1. Introduction
The rise of antibiotic resistance is a global health threat, associated with increased mortality and higher healthcare costs. In fact, the United Nations General Assembly met to address this threat in September 2016, indicating a current issue that requires immediate solutions. In addition to resistance, antibiotics are a common cause of serious adverse effects that compromise patient health. Therefore, the primary means to decrease antibiotic resistance and adverse effects is to minimize unnecessary antibiotic use. To mitigate suboptimal antibiotic use and improve patient outcomes, the World Health Organization, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), Joint Commission, Centers for Medicare, and Medicaid Services (CMS) have advocated for antibiotic stewardship programs (ASPs) 1.
Antibiotic use and prescribing in approximately 50% of cases are inappropriate, thus promoting the emergence of bacterial resistance, as mentioned above. Therefore, it is necessary to ASPs, which aim to facilitate the rational use of antibiotics and improve the outcomes of patients receiving antibacterial treatment 2.
Antimicrobial resistance can be prevented by interventions aimed at reducing overprescribing of antibiotics to hospitalized patients through ASPs, characterized by being based on seven basic elements; leadership commitment, multidisciplinary team, situation assessment, interventions to improve antibiotic use, surveillance, reporting and education; and are designed to optimize antibiotic therapy, leading to significant reductions in antibiotic administration and consumption, bringing as a benefit decreases in antibiotic resistance, toxicity and costs. Guidelines for empiric therapy, checklists, dedicated teams, mandatory rules, alerts on antibiotic misuse and monitoring of antibiotic consumption have been described as ASPs interventions that had significant benefits in clinical outcomes 3.
In the case of Colombia, there have been many ASPs implementations, in which beneficial results have been achieved in terms of rational antibiotic use and reducing the negative impact of inappropriate antibiotic consumption. Among these is the Colsubsidio Children's Clinic for June 2016 to December 2019, in which the identification of controlled antibiotics, review of medical records by the infectologist, characterization of antibiotic prescriptions, analysis and identification of ASP indicators, audit and feedback, and finally education and reports were proposed 4.
Another implementation of an ASP was in the Pediatric Hospital of IV level in Bogotá (HOMI), with which they achieved beneficial results, such as optimization of antibiotic use, improvement of clinical outcomes, reduction of 20 to 50% of antimicrobial use and significant cost reduction 5 17.
This article aims to establish how the implementation of the use of antimicrobial stewardship programs at hospital and ICU level in a clinic in Sincelejo Sucre has had a significant impact on the improvement of rational use of antibiotics.
2. Materials and Methods
A retrospective observational study of an Excel database of the Salud Total clinic at the hospitalization level and in ICU from 2018 to 2022 was performed. This is a medium-level clinic. Regarding its facilities, they have 29 beds for ICU, 125 in hospitalization and 6 operating rooms: 20 beds are enabled, which are distributed in 10 intensive, 4 intermediate and 6 basic neonatal beds. The implementation of ASP in this hospital was carried out in 2018, which is formed by an infectologist, a microbiologist-pharmacologist physician, a nurse, and a chemist. The mechanism of operation of this program is through the persuasive methodology, which consists of the use of guidelines and therapeutic recommendations for the use of antibiotics against certain infectious pathologies, likewise as a fundamental component the initial individual or group initial education of clinicians, followed by continuing education. In this study, the antibiotics selected for analysis of the ASP were ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, meropenem and vancomycin. The objective was to analyze the pre-ASP (2017) and post-ASP (2018-2022) of the use of the 4 antibiotics mentioned, measured in defined daily doses (DDD) per 100 beds/day, allowing to establish the impact with the use of the program. Analysis of DDD before the implementation of the 2017 pre-ASP program was also performed, comparing whether antibiotic use was reduced.
Statistical analysis: Data were collected in a database in Excel program and the results are expressed as the average monthly DDD for each year of pre-ASP and post-ASP. To evaluate the effect of the ASP program, Cohen's D was used, whose values lower than 0.20, indicate no effect; values between 0.21 to 0.49 refer to a small effect; likewise, values oscillating between 0.50 to 0.70 indicate a moderate effect; finally, values higher than 0.80 indicate a large effect 6,7. The statistical analysis was performed using the statistical program Prism 5 for Windows version 5.0. To determine the existence of significant difference between pre-ASP and post-ASP DDD data, an analysis of variance with one-way Anova was performed, previously the normality of the data was evaluated with the Shapiro-Wilk test, in all cases the P value was greater than 0.05 and finally a Dunnet's posttest was run. P values less than 0.05 indicate a significant difference between the pre-ASP and post-ASP periods.
3. Results
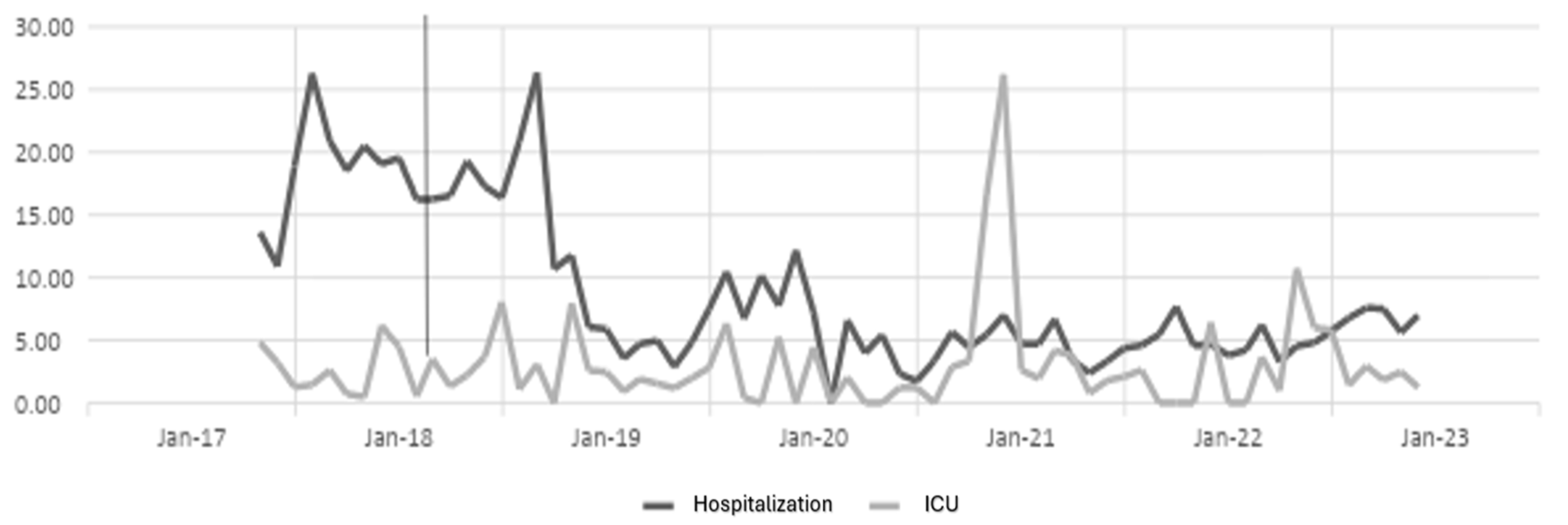
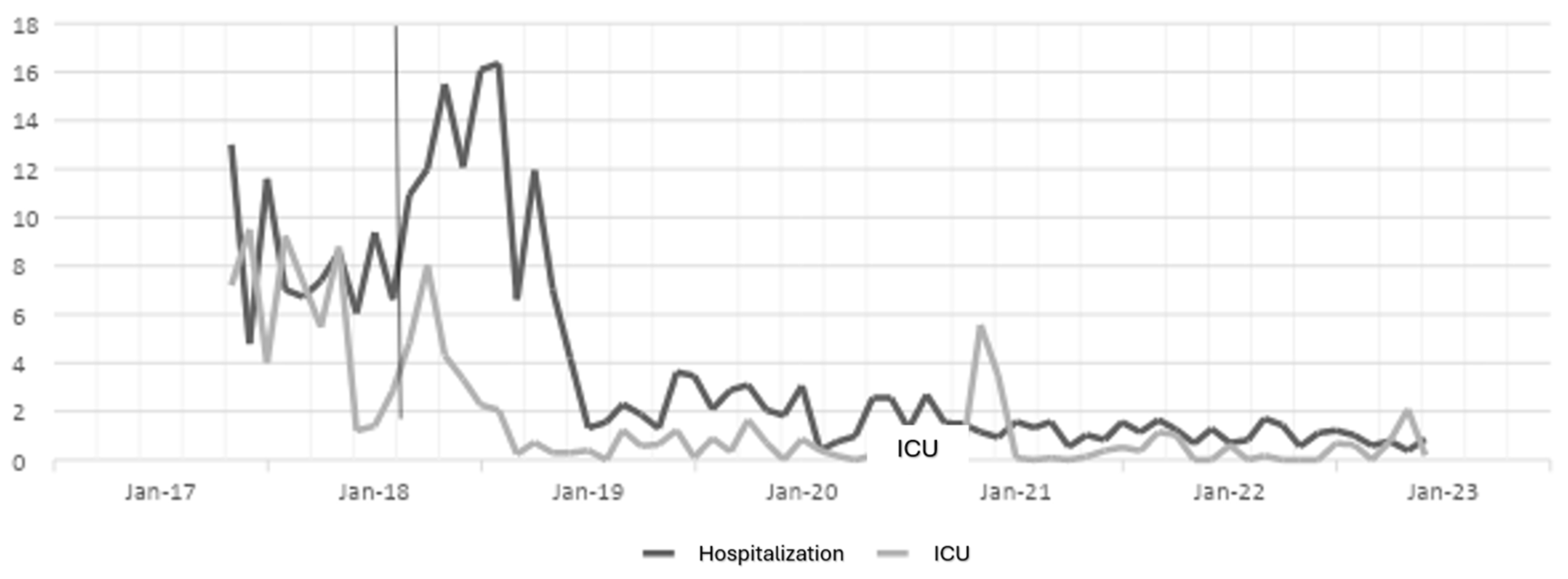
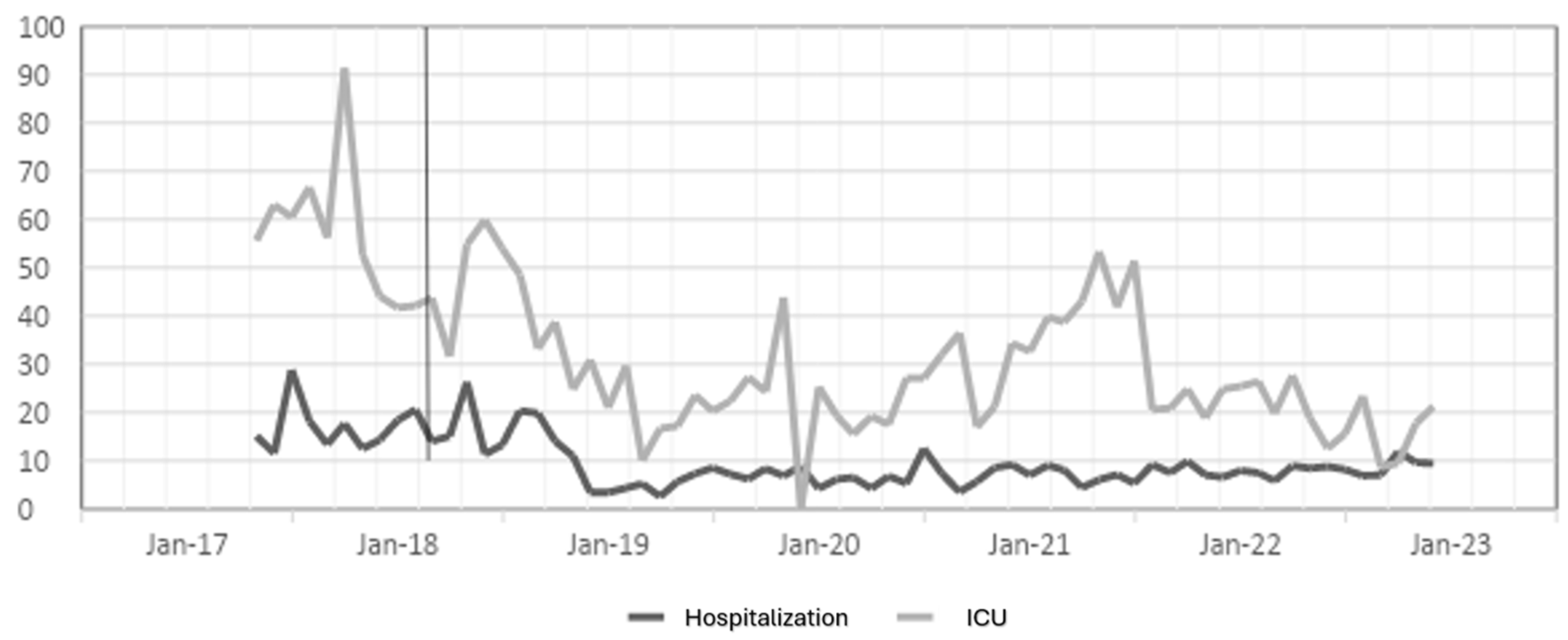
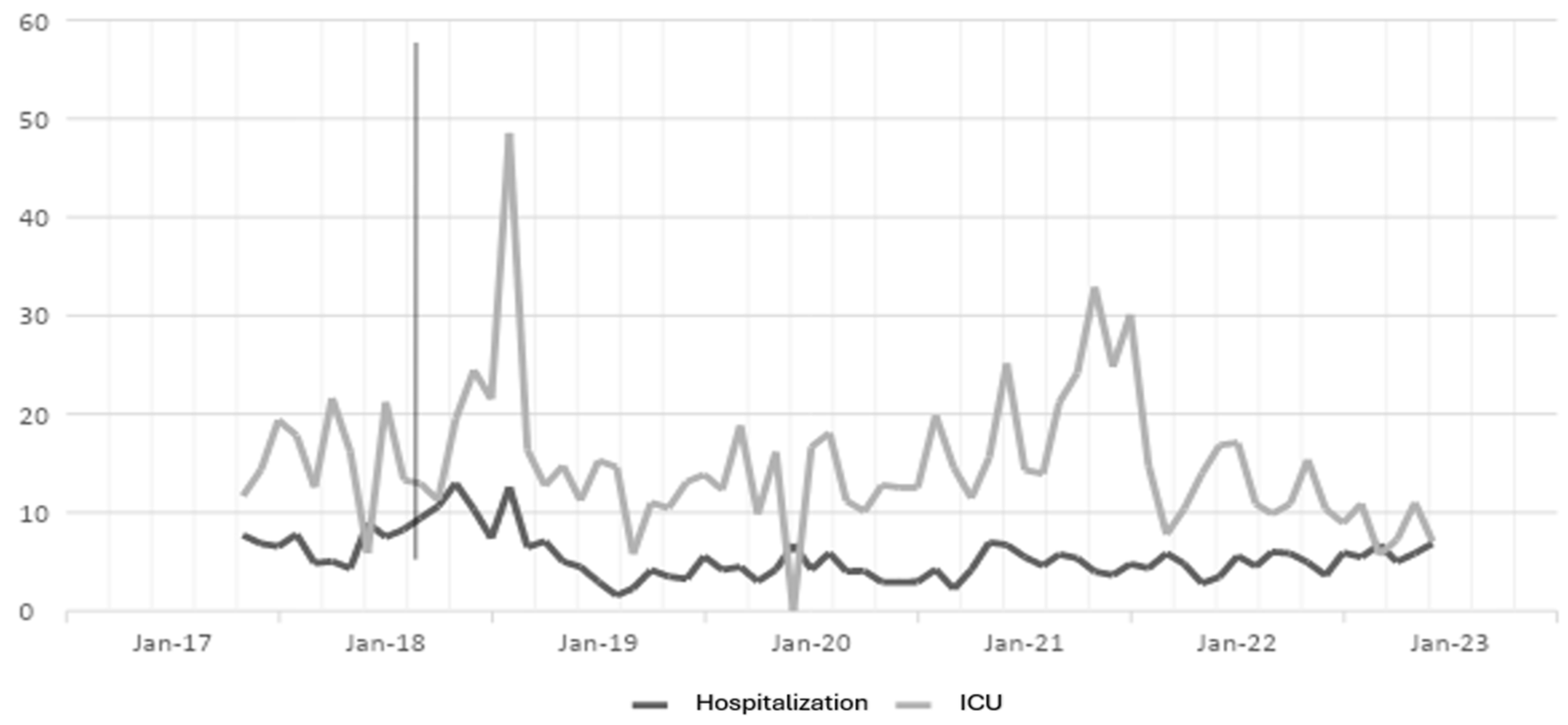
The antibiotic optimization program was implemented from the year 2018, corresponding post-ASP period, the year 2017 is the pre-ASP period, therefore below are the results of defined daily doses for the antibiotics ceftriaxone, ciprofloxacin, meropenem and vancomycin for hospitalization and ICU services in a clinic in Sincelejo, Sucre (
Figure 1,
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4), where the decrease in DDD from the post-ASP period can be evidenced.
In order to determine the effect of the antibiotic optimization program, a Cohen's D analysis was performed, and the results are shown in
Table 1.
Analyzing the results obtained from
Table 1, it is evident that for the case of the antibiotic ceftriaxone, in the first year of implementation of the antibiotic optimization program the effect was small in hospitalization, but in subsequent years a large effect is observed and in ICU for the years 2018, 2020 and 2022 there is a moderate effect, but in the years 2019 and 2021 there is no effect.
For the case of ciprofloxacin, a large effect is evident from the first year of implementation of the ASP until the last year of the study and in ICU it had a moderate effect the first year, but the second and third year the effect was small, while for the year 2021 the program had no effect, perhaps this result is due to the Covid-19 pandemic, because for the last year the effect was large.
The results for the antibiotic meropenem show a moderate effect in the first year, but over the years the effect becomes large in hospitalization and in ICU a large effect is observed in the first and last year, a moderate effect in the second and third year and for 2021 a small effect.
The results for the antibiotic vancomycin, which shows a large effect in the first and third year, and a small effect in 2019 and 2022, while for 2021 there was no effect in hospitalization, and for ICU the first and fourth year shows a large effect, the second and third year a moderate effect, while for 2022 there was no effect. In the case of hospitalization, the impact of the ASP was greater than in ICU, in addition, for 2021 in ICU, in the case of all antibiotics no effect of the ASP was found, perhaps as a response to the pandemic with Covid-19.
On the other hand, considering the DDD reported by WHO for each of the antibi-otics, we evaluated the significant differences compared with the DDD obtained in the clinic in the hospitalization and ICU services, as shown in
Table 2. Shapiro-Wilk test was performed to determine the normality of the data, in all cases the P value was greater than 0.05, therefore, all data are normal. After checking the normality of the data we proceeded to perform one-way Anova to compare the DDD of the year 2017 (pre-ASP) with the years from 2018 to 2022 (post-ASP), for which a Dunnet's posttest was performed , the Anova analysis for the hospitalization data gives us as a result p-value less than 0, 05, proving that there is a statistically significant difference and with the post-test it was proved that there is a significant difference between the pre-ASP and post-ASP, therefore it is demonstrated that the antibiotic optimization program is effective. But, for the case of meropenem and ceftriaxone in hospitalization no significant difference was observed between 2017 and 2018.
Analysis of ICU outcomes, for ceftriaxone and vancomycin gives us that there is no significant difference between pre-ASP and post-ASP (P value greater than 0.05). While for the case of ciprofloxacin and meropenem there are significant differences between pre-ASP and post-ASP DDD (P value less than 0.05).
Now, if we compare the DDD given by WHO with those obtained each year, it is evident that for the case of meropenem hospitalization in 2019 there were no significant differences, ciprofloxacin from 2019 to 2022 there were no significant differences and ceftriaxone from 2020 to 2021 there were also no significant differences for the rest there were significant dif-ferences, What is striking is that the year’s corresponding to the post-ASP are those that did not give differences compared to the WHO DDD, which shows that the DDD values are very close to those recommended by the WHO, and this in turn demon-strates the effectiveness of the ASP in this clinic.
For the case of ICU, there is no evi-dence of significant differences between the DDD values recommended by WHO and ceftriaxone from 2017 to 2022 and ciprofloxacin from 2018 to 2022 there were no sig-nificant differences, this demonstrates the relevance of ASP because we have compa-rable DDD data with those provided by WHO.
4. Discussion
The implementation of the ASP at the Salud Total Clinic has proven crucial in improving the appropriate use of antibiotics and reducing the risk of antimicrobial resistance. The results indicate that the ASP has achieved a significant reduction in inappropriate antibiotic use, particularly in hospitalization, where large and sustained effects were observed over time. Furthermore, the alignment of the DDD with WHO recommendations underscores the effectiveness of the ASP in standardizing and optimizing administered doses. Although the impact in the ICU was variable and diminished during the Covid-19 pandemic, the data still show improvements in antibiotic administration. These findings highlight the importance of maintaining and adapting the ASP to ensure proper antibiotic management, thereby enhancing patient care quality and combating antimicrobial resistance. 8
It is important to mention that the effect of the antimicrobial optimization program at the Salud Total clinic was reflected in the good use of the 4 antibiotics analyzed, since the DDD used over the years were correct, and were used only In the case in which they were needed, this has had an impact not only on reducing the clinic's bacterial resistance but also on better health outcomes for its patients.
To improve the program, analysis of all the antibiotics used in the clinic should continue to be carried out and also train the entire team so that the use of each antibiotic used can be improved, depending on the clinical case that the doctor is facing.
Another similar study on the implementation of the ASP in an intensive care unit against multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacteria infections has shown that the program is an effective and safe tool that reduces and adjusts the use of antimicrobials in clinical practice. This has a double benefit: on the one hand it reduces antibiotic pressure and, therefore, the selection of multidrug-resistant strains, and on the other hand it reduces the possible deleterious effects on the individual patient and even improves the prognosis by adjusting the choice of drug, the dosage and the possible adverse effects and interactions; as in our research, everything was reflected in the use of optimization indicators was DDD 9. In the implementation of this same program in the intensive care unit of a Public Hospital of Santa Elena in Ecuador, the amount of antibiotic consumed between 2018 and 2019 was evaluated, in which the use of cephalosporins such as ceftriaxone, cefepime and ceftazidime was reduced and the consumption of ampicillin + sulbactam and Piperacillin + tazobactam was increased. Comparing it with our study, it can be seen how the implementation of the ASP, allows the correct optimization of antibiotic use against the different infections of patients 10.
Antimicrobial stewardship programs have had a great impact at international, national, and local level, allowing to improve and reduce the negative ecological impact of their use. Spain is one of the countries in the world with the highest consumption of antimicrobials. It is estimated that up to 45% of patients admitted to Spanish hospitals receive at least one dose of antibiotics during their stay. At the University Clinical Hospital of Spain, in the Urology Department, the result was a reduction in the average DDD/100 stays of meropenem, ciprofloxacin and ceftriaxone. This made it possible to optimize communication and identification of points for improvement in clinical practice, daily control of the use of antimicrobials, which made it possible to reduce the use of certain molecules, especially in scheduled surgical procedures 11. It is important to mention that due to the current resistance of antibiotics, it is necessary to use ASPs to improve their use, allowing safe interventions and processes. In the case of 3 Portuguese hospitals, a participatory approach was used between researchers and workers, resulting in a clinical decision support system and real-time surveillance that integrates patient, microbiology and pharmacy data and facilitates clinical decision making, this means that resistance is monitored, and antibiotic prescription is tailored to the patient's needs. This is the case of the way in which the program was implemented at the Salud Social Clinic, in which the ASP work team complements the physician in the selection of antibiotics by means of persuasive methodology 12. The above, is complemented by the information found in the article on the effectiveness of an ASP in a tertiary hospital in Vietnam, in March 2016, the Ministry of Health of this country, 772 guidelines were issued for antibiotic prescription in hospital settings, with which as they updated it was possible to reduce the consumption of antibiotics and improve clinical outcomes among patients with infection 13 17.
In another study, the implementation of the use of antimicrobials is presented as the main tool for optimizing hospitals, improving clinical outcomes, reducing adverse effects and the spread of resistance. The result obtained with respect to the consumption of all the antibacterials studied by the ASP decreased both per stay and per discharge, from 36.62 to 35.72 DDD/100 stays (-2.5%) and from 236.02 to 227.03 DDD/100 discharges respectively (-3.8%). Among the antimicrobials that decreased the most was ciprofloxacin by 20.40% 14. At the Carlos Van Buren Hospital in Valparaiso, Chile, the implementation of ASP in the adult emergency unit was used for the treatment of high urinary tract infection, in which the impact on the consumption of amikacin and ceftriaxone was determined; the results were measured in DDD where a decrease in the consumption of ceftriaxone and an increase in amikacin was observed 15. At the Hospital de Mexico in 2014, an ASP program was implemented in the orthopedics service as a protocol for pre-surgical prophylaxis, which resulted in a decrease in the use of beta-lactams, mainly cephalosporins and penicillins, indicating an improvement in the optimization of antibiotic use. In the case of those that increased are vancomycin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, clindamycin, and gentamicin. With respect to the results, it can be said that it is evident that the intervention by ASP has produced important changes in consumption patterns, which on the one hand shows compliance with the intervention, which may indicate that there is an improvement in the quality of prescription of antibiotics used as antibiotic prophylaxis 16.
In the case of Colombia, several ASP implementations have also been carried out in order to reduce the irrational use of antibiotics and control their use for the benefit of the patient. In the Colsubsidio Children's Clinic for the year June 2016 to December 2019, this involved the identification of controlled antibiotics, review of medical records by the infectologist, characterization of antibiotic prescriptions, analysis and identification of ASP indicators, audit, and feedback, and finally education and reports. In the same way, this program has been implemented in the department of Sucre in the Salud Total Clinic, since there are few clinics in this territory that have obtained good results thanks to these improvements 4. Another ASP implementation was in the IV level Pediatric Hospital in Bogotá (HOMI), with which they achieved beneficial results, such as optimization of antibiotic use, improvement of clinical outcomes, reduction of 20 to 50% in the use of antimicrobials and significant cost reduction 5.
5. Conclusions
According to the results obtained, we can conclude that the antibiotic optimization program is an effective tool to reduce antibiotic consumption and promote the appropriate use of antibiotics. Because our results showed a reduction of DDD in the post-ASP period compared to the pre-ASP period, both in hospitalization and in the ICU.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the execution of the research work, data analysis, and writing of the article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Salud Social clinic in Sincelejo-Sucre-Colombia for providing the information for the study and the University of Sucre. Minciencias call for postdoctoral stays oriented by missions 934, contract 320-2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declares that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Ethical responsibilities
All authors accept ethical responsibility during the execution of the project, we protect the confidentiality of the data and we comply with the ethical values to be authors.
References
- Gross, A.E.; Hanna, D.; Rowan, S.A.; Bleasdale, S.C.; Suda, K. Successful Implementation of an Antibiotic Stewardship Program in an Academic Dental Practice. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019, 6, ofz067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simões, A.S.; Maia, M.R.; Gregório, J.; Couto, I.; Asfeldt, A.M.; Simonsen, G.S.; et al. Participatory implementation of an antibiotic stewardship programme supported by an innovative surveillance and clinical decision-support system. J Hosp Infect. 2018, 100, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riaño-Galvis, O.; Cerinza-Villanueva, D. Caracterización de un programa de optimización de antimicrobianos en la prescripción de Ampicilina/sulbactam en un hospital pediátrico, 2021. Available online: https://repository.urosario.edu.co/bitstream/handle/10336/30924/Caracterizaci%F3n%20de%20un%20PROA%20.pdf;jsessionid=DE8605C55B057267ED824AD9D0241EF9?sequence=1 (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Tobar, F. Experiencia PROA Clínica Infantil Colsubsidio implementación a su impacto. 2019. Available online: http://www.saludcapital.gov.co/DSP/Infecciones%20Asociadas%20a%20Atencin%20en%20Salud/Comites/2019/Diciembre/PROA_2019.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Moreno, G. Programa de optimización del uso de antibioticos (PROA), experiencia en un hospital pediátrico de IV nivel en Bogota (Colombia). 2019. Available online: https://webbertraining.com/files/library/docs/828.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Caycho, T.; Ventura-León, J.; Castillo-Blanco, R. Magnitud del efecto para la diferencia de dos grupos en ciencias de la salud. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2016, 39, 459–461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences, (2ª ed.); Erlbaum: Hillsdale, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-de la Cruz, P.; Moreno-Núñez, L.; Álvarez-Atienza, S.; Sanz-Márquez, S.; Valverde-Canovas, J.F.; Losa-García, J.E. Discontinuation of antibiotics through an antimicrobial treatment optimization program in patients attended in Emergency Departments with low suspicion of infection. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. 2022, S2529-993X(22)00212-X. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ramos, J.; Ramírez-Galleymore, P. Antibiotic optimization programs in the intensive care unit for infections caused by multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacilli. Med Intensiva (Engl Ed). 2023, 47, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruales-Carrion, P.; Mariscal-Santi, W.; Jimenez-Jimenez, W. La implementación de un programa de optimización de antibióticos en la unidad de cuidados intensivos de un Hospital Público de Santa Elena. Revista UG. 2021, 133, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, G. Intervención en el servicio de urología mediante un programa de optimización del uso de antimicrobianos. 2022. Available online: https://digitum.um.es/digitum/handle/10201/125412 (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Simões, A.S.; Maia, M.R.; Gregório, J.; Couto, I.; Asfeldt, A.M.; Simonsen, G.S.; et al. Participatory implementation of an antibiotic stewardship program supported by an innovative surveillance and clinical decision-support system. J Hosp Infect. 2018, 100, 257–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.Q.; Nguyen-Thi, H.-Y.; Huynh, P.-T.; Le, N.D.T.; Nguyen, N.T.-Q.; Hsia, Y. Effectiveness of an enhanced antibiotic stewardship program among pediatric patients in a tertiary hospital in Vietnam. J Hosp Infect. 2022, 127, 121–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collado, R.; Losa, J.; Alba, E.; Toro, A.; Moreno, L.; Pérez, M. Evaluación del consumo de antimicrobianos mediante DDD/100 estancias versus DDD/100 altas en la implantación de un Programa de Optimización del Uso de Antimicrobianos. Rev Esp Quimioter 2015, 28, 317–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cruz, R.; Sandoval, R.; González, G.; Pérez, P.; Sánchez, L. Impact on the consumption of amikacin and ceftriaxone in an adult emergency unit, after the implementation of a guide for the treatment of high urinary tract infections. Infection 2019, 23, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, R.; Sandoval, R.; González, G.; Pérez, P.; Sánchez, L. Impact on the consumption of amikacin and ceftriaxone in an adult emergency unit, after the implementation of a guide for the treatment of high urinary tract infections. Infectio 2019, 23, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Baño, J.; Paño-Pardo, J.R.; Alvarez-Rocha, L.; Asensio, Á.; Calbo, E.; Cercenado, E.; et al. Antimicrobial use optimization programs (PROA) in Spanish hospitals: GEIH-SEIMC, SEFH and SEMPSPH consensus document. Disease Infection Microbiol Clin [Internet] 2012, 30, 22.e1–22.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).