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 799-800. IEEE, 2018.
- WafaNjima, Marwa Chafii, and Raed M. Shubair. "Gan based data augmentation for indoor localization using labeled and unlabeled data." In 2021 International Balkan Conference on Communications and Networking (BalkanCom), pp. 36-39. IEEE, 2021.
- Melissa Eugenia Diago-Mosquera, Alejandro Aragón-Zavala, Fidel Alejandro Rodríguez-Corbo, Mikel Celaya-Echarri, Raed M. Shubair, and Leyre Azpilicueta. "Tuning Selection Impact on Kriging-Aided In-Building Path Loss Modeling." IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 21, no. 1 (2021): 84-88. [CrossRef]
- Nishtha Chopra, Mike Phipott, Akram Alomainy, Qammer H. Abbasi, Khalid Qaraqe, and Raed M. Shubair. "THz time domain characterization of human skin tissue for nano-electromagnetic communication." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- M. I. AlHajri, N. T. Ali, and R. M. Shubair. "2.4 ghz indoor channel measurements data set.” UCI Machine Learning Repository, 2018.".
- Yazan Al-Alem, Raed M. Shubair, and Ahmed Kishk. "Clock jitter correction circuit for high speed clock signals using delay units a nd time selection window." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- Abdul Karim Gizzini, Marwa Chafii, Ahmad Nimr, Raed M. Shubair, and Gerhard Fettweis. "Cnn aided weighted interpolation for channel estimation in vehicular communications." IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 70, no. 12 (2021): 12796-12811. [CrossRef]
- M. I. AlHajri, N. T. Ali, and R. M. Shubair. "2.4 ghz indoor channel measurements data set." UCI Machine Learning Repository (2018).
- Asimina Kiourti, and Raed M. Shubair. "Implantable and ingestible sensors for wireless physiological monitoring: a review." In 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 1677-1678. IEEE, 2017.
- Hadeel Elayan, Hadeel, and Raed M. Shubair. "Towards an Intelligent Deployment of Wireless Sensor Networks." In Information Innovation Technology in Smart Cities, pp. 235-250. Springer, Singapore, 2018.
- Raed, M. Shubair, and Hadeel Elayan. "Enhanced WSN localization of moving nodes using a robust hybrid TDOA-PF approach." In 2015 11th International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT), pp. 122-127. IEEE, 2015.
- Nadeen, R. Rishani, Raed M. Shubair, and GhadahAldabbagh. "On the design of wearable and epidermal antennas for emerging medical applications." In 2017 Sensors Networks Smart and Emerging Technologies (SENSET), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2017.
- Hadeel Elayan, Cesare Stefanini, Raed M. Shubair, and Josep M. Jornet. "Stochastic noise model for intra-body terahertz nanoscale communication." In Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on Nanoscale Computing and Communication, pp. 1-6. 2018.
- Mohamed Ibrahim Alhajri, N. T. Ali, and R. M. Shubair. "2.4 ghz indoor channel measurements." IEEE Dataport (2018).
- Yazan Al-Alem, Raed M. Shubair, and Ahmed Kishk. "Efficient on-chip antenna design based on symmetrical layers for multipath interference cancellation." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- S. Elmeadawy, and R. M. Shubair. "Enabling technologies for 6G future wireless communications: Opportunities and challenges. arXiv 2020. arXiv:2002.06068.
- E. M. Ardi, R. M. Shubair, and M. E. Mualla. "Adaptive beamforming arrays for smart antenna systems: A comprehensive performance study." In IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society Symposium, 2004., vol. 3, pp. 2651-2654. IEEE, 2004.
- Yazan Al-Alem, Ahmed A. Kishk, and Raed M. Shubair. "One-to-two wireless interchip communication link." IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 18, no. 11 (2019): 2375-2378.
- Mayar Lotfy, Raed M. Shubair, Nassir Navab, and Shadi Albarqouni. "Investigation of focal loss in deep learning models for femur fractures classification." In 2019 International Conference on Electrical and Computing Technologies and Applications (ICECTA), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2019.
- R. M. Shubair, and A. Merri. "A convergence study of adaptive beamforming algorithms used in smart antenna systems." In 11th International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics [ANTEM 2005], pp. 1-5. IEEE, 2005.
- Yazan Al-Alem, Ahmed A. Kishk, and Raed M. Shubair. "Enhanced wireless interchip communication performance using symmetrical layers and soft/hard surface concepts." IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 68, no. 1 (2019): 39-50. [CrossRef]
- Dana Bazazeh, Raed M. Shubair, and Wasim Q. Malik. "Biomarker discovery and validation for Parkinson's Disease: A machine learning approach." In 2016 International Conference on Bio-engineering for Smart Technologies (BioSMART), pp. 1-6. IEEE, 2016.
- Raed, M. Shubair. "Improved smart antenna design using displaced sensor array configuration." Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Journal 22, no. 1 (2007): 83.
- Sandip Ghosal, Arijit De, Ajay Chakrabarty, and Raed M. Shubair. "Characteristic mode analysis of slot loading in microstrip patch antenna." In 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 1523-1524. IEEE, 2018.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Josep M. Jornet. "Characterising THz propagation and intrabody thermal absorption in iWNSNs." IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation 12, no. 4 (2018): 525-532. [CrossRef]
- WafaNjima, Marwa Chafii, ArseniaChorti, Raed M. Shubair, and H. Vincent Poor. "Indoor localization using data augmentation via selective generative adversarial networks." IEEE Access 9 (2021): 98337-98347. [CrossRef]
- Raed, M. Shubair, Amer Salah, and Alaa K. Abbas. "Novel implantable miniaturized circular microstrip antenna for biomedical telemetry." In 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 947-948. IEEE, 2015.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Nawaf Almoosa. "In vivo communication in wireless body area networks." In Information Innovation Technology in Smart Cities, pp. 273-287. Springer, Singapore, 2018.
- M. I. AlHajri, R. M. Shubair, L. Weruaga, A. R. Kulaib, A. Goian, M. Darweesh, and R. AlMemari. "Hybrid method for enhanced detection of coherent signals using circular antenna arrays." In 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation & USNC/URSI National Radio Science Meeting, pp. 1810-1811. IEEE, 2015.
- Omar Masood Khan, Qamar Ul Islam, Raed M. Shubair, and Asimina Kiourti. "Novel multiband Flamenco fractal antenna for wearable WBAN off-body communication applications." In 2018 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES), pp. 1-2. IEEE, 2018.
- Hadeel Elayan, and Raed M. Shubair. "On channel characterization in human body communication for medical monitoring systems." In 2016 17th International Symposium on Antenna Technology and Applied Electromagnetics (ANTEM), pp. 1-2. IEEE, 2016.
- Raed, M. Shubair, Abdulrahman S. Goian, Mohamed I. AlHajri, and Ahmed R. Kulaib. "A new technique for UCA-based DOA estimation of coherent signals." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- Hari Shankar Singh, SachinKalraiya, Manoj Kumar Meshram, and Raed M. Shubair. "Metamaterial inspired CPW-fed compact antenna for ultrawide band applications." International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering 29, no. 8 (2019): e21768. [CrossRef]
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Josep M. Jornet. "Bio-electromagnetic thz propagation modeling for in-vivo wireless nanosensor networks." In 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), pp. 426-430. IEEE, 2017.
- Raed Shubair, and Rashid Nuaimi. "Displaced sensor array for improved signal detection under grazing incidence conditions." Progress in Electromagnetics Research 79 (2008): 427-441. [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A. Ibrahim, and Raed M. Shubair. "Reconfigurable band-notched UWB antenna for cognitive radio applications." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2016.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, Akram Alomainy, and Ke Yang. "In-vivo terahertz em channel characterization for nano-communications in wbans." In 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), pp. 979-980. IEEE, 2016.
- Satish, R. Jondhale, Raed Shubair, Rekha P. Labade, Jaime Lloret, and Pramod R. Gunjal. "Application of supervised learning approach for target localization in wireless sensor network." In Handbook of Wireless Sensor Networks: Issues and Challenges in Current Scenario's, pp. 493-519. Springer, Cham, 2020.
- Muhammad, S. Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Raed M. Shubair, Antonio D. Capobianco, Benjamin D. Braaten, and Dimitris E. Anagnostou. "A four element, planar, compact UWB MIMO antenna with WLAN band rejection capabilities." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 62, no. 10 (2020): 3124-3131. [CrossRef]
- Hadeel Elayan, Cesare Stefanini, Raed M. Shubair, and Josep Miquel Jornet. "End-to-end noise model for intra-body terahertz nanoscale communication." IEEE transactions on nanobioscience 17, no. 4 (2018): 464-473. [CrossRef]
- E. M. Al-Ardi, R. M. Shubair, and M. E. Al-Mualla. "Performance evaluation of the LMS adaptive beamforming algorithm used in smart antenna systems." In 2003 46th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, vol. 1, pp. 432-435. IEEE, 2003.
- Amjad Omar, Maram Rashad, Maryam Al-Mulla, Hussain Attia, Shaimaa Naser, Nihad Dib, and Raed M. Shubair. "Compact design of UWB CPW-fed-patch antenna using the superformula." In 2016 5th International Conference on Electronic Devices, Systems and Applications (ICEDSA), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2016.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Asimina Kiourti. "On graphene-based THz plasmonic nano-antennas." In 2016 16th mediterranean microwave symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- Mohamed, I. AlHajri, Nazar T. Ali, and Raed M. Shubair. "A machine learning approach for the classification of indoor environments using RF signatures." In 2018 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), pp. 1060-1062. IEEE, 2018.
- Muhammad Saeed Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Raed M. Shubair, Antonio-Daniele Capobianco, Sajid Mehmood Asif, Benjamin D. Braaten, and Dimitris E. Anagnostou. "Ultra-compact reconfigurable band reject UWB MIMO antenna with four radiators." Electronics 9, no. 4 (2020): 584. [CrossRef]
- Maryam AlNabooda, Raed M. Shubair, Nadeen R. Rishani, and GhadahAldabbagh. "Terahertz spectroscopy and imaging for the detection and identification of illicit drugs." 2017 Sensors networks smart and emerging technologies (SENSET) (2017): 1-4.
- R. M. Shubair, A. Merri, and W. Jessmi. "Improved adaptive beamforming using a hybrid LMS/SMI approach." In Second IFIP International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks, 2005. WOCN 2005., pp. 603-606. IEEE, 2005.
- Ala Eldin Omer, George Shaker, Safieddin Safavi-Naeini, Kieu Ngo, Raed M. Shubair, Georges Alquié, Frédérique Deshours, and Hamid Kokabi. "Multiple-cell microfluidic dielectric resonator for liquid sensing applications." IEEE Sensors Journal 21, no. 5 (2020): 6094-6104. [CrossRef]
- Samar Elmeadawy and Raed M. Shubair. "6G wireless communications: Future technologies and research challenges." In 2019 international conference on electrical and computing technologies and applications (ICECTA), pp. 1-5. IEEE, 2019.
- Zhenghua Chen, Mohamed I. AlHajri, Min Wu, Nazar T. Ali, and Raed M. Shubair. "A novel real-time deep learning approach for indoor localization based on RF environment identification." IEEE Sensors Letters 4, no. 6 (2020): 1-4. [CrossRef]
- Mohammed S Al-Basheir, Raed M Shubai, and Sami M. Sharif. "Measurements and analysis for signal attenuation through date palm trees at 2.1 GHz frequency." (2006).
- Rui Zhang, Ke Yang, Akram Alomainy, Qammer H. Abbasi, Khalid Qaraqe, and Raed M. Shubair. "Modelling of the terahertz communication channel for in-vivo nano-networks in the presence of noise." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2016.
- R. M. Shubair, and A. Merri. "Convergence of adaptive beamforming algorithms for wireless communications." In Proc. IEEE and IFIP International Conference on Wireless and Optical Communications Networks, pp. 6-8. 2005.
- R. Karli, H. Ammor, R. M. Shubair, M. I. AlHajri, and A. Hakam. "Miniature Planar Ultra-Wide-Band Microstrip Patch Antenna for Breast Cancer Detection." Skin 1 (2016): 39" Skin 1 (2016): 39.
- Hadeel Elayan, Pedram Johari, Raed M. Shubair, and Josep Miquel Jornet. "Photothermal modeling and analysis of intrabody terahertz nanoscale communication." IEEE transactions on nanobioscience 16, no. 8 (2017): 755-763. [CrossRef]
- Raed M. Shubair, and Ali Hakam. "Adaptive beamforming using variable step-size LMS algorithm with novel ULA array configuration." In 2013 15th IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, pp. 650-654. IEEE, 2013.
- M. S. Khan, F. Rigobello, Bilal Ijaz, E. Autizi, A. D. Capobianco, R. Shubair, and S. A. Khan. "Compact 3-D eight elements UWB-MIMO array." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 60, no. 8 (2018): 1967-1971.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, Josep Miquel Jornet, and Raj Mittra. "Multi-layer intrabody terahertz wave propagation model for nanobiosensing applications." Nano communication networks 14 (2017): 9-15.
- Goian, Mohamed I. AlHajri, Raed M. Shubair, Luis Weruaga, Ahmed Rashed Kulaib, R. AlMemari, and Muna Darweesh. "Fast detection of coherent signals using pre-conditioned root-MUSIC based on Toeplitz matrix reconstruction." In 2015 IEEE 11th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), pp. 168-174. IEEE, 2015.
- Saad Alharbi, Raed M. Shubair, and Asimina Kiourti. "Flexible antennas for wearable applications: Recent advances and design challenges." (2018): 484-3.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Asimina Kiourti. "Wireless sensors for medical applications: Current status and future challenges." In 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), pp. 2478-2482. IEEE, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed AlHajri, Abdulrahman Goian, Muna Darweesh, Rashid AlMemari, Raed Shubair, Luis Weruaga, and Ahmed AlTunaiji. "Accurate and robust localization techniques for wireless sensor networks. arXiv:1806.05765 (2018).
- Muhammad S. Khan, Syed A. Naqvi, Adnan Iftikhar, Sajid M. Asif, Adnan Fida, and Raed M. Shubair. "A WLAN band-notched compact four element UWB MIMO antenna." International Journal of RF and Microwave Computer-Aided Engineering 30, no. 9 (2020): e22282.
- Raed M. Shubair and Hadeel Elayan. "In vivo wireless body communications: State-of-the-art and future directions." In 2015 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), pp. 1-5. IEEE, 2015.
- M. I. AlHajri, N. Alsindi, N. T. Ali, and R. M. Shubair. "Classification of indoor environments based on spatial correlation of RF channel fingerprints." In 2016 IEEE international symposium on antennas and propagation (APSURSI), pp. 1447-1448. IEEE, 2016.
- Ala Eldin Omer, George Shaker, Safieddin Safavi-Naeini, Georges Alquié, Frédérique Deshours, Hamid Kokabi, and Raed M. Shubair. "Non-invasive real-time monitoring of glucose level using novel microwave biosensor based on triple-pole CSRR." IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems 14, no. 6 (2020): 1407-1420. ttps://doi.org/10.1109/tbcas.2020.3038589.
- Hadeel Elayan, Raed M. Shubair, and Asimina Kiourti. "Wireless sensors for medical applications: Current status and future challenges." In 2017 11th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EUCAP), pp. 2478-2482. IEEE, 2017.
- E. M. Al-Ardi, Raed M. Shubair, and M. E. Al-Mualla. "Performance evaluation of direction finding algorithms for adapative antenna arrays." In 10th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, 2003. ICECS 2003. Proceedings of the 2003, vol. 2, pp. 735-738. IEEE, 2003.
- Raed M. Shubair, Amna M. AlShamsi, Kinda Khalaf, and Asimina Kiourti. "Novel miniature wearable microstrip antennas for ISM-band biomedical telemetry." In 2015 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Raed M. Shubair and Hadeel Elayan. "In vivo wireless body communications: State-of-the-art and future directions." In 2015 Loughborough Antennas & Propagation Conference (LAPC), pp. 1-5. IEEE, 2015.
- E. M. Al-Ardi, R. M. Shubair, and M. E. Al-Mualla. "Investigation of high-resolution DOA estimation algorithms for optimal performance of smart antenna systems." (2003): 460-464.
- Malak Y. ElSalamouny, and Raed M. Shubair. "Novel design of compact low-profile multi-band microstrip antennas for medical applications." In 2015 loughborough antennas & propagation conference (LAPC), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2015.
- Ebrahim M. Al-Ardi, Raed M. Shubair, and Mohammed E. Al-Mualla. "Computationally efficient DOA estimation in a multipath environment using covariance differencing and iterative spatial smoothing." In 2005 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, pp. 3805-3808. IEEE, 2005.
- Amjad Omar, and Raed Shubair. "UWB coplanar waveguide-fed-coplanar strips spiral antenna." In 2016 10th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), pp. 1-2. IEEE, 2016.
- R. M. Shubair and Y. L. Chow. "A closed-form solution of vertical dipole antennas above a dielectric half-space." IEEE transactions on antennas and propagation 41, no. 12 (1993): 1737-1741. https://doi.org/10.1109/8.273319. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad Saeed Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Raed M. Shubair, Antonio-D. Capobianco, Benjamin D. Braaten, and Dimitris E. Anagnostou. "Eight-element compact UWB-MIMO/diversity antenna with WLAN band rejection for 3G/4G/5G communications." IEEE Open Journal of Antennas and Propagation 1 (2020): 196-206. [CrossRef]
- Pradeep Kumar Singh, Bharat K. Bhargava, Marcin Paprzycki, Narottam Chand Kaushal, and Wei-Chiang Hong, eds. Handbook of wireless sensor networks: issues and challenges in current Scenario's. Vol. 1132. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer, 2020.
- Muhammad Saeed Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Antonio-Daniele Capobianco, Raed M. Shubair, and Bilal Ijaz. "Pattern and frequency reconfiguration of patch antenna using PIN diodes." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 59, no. 9 (2017): 2180-2185. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Shubair and A. Al-Merri. "Robust algorithms for direction finding and adaptive beamforming: performance and optimization." In The 2004 47th Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 2004. MWSCAS'04., vol. 2, pp. II-II. IEEE, 2004.
- Muhammad Saeed Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Antonio-Daniele Capobianco, Raed M. Shubair, and Bilal Ijaz. "Pattern and frequency reconfiguration of patch antenna using PIN diodes." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 59, no. 9 (2017): 2180-2185. [CrossRef]
- R. M. Shubair. "Robust adaptive beamforming using LMS algorithm with SMI initialization." In 2005 IEEE Antennas and Propagation Society International Symposium, vol. 4, pp. 2-5. IEEE, 2005.
- M. Saeeed Khan, Adnan Iftikhar, Sajid M. Asif, Antonio-Daniele Capobianco, and Benjamin D. Braaten. "A compact four elements UWB MIMO antenna with on-demand WLAN rejection." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 58, no. 2 (2016): 270-276. [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim M. Al-Ardi, \Raed M. Shubair, and Mohammed E. Al-Mualla. "Direction of arrival estimation in a multipath environment: An overview and a new contribution." Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Journal 21, no. 3 (2006): 226.
- M. Saeed Khan, A-D. Capobianco, Sajid M. Asif, Adnan Iftikhar, Benjamin D. Braaten, and Raed M. Shubair. "A pattern reconfigurable printed patch antenna." In 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), pp. 2149-2150. IEEE, 2016.
- Ali Hakam, Raed M. Shubair, and Ehab Salahat. "Enhanced DOA estimation algorithms using MVDR and MUSIC." In 2013 International Conference on Current Trends in Information Technology (CTIT), pp. 172-176. IEEE, 2013.
- Ahmed A. Ibrahim, Jan Machac, and Raed M. Shubair. "Compact UWB MIMO antenna with pattern diversity and band rejection characteristics." Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 59, no. 6 (2017): 1460-1464. [CrossRef]
- Fahad Belhoul, Raed M. Shubair, and Mohammed E. Al-Mualla. "Modelling and performance analysis of DOA estimation in adaptive signal processing arrays." In ICECS, pp. 340-343. 2003.
- Menna El Shorbagy, Raed M. Shubair, Mohamed I. AlHajri, and Nazih Khaddaj Mallat. "On the design of millimetre-wave antennas for 5G." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-4. IEEE, 2016.
- M. A. Al-Nuaimi, R. M. Shubair, and K. O. Al-Midfa. "Direction of arrival estimation in wireless mobile communications using minimum variance distortionless response." In The Second International Conference on Innovations in Information Technology (IIT’05), pp. 1-5. 2005.
- M. I. AlHajri, A. Goian, M. Darweesh, R. AlMemari, R. M. Shubair, L. Weruaga, and A. R. Kulaib. "Hybrid RSS-DOA technique for enhanced WSN localization in a correlated environment." In 2015 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Research (ICTRC), pp. 238-241. IEEE, 2015.
- Mohamed I. AlHajri, Nazar T. Ali, and Raed M. Shubair. "Indoor localization for IoT using adaptive feature selection: A cascaded machine learning approach." IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 18, no. 11 (2019): 2306-2310. [CrossRef]
- Mohamed I. AlHajri, Nazar T. Ali, and Raed M. Shubair. "Classification of indoor environments for IoT applications: A machine learning approach." IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters 17, no. 12 (2018): 2164-2168. [CrossRef]
- Nishtha Chopra, Mike Phipott, Akram Alomainy, Qammer H. Abbasi, Khalid Qaraqe, and Raed M. Shubair. "THz time domain characterization of human skin tissue for nano-electromagnetic communication." In 2016 16th Mediterranean Microwave Symposium (MMS), pp. 1-3. IEEE, 2016.
- Z. Chu, Z. Z. Chu, Z. Zhu, X. Li, F. Zhou, L. Zhen and N. Al-Dhahir, "Resource Allocation for IRS Assisted Wireless Powered FDMA IoT Networks," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal. [CrossRef]
- X. Li, Q. X. Li, Q. Zhu and Y. Wang, "IRS-Assisted Crowd Spectrum Sensing in B5G Cellular IoT Networks," 2020 International Conference on Wireless Communications and Signal Processing (WCSP), 2020, pp. 761-765.
- S. Verma, S. S. Verma, S. Kaur, M. A. Khan and P. S. Sehdev, "Toward Green Communication in 6G-Enabled Massive Internet of Things," in IEEE Internet of Things Journal, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 5408-5415, 21. 20 April. [CrossRef]
- F. C. Okogbaa et al., “Design and Application of Intelligent Reflecting Surface (IRS) for Beyond 5G Wireless Networks: A Review,” MDPI-Sensors, vol. 22, no. 7, 22. 20 March. [CrossRef]
- N. Hassan and X. Fernando, "Interference Mitigation and Dynamic User Association for Load Balancing in Heterogeneous Networks," in IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, vol. 68, no. 8, pp. 7578-7592, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- W. Tang et al., "Wireless Communications With Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface: Path Loss Modeling and Experimental Measurement," in IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 421-439, Jan. 2021. ttps://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2020.3024887.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




