Preprint
Article
Polyelectrolyte - Surfactant Mixture Effects on Bulk Properties and Antibacterial, Cytotoxic Activity of Sulfur Nanoparticles
Altmetrics
Downloads
109
Views
72
Comments
0
A peer-reviewed article of this preprint also exists.
Submitted:
13 June 2024
Posted:
13 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Alerts
Abstract
Elemental sulfur, commonly known for its wide range of biological activity, has a long history of being used to protect all garden and vegetable crops from a range of pests and diseases, including powdery mildew, ascochyta blight, clubroot, plant mites, oidium, anthracnose, and scab. In the present study, a quick and environmentally friendly approach has been developed for the synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles with antibacterial activity. Sulfur nanoparticles (SNPs) were prepared by modifying the surface of elemental sulfur using various polyelectrolyte-surfactant mixtures (PSM) including NaCMC-SDBS and PHMG-CTAB. The SNPs were characterized by UV–visible spectrophotometry, X-ray diffraction (XRD), and thermogravimetric analysis (TG/DSC), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), with the SNPs showing an almost spherical shape with an average size in the range of 150-200 nm. The antibacterial activity of the sulfur nanoparticles was tested using against gram-positive S. aureus and E. faecium and gram-negative E. coli and P. aeruginosa bacteria. From this, it could be seen that SNPs exhibited significant antimicrobial activity against gram-positive bacteria, i.e., S. aureus and E. faecium. The in vitro cytotoxicity of the SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 studied to normal (MeT-5A) and tumorous (MCF-7) human cell lines was assessed in the concentration range from 500 μg/ml to 0.12 mg/ml, from which it was determined as being non-cytotoxic. The received products can be considered for potential application in agriculture and medicine.
Keywords:
Subject: Chemistry and Materials Science - Materials Science and Technology
1. Introduction
Element sulfur is naturally a pale yellow, insoluble solid that is odorless and brittle, and chemically and biologically active, and which has accordingly seen extensive application in the field of agriculture to combat various kind of mites (ixodid mites, scabies, chicken mites, spider mites), lice, bedbugs, fleas, etc. [1].
However, sulfur has been employed in various forms in contemporary times for crop protection, and has been recognized as safe for such [2,3,4]. It is a significant element in the promotion of plant growth and is synthesized naturally in several plants as a part of their defense against pathogenic infections and invasions [5,6]. In spite of soil supplementation, low-dimensional sulfur particles have shown considerable antimicrobial potential with regard to various fungal (Fusraium, Venturia, Aspergellus, Candida, etc.) and bacterial (Pseudomonas, Staphylococcus, etc.) species, and shows considerable promise for use as a broad spectrum pesticide [7,8]. Furthermore, field resistance to elemental sulfur has not been reported as it has multimodal action that targets multiple sites in phytopathogens [7,9]. Active research focused on the development of new materials based on sulfur nanoparticles with anti-infectious properties is a particular area of study in the modern science of nanodispersed materials. A number of different methods of synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles have been reported in the literature, such as electrochemical methods [10], water-oil microemulsion [11,12], eggshell membrane templating [13], heating sublimed sulfur and polyethylene glycol-200 [14], chemical precipitation [15], the supersaturated solvent method [16], the surfactant-assisted route [17,18], liquid phase precipitation [19], H2S reduction by iron chelates in W/O microemulsion [20], and ultrasonic treatment of sulfur-cystine solution [21]. These methods have many disadvantages due to difficulties in scaling up such processes, separation and purification of nanoparticles from the microemulsion, having multistage synthetic processes, and the use of various inorganic and organic acids which requires multiple treatments, and which could potentially incur significant harm to human health when using poisonous gases such as hydrogen sulfide.
Polyelectrolytes (PELs), surfactants, and their mixtures are ubiquitous in nature and technology due to their unique properties and versatile functionality. This combination offers synergistic effects that enhance performance in different formulations [22]. When combined, surfactants and polymers can enhance each other's performance, and indeed provide additional benefits; for instance, surfactants can improve the dispersibility of the particles, while polymers can contribute to the stability and rheological properties of the suspension. Such combinations are often used in formulations such as emulsions, gels, coatings, and flocculants. Overall, the synergy between surfactants and polymers offers a wide range of applications and benefits, making them valuable components in many industrial and consumer products [23].
In this study, a method for obtaining SNPs through mechanical and ultrasonic grinding is presented. SNPs were obtained by modifying the surface of sulfur with various polyelectrolyte-surfactant mixtures, including NaCMC-SDBS (SNPs-1) and PHMG-CTAB (SNPs-2). The synthesized SNPs were characterized using various analytical techniques. The antibacterial activities of the synthesized SNPs were assessed using various cell lines, and the in vitro cytotoxicity of the studied SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 against normal (MeT-5A) and tumor (MCF-7) human cell lines was assessed in the concentration range 500 μg/ml to 0.12.mg/ml.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Sulfur (98%, GOST 127.1, Tengizchevroil, Kazakhstan), cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate (SDBS) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA, ≥ 99%), whilst sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC, 99%) was purchased from Tianjin Heowns Biochem. LLC., (China), and polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride (PHMG-HCl) from Quzhou Ebright chemicals. Co. Ltd. (China).
2.2. Test Strains
The antimicrobial properties of SNPs were tested against gram-positive bacteria (Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P, Enterococcus faecium ATCC 700221), gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli ATCC 8739, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 1790, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 10031), two strains of yeasts (Candida albicans ATCC 10231, Candida utilis), as well as one fungus (Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404). All test strains were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC).
2.3. Test System
The cytotoxicity of sulfur nanoparticle assays were evaluated in two different types of human tumor cell lines, MeT-5A and MCF7.
The MeT-5A cell culture consists of SV40-transformed human mesothelial cells. The cells effectively proliferate at a concentration of 1 × 105 cells/cm2, reaching 100% growth within two to three days of cultivation. The culture medium used is RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% FBS. The cells are cultivated under the following conditions: 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. Viability after cryopreservation is ≥ 90% (staining with trypan blue before cultivation). The source of the cell culture is ATCC.
The MCF7 cell culture is a line of human breast adenocarcinoma. The MCF7 line retains some characteristics of differentiated mammary epithelium, including the ability to process estradiol via cytoplasmic estrogen receptors and express the oncogene WNT7B. This cell line is intended solely for scientific laboratory research. The cells effectively proliferate at a concentration of 1 × 105 cells/cm2, reaching 100% growth within two to three days of cultivation. The culture medium is RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. The cells are cultivated under the following conditions: 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% humidity. Viability after cryopreservation is ≥ 90% (staining with trypan blue before cultivation). The source of the cell culture is ATCC.
2.4. Preparation of Sulfur Nanoparticles
Preparation of SNPs was carried out in two stages. In the first stage, 10 g of crystalline sulfur was milled in an Ultra Centrifugal Mill ZM 300 (Retsch, Germany) for 3 min. The size of the sulfur powder grains was in the range 5-60 microns. In the second stage, the milled sulfur powders were dispersed into 100 ml of PSM aqueous solution and ultrasonicated (Sonopuls, Bandelin Electronic UW 200, Germany) for 10 min at an amplitude of 60%, which corresponded to an energy input of 367 J/cm3. On/off pulses of 2/2 s were used to reduce heat generation. The suspension temperature after treatment was about 50 °C. Then the crushed sulfur was dried in the device Christ ALPHA 1-1 LD plus (Germany) and the experiment was replicated three times.
2.5. Characterization
The surface charge of SNPs was evaluated via zeta potential and particle size using the dynamic light scattering (DLS) method using a Photocor Compact-Z (Fotokor LLC, Moscow, Russian). The UV-vis electronic absorption patterns of the SNPs were examined in the range of 190-1100 nm using a LAMBDA-35 UV-vis spectrophotometer (PerkinElmer, USA) to confirm the formation of SNPs. The thermal stability of the SNPs was evaluated using a thermogravimetric analyzer (STA 449 F1 Jupiter, NETZSCH, Germany). About 10 mg of each sample in a standard aluminum pan was heated from room temperature to 600 °C at a heating rate of 10 °C/min under a nitrogen flow rate of 50 cm3/min. Derivatives of TG/DSC were determined using the central finite difference method. The X-ray diffraction patterns of SNPs were investigated using an XRD diffractometer (PANalytical X’pert Pro MRD Diffractometer, Amsterdam, Netherlands). The spectra were recorded using Cu Kα radiation (wavelength of 0.1541 nm) and a nickel monochromator operated at a voltage of 40 kV and a current of 40 mA at diffraction angles in the range of 2θ = 5-80° at a scanning speed of 0.4°/min. The morphologies, such as size and shape, of the SNPs were evaluated using a scanning electron microscopy (SEM). For this purpose, 10 μL of SNP water suspension was applied dropwise onto a carbon-coated copper grid and allowed to dry, the morphological image of which was recorded using a Quanta 3D 200i (FEITM (Netherlands)) operated at an accelerating voltage of 30 kV. Elemental analysis of the SNPs was performed using energy-dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) as part of an SEM instrument (Quanta 3D 200i (FEITM) (Netherlands)).
2.6. Antibacterial Activity of SNPs
2.6.1. Preparation of Inoculum
The gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria were precultured overnight in a Mueller Hinton broth (MHB) in a rotary shaker at 37 ± 1 °C. Afterward, each strain was adjusted at a concentration of 1.5 × 108 cfu/ml using 0.5 McFarland standard and densitometer DEN-1 [24]. The yeast and fungal inoculums were prepared from the 48 h culture of isolates in Sabouraud agar. The densitometer (DEN-1, Biosan) was used to adjust the density to a final concentration of 2.5 × 106 spores/ml for fungi, and 2.5 × 106 cells/ml for yeasts.
2.6.2. Procedure
The Agar well diffusion method was used to screen the antibacterial and antifungal activities of SNPs as displayed by Daoud et al. [25] One ml of fresh bacterial or fungi culture was pipetted into the center of a sterile Petri dish. Molten cooled Muller Hinton (MHA) for bacteria, and Sabouraud agar for fungi, was then poured into the Petri dish containing the inoculum and mixed well. Upon solidification, wells were made using a sterile cork borer (6 mm in diameter) into agar plates containing inoculums. Then, 100 μl of each sample (hydrophilic sulfur nanoparticles) was added to respective wells. The concentration of nanoparticles was 10 mg/ml. The plates were placed at room temperature for 30 min to allow the samples to diffuse well into the agar. Then, the plates were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 h. Antimicrobial activity was detected by measuring the zone of inhibition (including well diameter) that appeared after the incubation period. Sulfur at a concentration of 10 mg/ml was used as a reference item.
2.7. Determination of Cytotoxicity of SNPs In Vitro
The investigated SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 were provided at a concentration of 1 mg/ml diluted in dH2O. The investigated substances were added once to wells containing cell suspensions of tumor cell lines at the following concentrations: 500.0, 250.0, 125.0, 62.5, 31.25, 15.63, 7.81, 3.91, 1.95, 0.98, 0.49, and 0.24 µg/ml. Each dilution was used in triplicate. RPMI-1640 medium was used as a diluent. The duration of exposure of the investigated substances to the tumor cell lines was 48 hours in a CO2 incubator. Cells without the addition of the investigated substances were used as a negative control.
The arithmetic average of the optical density (Y) for the negative control was calculated via equation (1):
where is the measurement of the optical density (OD) of each object of the group, and n is the number of objects in the group;
The percentage of surviving cells for each repetition of each concentration of the test substance was calculated according to equation (2):
where is the OD measured for each group, and is the arithmetic average OD () for negative control.
The standard deviation and a percentage of surviving cells were calculated for each test substance was calculated as per equation (3):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Surfactants on the Particle Size of Sulfur
It is well known that surfactants capable of adsorbing onto the surface of solid microcrystals reduce the surface tension at the solid/liquid interface and create two-dimensional pressure [26]. This, in turn, weakens intermolecular interactions, reduces aggregate formation, and increases the number of nanoparticles. This phenomenon is a good illustration of the Rehbinder effect [27]. We previously investigated the influence of the surfactants CTAB and SDBS on the particle sizes and zeta potentials of SNPs, and the results determined the optimal surfactant concentration [28].
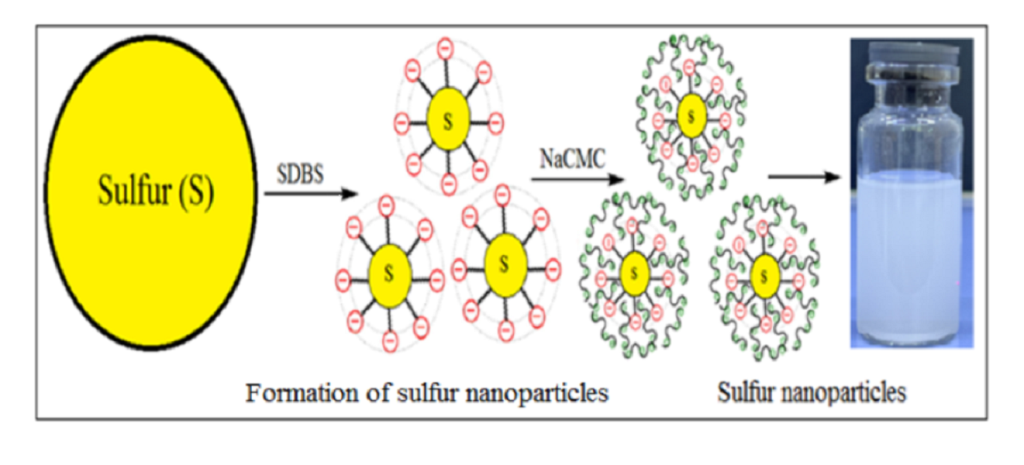
In this study, we demonstrate how polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes affect the size and stability of sulfur particles when different concentrations of polyelectrolytes are added to the surfactant (at optimal concentration). For the first time, the effects of adding two mixtures of polyelectrolyte and surfactants, NaCMC-SDBS and PHMG-CTAB, on the size distributions and zeta potentials of SNPs were investigated, the results of which are presented in Table 1. As shown in Table 1, the composition of 0.01% NaCMC-SDBS + Sulfur (SNPs-1) and 0.01% PHMG-CTAB + Sulfur (SNPs-2) represented the optimal polyelectrolyte concentrations in each instance, providing smaller particle sizes of 178 and 175 nm, respectively. The zeta potentials of these particles were approximately -27.28 and 38.16, respectively, indicating that in the presence of the NaCMC-SDBS and PHMG-CTAB mixture that, first, the polyelectrolytes adsorb onto the surface of the sulfur along with the surfactant, increasing the electrostatic repulsion force and reducing aggregate formation and, second, that increasing the viscosity of the medium leads to the stabilization of sulfur nanoparticles. This process is depicted in Scheme 1.
Thus, the use of polyelectrolytes and control of medium viscosity represent effective strategies for stabilizing sulfur nanoparticles and ensuring optimal process conditions.
3.2. UV–Visible Spectrophotometry of SNPs
The progress with regard to the formation of SNPs synthesized from various PSMs was monitored using a UV–visible spectrophotometer in the range of 200–800 nm, as shown in Figure 1. The characteristic UV-visible peaks of SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 synthesized from NaCMC-SDBS, and PHMG-CTAB, were observed at 285, and 280 nm, respectively, indicating the formation of SNPs. Suryavanshi et al. [29] also found the maximum absorption peak of SNPs to be around 290 nm. The appearance of absorption peaks at 223 and 199 nm, characteristic of SDBS and CTAB, respectively, indicated the adsorption of surfactants onto the surface of the sulfur nanoparticles. This confirms the presence of surfactants in the structure of the obtained nanoparticles [30]. The absence of characteristic peaks of polyelectrolytes in the UV spectrum may be due to the low concentration of polyelectrolytes, as well as the presence of surfactants, which can mask the absorption peaks of polyelectrolytes in the UV spectrum [31].
3.3. Thermal Stability of Hydrophilic SNPs
Figure 2 Shows the TGA and DSC thermograms of the SNPs at heating rates of 10 K min−1. In the DSC curve, the endothermic peaks at around 100 and 121 °C can be, respectively, attributed to the transition of rhombic to monoclinic forms and the solid–liquid transition of sulfur nanoparticles. The endothermic peak at around 170 °C can be attributed to the polymerization of sulfur nanoparticles [32]. The endothermic peaks at around 300~400 °C and can be attributed to the degradation of PSMs, indicative of that there is a PSM on the surface of the sulfur nanoparticles. The endothermic peaks at around 400~450 °C can be attributed to the strong volatilization of sulfur nanoparticles. In the TG curves in Figure 2, the obvious mass losses begin at about 250 °C, where the vapor pressure of sulfur is 13 mm Hg. The mass losses end at 378 °C for the curve associated with SNPs-1, and 385 °C for the curve associated with SNPs-2. Due to the volatilization of sulfur, 100% mass loss is achieved before its melting point is achieved. The char content after 400 °C was between 3.25 and 4.13% of the initial weight, which indicated that the SNPs are thermostable, as their degradation was not complete over the tested temperature range.
3.4. XRD Analysis of Hydrophilic SNPs
XRD analyses of SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 are illustrated in Figure 3. The analyses showed that the positions and intensities of the diffraction peaks of SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 are in good agreement with the literature and Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction standard values for orthorhombic α sulfur with and S8 structure (74-1465 from JCPDSPDF Number). The analyzed particles showed XRD peaks at 21.47°, 22.18°, 23.23°, 23.37°, 25.19°, 26.41°, and 27.63° [11].
3.5. SEM Analysis of Hydrophilic SNPs
Figure 4 Shows the SEM images of SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 (images a and b). The SEM micrographs showed that SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 were spherical to ellipsoidal in shape with smooth surfaces, with the addition of either NaCMC-SDBS or PHMG-CTAB. The morphologies of sulfur nanoparticles (NPs) have previously been investigated by Dop R. A. et al. [34], who found that they exhibited an ellipsoidal morphology with a mean diameter of 30 µm. The particle size of the nanosulfur particles observed in the SEM images was consistent with the results obtained from dynamic light scattering (DLS) experiments. The accumulation of small particles could be what led to the formation of large particles, the size of which ranged from 150 to 200 nm. The SEM images confirmed the influence of the polyelectrolyte-surfactant in terms of decreasing the size of the nanosulfur particles. Interestingly, there was no significant difference in the effect of cationic or anionic surfactants on their ultimate shape.
3.6. Elemental Analysis of SNPs
The atomic contents of the SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 were confirmed by EDX, the results of which are presented in Figure 5. The EDX spectra of SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 show peaks around 2.4 keV, confirming the purity of the SNPs. The studied samples contain 89.64% and 88.09% sulfur, low intensity 2.78% and 4.20% carbon. 3.77% and 8.85% oxygen peaks were found, indicating the capping of PCM NaCMC-SDBS and PHMG-CTAB on the surface of SNPs. The absence of any other signal indicated that the prepared SNPs were of a high degree of purity.
3.7. Antibacterial Activity of Hydrophilic SNPs
The antimicrobial properties of SNPs have been assessed in this study. The results revealed that the SNPs particles efficiently suppressed the growth of test strains with variable potencies.
As shown in Table 2, SNPs-1 had the largest zone of inhibition against the gram-positive bacteria Enterococcus faecium ATCC 700221 (19.7 ± 0.58 mm) and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P (20.0 ± 0.0), whereas the sample showed a zone of inhibition for the yeast Candida albicans ATCC 10231 of 7.3 ± 0.58 mm. The antifungal effect the SNPs-1 were showed against Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 was characterized by a growth inhibition zone of 14.7 ± 0.58 mm. The test item was not active against gram-positives and Candida utilis cells, however. The SNPs-2 exhibited an inhibitory effect against one gram-negative bacterial strain, Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 10031, with a zone of inhibition of 18.0 ± 0.0 mm, The Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 1790 zone of inhibition was 17.3 ± 2.30 mm, whilst that for Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 was 22.3 ± 0.58 mm; the sample was not effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, however. Growth inhibition zones of the gram-positive strains Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P and Enterococcus faecium ATCC 700221 were 17.7 ± 0.58 mm and 21.7 ± 1.15 mm, respectively. In the antifungal analysis, Sulfur + PHMG – CTAB was effective against Candida albicans ATCC 10231 and Candida utilis, with inhibition zones of 30.7 ± 0.58 mm and 51.3 ± 1.15 mm, respectively. The growth inhibition zone of Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 was 35.3 ± 0.58 mm. As shown in Table 2, pure PHMG – CTAB, NaCMC-SDBS mixtures and the control powder of sulfur samples did not exhibit any inhibition activities against any kind of bacterium.
While the antimicrobial potential of sulfur nanoparticles (SNPs) has been acknowledged, there remains a scarcity of research evaluating their antibacterial effects. Choudhury et al. [4] recently demonstrated that nanosized sulfur exhibited antibacterial properties against both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, unlike elemental sulfur, which showed no such inhibition of bacterial growth. Conversely, Suleiman et al. [11] observed significant antibacterial activity of sulfur nanoparticles against the gram-positive bacterium S. aureus, but not against E. coli. In our study, we selected both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria as test organisms and found that the SNPs-1 exhibited no inhibitory effect against gram-negatives. SNPs-2, however, exhibited remarkable bactericidal effects against both gram-negatives and gram-positives, demonstrating exceptional antibacterial efficiency. The higher antibacterial activity of SNPs-2 compared to SNPs-1 may be attributed to the cationic surface charge of SNPs-2 due to the polyelectrolyte-surfactant mixtures. This positive charge potentially facilitates binding of SNPs-2 to the negatively charged bacterial cell membrane. Although the precise mechanism of action of SNPs remains unclear, it is theorized that they bind to the bacterial cell wall, leading to membrane rupture, cell lysis and, ultimately, cell death.
3.8. Cytotoxic Effects of SNPs In Vitro
The aim of the study was to investigate the in vitro cytotoxicity of the investigated substances SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 against normal (MeT-5A) and tumor (MCF-7) human cell lines. The substances were initially dissolved in distilled water at concentrations of 1 mg/ml, and for cytotoxicity testing, further dilution was performed with a culture medium in a 1:1 ratio. Cytotoxicity was evaluated in the concentration range from 500 µg/ml to 0.12 µg/ml. The quantitative assessment of the cytotoxic effect of the investigated substances was carried out using the MTT assay. The results of the study showed a dose-dependent decrease in the percentage of viable cells relative to the investigated substances, as depicted in Figure 6.
Table 3 presents the half-maximal inhibitory concentrations (IC50) for the investigated substances SNPS-1 and SNPS-2, as well as for the comparator drug, doxorubicin.
Based on the results obtained, it can be concluded that the investigated substances exhibit cytotoxic effects over a 48-hour exposure period. After 48 hours of exposure, the IC50 were as follows: for SNPs-1 on MeT-5A, 19.16 µg/ml; on MCF7, 4.26 µg/ml; for SNPs-2 on MeT-5A, 10.66 µg/ml; and on MCF7, 3.14 µg/ml.
A comparative analysis of the IC50s of the investigated substances, SNPs-1 and SNPs-2, was also conducted (Figure 7).
As evident from the obtained data, the investigated substances, SNPs-1 and SNPs-2, exhibit cytotoxic effects at different concentrations.
Analysis of the cytotoxicity of SNPs-1 showed that the introduction of the solution at concentrations of 19 µg/ml and 20 µg/ml led to moderate cytotoxicity, i.e., resulted in more than 50% cell death in the non-tumor cell line, MeT-5A and, at concentrations above 14 µg/ml, exhibited moderate cytotoxicity towards the tumor cell line, MCF7. The cytotoxic effect on the tumor cell line showed no significant difference in comparison to the MeT-5A cell line.
Analysis of the cytotoxicity of SNPs-2 showed a cytotoxic effect on the non-tumor cell line, MeT-5A, at concentrations from 5 µg/ml, and on the tumor cell line, MCF7, at concentrations of 3 µg/ml and 6 µg/ml. Remarkably, statistical analysis of SNPs-2 data showed a significant cytotoxic difference towards the tumor cell line, which is 2.5 times lower than for normal cells.
It was established that SNPs-1 exhibits non-significant selective cytotoxicity towards the human tumor cell line, MCF7, while being minimally toxic towards the normal cell line, MeT-5A.
Summarizing the obtained data, it can be concluded that SNPs-2 possess significant selective cytotoxicity towards the tumor cell line, MCF7, making this substance highly promising for further investigation.
4. Conclusion
The SNPs were prepared by modifying the surface of elemental sulfur via various water-soluble polyelectrolyte-surfactants mixtures, including NaCMC-SDBS and PHMG-CTAB. The synthesized nanoparticles had a narrow size distribution of 150-200 nm. XRD analysis indicated that the hydrophilic SNPs have an orthorhombic α sulfur with S8 structure. Based on the results, it can be concluded that SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 have certain antimicrobial activities, where SNPs-1 could potentially inhibit the growth of gram-positives bacteria, yeasts, and fungi, whilst the SNPs-2 showed antimicrobial activity against all tested microorganisms except three gram-negatives, namely Escherichia coli ATCC 8739, Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027, and Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 1790. These findings indicate that samples SNPs-1 and SNPs-2 represent potential antibacterial agents, which might be further optimized and developed as new antibacterial and fungicidal agents. Based on the studies conducted to assess cytotoxicity, it was established that SNPs-1 exhibits unreliable selective cytotoxicity towards the human tumor cell line, MCF7, while being slightly toxic towards the normal cell line, MeT-5A. SNPs-2, by comparison, showed significant selective cytotoxicity against the MCF7 tumor cell line, which makes this substance highly promising for further study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.T. and S.A.; investigation, S.T. and A.I.; writing—original draft preparation, S.T., S.A. and A.S.; writing—review and editing, S.T.; visualization, Zh.I. and G.T.; supervision, S.T., A.S. and A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by grant number AR14972917 “Development of novel highly effective bactericidal and fungicidal sulfur nanoparticles to create anti-infectious agents and ensure biosafety for 2022-2024”, provided by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Republic of Kazakhstan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the control and analytical laboratory, “SCAID”, for assisting in the preparation of the materials for this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Chantongsri, A.; Phuektes, P.; Borlace, G.N.; Aiemsaard, J. Antifungal activity of green sulfur nanoparticles synthesized using Catharanthus roseus extract against Microsporum canis. The Thai Journal of Veterinary Medicine 2021, 51, 705–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.J.; Paria, S. Use of sulfur nanoparticles as a green pesticide on Fusarium solani and Venturia inaequalis phytopathogens. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10471–10478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awwad, A.M.; Salem, N.M.; Abdeen, A.O. Noval approach for synthesis sulfur (S-NPs) nanoparticles using Albizia Julibrissin Fruits Extract. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2015, 6, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Ghosh, M.; Mandal, A.; Chakravorty, D.; Pal, M.; Pradhan, S.; Goswami, A. Surface-modified sulfur nanoparticles: an effective antifungal agent against Aspergillus niger and Fusarium oxysporum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2011, 90, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H.; Kawano, G.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Isolation of elemental sulfur as a self-growth-inhibiting substance produced by Legionella pneumophila. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 4809–4811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, C.G.; Xia, J.L.; Peng, A.A.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, H.C.; Zheng, L.; Ma, C.Y.; Zhao, Y.D.; Nie, Z.Y.; Qiu, G.Z. Investigation of elemental sulfur speciation transformation mediated by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Jaiswal, L.; Rhim, J.W. New insight into sulfur nanoparticles: synthesis and applications. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 2329–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahab, S.; Mastaneh, S.; Rhim, J.W. Antimicrobial activity of sulfur nanoparticles: Effect of preparation methods. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13, 6580–6588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, R.M.; Williams, J.S. Elemental sulphur as an induced antifungal substance in plant defence. J. Exp. Bot. 2004, 55, 1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Pourmortazavi, S.M.; Roushani, M.; Kohsari, I.; Hajimirsadeghi, S.S. Novel approach for electrochemical preparation of sulfur nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 2011, 173, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimani, M.; Aflatouni, F.; Khani, A. A new and simple method for sulfur nanoparticles synthesis. Colloid Journal 2013, 75, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, K.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Preparation and characterization of monoclinic sulfur nanoparticles by water-in-oil microemulsions technique. Powder Technology 2006, 162, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Cheng, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, X. Synthesis and Characterizations of Nanoparticle Sulfur Using Eggshell Membrane as Template. Materials Science and Technology 2011, 675, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Zheng, P.S.; Zheng, W.J.; Bai, Y.; Cheng, T.F.; Liu, J. Preparation of sulfur sheets by supersaturated solvent method in the presence of organic modifiers. Materials Research Bulletin 2012, 47, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massalimov, I.A.; Shainurova, A.R.; Khusainov, A.N.; Mustafin, A.G. Production of sulfur nanoparticles from aqueous solution of potassium polysulfide. Russian Journal of Applied Chemistry 2012, 85, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, A.; Yin, H.; Zhang, D.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y. Preparation of sulfur sheets by supersaturated solvent method in the presence of organic modifiers. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.G.; Paria, S. Synthesis of sulfur nanoparticles in aqueous surfactant solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2010, 343, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, R.G.; Paria, S. Growth kinetics of sulfur nanoparticles in aqueous surfactant solutions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2011, 354, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokoglu, N. Novel natural food preservatives and applications in seafood preservation: a review. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2019, 99, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.S.; Khomane, R.B.; Vaidya, B.K.; Joshi, R.M.; Harle, A.S.; Kulkarni, B.D. Sulfur nanoparticles synthesis and characterization from H2S gas, using novel biodegradable iron chelates in W/O microemulsion. Nanoscale Research Letters 2008, 3, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.Y.; Zheng, W.-J.; Bai, Y.; Liu, J. Cystine modified nano-sulfur and its spectral properties. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ksenija Kogej, Chapter Seven—Polyelectrolytes and Surfactants in Aqueous Solutions: From Dilute to Concentrated Systems, Editor(s): Aleš Iglič, Advances in Planar Lipid Bilayers and Liposomes, Academic Press 2012, Volume 16. [CrossRef]
- Tulpar, A.; Tilton, R.D.; Walz, J.Y. Synergistic effects of polymers and surfactants on depletion forces. Langmui 2007, 23, 4351–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalodia, N.R.; Shukla, V.J. Antibacterial and antifungal activities from leaf extracts of Cassia fistula l.: an ethnomedicinal plant. Journal of Advanced Pharmaceutical Technology & Research 2011, 2, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, A.; Malika, D.; Bakari, S.; Hfaiedh, N.; Mnafgui, K.; Kadri, A.; Gharsallah, N. Assessment of polyphenol composition, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of various extracts of Date Palm Pollen (DPP) from two Tunisian cultivars. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2019, 12, 3075–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourougou-Candoni, N.; Prunet-Foch, B.; Legay, F.; Vignes-Adler, M.; Wong, K. Influence of dynamic surface tension on the spreading of surfactant solution droplets impacting onto a low-surface-energy solid substrate. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 1997, 192, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkin, A.I. Regularities and mechanisms of the Rehbinder’s effect. Colloid Journal 2012, 74, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turganbay, S.; Aidarova, S.; Kumargaliyeva, S.; Argimbayev, D.; Sabitov, A.; Iskakbayeva, Zh.; Lyu, M. Mechanochemical synthesis of hydrophilic sulfur nanoparticles in aqueous surfactant solutions and their antibacterial activity and acute toxicity in mice. ES Materials and Manufacturing 2024, 23, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryavanshi, P.; Pandit, R.; Gade, A.; Derita, M.; Zachino, S.; Rai, M. Colletotrichum sp.-mediated synthesis of sulphur and aluminium oxide nanoparticles and its in vitro activity against selected food-borne pathogens. LWT Food Science and Technology 2017, 81, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, S.; Pangeni, R.; Park, J.W.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation of sulfur nanoparticles and their antibacterial activity and cytotoxic effect. Materials Science and Engineering C 2018, 92, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehlot, P.S.; Kulshrestha, A.; Bharmoria, P.; Damarla, K.; Chokshi, K.; Kumar, A. Surface-active ionic liquid cholinium dodecylbenzenesulfonate: self-assembling behavior and interaction with cellulose. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 7451–7460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, V.B.; Pięta, M.; Pietrasik, J.; Plummer, Ch.M. Recent advances in the ring-opening polymerization of sulfur-containing monomers. Polymer Chemistry 2022, 13, 4858–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dop, R.A.; Neill, D.R.; Hasell, T. Sulfur-Polymer Nanoparticles: Preparation and Antibacterial Activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2023, 15, 20822–20832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Scheme 1.
Formation of sulfur nanoparticles.
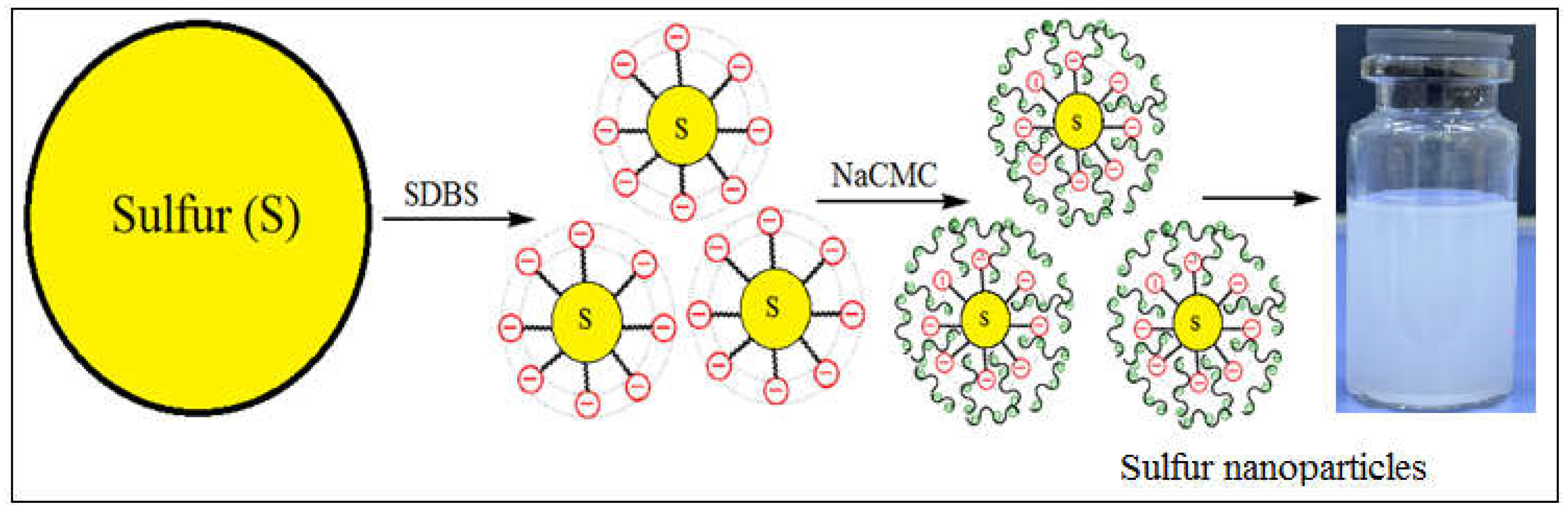
Figure 1.
UV–visible spectra of SNPs.

Figure 2.
TGA and DSC thermograms of SNPs. a, a1-TG/DSC of SNPs-1; b, b1-TG/DSC of SNPs-2.
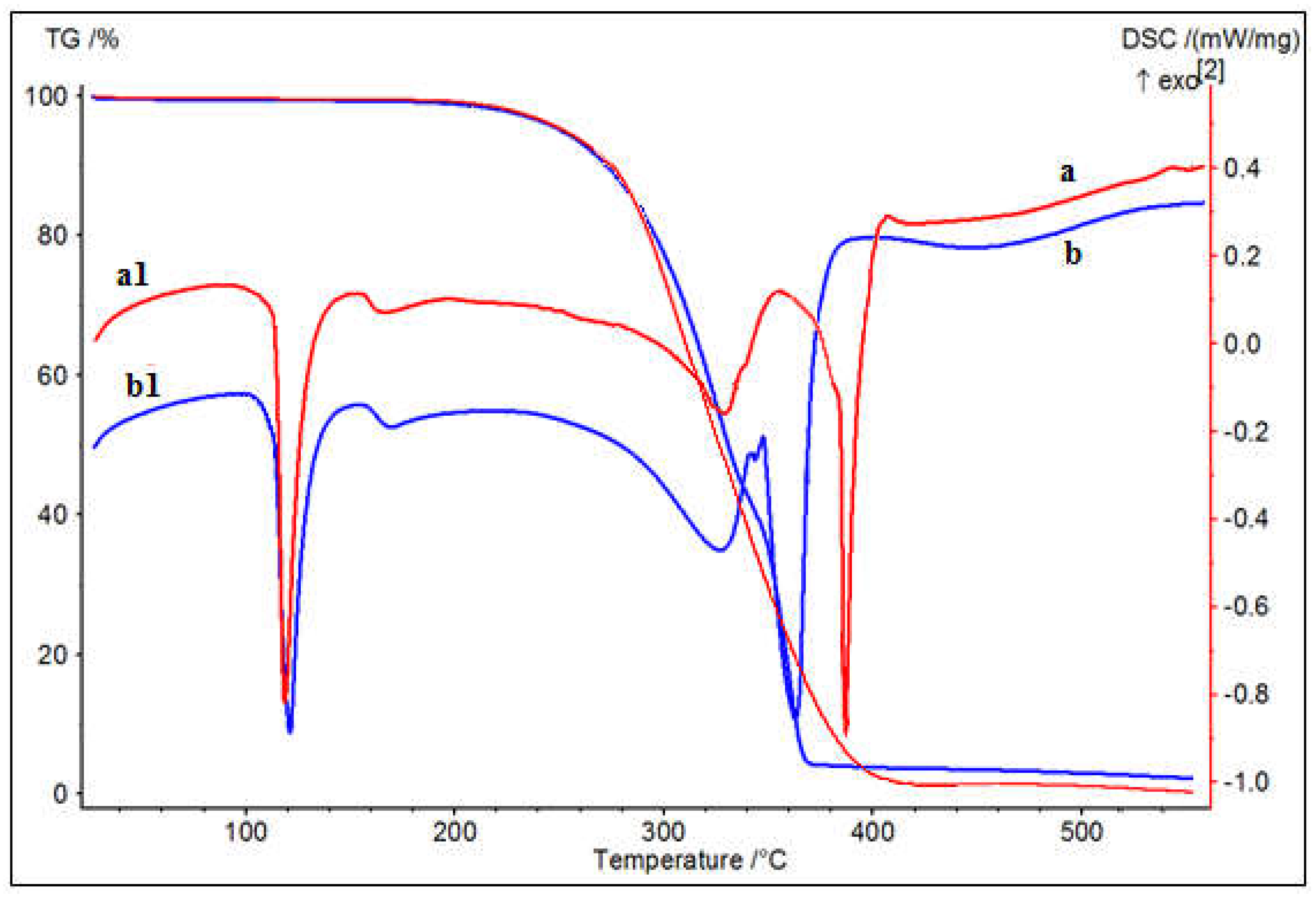
Figure 3.
XRD pattern of SNPs: a - SNPs-1, b - SNPs-2.
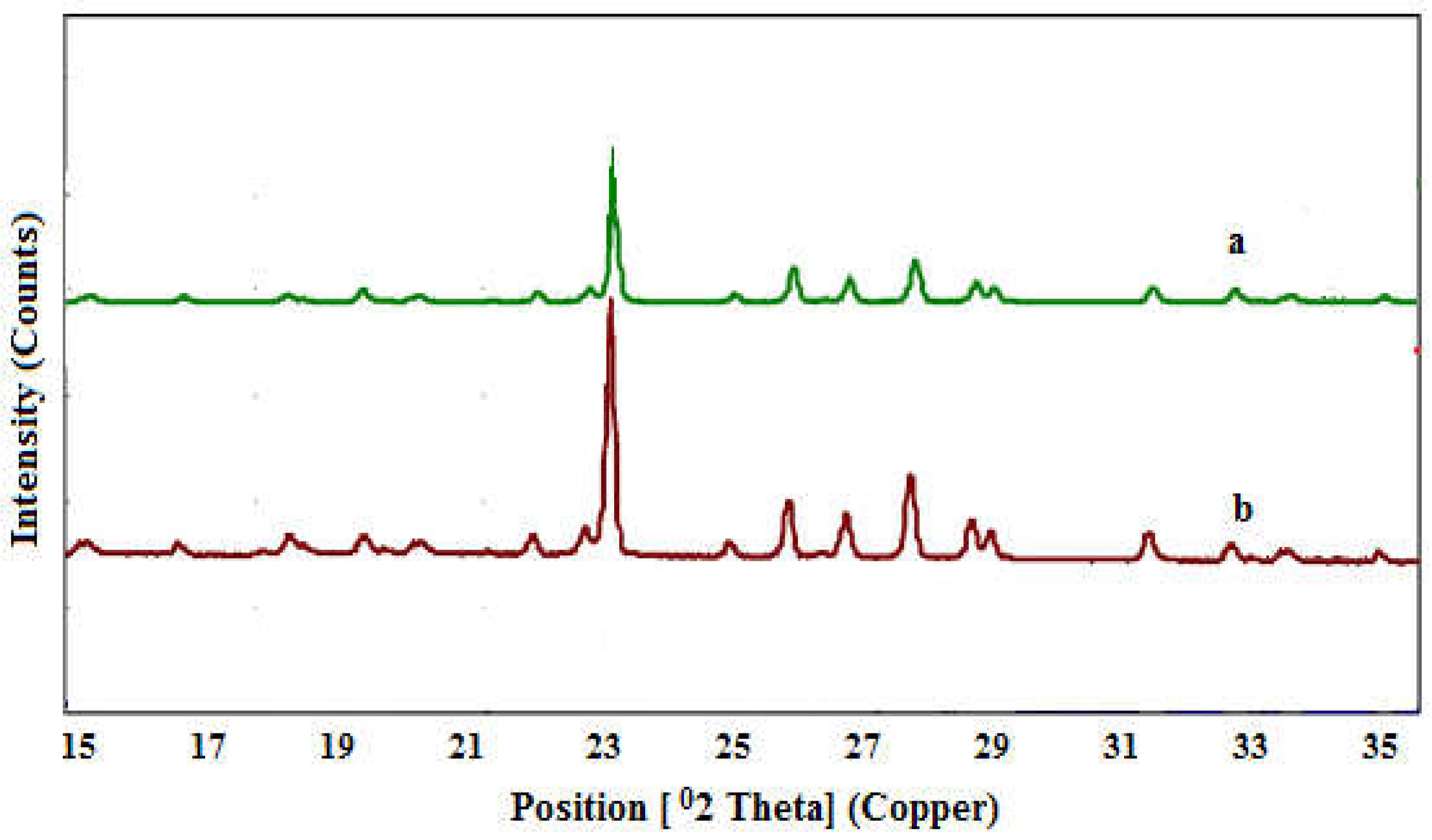
Figure 4.
SEM micrographs of SNPs. a - SNPs-1, b - SNPs-2.
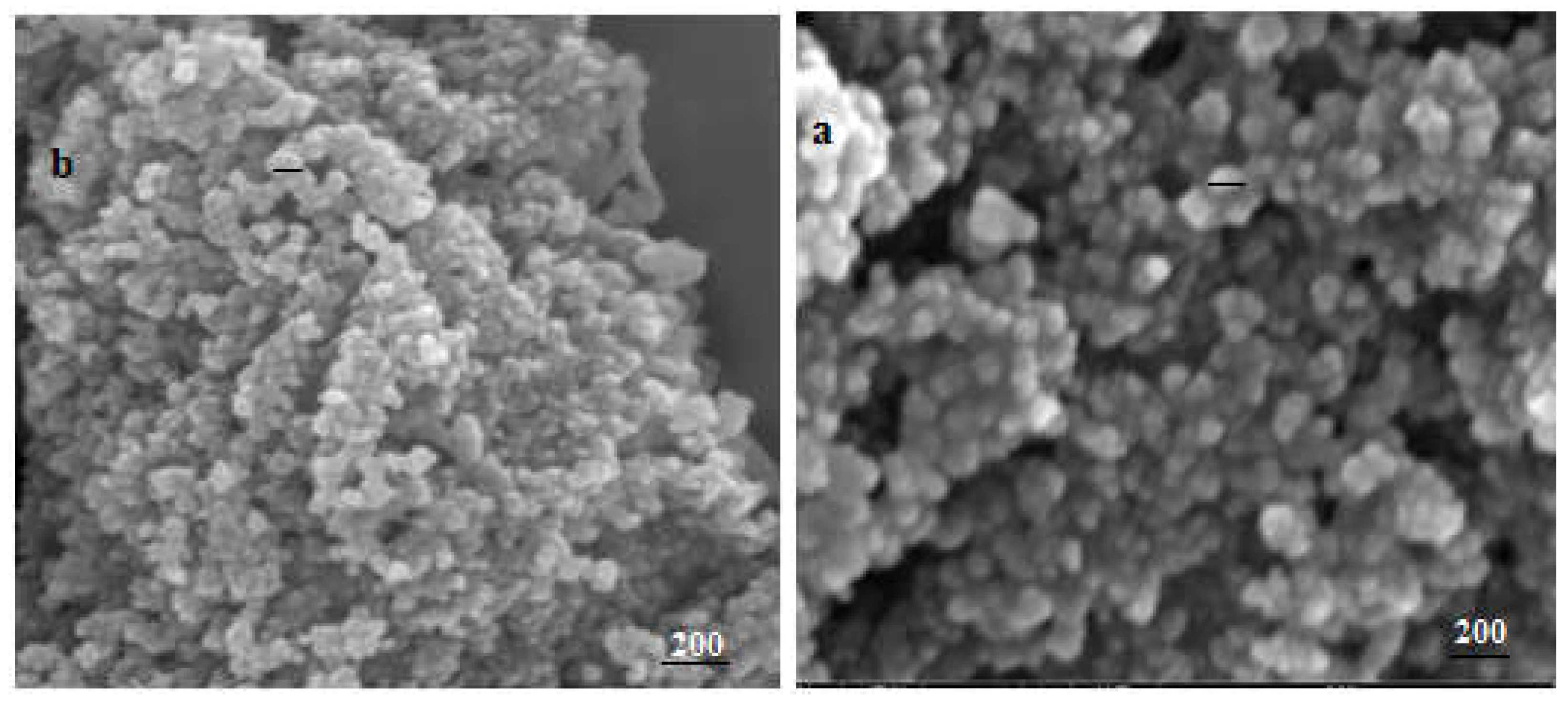
Figure 5.
EDX spectra of SNPs. a - SNPs-1, b - SNPs-2.
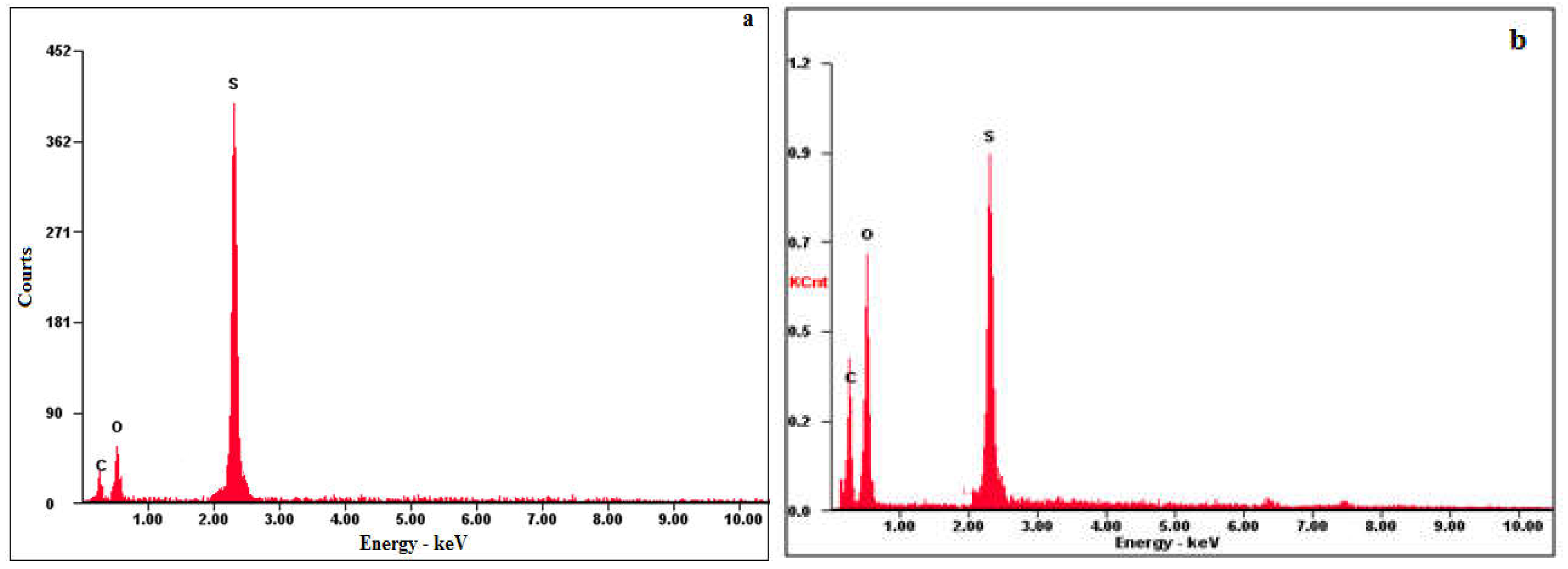
Figure 6.
Determination of the concentration of the investigated substances at 50% viability a) Substance SNPS-1 at 24 hours’ exposure, b) Substance SNPS-1 at 48 hours’ exposure, c) Substance SNPS-2 at 24 hours’ exposure, d) Substance SNPS-2 at 48 hours’ exposure.
Figure 6.
Determination of the concentration of the investigated substances at 50% viability a) Substance SNPS-1 at 24 hours’ exposure, b) Substance SNPS-1 at 48 hours’ exposure, c) Substance SNPS-2 at 24 hours’ exposure, d) Substance SNPS-2 at 48 hours’ exposure.
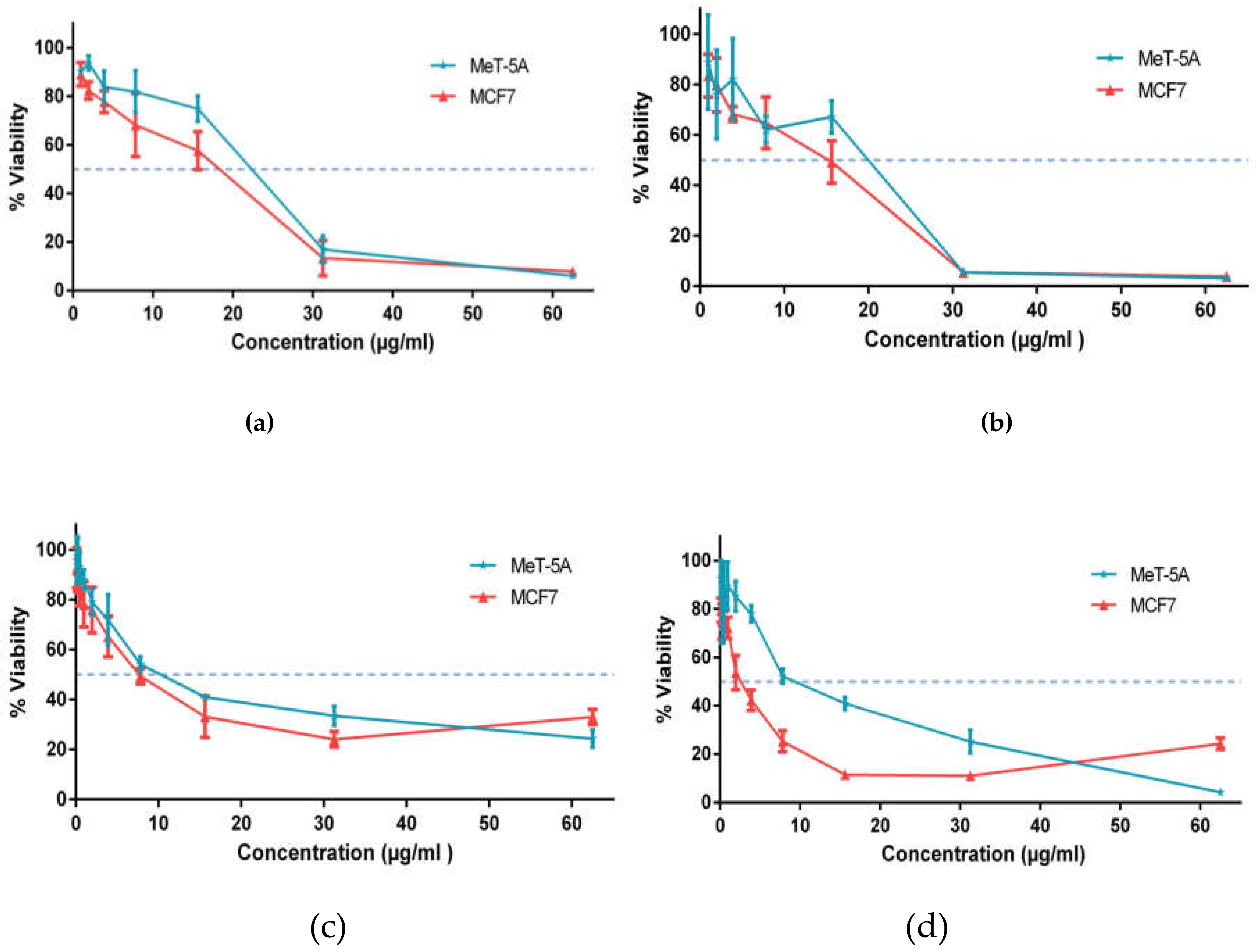
Figure 7.
Comparative analysis of the effects of the investigated substances on normal and tumor cell lines (IC50, mean ± StD; n = 4).
Figure 7.
Comparative analysis of the effects of the investigated substances on normal and tumor cell lines (IC50, mean ± StD; n = 4).
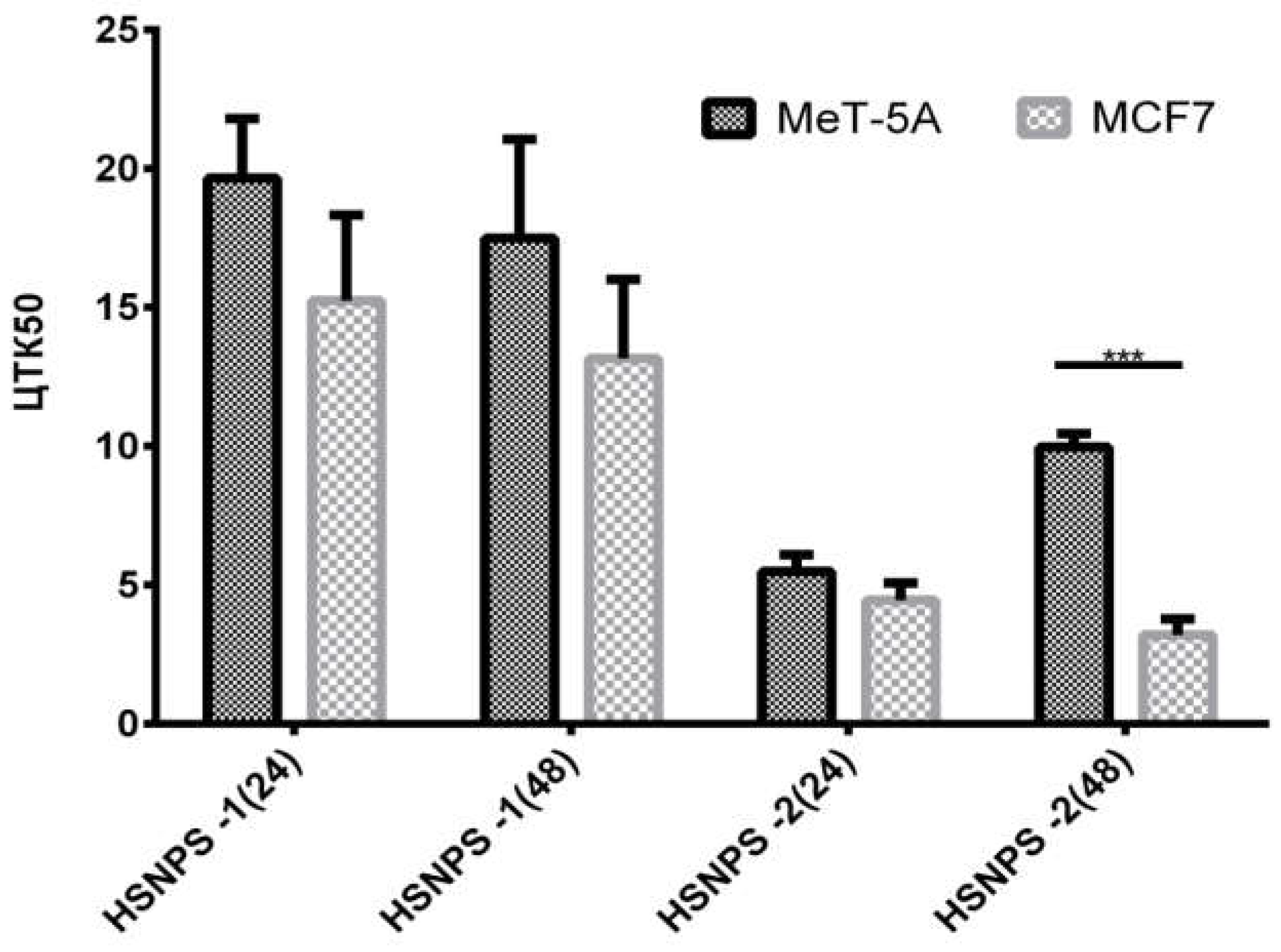
Table 1.
Effects of different concentrations of NaCMC and PHMG polyelectrolytes on sizes and zeta potentials of SNPs.
Table 1.
Effects of different concentrations of NaCMC and PHMG polyelectrolytes on sizes and zeta potentials of SNPs.
| Surfactant type | Polyelectrolyte type | Polyelectrolyte concentration % | Particle size (nm) | Zeta potential (mV) |
| Anionic SDBS | Anionic NaCMC | 0.001 | 183 ± 6.11 | -21.38 ± 0.63 |
| 0.01 | 178 ± 3.78 | -27.28 ± 1.27 | ||
| 0.1 | 182 ± 3.52 | -31.33 ± 0.33 | ||
| 0.25 | 190 ± 3.18 | -38.90 ± 1.48 | ||
| Cationic CTAB | Cationic PHMG | 0.001 | 188 ± 4.23 | 28.45 ± 2.07 |
| 0.01 | 175 ± 6.83 | 38.16 ± 0.42 | ||
| 0.1 | 180 ± 4.26 | 53.00 ± 2.49 | ||
| 0.25 | 183 ± 3.71 | 53.60 ± 2.57 |
Table 2.
Antimicrobial activities of hydrophilic SNPs.
| Microorganism | Zone of inhibition, M ± StD, mm (according to CLSI) | ||||
| SNPs-1 | NaCMC-SDBS | SNPs-2 | PHMG-CTAB | Sulfur | |
| Gram negatives | |||||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 8739 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 22.3 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Acinetobacter baumannii ATCC 1790 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 17.3 ± 2.3 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 10031 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 18.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Gram positives | |||||
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P | 20.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 17.7 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Enterococcus faecium ATCC 700221 | 19.7 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 21.7 ± 1.15 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Yeasts | |||||
| Candida albicans ATCC 10231 | 7.3 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 30.7 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
| Candida utilis | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 51.3 ± 1.15 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | |
| Fungi | |||||
| Aspergillus brasiliensis ATCC 16404 | 14.7 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 35.3 ± 0.58 | 6.0 ± 0.0 | 6.0 ± 0.0 |
Note: meanings ≤ 6.0 ± 0.0 indicates the absence of antimicrobial activity.
Table 3.
Cytotoxic effects of the investigated substances SNPS-1 and SNPS-2 on normal and tumor human cell lines after 24- and 48 hours’ exposure.
Table 3.
Cytotoxic effects of the investigated substances SNPS-1 and SNPS-2 on normal and tumor human cell lines after 24- and 48 hours’ exposure.
| Test substances | Cytotoxic concentration 50 ± StD (µg/ml) | |||
| 24 hours | 48 hours | |||
| MeT-5A | MCF7 | MeT-5A | MCF7 | |
| substances SNPS-1 | 20.50 ± 2.13 | 15.06 ± 3.08 | 19.16 ± 3.51 | 14.26 ± 2.85 |
| substances SNPS-2 | 5.97 ± 0.59 | 4.55 ± 0.62 | 10.66 ± 0.48 | 3.14 ± 0.57 |
| Doxorubicin | NA | 0.087 ± 0.03 | NA | 0.058 ± 0.02 |
| Note: Average values from three independent experiments; NA - no activity. | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Copyright: This open access article is published under a Creative Commons CC BY 4.0 license, which permit the free download, distribution, and reuse, provided that the author and preprint are cited in any reuse.
MDPI Initiatives
Important Links
© 2024 MDPI (Basel, Switzerland) unless otherwise stated







