1. Introduction
The report of the Party's 20th National Congress clearly stated that “adhere to high-quality development and promote green economic transformation.” Green total factor productivity, which takes economy, energy and environment into consideration, has become one of the important indicators to measure the high-quality development of regional economy [
1]. Resource-based cities, as the key components of China's high-quality economic development, and relying on their rich natural resources and unique industrial system, have made great contributions to ensuring the stability of energy resources in China and promoting the development of national economy. However, due to the low-end industrial structure and excessive dependence on resources, the development of resource-based cities is also accompanied by high energy consumption, high pollution and high emission [
2]. Especially in the context of national economic transformation and upgrading and optimization of production capacity structure, resource-based cities are faced with problems such as unbalanced production capacity structure, excessive resource consumption and deterioration of ecological environment [
3], and have gradually become problem-oriented cities. To this end, The State Council issued the National Plan for the Sustainable Development of Resource-Based Cities (2013-2020) in November 2013 (hereinafter referred to as the Plan), aiming to promote the sustainable development of resource-based cities and guide the transformation of green economic development.
Nowadays, with the continuous development of China's digital economy, it has gradually become a major driving force to promote China's economic development [
4]. According to the White Paper on China's Digital Economy Development released by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), the digital economy's share of GDP will rise from 20.9 percent to 39.8 percent from 2013 to 2022. At the same time, the Implementation Plan for Promoting High-quality Development in Resource-Based Areas approved by The State Council in 2021 clearly states that it is necessary to accelerate the construction of new infrastructure such as 5G, cloud computing, and big data centers in resource-based areas, encourage the development of a new generation of information technology and the Internet of Things, and promote the intelligent transformation of traditional industries. It can be seen that promoting the deep integration of digital economy and real economy is of great practical significance for resource-based cities to achieve high-quality economic development.
At present, the research results on the impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity are constantly abundant, which are mainly discussed from three levels: micro enterprise, medium industry and macro economy. At the micro enterprise level, the development of urban digital economy can alleviate the financing constraints of enterprises, improve the innovation level of enterprises and the speed of digital transformation, and achieve high-quality development of enterprises [
5]. At the same time, through digital transformation, manufacturing enterprises can promote green technology innovation and strengthen human resource allocation, which will have a positive impact on the green total factor productivity of enterprises [
6]. At the mesoindustrial level, the digital economy can promote the transformation of industrial organization, reshape market concepts, and promote the green transformation and development of different industries [
7]. Huining (2022) takes human capital and entrepreneurial activities as research perspectives and finds that digital economy can improve the green total factor productivity of manufacturing [
8]. At the macroeconomic level, digital economy can improve urban green total factor productivity by influencing factors such as factor allocation efficiency [
9], green innovation capability [
10] and industrial structure upgrading [
11]. Furthermore, some researchers have found that digital economy has a spatial spillover effect on urban green total factor productivity, and believe that urban digital economy has an important contribution to the improvement of green total factor productivity in other cities [
12,
13].
In addition, the nonlinear characteristics of digital economy on green total factor productivity are also the focus of attention. Cheng Wenxian (2021) found that the impact of digital economy on China's industrial green total factor productivity is non-linear with industry scale and regional institutional environment as thresholds [
14]. Zhang Yinghao (2022) found that the impact of digital economy on urban green total factor productivity has phased characteristics, and the two show a U-shaped relationship [
15]. However, Wang Qiaoran (2023) found that the impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity is significantly positive and the marginal effect increases [
16]. In addition, urban environmental regulation intensity [
17], geographical location [
18], industrial structure [
19] and other heterogeneous factors also affect the effect of digital economy on urban green total factor productivity to varying degrees.
Based on the above literature, it can be found that existing studies have conducted in-depth analysis of the relationship between the two, but there are still the following shortcomings: First, most studies focus on the level of enterprises, industries, provincial and national prefecture-level cities, and few studies on resource-based cities alone; Second, from the perspective of urban energy efficiency and industrial structure optimization, there is no research on the impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity. Compared with general cities, resource-based cities have their particularities. Their economic development mostly depends on the richness of natural resources, and the leading industry is often the traditional manufacturing industry, which mainly focuses on resource exploitation and processing. The development of the primary and secondary industries is seriously lagging behind, and the environmental pollution problem is more serious than that of other cities [
20]. Therefore, there may be differences in the effect and action path of digital economy on green total factor productivity. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the special sample of resource-based cities, and further explore the impact mechanism of digital economy on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities from the perspective of industrial structure optimization and urban energy efficiency.
The possible marginal contributions of this paper are as follows: First, using the panel data of resource-based cities to empirically test the impact of digital economy on green TFP of resource-based cities, and enrich and expand the research literature on green TFP; Secondly, from the perspective of urban energy efficiency and industrial structure optimization, the influence path of digital economy and green total factor productivity is found, which greatly enriched the research literature on how to combine digital economy and real economy, and also has good practical guidance significance. Thirdly, from the perspective of city type and regional heterogeneity, this paper explores the heterogeneous impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities, which has certain reference value for formulating more accurate development policies of resource-based cities.
2. Theoretical Analysis and Research Hypothesis
2.1. Direct Impact of Digital Economy on Green Total Factor Productivity of Resource-Based Cities
Digital economy plays an important role in promoting the economic green exhibition of resource-based cities, which is mainly reflected in three aspects: promoting green production mode, developing green industry and improving green ecological environment. First, in promoting green production methods. Through the application of technologies such as big data, cloud computing and the Internet of Things, the digital economy can digitize and automate the existing traditional industries [
21], realize the transformation of traditional resource-based industrial enterprises to intelligent manufacturing, and reduce the consumption intensity of resources and energy. At the same time, with the development of industries related to the digital economy and the improvement of digital infrastructure, the diffusion barriers of information technology have been reduced, which can bring low-carbon green technology and production mode [
12], promote resource-based industrial enterprises to reduce the production mode of high energy consumption and high pollution, and thus promote green production. Second, the development of green industries. The digital economy is an environmentally friendly industry, and its development premise is the construction of information infrastructure, which will not directly affect the environment. At present, more and more resource-based regions such as Guizhou and Inner Mongolia are actively building information infrastructure such as 5G, big data and cloud computing, and vigorously developing strategic emerging industries such as information industry and software, which has promoted the development of green industries. Third, to improve the green ecological environment. Based on digital technologies such as biosensors and infrared sensors, government departments can achieve comprehensive supervision and efficient protection of the ecological environment [
22], and the public can also become the main force of environmental supervision through digital technology, strengthening the environmental awareness of enterprises and improving the green ecological environment. Based on this, this paper proposes:
Hypothesis 1: Digital economy can promote the improvement of green total factor productivity in resource-based cities.
2.2. Indirect Impact of Digital Economy on Green Total Factor Productivity of Resource-Based Cities
Previous studies have shown that improving energy efficiency is an effective way to promote green total factor productivity [
23]. Compared with the traditional economy, the digital economy relies on massive data and digital technology, which can break through the restrictions of knowledge and technology exchange and promote new technologies related to energy production and consumption [
24]. On a macro level, digital technology has gradually penetrated into the production process, organizational form and business promotion of traditional industries [
25], enabling scientific and efficient integration and utilization of various production factors such as energy and data, reducing unnecessary factor and energy consumption, and alleviating the dilemma of the continuous flow of traditional production factors to resource-based sectors in resource-based cities [
26]. To optimize the energy allocation structure, reduce the energy intensity of various industries, improve energy efficiency; At the micro level, the digital economy can promote the digital development of enterprises and governments, and improve the efficiency of transactions, production and distribution. For example, the application of digital technology to the mining and beneficiation of natural resources can greatly improve production efficiency; In the smelting process of natural resources, the digital green production process can reduce pollutant emissions and reduce energy consumption in the production process. At the same time, big data technology can analyze the price trend and market demand of natural resources, which is convenient to predict the uncertainty of the market and conducive to the operation and production decision-making of enterprises. Based on this, this paper proposes:
Hypothesis 2: Digital economy promotes the improvement of green total factor productivity of resource-based cities by improving energy efficiency.
Previous studies have suggested that the optimization of industrial structure will have a direct impact on the green total factor productivity of resource-based cities [
27,
28], while the optimization of industrial structure of resource-based cities is mainly manifested by the transformation of resource-based industries into tertiary industries, high-tech industries and emerging industries [
29]. The digital economy provides the necessary conditions for the optimization of the industrial structure of resource-based cities. First of all, the digital economy can directly drive the development of the tertiary industry. In the process of digital transformation of industry and agriculture using digital technology, many service industries will be created, such as e-commerce and smart logistics, which will drive the development of upstream and downstream service industries and increase the proportion of added value of service industries in GDP. Secondly, digital economy can promote the development of primary and secondary industries. For the primary industry, the digital economy has greatly improved agricultural production efficiency and production quality through intelligent and refined management and cultivation, and greatly expanded sales channels through rural e-commerce; For the secondary industry, based on the resource advantages of resource-based areas, the use of digital technology can promote the production of high-end products, thereby increasing the added value of products and extending the industrial chain. In addition, the digital economy can promote the transformation of traditional industries into digital industries and promote industrial integration, such as smart mines and digital oil fields. Based on this, this paper proposes:
Hypothesis 3: The digital economy promotes the improvement of green total factor productivity of resource-based cities through the optimization of industrial structure.
3. Research Design
3.1. Model Setting
According to the theoretical mechanism mentioned above, this paper builds the basic model as follows:
In formula (1), i represents each resource-based city, and t represents the year. is the explained variable, representing green total factor productivity; is the core explanatory variable of this paper, representing digital economy; represents a set of control variables; represents the unobservable regional individual effect, represents the time effect, and is the random disturbance term.
Secondly, in order to test whether the digital economy affects green total factor productivity through energy efficiency (Ee) and industrial structure optimization (Ins), this paper draws on Wen Zhonglin's (2004) intermediary effect model [
30] and constructs the following regression model:
The first step is to construct regression models of digital economy and energy efficiency and industrial structure optimization.
The second step is to test whether the digital economy promotes green total factor productivity through energy efficiency and industrial structure optimization, as shown in formula (4) and (5).
3.2. Description of Variables
3.2.1. Explained Variable: Green Total Factor Productivity (Gtfp)
The methods of measuring green total factor productivity can be divided into stochastic frontier method (SFA) and data envelopment analysis (DEA). After comparing the two types of methods, this paper selects the non-expected output Super-SBM (Slack-based Measure) model [
31] based on variable returns to scale (VRS), and combines the Global Malmquist-Luenberger (GML) index for measurement. On the one hand, the Super-SBM model allows the proportional improvement of all elements and the efficiency value of effective DMU >1 [
32]. On the other hand, the GML index can make up for the possible problems of non-solution and non-transitivity in linear programming when ML index is used to measure the inter-temporal directional distance function, and realize the inter-temporal comparison between different years. Since the GML index is the sequential rate between years, this paper draws on the practice of Qi Shaozhou (2018) [
33], and sets 2013 as the base period and
Gtfp as 1, and multiplicates with the GML value of each year in turn, and finally gets the
Gtfp of each city in each year. Specific measurement indicators are as follows:
(1) Input indicators: including labor, capital and energy input. Among them, labor input is measured by the number of urban employment at the end of the year in prefecture-level cities. Referring to the practice of Zhang Jun (2004), capital input adopts the method of perpetual inventory [
34] to calculate the actual capital stock of cities and uses the provincial fixed asset investment price index to deflate. Energy input is measured by the annual electricity consumption of prefecture-level cities.
(2) Expected output index: measured by regional gross domestic product (GDP) of prefecture-level cities and adjusted to constant price data.
(3) Non-expected output index: Industrial wastewater, sulfur dioxide and smoke (powder) dust emissions are selected as non-expected output.
3.2.2. Explanatory Variables: Digital Economy (Dig)
With reference to the approach of Zhao Tao (2020), the development level index of urban digital economy is measured from the level of Internet development [
35]. Specifically, four indicators were used to measure the number of Internet broadband access users per 100 people, the number of mobile phone users at the end of the year, the total number of telecommunications services per capita, and the proportion of computer software industry employees in urban units, and the principal component analysis was used to reduce dimension as an indicator, and standardized processing to the range of 0 to 1.
3.2.3. Intermediate Variables: Energy Efficiency (Ee) and Industrial Structure Optimization (Ins)
Energy efficiency: Referring to existing literature [
36,
37], this paper uses the reciprocal power consumption per unit GDP to measure the energy efficiency of each region. In order to eliminate the impact of dimension on calculation results, the standardized processing is carried out to the range of 0~1.
Industrial structure optimization: Referring to the practice of Xu Min (2015) [
38], the industrial structure upgrading coefficient is constructed to measure the optimization level of the industrial structure of resource-based cities. The calculation formula is as follows:
In Formula (6), Ii represents the proportion of output value of industry i in GDP of the sample city. In order to eliminate the impact of dimension on the calculation results, the standardized processing is in the range of 0~1.
3.2.4. Control Variables
Referring to previous studies [
39,
40,
41,
42], four characteristic indicators that may affect urban green total factor productivity were controlled: environmental regulation intensity (
Er). The emission of three industrial wastes (wastewater, SO2 and smoke (powder) dust) in resource-based cities was synthesized into an environmental regulation intensity index using entropy method. The level of opening to the outside world (
Open) is expressed by the proportion of the total volume of imports and exports in the GDP of prefecture-level cities; Human capital level (
Hum), expressed as number of undergraduate students per 10000; Resource endowment (
Re), expressed by the proportion of people employed in extractive industries to total employment.
3.3. Data Sources
In this paper, 262 resource-based cities were selected and 114 resource-based cities were selected. The data are mainly from China City Statistical Yearbook, provincial and municipal Statistical Yearbook, municipal government official websites and local statistics bureau websites.
3.4. Descriptive Statistics of Variables
Descriptive statistics of the main variables are shown in
Table 1. As can be seen from
Table 1, the minimum value of green total factor productivity (
Gtfp) in resource-based cities is 0.340, the maximum is 5.521, and the median is 1.000, which is lower than the mean value of 1.144, indicating that there are great differences in
Gtfp in resource-based cities and the polarization is serious. Digital Economy (
Dig) is similar to
Gtfp, but varies widely between cities. The median of energy efficiency (
Ee) is 0.260, and the average is 0.285, which indicates that there is a large gap in energy efficiency among resource-based cities. The median of industrial structure optimization (
Ins) is 0.561, and the average is 0.555, which is lower than the median, indicating that the difference of industrial structure among resource-based cities is small.
3.5. Analysis of the Calculation Results of Green Total Factor Productivity
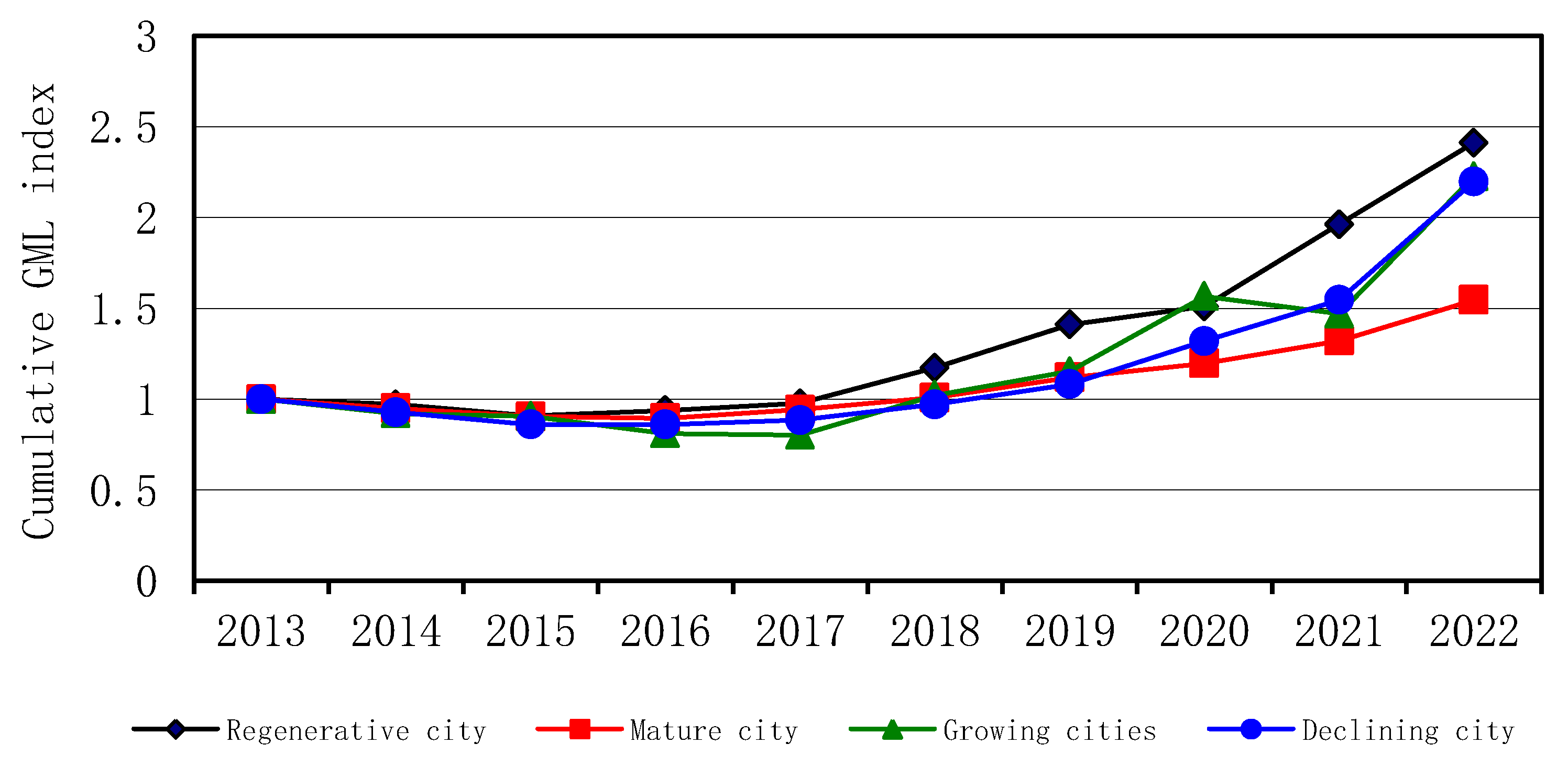
According to the “Planning”, the research samples were classified according to city types, and 14 growth cities, 64 mature cities, 13 regenerative cities and 23 declining cities were finally determined. maxDEA software was used to calculate the GML index of different resource-based cities from 2013 to 2022, and accumulated year by year to obtain the cumulative GML index change value of different resource-based cities, as shown in
Figure 1. It can be seen that the cumulative value of GML index of the four resource-based cities showed a fluctuating downward trend from 2012 to 2015, and an upward trend after 2015, which is consistent with the research conclusion of Xiao Ying (2019) [
26]. In addition, the GML index values of regenerative, growing and declining cities are larger, indicating that the average annual growth of green total factor productivity is faster, while that of mature cities is relatively slow.
4. Analysis of Empirical Results
4.1. Baseline Regression Results
In this paper, fixed effects, random effects and mixed OLS models were selected for regression. After Hausmann test, fixed effects models with better fitting effect and more robust results were selected. The benchmark regression results are shown in
Table 2. Referring to the test idea of Weschway (2022) [
43], this paper adopts a progressive regression processing method. As shown in
Table 2, the digital economy of the core explanatory variable is significant at the 1% level, and when the digital economy level of resource-based cities increases by 1%, the green total factor productivity will increase by 2.588. Hypothesis 1 is proved.
4.2. Robustness Test
4.2.1. Sample Tailing Processing
Considering that the research conclusion may be affected by extreme values and outliers, the main explanatory variables are further shrinked at the 1% level in this paper, and the regression results are shown in
Table 3. So the conclusion is still sound.
4.2.2. Explanatory Variable Lag
Considering that the impact of digital economy may have a certain time lag effect, the core explanatory variables are further tested after a delay of 1 to 3 periods, respectively, and the results are shown in
Table 3. The regression coefficients in the lag model all increase successively, indicating that the digital economy has a greater long-term impact on urban green development than the short-term impact, and the conclusion is still robust.
4.2.3. Change the Measurement Method of Explained Variables
The explained variable in this paper is resource-based city
Gtfp. By referring to the measurement method of Qi Shaozhou (2018) [
33], the original Super-SBM model is changed to SBM model, and the resource-based city
Gtfp is calculated by combining the GML index, with the input and output indexes unchanged. Regression results are shown in
Table 3. So the conclusion is still sound.
4.3. Endogeneity Analysis
4.3.1. Tool Variable Method
Considering that
Gtfp in resource-based cities may be interfered by regional institutional environment, technological innovation and other factors, and there may be a potential reverse causality between digital economy and
Gtfp, which may lead to endogeneity problems. Therefore, further instrumental variables are adopted to alleviate the above problems. Based on the research ideas of Huang Qunhui (2019) and CAI Ling (2022), the interaction term between the number of post offices in resource-based cities at the end of 1993 and the investment in fixed assets of information, software and information technology services in the previous year (which is related to time) is taken as the instrumental variable of the development level of digital economy in resource-based cities [
44]. The reasons are as follows: the regions with a large number of post offices in history have more demand for “online” communication, and the infrastructure of post and telecommunications will also have an impact on the information infrastructure construction of the current resource-based cities, meeting the relevant conditions; At the same time, with the development of information technology, the related business and main functions of the post office will be replaced by new information tools, so it is unlikely to have a certain impact on the current resource-based city
Gtfp.
In this paper, 2SLS model is used for testing, and the results are shown in
Table 4. From the first stage of 2SLS, the selected instrumental variables are correlated with the level of digital economy of resource-based cities, and pass the 1% correlation test, and the F statistic is 12.61, greater than the critical value 10, so there is no need to worry about the problem of weak instrumental variables. From the results of the second stage, the unrecognizable LM test is passed, which shows the rationality of the choice of instrumental variables. Therefore, after considering the possible endogeneity problem, the conclusion of this study is still robust.
4.3.2. Dynamic GMM Panel Analysis
Considering that the green total factor productivity of the current period will be affected by the previous period (that is, sequence correlation), the research conclusion will be affected. Therefore, the dynamic panel estimation benchmark model is adopted, and the possible endogeneity problem between variables is solved by the system GMM estimation method. The results are shown in
Table 4. The Dig coefficient is significantly positive at the 5% level, and it passes the over recognition test and the differential autocorrelation test of the disturbance term, indicating that the results in this paper are still robust.
5. Mechanism Analysis
5.1. Mediation Effect Test
In order to test hypothesis 2 and 3, regression was performed using the intermediary effect model, and the results were shown in
Table 5. Among them, the estimation results in
Table 5 (2) and (3) are based on energy efficiency as the intermediary variable. The results show that the coefficients of digital economy and energy efficiency are both significantly positive, and the influence coefficient of digital economy on green total factor productivity becomes smaller, indicating that digital economy can promote the improvement of green total factor productivity of resource-based cities by improving energy efficiency. Hypothesis 2 is proved.
In
Table 5, columns (4) and (5) are the estimated results of industrial structure optimization as the intermediary variable. The results show that the coefficients of digital economy and industrial structure optimization are significantly positive, and the influence coefficient of digital economy on green total factor productivity becomes smaller, indicating that digital economy can promote the improvement of green total factor productivity of resource-based cities through industrial structure optimization. Hypothesis 3 proves.
The Sobel test was further performed for the two effects, and the Z-statistic value in the regression of energy efficiency was 2.24 (significant at 5% confidence level), and the proportion of intermediary effect in the total effect was 9.07%. The Z-statistic value in the regression of industrial structure optimization is 4.91 (significant at 1% confidence level), and the proportion of intermediary effect in the total effect is 12.73%.
6. Heterogeneity Analysis
6.1. Different Types of Resource-Based Cities
Considering the large differences in digital economy among different types of resource-based cities and the differences in green total factor productivity among different types of resource-based cities, it is necessary to conduct sub-sample regression according to resource-based city types, and the results are shown in columns (1) ~ (4) of
Table 6.
It can be seen that the estimated coefficients of the digital economy of mature cities, growing cities and declining cities on green total factor productivity are 5.448, 1.434 and 2.307, respectively, and all are significant, while the regression coefficient of the digital economy of regenerative cities on green total factor productivity is 4.064, but not significant. At the same time, it shows that digital economy has the greatest effect on promoting green total factor productivity in mature cities. The possible reasons for the above results are as follows: first, in the core areas of China's natural resources supply in mature cities, traditional resource-based industries account for a high proportion, and industrial equipment is slowly updated. Digital economy promotes the upgrading and transformation of resource-based industries' technical level and industrial equipment, improves the mining efficiency of natural resources, and is conducive to the green transformation of the overall industry; Second, growth cities have strong capacity to secure follow-up resources, and resource-based enterprises are gradually developing and expanding. Digital economy has improved urban industrial level, facilitated the combination of industrial production and information technology, improved the level of deep processing of resources, and accelerated the construction of new industrialization. Thirdly, resources in declining cities are exhausted, and there are many unemployed people in cities, resulting in serious population loss. Digital economy promotes the promotion of other industries, which is conducive to the development of alternative industries. Fourth, regenerative cities have basically got rid of the dependence on resources, leading industries in cities no longer depend on natural resources, non-resource industries are booming, digital economy not only increases the proportion of service industries, but also benefits the development of urban emerging industries.
6.2. Geographical Location of the City
Considering that different resource-based cities are located in different geographical locations, and there are great differences in the level of digital economy and green total factor productivity in different regions. Although the digital economy has a significant promotion effect on the green total factor productivity of resource-based cities, it is necessary to conduct heterogeneity analysis based on the perspective of geographical location considering that geographical location factors will have an impact on the basic conclusion of this paper. In order to explore the differential impact that geographical location factors may bring to the development of digital economy, this paper divides all resource-based cities into central, western and eastern regions according to geographical location. The results are shown in columns (1) ~ (3) of
Table 7.
The results of
Table 7 show that the digital economy coefficient of eastern cities is 3.355 and significant at 5% level, that of central cities is 3.001 and significant at 5% level, and that of western cities is positive but not significant, indicating that in eastern and central regions, digital economy has a significant promoting effect on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities. In the western region, digital economy has no significant effect on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities.
The possible reasons for the above results are as follows: First, due to the better digital infrastructure in the eastern region, the first-mover advantage in talent, technology and location, and the higher level of digital economy development. The resource-based cities in the eastern region are mostly dominated by steel, chemicals and building materials, etc. Digital economy plays a great role in promoting urban green technology innovation, energy conservation and emission reduction, and industrial structure upgrading, which can bring opportunities for the development of resource-based cities in the eastern region, and then have a significant positive impact on the green total factor productivity of resource-based cities. Secondly, most of the resource-based cities in the central region are dominated by smelting industry, petrochemical industry and agriculture, and are the places to undertake the transfer of low-end production capacity in the eastern region, and some resource-based cities have huge energy consumption. At the same time, this also provides a rich development carrier and market space for digital technology application and innovation. Although the digital infrastructure in the central region is not yet perfect, the level of digital technology application and innovation is constantly developing, and has become an important driving force for industrial transformation and upgrading, combining the digital economy with the real economy. Therefore, the digital economy can promote the green all-factor industry of resource-based cities. Finally, the digital economy industry in the western region is relatively weak, and the level of digital technology application and innovation is relatively lagging behind. Although the resource-based cities in the western region are relatively rich in energy resources and the national policy support is strong, the integration level of informatization and industrialization lags behind that of the eastern and central regions. Therefore, the positive impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities needs to be further improved.
7. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
Based on the panel data of 114 resource-based cities in China during 2013-2022, this paper calculates the digital economy development level and green total factor productivity of resource-based cities by using principal component analysis and Super-SBM and Malmquist index respectively. This paper empirically studies the effect and mechanism of digital economy on green total factor productivity of resource-based cities. The main research conclusions are as follows: First, the green total factor productivity of resource-based cities in China shows an overall upward trend from 2013 to 2022, and the cumulative growth rate index in the ten years is in the order of regenerative cities > growing cities > declining cities > mature cities. Second, digital economy has significantly promoted the improvement of green total factor productivity in resource-based cities, and this conclusion is still valid through various robustness tests. And the digital economy is more capable of long-term effects than short-term ones. Third, the results of intermediate effect model test show that digital economy can promote the improvement of green total factor productivity through energy efficiency and industrial structure optimization; Fourth, the heterogeneity study shows that digital economy has the largest effect on green total factor productivity in mature cities and the least effect on growth cities. In addition, digital economy has the strongest effect on green total factor productivity of cities in eastern region, followed by cities in central region, and the weakest effect on cities in western region.
Based on the above research conclusions, this paper puts forward the following five suggestions:
First, define the green development direction of different types of resource-based cities. The green total factor productivity of regenerative cities is higher, so the research and development of key technologies should be strengthened to improve the level of scientific and technological innovation. The green total factor productivity of growing cities is in a wave rising stage, so resource exploitation intensity should be rationally planned to gradually get rid of dependence on natural resources and further reduce environmental impact. The green total factor productivity of mature cities rises slowly, so we should focus on solving the problem of environmental pollution and breaking the dominant situation of resource-based industries, standardize the order of resource development, and promote the development of other industries. The green total factor productivity (TFP) of declining cities is on the rise gradually, so we should pay attention to the green transformation of traditional industries and the development of alternative industries to enhance the ability of sustainable development.
Second, Scientifically deploy digital economy and green development path of different resource-based cities. For regenerative cities, we should actively explore the development of digital economy, use digital technology to cultivate new business forms, transform and upgrade advantageous industries, and develop future digital industries. For growth cities, we should promote the development of digital economy, open up the upstream and downstream data channels of enterprises, and extend the industrial chain. Mature cities should tap the development potential of digital economy, use digital technology to guide the production of traditional industries, accelerate the transformation of original technologies and research and development of new technologies, and improve the scientific and technological content and added value of resource products. For recession-type cities, they should actively seize the opportunities of digital economy, integrate existing resources with the help of digital economy platforms, carry out intensive production and operation, and actively develop replacement industries. At the same time, it is necessary to recognize the time-lag effect of the digital economy and formulate a coherent and stable long-term digital economy plan.
Third, promote the coordinated development of digital economy in different resource-based regions. Strengthen the development of digital economy in the resource-based regions of central and western China, gradually narrow the digital gap with the eastern region, and better serve the upgrading of traditional industries, industrial undertaking and the cultivation of emerging industries in the resource-based regions of central and western China. At the same time, according to the current situation of digital economy development in various resource-based regions, combined with the national strategic layout of digital economy, formulate differentiated digital economy development policies, release the contribution capacity of digital economy to resource-based regions, and gradually promote the process of digital industrialization in resource-based regions.
Fourth, we need to improve energy efficiency in resource-based areas. Enterprises should be encouraged to apply digital technologies to the manufacturing process, guide enterprises and scientific research institutions to conduct research and development of digital technologies, energy saving and emission reduction technologies, and strengthen the awareness of the deep integration of the digital economy and the resource industry. Governments should use the digital economy to improve regional resource allocation and maximize energy efficiency, while taking advantage of the convenience provided by digital technologies to monitor energy consumption.
Fifth, promote the optimization of industrial structure in resource-based areas. Through the digital economy to empower the traditional industries in resource-based areas, and combined with their own positioning, explore new industrial exhibition models, create distinctive industrial clusters, resource advantages into industrial advantages.
Author Contributions
MZ: funding acquisition, project administration, resources, and writing–review and editing. LL: data curation, methodology, and writing–original draft. DW: project administration, supervision, and writing–review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by Chinese National Funding of Social Sciences (No. 22XGL003).
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusion of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the reviewers and editors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Feng G, SERLETIS A. Undesirable outputs and a primal divisia productivity index based on the directional output distance function [J].Journal of econometrics,2014(1):135-146.
- Li H, Zou Q. Environmental regulation, resource endowment and urban industrial transformation: A comparative analysis of resource-based cities and non-resource-based cities [J]. Economic Research,2018(11):182-198.
- Cui Dan, BU Xiaoyan, Xu Zhen, LI Guoping, WU Dianting. Comprehensive evaluation and influencing mechanism of high-quality development of resource-based cities in China [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2021,76(10):2489-2503.
- Liu Shuchun.The targeted path and policy supply of high-quality development of China's digital economy [J]. Economist,2019(06):52-61.
- Guo Feng, Yang Shangguang, Jin Huan. The impact of digital Economy on Total Factor Productivity of enterprises and its mechanism [J]. Modern Finance and Economics (Journal of Tianjin University of Finance and Economics),2022,42(09):20-36.
- Liu Wenjun, Peng Hui. Spatial effects of digital transformation on green total factor productivity in regional manufacturing enterprises [J]. Economic Geography, 2019,43(06):33-44.
- Jing Wenjun, Sun Baowen. Digital economy promoting high-quality economic development: a theoretical framework [J]. Economist,2019(02):66-73.
- Hui Ning, Yang Xin. Digital economy driving and high-quality development of China's Manufacturing Industry [J]. Journal of Shaanxi Normal University (Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition),2022,51(01):133-147.
- Wen Fengan. Digital economy development, factor allocation efficiency and urban green production efficiency [J]. Industrial Economics Research,2023(03):57-71+86.
- CAI Ling, Wang Ping. Digital economy and urban green total factor productivity: influencing mechanism and empirical evidence [J]. Statistics and Decision,2022,38(09):11-16.
- Zou Jing, WANG Qiang, YAN Huili, et al. How does the digital economy affect green total factor Productivity? Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China [J]. Soft Science, 2019,38(03):44-52.
- Zhang Yuan. The spatial effect of urban digital economy on green total factor productivity: Theoretical mechanism and empirical test [J]. Economic System Reform,2022(04):43-50.
- Yang Youcai, Wang Yucong, Wei Tao. Does the digital economy improve green total factor Productivity? [J]. Learning and Exploration,2022(12):114-123.
- Cheng Wenxian, Qian Xuefeng. Digital economy and China's industrial green total factor productivity growth [J]. Economic Issues Exploration,2021(08):124-140.
- ZHANG Yinghao, Wang Mingfeng, Cui Luming, Kuang Aiping. The impact of digital economy on green total factor productivity in Chinese cities [J]. Economic Geography,202,42(09):33-42.
- Wang Qiaoran. Digital economy development and green total factor productivity in urban agglomeration: Mechanism and inclusive nature [J]. China Circulation Economy, 2019,37(06):51-64.
- Zhao Wei. Digital economy and urban green total factor productivity: mechanism and threshold effect. China Circulation Economy,2022,36(11):15-26.
- CAI Ling, Wang Ping. Digital economy and urban green total factor productivity: influencing mechanism and empirical evidence [J]. Statistics and Decision,2022,38(09):11-16.
- Zhu Xi 'an, Ma Yingge. Study on the impact of digital economy on the change of green total factor productivity [J]. Economic Issues,2022(11):1-11.
- Zeng Gang, Lu Linyi, He Jinliao. Impact of ecological innovation on industrial structure and industrial green efficiency of resource-based cities [J]. Resources Science, 2019,43(01):94-103.
- Ding Zhifan. Research on the mechanism of Digital Economy driving high-quality economic development: a theoretical analysis framework [J]. Modern Economic Research,2020(01):85-92.
- Han Jing, Chen Xi, Feng Xiaohu. The practical challenges and path choice of enabling green development of digital economy [J]. Reform,2022(09):11-23.
- Liu Yingshi, Tian Yinhua, Luo Ying. Industrial structure upgrading, energy efficiency and green total factor productivity [J]. Finance Theory and Practice,2018,39(01):118-126.
- Zhang Jie, Fu Kui, Liu Bingrong. How the digital economy enables the low-carbon transformation of cities: Based on the dual goal constraint perspective [J]. Modern Finance and Economics (Journal of Tianjin University of Finance and Economics),2022,42(08):3-23.
- Matthess M, Kunkel S. Structural change and digitalization in developing countries: Conceptually linking the two transformations[J]. Technology in society, 2020, 63: 101428. [CrossRef]
- Xiao Ying, Lu Liwen. Measurement of industrial green transformation in Resource-based cities: Based on panel data analysis of 108 resource-based cities in China [J]. Science of Finance and Economics,2019(09):86-98.
- Li Bo, Qin Huan, Sun Wei. The interactive relationship between industrial transformation and upgrading and green total factor productivity improvement: An empirical study of 116 resource-based cities in China [J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2019,37(01):186-199.
- Zhang Guoqing, Yan Huizhen. Effect of industrial structure optimization on regional green total factor productivity under the guidance of high-quality development [J]. Jiangxi Social Sciences, 2019,40(05):63-71.
- Liu Xiaoling, Tang Zhuowei, Sun Xiaohua, Yu Runqun. Factor mismatch: Unlocking the dilemma of resource-based city transformation [J]. China Population, Resources and Environment,202,32(10):88-102.
- Wen Zhonglin. Zhang Lei, HOU Jietai, Liu Hongyun. Mediation effect test and its application [J]. Acta Psychologica Sinica,2004(05):614-620.
- TONE K., A. Slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis [J].European journal of operational Research, 2002143 (1), 321-41.
- Wei Lili, Hou Yuqi. Study on the impact of digital economy on China's urban green development [J]. Journal of Quantitative and Technical Economics,2022,39(08):60-79.
- Qi Shaozhou, Xu Jia. The impact of trade opening on green total factor productivity in countries along the Belt and Road [J]. China Population, Resources and Environment,2018,28(04):134-144.
- Zhang Jun, Wu Guiying, Zhang Jipeng. Estimation of China's provincial physical capital stock: 1952-2000. Economic Research Journal,2004(10):35-44.
- Zhao Tao, Zhang Zhi, Liang Shangkun. Digital economy, entrepreneurial activity and high-quality development: Empirical evidence from Chinese cities [J]. Management World, 2019,36(10):65-76.
- Shen Bing, Li Xin. Financial development, upgrading of industrial structure and improvement of energy efficiency [J]. Economic Issues Exploration,2020(12):131-138.
- Li Shunyi. Effect of pilot policies on energy consumption intensity in low-carbon cities: An analysis based on synthetic control method [J]. Urban Problems,2018(07):38-47.
- Xu Min, Jiang Yong. Can upgrading China's industrial structure narrow the gap between urban and rural consumption? [J]. Journal of Quantitative and Technical Economics,2015,32(03):3-21.
- Li Deshan, Zhang Zhengqiu. The impact of environmental regulation on urban green total factor productivity [J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology (Social Sciences Edition), 2019,22(04):39-48.
- ZHAO Mingliang, Liu Fangyi, Wang Huan, Sun Wei. FDI, environmental regulation and urban green total factor productivity in the Yellow River Basin [J]. Economic Geography,2020,40(04):38-47.
- Su Ke, Zhou Chao. Human capital, scientific and technological innovation and green total factor productivity: Based on urban data analysis in the Yangtze River Economic Belt [J]. Economic Issues,2021(05):71-79.
- Zheng Tingting, Fu Wei, Chen Jing. Informatization development level, resource dependence and green total factor productivity: An analysis of panel data from prefecture-level cities [J]. Science and Technology Progress and Countermeasures,2019,36(23):44-52.
- Weschway, Du Jinmin, Pan Shuang. How digital economy promotes green innovation: Empirical evidence from Chinese cities [J]. Journal of Finance and Economics,2022,(11):10-20. [CrossRef]
- Huang Qunhui, Yu Yongze, Zhang Songlin. Internet development and manufacturing productivity improvement: Internal mechanism and China's experience [J]. China Industrial Economics,2019(08):5-23.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).