1. Introduction
The search for sustainable production models and a more sustainable lifestyle is evident, which is why numerous natural bioactive compounds have become the focus of scientific research. These compounds can be classified into four main categories: macronutrients (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins), micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), phytochemicals (terpenes, alkaloids, phenolics, and organosulfur compounds), and intestinal microbiome regulators (probiotics, prebiotics, symbiotic, and postbiotics) [
1]. They can be obtained from plant, microbiological, and animal sources. Plant bioactive compounds are natural chemical substances derived from highly promising and attractive sources due to their beneficial properties in various sectors. From an agricultural perspective, the biological effect of these compounds is noteworthy, particularly their antimicrobial activity, which has been employed in the control of post-harvest diseases, and their antioxidant activity, which has been extensively used as a natural food additive [
2,
3]. Thus, the cultivation of functional foods emerges as a promising strategy aimed at meeting health, agriculture, and food-related demands, promoting sustainable socioeconomic development.
In this context, functional foods are dietary components that offer health benefits beyond their basic nutrition. The growing interest in functional foods has driven a new market strategy for halophyte plants which exhibit distinct and conserved metabolic responses compared to conventional plants [
4]. These responses are justified by their antioxidant and antimicrobial activities, making them ideal sources of bioactive molecules [
5]. Among various halophytes, Salicornia sp. has gained prominence in the global functional food market due to its richness in bioactive compounds with functional properties. This genus is categorized as a salt-accumulating halophyte with nutrients in its aerial parts, being an edible plant belonging to the Amaranthaceae family, highly tolerant to salinity (above 500 mM), with an estimated number of species between 25 and 30. Due to its content of bioactive compounds, it is a significant food source highly appreciated by consumers. Species of this genus are consumed in salads and used as green salt, which results in a lower risk of cardiovascular diseases [
6,
7,
8,
9]. Studies on
Salicornia sp. directed at agriculture and food indicate that species of this genus are widely used, especially extracts rich in bioactive compounds, which increase the nutritional value of processed foods such as pasta and wheat [
10], preservatives in fish fillets [
11], and biocides [
12].
The
Salicornia genus has a single species in Brazil, commonly known as sea asparagus. This species was botanically defined as
Salicornia ambigua (Michaux),
Sarcocornia a
mbigua, or
Sacocornia perennis, but has recently been molecularly classified as
Salicornia neei Lag. [
13].
Salicornia neei is a hydrohalophyte, succulent, and herbaceous plant widely used in gourmet cuisine. It has been described as containing a large amount of important nutrients and functional metabolites [
14]. However, there is a scarcity of studies related to
S. neei, with most research focused on cultivation management practices to promote better productivity of the species, and few studies on its bioactive compounds. Therefore, this research aimed to evaluate the nutritional composition and potential of extracts with different solvents (milli-Q water, ethanol, and ethanol-acetone) from the leaf, stem, and root structures of
S. neei for antioxidant and antimicrobial activity.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
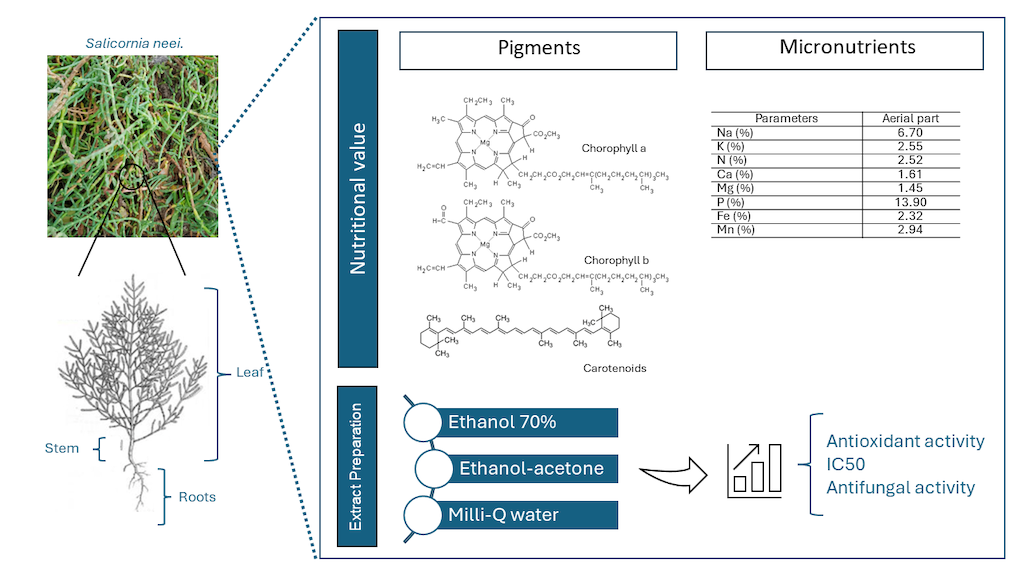
Salicornia neei was obtained from the Agronomic Institute of Pernambuco (IPA), located at Metropolitan Region of Recife. The experiments were carried out using Salicornia neei seedlings grown in organic soil and irrigated daily with saline water obtained from the desalination plant in the municipality of Riacho das Almas – PE, Brazil. After 6 months of cultivation, samples were collected, with part of the material dried in oven for mineral and pigment analysis, while another part was stored in a refrigerator at 5°C for the preparation of extracts.
2.2. Nutritional Composition
Samples of
Salicornia neei were dehydrated in an oven at 50°C for 24 hours. Subsequently, they were ground using a pestle, and 0.5 grams of each sample were weighed in triplicate, adding 7 mL of nitroperchloric solution to test tubes. Then, the mixtures were subjected to digestion in a digestion block for 3 hours at 250°C. Finally, the digested samples were diluted for analysis by ICP of the following mineral constituents: sodium (Na), potassium (K), nitrogen (N), calcium (Ca), zinc (Zn), phosphorus (P), magnesium (Mg), manganese (Mn), and aluminum (Al) according to Bezerra Neto and Barreto [
15].
2.3. Chlorophyll and Carotenoid Content
According to the methodology describe by Rahmani et al. [
16], for the extraction of pigments from
Salicornia neei, 1g of fresh material was weighed, macerated in 8 mL of 80% acetone, and centrifuged for 15 min at 4,000 rpm at 38°C. Subsequently, the supernatant was collected for the quantification of pigments and carotenoids in a spectrophotometer (BioChrom Model Libra S32 UV-vis), determining absorbance at wavelengths of 460 nm, 645 nm, and 663 nm. The pigments were calculated using the formulas described by Najar et al. [
17]:
Pigments contents were expressed as mg/g off w.
2.4. Preparation of Salicornia neei Extracts
The extraction of plant constituents was carried out following the method proposed by Hafsa et al. [
18].
Salicornia neei seedlings were separated into leaves, stems, and roots, and cut into small pieces of 5cm for weighing. Leaf (50g), stem (15g), and root (7.5g) samples were placed in Erlenmeyer flasks, adding three different solvents: milli-Q water, commercial ethanol (70%), and ethanol-acetone (1:1), for 4 hours for milli-Q water and 2 hours for the respective solvents, resulting in a final concentration of 0.2 mg/mL. The resulting aqueous, ethanolic, and ethanol-acetone extracts were filtered through paper filter and then stored in amber vials with aluminum foil at 4°C to preserve the extracts contained the biomolecules until further analysis.
2.5. Antioxidant Activity of Salicornia neei Extracts
The DPPH activity was based on the capacity to eliminate the DPPH radical by antioxidants, using the method described by Brand-Williams et al. [
19], with some modifications. Initially, a DPPH solution (60 µM) was prepared in methanol to obtain an absorbance between 0.6 to 0.7 at a wavelength at 517 nm. The extracts were diluted into three concentrations of 20, 40, and 60 mg/mL in triplicate. Then, 1 mL of the extracts was mixed with 2.5 mL of the DPPH solution and incubated in the dark for 30 min. After incubation, absorbances were measured at the same wavelength mentioned above. The obtained data were used to calculate the antioxidant activity according to the following equations:
2.6. Determination of IC50
The IC50 (50% inhibition concentration) estimates the concentration of an antioxidant required to inhibit 50% of the DPPH free radical activity. For this, the probit regression analysis method was used.
2.7. Microorganisms
The microorganisms used to determine antimicrobial activity were provided by the Culture Bank of UCP (Catholic University of Pernambuco), which are registered in the WFCC Bank (World Federation for Culture Collection). The following microorganisms were used: Escherichia coli UCP 1575, Bacillus subtilis UCP 1559, Staphylococcus aureus UCP 1576, Salmonella sp. UCP 1560, Pseudomonas aeruginosa UCP 1551, Candida albicans UCP 0993, C. guilliermondii UCP 1592, and C. tropicalis UCP 0996.
2.8. Determination of Antimicrobial Activity of Salicornia neei Extracts
The antimicrobial activity was tested only the solvent with the highest antioxidant activity at a concentration of 24 mg/mL with the structures (leaf, stem, and root) of
Salicornia neei. The disk diffusion method was performed as described by Murray et al. [
20]. Each microorganism was uniformly inoculated onto the surface of Sabouraud agar plates for fungi and Mueller Hinton agar plates for bacteria using sterile swabs. After inoculation, filter paper disks with a diameter of 1 cm were soaked with 10 µL of ethanol-acetone extract at a concentration of 24 mg/mL and placed onto the agar plates. The solvent of the extract was used as control. Bacteria were incubated at 37°C for 24 hours, while fungi strains were incubated at 28°C for 48 hours. The test was performed in triplicate, and antimicrobial activity was determined by measuring the diameter of the inhibition halo around the disks in millimeters (mm).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The percentages of DPPH inhibition from the extracts were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The results were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test (p < 0.05) for comparison between treatments. The IC50 determination used the non-linear regression method. All analyses were performed using STATISCA 12 software.
3. Results
3.1. Micronutrients and Pigments
From the results of the micronutrients and pigments of
S. neei (
Table 1), it was observed that phosphorus was the most abundant element (13.90%), followed by sodium (6.70%). Regarding pigments, chlorophyll b was the most significant (4.76%). The Na+/K+ ratio was low at (2.63 mg/gFW), and the mineral accumulation pattern observed in S. neei was P > Na > Mn > K > N > Fe > Ca > Mg.
3.2. Antioxidant Activity
After mixing the DPPH stock solution with each extract (milli-Q water, ethanol, and ethanol-acetone), the resulting reaction caused a colorimetric change in the samples. Purple coloration was observed in the milli-Q water extracts, while yellow coloration was observed in the ethanol and ethanol-acetone extracts. The extracts of
Salicornia neei showed a high capacity for scavenging free radicals, with a maximum reduction of the DPPH radical by 96.72% and a minimum of 73.88% (
Figure 1A). These values increased as the concentration of the extracts was incremented (8, 16, and 24 mg/mL). Overall, all extracts showed a low IC50 (
Figure 1B), with the lowest IC50 observed for the ethanolic extract of the root (4.15 mg/mL) and the highest IC50 for the milli-Q water extract of the stem.
Regarding the solvents used in the extraction of bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties from
Salicornia neei, a statistically significant difference was observed among the means. The ethanol-acetone solvent proved to be the most effective for extracting these compounds, followed by ethanol and milli-Q water. However, for the different plant structures of
S. neei (leaf, stem, and root), no significant differences were observed among the treatments, considering a significance level of p < 0.05 (
Table 2).
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity Against Bacteria and Fungi
In the analysis of antimicrobial activity against bacteria strains, no inhibition zones were observed. However, for fungal species, small inhibition areas were observed for Candida albicans (leaf: 9mm ± 2.0; stem: 8mm ± 2.0; root: 12mm ± 4.0), C. guilliermondii (leaf: 8mm ± 2.2), and C. tropicalis (leaf: 8mm ± 1.0; stem: 8mm ± 4.3; root: 10mm ± 4.0). It is worth noting that the root structure showed higher inhibition activity against fungal growth, with a 12 mm diameter halo.
4. Discussion
4.1. Mineral Composition and Pigments
Determining the mineral fraction of foods is essential for assessing their quality for human consumption. In this context, the presence of bioactives from the class of micronutrients essential in human nutrition was found, with recommended doses for daily intake, including sodium, potassium, nitrogen, calcium, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, and magnesium, as established in the technical regulation on recommended daily intake (RDI).
The Na+/K- ratio is a relevant factor related to plant tolerance to salinity. A low Na+/K- ratio indicates the plant's resistance to salt stress, as the ability to accumulate K+ in high salinity environments neutralizes the toxicity of Na+ in the cytoplasm [
21]. Another important aspect of this ratio is associated with nutrition, as lower values are more suitable for human consumption, as elevated values have been associated with the incidence of hypertension [
22]. In our study, we observed a low Na+/K+ ratio indicating the resistance of
S. neei to salt stress and its suitability for human consumption. In terms of nutrition, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a daily intake of 2g of sodium, equivalent to 5g of table salt. In this study, we found that in 0.5g of
S. neei contains 0.0067g of sodium, meaning that in 5g we would have 0.07g of sodium, which is considerably lower than the salt used in culinary/domestic environments.
Regarding the pattern of mineral accumulation, several studies have demonstrated the ability of
Salicornia sp. species to extract and accumulate minerals from the soil in their aerial parts. However, there is no fixed pattern of mineral accumulation, as plants are influenced by biotic and abiotic factors [
23]. According to Lima et al. [
24], the higher the sodium content in halophytes, the lower the calcium, magnesium, and potassium contents due to competition for excess sodium. Additionally, other factors such as solar radiation levels and nitrogen fertilization also affect mineral composition [
25]. Therefore, it is evident that growing conditions can result in plants with improved nutritional properties, and the mentioned factors did not negatively affect the mineral profile of
S. neei in this study. Chlorophylls are pigment molecules that play fundamental roles in the photosynthetic process. While chlorophyll a absorbs most of the light necessary for photosynthesis, chlorophyll b acts as an accessory pigment, increasing the efficiency of the process [
26]. Reductions in chlorophyll levels typically indicate nutritional deficiency or biotic or abiotic stress. Although Salicornia sp. are halophytes and therefore salt-tolerant, a reduction in chlorophyll content is observed under conditions of high salinity stress, due to the destruction of photosynthetic pigments and carotenoids. Additionally, the increase in carotenoids under saline stress is attributed to greater antioxidant capacity, which protects photosystems against photo-oxidation. Comparing with recent studies by Hulkko, Chaturvedi, and Thomsen [
27] and Rahmani et al. [
28] we observed that the values of all pigments are within ideal conditions as expected, suggesting an efficient photosynthetic process and an increase in bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties.
4.2. Antioxidant Activity
According to Widowati et al. [
29], the change in color from purple to yellow is directly related to the DPPH free radical scavenging activity. Antioxidant compounds are classified as very strong if the free radical scavenging is greater than 80%, strong if it falls between 50% and 80%, and weak if it is less than 50%. In this study, the milli-Q water solvent extract was considered strong, while the ethanol and ethanol-acetone extracts were classified as very strong. The IC50 indicates the concentration required to inhibit 50% of the free radicals and is inversely proportional to the percentage inhibition of DPPH, meaning lower values reflect higher antioxidant activity. Thus, the highest antioxidant activity was found in the ethanolic extract of the root, with an IC50 of 4.15 mg/mL, while the highest value was found in the milli-Q water extract of the stem, with an IC50 of 13.85. Overall, all extracts showed low IC50 values, highlighting their great antioxidant potential. These results are consistent with previous studies on Salicornia sp. species, which demonstrated
Salicornia europea (IC50 = 10.2 µg/g and 7.5 µg/g) [
30], and
Salicornia ramosissima IC50 = 824 µg/mL [
31].
One of the main characteristics attributed to the Salicornia sp. genus is the richness of functional bioactive compounds, especially those with antioxidant properties. Due to the stressful halophytic conditions, species of this genus produce antioxidants to detoxify reactive oxygen species (ROS) caused by stress. Thus, the results of this study are aligned with the hypothesis of bioactive compound synthesis with antioxidant properties by Salicornia species under saline stress conditions.
Extraction of bioactive plant compounds is directly associated with the polarity of the solvent. As observed by Roberto et al. [
32], nonpolar antioxidants generally exhibit more pronounced activities due to their high solubility in nonpolar solvents compared to polar antioxidants. Therefore, the low extractive capacity of mili-Q water solvent suggests that the
S. neei species contains a higher concentration of active biomolecules with nonpolar antioxidant properties. On the other hand, ethanol, and ethanol-acetone solvents, being bipolar, are capable of dissolving antioxidant compounds with different polarities, which confers a high extractive efficiency of these compounds in
S. neei when these solvents are used.
The better extractive capacity of nonpolar solvents suggests that S. neei contains a higher quantity of nonpolar antioxidants. Many studies have correlated the presence of phenolic compounds with antioxidant activity, suggesting the need for additional investigations to correlate this activity with the phenolic compounds present in the plant. According to Limongelli et al..[
33], they emphasize the high content of phenolic compounds in Salicornia sp., which can vary from 1.2 to 2 mg GAE fw and their benefits to human health. Thus, studies are proposed to verify the relationship of phenolic compounds with antioxidant activity.
The extracts from each structure of S. neei showed the same pattern of response regarding the extraction of bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties. Therefore, there is no specific structure (plant, stem, and root) that presents a higher content of these compounds. Therefore, the presence of bioactive compounds in all plant structures reinforces its potential as a functional food in the human diet, offering health benefits.
4.3. Antimicrobial Activity
Microbial growth inhibition in antimicrobial tests is indicated by the formation of the inhibition halo. In this study, it was observed that the ethanol-acetone extract from the structures (leaf, stem, and root) did not demonstrate the capacity to inhibit the growth or destroy the bacteria. This response may have occurred due to the low concentration of the extracts, or the incompatible interaction of the biomolecules present in the extracts with the Sabouraud agar culture medium. On the other hand, halos were observed in three fungal species (
Candida albicans,
C. guilliermondii, and
C. tropicalis), with the highest average inhibition halo for
C. albicans. However, this inhibition was considered low compared to the extracts reported in studies of
Salicornia sp., with inhibition halos ranging from 11.94 to 14.93 mm [
34]. Furthermore, according to Lopes et al. [
35], the ability of
Salicornia neei extracts to inhibit microorganisms is attributed to the presence of phenolic compounds, which act synergistically with fatty acids and other osmotic compounds. Therefore, it is possible that the ethanol-acetone extract from the root contains biomolecules of the phenolic compound class mentioned.
5. Conclusions
Considering the native Brazilian halophyte Salicornia neei can be considered a food source with good nutritional quality and notable antioxidant properties, thus characterizing it as a functional plant. Furthermore, its low sodium content was considerably lower compared to the salt commonly used in domestic and commercial settings, suggesting that its consumption may contribute to reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. In summary, S. neei constitutes a natural source of bioactive compounds with interesting antioxidant and antifungal properties for various sectors, especially in the food and agricultural industries, for the utilization of biomolecules as food additives and the large-scale production of widely appealing functional foods.
Author Contributions
C.F.M. and G. M. C.T. conceived and designed the experiments; C.F.M. performed the experiments; G. M. C.T., A.F.S., C.M. B. F. and R. F. S. A. analyzed the data; G. M. C. T. and J.F.G. contributed reagents/materials; : C.F.M, G.M. C.T and C. M. B. F analysis tools; C.F.M, A.F.S. J.F.G. and G. M. C.T wrote the paper. All authors read, reviewed, and approved the final manuscript.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Catholic University of Pernambuco and the Agronomic Institute of Pernambuco. This study was funded by the Foundation for the Support of Science and Technology of the State of Pernambuco (FACEPE), process number IBPG-1497-2.12/19, the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq), process number 312241/2022, and CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel) CAPES Pro-Equipment grant number 11/2014.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kussmann, M.; Cunha, D.H.A.; Berciano, S. Bioactive compounds for human and planetary health. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1193848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xing, M.; Chen, T.; Tian, S.; Li, B. Effects and mechanisms of plant bioactive compounds in preventing fungal spoilage and mycotoxin contamination in postharvest fruits: A review. Fd. Chem. 2023, 415, 135787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadidi, M.; Tan, C.; Assadpour, E.; Kharazmi, M.S.; Jafari, S.M. Emerging plant proteins as nanocarriers of bioactive compounds. J. Control. Rel. 2023, 355, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekanayake, S.; Egodawatta, C.; Attanayake, R.N.; Perera, D. From salt pan to saucepan: Salicornia, a halophytic vegetable with an array of potential health benefits. Fd. Front. 2023, 4, 641–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M.; Castilho, M.D.C.; Sanches-Silva, A.; Freitas, A.; Barbosa, J.; Gonçalves, M.J.; Ramos, F. Evaluation of the mycotoxins content of Salicornia spp.: A gourmet plant alternative to salt. Fd. Add. & Cont.: Part B. 2020, 13, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantin, C.G.; Zugravu, M.M.; Georgescu, M.; Constantin, M.F.; Moț, A.; Paraschiv, M.; Dobrin, A. The Impact of the Growing Substrate on Morphological and Biochemical Features of Salicornia europaea L. Ap. Sci. 2023, 13, 10835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fredsgaard, M.; Kaniki, S.E.K.; Antonopoulou, I.; Chaturvedi, T.; Thomsen, M.H. Phenolic compounds in Salicornia spp. and their potential therapeutic effects on H1N1, HBV, HCV, and HIV: A review. Mol. 2023, 28, 5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penteado, G.M.; de Sá, L.C.F.V.; Cavalini, G.R.; do Amaral, V.; Charlo, P.B. Salicornia como um substituto ao sal na hipertensão induzida por obesidade: Uma revisão integrativa. Gl. Acad. Nurs. J. 2022, 3, 266–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcios, A.E.; Braem, L.; Jonard, C.; Lemans, T.; Cybulska, I.; Papenbrock, J. Compositional Changes in Hydroponically Cultivated Salicornia europaea at Different Growth Stages. Plant. 2023, 12, 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, G.Y.Y.; Souza, M.M.; Oliveira, J.R.M.; Costa, C.S.B.; Collares, M.P.; Prentice, C. Effect of ultrasound-assisted cold plasma pretreatment to obtain sea asparagus extract and its application in Italian salami. Fd. Res. Int. 2020. 137, 109435. [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Dong, G.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Li, F.; Yu, X. The chemical composition analysis of dwarf saltwort (Salicornia bigelovii Torr.) and its preservative effects on snakehead fish fillets. J. Fd. Proc. Pres. 2022, 46, e16433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.L.; Chaturvedi, T.; Skovhus, T.L.; Thomsen, M.H. Halophyte-based Biocides for Mitigation of Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC) in Industrial Water Systems. In Petrol. Microbiol. 2024, 154-166. CRC Press. /: https. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, M.R.; Navarro, D.A.; Ponce, N.M.; Rojas, A.M.; Stortz, C.A. Perennial halophyte Salicornia neei Lag.: Cell wall composition and functional properties of its biopolymers. Fd. Chem. 2020, 350, 128659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, M.R.; Araneda, J.; Osses, A.; Orellana, J.; Gallardo, J.A. Efficiency of Salicornia neei to treat aquaculture effluent from a hypersaline and artificial wetland. Agricult. 2020, 10, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezerra Neto; Barreto, L.P. Análises químicas e bioquímicas em plantas, 2011; 261p.
- Rahmani, R.; Arbi, K.E.; Aydi, S.S.; Hzami, A.; Tlahig, S.; Najar, R.; Aydi, S.; Debouba, M. Biochemical composition and biological activities of Salicornia europeae L. from southern Tunisia. J. Fd. Meas. Character 2022, 16, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Najar, R.; Aydi, S.; Sassi-Aydi, S.; Zarai, A.; Abdelly, C. Effect of salt stress on photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in Medicago truncatula. Pl. Bios.Int. J. Deal. Asp. Pl. Biol. 2019, 153, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafsa, M.B.; Ismail B,; Garrab, M. ; Aly, R.; Gagnon, K.; Naghmouchi, K. Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of essential oils and some extracts from the halophytic plant Salicornia arabica L. Tunisian. J. Med. Pl. Nat. Prod. 2011, 6, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Brand-Williams, W.; Cuvelier, M.; Berset, C. Use of a radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. F. Sci. Technnol, 1995, 28, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, P.R.; Baron, E.J.; Pfaller, M.D.; Tenover, F.C.; Yolke, R.H. Clinic manual. Microbiol. 1995. 6th (ed.). Washington. CC, ASM., 300.
- Alves, P.R.; de Lucena, E.M.P.; Bonilla, O.H.; Marques, E.C.; Gomes-Filho, E.; Costa, C.S.B. Organic and inorganic solutes in Salicornia neei Lag. under blades of irrigation and fertilization in Ceara semiarid, Brazil. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Okudur, E.; Tuzel, Y. Effect of EC Levels of Nutrient Solution on Glasswort (Salicornia perennis Mill.) Production in Floating System. Hort. 2023, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castilla-Gavilán, M.; Muñoz-Martínez, M.; Zuasti, E.; Canoura-Baldonado, J.; Mondoñedo, R.; Hachero-Cruzado, I. Yield, nutrients uptake and lipid profile of the halophyte Salicornia ramosissima cultivated in two different integrated multi-trophic aquaculture systems (IMTA). Aqua. 2024, 583, 740547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Castaneda-Loaiza, V.; Salazar, M.; Nunes, C.; Quintas, C.; Gama, F.; Barreira, L. Influence of cultivation salinity in the nutritional composition, antioxidant capacity and microbial quality of Salicornia ramosisima commercially produced in soilless systems. F. Chem. 2020, 333, 127525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, M.; Silva, A.S.; Sendon, R.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Characterization, Phenolics Composition, and Potential Contaminants Analysis of Salicornia ramosissima and Sarcocornia perennis alpine. Mols. 2023, 28, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wientjes, E.; Croce, R. The light-harvesting complexes of higher-plant Photosystem I: Lhca1/4 and Lhca2/3 form two red-emitting heterodimers. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) – Bioenergetics. 2020, 7, 148046–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulkko, L.S.; Chaturvedi, T.; Thomsen, M.H. Extraction and quantification of chlorophylls, carotenoids, phenolic compounds, and vitamins from halophyte biomasses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulkko, L.S.S.; Chaturvedi, T.; Thomsen, M.H. Extraction and Quantification of Chlorophylls, Carotenoids, Phenolic Compounds, and Vitamins from Halophyte Biomasses. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widowati, R.; Handayani, S.; Suprihatin Rahayu, I.L. Phytochemicals And Antioxidant Of Methanol Extract Of Gracilaria Salicornia, Halimeda Gracilis, Halimeda Macroloba, And Hypnea Asperi From Tidung Island Coastal Region. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2021, 8, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, M.; Silva, A.S.; Séndon, R.S.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.B. Plants: Nutritional Characterisation, Phenolics Composition, and Potential Contaminants Analysis of Salicornia ramosissima and Sarcocornia perennis alpine. Mols. 2023, 28, 2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, A.; Silva, A.M.; Moreira, M.; Salazar, M.; Svarc-gajic, J.; Brezo-Borjan, T. Salicornia ramosissima: A New Green Cosmetic Ingredient with Promising Skin Effects. Antioxid. 2022, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberto, P.V.; Surget, G.; Lann, K.L.; Mira, S.; Tarasco, M.; Guerard, F. Antioxidant, Mineralogenic and Osteogenic Activities of Spartina alterniflora and Salicornia fragilis Extracts Rich in Polyphenols. Sec F. Chem. 2021, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limongelli, F.; Crupi, P.; Clodoveo, M.L.; Corbo, F.; Muraglia, M. Overview of the polyphenols in Salicornia: From recovery to health-promoting effect. Mols. 2022, 27, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, N.; Heydarian, Z. Investigation of in vitro antifungal activity of Salicornia iranica Akhani. Trad Integr Med. 2016, 1, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, S.A.; Castilho, M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Ramos, F. Halophytes as source of bioactive phenolic compounds and their potential applications. Crit. Rev. F. Sci. Nut. 2021, 61, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).