1. Introduction
The group-specific component (Gc) protein is a 51–58 kDa glycoprotein that functions as a vitamin D transporter and actin scavenger in the blood [
1,
2,
3]. In vivo, galactose and sialic acid of Gc protein are cleaved by β-galactosidase derived from B cells and sialidase derived from T cells, respectively, to form the Gc protein-derived macrophage-activating factor (GcMAF) with an N-acetylgalactosamine residue [
4]. GcMAF induces superoxide production in macrophages and inhibits angiogenesis in cancer cells [
5]. We have previously observed that GcMAF enhances the phagocytic activity of peritoneal macrophages [
6], inhibits angiogenesis, and reduces tumor size in tumor-bearing mice [
7]. Furthermore, we report a cancer immunotherapeutic strategy to enhance the immune activity of patients with cancer using artificially glycosylated GcMAF [
8].
Tumor growth is greatly influenced by the tumor microenvironment formed by the tumor and surrounding stromal cells. Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), fibroblasts, and vascular endothelial cells are the major components of tumor stromal cells that promote tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression [
9]. There are two main types of macrophages: M1 macrophages, which are important in innate immunity, such as the production of inflammatory cytokines and phagocytosis, and M2 macrophages, which exert anti-inflammatory effects and induce immunosuppressive cytokines [
10]. Although macrophages are a mixture of these two types, many TAMs in malignant tumors are of the M2 type [
11]. Recent studies reported that the M2 type is a collection of multiple functionally distinct subsets and can be divided into M2a/M2b/M2c/M2d phenotypes according to different gene expression profiles [
12], TAMs can be reprogrammed between M1 and M2 depending on the surrounding environment [
13], and TAMs sometimes co-expresses M1 and M2 related genes[
14].TAMs induce immunosuppression via various factors, such as interleukin (IL)-10 and transforming growth factor-β, in tumors [
15], and produce various factors, such as the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), IL-8, and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), under hypoxic stimulation [
16,
17]. They activate the factors involved in angiogenesis [
18], creating a favorable tumor microenvironment. Controlling macrophage function in the tumor microenvironment is important for inhibiting tumor progression.
GcMAF has been reported to have anti-tumor effects in in vitro models via macrophage activation [
19,
20,
21,
22], biological activities such as inhibition of angiogenesis in tumor tissue [
5,
23,
24], and anti-tumor effects against several types of cancer in clinical trials using GcMAF [
7,
25,
26,
27]; research is being conducted to elucidate the mechanism of action and its usefulness as a new therapeutic agent. This study clarifies the effects of GcMAF-stimulated macrophages on adjacent tumor cells in a noncontact environment and assesses the effects of GcMAF on M2 macrophages. We investigated the anti-tumor mechanisms of GcMAF in the tumor microenvironment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
Gc protein was extracted from human serum using 25(OH)D3-sepharose column chromatography as previously described [
6]. Gc protein was treated with β-D-galactosidase (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp., Osaka, Japan) at 37 °C for 3 h and then with sialidase enzyme (Sigma-Aldrich Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan) at 37 °C for 3 h to produce the GcMAF. GcMAF was purified using a 25(OH)D3-sepharose column.
2.2. Cells
RAW264.7 mouse monocyte-derived macrophage cells (RIKENKAC Co., Ltd., Kyoto, Japan) were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS; Nichirei Biosciences Inc., Tokyo, Japan), 100 units/mL penicillin G, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.). EMT6 mouse breast cancer cells (kindly provided by Professor Osaki, Tottori University, Tottori, Japan) were cultured in Eagle’s minimum essential medium (EMEM; Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.) supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 units/mL penicillin G, and 100 μg/mL streptomycin.
2.3. Co-Culture of RAW264.7 Cells and EMT6 Cells
RAW264.7 cells were seeded in 0.4-μm pore 6-well cell culture inserts (Griner Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan) at 5 × 105 per insert, set in a 6-well plate (AS ONE Corp., Osaka, Japan), and cultured overnight. After washing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan), GcMAF (0.1 μg/mL) or lipopolysaccharide (LPS; Escherichia coli O111:B4; 1 μg/mL; Sigma-Aldrich Japan) was added to FBS-free DMEM, and cells were cultured for 24 h. EMT6 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate at 5 × 105 per well, cultured overnight, and subsequently co-cultured with stimulated RAW264.7 cells (ratio 1:1) in FBS-free EMEM for 24 h. After incubation, cells, and the supernatant were collected and kept at -80 °C for further use.
2.4. Quantitative Reverse Transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR)
RNA was extracted from the cells using NucleoSpin RNA (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) and reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a PrimeScript II 1st strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Takara Bio Inc.). RT-qPCR was performed using Power Up SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) with the StepOne Plus Real-Time System (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). The real-time PCR applied 40 cycles of amplification consisting of 3 s at 95 °C (denaturation) and 30 s at 60 °C (annealing and extension). The relative expression calculated using the 2
-ΔΔCt method was applied to analyze the results with glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (
GAPDH) as an internal control. Sequences of all primers (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.) used here are as follows[
28,
29,
30]:
GAPDH (Forward, 5’-ATGGCCTTCCGTGTTCCTAC-3’ and Reverse, 5’-TAGCCCAAGATGCCCTTCAG-3’), tumor necrosis factor-α (
TNF-α; Forward, 5’-AATGGCCTCCCTCTCATCAG-3’ and Reverse, 5’-ACTTGGTGGTTTGCTACGAC-3’), inducible nitric oxide synthase (
iNOS; Forward, 5’-GGAATCTTGGAGCGAGTTGT-3’ and Reverse, 5’-GCAGCCTCTTGTCTTTGACC-3’),
CD206 (Forward, 5’-GGAGGCTGATTACGAGCAGT-3’ and Reverse, 5’-CATAGGAAACGGGAGAACCA-3’),
COX-2 (Forward, 5’-CCACTTCAAGGGAGTCTGGA-3’ and Reverse, 5’-AGTCATCTGCTACGGGAGGA-3’), and
VEGF (Forward, 5’-TACCTCCACCATGCCAAGTGGT-3’ and Reverse, 5’-AGGACGGCTTGAAGATGTAC-3’).
2.5. Nitric Oxide (NO) Assay
The collected supernatants were evaluated using the Griess assay to measure NO production by determining the amount of nitrite ions (NO2-) in the solution. The Griess reagent containing 1% sulfanilamide (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.), 2.5% phosphoric acid (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.), and 0.1% N-1-naphthylethylenediamine hydrochloride (Tokyo Chemical Industry Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was prepared and mixed with nitrous acid. The absorbance of a sample of known concentration prepared with an aqueous sodium solution (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.) and the culture supernatant was measured at 550 nm using a microplate reader (Tecan Group Ltd., Männedorf, Switzerland), and the amount of nitrite ions was calculated.
2.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The concentrations of TNF-α in the cell supernatant were gauged using an ELISA kit (ThermoFisher Scientific Inc.), according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.7. Evaluation of EMT6 Cell Number for Crystal Violet Staining Assay
EMT6 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at 5 × 105 per well and co-cultured with GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells (ratio 1:1) for 48 h. EMT6 cells were washed with PBS and stained with a crystal violet solution containing 0.5% crystal violet (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.) and 20% methanol (Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.) for 15 min. The solution was removed, and the cells were washed four times with tap water. The stained cells were eluted with 1% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS, Fujifilm WAKO Pure Chemical Corp.). Using a microplate reader, the number of live cells was evaluated by measuring the absorbance at 570 nm with a reference wavelength of 720 nm.
2.8. DNA Microarray Analysis
RAW264.7 cells were seeded in a 60-mm culture-dish plate at 6 × 106 cells per well and cultured overnight. RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with GcMAF at a final concentration of 1 μg/mL for 24 h, and RNA was extracted. DNA microarray analysis was performed by Filgen Inc. (Aich, Japan) using a mouse GeneChip Clariom S Assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.). Microarray data were analyzed using the Microarray Data Analysis Tool v.3.2. (Filgen Inc.).
2.9. M2 Polarization of RAW264.7 Cells
RAW264.7 cells were seeded in a 6-well plate at 8 × 105 per well and cultured overnight. After washing with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; Nacalai Tesque, Inc., Kyoto, Japan), the cells were cultured for 72 h in FBS-free DMEM supplemented with IL-4 and IL-13 (20 ng/mL each; Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., MA, USA) for M2 polarization. M2-stimulated RAW264.7 cells were treated with GcMAF (0.1 μg/mL) for 24 h, and the treated cells supernatant was collected.
2.10. Evaluation of EMT6 Cell Number for Cell Counting kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
EMT6 cells were seeded in 24-well plates at 3 × 104 per well and co-cultured with GcMAF-stimulated M2 RAW264.7 cells (ratio 1:1) for 48 h. EMT6 cells were washed with PBS and analyzed using the cell counting kit-8 (Dojindo, Kumamoto, Japan). The number of live cells was determined by measuring the absorbance at 450 nm with a reference wavelength of 600 nm using a microplate reader.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
A two-tailed Student’s t-test was used to assess significance. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Changes in GcMAF-Stimulated Cells in a Non-Contact Co-Culture System
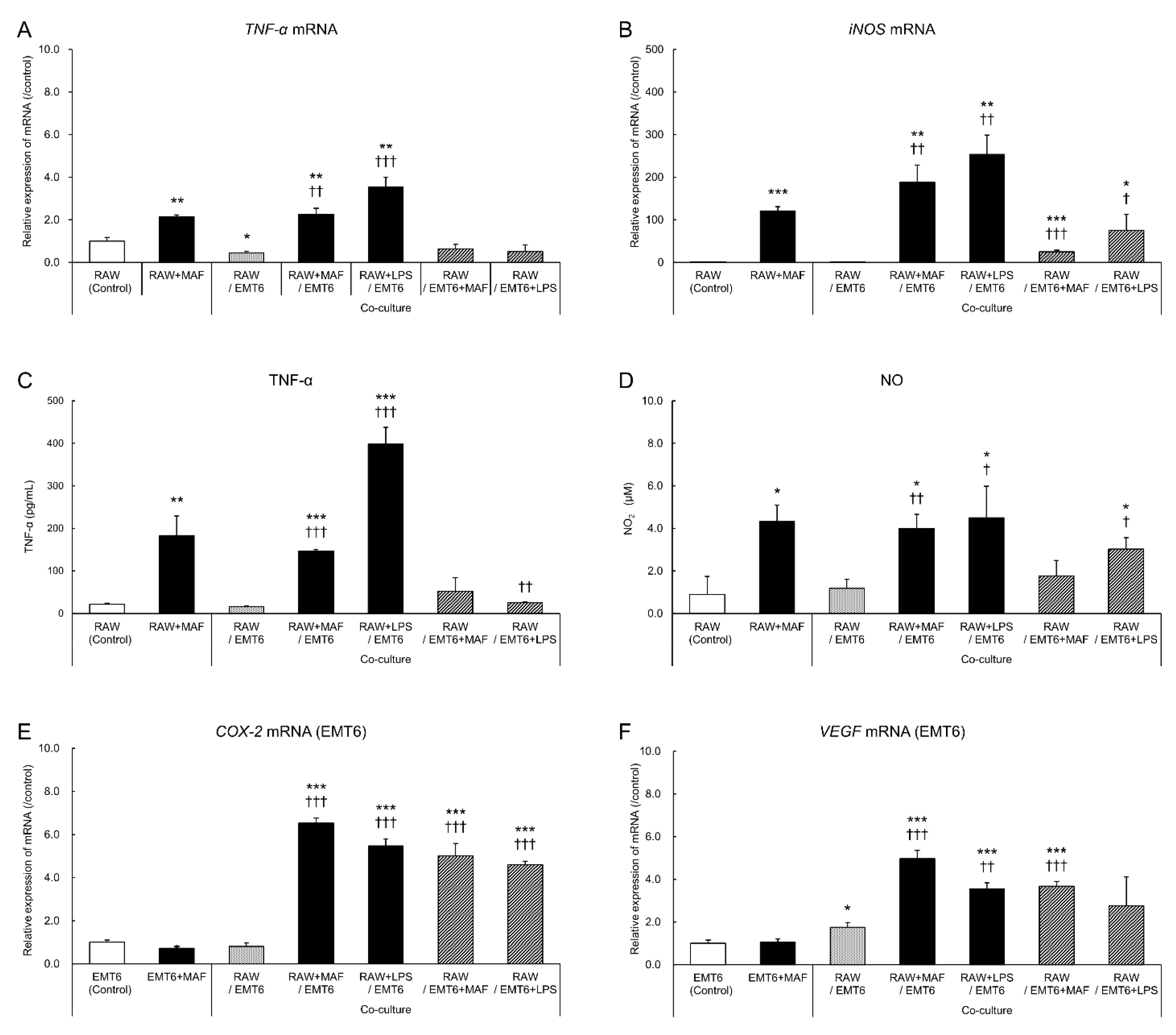
Here, we examined the macrophage-derived humoral factors that influence the anti-tumor activity of GcMAF in the tumor microenvironment by co-culturing GcMAF-stimulated macrophages with tumor cells in a non-contact manner. GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells and EMT6 cells were co-cultured in a 0.4-μm pore cell culture insert, RNA was extracted from the cells, and gene and protein expression levels in the supernatant were determined using PCR, ELISA, and NO assays (
Figure 1).
GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells exhibited higher mRNA expression levels of
TNF-α and
iNOS than the unstimulated monocultures (
Figure 1A, B). The gene expression levels remained high even after co-culture with EMT6 cells. Similar TNF-α and NO level changes were observed in the culture supernatant, confirming the results (
Figure 1C, D). These results suggest that GcMAF induces inflammatory cytokine production by macrophages and that its activity is unaffected by the presence of tumor cells. In EMT6 cells, the mRNA expression levels of
COX-2 and
VEGF, which are associated with tumor growth and invasion, increased after GcMAF stimulation (
Figure 1E, F). GcMAF-stimulated changes in RAW264.7 cells were confirmed following LPS treatment. Therefore, GcMAF may effectively activate macrophages.
3.2. Changes in EMT6 Cells Induced by GcMAF-Stimulated RAW264.7 Cells
LPS-activated macrophages suppress the proliferation of co-cultured tumor cells [
31]. Here, we evaluated whether GcMAF, which activates macrophages similarly to LPS, alters the survival of co-cultured EMT6 cells (
Figure 2).
Similar to the co-culture with LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, 48-h co-culture with GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells significantly suppressed the proliferation of EMT6 cells. Co-culture of GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 and EMT6 cells (
Figure 1E, F) revealed that GcMAF- or LPS-stimulated EMT6 cells exhibited enhanced gene expression and tumor growth as a survival response. The inhibitory effect of RAW264.7 cells on tumor cell proliferation was stronger than that of EMT6 cells.
3.3. Comprehensive Analysis of Gene Levels in GcMAF-Stimulated Macrophages using DNA Arrays
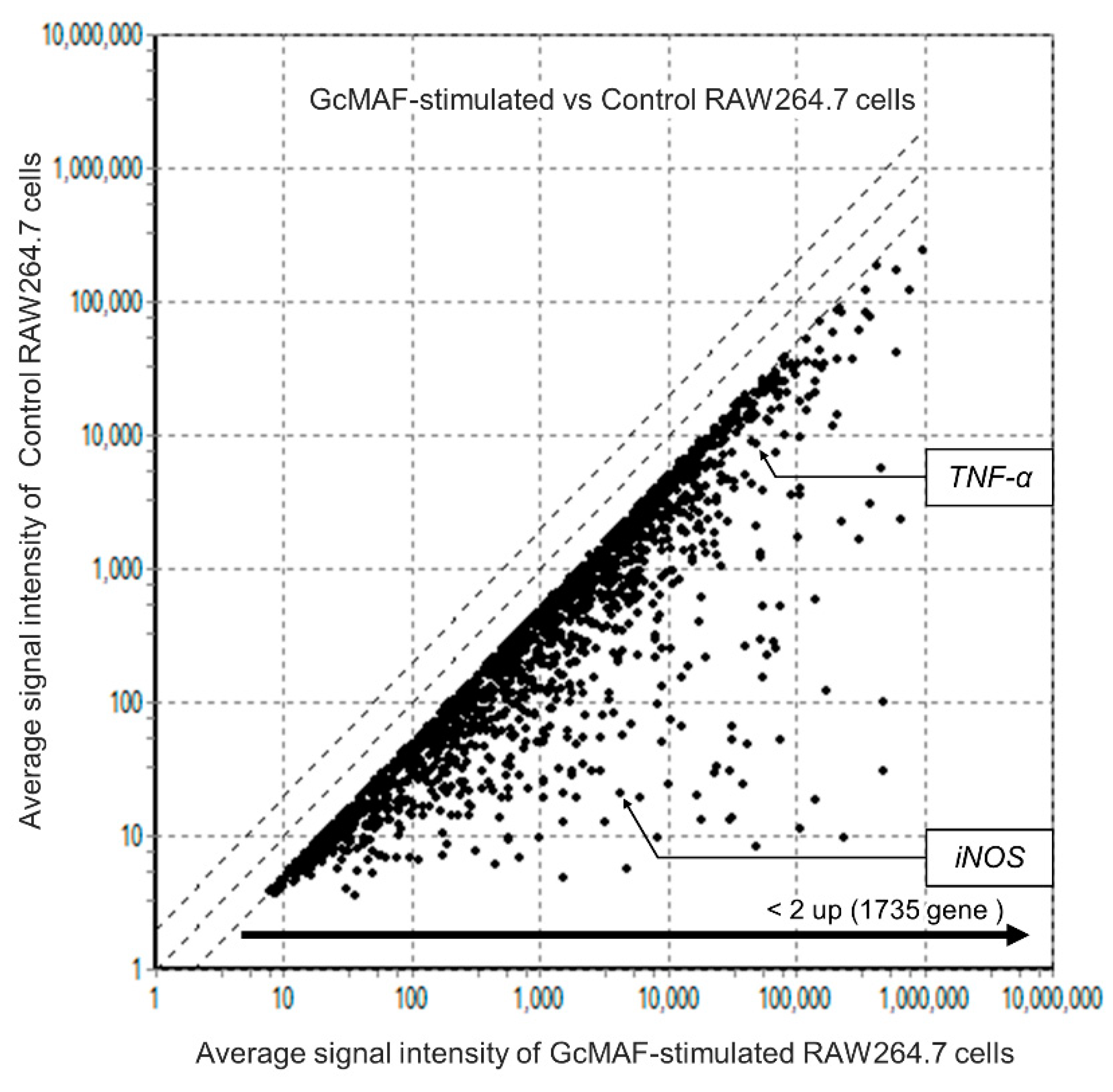
DNA arrays were used to analyze GcMAF-induced gene expression changes in macrophages (
Figure 3).
In GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, levels of 1735 genes, including TNF-α, iNOS, IL-1β, IL-6, C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2, and C-C motif chemokine ligand 5, were upregulated more than 2-fold compared to unstimulated cells. The expression of several genes related to inflammatory cytokines was upregulated. Although a few genes related to anti-inflammatory cytokines were upregulated, the increase in the expression of M1-related genes was more significant. These results suggested that GcMAF induces M1 polarization in macrophages.
3.4. Evaluation of M2-to-M1 Macrophage Reprogramming by GcMAF
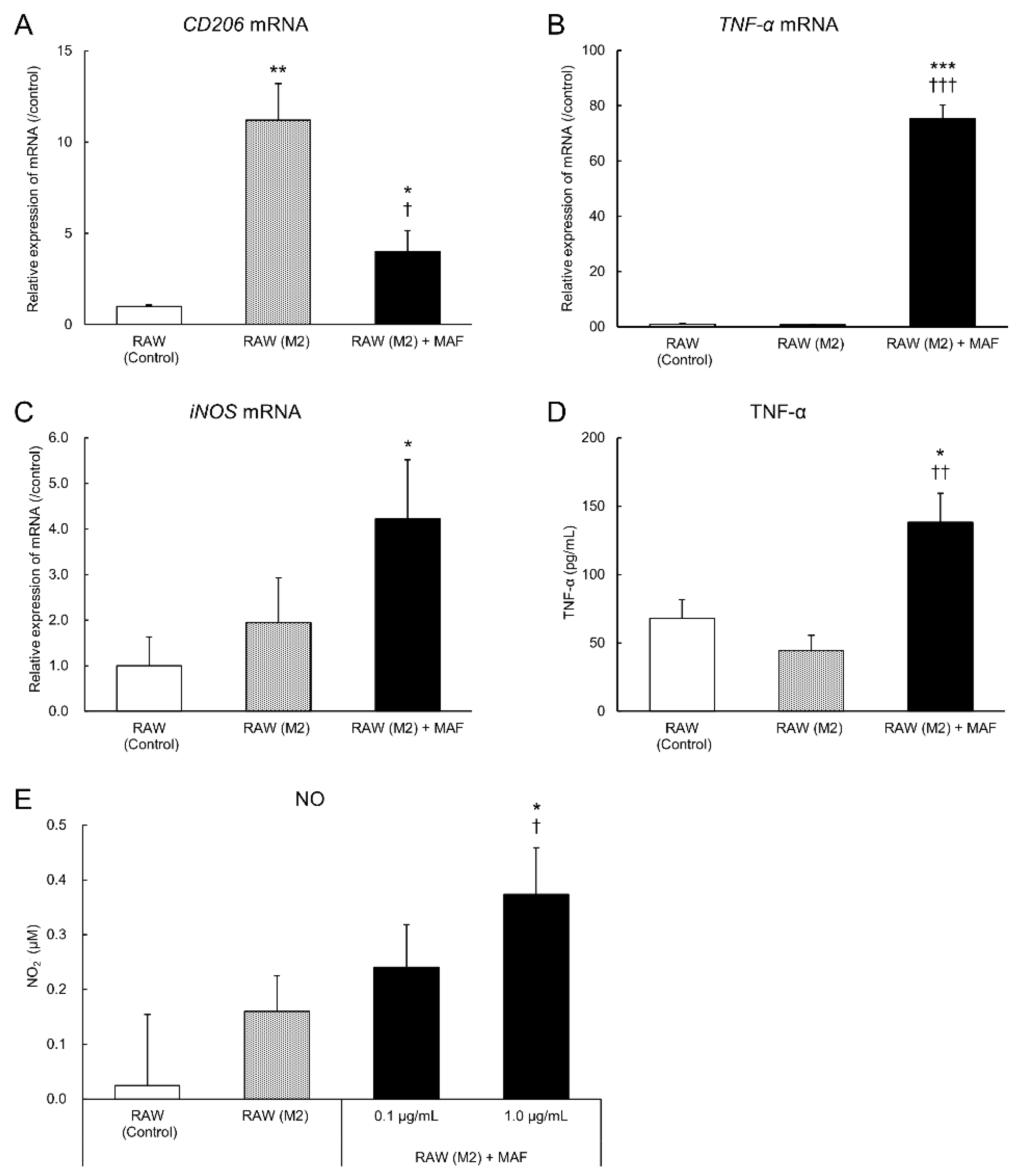
GcMAF activates macrophages to convert them into inflammatory cells and exerts anti-tumor effects. Whether TAMs exert the same effects in the tumor microenvironment remains unclear. We examined the effect of GcMAF on the M2 polarization of macrophages to verify whether GcMAF activates TAMs in the tumor microenvironment. RAW264.7 cells were stimulated with IL-4 and IL-13 to acquire the M2 type [
32]. After the addition of GcMAF, the cells were cultured for 24 h to determine whether M2 RAW 264.7 cells were reprogrammed to attain the M1 type (
Figure 4).
Expression levels of
CD206 in mRNA were increased in the M2 RAW264.7 cells compared to those in the unstimulated cells, but this effect was significantly suppressed in GcMAF-stimulated M2 RAW264.7 cells (
Figure 4A). GcMAF-stimulated M2 RAW264.7 cells exhibited increased mRNA expression levels of
TNF-α and
iNOS, which are M1 macrophage-related genes, compared to the unstimulated cells (
Figure 4B, C). A similar trend was observed in the TNF-α and NO levels in the culture supernatant. According to the previous results, TNF-α and NO production were increased in the GcMAF-stimulated cells compared to the unstimulated and IL-4- and IL-13-stimulated RAW264.7 cells (
Figure 4D, E). These results suggested that GcMAF induces M2-to-M1 macrophage reprogramming.
3.5. Suppression of EMT6 Cell Proliferation by GcMAF-Stimulated M2 RAW264.7 Cells
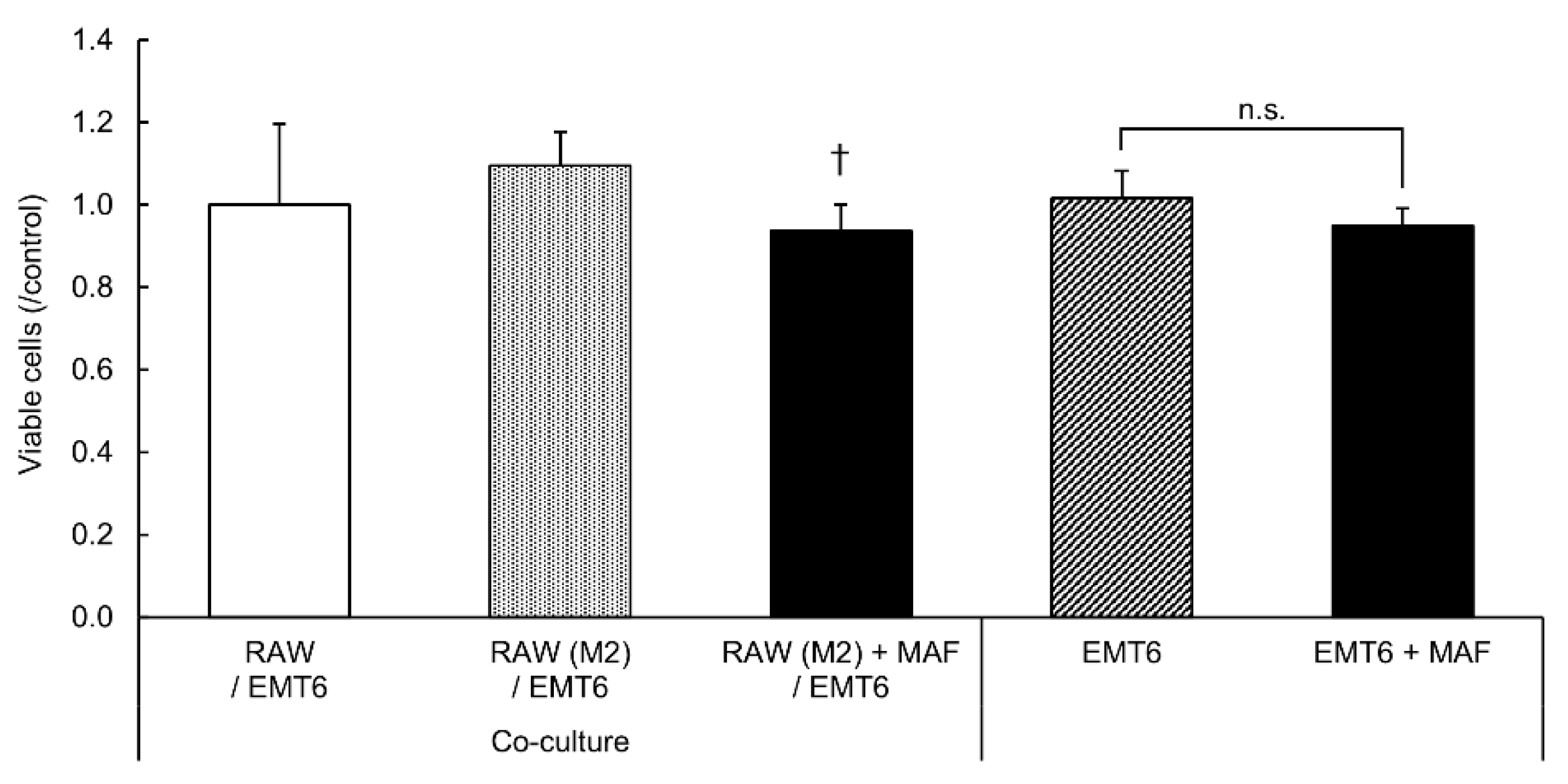
We verified whether GcMAF exerts anti-tumor effects on M2 RAW264.7 cells (
Figure 5).
Cell viability analysis using CCK-8 revealed that co-culture with GcMAF-stimulated M2 RAW264.7 cells inhibited the proliferation of EMT6 cells more significantly than the co-culture with unstimulated M2 RAW264.7 cells. Therefore, GcMAF acts on M2 macrophages and suppresses the proliferation of coexisting tumor cells. No significant differences in cell proliferation were observed between EMT6 cells cultured alone for 24 h in GcMAF medium and EMT6 cells co-cultured with RAW264.7 cells. These results suggest that GcMAF has no direct cytotoxic or proliferative effects on tumor cells; however, stimulation of macrophages with GcMAF induces anti-tumor effects and cell death in tumor cells.
4. Discussion
This study observed that GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells induced inflammatory cytokine production and suppressed the proliferation of adjacent EMT6 cells in a non-contact environment via humoral factors. In a previous study, enzyme-treated bovine colostrum MAF enhanced the phagocytic activity of mouse peritoneal macrophages but did not induce the production of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β [
33]. This suggests that GcMAF purified from serum and colostrum MAF (a mixture of proteins including GcMAF) exhibits different properties. When co-cultured with GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, EMT6 cells exhibited enhanced gene expression levels of
COX-2 and
VEGF, which are involved in cell invasion and proliferation. During damage or death, cells emit various factors that signal to the cells surrounding abnormalities. Proteins produced by dead tumor cells induce immunosuppressive white blood cells around the tumors via macrophages [
34]. Suppression of cell proliferation by GcMAF-stimulated macrophages may be due to the action of the surrounding surviving cells, which emit survival signals. Cell proliferation was decreased in EMT6 cells co-cultured with GcMAF-stimulated RAW264.7 cells, suggesting that GcMAF suppresses tumor cell proliferation signals via macrophage activation.
In the tumor microenvironment, TAMs stimulated by colony-stimulating factor-1 produced by tumor cells exist as M2 macrophages that secrete epidermal growth factors and promote tumor cell proliferation and invasion [
35]. In contrast, M1 macrophages attack tumor cells directly by producing reactive oxygen species and NO or indirectly via antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by anti-tumor antibodies [
36,
37]. To verify whether GcMAF exerted anti-tumor effects in M2 macrophage-dominant tumor microenvironment, we examined its effects on M2 macrophages. The cells were cultured in a medium containing IL-4 and IL-13 to differentiate undifferentiated macrophages into the M2 type in vitro [
32]. In this study, when RAW264.7 cells induced to M2 type were stimulated with GcMAF, a shift to M1 type was observed by analyzing the mRNA expression and components produced in the culture supernatant. The survival rate of the co-cultured EMT6 cells decreased, similar to the results of in vivo studies using a mouse model in which tumor cells were implanted subcutaneously [
38]. These results suggest that GcMAF exerts anti-tumor effects by stimulating macrophages in the tumor microenvironment to exert M1-type functions or reprogramming M2 macrophages to express M1-type functions. Our study revealed the anti-tumor action mechanisms of GcMAF-stimulated macrophages on adjacent tumor cells, highlighting the potential use of GcMAF in cancer immunotherapy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.T, R.T. and Y.U.; methodology, A.K. and S.A..; validation, A.K., H.S. and S.A.; formal analysis, A.K., H.S. and S.A.; investigation, A.K., H.S. and S.A.; resources, A.K., H.S. and Y.S.; data curation, A.K., H.S. and S.A.; writing—original draft preparation, T.T., A.K. and S.A.; writing—review and editing, T.T., Y.S. and Y.U.; visualization, A.K. and S.A.; supervision, Y.U.; project administration, T.T. and Y.U.; funding acquisition, T.T., R.T. and Y.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Takara Clinic (Tokyo, Japan) and Mori Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan).
Data Availability Statement
Data contained in this article will be made available upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Editage (
www.editage.jp) for English language editing.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Shinobu Ambai is employed by Mori Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan. The authors declare that the research was conducted without commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Daiger, S.P.; Schanfield, M.S.; Cavalli-Sforza, L.L. Group-Specific Component (Gc) Proteins Bind Vitamin D and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1975, 72, 2076–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.; Cooke, N. The Multifunctional Properties and Characteristics of Vitamin D-Binding Protein. Trends Endocrinol Metabol 2000, 11, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Homma, S. Vitamin D3 Binding Protein (Group-Specific Component) Is a Precursor for the Macrophage-Activating Signal Factor from Lysophosphatidylcholine-Treated Lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1991, 88, 8539–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, N.; Kumashiro, R. Conversion of Vitamin D3 Binding Protein (Group-Specific Component) to a Macrophage Activating Factor by the Stepwise Action of Beta-Galactosidase of B Cells and Sialidase of T Cells. J Immunol 1993, 151, 2794–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisker, O.; Onizuka, S.; Becker, C.M.; Fannon, M.; Flynn, E.; D’Amato, R.; Zetter, B.; Folkman, J.; Ray, R.; Swamy, N.; et al. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor (DBP-Maf) Inhibits Angiogenesis and Tumor Growth in Mice. Neoplasia 2003, 5, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uto, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Takeuchi, R.; Nakagawa, Y.; Hirota, K.; Terada, H.; Onizuka, S.; Nakata, E.; Hori, H. Effect of the Gc-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor Precursor (PreGcMAF) on Phagocytic Activation of Mouse Peritoneal Macrophages. Anticancer Res 2011, 31, 2489–2492. [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka, K.; Onizuka, S.; Ishibashi, H.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Nakayama, T.; Matsuura, N.; Kanematsu, T.; Fujioka, H. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor Inhibits HCC in SCID Mice. J Surg Res 2012, 172, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inui, T.; Kuchiike, D.; Kubo, K.; Mette, M.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Sakamoto, N. Clinical Experience of Integrative Cancer Immunotherapy with GcMAF. Anticancer Res 2013, 33, 2917–2919. [Google Scholar]
- DeNardo, D.G.; Ruffell, B. Macrophages as Regulators of Tumour Immunity and Immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol 2019, 19, 369–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orecchioni, M.; Ghosheh, Y.; Pramod, A.B.; Ley, K. Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. Classically and M2(LPS–) vs. Alternatively Activated Macrophages. Front Immunol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Q.; Han, M. The Role of Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in Tumor Progression and Relevant Advance in Targeted Therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B 2020, 10, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rőszer, T. Understanding the Mysterious M2 Macrophage through Activation Markers and Effector Mechanisms. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, I.; Manic, G.; Coussens, L.M.; Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab 2019, 30, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, S.; Kohanbash, G.; Liu, S.J.; Alvarado, B.; Carrera, D.; Bhaduri, A.; Watchmaker, P.B.; Yagnik, G.; Di Lullo, E.; Malatesta, M.; et al. Single-Cell Profiling of Human Gliomas Reveals Macrophage Ontogeny as a Basis for Regional Differences in Macrophage Activation in the Tumor Microenvironment. Genome Biol 2017, 18, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liang, R.; Lan, T.; Ding, D.; Huang, S.; Shao, J.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophage-Specific CD155 Contributes to M2-Phenotype Transition, Immunosuppression, and Tumor Progression in Colorectal Cancer. J Immunother Cancer 2022, 10, e004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, P.; Shi, P.; Jiang, T.; Yin, H.; Chu, S.; Shi, M.; Bai, J.; Song, J. DKC1 Enhances Angiogenesis by Promoting HIF-1α Transcription and Facilitates Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Br J Cancer 2020, 122, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delprat, V.; Tellier, C.; Demazy, C.; Raes, M.; Feron, O.; Michiels, C. Cycling Hypoxia Promotes a Pro-Inflammatory Phenotype in Macrophages via JNK/P65 Signaling Pathway. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, G.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z.; Shi, L.; Deng, Y.; Li, H. Calmodulin 2 Facilitates Angiogenesis and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer via STAT3/HIF-1A/VEGF-A Mediated Macrophage Polarization. Front Oncol 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacini, S.; Punzi, T.; Morucci, G.; Gulisano, M.; Ruggiero, M. Effects of Vitamin D-Binding Protein-Derived Macrophage-Activating Factor on Human Breast Cancer Cells. Anticancer Res 2012, 32, 45–52. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, K.J.; Zhao, B.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Dridi, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W.; Huang, B.; Pirie-Shepherd, S.; Fannon, M. Vitamin D Binding Protein-Macrophage Activating Factor Directly Inhibits Proliferation, Migration, and UPAR Expression of Prostate Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyer, L.; Ward, E.; Smith, R.; Fiore, M.; Magherini, S.; Branca, J.; Morucci, G.; Gulisano, M.; Ruggiero, M.; Pacini, S. A Novel Role for a Major Component of the Vitamin D Axis: Vitamin D Binding Protein-Derived Macrophage Activating Factor Induces Human Breast Cancer Cell Apoptosis through Stimulation of Macrophages. Nutrients 2013, 5, 2577–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, G.; Rath, B.; Klameth, L.; Hochmair, M.J. Small Cell Lung Cancer: Recruitment of Macrophages by Circulating Tumor Cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1093277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, S. Bin; Nagasawa, H.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H. Preparation of Gc Protein-Derived Macrophage Activating Factor (GcMAF) and Its Structural Characterization and Biological Activities. Anticancer Res 2002, 22, 4297–4300. [Google Scholar]
- Hirota, K.; Nakagawa, Y.; Takeuchi, R.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Onizuka, S.; Terada, H. Antitumor Effect of Degalactosylated Gc-Globulin on Orthotopic Grafted Lung Cancer in Mice. Anticancer Res 2013, 33, 2911–2915. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inui, T.; Makita, K.; Miura, H.; Matsuda, A.; Kuchiike, D.; Kubo, K.; Mette, M.; Uto, Y.; Nishikata, T.; Hori, H.; et al. Case Report: A Breast Cancer Patient Treated with GcMAF, Sonodynamic Therapy and Hormone Therapy. Anticancer Res 2014, 34, 4589–4593. [Google Scholar]
- Inui, T.; Kubo, K.; Kuchiike, D.; Uto, Y.; Nishikata, T.; Sakamoto, N.; Mette, M. Oral Colostrum Macrophage-Activating Factor for Serious Infection and Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Three Case Reports. Anticancer Res 2015, 35, 4545–4549. [Google Scholar]
- Inui, T.; Katsuura, G.; Kubo, K.; Kuchiike, D.; Chenery, L.; Uto, Y.; Nishikata, T.; Mette, M. Case Report: GcMAF Treatment in a Patient with Multiple Sclerosis. Anticancer Res 2016, 36, 3771–3774. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Sha, M.-L.; Li, D.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Wang, X.-J.; Jiang, C.-Y.; Xia, S.-J.; Shao, Y. Relaxin Abrogates Renal Interstitial Fibrosis by Regulating Macrophage Polarization via Inhibition of Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21044–21053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font-Nieves, M.; Sans-Fons, M.G.; Gorina, R.; Bonfill-Teixidor, E.; Salas-Pérdomo, A.; Márquez-Kisinousky, L.; Santalucia, T.; Planas, A.M. Induction of COX-2 Enzyme and Down-Regulation of COX-1 Expression by Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) Control Prostaglandin E2 Production in Astrocytes. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 6454–6468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Watters, A.; Zhou, W.; Leibovich, S.J. Leptin Upregulates VEGF in Breast Cancer via Canonic and Non-Canonical Signalling Pathways and NFκB/HIF-1α Activation. Cell Signal 2010, 22, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.; Young, H.; Hurlstone, A.; Wellbrock, C. Differentiation of THP1 Cells into Macrophages for Transwell Co-Culture Assay with Melanoma Cells. Bio Protoc 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Yu, J.; Li, H.; Li, Q.; Li, W. 13-Methyl-Palmatrubine Shows an Anti-Tumor Role in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer via Shifting M2 to M1 Polarization of Tumor Macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol 2022, 104, 108468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uto, Y.; Kawai, T.; Sasaki, T.; Hamada, K.; Yamada, H.; Kuchiike, D.; Kubo, K.; Inui, T.; Mette, M.; Tokunaga, K.; et al. Degalactosylated/Desialylated Bovine Colostrum Induces Macrophage Phagocytic Activity Independently of Inflammatory Cytokine Production. Anticancer Res 2015, 35, 4487–4492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hangai, S.; Kawamura, T.; Kimura, Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Hibino, S.; Yamamoto, D.; Nakai, Y.; Tateishi, R.; Oshima, M.; Oshima, H.; et al. Orchestration of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment by Ubiquitous Cellular Protein TCTP Released by Tumor Cells. Nat Immunol 2021, 22, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyckoff, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, E.Y.; Wang, Y.; Pixley, F.; Stanley, E.R.; Graf, T.; Pollard, J.W.; Segall, J.; Condeelis, J. A Paracrine Loop between Tumor Cells and Macrophages Is Required for Tumor Cell Migration in Mammary Tumors. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 7022–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.S.; Landers, R.J.; Underwood, J.C.; Harris, A.L.; Lewis, C.E. Expression of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor by Macrophages Is Up-Regulated in Poorly Vascularized Areas of Breast Carcinomas. J Pathol 2000, 192, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruns, H.; Büttner, M.; Fabri, M.; Mougiakakos, D.; Bittenbring, J.T.; Hoffmann, M.H.; Beier, F.; Pasemann, S.; Jitschin, R.; Hofmann, A.D.; et al. Vitamin D–Dependent Induction of Cathelicidin in Human Macrophages Results in Cytotoxicity against High-Grade B Cell Lymphoma. Sci Transl Med 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgova, E. V.; Kirikovich, S.S.; Levites, E. V.; Ruzanova, V.S.; Proskurina, A.S.; Ritter, G.S.; Taranov, O.S.; Varaksin, N.A.; Ryabicheva, T.G.; Leplina, O.Yu.; et al. Analysis of the Biological Properties of Blood Plasma Protein with GcMAF Functional Activity. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 8075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).