Submitted:
17 June 2024
Posted:
17 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset Overview
2.2. Variables
- Medical history variables: family history of diabetes among first-degree relatives (famdb), reported high blood pressure (hbp), reported high blood cholesterol at/before blood draw (chol)
- Intake variables: alcohol intake (alcohol)
- Nutrient variables: heme iron intake (heme), magnesium intake (magn), cereal fiber intake (ceraf), polyunsaturated fat intake (pufa), trans fat intake (trans), glycemic load (gl)
- Lifestyle variables: cigarette smoking (smk), exercise habits (total physical activity, act)
- Body measurements: body mass index (BMI or bmi)
- Gender (for total data)
2.3. Data preprocessing
2.4. PyCaret Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Results of The Statistical Analysis
3.2. The Results of the Machine Learning Analysis
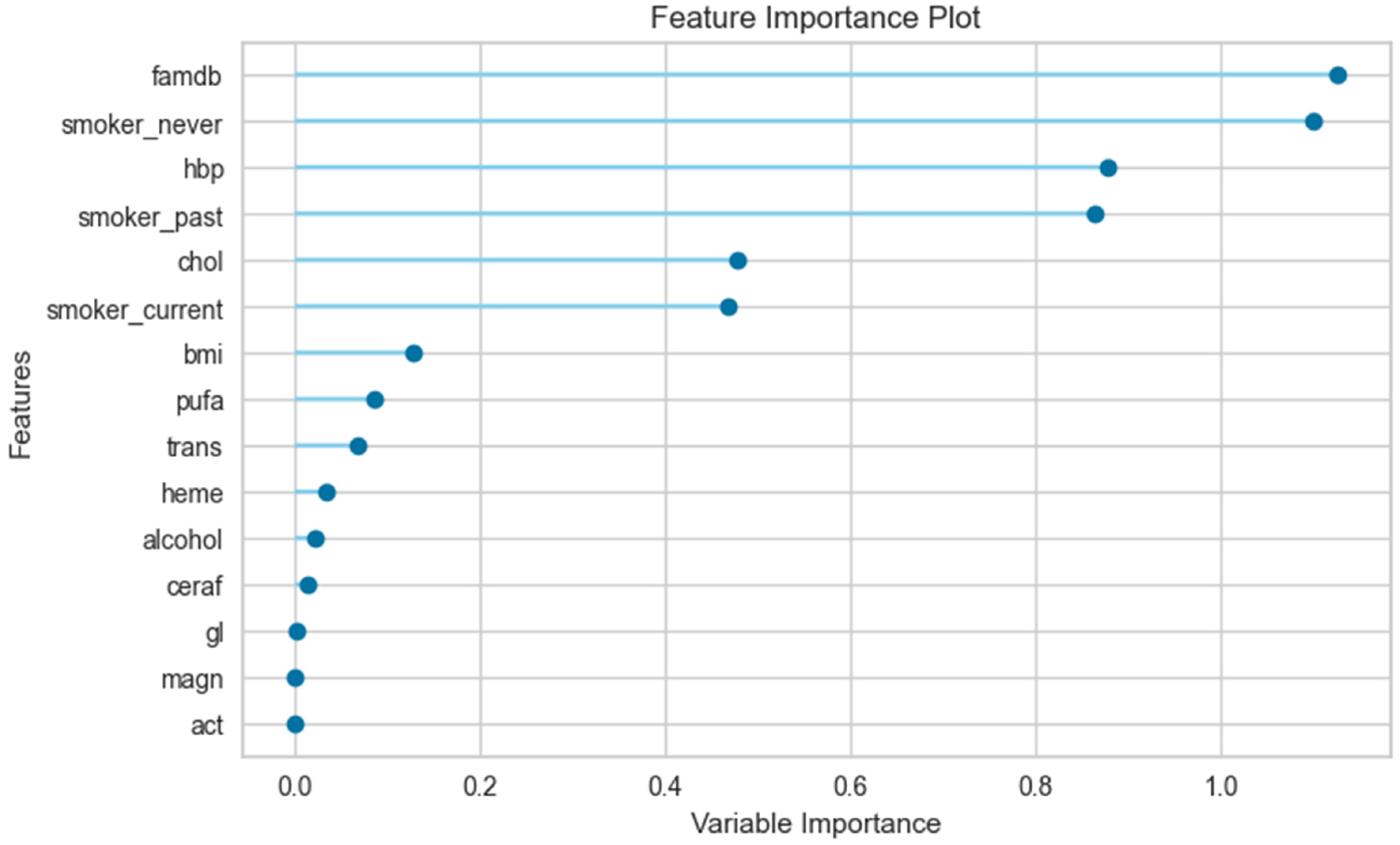
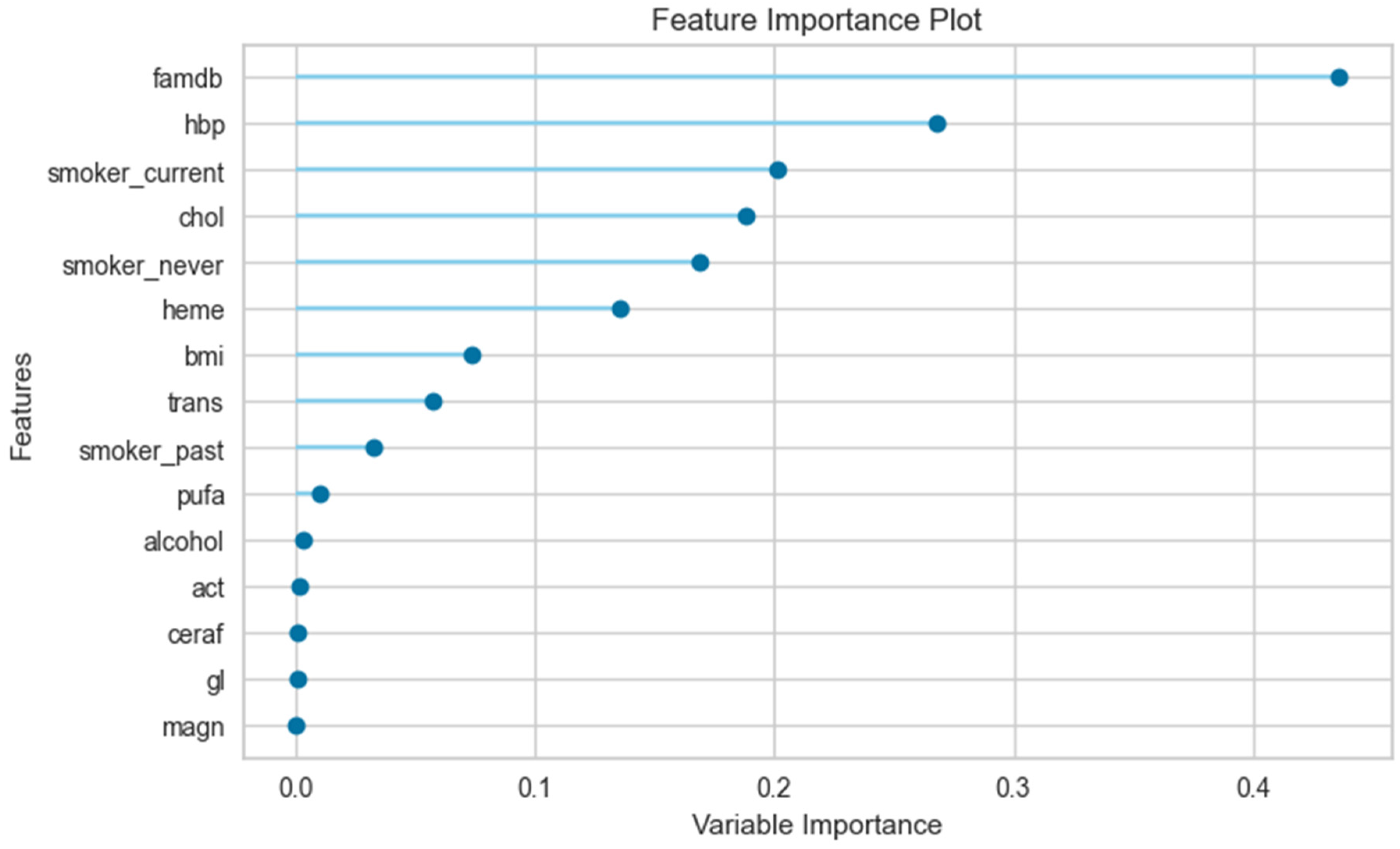
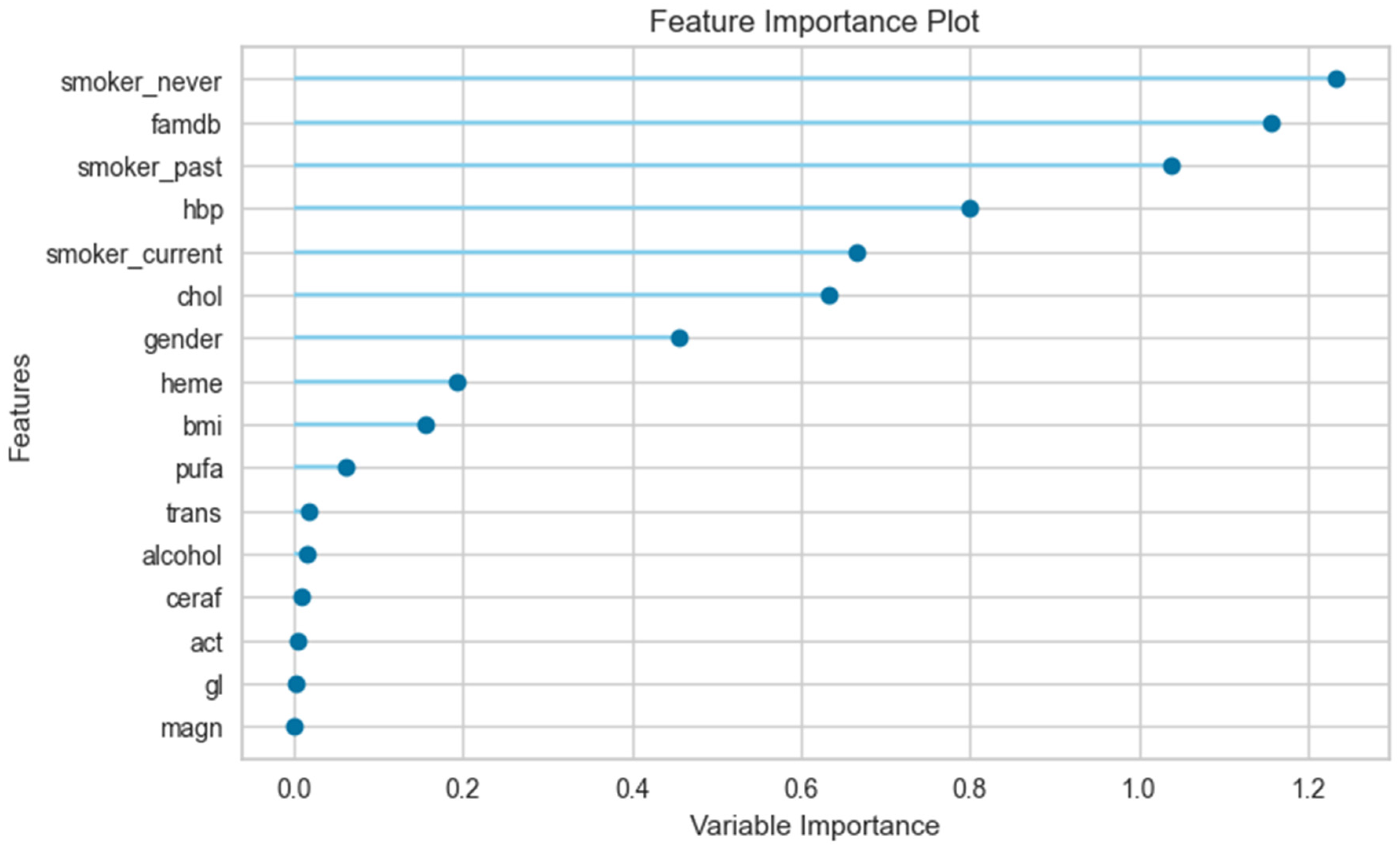
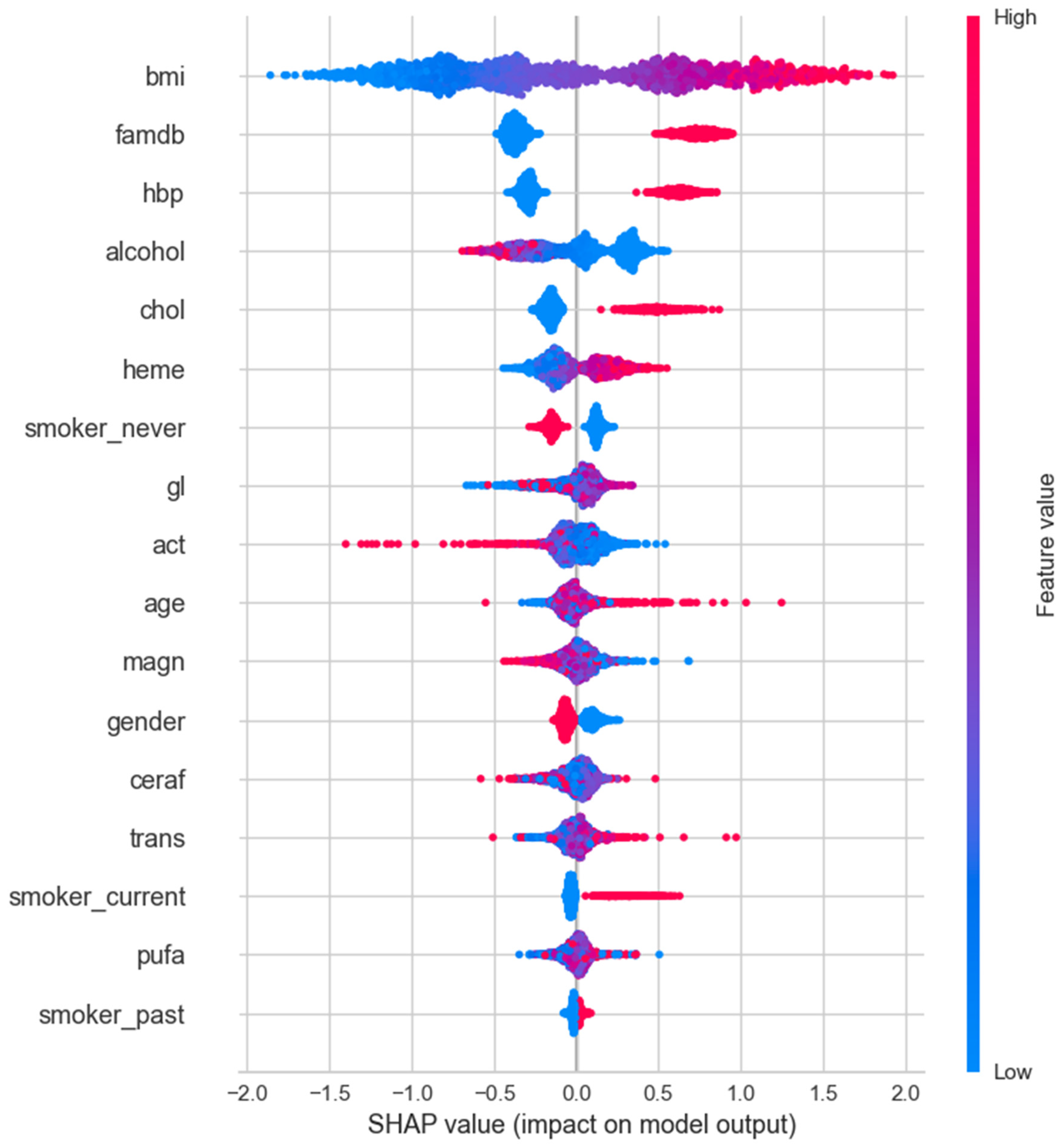
3.3. The Results of the Feature Importance Plot
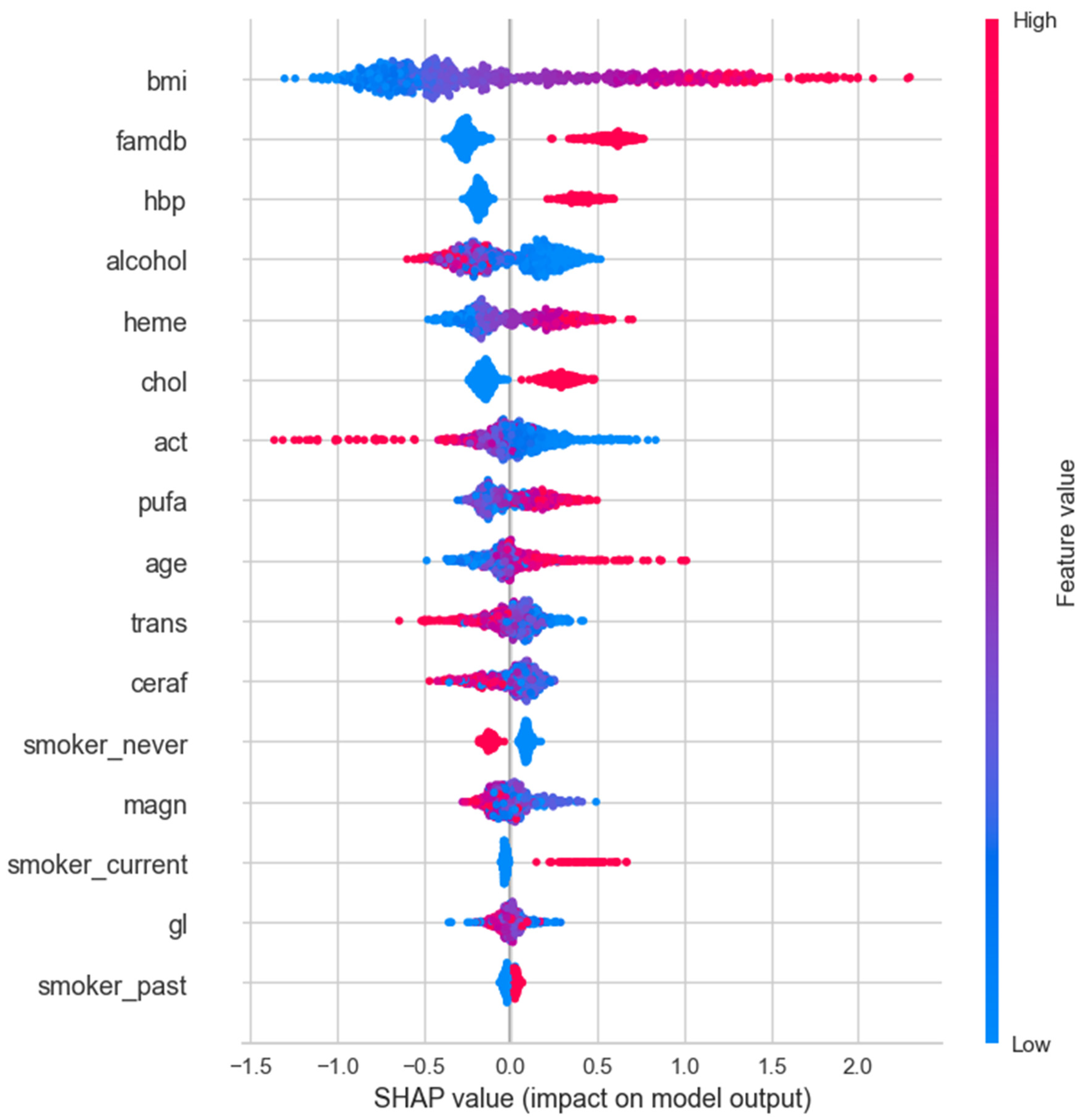
3.4. SHAP Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hill-Briggs, F.; Adler, N.E.; Berkowitz, S.A.; Chin, M.H.; Gary-Webb, T.L.; Navas-Acien, A.; Thornton, P.L.; Haire-Joshu, D. Social Determinants of Health and Diabetes: A Scientific Review. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 258–279. [CrossRef]
- Deberneh, H.M.; Kim, I. Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes Based on Machine Learning Algorithm. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 3317. [CrossRef]
- Rajula, H.S.R.; Verlato, G.; Manchia, M.; Antonucci, N.; Fanos, V. Comparison of Conventional Statistical Methods with Machine Learning in Medicine: Diagnosis, Drug Development, and Treatment. Medicina (Mex.) 2020, 56, 455. [CrossRef]
- Bzdok, D.; Altman, N.; Krzywinski, M. Statistics versus Machine Learning. Nat. Methods 2018, 15, 233–234. [CrossRef]
- Spooner, A.; Chen, E.; Sowmya, A.; Sachdev, P.; Kochan, N.A.; Trollor, J.; Brodaty, H. A Comparison of Machine Learning Methods for Survival Analysis of High-Dimensional Clinical Data for Dementia Prediction. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20410. [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Valdez, R.; Gwinn, M.; Khoury, M.J. Application of Support Vector Machine Modeling for Prediction of Common Diseases: The Case of Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2010, 10, 16. [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.P.; Parikh, J.R.; Shenfeld, D.K.; Ivanov, V.; Marks, C.; Church, B.W.; Laramie, J.M.; Mardekian, J.; Piper, B.A.; Willke, R.J.; et al. Reverse Engineering and Evaluation of Prediction Models for Progression to Type 2 Diabetes: An Application of Machine Learning Using Electronic Health Records. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2016, 10, 6–18. [CrossRef]
- Cahn, A.; Shoshan, A.; Sagiv, T.; Yesharim, R.; Goshen, R.; Shalev, V.; Raz, I. Prediction of Progression from Pre-Diabetes to Diabetes: Development and Validation of a Machine Learning Model. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3252. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, J.; Ko, T.; Lee, K.; Choi, Y.; Kim, H.-S. Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1899. [CrossRef]
- Gül, H.; Aydin Son, Y.; Açikel, C. Discovering Missing Heritability and Early Risk Prediction for Type 2 Diabetes: A New Perspective for Genome-Wide Association Study Analysis with the Nurses’ Health Study and the Health Professionals’ Follow-Up Study. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 44, 946–954. [CrossRef]
- Dinh, A.; Miertschin, S.; Young, A.; Mohanty, S.D. A Data-Driven Approach to Predicting Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease with Machine Learning. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2019, 19, 211. [CrossRef]
- Viloria, A.; Herazo-Beltran, Y.; Cabrera, D.; Pineda, O.B. Diabetes Diagnostic Prediction Using Vector Support Machines. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 170, 376–381. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, A.; Jin, X.; Che, H. Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes Risk and Its Effect Evaluation Based on the XGBoost Model. Healthcare 2020, 8, 247. [CrossRef]
- Ali, M. PyCaret: An Open Source, Low-Code Machine Learning Library in Python. PyCaret Version 2020, 2.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/projects/gap/cgi-bin/study.cgi?study_id=phs000091.v2.p1.
- Zaiontz, C. Real Statistics Resource Pack for Excel.
- Stangroom, J. Chi-Square Test Calculator.
- Chen, G.; Dai, X.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Z.; Jin, X.; Mei, K.; Huang, H.; Wu, Z. Machine Learning-Based Prediction Model and Visual Interpretation for Prostate Cancer. BMC Urol. 2023, 23, 164. [CrossRef]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions. SN Comput. Sci. 2021, 2, 160. [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, U.; Xiang, A.; Sharma, S.; Weller, A.; Taly, A.; Jia, Y.; Ghosh, J.; Puri, R.; Moura, J.M.F.; Eckersley, P. Explainable Machine Learning in Deployment. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Saarela, M.; Jauhiainen, S. Comparison of Feature Importance Measures as Explanations for Classification Models. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 272. [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Huang, H.; Keshavjee, K.; Guergachi, A.; Gao, X. Predictive Models for Diabetes Mellitus Using Machine Learning Techniques. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 101. [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Prescod, F.; Shah, B.; Dong, L.; Keshavjee, K.; Guergachi, A. Evaluating the Performance of the Framingham Diabetes Risk Scoring Model in Canadian Electronic Medical Records. Can. J. Diabetes 2015, 39, 152–156. [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.W.F.; Meigs, J.B.; Sullivan, L.; Fox, C.S.; Nathan, D.M.; D’Agostino, R.B. Prediction of Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Middle-Aged Adults: The Framingham Offspring Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1068–1074. [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.; Hayes, K.; Kleczyk, E.J.; Mehta, R. Similarities and Differences between Machine Learning and Traditional Advanced Statistical Modeling in Healthcare Analytics. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, A.J.; Ahlqvist, E.; Udler, M.S. Phenotypic and Genetic Classification of Diabetes. Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1758–1769. [CrossRef]

| Male | female | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | T2DM | p value | Control | T2DM | p value | |
| n | 1289 | 1127 | 1774 | 1482 | ||
| Age | 59.22 ± 8.36 | 59.38 ± 8.48 | 0.64 | 55.63 ± 6.74 | 55.97 ± 6.76 | 0.16 |
| Body mass index | 25.21 ± 2.83 | 27.89 ± 4.13 | 7.94E-74 | 25.36 ± 4.80 | 29.88 ± 5.73 | 1.8E-121 |
| Activity | 40.8 ± 42.96 | 29.98 ± 33.10 | 8.73E-12 | 15.57 ± 18.50 | 12.86 ± 15.61 | 9.44E-6 |
| Alcohol | 11.05 ± 15.02 | 9.57 ± 14.69 | 0.006 | 6.55 ± 10.32 | 4.04 ± 9.44 | 6.96E-13 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acid | 5.88 ± 1.55 | 6.12 ± 1.68 | 0.00014 | 6.32 ± 1.68 | 6.17 ± 1.57 | 0.006 |
| Trans | 1.51 ± 0.62 | 1.56 ± 0.61 | 0.027 | 1.69 ± 0.53 | 1.73 ± 0.55 | 0.026 |
| Magnesium | 386.01 ± 87.67 | 378.08 ± 86 | 0.013 | 304.66 ± 71.83 | 300.29 ± 69.12 | 0.042 |
| Ceraf | 7.26 ± 4.33 | 6.61 ± 3.8 | 6.2E-05 | 4.59 ± 3.19 | 4.39 ± 2.74 | 0.03 |
| Heme | 1.19 ± 0.45 | 1.34 ± 0.5 | 1.91E-15 | 1.13 ± 0.45 | 1.2 ± 0.45 | 1.27E-05 |
| Glycemic Index | 130.85 ± 25.75 | 124.14 ± 24.38 | 4.53E-11 | 97.52 ± 19.58 | 98.58 ± 18.5 | 0.06 |
| Male | Female | ||||||||||||
| Control | T2DM | χ2 | p value |
Control | T2DM | χ2 | P value |
||||||
| n | % | n | % | n | % | n | % | ||||||
| Famdb | no | 1014 | 78.7 | 642 | 57.0 | 131.32 | <0.00001 | 1382 | 77.9 | 749 | 50.5 | 267.35 | <0.00001 |
| yes | 275 | 21.3 | 485 | 43.0 | 392 | 22.1 | 733 | 49.5 | |||||
| Hbp | no | 1008 | 78.2 | 667 | 59.2 | 102.26 | <0.00001 | 1421 | 80.1 | 760 | 51.3 | 303.24 | <0.00001 |
| yes | 281 | 21.8 | 460 | 40.8 | 353 | 19.9 | 722 | 48.7 | |||||
| Cholesterol | no | 923 | 71.7 | 668 | 59.3 | 40.67 | <0.00001 | 1585 | 89.3 | 1134 | 76.5 | 96.47 | <0.00001 |
| yes | 366 | 28.3 | 459 | 40.7 | 189 | 10.7 | 348 | 23.5 | |||||
| Cigarette smoking | current | 75 | 6.0 | 102 | 9.3 | 26.70 | <0.00001 | 190 | 10.8 | 210 | 14.2 | 14.97 | <0.00056 |
| never | 597 | 47.8 | 415 | 38.0 | 883 | 50.0 | 652 | 44.0 | |||||
| past | 576 | 46.2 | 576 | 52.7 | 693 | 39.2 | 618 | 41.8 | |||||
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Recall | Prec. | F1 | Kappa | MCC | TT (Sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ridge | Ridge Classifier | 0.70 | 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.04 |
| lda | Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.04 |
| lr | Logistic Regression | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.40 | 0.65 |
| gbc | Gradient Boosting Classifier | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.20 |
| nb | Naive Bayes | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.03 |
| ada | Ada Boost Classifier | 0.69 | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.08 |
| catboost | CatBoost Classifier | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.36 | 1.30 |
| rf | Random Forest Classifier | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.17 |
| et | Extra Trees Classifier | 0.68 | 0.73 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.12 |
| xgboost | Extreme Gradient Boosting | 0.67 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.11 |
| lightgbm | Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 0.66 | 0.71 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.66 | 0.32 | 0.32 | 0.07 |
| svm | SVM - Linear Kernel | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.66 | 0.54 | 0.18 | 0.23 | 0.04 |
| dt | Decision Tree Classifier | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.59 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.04 |
| qda | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.60 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.04 |
| dummy | Dummy Classifier | 0.53 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.28 | 0.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
| knn | K Neighbors Classifier | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Recall | Prec. | F1 | Kappa | MCC | TT (Sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lr | Logistic Regression | 0.71 | 0.789 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.81 |
| ridge | Ridge Classifier | 0.71 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.09 |
| lda | Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.71 | 0.790 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.10 |
| ada | Ada Boost Classifier | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.41 | 0.28 |
| catboost | CatBoost Classifier | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 3.21 |
| nb | Naive Bayes | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.10 |
| rf | Random Forest Classifier | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.52 |
| gbc | Gradient Boosting Classifier | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.69 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.65 |
| et | Extra Trees Classifier | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.69 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.37 |
| lightgbm | Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.36 | 0.18 |
| xgboost | Extreme Gradient Boosting | 0.67 | 0.74 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.34 | 0.34 | 0.34 |
| qda | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.28 | 0.28 | 0.09 |
| dt | Decision Tree Classifier | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.24 | 0.24 | 0.12 |
| svm | SVM - Linear Kernel | 0.60 | 0.00 | 0.60 | 0.67 | 0.53 | 0.18 | 0.22 | 0.10 |
| knn | K Neighbors Classifier | 0.59 | 0.61 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.11 |
| dummy | Dummy Classifier | 0.55 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.09 |
| Model | Accuracy | AUC | Recall | Prec. | F1 | Kappa | MCC | TT (Sec) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lr | Logistic Regression | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.76 |
| gbc | Gradient Boosting Classifier | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.40 |
| catboost | CatBoost Classifier | 0.72 | 0.78 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 1.79 |
| ada | Ada Boost Classifier | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.14 |
| lda | Linear Discriminant Analysis | 0.71 | 0.79 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.04 |
| ridge | Ridge Classifier | 0.71 | 0.00 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.04 |
| nb | Naive Bayes | 0.71 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 0.05 |
| lightgbm | Light Gradient Boosting Machine | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.09 |
| rf | Random Forest Classifier | 0.71 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 0.35 |
| et | Extra Trees Classifier | 0.70 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.20 |
| xgboost | Extreme Gradient Boosting | 0.70 | 0.76 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.39 | 0.39 | 0.20 |
| qda | Quadratic Discriminant Analysis | 0.67 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.34 | 0.05 |
| dt | Decision Tree Classifier | 0.63 | 0.62 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.25 | 0.25 | 0.06 |
| svm | SVM - Linear Kernel | 0.61 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.64 | 0.54 | 0.19 | 0.24 | 0.06 |
| dummy | Dummy Classifier | 0.54 | 0.50 | 0.54 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





