Submitted:
14 June 2024
Posted:
18 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Bacteria Strains
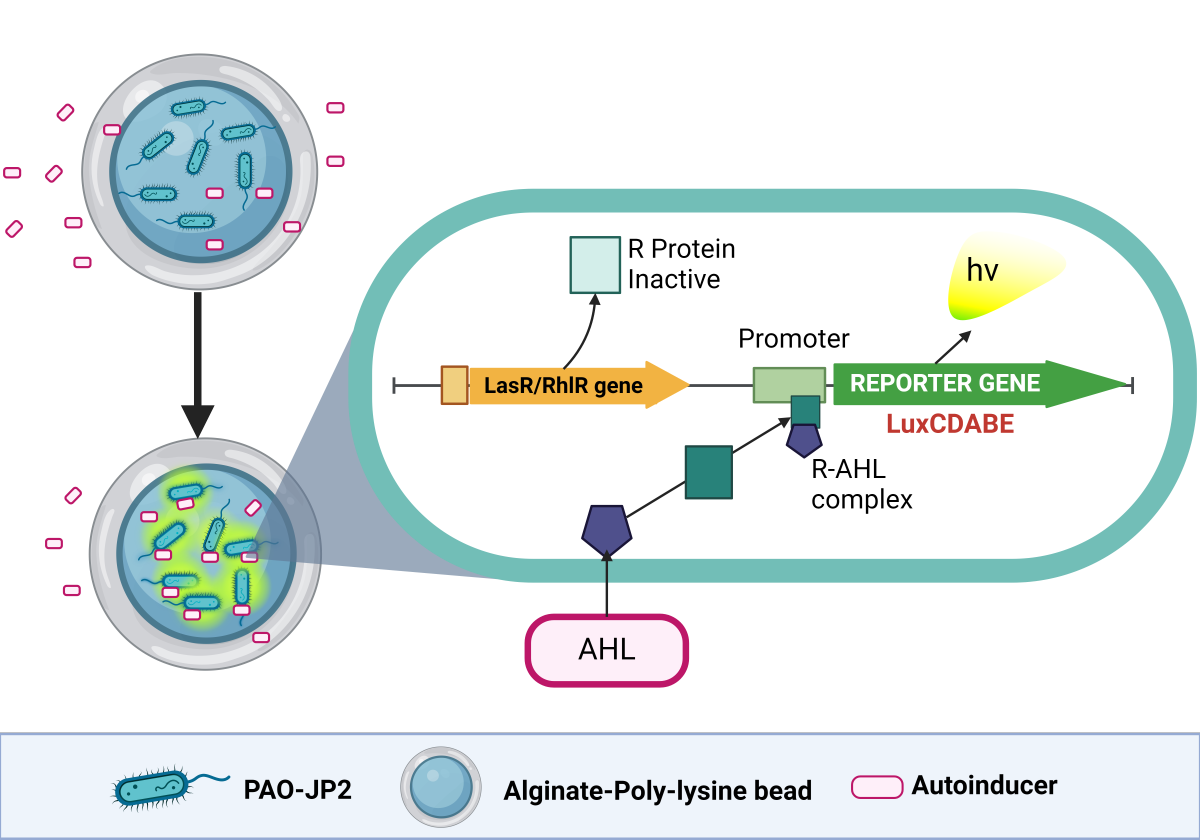
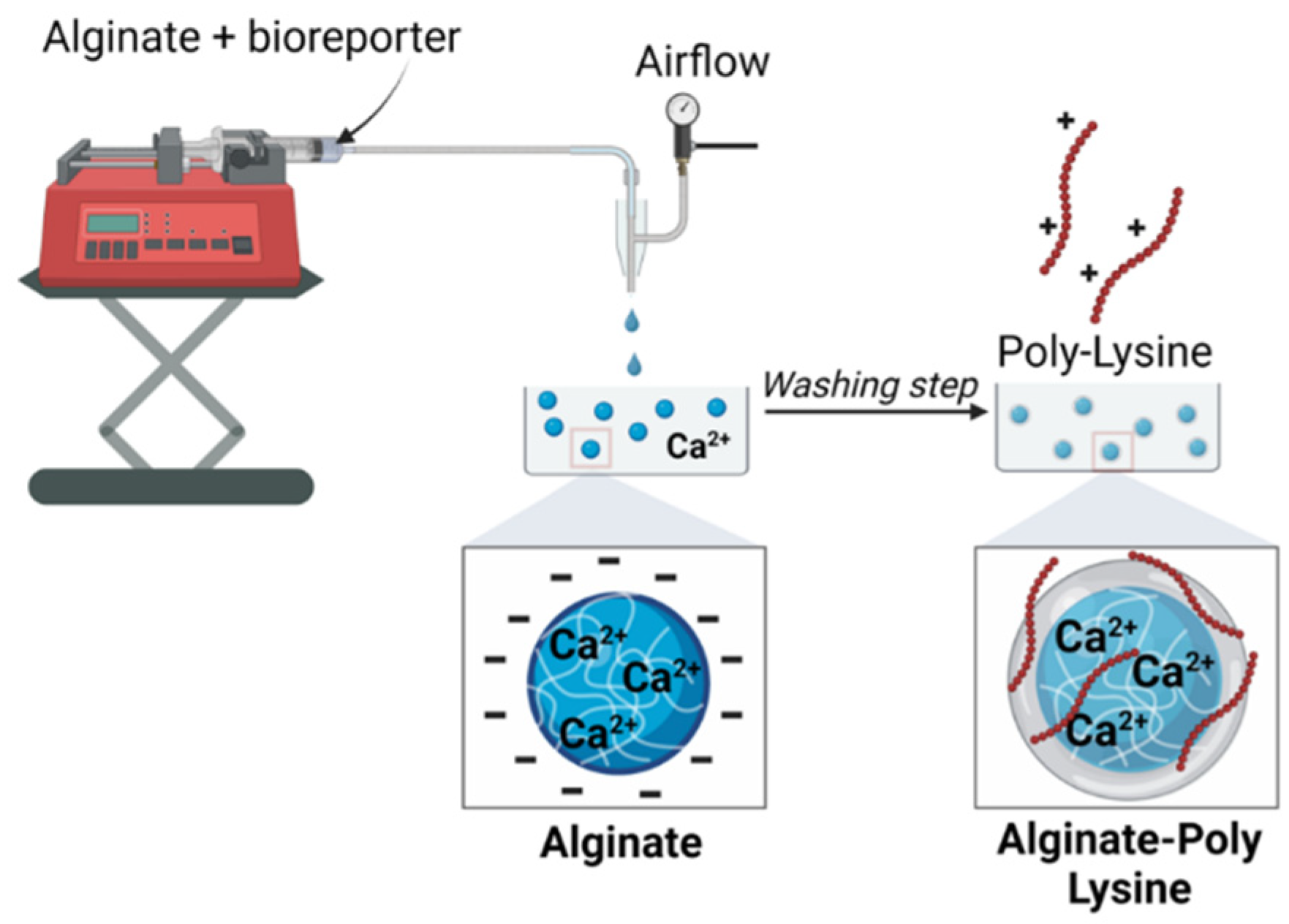
2.2. Synthesis of Microcapsules
2.3.1. Bacteria Strain Growth Conditions
2.3.2. Encapsulation of Bacteria in Single/Multiple-Layer Microcapsules
2.4. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Analysis
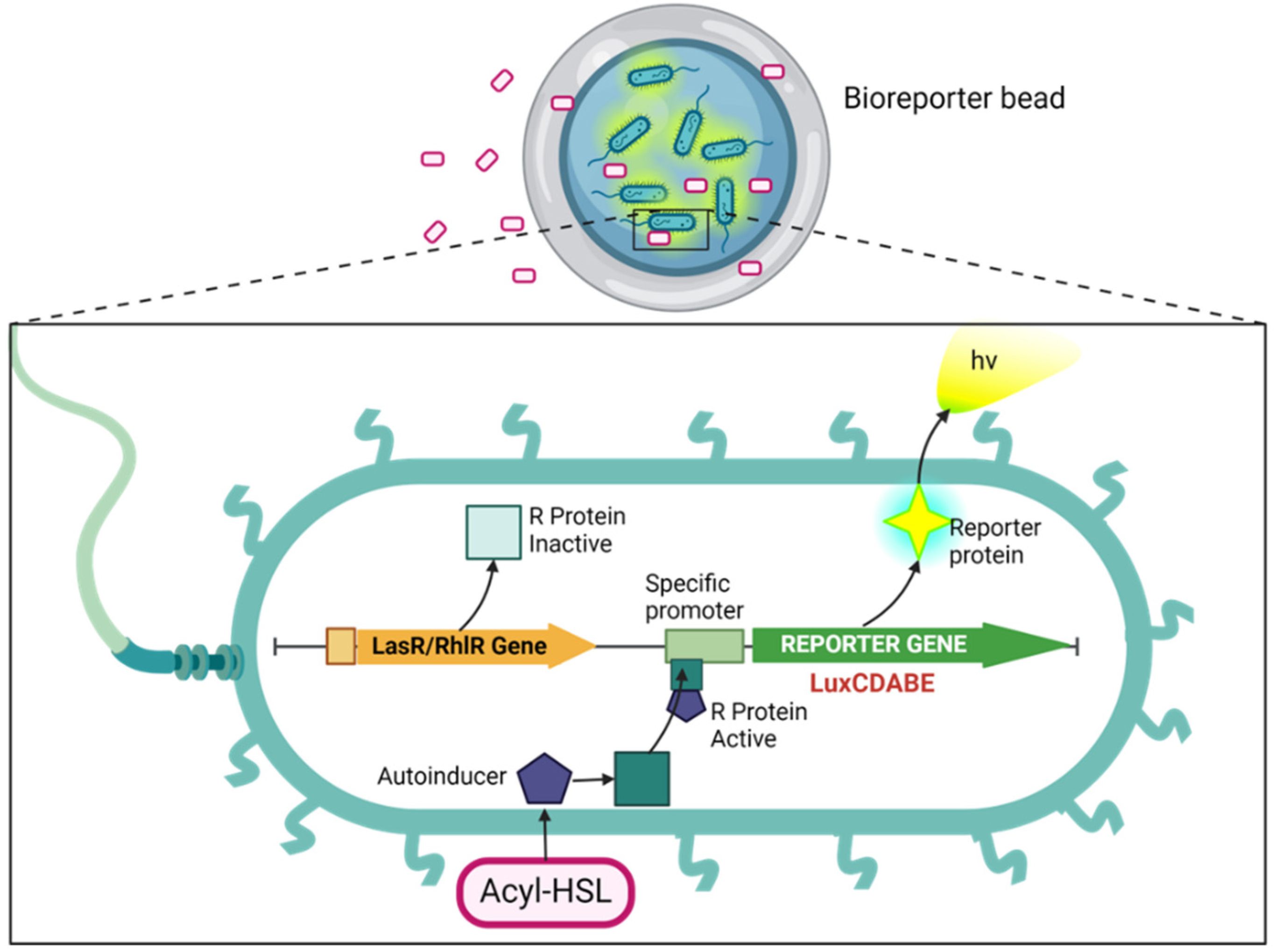
2.5. Bioluminescent Assay
2.5.1. Viability Assay of the Immobilized Bacterial Strains
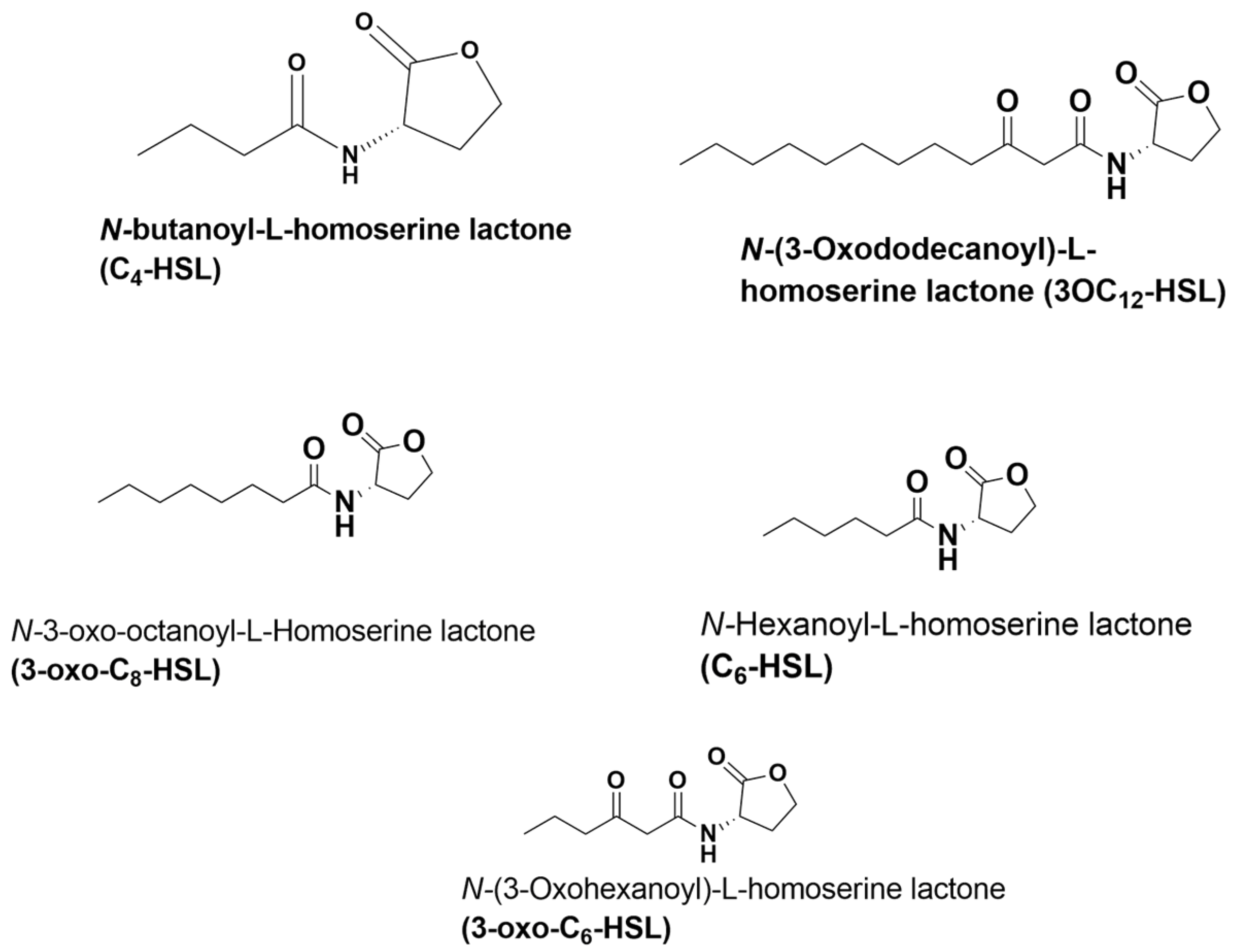
2.5.2. The Detection of Synthetic AHLs (3-Oxo-C12-HSL and C4-HSL)
2.5.3. Detection of AHLs in the Supernatant of Wild Cultures of PAO1 Strains
2.5.4. The Detection of AHLs in the Biofilm Effluent Obtained in the Flow Cell Experiment
2.5.5. Quorum Sensing Inhibition Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Encapsulation and Optimization
3.1.1. Optimization of Microbeads Formation
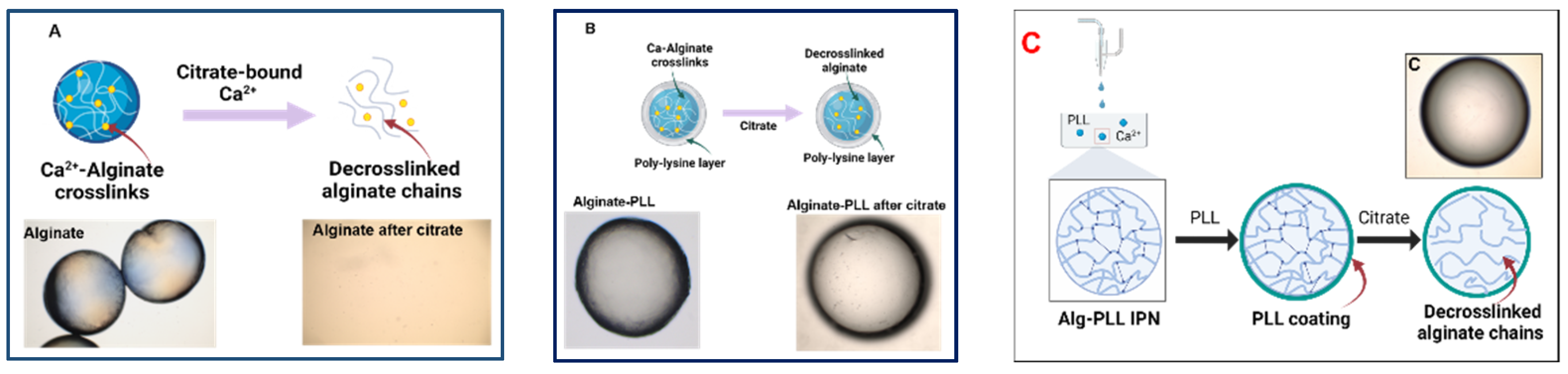
3.1.2. Effect of Encapsulation Methods
3.1.3. XPS Data
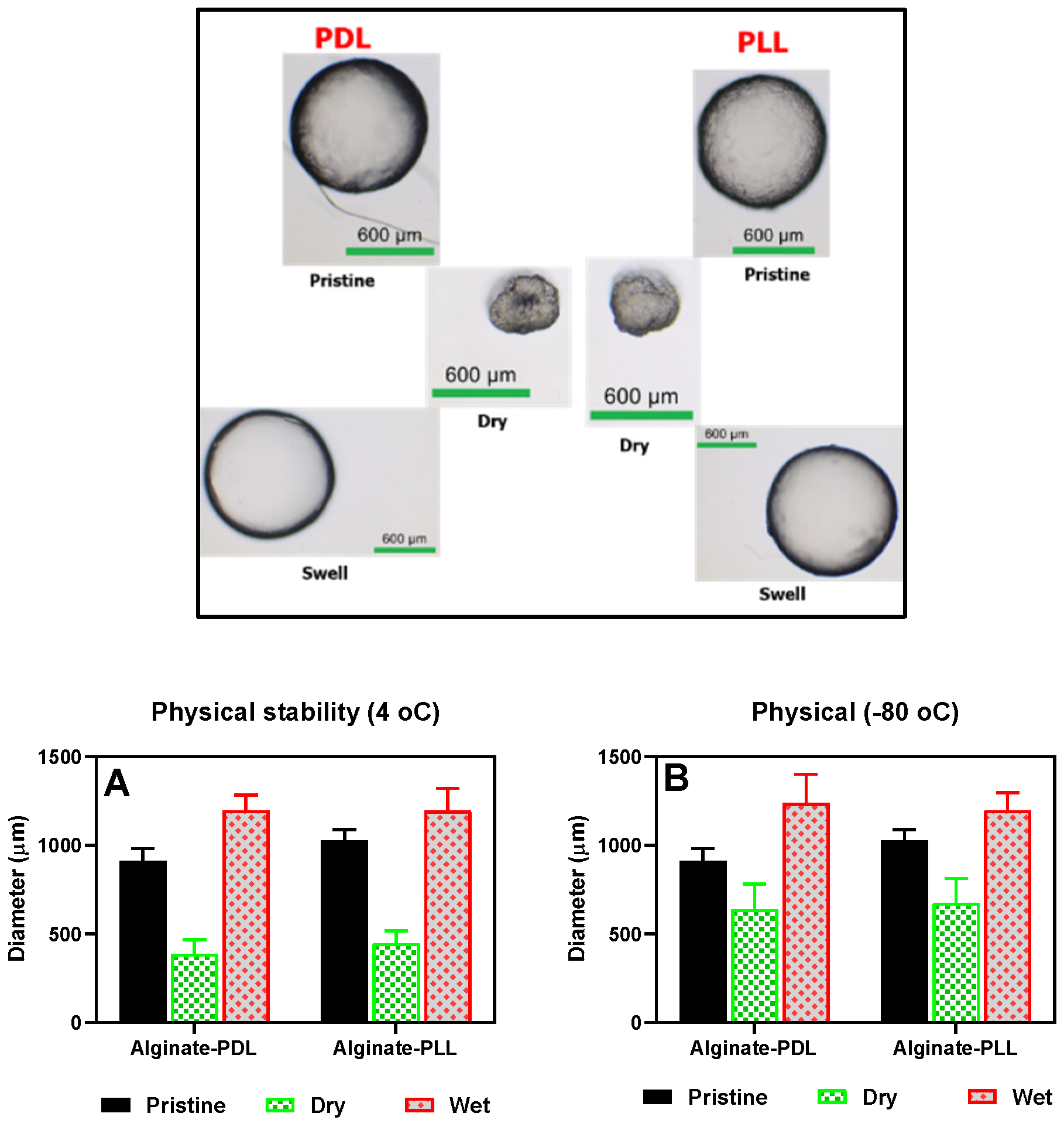
3.1.4. Microbead Stability and Swelling
3.2. Biological Activity Tests
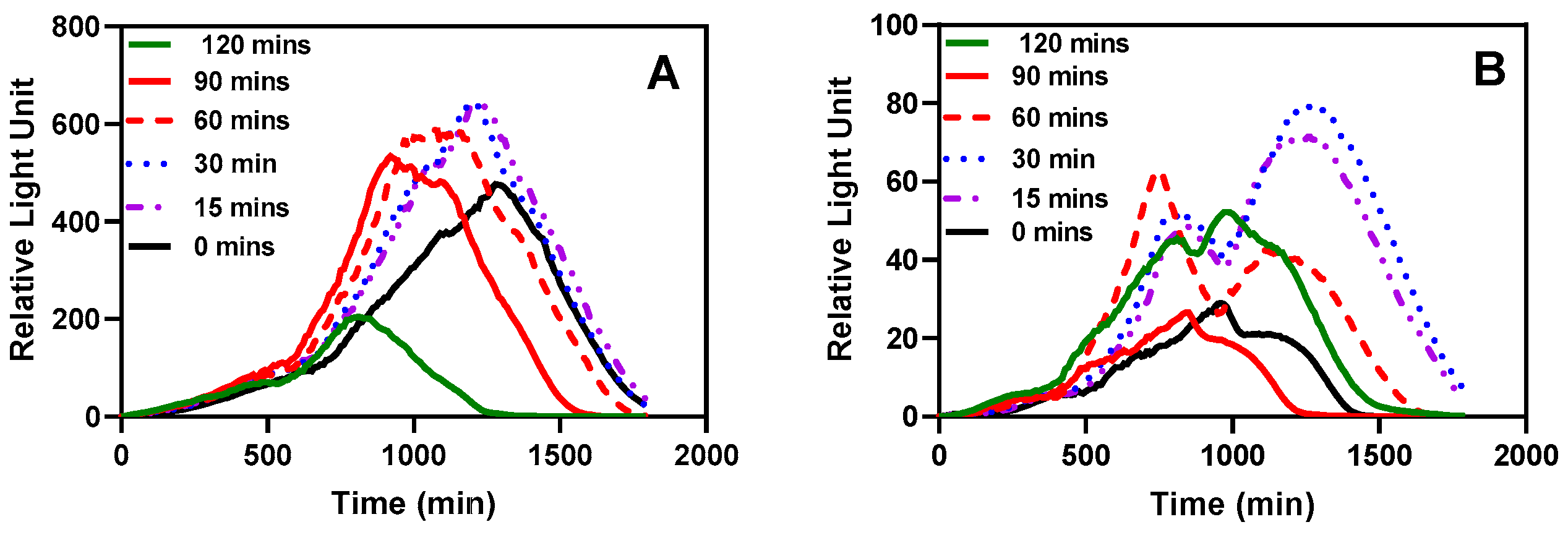
3.2.1. Viability and Bioluminescence
3.2.2. Bioluminescent Response of Alginate Reinforced with L and D Isomers of Poly-Lysine.
3.2.3. Effect of Activation
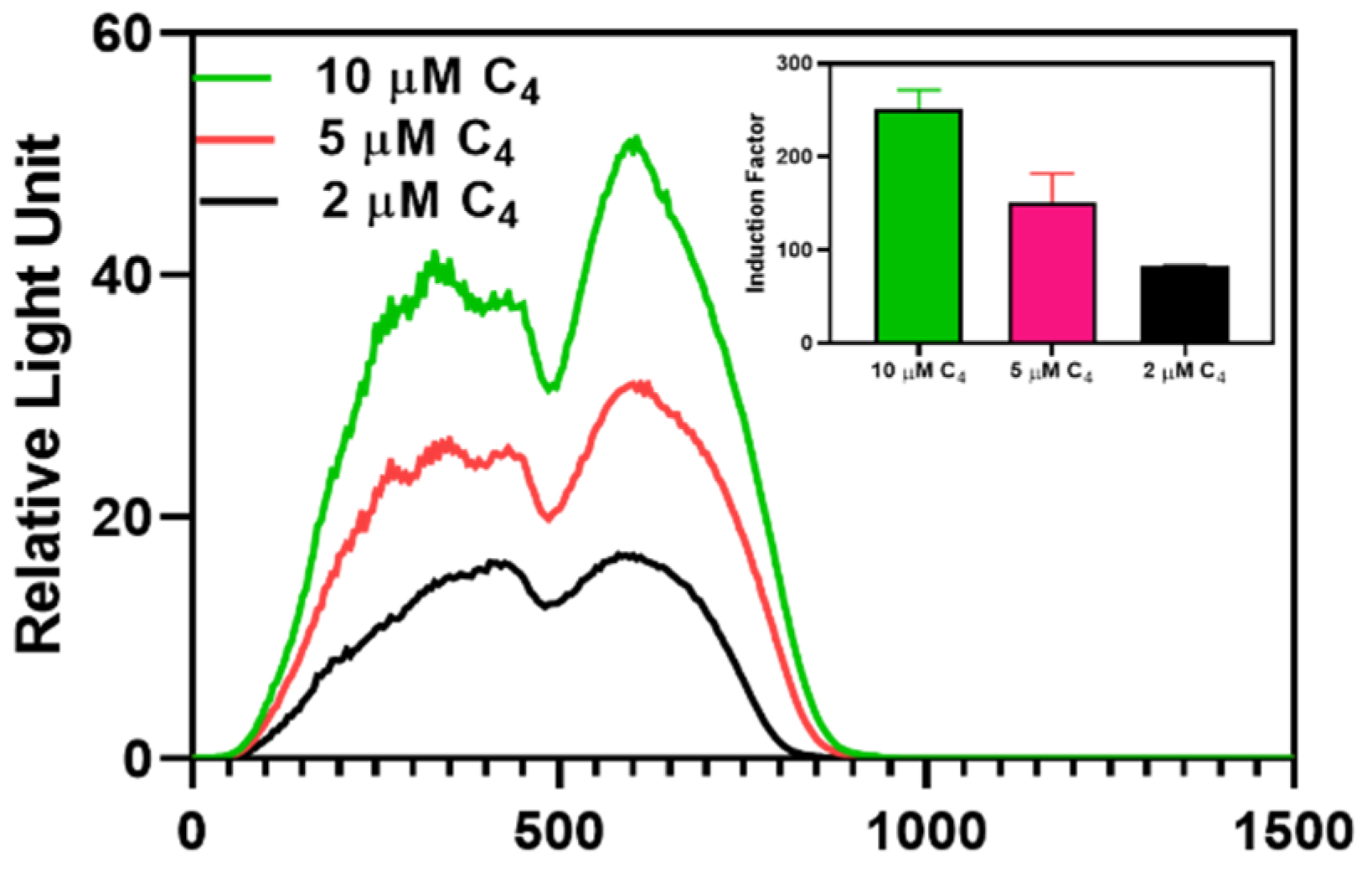
3.2.4. The Construction of the Calibration Curves
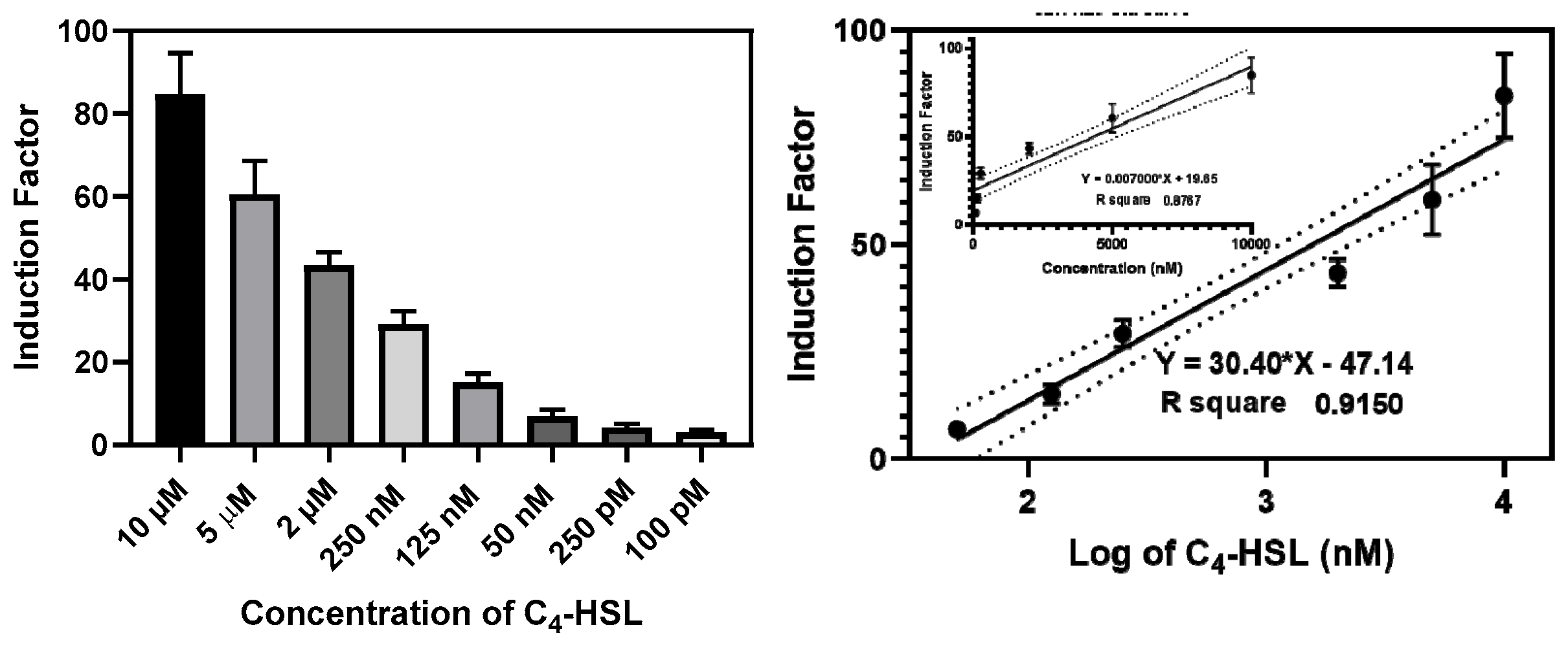
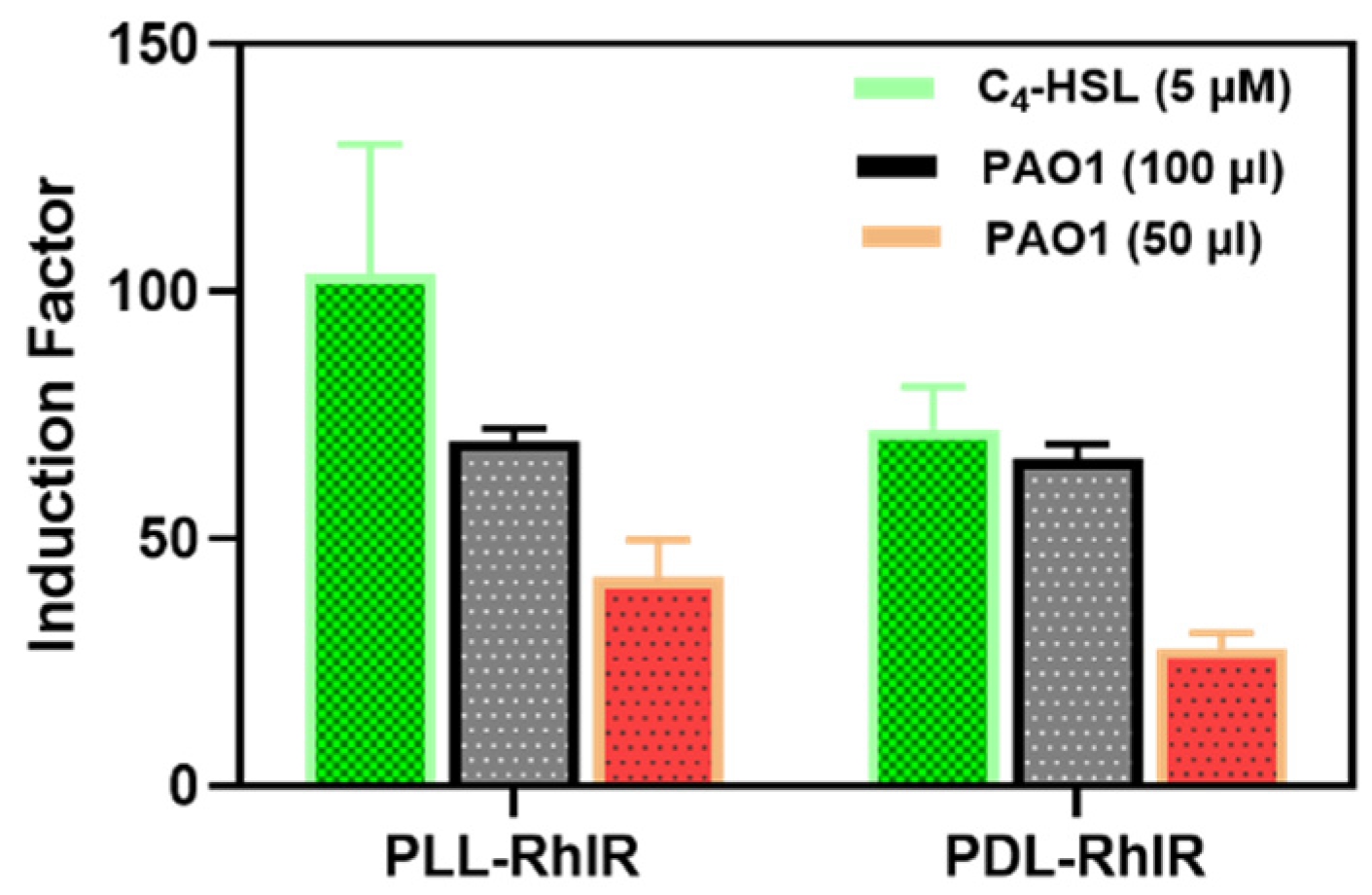
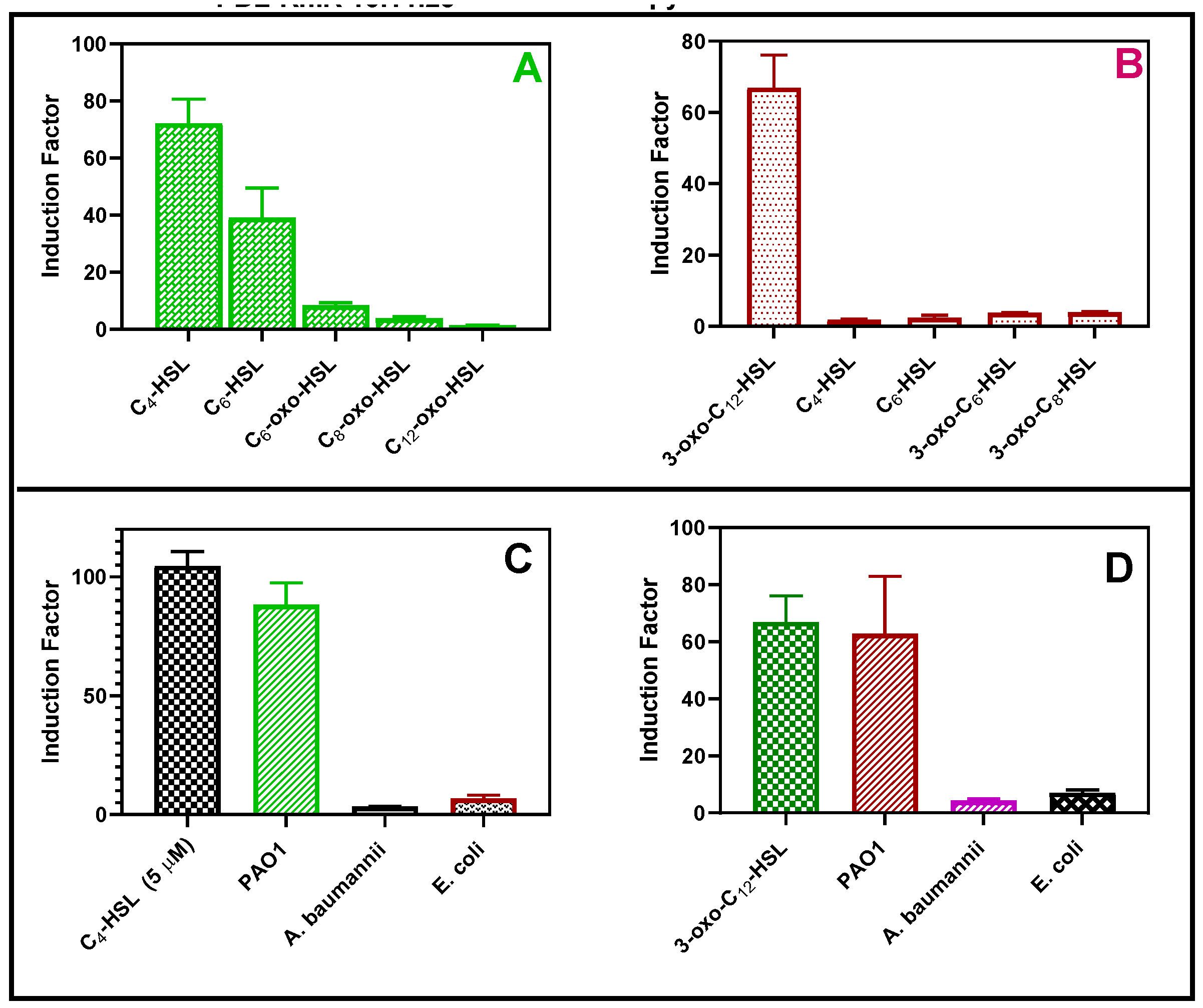
3.3. Selectivity and Inhibition Studies
3.3.1. Selectivity of the Bioreporters to the Synthetic and Secreted QS Molecules
3.3.2. Determination of AIs in the flow-Cell Biofilm Effluent
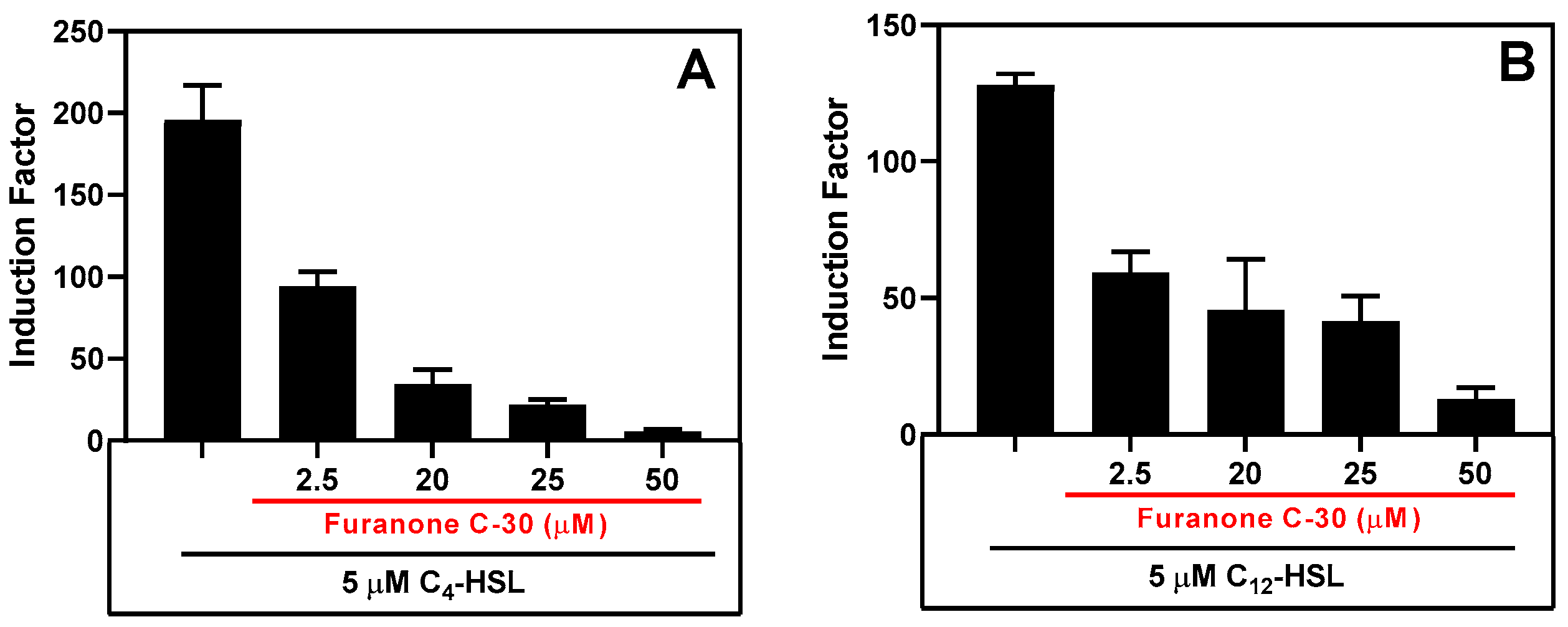
3.3.3. Inhibition Studies
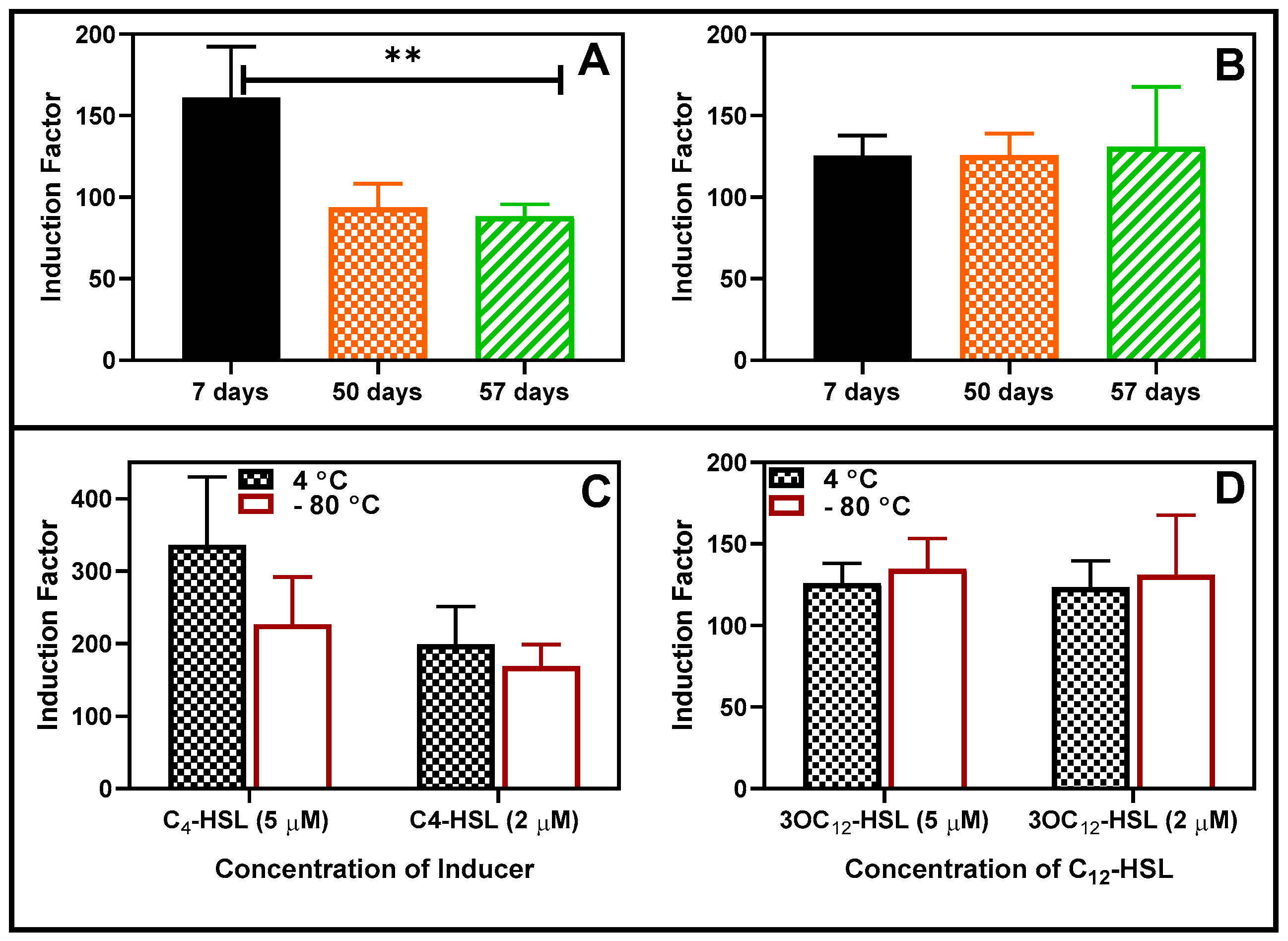
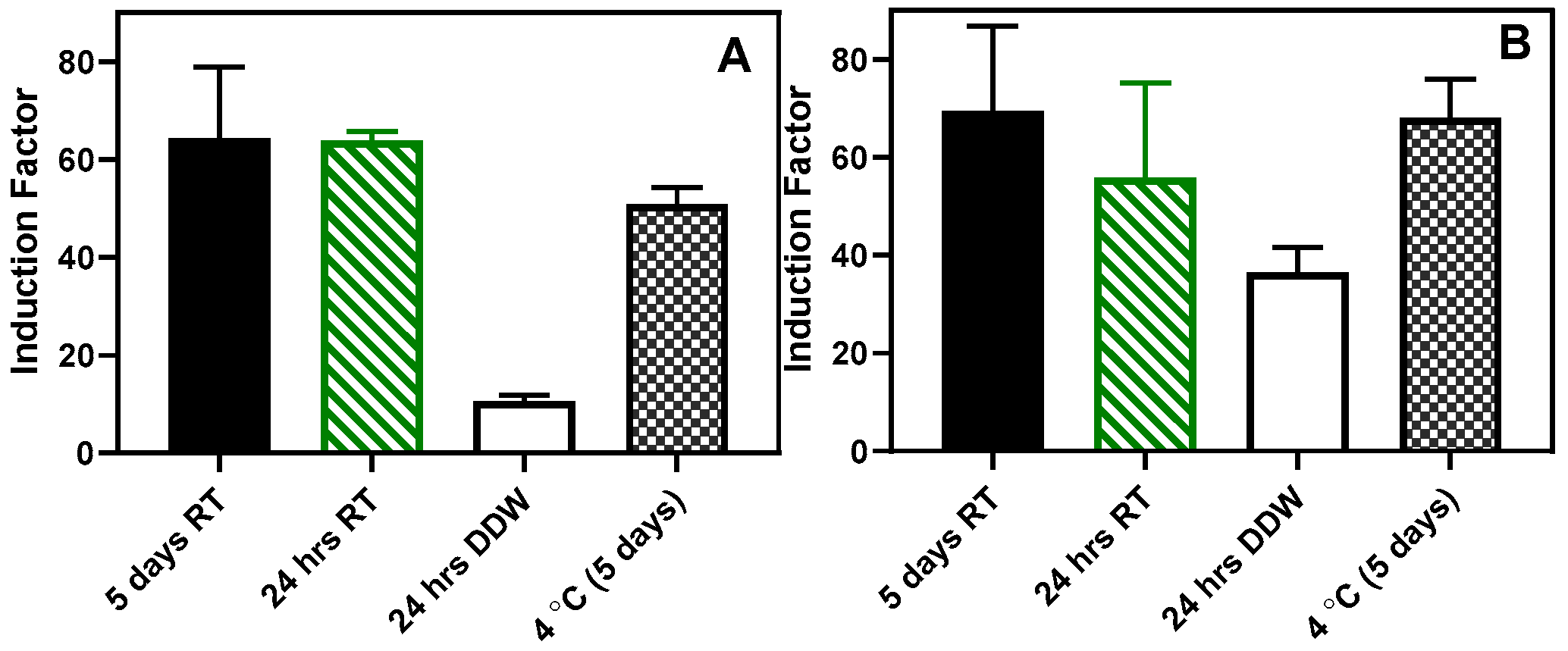
3.4. Storability Assessments
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Delden, C.; Iglewski, B.H.J.E.i.d. Cell-to-cell signaling and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. 1998, 4, 551. [CrossRef]
- Lyczak, J.B.; Cannon, C.L.; Pier, G.B.J.C.m.r. Lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. 2002, 15, 194-222. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Kievit, T.R.; Iglewski, B.H.J.I.; immunity. Bacterial quorum sensing in pathogenic relationships. 2000, 68, 4839-4849. [CrossRef]
- Winson, M.K.; Camara, M.; Latifi, A.; Foglino, M.; Chhabra, S.R.; Daykin, M.; Bally, M.; Chapon, V.; Salmond, G.; Bycroft, B.W.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Multiple N-acyl-L-homoserine lactone signal molecules regulate production of virulence determinants and secondary metabolites in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1995, 92, 9427-9431. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, D.J.N.r.D.d. Understanding biofilm resistance to antibacterial agents. 2003, 2, 114-122. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.Y.; Fan, Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Zhang, H.-B.; Ong, S.L.; Dong, N.; Xu, J.-L.; Ng, W.J.; Zhang, L.-H.J.R.i.m. Microbial diversity and prevalence of virulent pathogens in biofilms developed in a water reclamation system. 2003, 154, 623-629. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuqua, W.C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P.J.J.o.b. Quorum sensing in bacteria: the LuxR-LuxI family of cell density-responsive transcriptional regulators. 1994, 176, 269-275.
- Erickson, D.L.; Endersby, R.; Kirkham, A.; Stuber, K.; Vollman, D.D.; Rabin, H.R.; Mitchell, I.; Storey, D.G.J.I.; immunity. Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing systems may control virulence factor expression in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis. 2002, 70, 1783-1790. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, J.P.; Gray, K.M.; Passador, L.; Tucker, K.D.; Eberhard, A.; Iglewski, B.H.; Greenberg, E.P.J.P.o.t.N.A.o.S. Structure of the autoinducer required for expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence genes. 1994, 91, 197-201. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, B.; Rodgers, H.C.; Cámara, M.; Knox, A.J.; Williams, P.; Hardman, A.J.F.m.l. Direct detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones in cystic fibrosis sputum. 2002, 207, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Favre-Bonté, S.; Pache, J.-C.; Robert, J.; Blanc, D.; Pechère, J.-C.; van Delden, C.J.M.p. Detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell-to-cell signals in lung tissue of cystic fibrosis patients. 2002, 32, 143-147. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, C.E.; Visser, M.B.; Schwab, U.; Sokol, P.A.J.F.m.l. Identification of N-acylhomoserine lactones in mucopurulent respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients. 2005, 244, 297-304. [CrossRef]
- Barr, H.L.; Halliday, N.; Cámara, M.; Barrett, D.A.; Williams, P.; Forrester, D.L.; Simms, R.; Smyth, A.R.; Honeybourne, D.; Whitehouse, J.L.J.E.R.J. Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing molecules correlate with clinical status in cystic fibrosis. 2015, 46, 1046-1054. [CrossRef]
- Massai, F.; Imperi, F.; Quattrucci, S.; Zennaro, E.; Visca, P.; Leoni, L.J.B.; Bioelectronics. A multitask biosensor for micro-volumetric detection of N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing signal. 2011, 26, 3444-3449. [CrossRef]
- Ortori, C.A.; Atkinson, S.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Barrett, D.A.J.A.; chemistry, b. Comprehensive profiling of N-acylhomoserine lactones produced by Yersinia pseudotuberculosis using liquid chromatography coupled to hybrid quadrupole–linear ion trap mass spectrometry. 2007, 387, 497-511. [CrossRef]
- McLean, R.J.; Pierson III, L.S.; Fuqua, C.J.J.o.m.m. A simple screening protocol for the identification of quorum signal antagonists. 2004, 58, 351-360. [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Pasini, P.; Deo, S.K.; Flomenhoft, D.; Shashidhar, H.; Daunert, S.J.A.c. Biosensing systems for the detection of bacterial quorum signaling molecules. 2006, 78, 7603-7609. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Pasini, P.; Daunert, S.J.A.; chemistry, b. Detection of bacterial quorum sensing N-acyl homoserine lactones in clinical samples. 2008, 391, 1619-1627. [CrossRef]
- Horáček, O.; Portillo, A.E.; Dhaubhadel, U.; Sung, Y.-S.; Readel, E.R.; Kučera, R.; Armstrong, D.W.J.T. Comprehensive chiral GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS methods for identification and determination of N-acyl homoserine lactones. 2023, 253, 123957. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Checa, S.K.; Zurbriggen, M.D.; Soncini, F.C.J.C.o.i.b. Bacterial signaling systems as platforms for rational design of new generations of biosensors. 2012, 23, 766-772. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tang, S.-Y.; Yang, S.J.F.o.C.S.; Engineering. Genetic biosensors for small-molecule products: Design and applications in high-throughput screening. 2017, 11, 15-26. [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.; Novoyatlova, U.; Scheglova, E.; Prazdnova, E.; Mazanko, M.; Kessenikh, A.; Kononchuk, O.; Gnuchikh, E.; Liu, Y.; Al Ebrahim, R.J.B.; et al. Bacterial lux-biosensors: Constructing, applications, and prospects. 2023, 13, 100323. [CrossRef]
- Struss, A.; Pasini, P.; Ensor, C.M.; Raut, N.; Daunert, S.J.A.c. Paper strip whole cell biosensors: a portable test for the semiquantitative detection of bacterial quorum signaling molecules. 2010, 82, 4457-4463. [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Zhuang, G.; Ma, A.; Yu, Q.; Zhuang, X.J.J.o.E.S. Construction of a dual fluorescence whole-cell biosensor to detect N-acyl homoserine lactones. 2014, 26, 415-422. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubkowicz, D.; Ho, C.L.; Hwang, I.Y.; Yew, W.S.; Lee, Y.S.; Chang, M.W.J.A.s.b. Reprogramming probiotic Lactobacillus reuteri as a biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus derived AIP-I detection. 2018, 7, 1229-1237. [CrossRef]
- Van Dyk, T.K.; Rosson, R.A.J.B.M.; Protocols. Photorhabdus luminescens luxCDABE promoter probe vectors. 1998, 85-95. [CrossRef]
- Daunert, S.; Barrett, G.; Feliciano, J.S.; Shetty, R.S.; Shrestha, S.; Smith-Spencer, W.J.C.r. Genetically engineered whole-cell sensing systems: coupling biological recognition with reporter genes. 2000, 100, 2705-2738. [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jin, X.J.M.d. Dual crosslinked methacrylated alginate hydrogel micron fibers and tissue constructs for cell biology. 2019, 17, 557. [CrossRef]
- Paul, A.A.; Markus, V.; Kristollari, K.; Marks, R.S. Alginate-Based Applications in Biotechnology with a Special Mention to Biosensors. 2023.
- Mehrotra, T.; Dev, S.; Banerjee, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, R.; Aggarwal, S.J.J.o.E.C.E. Use of immobilized bacteria for environmental bioremediation: a review. 2021, 9, 105920. [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Martínez-Sanz, M.; Hogan, S.A.; López-Rubio, A.; Brodkorb, A.J.C.P. Nano-and microstructural evolution of alginate beads in simulated gastrointestinal fluids. Impact of M/G ratio, molecular weight and pH. 2019, 223, 115121. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Terrell, J.L.; Fernandes, R.; Dowling, M.B.; Payne, G.F.; Raghavan, S.R.; Bentley, W.E.J.B.; bioengineering. Encapsulated fusion protein confers “sense and respond” activity to chitosan–alginate capsules to manipulate bacterial quorum sensing. 2013, 110, 552-562. [CrossRef]
- Budianto, E.; Saepudin, E.; Nasir, M. The encapsulation of Lactobacillus casei probiotic bacteria based on sodium alginate and chitosan. In Proceedings of the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2020; p. 012043. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Nothias, J.-M.; Scavone, A.; Garfinkel, M.; Millis, J.M.J.A.j. Biocompatibility investigation of polyethylene glycol and alginate-poly-L-lysine for islet encapsulation. 2010, 56, 241-245. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganin, H.; Tang, X.; Meijler, M.M.J.B.; letters, m.c. Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by AI-2 analogs. 2009, 19, 3941-3944. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, K.; Surette, M.G.J.J.o.b. Environmental regulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 Las and Rhl quorum-sensing systems. 2007, 189, 4827-4836. [CrossRef]
- Gugerli, R.; Cantana, E.; Heinzen, C.; Stockar, U.v.; Marison, I.J.J.o.m. Quantitative study of the production and properties of alginate/poly-L-lysine microcapsules. 2002, 19, 571-590. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golberg, K.; Markus, V.; Kagan, B.-e.; Barzanizan, S.; Yaniv, K.; Teralı, K.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A.J.P. Anti-Virulence Activity of 3, 3′-Diindolylmethane (DIM): A Bioactive Cruciferous Phytochemical with Accelerated Wound Healing Benefits. 2022, 14, 967. [CrossRef]
- Hunt, N.; Smith, A.M.; Gbureck, U.; Shelton, R.; Grover, L.J.A.b. Encapsulation of fibroblasts causes accelerated alginate hydrogel degradation. 2010, 6, 3649-3656. [CrossRef]
- de Vos, P.; Hoogmoed, C.G.; Busscher, H.J.J.J.o.B.M.R.A.O.J.o.T.S.f.B., The Japanese Society for Biomaterials,; Biomaterials, T.A.S.f.; Biomaterials, t.K.S.f. Chemistry and biocompatibility of alginate-PLL capsules for immunoprotection of mammalian cells. 2002, 60, 252-259. [CrossRef]
- French, T.; So, P.; Weaver, J., DJ; Coelho-Sampaio, T.; Gratton, E.; Voss, J., EW; Carrero, J.J.J.o.m. Two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy of macrophage-mediated antigen processing. 1997, 185, 339-353. [CrossRef]
- Creighton, T.E. Proteins: structures and molecular properties; Macmillan: 1993.
- Maurer, P.H.J.T.J.o.e.m. Antigenicity of polypeptides (poly alpha amino acids) XIII. Immunological studies with synthetic polymers containing only D-or D-and L-α-amino acids. 1965, 121, 339-349. [CrossRef]
- Sela, M.J.A.i.i. Immunological studies with synthetic polypeptides. 1966, 5, 29-129. [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.B.; Mitchell, R.J.; Kim, B.C.J.B. Whole-cell-based biosensors for environmental biomonitoring and application. 2004, 269-305. [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.K.; Dusseault, J.; Polizu, S.; Ménard, M.; Hallé, J.-P.J.B. Physicochemical model of alginate–poly-l-lysine microcapsules defined at the micrometric/nanometric scale using ATR-FTIR, XPS, and ToF-SIMS. 2005, 26, 6950-6961. [CrossRef]
- de Vos, P.; van Hoogmoed, C.G.; van Zanten, J.; Netter, S.; Strubbe, J.H.; Busscher, H.J.J.B. Long-term biocompatibility, chemistry, and function of microencapsulated pancreatic islets. 2003, 24, 305-312. [CrossRef]
- Thu, B.; Bruheim, P.; Espevik, T.; Smidsrød, O.; Soon-Shiong, P.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.J.B. Alginate polycation microcapsules: I. Interaction between alginate and polycation. 1996, 17, 1031-1040. [CrossRef]
- Strand, B.L.; Mørch, Y.A.; Espevik, T.; Skjåk-Bræk, G.J.B.; bioengineering. Visualization of alginate–poly-L-lysine–alginate microcapsules by confocal laser scanning microscopy. 2003, 82, 386-394. [CrossRef]
- Medina, G.; Juárez, K.; Valderrama, B.; Soberón-Chávez, G.J.J.o.B. Mechanism of Pseudomonas aeruginosa RhlR transcriptional regulation of the rhlAB promoter. 2003, 185, 5976-5983. [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.B.; Bassler, B.L.J.A.R.i.M. Quorum sensing in bacteria. 2001, 55, 165-199. [CrossRef]
- Winson, M.K.; Swift, S.; Fish, L.; Throup, J.P.; Jørgensen, F.; Chhabra, S.R.; Bycroft, B.W.; Williams, P.; Stewart, G.S.J.F.m.l. Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. 1998, 163, 185-192. [CrossRef]
- Chugani, S.A.; Whiteley, M.; Lee, K.M.; D'Argenio, D.; Manoil, C.; Greenberg, E.J.P.o.t.n.a.o.s. QscR, a modulator of quorum-sensing signal synthesis and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 2001, 98, 2752-2757. [CrossRef]
- Markus, V.; Golberg, K.; Teralı, K.; Ozer, N.; Kramarsky-Winter, E.; Marks, R.S.; Kushmaro, A.J.M. Assessing the molecular targets and mode of action of furanone C-30 on Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. 2021, 26, 1620. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




