1. Introduction
Sustainable economic growth is the most important goal for governments. In this effort, the performance of local governments plays an important role in shaping the economy's trajectory. Regional autonomy gives regions authority to manage their affairs so that regional performance will directly impact community welfare. [
1]An autonomous region must have the financial capacity to run the wheels of government; an independent region is characterised by reduced financial dependence on the centre. [
2]. In Banten province, Indonesia, as in many regions globally, the interaction between local government financial performance and capital expenditure has significant implications for sustainable development. Local government financial performance covers various aspects, including revenue generation, expenditure efficiency and fiscal accountability. [
3]. Effective financial management ensures prudent resource allocation and fosters investor confidence and economic stability. [
4].
Capital expenditure, which consists of investments in infrastructure, public services, and community development projects, serves as a foundation for economic growth, which impacts productivity, employment, and social welfare. Money management is likely to increase the community's income. [
5].While having a positive impact on economic growth [
6]. The growth of the financial sector also has an impact not only on economic growth. [
7]. Economic growth is also an important part of sustainable economic sustainability. [
8].
This study seeks to explain local government financial management and capital expenditure dynamics in promoting sustainable economic growth in Banten province, Indonesia. The main objective is to analyse the relationship between local government financial performance, capital expenditure, and sustainable economic growth in Banten province. By exploring this relationship, this study aims to identify the key determinants and mechanisms through which local government actions impact economic sustainability.
This research makes a novel contribution to the existing literature by focusing on the specific context of Banten province in Indonesia, thus providing insights relevant to local policymakers and stakeholders. By examining the nuances of local government financial management and capital expenditure in this regional context, this study aims to offer customised recommendations to improve sustainable economic development practices. The urgency of this study lies in the imperative to address the pressing challenges of economic development, environmental degradation, and social inequality in Banten province. As a region experiencing rapid urbanisation and industrialisation, Banten faces critical resource allocation and infrastructure development decisions requiring evidence-based policy interventions. This study aims to inform the policy-making process and catalyse positive change towards a more prosperous and sustainable future for Banten province and its residents by highlighting the relationship between local government finance, capital expenditure, and sustainable economic growth.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Financial Performance and Economic Growth
Local government financial performance is closely related to a region's economic growth. Strong financial performance provides a solid foundation for sustainable economic development. Factors such as the ratio of independence, effectiveness, efficiency, fiscal decentralisation, dependency, and compatibility can be indicators of financial performance that affect economic growth. Financial performance tends to evolve in anticipation of future economic growth. [
9]. Finance plays an important role and actively contributes to economic growth. [
10]. Finance affects economic growth. [
11,
12,
13]Financial management can help local governments allocate resources efficiently, improve infrastructure, and encourage investment and growth in key economic sectors. Good financial development will also contribute to economic growth.[
14].
H1. financial performance, as measured by the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio and compatibility ratio, is expected to affect economic growth significantly.
2.2. Relationship between Financial Performance and Capital Expenditure
Local government capital expenditure, which includes investments in physical infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and other public facilities, is one of the main ways financial performance can influence economic growth. Good financial performance can support the local government's ability to allocate a budget for productive and effective capital expenditure. A high independence ratio, good efficiency in the use of resources, and appropriate fiscal decentralisation can result in an increase in capital expenditure, which has a positive impact on economic growth. Studies conducted [
15,
16] have explored various factors that influence local government financial performance, including the impact of capital expenditure. Research [
15,
16] shows a positive relationship between financial performance and capital expenditure. Capital expenditure is an important factor in determining financial performance. However, some studies present contrasting findings, suggesting a negative but significant effect of financial performance on capital expenditure, suggesting a more complex relationship between these variables. [
17,
18]. Performance affects capital expenditure, affecting economic growth [
19,
20].
H2. Financial performance, as measured by the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio, is expected to affect capital expenditures significantly.
2.3. Impact of Capital Expenditure on Economic Growth
Capital expenditure has a significant impact on the economic growth of a region. Investments in infrastructure and other fixed assets can increase labour productivity, lower production costs, and improve the region's competitiveness. In addition, capital expenditure can also create new employment opportunities, improve accessibility, and enhance the quality of life in the community. Therefore, appropriate and efficient capital expenditure spending is crucial in promoting sustainable economic growth. Several studies have highlighted the positive impact of capital expenditure on economic growth in developing countries, finding a significant positive effect of government capital expenditure on economic growth. [
21,
22]. The importance of central government capital expenditure in driving economic progress [
23]. Capital expenditure stimulates economic growth. [
24]. Restructure government spending to increase economic growth through increased capital expenditure. [
25].
H3. Capital expenditure is expected to have a significant effect on economic growth.
2.4. Mediating Impact of Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure can mediate local government financial performance and economic growth. Local governments can transform budgets into productive investments through appropriate capital expenditure, increasing economic growth. In mediation analysis, capital expenditure is an intermediary between financial performance variables and economic growth, strengthening the relationship and optimising their impact on overall community welfare. The path coefficient of capital expenditure was found to have a positive value, indicating its mediating role. [
26]. With this theoretical basis, this study hypothesises that local government financial performance, measured through various financial ratios, will positively influence capital expenditure, mediating the relationship between financial performance and economic growth. Using the path analysis method, this hypothesis will be tested using empirical data from various local governments in Indonesia.
H4. financial performance, as measured by the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio and compatibility ratio, is expected to positively and significantly affect economic growth through capital expenditure.
2.5. Conceptual Model
Figure 1 illustrates the conceptual model of financial performance measured by the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio through the mediation of capital expenditure on economic growth.
3. Materials and Method
3.1. Sampling and Data Collection
The author uses a quantitative approach to examine the relationship between financial performance, capital expenditure, and economic growth. The data used in this study are secondary data consisting of Regional Revenue and Expenditure Budget data and economic growth data. The sampling technique used is purposive sampling; the sample used is data from the Banten Provincial Government of Indonesia, which consists of eight cities/districts consisting of Pandeglang Regency, Lebak Regency, Tanggerang Regency, Serang Regency, Tanggerang City, Cilegon City, Serang City, South Tanggerang City. The data includes data from 2018 to 2022. To measure regional financial performance, several ratios are used as variables: the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, regional financial efficiency ratio, and compatibility ratio.
3.2. Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis used uses quantitative analysis using Path Analysis, previously calculated for local government financial performance consisting of the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, regional financial efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio and compatibility ratio, as well as capital expenditure and economic growth. The following is the formula for calculating each variable:
4. Results
This study utilises SPSS software to examine the relationship between local government financial performance and economic growth through the mediating role of capital expenditure. The path coefficient of Sub Structure 1 refers to the regression output of model 1 in
Table 1.
The variable independence ratio (X1) = 0.000, effectiveness ratio (X2) = 0.000, efficiency ratio (X3) = 0.000, fiscal decentralization ratio (X4) = 0.000, dependency ratio (X5) = 0.000, and compatibility ratio (X6) = 0.001. These results conclude that the variable independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio affect capital expenditure. Furthermore, the measurement of the R Square value is in
Table 2.
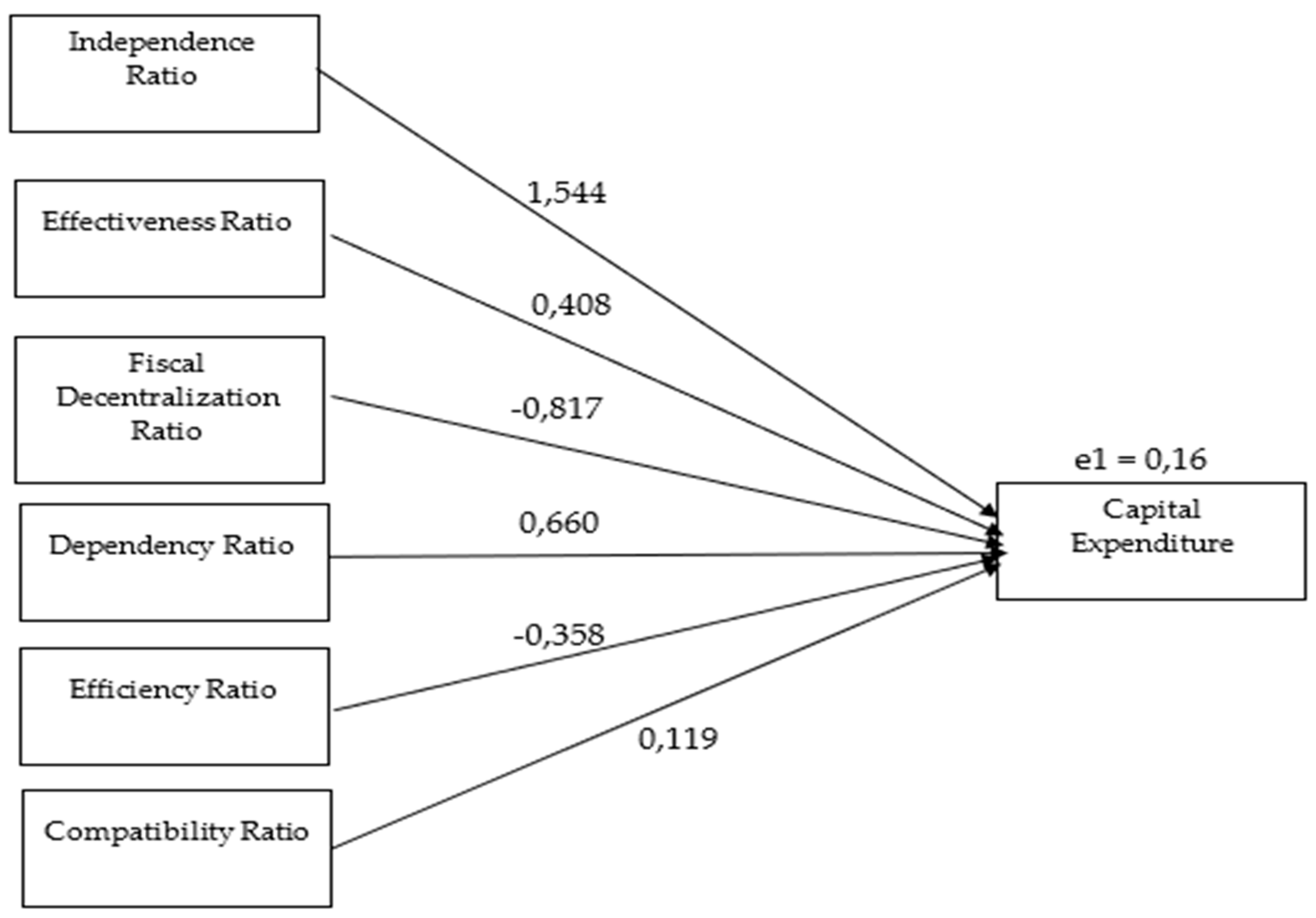
The R Square value of 0.975 means that the contribution of the influence of the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio on capital expenditure is 97.5%. In comparison, the remaining 2.5% is another variable not included in the study. Meanwhile, the value of e1 can be found with the formula. = 0,158.
Figure 2.
Testing Results of Sub-Structure 1.
Figure 2.
Testing Results of Sub-Structure 1.
The figure above shows the direct effect of local government financial performance on capital expenditure. The independence, effectiveness, dependency, and compatibility ratios positively correlate with capital expenditure. In contrast, the efficiency ratio and fiscal decentralisation ratio have a negative influence on it. Further path coefficients refer to the output of
Table 2.
Table 3.
Regression output of model 2.
Table 3.
Regression output of model 2.
| Coefficientsa |
| Model |
Unstandardized Coefficients |
Standardized Coefficients |
t |
Sig. |
| B |
Std. Error |
Beta |
| 1 |
(Constant) |
1699.672 |
601.455 |
|
2.826 |
.008 |
| Independence |
-.385 |
.088 |
-5.946 |
-4.385 |
.000 |
| Effectiveness |
-.261 |
.065 |
-1.468 |
-4.004 |
.000 |
| Fiscal Decentralization |
.434 |
.121 |
3.035 |
3.572 |
.001 |
| Dependency |
-.455 |
.117 |
-2.510 |
-3.893 |
.000 |
| Efficiency |
.068 |
.021 |
1.648 |
3.222 |
.003 |
| Compatibility |
-.067 |
.042 |
-.299 |
-1.586 |
.123 |
| Capital Expenditure |
2.985 |
.633 |
3.908 |
4.712 |
.000 |
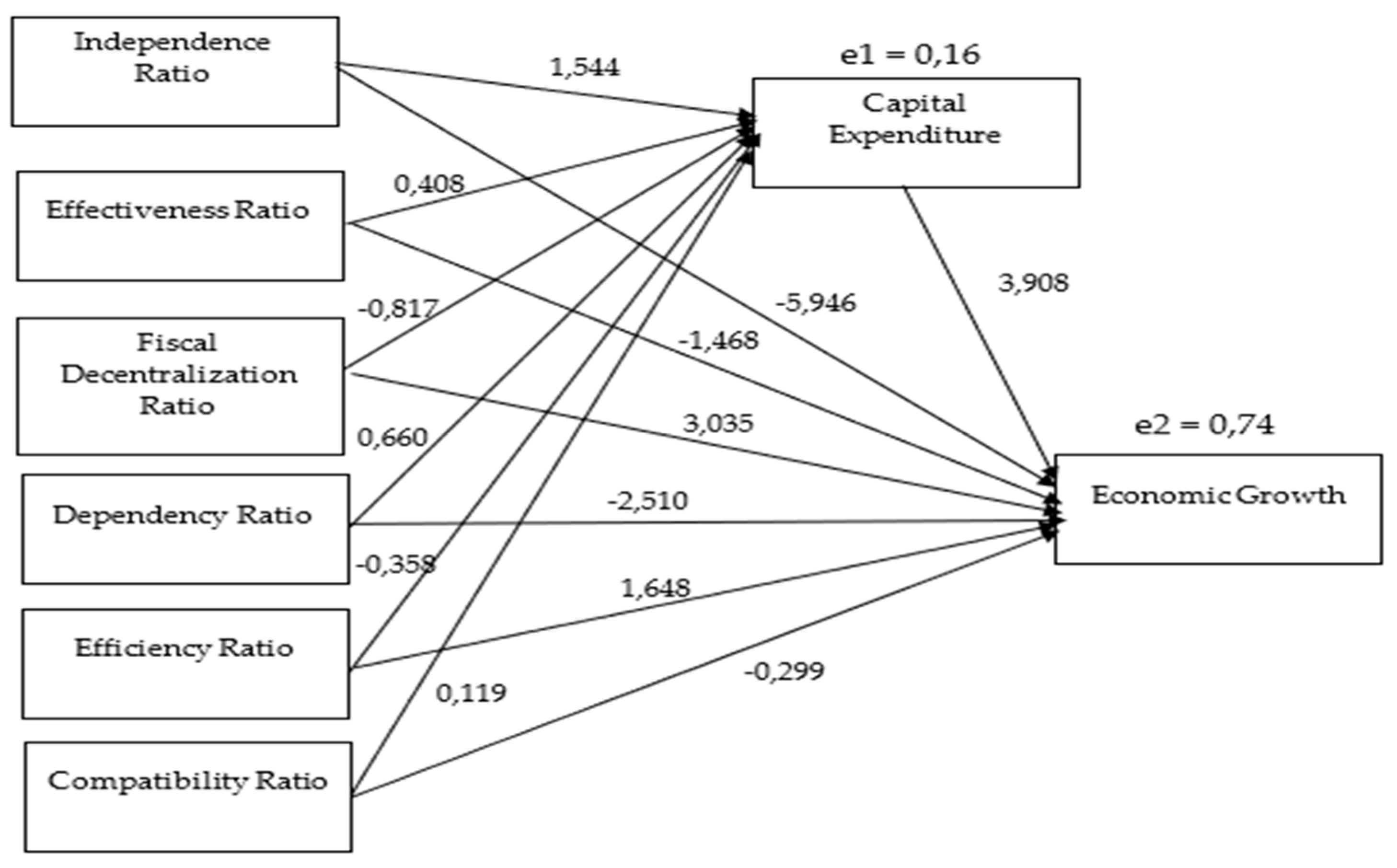
In the variable ratio of independence (X1) = 0.000, the ratio of effectiveness (X2) = 0.000, the ratio of fiscal decentralisation (X4) = 0.001, the ratio of dependence (X5) = 0.000, the ratio of efficiency (X3) = 0.003, the ratio of compatibility (X6) = 0.123, and capital expenditure (Z) = 0.000. The results conclude that the variables of the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio and capital expenditure affect economic growth. At the same time, the compatibility ratio does not affect economic growth.
The R Square value in
Table 4 of 0.456 indicates that the variables studied, namely the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, compatibility ratio, and capital expenditure, contribute 45.6% to economic growth. This means that more than half, 54.4%, is influenced by other variables not included in this study. This indicates that other factors may be equally important in influencing economic growth, such as the quality of human resources, the level of private investment, and broader national economic policies. Therefore, further research needs to consider these additional variables to get a more comprehensive picture of the determinants of economic growth. The e2 value calculated as
, also indicates considerable variability that this model cannot explain, emphasizing the importance of a more in-depth and holistic analysis in examining the factors that influence regional economic growth.
From the picture above, the results of the path analysis made in
Table 5 can be seen.
The results of this study show that the influence of financial ratio variables on economic growth through capital expenditure varies. The path coefficient value for the independence ratio of 6.034 is greater than the direct influence, which means that the ratio of independence through capital expenditure significantly influences economic growth. Similarly, the effectiveness ratio with a value of 1.595 and the dependency ratio with a value of 2.579 shows a more significant influence than the direct influence, indicating that these two variables through capital expenditure also positively affect economic growth.
In contrast, the fiscal decentralisation and efficiency ratios show path coefficient values of -3.192 and -1.3990, respectively, smaller than their direct influence. This indicates that these two variables, through capital expenditure, do not significantly affect economic growth. Although the fiscal decentralisation ratio has a negative value, it shows that an increase in this ratio can hinder economic growth if done through capital expenditure. Similarly, the efficiency ratio shows similar results.
Meanwhile, the compatibility ratio with a value of 0.465 shows a more significant influence than the direct influence, indicating that the compatibility ratio through capital expenditure positively affects economic growth. These results emphasise the importance of managing capital expenditure well to ensure that these financial variables can significantly contribute to economic growth. Overall, the study shows that some financial variables have a more significant impact when mediated by capital expenditure, while some do not.
Overall, regional financial management supports sustainable economic growth. [
27]Applying sound and efficient financial management principles ensures that resources are used optimally to maximize economic growth and people's well-being. Financial performance positively affects capital expenditure and economic growth. [
27]. Implementation of appropriate regional financial management policies can increase sustainable economic growth. [
28].
5. Discussion
This study aims to analyse the effect of local governments' variable financial ratios on capital expenditure and economic growth. Implementing regional financial management policies is important in enhancing sustainable economic growth through improved financial performance and capital expenditure. [
29]. The analysis results show that all variables studied, namely the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio, significantly influence capital expenditure. Financial performance affects economic growth through capital expenditure allocation. [
30,
31]. In addition, the importance of transparent and accountable financial management in promoting public scrutiny and trust is also a crucial factor. [
32].
The path coefficient indicates that some variables have a more significant influence than others on economic growth through capital expenditure. A positive path coefficient suggests that the variable positively impacts economic growth through capital expenditure, while a negative value indicates a negative impact. Training programs for expenditure treasurers improve regional financial management skills and governance. [
33].
The independence, effectiveness, dependency, and compatibility ratio variables significantly influence capital expenditure. This indicates that increasing these variables will encourage local governments to increase capital expenditure. On the other hand, the efficiency ratio and fiscal decentralisation ratio variables negatively influence capital expenditure. This suggests that increasing these variables will reduce local governments' capital expenditure. Implementing financial management principles, such as efficiency, transparency, and responsibility, is essential for regional autonomy and the welfare of the people. [
34].
In addition, the results of path analysis show that the influence of the independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, dependency ratio, and compatibility ratio variables through capital expenditure on economic growth is greater than the direct influence of these variables. This indicates the importance of capital expenditure in promoting economic growth and policy implications to encourage an increase in effective capital expenditure by local governments. Financial performance and capital expenditure play an important role in economic growth. [
35].
Overall, the implementation of regional financial management policies supports the sustainability of economic growth. [
27]. Implementing a mechanism for managing financial potential in local development is key to achieving this goal. [
36]The government plays an important role in development and the economy, ultimately improving society's welfare. [
37]. Regional financial efficiency varies from inefficient to highly efficient. [
38], which impacts on how financial policies can promote sustainable regional economic growth [
28].
6. Conclusions
This study examines the relationship between local government financial performance and economic growth through the mediating role of capital expenditure. This study tests the proposed model using multivariate analysis and provides empirical support for the hypothesised relationship. This study reveals that several financial ratio variables significantly influence economic growth directly and indirectly through capital expenditure as a mediating variable. The independence ratio, effectiveness ratio, efficiency ratio, fiscal decentralisation ratio, dependency ratio, and capital expenditure influence economic growth directly. The independence and effectiveness ratios have a significant positive effect, indicating that increasing these variables can boost economic growth. However, the efficiency and fiscal decentralisation ratios have a negative effect, meaning an increase in these variables can reduce economic growth. On the other hand, the compatibility ratio does not show a significant direct impact on economic growth.
Indirectly, through capital expenditure as the mediating variable, the independence, effectiveness, dependency, and compatibility ratios significantly influence economic growth. The independence ratio has the most dominant indirect effect with a coefficient value greater than its direct effect, followed by the dependency and effectiveness ratios. In contrast, the fiscal decentralisation and efficiency ratios do not show significant indirect effects and even have smaller negative values than their direct effects, suggesting that capital expenditure cannot effectively mediate the effects of these variables. Overall, the results of this study indicate that capital expenditure can be a good mediator for variables that have a positive impact, such as independence, effectiveness, and dependency ratios. Still, it is ineffective for variables with a negative or insignificant effect.
The findings confirm the relationship between (1) independence ratio and capital expenditure, (2) effectiveness ratio and capital expenditure, (3) dependency ratio and capital expenditure, (4) equity ratio and capital expenditure, as well as the negative influence of (5) efficiency ratio and capital expenditure; and (6) fiscal decentralisation ratio and capital expenditure. In addition, the findings show that capital expenditure significantly influences economic growth. This study also confirms the mediating role of capital expenditure between local government financial ratios and economic growth. Finally, this study presents many theoretical and practical implications worth noting.
6.1. Practical Implications of Research
The practical implications of this research extend to various sectors, significantly improving the effectiveness of local financial management and capital expenditures to support economic growth. This study shows that increasing self-reliance, effectiveness, dependency, and compatibility ratios can significantly increase capital expenditures, which drives economic growth. Therefore, local governments need to focus on improving fiscal independence through policies that encourage an increase in local own-source revenue (PAD).
For policymakers, these findings underscore the need to create an enabling environment to promote efficiency and transparency in local financial management. Efforts could be directed at strengthening managerial and technical capacity at the regional level, including training programs to improve financial literacy and budget management. In addition, fiscal decentralisation policies should be designed so that they do not reduce the ability of regions to make productive investments in capital expenditures.
This study highlights the importance of active participation in the oversight and accountability of local financial management for entrepreneurs and communities. Public involvement in planning and budgeting can increase local government transparency and trust. In addition, the results show that effective capital expenditure can open up investment opportunities and job creation, promoting sustainable regional economic growth.
The research also points to the need for collaboration between government, the private sector and educational institutions to create an ecosystem that supports good financial management and effective capital spending. For example, public-private partnerships can be initiated to fund critical infrastructure projects, while educational institutions can develop curricula that integrate elements of financial literacy and public management. By acting on these practical implications, stakeholders can collectively work towards more inclusive and sustainable economic growth.
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
This study has several limitations that need to be considered. First, this study only includes a few financial ratio variables that affect capital expenditure and economic growth. Many other variables may have an effect, such as the quality of human resources, the level of private investment, national economic policy, and other external factors that should have been included in this study. Therefore, future research needs to consider these additional variables to provide a more comprehensive picture of the determinants of economic growth. Secondly, this study uses data limited to a certain period and region. The results may only be generalisable to some regions or different periods. Future research needs to expand the data coverage both temporally and geographically to ensure the study's results can be applied more broadly. Third, this study used a quantitative approach with regression analysis, which, although providing significant results, may not fully illustrate the complexity of the relationship between the variables studied. Future research could use a qualitative approach or mixed methods to understand better the mechanisms and processes behind the influence of financial ratio variables on capital expenditure and economic growth.
Fourth, this study is also limited regarding the analytical methods used. SPSS is a powerful tool, but other analytical tools and techniques can provide additional insights, such as structural path analysis (SEM), panel data analysis, or machine learning techniques. Future research could use these methods to test more complex hypotheses and provide more accurate results. In addition, this study also did not consider the contextual influence of national and global economic policies that may impact regional financial performance. Factors such as changes in fiscal policy, macroeconomic conditions, and political dynamics may affect the effectiveness of local financial management and capital expenditure. Future research needs to include these variables to get a more comprehensive picture of the factors influencing economic growth.
This study contributes significantly to understanding the influence of local government financial ratio variables on capital expenditures and economic growth. Policymakers can use the resulting practical implications to design more effective strategies for improving regional economic growth. However, further research with broader coverage and more diverse methods is still needed to gain a more comprehensive and in-depth understanding of the factors that influence economic growth.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.H.Z and S.S.; methodology, M.M and S.S.; validation, M.H.Z., M.M. and S.S.; data curation, M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.H.Z. and S.S.; writing—review and editing, M.M.; visualisation, S.S.; supervision, M.H.Z All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- M. I. Umsohy, C. F. Ananda, and S. T. Wahyudi, “The Effect Of Capital Allocations On Economic Growth, Human Development Index And Poverty In North Maluku Of Indonesia During 2010-2016,” Russ. J. Agric. Socio-Economic Sci., vol. 80, no. 8, pp. 11–18, Aug. 2018. [CrossRef]
- E. Ermawati and K. Aswar, “Assessing Regional Finance Independence in Indonesian Local Governments,” Eur. J. Bus. Manag. Res., vol. 5, no. 1, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Thalib and D. Ekaningtias, “The effect of original LG revenue, balancing fund, and capital expenditure on LG financial performance in regencies in East Java Province,” Indones. Account. Rev., vol. 9, no. 1, p. 39, 2019.
- S. Astuti and M. Mispiyanti, “The Effect of Local Government Financial Performance on Economic Growth, Unemployment, Poverty, and Human Development Index with Case Studies of Districts in Central Java Province,” Proc. Natl. Semin. Fac. Econ. Untidar, 2019.
- J. H. Abrams, “Local Government Finance: Realties and Directions,” Public Budg. Financ., vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 3–8, Mar. 1982. [CrossRef]
- E. S. E. Mohamed, “Resource Rents, Human Development and Economic Growth in Sudan,” Economies, vol. 8, no. 4, p. 99, Nov. 2020. [CrossRef]
- C. Sugiyanto and Z. Yolanda, “The Effect of Financial Deepening on Economic Growth, Inequality, and Poverty: Evidence from 73 Countries,” South East Eur. J. Econ. Bus., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 15–27, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Ranis, F. Stewart, and A. Ramirez, “Economic Growth and Human Development,” World Dev., vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 197–219, Feb. 2000. [CrossRef]
- R. Levine, “Financial Development and Economic Growth: Views and Agenda,” J. Econ. Lit., vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 688–726, Nov. 1999. [CrossRef]
- C. Calderón and L. Liu, “The direction of causality between financial development and economic growth,” J. Dev. Econ., vol. 72, no. 1, pp. 321–334, Oct. 2003. [CrossRef]
- J. Greenwood and B. Jovanovic, “Financial Development, Growth, and the Distribution of Income,” J. Polit. Econ., vol. 98, no. 5, Part 1, pp. 1076–1107, Oct. 1990. [CrossRef]
- J.-L. Wu, H. J.-L. Wu, H. Hou, and S.-Y. Cheng, “The dynamic impacts of financial institutions on economic growth: Evidence from the European Union,” J. Macroecon., vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 879–891, Sep. 2010. [CrossRef]
- C. Liu, “An Empirical Study on the Relationship between Financial Development, Economic Growth and Income Disparity in China,” in Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Education, Management, Information and Management Society (EMIM 2018), Paris, France: Atlantis Press, 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. Cheng and H. Degryse, “The Impact of Bank and Non-Bank Financial Institutions on Local Economic Growth in China,” J. Financ. Serv. Res., vol. 37, no. 2–3, pp. 179–199, Jun. 2010. [CrossRef]
- S. Cohen, “Identifying The Moderator Factors Of Financial Performance In Greek Municipalities,” Financ. Account. Manag., vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 265–294, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- R. Oktaviani, S. Y. Wijaya, and. E., “Factors Affecting the Local Governments Financial Performance,” J. Econ. Behav. Stud., vol. 12, no. 4(J), pp. 84–89, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. K. Bolen and P. -, “The Effect of Financial Performance and Balanced Funds on Capital Expenditure of Local Government in District/City in Indonesia,” J. Public Adm. Gov., vol. 9, no. 4, p. 129, Nov. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. B. Widajanto, P. P. Dewi, and R. F. D. A. Anggraeni, “The Influence of Regional Original Revenues, Balancing Funds and Capital Expenditures on the Financial Performance of Regency/City Regional Governments of East Java Province,” Indones. Account. Res. J., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 40–47, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Hasanuddin, E. Elpisah, and M. Muslim, “The Influence of Financial Performance Dimensions on Local Government Capital Expenditure Allocation,” ATESTASI J. Ilm. Akunt., vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 291–300, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. R. Arsallya, A. Azwardi, and Y. Yusnaini, “Analysis of factors affecting capital expenditures and their implications on government financial performance provinces in Indonesia 2011-2019,” Int. J. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci. (2147- 4478), vol. 10, no. 5, pp. 95–106, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. T. Onifade, S. Çevik, S. Erdoğan, S. Asongu, and F. V. Bekun, “An empirical retrospect of the impacts of government expenditures on economic growth: new evidence from the Nigerian economy,” J. Econ. Struct., vol. 9, no. 1, p. 6, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Badrudin, M. W. Kusuma, and R. Y. Wardani, “The inclusive economic development model in Sulawesi island,” Econ. J. Emerg. Mark., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 128–136, Oct. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Bose, M. E. Haque, and D. R. Osborn, “Public Expenditure And Economic Growth: A Disaggregated Analysis For Developing Countries*,” Manchester Sch., vol. 75, no. 5, pp. 533–556, Sep. 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Ilemona and N. Sunday, “Budget Implementation and Economic Growth in Nigeria: An Exploratory Review (2014-2018),” Int. J. Acad. Res. Accounting, Financ. Manag. Sci., vol. 8, no. 4, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- B. Molonko and S. N. Ampah, “Moderating Effect of Political Risk on the Relationship between Capital Expenditure and Sectoral Economic Growth in Kenya,” Int. J. Econ. Financ., vol. 10, no. 1, p. 129, Dec. 2017. [CrossRef]
- F. Qoriiba, K. Aswar, and Ermawati, “Antecedents of Regional Financial Independence: A Moderating Effect of Capital Expenditure at Local Government Level in Indonesia,” J. Econ. Behav. Stud., vol. 13, no. 4(J), pp. 41–49, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Hermawan, H. Hartaty, and Suwito, “The Effect of Financial Performance on Capital Expenditure and Economic Growth of Districts/Cities in North Maluku Province.,” Public Policy Adm. Res., vol. 11, no. 3, 2021.
- S. Sug, “Regional Financial Management Policy that Implies To Criminal Administration,” J. Soc. Dev. Sci., vol. 7, no. 4(S), pp. 29–37, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- F. S. Kawatu, “Regional Public Service Agency’s Financial Management Implementation in Walanda Maramis North Minahasa Public Hospital,” Int. J. Account. Financ. Asia Pasific, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 87–96, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Ayu L, S. Rahayu, and J. Junaidi, “The Effect of Financial Performance on Economic Growth With Allocation of Capital Expenditures as Intervening Variable,” J. Akunt. Keuang. Unja, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 31–44, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. H. M. Zein and S. Septiani, “The Effect of Financial Performance on Capital Expenditure, Economic Growth, Human Development Index, and Poverty,” Qual. to Success, vol. 25, no. 200, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- W. Warman, “Policy Implementation, Financial Management, Bureaucratic Innovation, and Community Participation on Regional Development Planning’s Effectiveness,” Indones. J. Multidiscip. Sci., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 1898–1909, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Sipayung and R., D. Cristian, “The Influence Of The Implementation Of Regional Autonomy On Regional Financial Management Of East Kalimantan Province,” Citiz. J. Ilm. Multidisiplin Indones., vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 356–368, Jun. 2022. [CrossRef]
- R. Rasidah, L. Safrida, and M. Yuliastina, “Peningkatan Kapabilitas Bendahara Pengeluaran Sekretariat Dewan Kota, Kabupaten dan Provinsi Di Kalimantan Selatan,” Ekobis Abdimas J. Pengabdi. Masy., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 64–71, Dec. 2022. [CrossRef]
- N. V. Butar-Butar, D. Sagala, G. A. Simangunsong, B. R. M. Nainggolan, and D. M. Situmorang, “The Effect of Regional Original Revenue, Balancing Funds, Capital Expenditure, and Financial Performance on Economic Growth in Regency/City in North Sumatra Province for the Years 2017- 2021,” J. Res. Business, Econ. Educ., vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 13–22, Jun. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Chudaeva and, O. Sukach, “Modern Management Approaches To The Financial Security Of The Region Under Budgetary Decentralization,” Balt. J. Econ. Stud., vol. 5, no. 4, p. 227, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, J. Tong, and Z. Fang, “Assessing the Drivers of Sustained Agricultural Economic Development in China: Agricultural Productivity and Poverty Reduction Efficiency,” Sustainability, vol. 16, no. 5, p. 2073, Mar. 2024. [CrossRef]
- K. Ratri and Retnosari, “Analysis Of The Effectiveness And Efficiency Of The Magelang City Government Area’s Financial Performance For The 2017-2021 Fiscal Year,” CASHFLOW Curr. Adv. Res. SHARIA Financ. Econ. Worldw., vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 305–314, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).