Submitted:
17 June 2024
Posted:
18 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract

Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
2.2. ddPCR Method Validation
2.2.1. Primers and Probes Design
2.2.2. Digital Droplet PCR Validation
2.2.3. Data Analysis
2.3. Genomic DNA Reference Material Production
2.3.1. Culture and DNA Extraction
2.3.2. Material Preparation
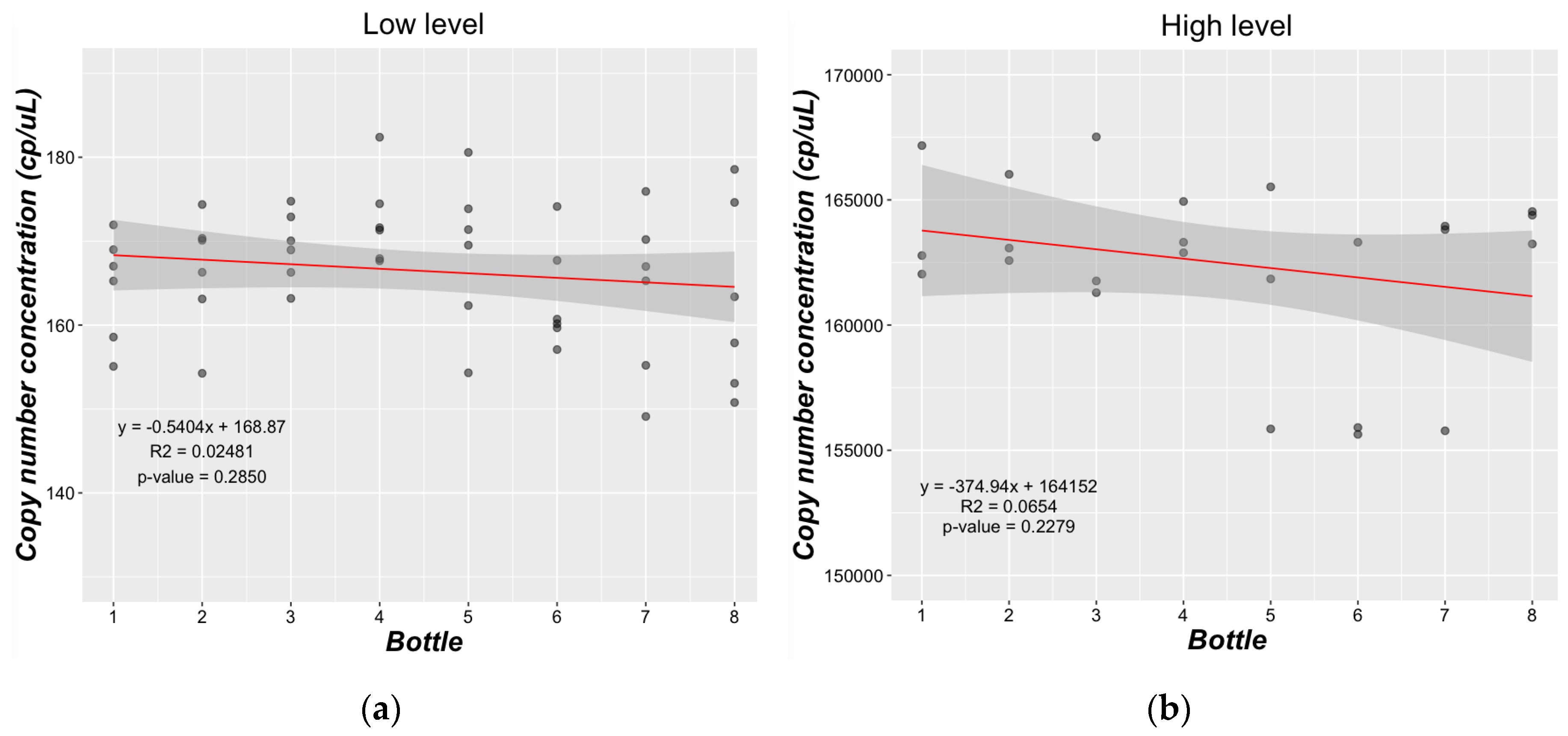
2.3.3. Homogeneity Study
2.3.4. Stability Study
2.3.5. Material Characterization and Value Assignment
3. Results
3.1. ddPCR Method Validation
3.1.1. Selectivity
| Group | Species | Reference | uidA | lacY | eaeA | rfbE | Stx1 | Stx2 | Z3276 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram (+) | Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC® 6538 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Staphylococcus aureus | ATCC® 25923 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Bacillus cereus | ATCC® 10876 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Enterococcus faecalis | ATCC® 14506 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Gram (-) | Proteus mirabilis | ATCC® 12453 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | ATCC® 17802 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Enterobacter aerogenes | ATCC® 13048 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Proteus vulgaris | ATCC® 33420 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Yersinia enterocolitica | ATCC® 23715 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Shigella | Shigella boydii | ATCC® 9207 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Shigella sonnei | ATCC® 9290 | + | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Escherichia coli | Escherichia coli | ATCC® 25922 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - |
| Escherichia coli | Donated1 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Escherichia coli | NCTC 10538 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Escherichia coli | ATCC® 8739 | + | + | - | - | - | - | - | |
| STEC* | Escherichia coli O104:H4 | ATCC® BAA-2326™ | + | + | - | - | - | + | - |
| Escherichia coli O145:NM | CDC 99-3311 | + | + | + | - | + | + | - | |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 | ATCC® 700728™ | + | + | + | + | - | - | + | |
| Escherichia coli O157:H7 | ATCC® 35150™ | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | |
| Salmonella | Salmonella Thyphimurium | Donated2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Salmonella Thyphi | Donated2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Salmonella enteritidis | Donated2 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
3.1.2. Working Interval
3.1.3. Precision
3.1.4. LOQ and LOD
3.1.5. Method Uncertainty
3.2. Preparation and Quality Control of E. coli DNA Reference
3.2.1. Culture and DNA Extraction
3.2.2. Homogeneity Study
3.2.3. Stability Study
3.3. Material Characterization and Value Assignment
4. Discussion
4.1. Method Validation
4.2. Reference Material Production
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S. Bouzari, A. Jafari, and M. M. Aslani, “Escherichia coli: A brief review of diarrheagenic pathotypes and their role in diarrheal diseases in Iran,” Iran. J. Microbiol., vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 102–117, 2012.
- J. S. Kim, M. S. Lee, and J. H. Kim, “Recent Updates on Outbreaks of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli and Its Potential Reservoirs,” Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol., vol. 10, no. June, pp. 1–10, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Rani, V. B. Ravindran, A. Surapaneni, N. Mantri, and A. S. Ball, “Review: Trends in point-of-care diagnosis for Escherichia coli O157:H7 in food and water,” Int. J. Food Microbiol., vol. 349, no. May, p. 109233, 2021. [CrossRef]
- K. D. A. Pangajam, K. Theyagarajan, “Highly sensitive electrochemical detection of E. coli O157 H7 using conductive carbon dot/ZnO nanorod/PANI composite electrode,” Sens. anf bio-sensing Res., p. 118214, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. W.-F. Law, N.-S. Ab Mutalib, K.-G. Chan, and L.-H. Lee, “Rapid methods for the detection of foodborne bacterial pathogens: Principles, applications, advantages and limitations.,” Front. Microbiol., vol. 5, no. January, p. 770, 2015. [CrossRef]
- I. O. for S. ISO, “ISO/TS 13136:2012 - Microbiology of food and animal feed -- Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based method for the detection of food-borne pathogens -- Horizontal method for the detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and the determination of O157, O111, O26, O103 and O145 serogroups,” 2012. https://www.iso.org/standard/53328.html (accessed Mar. 21, 2019).
- E. M. Nielsen and M. T. Andersen, “Detection and Characterization of Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli by Automated 5 ′ Nuclease PCR Assay Detection and Characterization of Verocytotoxin-Producing Escherichia coli by Automated 5Ј Nuclease PCR Assay,” J. Clin. Microbiol., vol. 41, no. 7, pp. 2884–2893, 2003. [CrossRef]
- E. T. Gensberg, M. Polt, M. Konrad-k, P. Kinner, A. Sessitsch, and T. Kostic, “Evaluation of quantitative PCR combined with PMA treatment for molecular assessment of microbial water quality,” Water Res., vol. 67, no. 0, pp. 367–376, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Das Mitrai et al., “Duplex PCR for specific detection of Escherichia coli and its differentiation from other Enterobacteriaceae,” Indian J. Anim. Sci., vol. 85, no. 8, pp. 16–19, 2015.
- K. Horakova, H. Mlejnkova, and P. Mlejnek, “Specific detection of Escherichia coli isolated from water samples using polymerase chain reaction targeting four genes: Cytochrome bd complex, lactose permease, ??-d-glucuronidase, and ??-d-galactosidase,” J. Appl. Microbiol., vol. 105, no. 4, pp. 970–976, 2008. [CrossRef]
- W. Liang et al., “Quantification of plasmid DNA reference materials for Shiga toxin - producing Escherichia coli based on UV , HR - ICP - MS and digital PCR,” pp. 1–10, 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Trapmann, P. Catalani, J. Hoorfar, J. Prokisch, P. Van Iwaarden, and H. Schimmel, “Development of a novel approach for the production of dried genomic DNA for use as standards for qualitative PCR testing of food-borne pathogens,” Accredit. Qual. Assur., vol. 9, no. 11–12, pp. 695–699, 2004. [CrossRef]
- L. Wang et al., “Development of a Reference Standard of Escherichia coli DNA for Residual DNA Determination in China,” vol. 8, no. 9, pp. 1–6, 2013. [CrossRef]
- H. J. He, J. L. Almeida, S. P. Lund, C. R. Steffen, S. Choquette, and K. D. Cole, “Development of NIST standard reference material 2373: Genomic DNA standards for HER2 measurements,” Biomol. Detect. Quantif., vol. 8, pp. 1–8, 2016. [CrossRef]
- I. Gutiérrez-Aguirre, N. Rački, T. Dreo, and M. Ravnikar, “Droplet digital PCR for absolute quantification of pathogens,” in Methods in Molecular Biology, Plant Path., vol. 1302, Humana Press, New York, NY, 2015, pp. 331–347. [CrossRef]
- S. Bhat and K. R. Emslie, “Digital polymerase chain reaction for characterization of DNA reference materials,” Biomol. Detect. Quantif., pp. 3–5, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. H. Cleveland, H. J. He, M. Milavec, Y. K. Bae, P. M. Vallone, and J. F. Huggett, “Digital PCR for the characterization of reference materials,” Mol. Aspects Med., vol. 96, no. January, p. 101256, 2024. [CrossRef]
- L. Deprez et al., “Validation of a digital PCR method for quantification of DNA copy number concentrations by using a certified reference material,” Biomol. Detect. Quantif., vol. 9, pp. 29–39, 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. Van Iwaarden et al., Certification of a Reference Material of Purified Genomic DNA from Escherichia Coli O157 Certified Reference Material IRMM-449, vol. 157, no. Edl 933.
- “SnapGene | Software for everyday molecular biology.” http://www.snapgene.com/ (accessed Mar. 28, 2018).
- R. Owczarzy et al., “IDT SciTools: A suite for analysis and design of nucleic acid oligomers,” Nucleic Acids Res., vol. 36, no. Web Server issue, pp. 163–169, 2008. [CrossRef]
- T. Madden, “The BLAST sequence analysis tool,” in NCBI Handbook, 2nd editio., National Center forBbiotechnology Information (US), Ed. Bethesda, 2013, pp. 1–17. [Online]. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK153387/.
- D. Morisset, S. Dejan, M. Milavec, K. Gruden, and J. Zel, “Quantitative Analysis of Food and Feed Samples with Droplet Digital PCR,” PLoS ONE, vol. 8, no. 5, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. L. R. Ellison, M. Rosslein, A. Williams, L. A. Konopelko, and A. V. Garmash, “EURACHEM/CITAC Guide: Quantifying Uncertainty in Analytical Measurement,” Journal of Analytical Chemistry, vol. 58, no. 2. European Federation of National Associations of Analytical Laboratories, p. 191, 2003. [CrossRef]
- B. Magnusson and U. Örnemark, “Eurachem Guide: The Fitness for Purpose of Analytical Methods – A Laboratory Guide to Method Validation and Related Topics,” Eurachem Guide. pp. 1–70, 2014. doi: 978-91-87461-59-0.
- C. V. Vallejo, C. P. Tere, M. N. Calderon, M. M. Arias, and J. E. Leguizamon, “Development of a genomic DNA reference material for Salmonella enteritidis detection using polymerase chain reaction,” Mol. Cell. Probes, vol. 55, no. December 2020, p. 101690, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Thermo Scientific, “T042-TECHNICAL BULLETIN NanoDrop Spectrophotometers.” Accessed: Oct. 24, 2019. [Online]. Available: www.nanodrop.com.
- D. Svec, A. Tichopad, V. Novosadova, M. W. Pfaffl, and M. Kubista, “How good is a PCR efficiency estimate: Recommendations for precise and robust qPCR efficiency assessments,” Biomol. Detect. Quantif., vol. 3, pp. 9–16, 2015. [CrossRef]
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO), “ISO/Guide 35:2017(en), Reference materials — Guidance for characterization and assessment of homogeneity and stability,” International Organisation for Standardisation, Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/#iso:std:iso:guide:35:ed-4:v1:en (accessed Jan. 14, 2020).
- International Organization for Standardization (ISO), “Evaluation of measurement data — Guide to the expression of uncertainty in measurement,” Int. Organ. Stand. Geneva ISBN, vol. 50, no. September, p. 134, 2008, [Online]. Available: http://www.bipm.org/en/publications/guides/gum.html.
- M. Lauwaars and E. Anklam, “Method validation and reference materials,” Accredit. Qual. Assur., vol. 9, no. 4–5, pp. 253–258, 2004. [CrossRef]
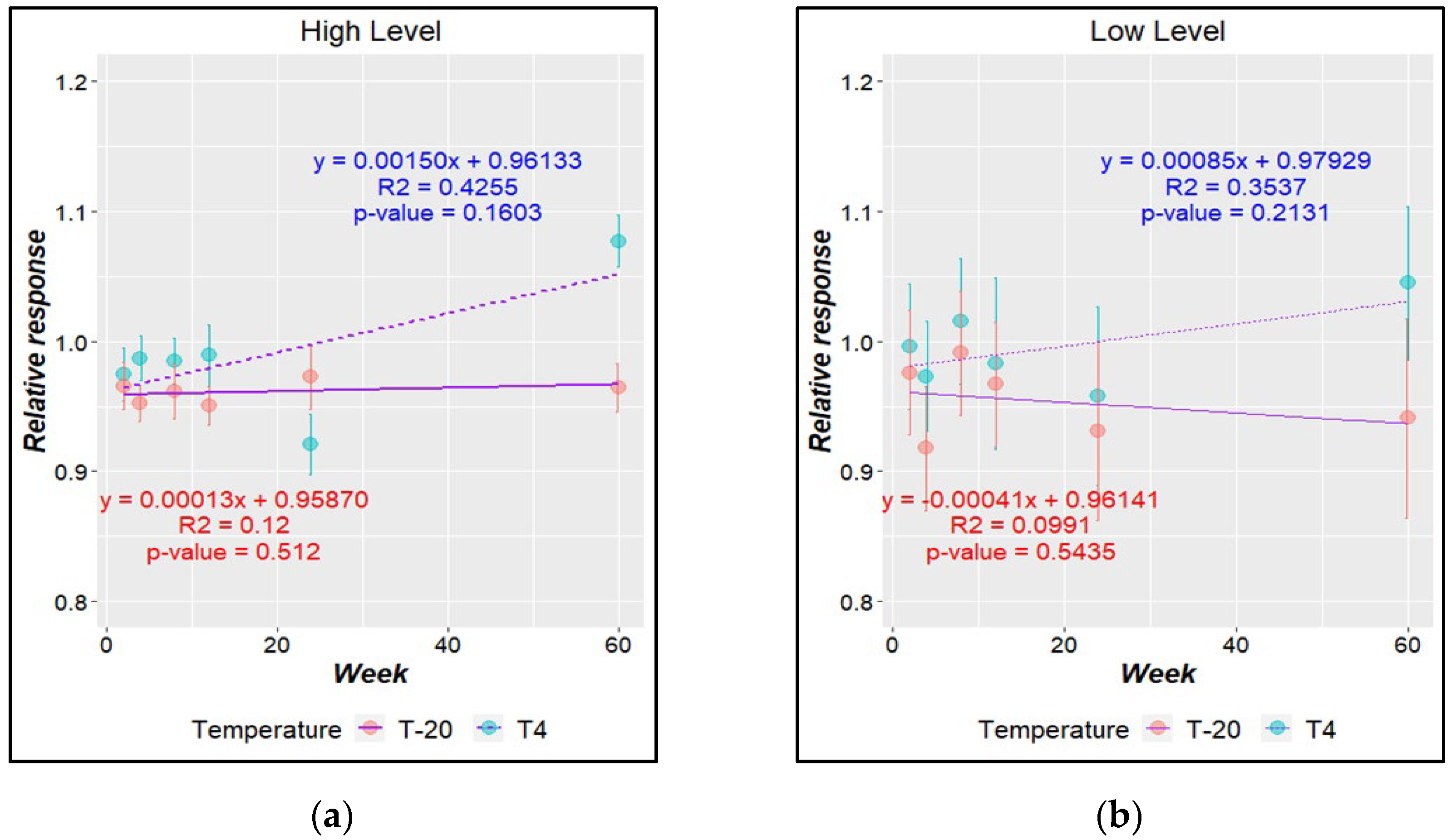
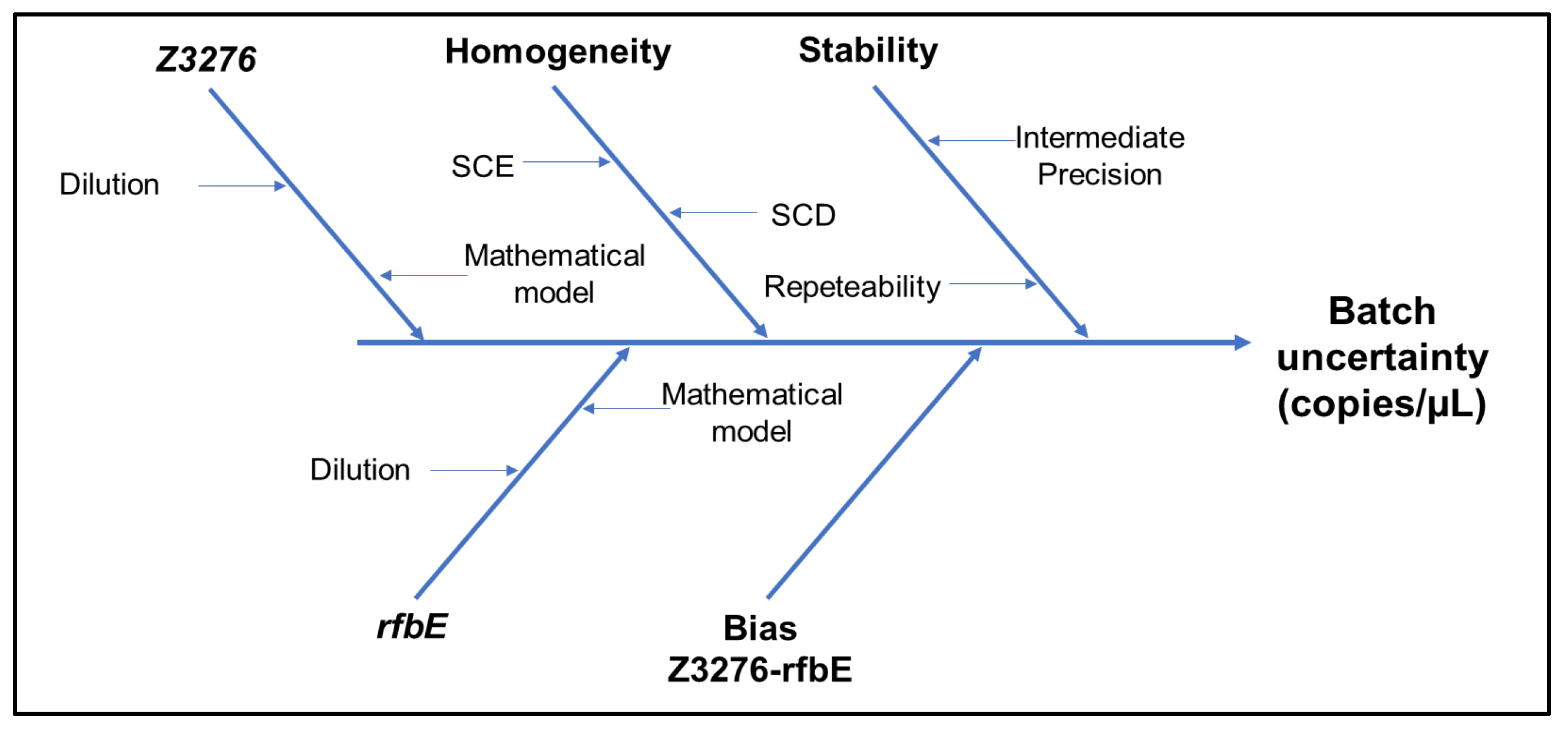
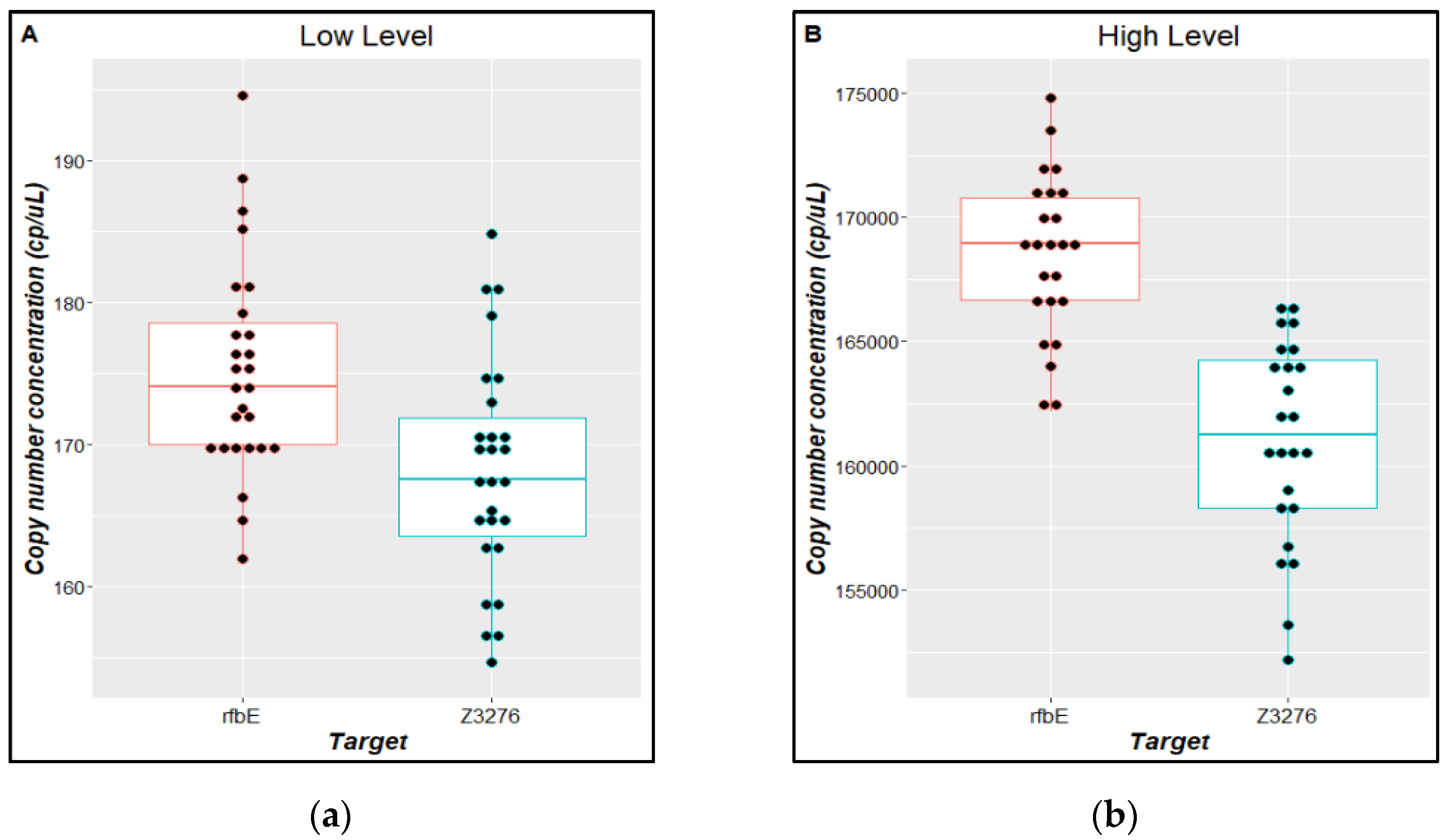
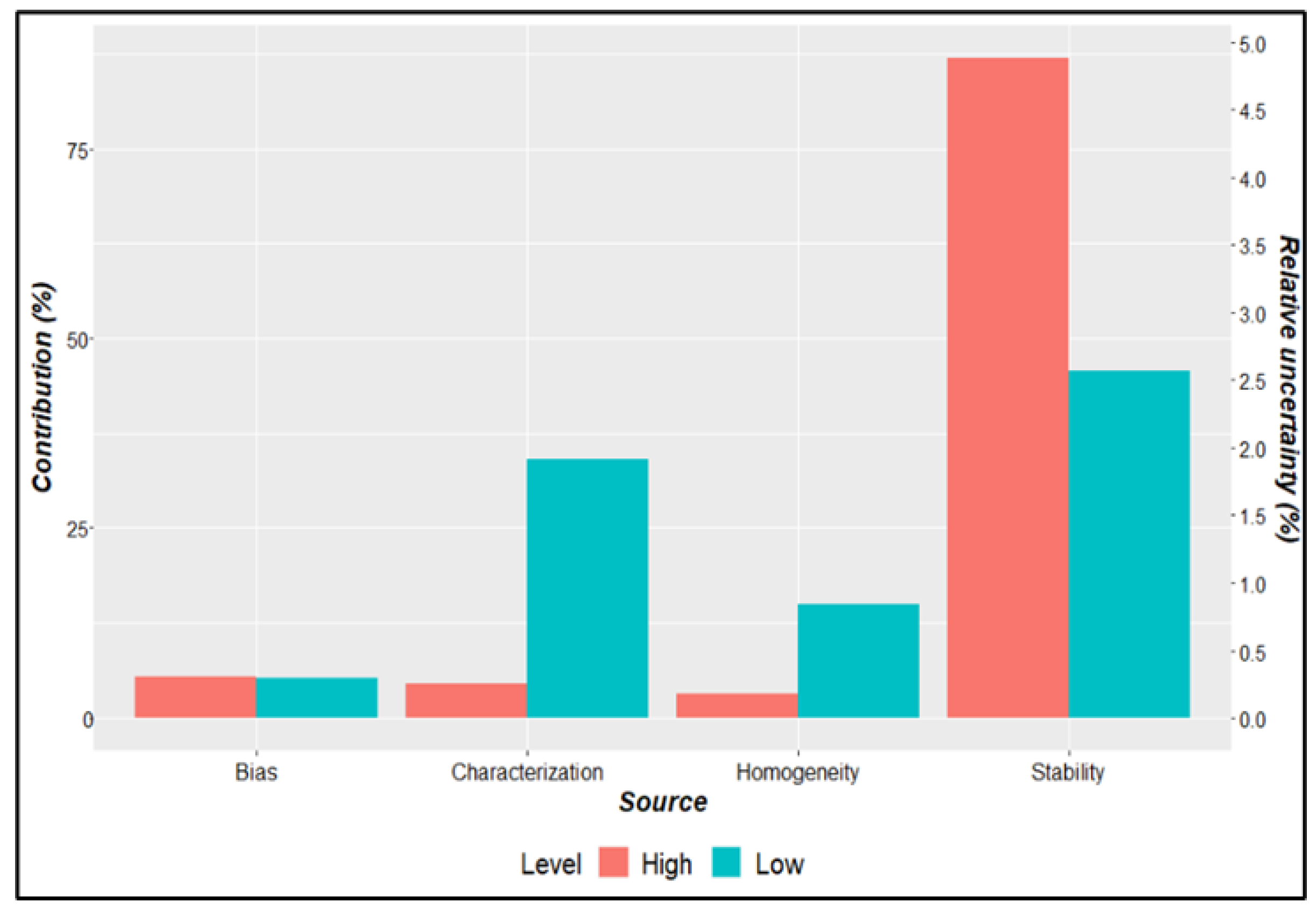
| Parameter | Description | Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Selectivity | Assessed by qPCR, amplifying each gene against a series of related and unrelated bacterial DNA samples. | Positive amplification in E. coli strains. Negative amplification in non-E. coli strains. |
| Working interval | Serial gravimetric dilutions of IRMM 449 over a 5-log DNA concentration range were measured in triplicate for each target gene. Regression analysis was performed to define the working interval. | Correlation coefficient >0.99, a slope significantly (p < 0.05) different from zero, an intercept significantly (p < 0.05) equal to zero, and a precision <25% as relative standard deviation (RSD) |
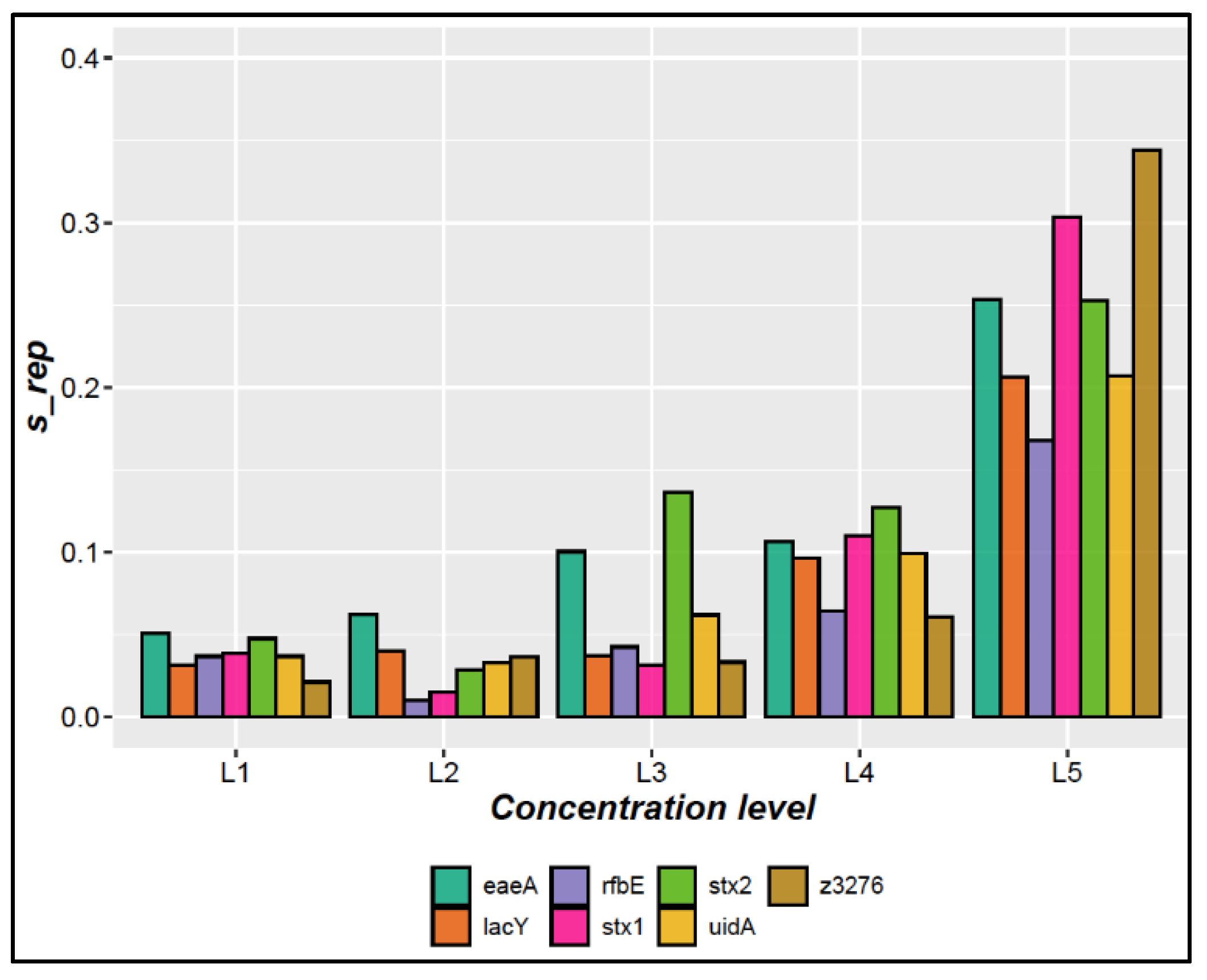
| Precision | Five concentration levels (L): L1 (7,920 copies/µL), L2 (718 copies/µL), L3 (66 copies/µL), L4 (6.6 copies/µL) and L5 (1.34 copies/µL) were measured in triplicate on three different days for each target gene. | A repeatability RSD <25% was used as acceptance criteria [23]. |
| Limit of quantification (LOQ) |
Defined as the lowest level of the working interval fulfilling linearity and precision criteria. | |
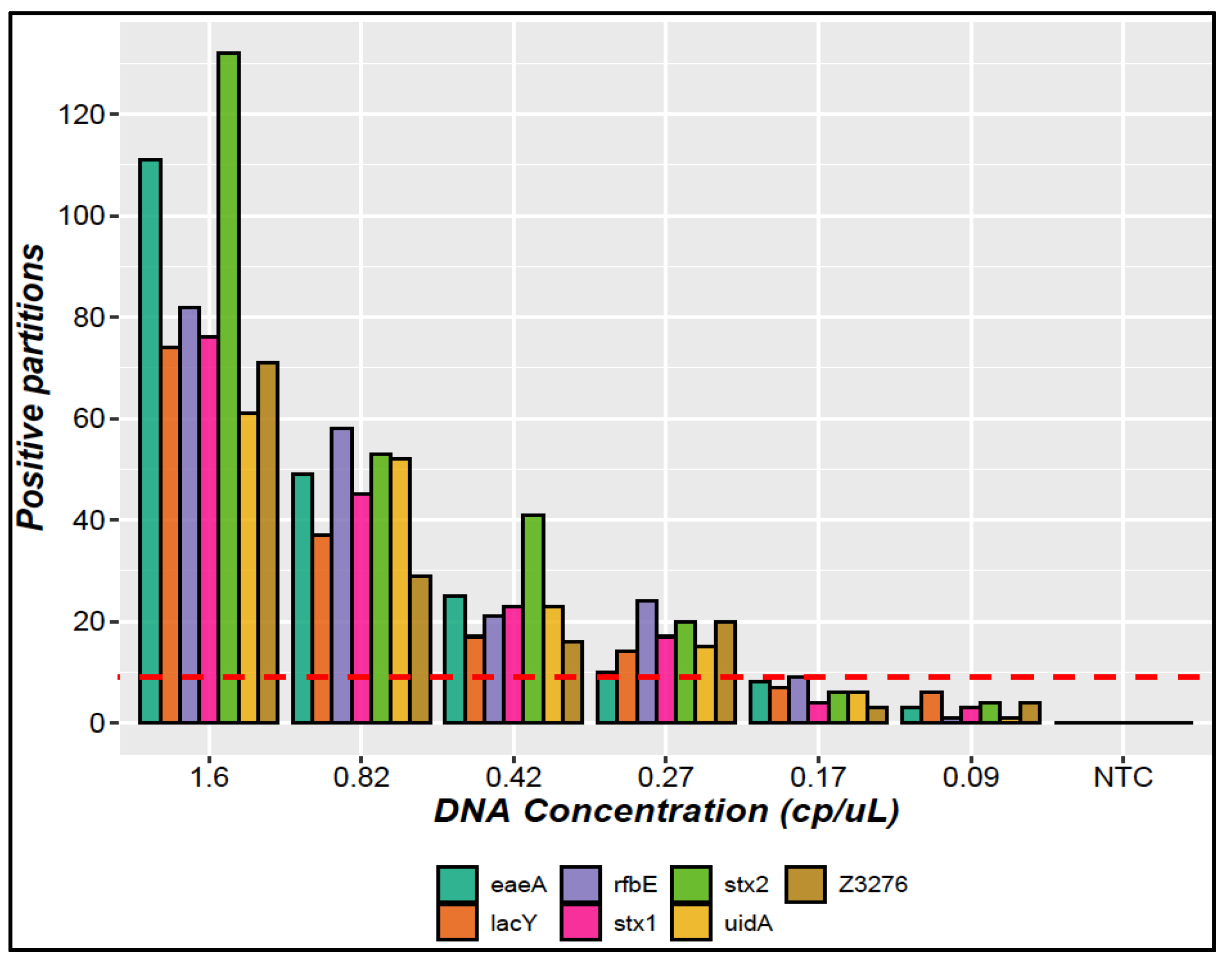
| Limit of detection (LOD) | Six concentration levels below the quantification limit were evaluated in triplicate. | The LOD was established as the lowest copy number concentration level (copies/μL) where three replicates amplify with at least nine positive partitions together [23]. |
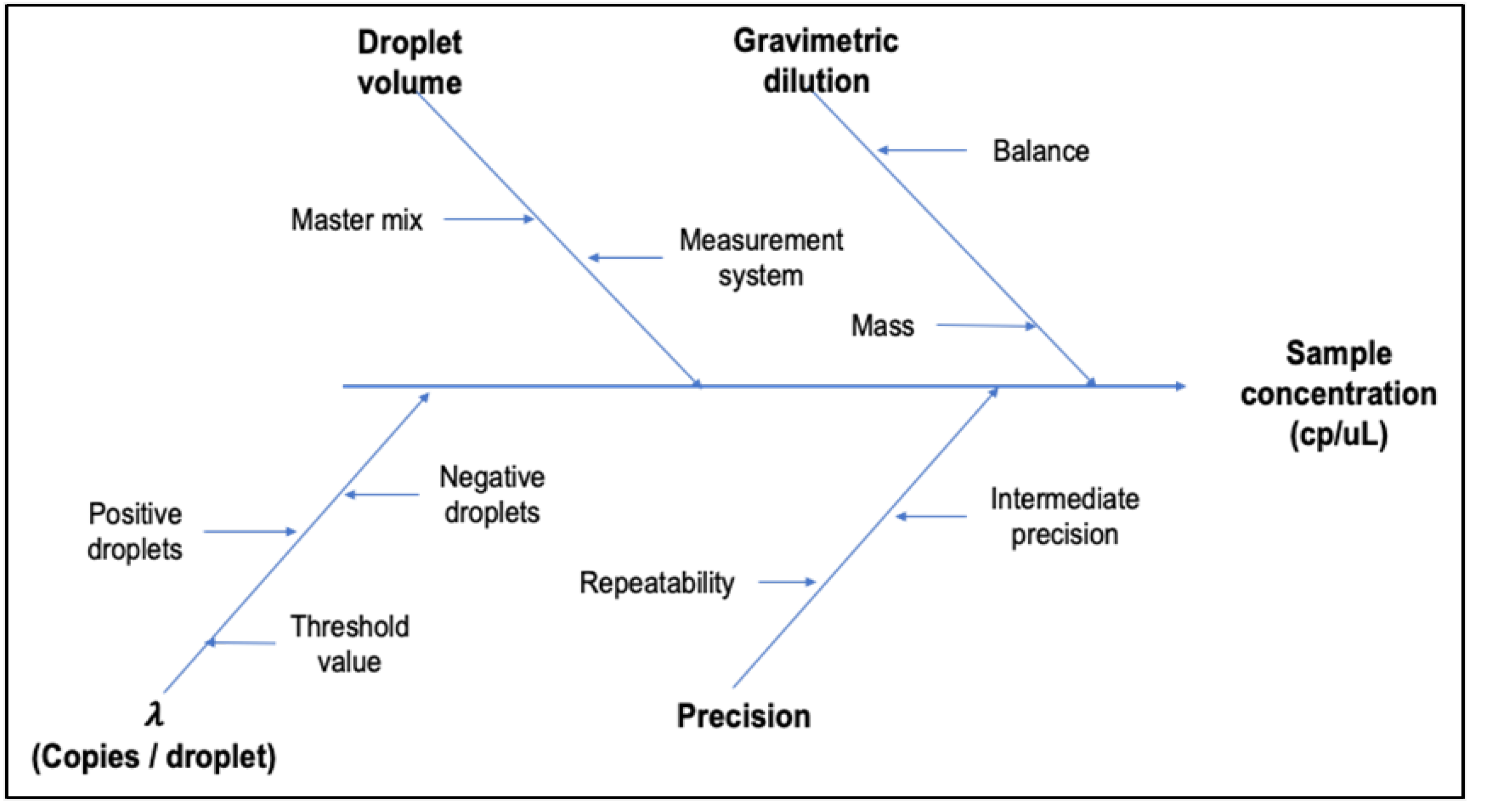
| Uncertainty1 | Evaluated for each DNA target in each copy number concentration level, from mathematical model and precision data, according to GUM and EURACHEM guide [24]. |
| Gene | Slope | Intercept | Correlation coefficient (r2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| uidA | 1,516,070 ± 7,553 | −5.3 ± 13.9 | 0.99980 |
| lacY | 1,652,697 ± 14,605 | −17.8 ± 26.5 | 0.99938 |
| eaeA | 1,732,747 ± 15,360 | −21.2 ± 28.8 | 0.99937 |
| rfbE | 1,688,518 ± 19,028 | −12.1 ± 34.8 | 0.99899 |
| stx1 | 1,683,566 ± 19,537 | −23.5 ± 35.4 | 0.99892 |
| stx2 | 1,894,405 ± 11,534 | −22.3 ± 27.3 | 0.99970 |
| Z3276 | 1,612,203 ± 12,551 | −6.5 ± 22.9 | 0.99952 |
| Concentration level (copies/µL) | uidA | lacY | eaeA | rfbE | stx1 | stx2 | Z3276 |
| 7,920 | 3.5% | 4.1% | 8.4% | 4.1% | 4.1% | 4.6% | 3.4% |
| 718 | 2.7% | 3.0% | 4.2% | 2.5% | 2.0% | 2.2% | 2.9% |
| 66 | 4.8% | 4.2% | 6.6% | 5.0% | 4.2% | 8.0% | 4.4% |
| 6.6 | 13.2% | 12.9% | 12.3% | 7.4% | 13.4% | 13.4% | 11.3% |
| Batch | Storage temperature | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4°C | −20°C | 4°C | −20°C | |
| ustb | urel (%) | ustb | urel (%) | |
| Low level | 5.95 | 3.4% | 6.37 | 3.7% |
| High level | 8,632 | 5.2% | 1,822 | 1.1% |
| Batch | Gene Z3276 | Gene rfbE | Uncertainty sources | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value (copies/µL) |
uZ3276 | Value | urfbE | ubias | ucharac. | uhomog. | ustab. | |
| High Level | 16.10 | 2.87 | 168.51 | 2.63 | 2.16 | 1.95 | 824 | 8.63 |
| Low Level | 168 | 7 | 175 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 6 |
| Value assignment | ||||||||
| Batch | Value | u | Relative u (%) | k | U | Relative U (%) | Batch | Value |
| High level | 164.770 | 9.140 | 5.5 | 2 | 18.280 | 11.1 | High level | 164.770 |
| Low level | 172 | 8 | 4.9 | 2 | 17 | 9.8 | Low level | 172 |
| Level | Concentration (copies/µL) |
log10 concentration |
Interpolated Ct* | ∆ Ct | ∆ Ct rel (%) |
| High | 100 000 | 5.00 | 23.4 | 0.29 | 1.24 |
| 90 000 | 4.95 | 23.5 | |||
| 110 000 | 5.04 | 23.3 | |||
| Low | 100 | 2 | 33.4 | 0.29 | 0.87 |
| 90 | 1.95 | 33.5 | |||
| 110 | 2.04 | 33.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





