Submitted:
17 June 2024
Posted:
18 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
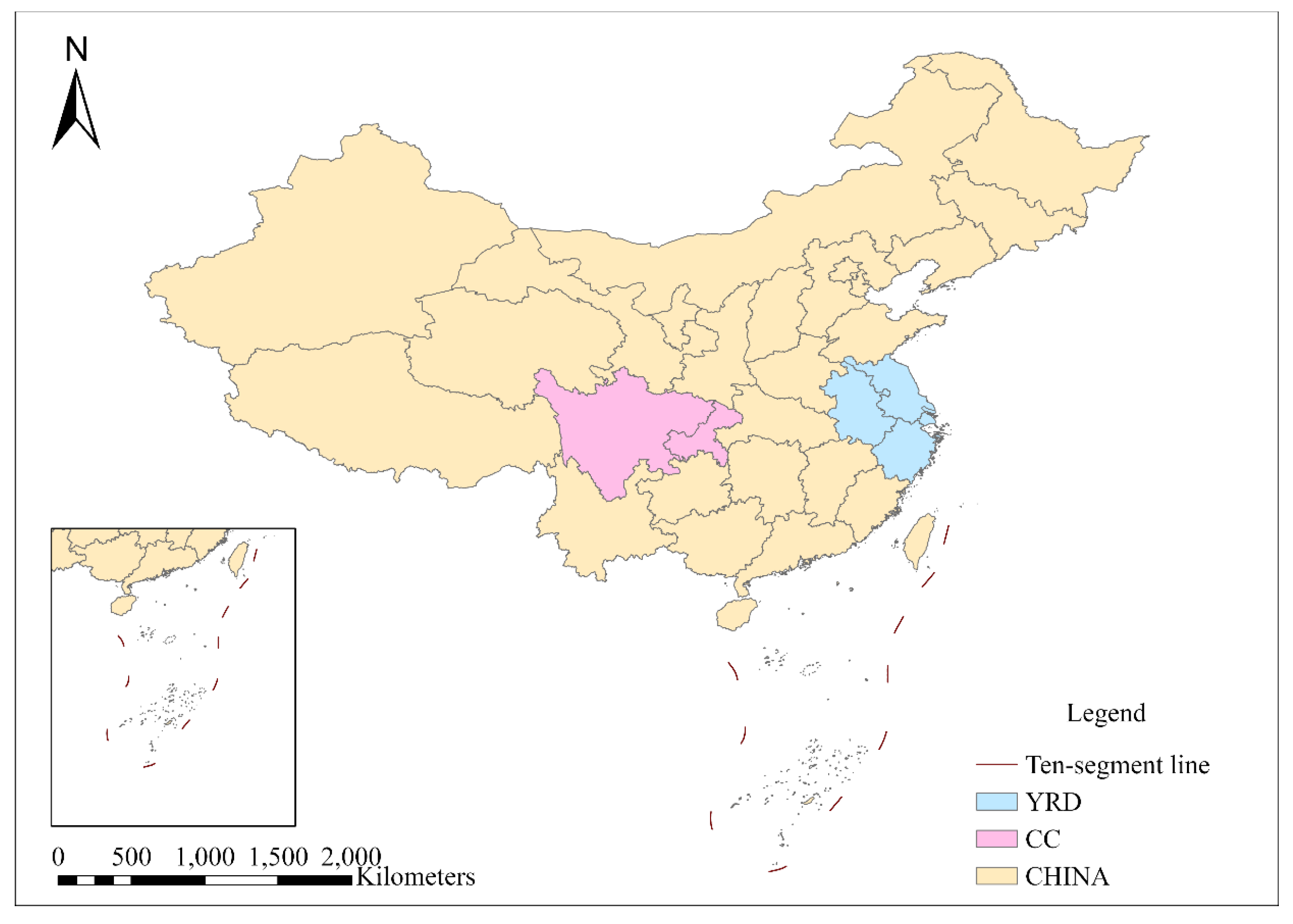
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Study Data
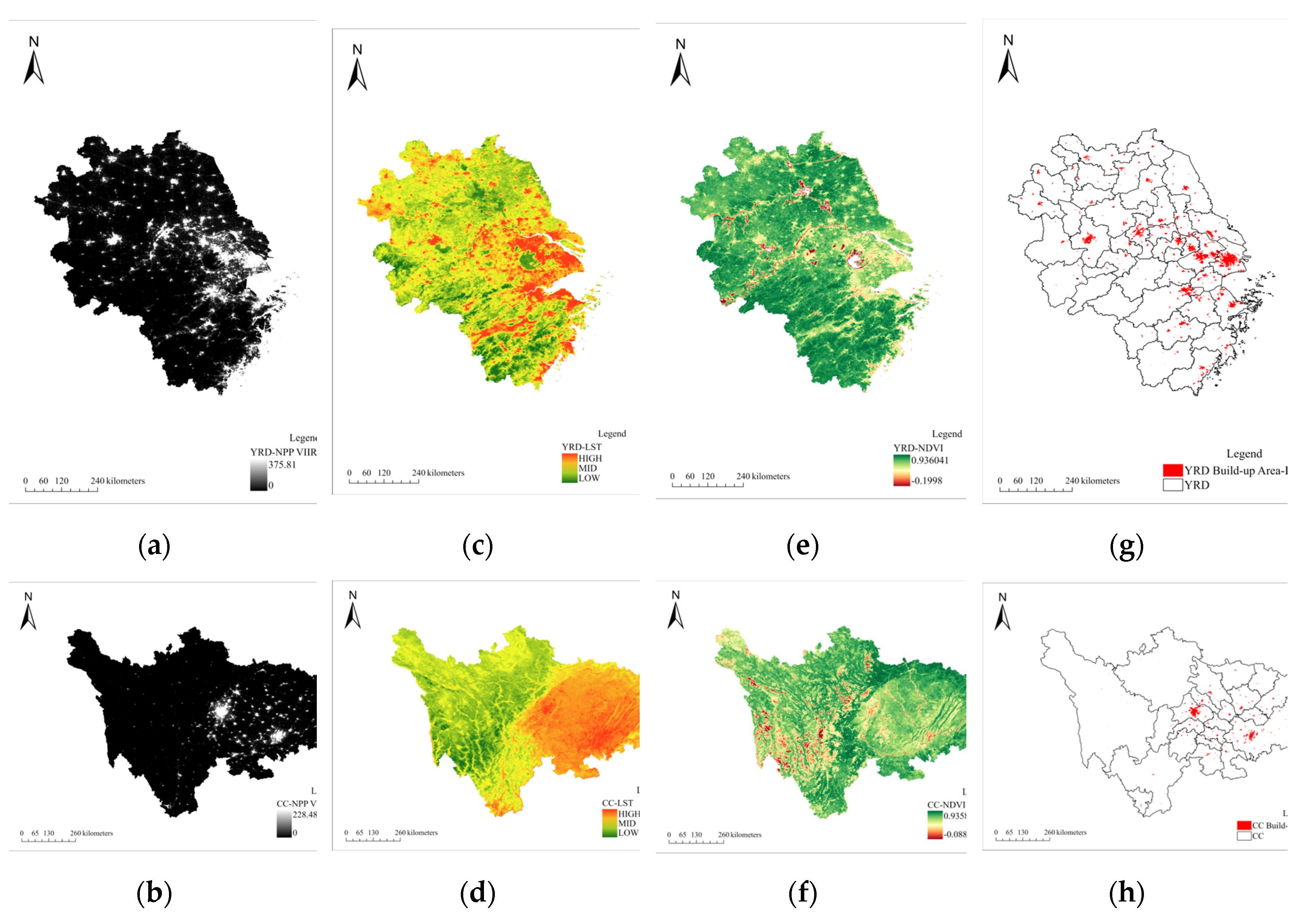
2.2.1. Land Use Data
2.2.2. Nighttime Light Data
2.2.3. LST and NDVI Data
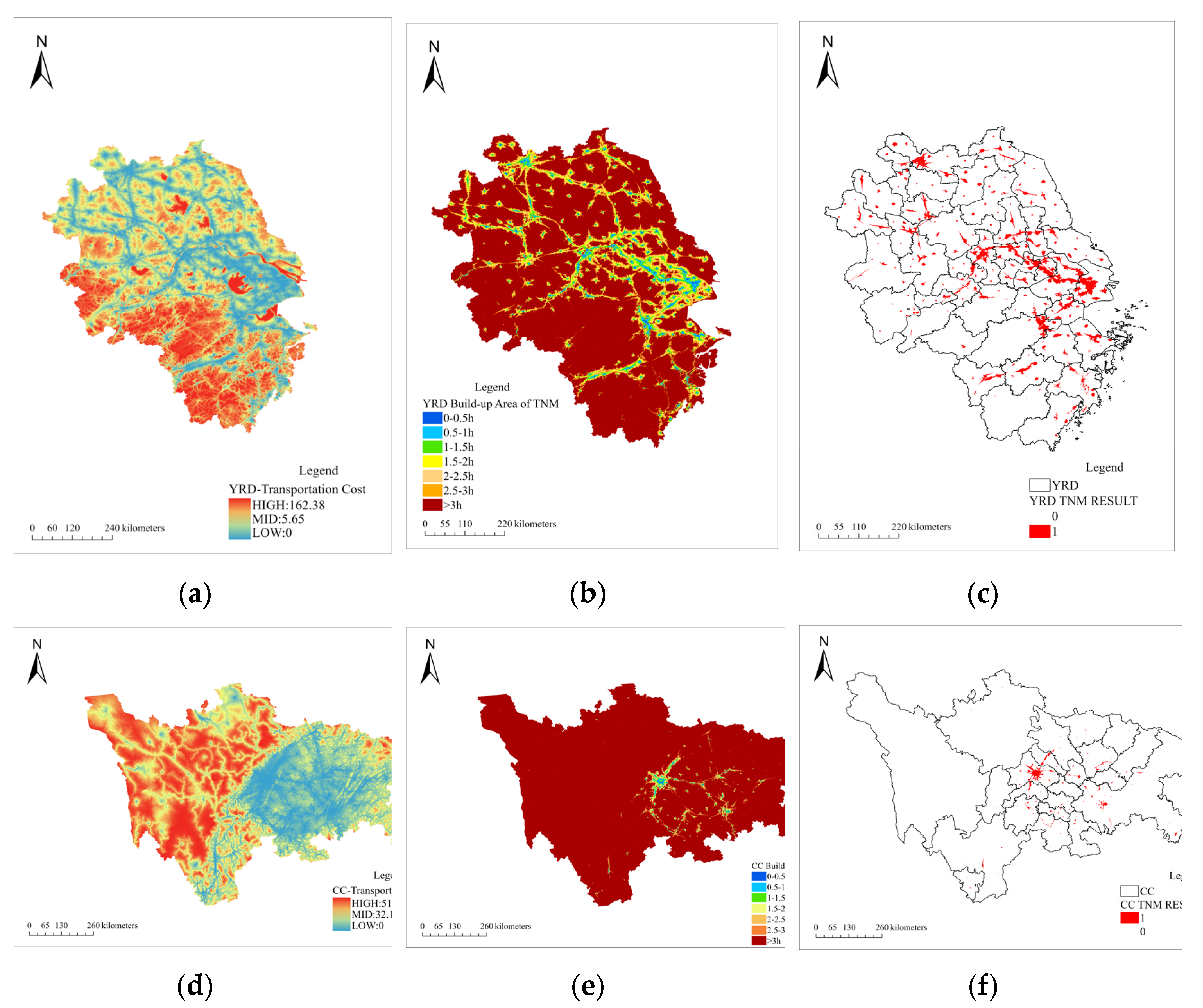
2.2.4. Road Network and POI Data
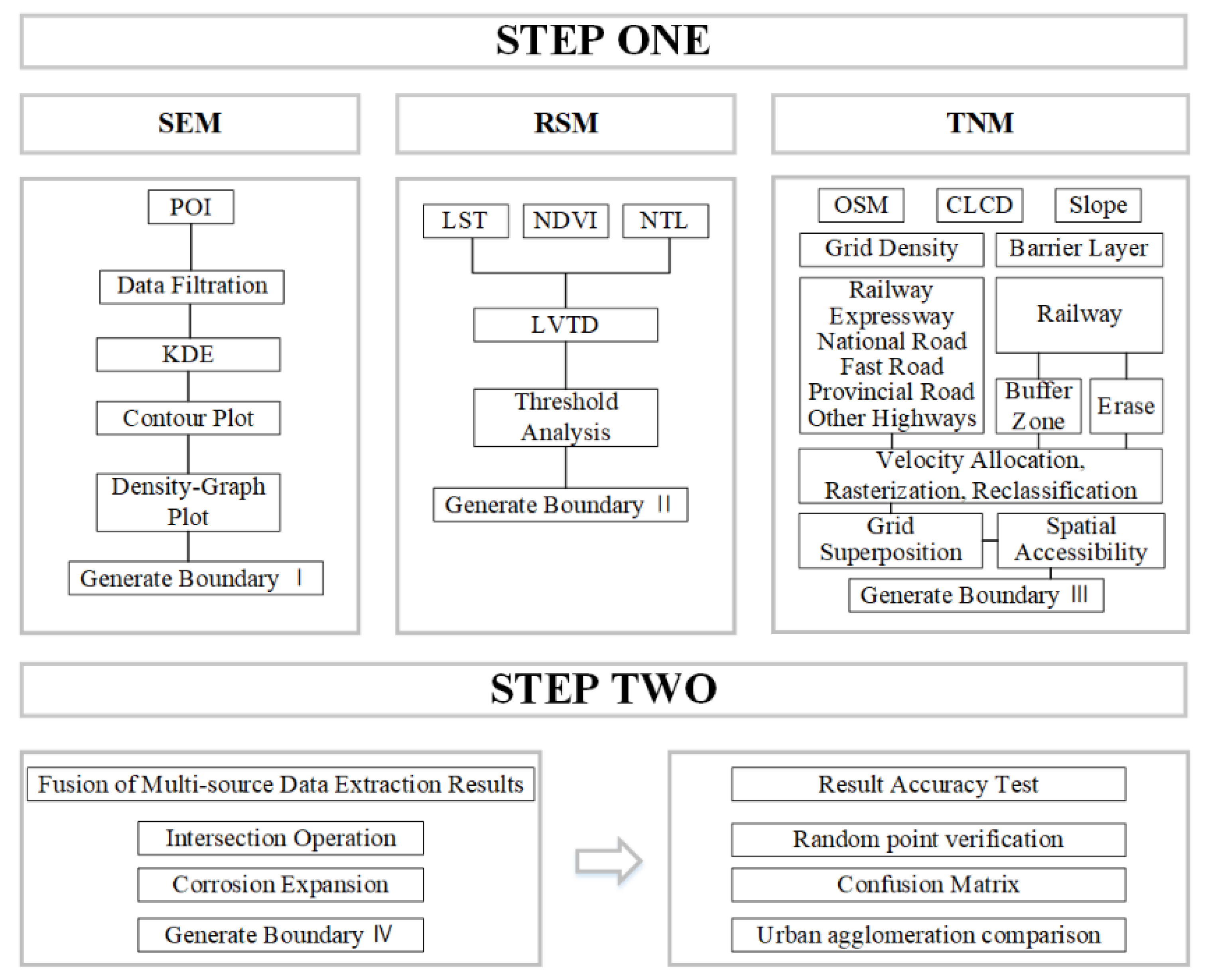
2.3. Method
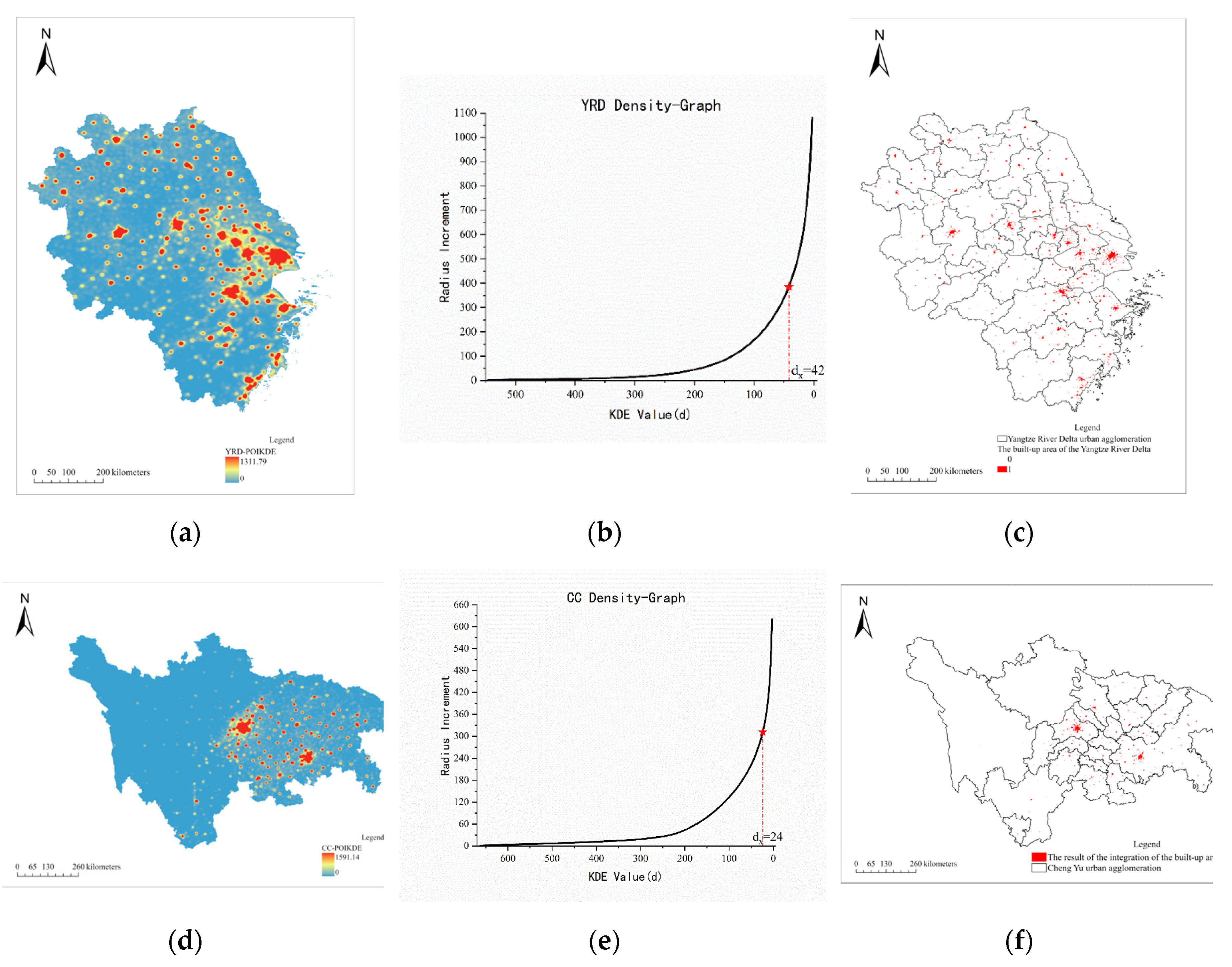
2.3.1. Recognition Method based on POI (POIM)
2.3.2. Recognition Method Based on Remote Sensing Data (RSM)
2.3.3. Recognition Method Based on Traffic Road (TRM)
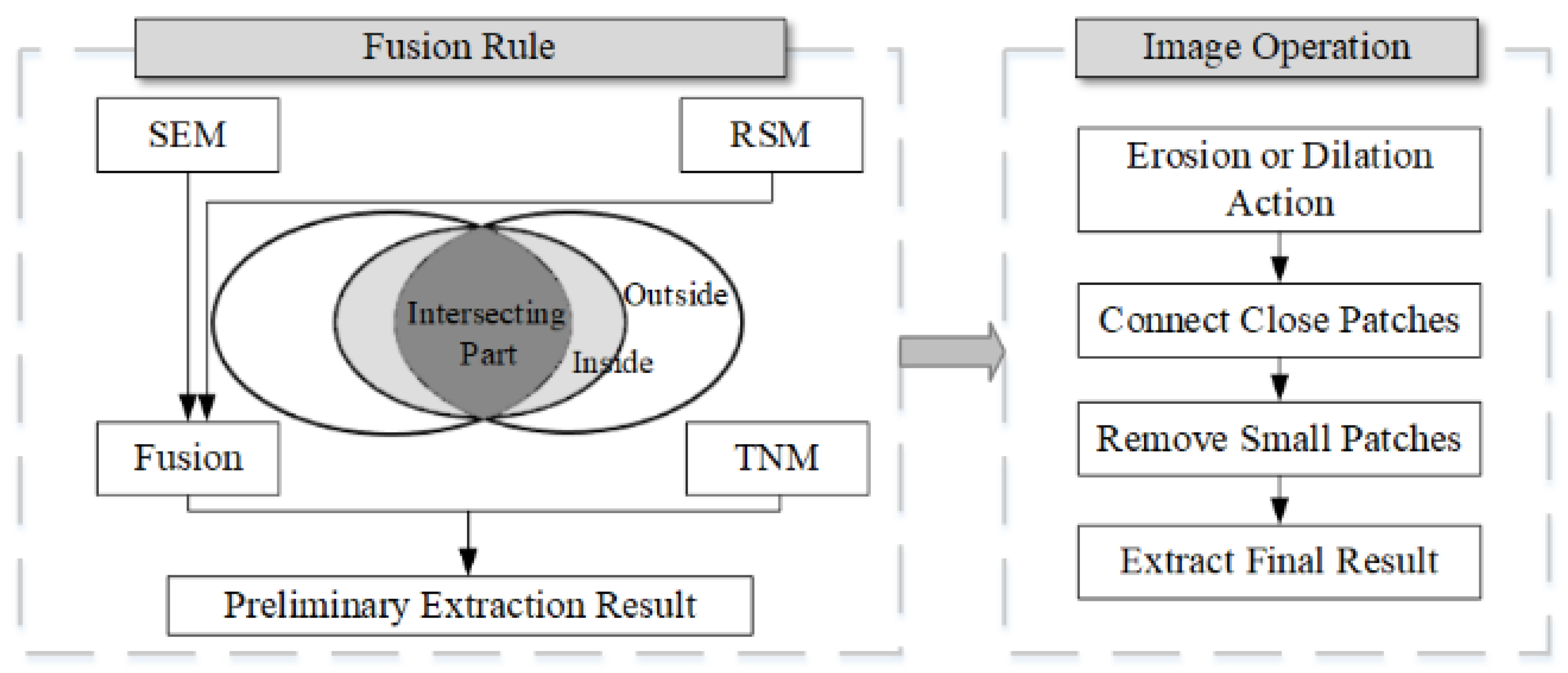
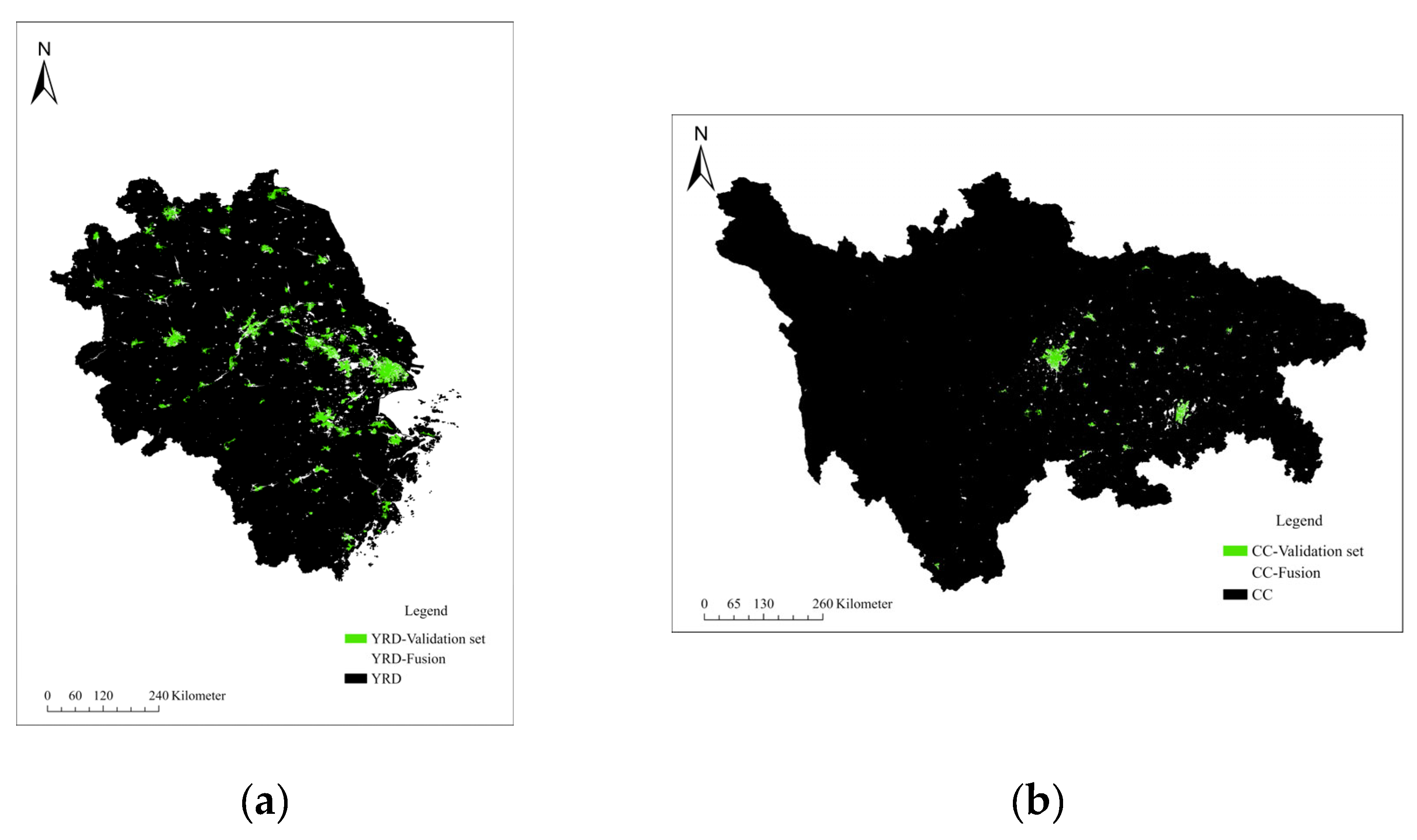
2.3.4. Fusion Method of Multi-Source Data Extraction Results
2.3.5. Accuracy Test Method
3. Results
3.1. Identification Result
3.2. Fusion Result
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2. Limits and Prospects
5. Conclusions
References
- Tan Minghong, Lu Changhe. Distribution of China City Size Expressed by Urban Built-up Area[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2003, 58(2): 285-293.
- Fang Chuanglin. Progress and the future direction of research into urban agglomeration in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2014, 69(8): 1130-1144.
- Tan Minghong, Li Xiubin, Lu Changhe. Analysis of the driving force of urban land expansion in China [J]. Economic geography,2003(05):635-639.
- Mei Zhuo. Research on the delineation method of built-up area under territorial spatial planning [C]. Urban Planning Society of China. People’s City, Planning Empowerment—Proceedings of China Urban Planning Annual Conference 2022,2023:8.
- Shi Kaifang, Huang Chang, Yu Bailang, Yin Bing, Huang Yixiu, Wu Jianping. Evaluation of NPP-VIIRS Night-Time Light Composite Data for Extracting Built-up Urban Areas[J]. Remote Sensing, 2014,5(4),358–66.
- Hu Ting, Huang Xin, Li Dongrui, Jin Shuanggen, Yan Qingyun. Comprehensive evaluation of the urban built-up areas mapping ability from Luojia 1-01 nighttime light imagery over China[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2023, 52(3): 432-442.
- Ascher, C.S.; Geddes, P.; The Outlook Tower Association, E. Cities in Evolution[J]. Land Economics,1951,27(1),83-84.
- Phillip O’Neill. Global city-regions: trends, theory, policy[J]. Area, 2003, 35, 326–327.
- Yu Qianyu, Li Meng, Li Qiao, Wang Yanan, Chen Wei, Economic agglomeration and emissions reduction: Does high agglomeration in China’s urban clusters lead to higher carbon intensity? , Urban Climate, 2022, 43, 101174. [CrossRef]
- Denis, Paul-Yves Hall, Peter, The World Cities. London, Weidenfeld and Nicolson, Third Edition, 276 p. Cahiers de géographie du Québec 1985,29(78): 441–442.
- Ning Yue-Min. Definition of Chinese Metropolitan Areas and Large Urban Agglomerations: Role of Large Urban Agglomerations in Regional Development[J]. SCIENTIA GEOGRAPHICA SINICA,2011,31(3): 257-263.
- Xu Zening, Gao Xiaolu. A novel method for identifying the boundary of urban built-up areas with POI data[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2016,71(6): 928-939.
- Bode, E. Delineating metropolitan areas using land prices[J]. Reg.Sci, 2010, 48, 131–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang Chuanglin. The Basic Law of the Formation and Expansion in Urban Agglomerations[J]. Geographical Sciences, 2019, 29, 1699–1712.
- Li Kaike and Niu Xinyi. Delineation of the Shanghai Megacity Region of China from a Commuting Perspective: Study Based on Cell Phone Network Data in the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Urban Plan.Dev. 2021, 147, 04021022.
- Bosker, M.; Park, J.; Roberts, M. Definition matters. Metropolitan areas and agglomeration economies in a large-developing country[J]. Urban Econ. 2021, 125, 103275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen Feng, Cao Yang, Qin Xiao and Wang Bo. Delineation of an urban agglomeration boundary based on Sina Weibo microblog ‘check-in’ data: A case study of the Yangtze River Delta[J]. Cities. 2017, 60, 180–191.
- Chen Jin, Zhuo Li, Shi Peijun, et al. The Study on Urbanization Process in China Based on DMSP/OLS Data: Development of a Light Index for Urbanization Level Estimation[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2003,(3):168-175.
- Mu Fengyun, Zhang Zengxiang, Chi Yaobin, et al. Dynamic Monitoring of Built-up Area in Beijing during 1973—2005 Based on Multi-original Remote Sensed Images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2007,(2):257-268.
- Hu Shougeng, Tong Luyi, Amy E. Frazier, Liu Yansui. Urban boundary extraction and sprawl analysis using Landsat images: A case study in Wuhan, China[J]. Habitat International, 2015, 47, 183–195.
- Luqman, M. , Rayner, P. J., & Gurney, K. R. Combining Measurements of Built-up Area, Nighttime Light, and Travel Time Distance for Detecting Changes in Urban Boundaries: Introducing the BUNTUS Algorithm[J]. Remote Sensing,2019,11(24),2969.
- Zhao Weifeng, Li Qingquan, Li Bijun. Extracting hierarchical landmarks from urban POI data[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2011,15(5):973-988.
- Li Fei, Yan Qingwu, Zou Yajing, Liu Baoli. Extraction Accuracy of Urban Built-up Area Based on Nighttime Light Data and POI: A Case Study of Luojia 1-01 and NPP/VIIRS Nighttime Light Images[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(6): 825-835.
- Meng Yingying, Zhou Size, Nie Yan, Zeng Huaiwen, Yu Jing. Spatial Delimitation of the Urban-Rural Fringe Based on POI and Nighttime Light Data: A Case Study of Wuhan City[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University.
- Lou Ge, Chen Qiuxiao, He Kang, Zhou Yue and Shi Zhou. Using Nighttime Light Data and POI Big Data to Detect the Urban Centers of Hangzhou[J]. Remote Sensing. 2019, 11, 1821.
- Liu Xinzhi, Zhang Pengfei, Shi Xiaoyu. Industrial Agglomeration, Technological Innovation and High-quality Economic Development: Empirical Research based on China’s Five Major Urban Agglomerations. Reform,2022, (04):68-87.
- Fang Chuanglin, Zhou Chenghu, Wang Zhenbo. Sustainable development strategy and priorities of spatially differentiated development of urban agglomerations along the Yangtze River Economic Belt[J]. PROGRESS IN GEOGRAPHY, 2015, 34(11): 1398-1408.
- Song Jitao, Fang Chuanglin, Song Dunjiang. Spatial Structure Stability of Urban Agglomerations in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2006, 61(12): 1311-1325.
- Yao Zuolin, Tu Jianjun, Niu Huimin, Ha Lin, Li Jianbo. The Research on Urban Agglomeration Spatial Structure of Cheng-Yu Economic Zone. Economic Geography, 2017,37(01):82-89.
- Song Yanhua, Jiao Limin, Liu Jiafeng, Xu Gang. Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Degree of Urban Expansion: Taking Wuhan City as an Example[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(3): 417-426.
- Ministry of Construction of the People ’s Republic of China. Standard for basic terms of urban planning(GB/T 50280-98). Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 1998.
- Zhang Yang, Zheng Fengjiao, Liu Yanfang, Liu Ying, Hu Huiping, Xu Pengfei. Extracting Urban Built-up Area Based on Impervious Surface Area and POI Data[J]. SCIENTIA GEOGRAPHICA SINICA,2022,42(3): 506-514.
- Tan Yihua, Xiong Shengzhou, Li Yansheng. Automatic extraction of built-up areas from panchromatic and multispectral remote sensing images using double stream deep convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2018, 11(11): 3988-4004.
- Zhao Pengxiang, Jia Tao, Qin Kun, Shan Jie, Jiao Chenjing. Statistical Analysis on the Evolution of OpenStreetMap Road Networks in Beijing [J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 420: 59-72.
- Hong Jiangtao, Li Xiaoshun, Wei Xuchen, Jiang Dongmei, Song Shuyan. Spatial and Temporal Pattern of Urban Built-up Areas in the Yangtze River Economic Belt Based on Data Fusion[J]. RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT IN THE YANGTZE BASIN, 2021, 30(10): 2325-2335.
- Zhou Yi, Xie Baopeng, Zhao Hongyan, Chen Ying,, Pei Tingting, Liu Shiqi. Study on Spatial-temporal Pattern and Dynamic Evolution of City Scale at County Level in China Based on Night-time Light Data[J]. RESOURCES AND ENVIRONMENT IN THE YANGTZE BASIN, 2019, 28(02): 250-260.
- Wang Gaoyuan, Wang Yixuan, Li Yangli, and Chen Tian. Identification of Urban Clusters Based on Multisource Data—An Example of Three Major Urban Agglomerations in China. Land 2023, 12, 1058.
- He, Xiong, Cao Yongwang, and Zhou Chunshan. Evaluation of Polycentric Spatial Structure in the Urban Agglomeration of the Pearl River Delta (PRD) Based on Multi-Source Big Data Fusion. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3639.
| Road network type | Speed (km/h) | Speed cost (min) | Barrier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Railway | 300 | 0.2 | Station |
| Highroad | 120 | 0.5 | / |
| National road, Express road | 80 | 0.75 | |
| Provincial road | 60 | 1 | |
| Township road, County road | 40 | 1.5 | |
| Other roads | 30 | 2 |
| TYPE | POIM | RSM | TRM | Fusion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 2784 | 92.80% | 2776 | 92.53% | 2767 | 92.23% | 2776 | 92.53% |
| TP | 118 | 3.93% | 166 | 5.53% | 84 | 2.80% | 175 | 5.83% |
| FN | 94 | 3.13% | 46 | 1.53% | 128 | 4.27% | 37 | 1.23% |
| FP | 4 | 0.13% | 12 | 0.40% | 21 | 0.70% | 12 | 0.40% |
| TN | 6956 | 69.56% | 6935 | 69.35% | 6935 | 69.35% | 6932 | 69.32% |
| TP | 1625 | 16.25% | 2358 | 23.58% | 1263 | 12.63% | 2470 | 24.70% |
| FN | 1405 | 14.05% | 672 | 6.72% | 1767 | 17.67% | 560 | 5.60% |
| FP | 14 | 0.14% | 35 | 0.35% | 35 | 0.35% | 38 | 0.38% |
| TYPE | POIM | RSM | TRM | Fusion | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 2565 | 85.50% | 2549 | 84.97% | 2483 | 82.77% | 2504 | 83.47% |
| TP | 175 | 5.83% | 237 | 7.90% | 184 | 6.13% | 273 | 9.10% |
| FN | 13 | 0.43% | 29 | 0.97% | 95 | 3.17% | 74 | 2.47% |
| FP | 247 | 8.23% | 185 | 6.17% | 238 | 7.93% | 149 | 4.97% |
| TN | 4787 | 47.87% | 4754 | 47.54% | 4746 | 47.46% | 4680 | 46.80% |
| TP | 2259 | 22.59% | 2906 | 29.06% | 1048 | 10.48% | 3363 | 33.63% |
| FN | 2920 | 29.20% | 2273 | 22.73% | 4131 | 41.31% | 1816 | 18.16% |
| FP | 34 | 0.34% | 67 | 0.67% | 75 | 0.75% | 141 | 1.41% |
| POIM | RSM | TRM | Fusion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | |
| OA | 96.7333% | 85.8100% | 98.0667% | 92.9300% | 95.0333% | 81.9800% | 98.3667% | 94.0200% |
| P | 96.7213% | 99.1458% | 93.2584% | 98.5374% | 80.0000% | 97.3035% | 93.5829% | 98.4848% |
| R | 55.6604% | 53.6304% | 78.3019% | 77.8218% | 39.6226% | 41.6832% | 82.5472% | 81.5182% |
| F1 | 0.7066 | 0.6961 | 0.8513 | 0.8696 | 0.5300 | 0.5836 | 0.8772 | 0.8920 |
| KAPPA | 0.6906 | 0.6140 | 0.8410 | 0.8220 | 0.5069 | 0.4912 | 0.8685 | 0.8512 |
| POIM | RSM | TRM | Fusion | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | 3000 | 10000 | |
| OA | 91.3333% | 70.4600% | 92.8667% | 76.6000% | 88.9000% | 57.9400% | 92.5667% | 80.4300% |
| P | 41.4692% | 98.5172% | 56.1611% | 97.7464% | 43.6019% | 93.3215% | 64.6919% | 95.9760% |
| R | 93.0851% | 43.6185% | 89.0977% | 56.1112% | 65.9498% | 20.2356% | 78.6744% | 64.9353% |
| F1 | 0.5738 | 0.6047 | 0.6890 | 0.7130 | 0.5250 | 0.3326 | 0.7100 | 0.7746 |
| KAPPA | 0.5333 | 0.4204 | 0.6510 | 0.5387 | 0.4651 | 0.1815 | 0.6678 | 0.6127 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





