Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
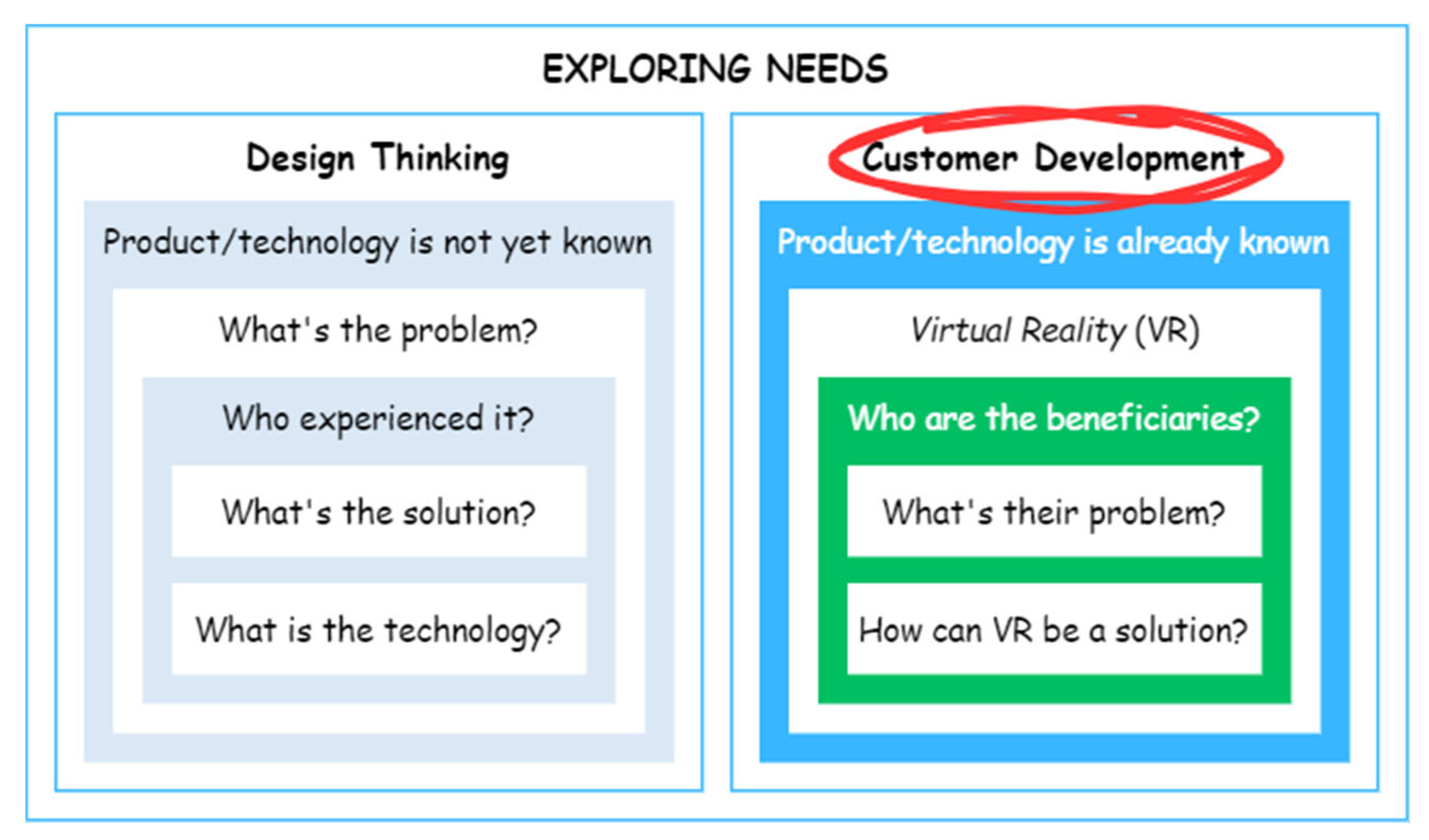
2.1. Method Background
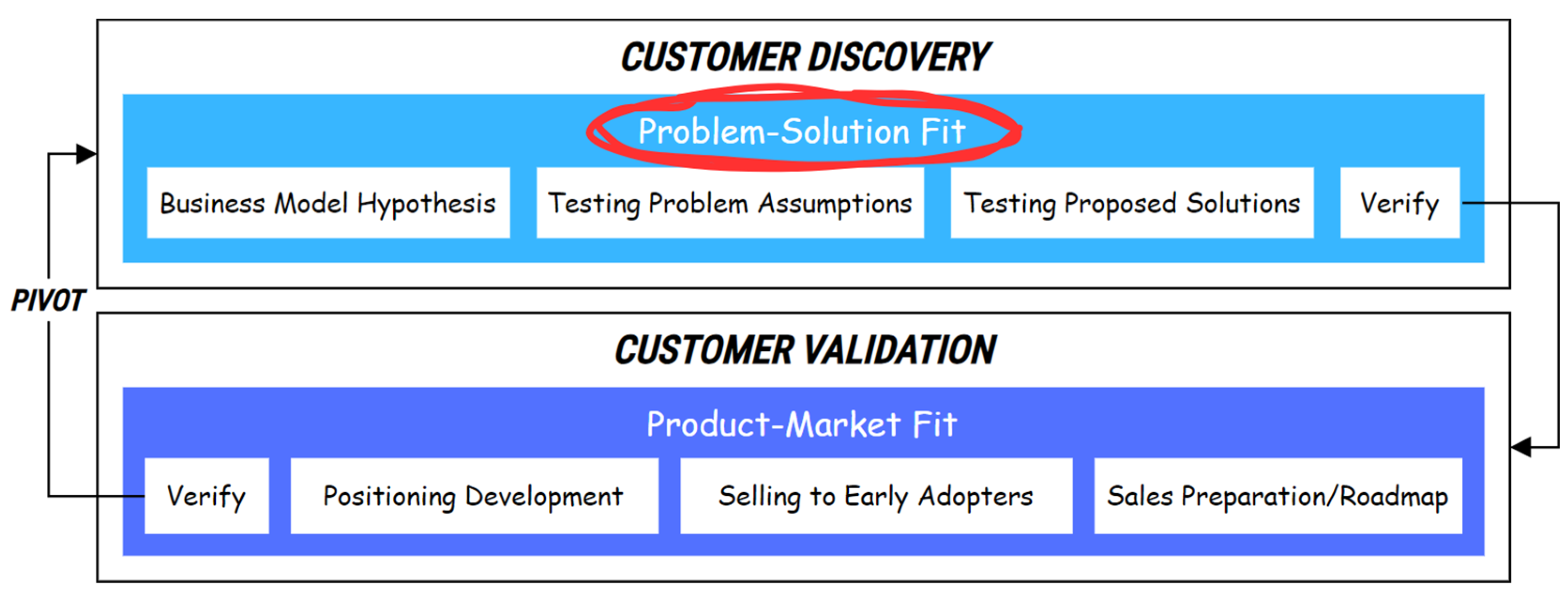
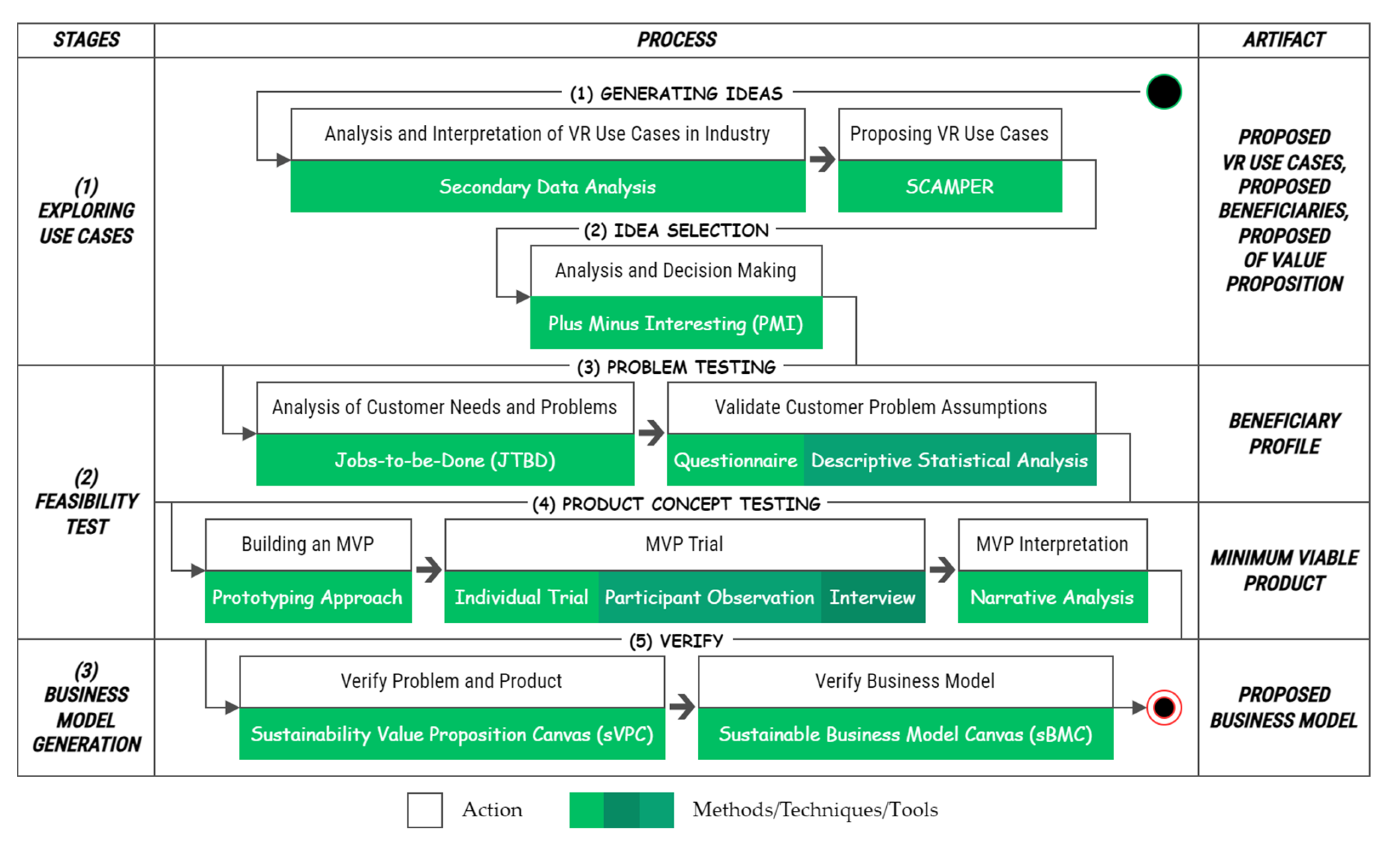
2.2. Research Flow
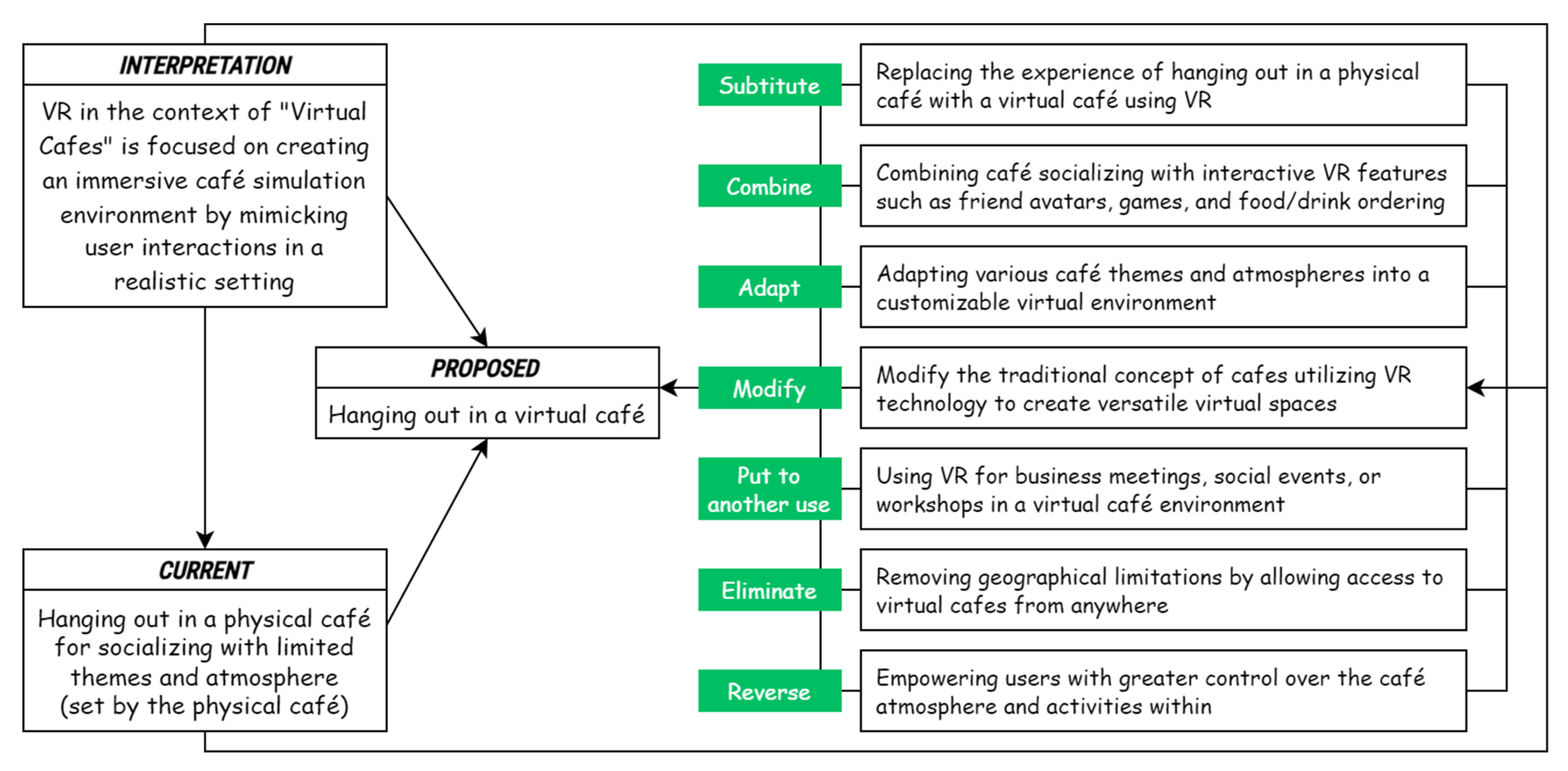
2.2.1. Generating Ideas
- Substitute: What can be substituted or changed?
- Combine: What elements can be combined to create something new?
- Adapt: What can be adapted or adjusted for different situations?
- Modify: What can be modified, altered, or reduced?
- Put to another use: How can something be used for a different purpose or in a different place?
- Eliminate: What can be eliminated or removed?
- Reverse: What if we reverse or invert the current situation?
2.2.2. Idea Selection
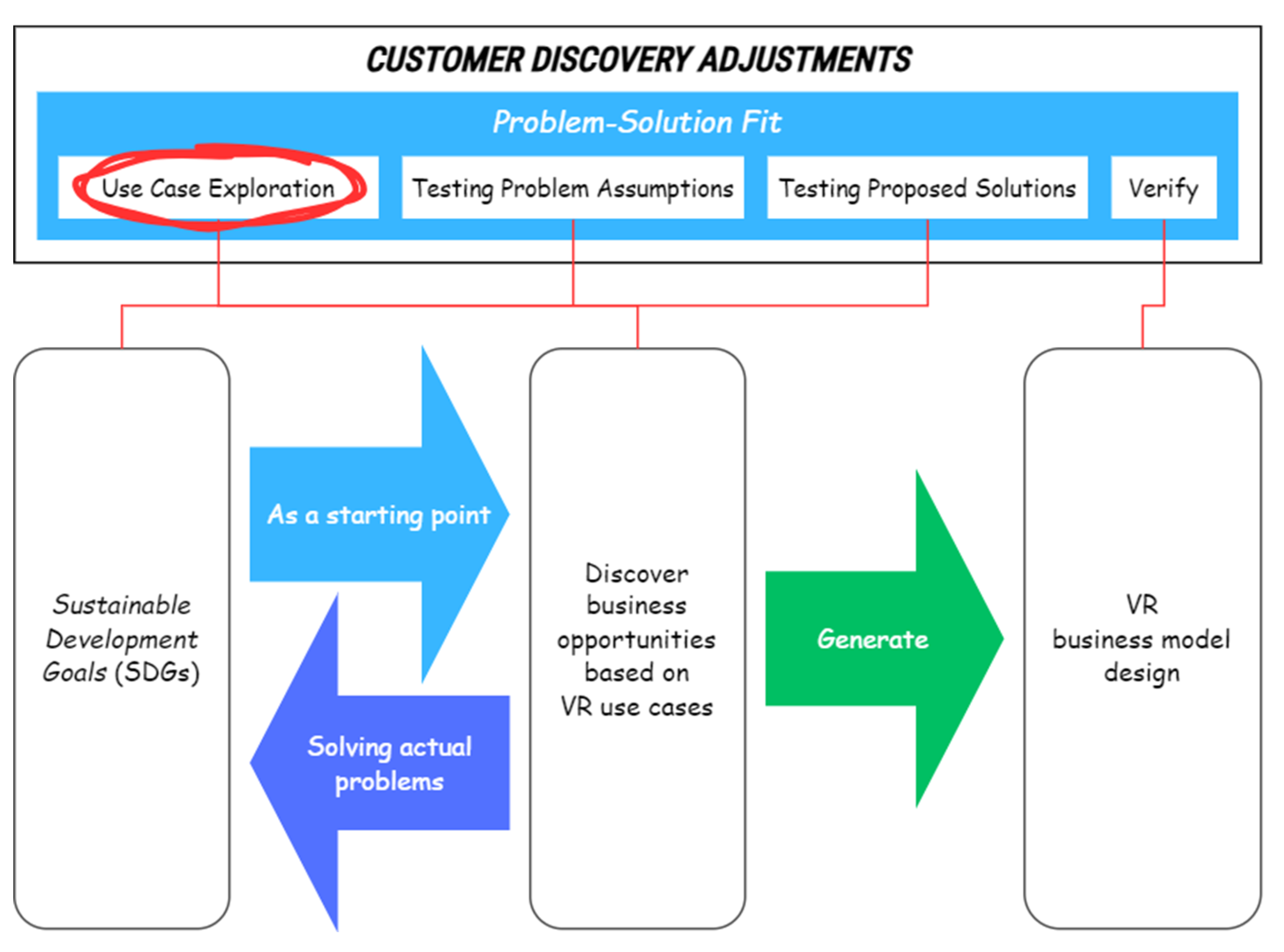
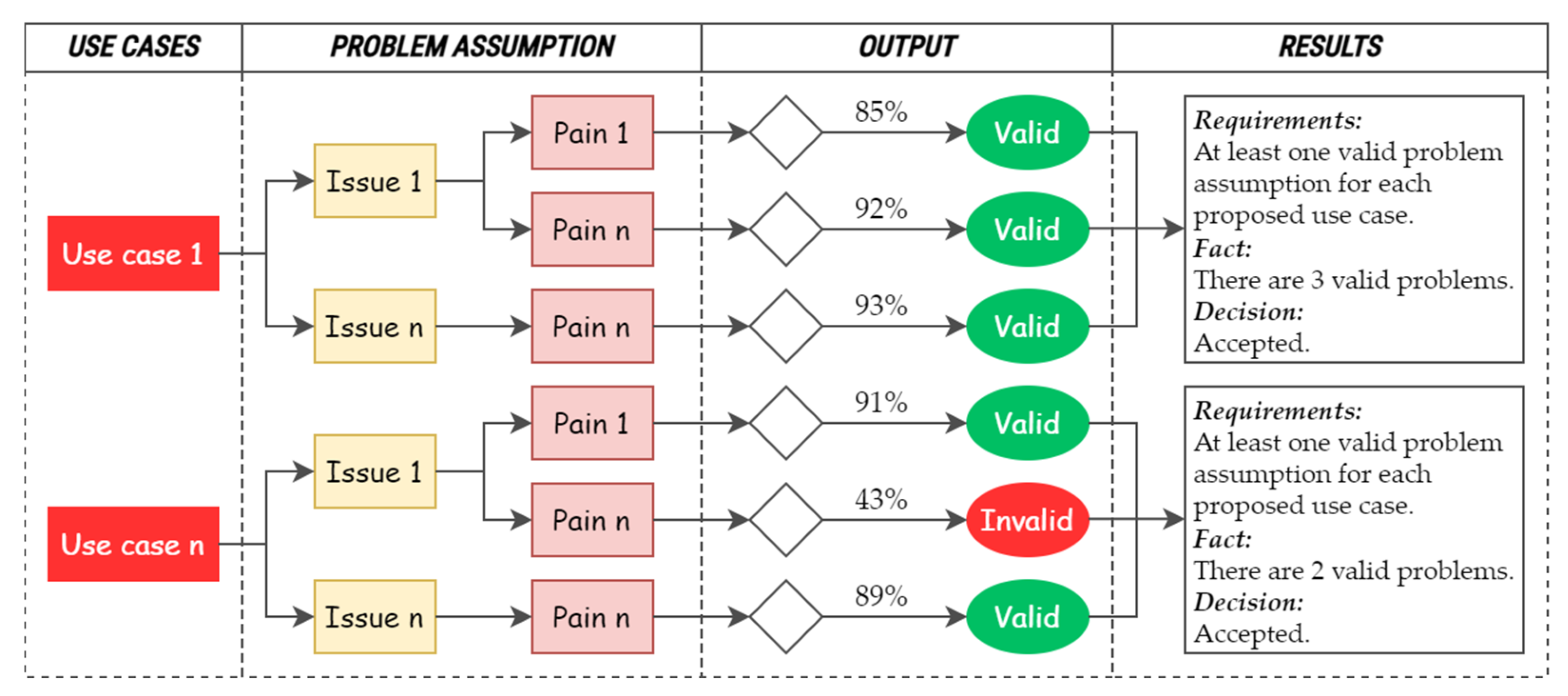
2.2.3. Problem Testing
2.2.4. Product Concept Testing
2.2.5. Verify
2.3. Research Design
3. Results and Analysis
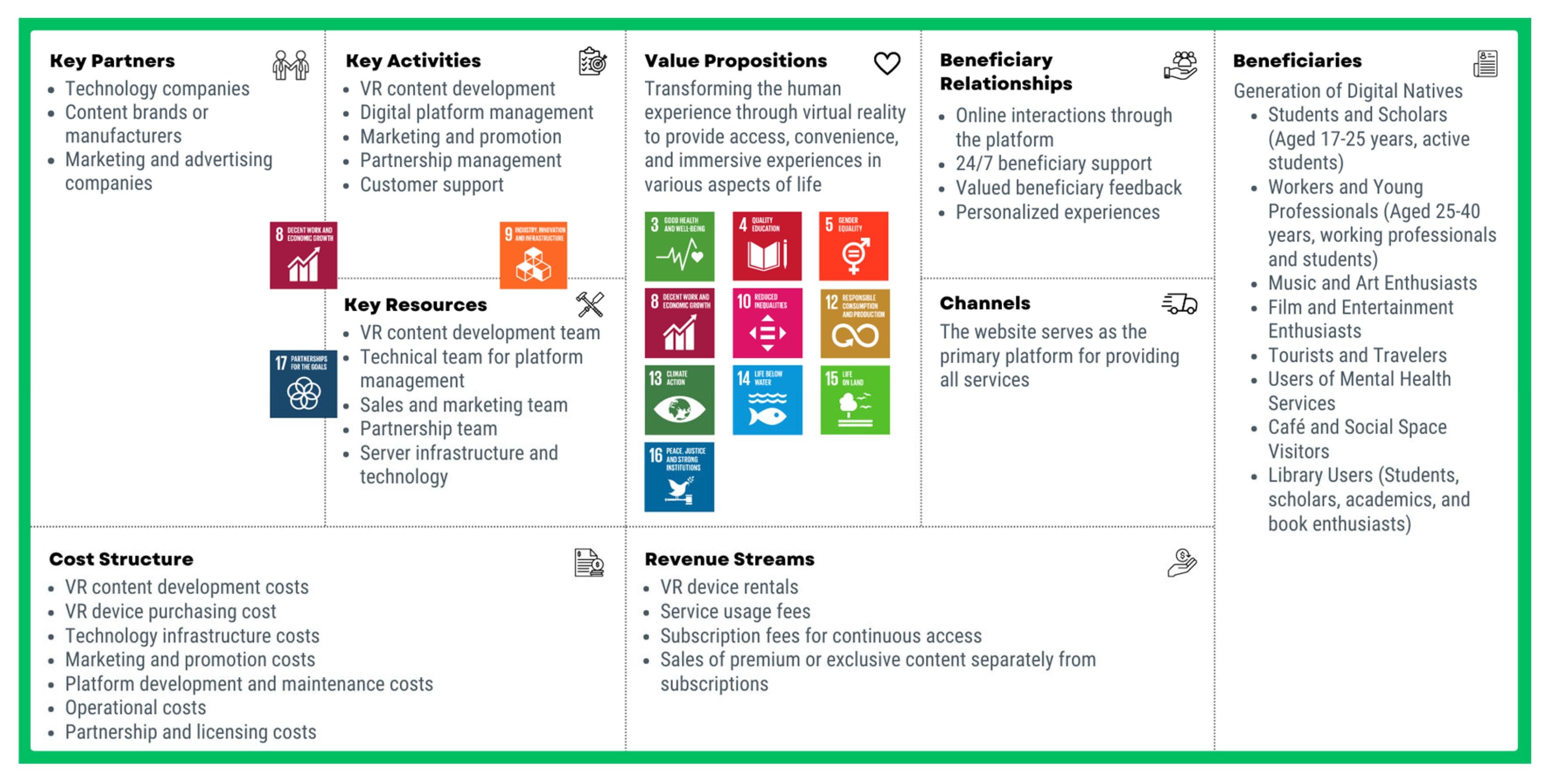
3.1. Proposed VR Use Cases, Beneficiaries, Value Proposition
3.1.1. Proposed VR Use Cases
3.1.2. Proposed Beneficiaries
3.1.3. Proposed of Value Proposition
3.2. Beneficiary Profiles
3.2.1. Analysis and Design
3.2.2. Quantitative Findings
3.2.3. Characteristics
3.2.4. Profile
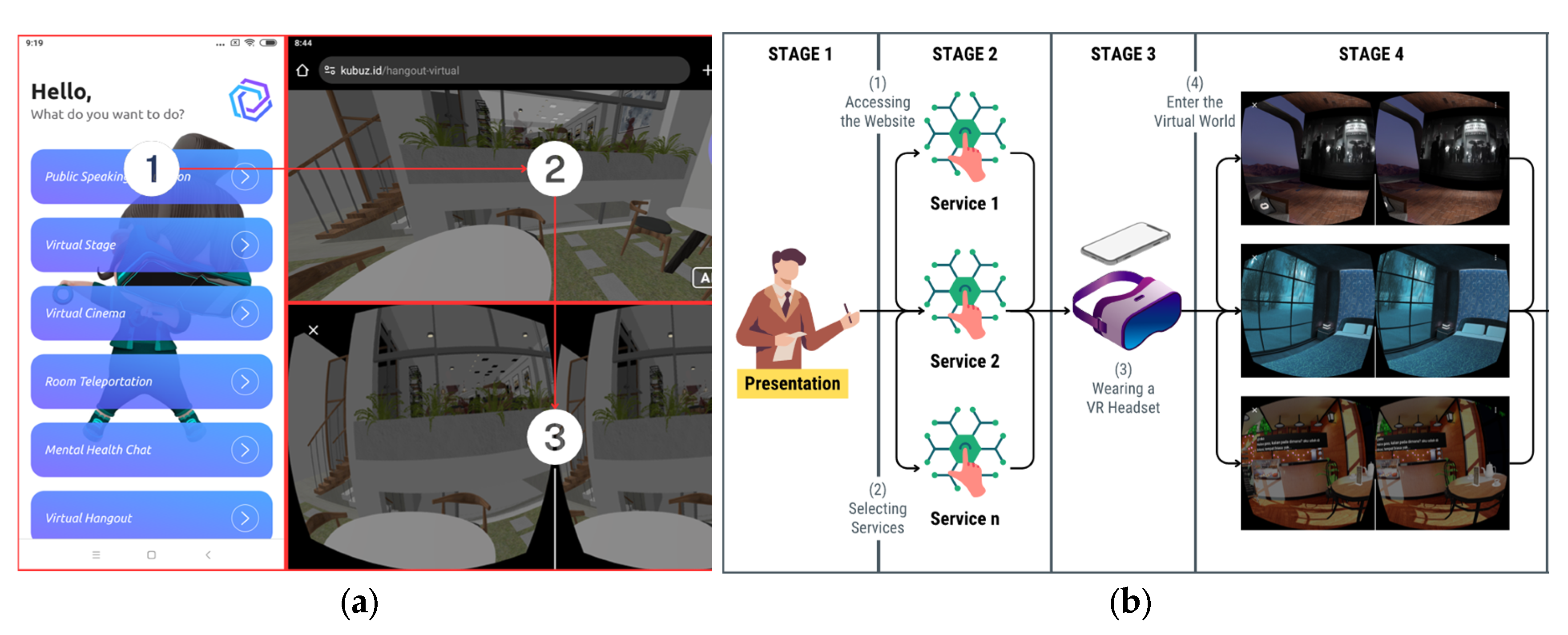
3.3. Minimum Viable Product
3.3.1. Concept
3.3.2. Demonstration
3.3.3. Qualitative Findings - Reaction
3.3.4. Qualitative Findings - Feedback
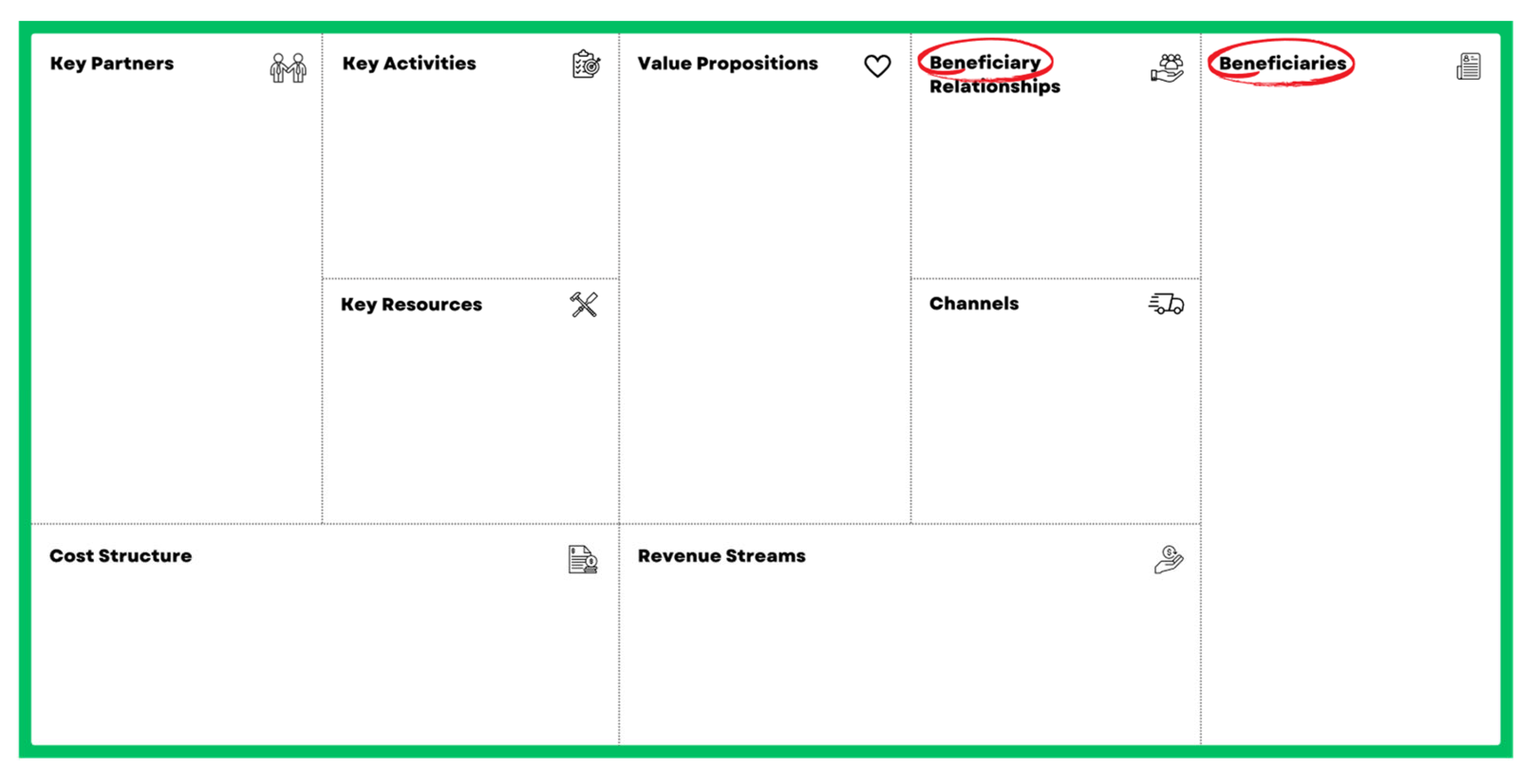
3.4. Proposed Business Model
3.4.1. Sustainability Value Proposition Canvas
3.4.2. Sustainable Business Model Canvas
4. Discussion
4.1. Findings
4.2. Implications
5. Conclusions
- The focus was primarily on exploring VR use cases in the entertainment, training, education, and tourism sectors, potentially limiting its relevance to other business sectors.
- The study confined itself to the Generation Y and Z consumer market, which may not fully reflect the interests or needs of other demographic segments.
- The MVP developed and tested centered around low-cost VR solutions for smartphones and headsets, highlighting the necessity for technical enhancements to improve user experience, thereby not fully capturing the user experience with more advanced VR devices.
- While the proposed method identifies potential business opportunities, its actual success hinges on complex environmental factors beyond consumer demand, including the popularization and portability of VR, as well as ethical and security concerns related to VR space usage.
- Strengthen problem testing through in-depth interviews to delve into issues and concept clarification before developing MVPs or prototypes (limited to presentations only). This sequential approach could mitigate weaknesses inherent in parallel Product Concept Testing, particularly when individuals may not fully agree with proposed solutions despite experiencing the actual issues they face.
- Explore the VR business potential across diverse markets and broader audience segments.
- Conduct further studies to validate consumer purchase intentions related to the benefits of VR technology.
- Utilize analytical tools such as SWOT analysis to evaluate internal and external factors influencing VR adoption.
- Develop more sophisticated MVPs to better simulate real-world conditions and user experiences.
- Implement ethical and security frameworks to address concerns related to VR space usage, ensuring user safety and privacy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bakhar, M.; Harto, B.; Gugat, R.M.D.; Hendrayani, E.; Setiawan, Z.; Surianto, D.F.; Salam, M.F.; Suraji, A.; Sukmariningsih, R.M.; Ssopiana, Y.; et al. PERKEMBANGAN STARTUP DI INDONESIA (Perkembangan Startup Di Indonesia Dalam Berbagai Bidang); 2023; ISBN 9786230926709.
- Blank & Dorf The Startup Owner’s Manual: The Step-By-Step Guide for Building a Great Company; K&S Ranch: Pescadero, California, 2012; ISBN 978-0984999309.
- Silva, D.S.; Ghezzi, A.; Aguiar, R.B. de; Cortimiglia, M.N.; ten Caten, C.S. Lean Startup, Agile Methodologies and Customer Development for Business Model Innovation: A Systematic Review and Research Agenda. Int. J. Entrep. Behav. Res. 2020, 26, 595–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, E. THE LEAN STARTUP; 2011; ISBN 9780307887917.
- Gbadegeshin, S.A.; Natsheh, A. Al; Ghafel, K.; Mohammed, O.; Koskela, A.; Rimpiläinen, A.; Tikkanen, J.; Kuoppala, A. Overcoming the Valley of Death: A New Model for High Technology Startups. Sustain. Futur. 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CBINSIGHTS The Top 12 Reasons Startups Fail. Available online: https://www.cbinsights.com/research/report/startup-failure-reasons-top/ (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- vOffice 15 Penyebab Startup Gagal Yang Harus Dihindari. Available online: https://voffice.co.id/blog/penyebab-start-up-gagal/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Grove, A. Is Your Startup Idea A Vitamin Or A Painkiller? And How to Test It! Available online: https://medium.com/lean-startup-circle/is-your-startup-idea-a-vitamin-or-a-painkiller-and-how-to-test-it-c2160a8ea122 (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Lauri Järvilehto Sustainable Development Goal Targets As Startup Business Opportunities. Aalto Univ. Publ. Ser. 2024.
- UNDP Sustainable Development Goals Available online: https://www.undp.org/sustainable-development-goals.
- Ronaghi, M.H. The Effect of Virtual Reality Technology and Education on Sustainable Behavior: A Comparative Quasi-Experimental Study. Interact. Technol. Smart Educ. 2023, 20, 475–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, L. Entrepreneurship Education and Sustainable Development Goals: A Literature Review and a Closer Look at Fragile States and Technology-Enabled Approaches. Sustain. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosio, L.D.; Buruk, O.; Fernández Galeote, D.; Bosman, I.D.V.; Hamari, J. Virtual and Augmented Reality for Environmental Sustainability: A Systematic Review. Conf. Hum. Factors Comput. Syst. - Proc. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Kunitake, Y.; Rights, V.; Field, V.R. The Potential of Virtual Reality for the SDGs: Infrastructure Development through Content and Cultural Policies. 2023.
- Statista Virtual Reality (VR) - Statistics & Facts Available online: https://www.statista.com/topics/2532/virtual-reality-vr.
- Edgar Avalos, Jose Maria Barrero, Elwyn Davies, Leonardo Iacovone, and J.T. Measuring Business Uncertainty in Developing and Emerging Economies. Available online: https://www.brookings.edu/articles/measuring-business-uncertainty-in-developing-and-emerging-economies/ (accessed on 17 October 2023).
- Riani, A. 4 Ways To Manage Startup Uncertainty. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/abdoriani/2021/03/11/4-ways-to-manage-startup-uncertainty/?sh=321360097c77 (accessed on 15 November 2023).
- 1000StartupDigital Vitamin Atau Painkiller? Menjadi Bagian Manakah Ide Startupmu? Available online:. Available online: https://1000startupdigital.id/vitamin-atau-painkiller-menjadi-bagian-manakah-ide-startupmu/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- The Investopedia Team Killer Application: What It Means, How It Works, Value. Available online: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/k/killerapplication.asp (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Wikipedia Killer Application. Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Killer_application (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Cardeal, G.; Höse, K.; Ribeiro, I.; Götze, U. Sustainable Business Models–Canvas for Sustainability, Evaluation Method, and Their Application to Additive Manufacturing in Aircraft Maintenance. Sustain. 2020, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deu, I. Business Model, Innovation, and Start-Up Sustainability in Indonesia. J. Inf. Syst. Technol. 2022, 03, 10–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ylipulli, J.; Pouke, M.; Ehrenberg, N.; Keinonen, T. Public Libraries as a Partner in Digital Innovation Project: Designing a Virtual Reality Experience to Support Digital Literacy. Futur. Gener. Comput. Syst. 2023, 149, 594–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghaei, N.; Ahmadi, A.; Khaliq, I.; Liang, H.N. Individualised Virtual Reality for Supporting Depression: Feedback from Mental Health Professionals. Proc. - 2021 IEEE Int. Symp. Mix. Augment. Real. Adjunct, ISMAR-Adjunct 2021 2021, 63–67. [CrossRef]
- Bridge, P.; Mehta, J.; Keane, P.; El-Sayed, O.; Mackay, S.; Ketterer, S.J.; West, H.; Wilson, N.; Higginson, M.; Hanna, J. A Virtual Reality Environment for Supporting Mental Wellbeing of Students on Remote Clinical Placement: A Multi-Methods Evaluation. Nurse Educ. Today 2024, 138, 106184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szita, K.; Moss-Wellington, W.; Sun, X.; Ch’ng, E. Going to the Movies in VR: Virtual Reality Cinemas as Alternatives to in-Person Co-Viewing. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2024, 181, 103150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, R.; Elliott, A.; Curran, D.; Dyer, K.; Hanna, D. 360° Video Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy for Public Speaking Anxiety: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Anxiety Disord. 2021, 83, 102451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkov, I.; Berggren, B.; Hellström, M.; Wikström, K. Navigating Uncharted Waters: Designing Business Models for Virtual and Augmented Reality Companies in the Medical Industry. J. Eng. Technol. Manag. - JET-M 2021, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brecht, P.; Hendriks, D.; Stroebele, A.; Hahn, C.H.; Wolff, I. Discovery and Validation of Business Models: How B2B Startups Can Use Business Experiments. Technol. Innov. Manag. Rev. 2021, 11, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satrio, S.; Budiarjo, E.K.; Rifki Shihab, M. Minimum Viable Product Analysis in Hyperlocal Marketplace Applications Using Customer Development Method. 2022 10th Int. Conf. Inf. Commun. Technol. ICoICT 2022 2022, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, S. Driving Corporate Innovation: Design Thinking vs. Customer Development . Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/steveblank/2014/07/29/driving-corporate-innovation-design-thinking-vs-customer-development/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Maurya, A. Customer Development Checklist for My Web Startup — Part 2 Available online: https://blog.leanstack.com/customer-development-checklist-for-my-web-startup-part-2/.
- Gündoğan, A. Scamper: Improving Creative Imagination of Young Children. Creat. Stud. 2019, 12, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonpracha, J. SCAMPER for Creativity of Students’ Creative Idea Creation in Product Design. Think. Ski. Creat. 2023, 48, 101282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Shin, S. Risk of Using Smartphones While Walking for Digital Natives in Realistic Environments: Effects of Cognitive–Motor Interference. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blankenburg, R.; Poitevien, P.; Gonzalez del Rey, J.; Degnon, L. Virtual Cafes: An Innovative Way for Rapidly Disseminating Educational Best Practices and Building Community During COVID-19. Acad. Pediatr. 2020, 20, 756–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prof. Hemant Lata Sharma, Priyamvada, C. PMI (Plus-Minus-Interesting): An Attention- Directed Strategy For Enhancing Creative Thinking Among Elementary School Students. Int. J. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bono, E. de DE BONO’S THINKING COURSE; 1982.
- Kivunja, C. Using De Bono’s Six Thinking Hats Model to Teach Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Skills Essential for Success in the 21st Century Economy. Creat. Educ. 2015, 06, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, C.M. The Innovator’s Dilemma: When New Technologies Cause Great Firms to Fail.; Harvard Business School Press: Boston, 1997; ISBN 0875845851. [Google Scholar]
- Anthony, W. Ulwick JOBS TO BE DONE - THEORY TO PRACTICE; 2016; ISBN 9780990576747.
- Settelen, C.; Seyff, N.; Hess, A. Is the “Job Map” the Next-Generation “Story Map”? Investigating the Application of Jobs-to-Be-Done for Requirements Engineering in Agile Projects. Proc. - 4th Int. Work. Learn. from Other Discip. Requir. Eng. D4RE 2020 2020, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Hair Jr, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R.E. Multivariate Data Analysis; 8th ed.; Cengage Learning, 2019.
- Alex Osterwalder, Yves Pigneur, Greg Bernarda, A.S. Value Proposition Design; 2014; ISBN 9781118968055.
- Umbreen, J.; Mirza, M.Z.; Ahmad, Y.; Naseem, A. Assessing the Role of Minimum Viable Products in Digital Startups. IEEE Int. Conf. Ind. Eng. Eng. Manag. 2022, 2022, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melegati, J.; Chanin, R.; Sales, A.; Prikladnicki, R.; Wang, X. MVP and Experimentation in Software Startups: A Qualitative Survey. Proc. - 46th Euromicro Conf. Softw. Eng. Adv. Appl. SEAA 2020 2020, 322–325. [CrossRef]
- Safitri, A.; Husin, N.; Fazlurrahman, H.; Dhenabayu, R.; Kautsar, A. Purwohandoko Variable on SME Fashion Industry with NFT Blockchain as the Design Protection and Counterfeiting Measurement Using Narrative Analysis. 2023 Int. Conf. Data Sci. Its Appl. ICoDSA 2023 2023, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterwalder, A.; Pigneur, Y.; Smith, A.; Movement, T. Business Model Generation; 2010; ISBN 9780470876411.
- Gillet, D.; Voneche-Cardia, I.; Scala, J. La Introducing Alternative Value Proposition Canvases for Collaborative and Blended Design Thinking Activities in Science and Engineering Education. Proc. - 2022 IEEE Int. Conf. Teaching, Assess. Learn. Eng. TALE 2022 2022, 252–257. [CrossRef]
- Manning, M. Lou; Renzi, J. The Business Model Canvas: A Tool to Enhance Nurse Business Acumen. Nurse Lead. 2023, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemell, K.K.; Elonen, A.; Suoranta, M.; Nguyen-Duc, A.; Garbajosa, J.; Chanin, R.; Melegati, J.; Rafiq, U.; Aldaeej, A.; Assyne, N.; et al. Business Model Canvas Should Pay More Attention to the Software Startup Team. Proc. - 46th Euromicro Conf. Softw. Eng. Adv. Appl. SEAA 2020 2020, 342–345. [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.D.; Costa, A.F. Da; Davis, A.; Linvill, D.L.; Hodges, L.F. . Virtualized Speech Practice for the College Classroom. Proc. - 2020 IEEE Conf. Virtual Real. 3D User Interfaces, VRW 2020 2020, 133–137. [CrossRef]
- Fehlmann, B.; Mueller, F.D.; Wang, N.; Ibach, M.K.; Schlitt, T.; Bentz, D.; Zimmer, A.; Papassotiropoulos, A.; de Quervain, D.J. Virtual Reality Gaze Exposure Treatment Reduces State Anxiety during Public Speaking in Individuals with Public Speaking Anxiety: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Affect. Disord. Reports 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girondini, M.; Stefanova, M.; Pillan, M.; Gallace, A. Speaking in Front of Cartoon Avatars: A Behavioral and Psychophysiological Study on How Audience Design Impacts on Public Speaking Anxiety in Virtual Environments. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2023, 179, 103106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorinelli, S.; Gallego, A.; Lappalainen, P.; Lappalainen, R. Virtual Reality Acceptance and Commitment Therapy Intervention for Social and Public Speaking Anxiety: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 2023, 28, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Irfan, H.; Lakhani, A.S.; Ahmed, B.; Shaikh, S.; Movania, M.M.; Farhan, M. Manifest: Public Speaking Training Using Virtual Reality. Proc. - 2023 IEEE Int. Symp. Mix. Augment. Real. Adjunct, ISMAR-Adjunct 2023 2023, 468–473. [CrossRef]
- van Veen, S.C.; Zbozinek, T.D.; van Dis, E.A.M.; Engelhard, I.M.; Craske, M.G. Positive Mood Induction Does Not Reduce Return of Fear: A Virtual Reality Exposure Study for Public Speaking Anxiety. Behav. Res. Ther. 2024, 174, 104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dis, E.A.M.; Landkroon, E.; Hagenaars, M.A.; van der Does, F.H.S.; Engelhard, I.M. Old Fears Die Hard: Return of Public Speaking Fear in a Virtual Reality Procedure. Behav. Ther. 2021, 52, 1188–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, M.; Sakib, M.N.; Nirjhar, E.H.; Feng, K.; Behzadan, A.H.; Chaspari, T. Exploring Individual Differences of Public Speaking Anxiety in Real-Life and Virtual Presentations. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2022, 13, 1168–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cabrera, D.; Alais, D. Modelling Audiovisual Seat Preference in Virtual Concert Halls. Appl. Acoust. 2023, 212, 109589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorolli, C.; Naddei Grasso, E.; Stacchio, L.; Armandi, V.; Matteucci, G.; Marfia, G. Would You Rather Come to a Tango Concert in Theater or in VR? Aesthetic Emotions & Social Presence in Musical Experiences, Either Live, 2D or 3D. Comput. Human Behav. 2023, 149, 107910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Gonzalez, A.; Kobayashi, S.; Horie, R. A Multiplayer VR Live Concert with Information Exchange Through Feedback Modulated by EEG Signals. IEEE Trans. Human-Machine Syst. 2022, 52, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuanain, C.O.; O’Mahony, K.; Maye, K.; De Juan, A.; Clarke, J.; McCarthy, H.; Griew, M.; Tucker, S.M. Ré: Creating Immersive and Accessible Experiences of Irish Traditional Music in Virtual Reality. 2023 4th Int. Symp. Internet Sounds, ISIoS 2023 2023. [CrossRef]
- Beacco, A.; Oliva, R.; Cabreira, C.; Gallego, J.; Slater, M. Disturbance and Plausibility in a Virtual Rock Concert: A Pilot Study. Proc. - 2021 IEEE Conf. Virtual Real. 3D User Interfaces, VR 2021 2021, 538–545. [CrossRef]
- Yakura, H.; Goto, M. Enhancing Participation Experience in VR Live Concerts by Improving Motions of Virtual Audience Avatars. Proc. - 2020 IEEE Int. Symp. Mix. Augment. Reality, ISMAR 2020 2020, 555–565. [CrossRef]
- Bogicevic, V.; Liu, S.Q.; Seo, S.; Kandampully, J.; Rudd, N.A. Virtual Reality Is so Cool! How Technology Innovativeness Shapes Consumer Responses to Service Preview Modes. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2021, 93, 102806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Xiong, W.; Guo, Y. Design of a Virtual Reality-Based Mandala Painting Assisted Therapy System. Proc. - 2023 15th Int. Conf. Intell. Human-Machine Syst. Cybern. IHMSC 2023 2023, 245–249. [CrossRef]
- Riches, S.; Nicholson, S.L.; Fialho, C.; Little, J.; Ahmed, L.; McIntosh, H.; Kaleva, I.; Sandford, T.; Cockburn, R.; Odoi, C.; et al. Integrating a Virtual Reality Relaxation Clinic within Acute Psychiatric Services: A Pilot Study. Psychiatry Res. 2023, 329, 115477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zandstra, E.H.; Kaneko, D.; Dijksterhuis, G.B.; Vennik, E.; De Wijk, R.A. Implementing Immersive Technologies in Consumer Testing: Liking and Just-About-Right Ratings in a Laboratory, Immersive Simulated Café and Real Café. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 84, 103934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureephong, P.; Chernbumroong, S.; Intawong, K.; Jansukpum, K.; Wongwan, N.; Puritat, K. The Effect of Virtual Reality on Knowledge Acquisition and Situational Interest Regarding Library Orientation in the Time of Covid-19. J. Acad. Librariansh. 2023, 49, 102789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iakovides, N.; Lazarou, A.; Kyriakou, P.; Aristidou, A. Virtual Library in the Concept of Digital Twin. 2022 Int. Conf. Interact. Media, Smart Syst. Emerg. Technol. IMET 2022 - Proc. 2022, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Constantinescu, G.; Stamate, V.; Filimon, D.; Iftene, A. Book Reckon - The Use of Virtual Reality in the Creation of Libraries of the Future. 17th Int. Conf. Innov. Intell. Syst. Appl. INISTA 2023 - Proc. 2023, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Idris; Pratikto, H.; Herdiani, A.; Kurniawan, N.C.; Maharani, D. Assisting Smart Tourism Through Virtual Reality Apps for Tourists Destination in Indonesia. ICEEIE 2023 - Int. Conf. Electr. Electron. Inf. Eng. 2023, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, E.S.; Lesmana, C. Developing 360 Degree Virtual Tour of Dharma Rakhita Temple as a Cultural Learning Source. 2023 1st IEEE Int. Conf. Smart Technol. Adv. Smart Technol. Sustain. Well-Being, ICE-SMARTec 2023 2023, 151–154. [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Fahy, C.; Feng, G.; Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Shell, J. Digital Storytelling in Virtual Reality: Bridging the Virtual and Reality in Cultural Tourism at the Great Bay Area. Proc. - 2024 IEEE Int. Conf. Artif. Intell. Ext. Virtual Reality, AIxVR 2024 2024, 355–359. [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Lai, I.K.W. Identifying the Response Factors in the Formation of a Sense of Presence and a Destination Image from a 360-Degree Virtual Tour. J. Destin. Mark. Manag. 2021, 21, 100640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiris, R.; Wen, J.; Gheisari, M. IVisit – Practicing Problem-Solving in 360-Degree Panoramic Site Visits Led by Virtual Humans. Autom. Constr. 2021, 128, 103754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arago, N.M.; De Guzman, D. V.; De Leon, N.A.; Esteves, R.; Pepino, T.L.F.; Socorro, L.D.; Amado, T.M.; Amon, V.M.; Fernandez, E.O.; Quijano, J.F.C.; et al. MNLTour: A Web and Mobile Application for Virtual Tour System of Select Tourist Spots Around Manila Using 360-Degree Imagery and Virtual Reality Technology. 2022 IEEE 14th Int. Conf. Humanoid, Nanotechnology, Inf. Technol. Commun. Control. Environ. Manag. HNICEM 2022 2022, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Q. The Effectiveness of Social Elements in Virtual Reality Tourism: A Mental Imagery Perspective. J. Hosp. Tour. Manag. 2023, 56, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Wang, Z. The Application of Virtual Reality Technology in the Coordination and Interaction of Regional Economy and Culture in the Sustainable Development of Ecotourism. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mambu, J.Y.; Wahyudi, A.K.; Posumah, F. Aplikasi Simulasi Public Speaking Berbasis Virtual Reality. CogITo Smart J. 2019, 4, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mystakidis, S.; Christopoulos, A. Teacher Perceptions on Virtual Reality Escape Rooms for STEM Education. Inf. 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, M.; Kim, N.; Faith, M.S. Statistical Power as a Function of Cronbach Alpha of Instrument Questionnaire Items Data Analysis, Statistics and Modelling. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2015, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agung, B. Langkah Berat Bisnis Virtual Reality Di Indonesia. Available online: https://www.cnnindonesia.com/teknologi/20180125180607-185-271600/langkah-berat-bisnis-virtual-reality-di-indonesia (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- MonsterAR Kisaran Harga Virtual Reality Untuk Pengalaman Game Dan Film Yang Makin Maksimal. Available online: https://monsterar.net/2022/09/27/harga-virtual-reality/ (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Pramudita, B.A. Duh! Implementasi VR Di Indonesia Rendah, Penyebabnya. Available online: https://wartaekonomi.co.id/read259662/duh-implementasi-vr-di-indonesia-rendah-penyebabnya (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Chang, E.; Kim, H.T.; Yoo, B. Virtual Reality Sickness: A Review of Causes and Measurements. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2020, 36, 1658–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, B. Impact of Virtual Reality Cognitive and Motor Exercises on Brain Health. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozumder, M.A.I.; Sheeraz, M.M.; Athar, A.; Aich, S.; Kim, H.C. Overview: Technology Roadmap of the Future Trend of Metaverse Based on IoT, Blockchain, AI Technique, and Medical Domain Metaverse Activity. Int. Conf. Adv. Commun. Technol. ICACT 2022, 2022-Febru, 256–261. [CrossRef]
- Hwang, G.J.; Chien, S.Y. Definition, Roles, and Potential Research Issues of the Metaverse in Education: An Artificial Intelligence Perspective. Comput. Educ. Artif. Intell. 2022, 3, 100082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, S. Deep Learning Computer Vision Algorithms, Customer Engagement Tools, and Virtual Marketplace Dynamics Data in the Metaverse Economy. J. Self-Governance Manag. Econ. 2022, 10, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiler, R.; Fankhauser, D.; Keller, T. Reducing Food Waste With Virtual Reality (Vr) Training - a Prototype and a/B-Test in an Online Experiment. Proc. Int. Conf. e-Society 2022 Mob. Learn. 2022 2022, 179–186. [CrossRef]
- Peck, T.C.; Seinfeld, S.; Aglioti, S.M.; Slater, M. Putting Yourself in the Skin of a Black Avatar Reduces Implicit Racial Bias. Conscious. Cogn. 2013, 22, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambiama, M.; Polona, C.; Maria, N.; Pol, L. Van de Metaverse Opportunities, Risks and Policy Implications. Eur. Parliam. Res. Serv. 2022, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Talwar, S.; Kaur, P.; Escobar, O.; Lan, S. Virtual Reality Tourism to Satisfy Wanderlust without Wandering: An Unconventional Innovation to Promote Sustainability. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 152, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ÖZDEMİR, Ö.G.; ÖZDEMİR, M.T. The Role of COVID-19 on Sustainability in Tourism Industry Through Green Marketing Perspective and A Conceptual Model Proposal on Virtual Reality Tourism. Pazarlama ve Pazarlama … 2023, 221, 0–3. [Google Scholar]
- Scurati, G.W.; Bertoni, M.; Graziosi, S.; Ferrise, F. Exploring the Use of Virtual Reality to Support Environmentally Sustainable Behavior: A Framework to Design Experiences. Sustain. 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danarahmanto, P.A.; Primiana, I.; Azis, Y.; Kaltum, U. The Sustainable Performance of the Digital Start-up Company Based on Customer Participation, Innovation, and Business Model. Bus. Theory Pract. 2020, 21, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Faria, V.F.; Santos, V.P.; Zaidan, F.H. The Business Model Innovation and Lean Startup Process Supporting Startup Sustainability. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 181, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skala, A. Sustainable Transport and Mobility—Oriented Innovative Startups and Business Models. Sustain. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, K.; Profeta, A.; Märdian, A.; Hollah, C.; Schmiedeknecht, M.H.; Heinz, V. Transforming the German Food System: How to Make Start-Ups Great! Sustain. 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikoano Web2VR - Dynamically Translate HTML and CSS to A-Frame 3D World for Virtual Reality Available online: https://github.com/kikoano/web2vr?tab=readme-ov-file.
- Oliveira-Dias, D.; Kneipp, J.M.; Bichueti, R.S.; Gomes, C.M. Fostering Business Model Innovation for Sustainability: A Dynamic Capabilities Perspective. Manag. Decis. 2022, 60, 105–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
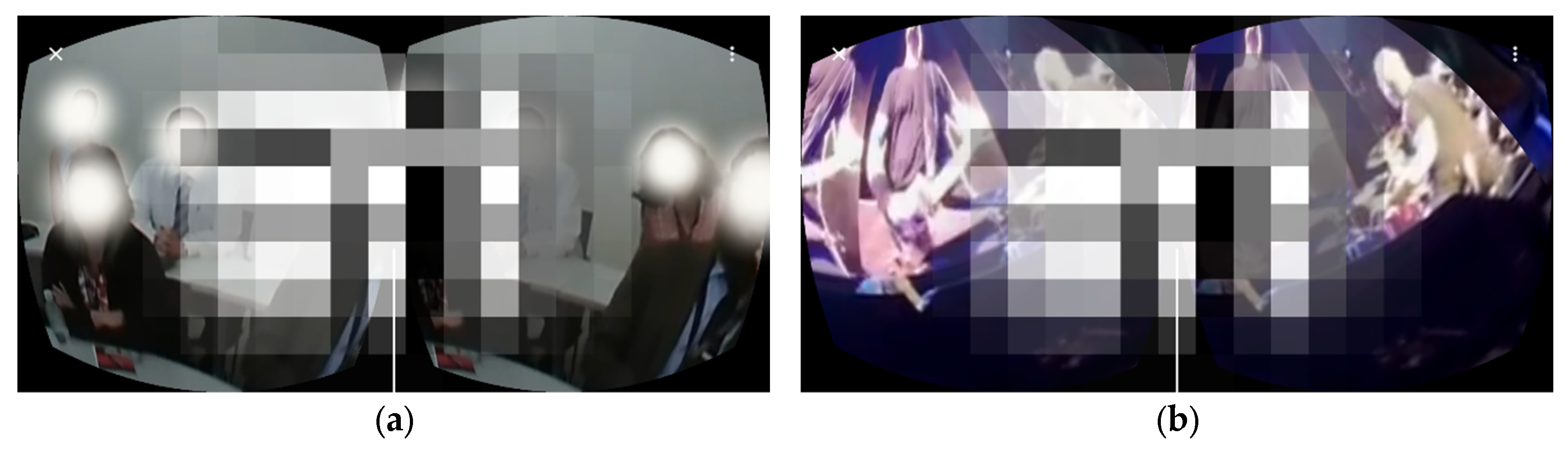
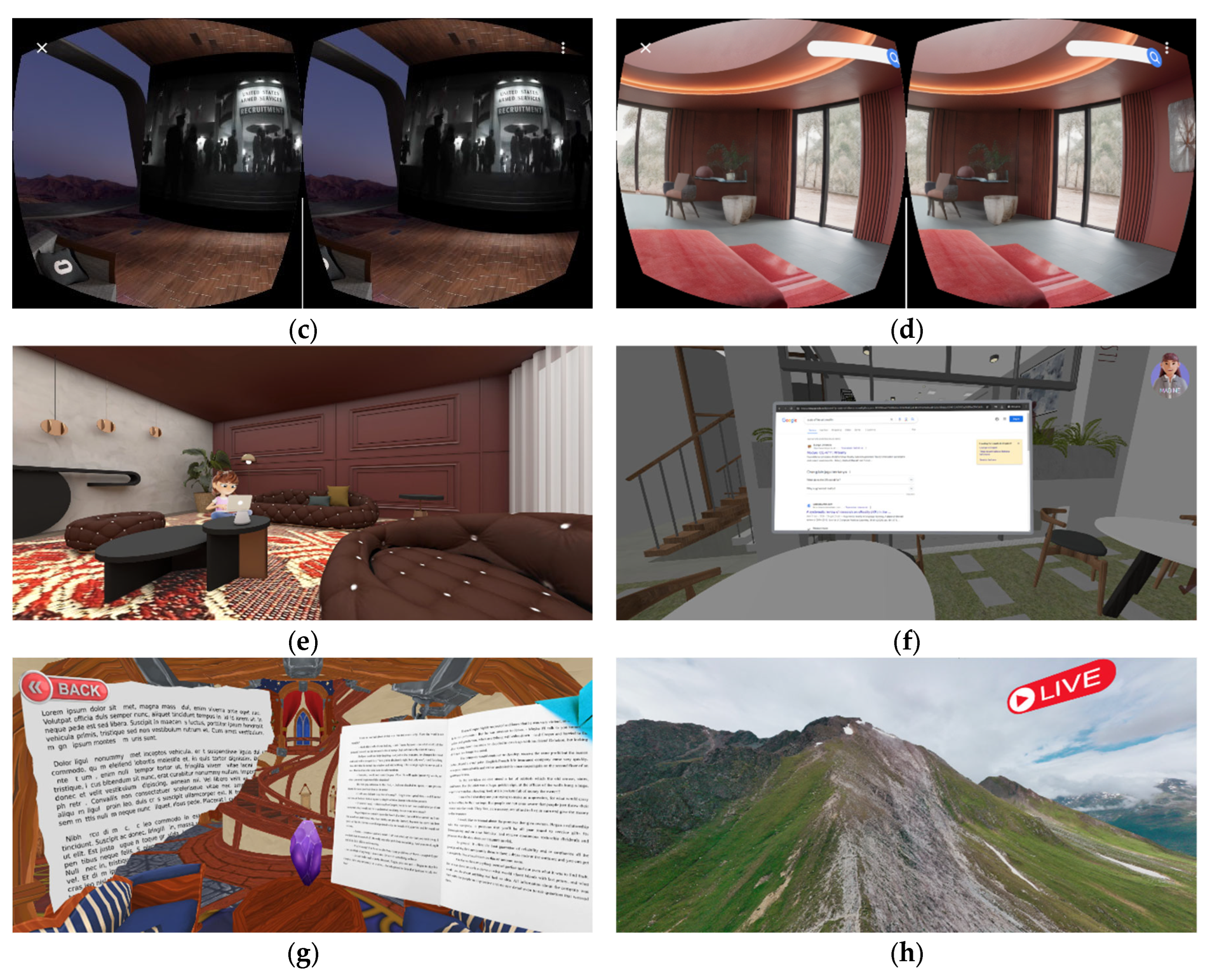



| Category | Aspect | Description | PMI | Relevance to SDGs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plus | Easy access to social environments | Reduces travel costs and time. | +3 | - |
| Global community | Potential to build a global community. | +3 | - | |
| Safe from physical disturbances | Provides social and entertainment experiences without the risk of disease transmission, such as COVID-19. | +3 | SDG 3 | |
| Support for SDG 12 | Reduces carbon footprint by decreasing travel and physical waste associated with operating physical cafés. | +3 | SDG 12 | |
| Minus | Lack of physical interaction | No direct physical contact. | -2 | - |
| Technological limitations | Requires good devices and internet connection. | -1 | - | |
| Interesting | Potential for creating a global community | Opportunities for new social interactions. | +3 | - |
| Market potential | Potential market for virtual café platforms. | +3 | - | |
| Total PMI | +15 | SDG 3, SDG 12 | ||
| Label | Placeholder/Options |
|---|---|
| Name (*) | Enter Name… |
| Email (*) | Enter Email… |
| Phone Number/WhatsApp | 08138619XXXX… |
| Age | 17 – 25 (default), 25 - 40 |
| Gender | Male (default), Female |
| Occupation | Student, Working Professional, Student who also works |
| Are you willing to be contacted for participation in the research? | Yes (default), No |
| How familiar are you with technology? | Highly familiar, Moderately familiar, Not familiar |
| Notes | (*) Required field, (default) Default answer |
| Score | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Irrelevant & Unimportant | Never experienced or known about it, and feel it does not need to be noticed and addressed. |
| 2 | Irrelevant & Somewhat Important | Never experienced or known about it, but if experienced or known, I would feel it somewhat important to be noticed and addressed. |
| 3 | Irrelevant & Important Enough | Never experienced or known about it, but if experienced or known, I would feel it quite important to be noticed and addressed. |
| 4 | Irrelevant & Important | Never experienced or known about it, but if experienced or known, I would feel it important to be noticed and addressed. |
| 5 | Relevant & Somewhat Important | I have experienced or known it occurs in the surrounding environment and feel it somewhat needs to be noticed and addressed. |
| 6 | Relevant & Important Enough | I have experienced or known it occurs in the surrounding environment and feel it is quite important to be noticed and addressed. |
| 7 | Relevant & Important | Have experienced or known it occurs in the surrounding environment and feel it is important to be noticed and addressed. |
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Research Hypothesis | Startups have great potential to leverage VR technology in addressing issues impacting the SDGs. |
| Research Question | How is the VR business model with use cases that are problem-solution fit and aligned with SDGs aspects? |
| Research Objective | To explore VR use cases based on solving actual problems related to the SDGs, in order to develop a business model design. |
| Outcome | Business Model Design. |
| Methodological Framework | Customer Discovery (adapted) in Customer Development, using a mixed approach (Quantitative and Qualitative). |
| Methodological Tools | SCAMPER, Plus Minus Interesting (PMI), Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD). |
| Data Collection Tools | Questionnaire applications (Google Forms), Video conferencing applications, and Instant messaging applications. |
| Data Collection Techniques | Questionnaires, Discussions, and Unstructured Interviews. |
| Testbed | WebXR-Based Functional Prototype, VR Headsets. |
| Documentation Tools | Sustainability Value Proposition Canvas (sVPC), Proposed Sustainable Business Model Canvas (sBMC). |
| Data Processing Tools | Statistical data processing application SPSS, Microsoft Excel, Generative AI ChatGPT. |
| Data Analysis Techniques | Descriptive Statistical Analysis, Narrative Analysis. |
| Code | Actors | Description | Field | Source of Ideas | SDGs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
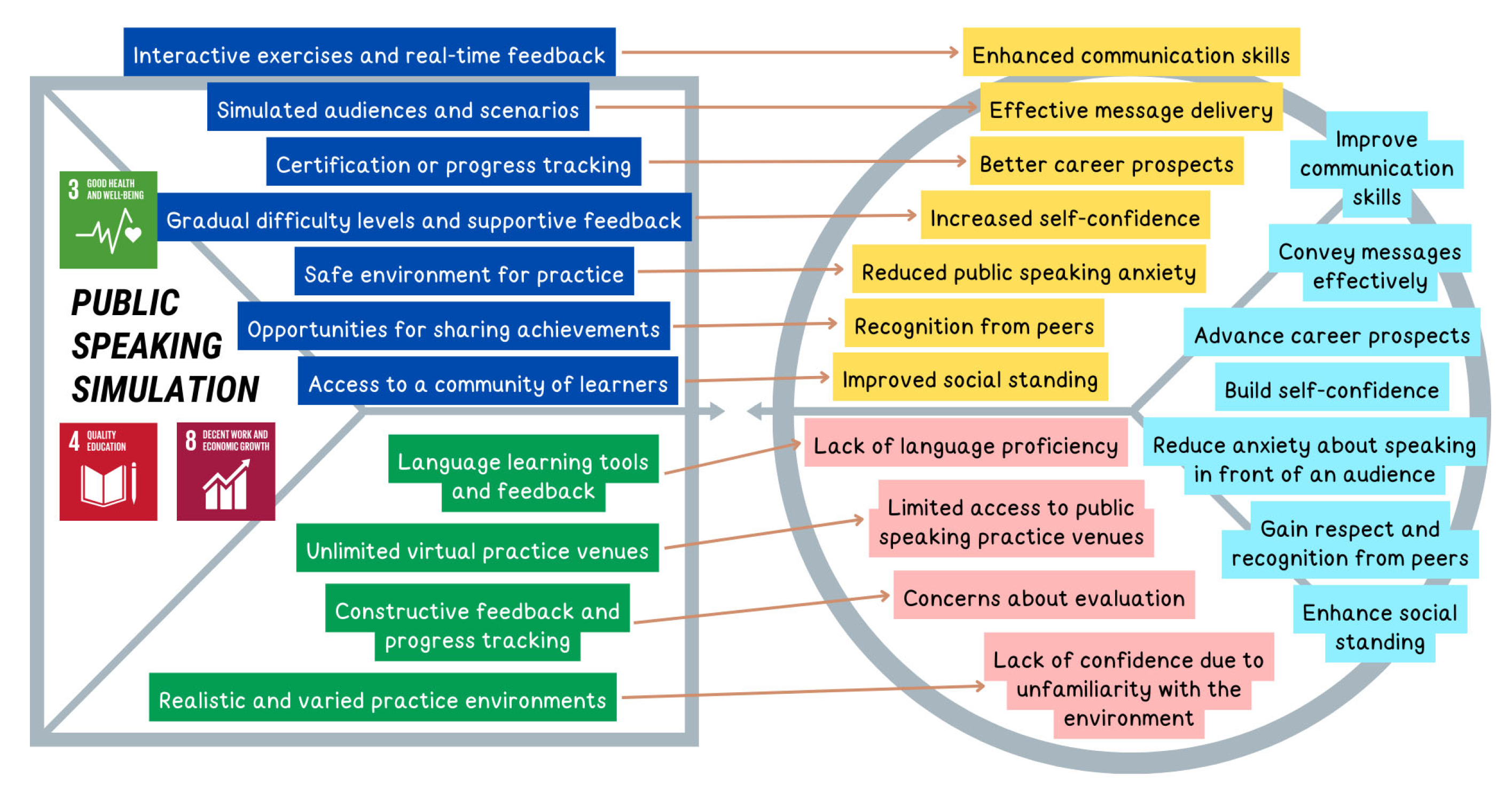
| U1 | Individual, Professional | Conducting public speaking training simulations | Training | [27,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59] | 3, 4, 8 |
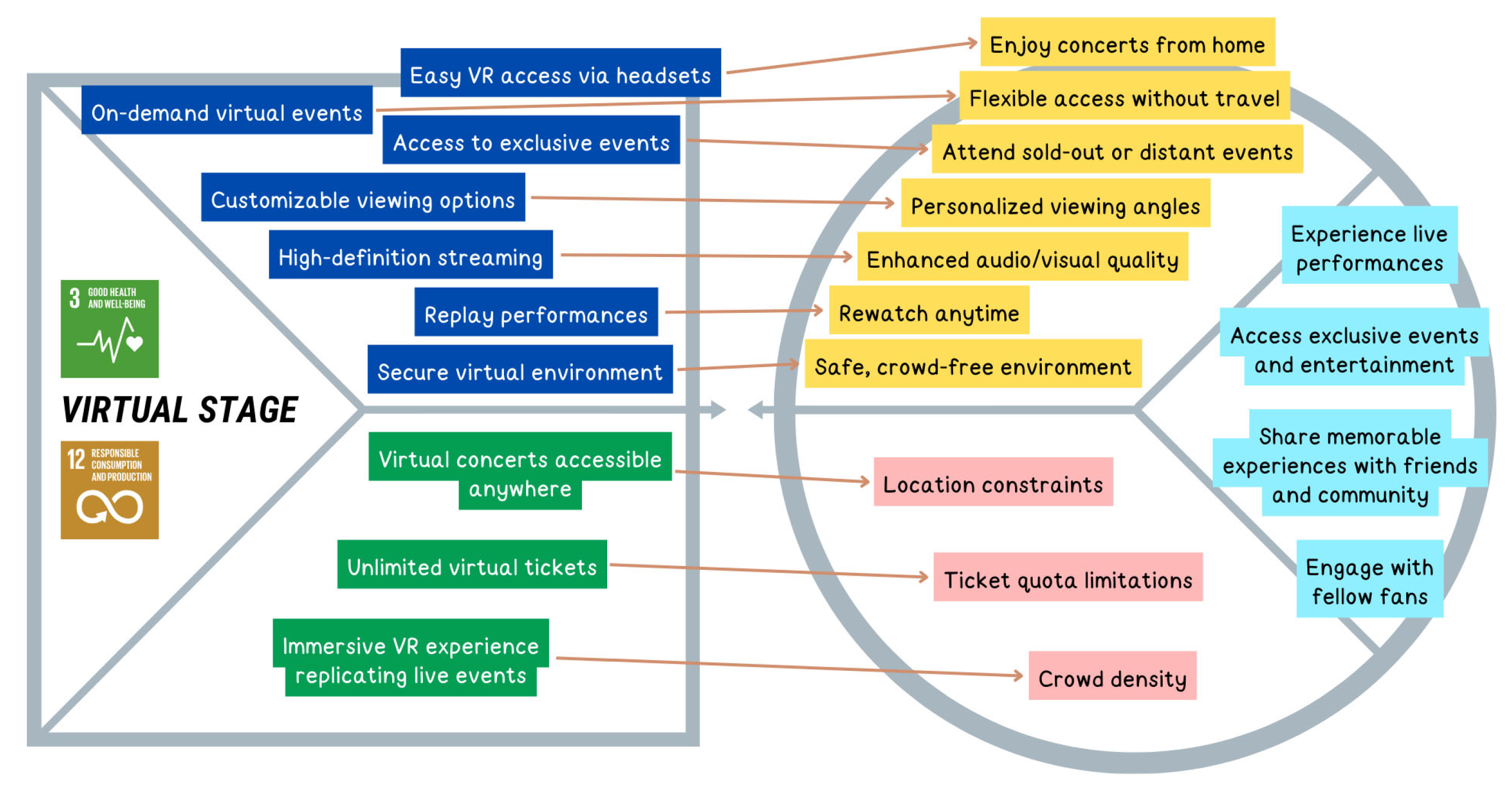
| U2 | Music fan | Attending concerts and festivals virtually | Entertainment | [60,61,62,63,64,65] | 3, 12 |
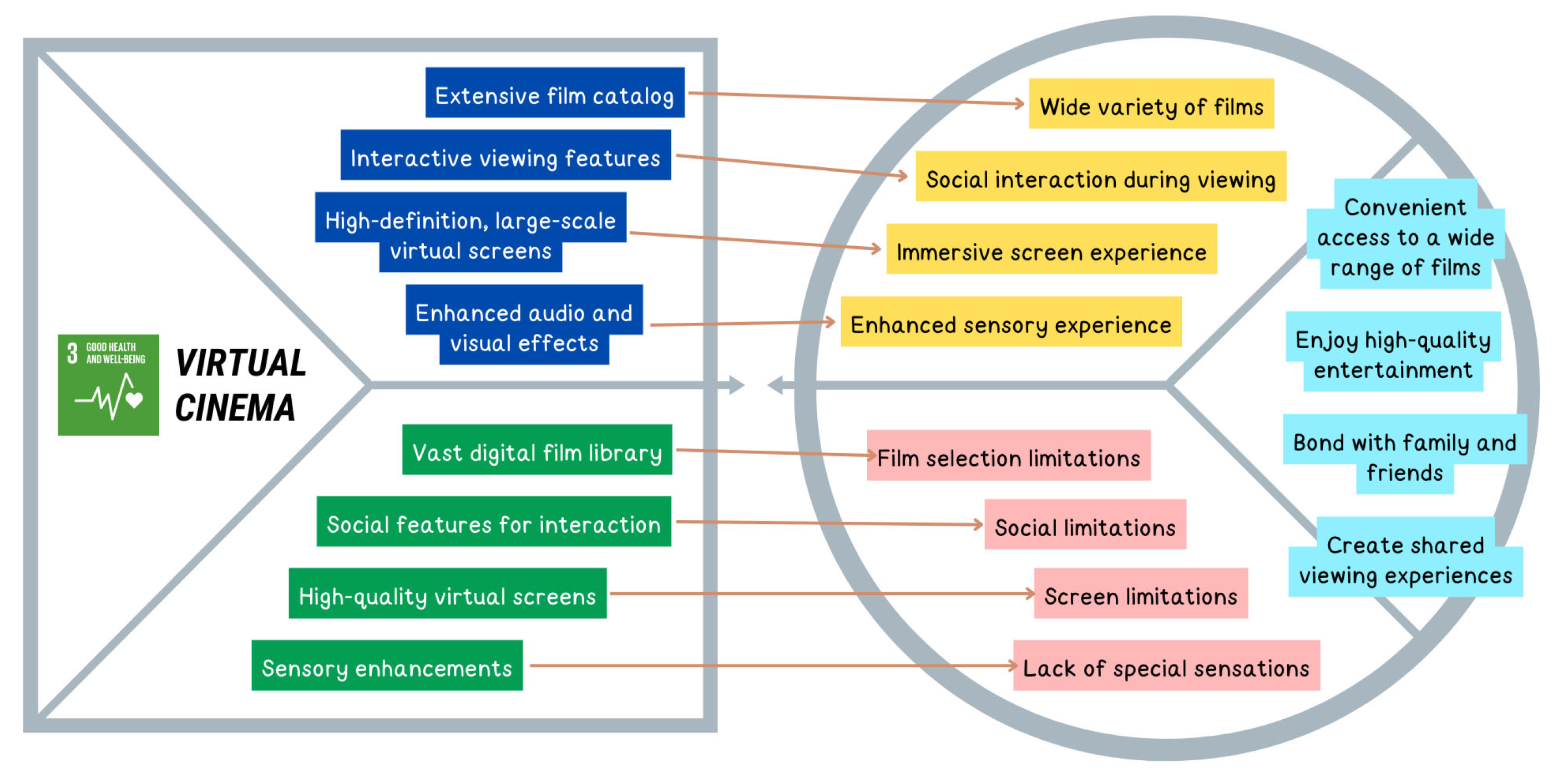
| U3 | Individual, Family, Community | Experiencing the sensation of watching in a movie theater | Entertainment | [26] | 3 |
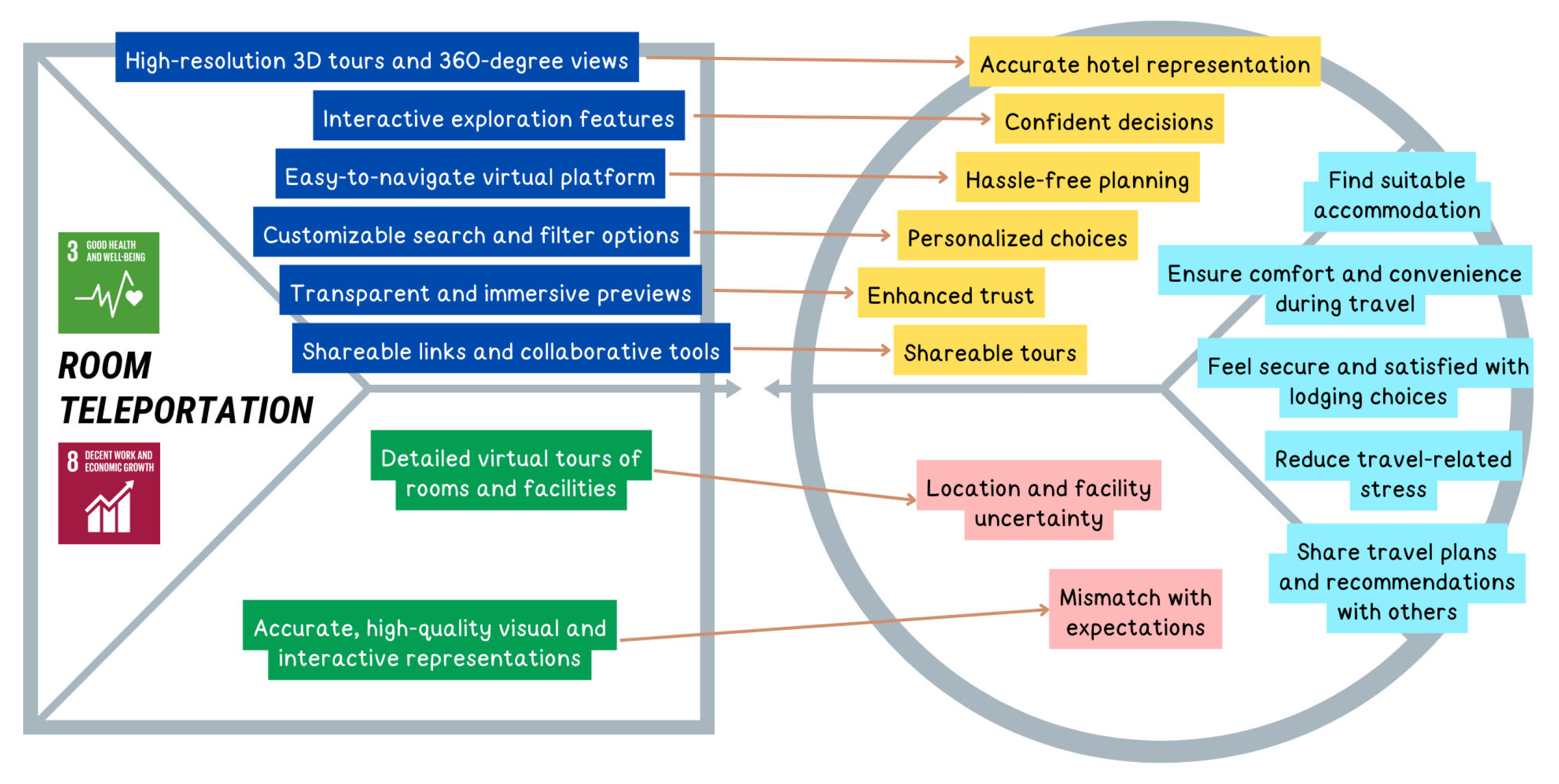
| U4 | Traveler | Exploring various hotels virtually for reservations | Tourism | [66] | 3, 8 |
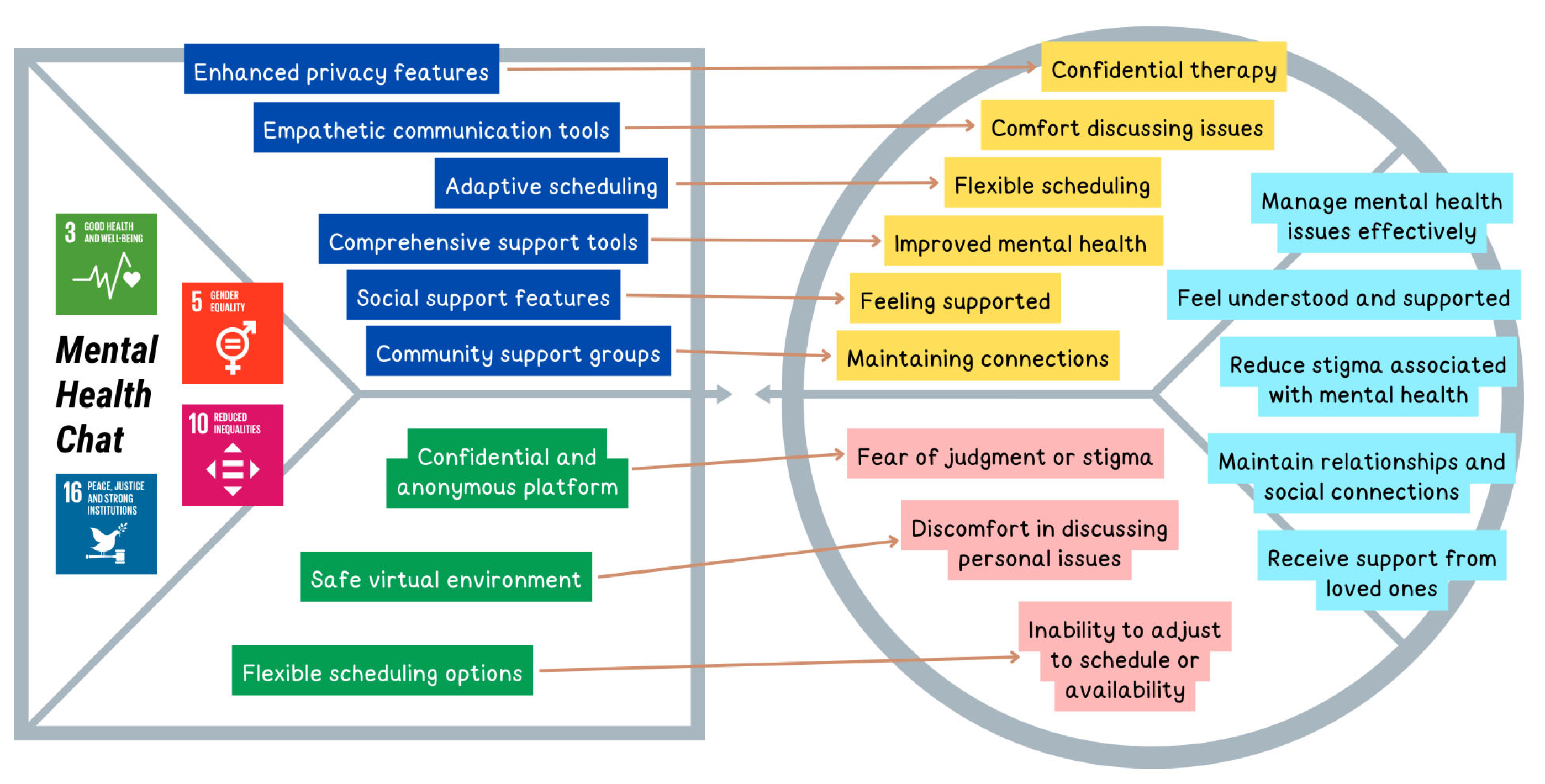
| U5 | Mental Patients | Conducting virtual private consultation sessions for mental health | Health | [24,25,67,68] | 3, 5, 10, 16 |
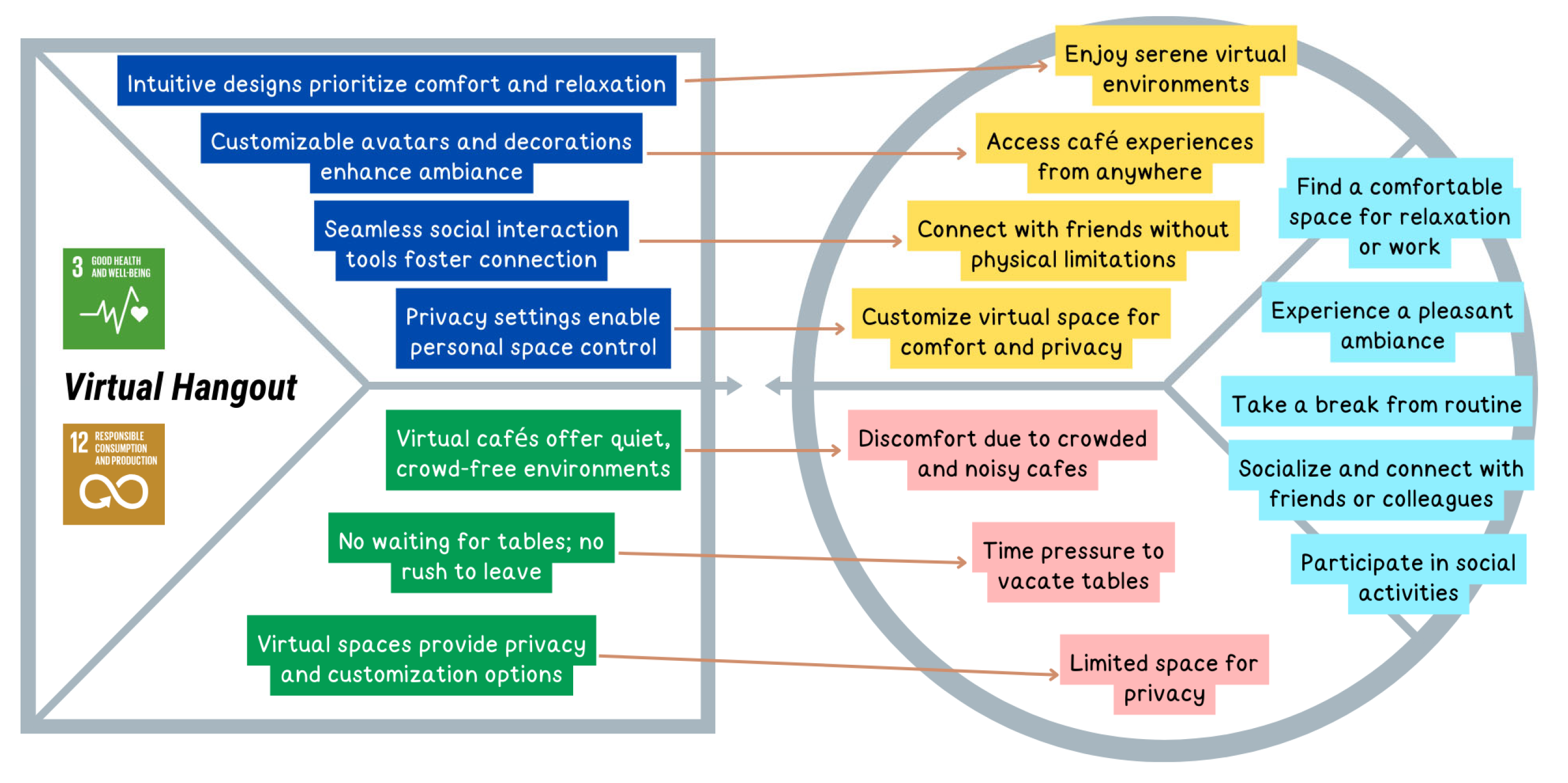
| U6 | Individual, Community | Hanging out in a virtual café | Entertainment | [36,69] | 3, 12 |
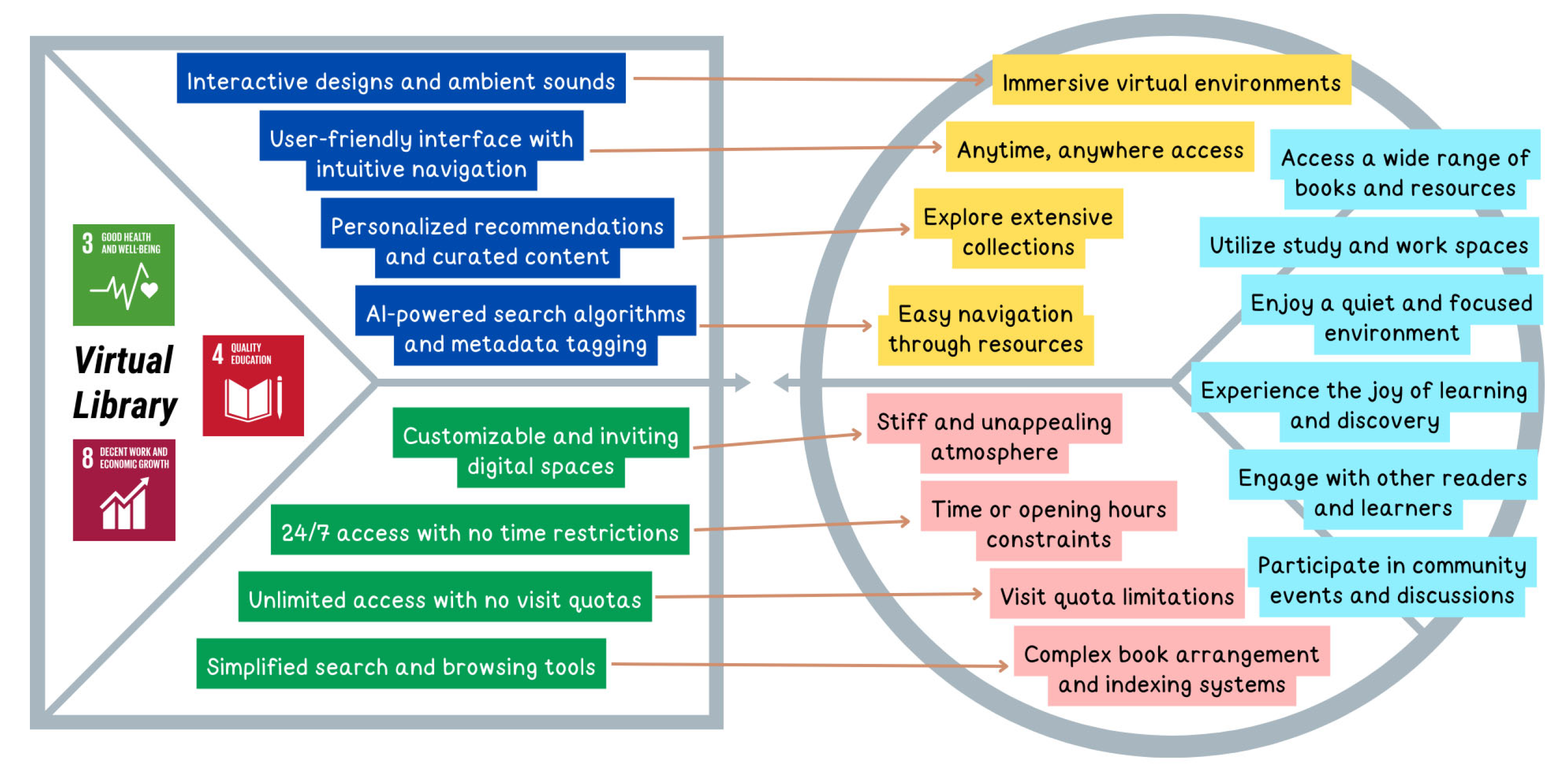
| U7 | Avid reader, Literacy activist | Exploring book collections and library facilities without the need for physical presence | Education | [23,70,71,72] | 3, 4, 8 |
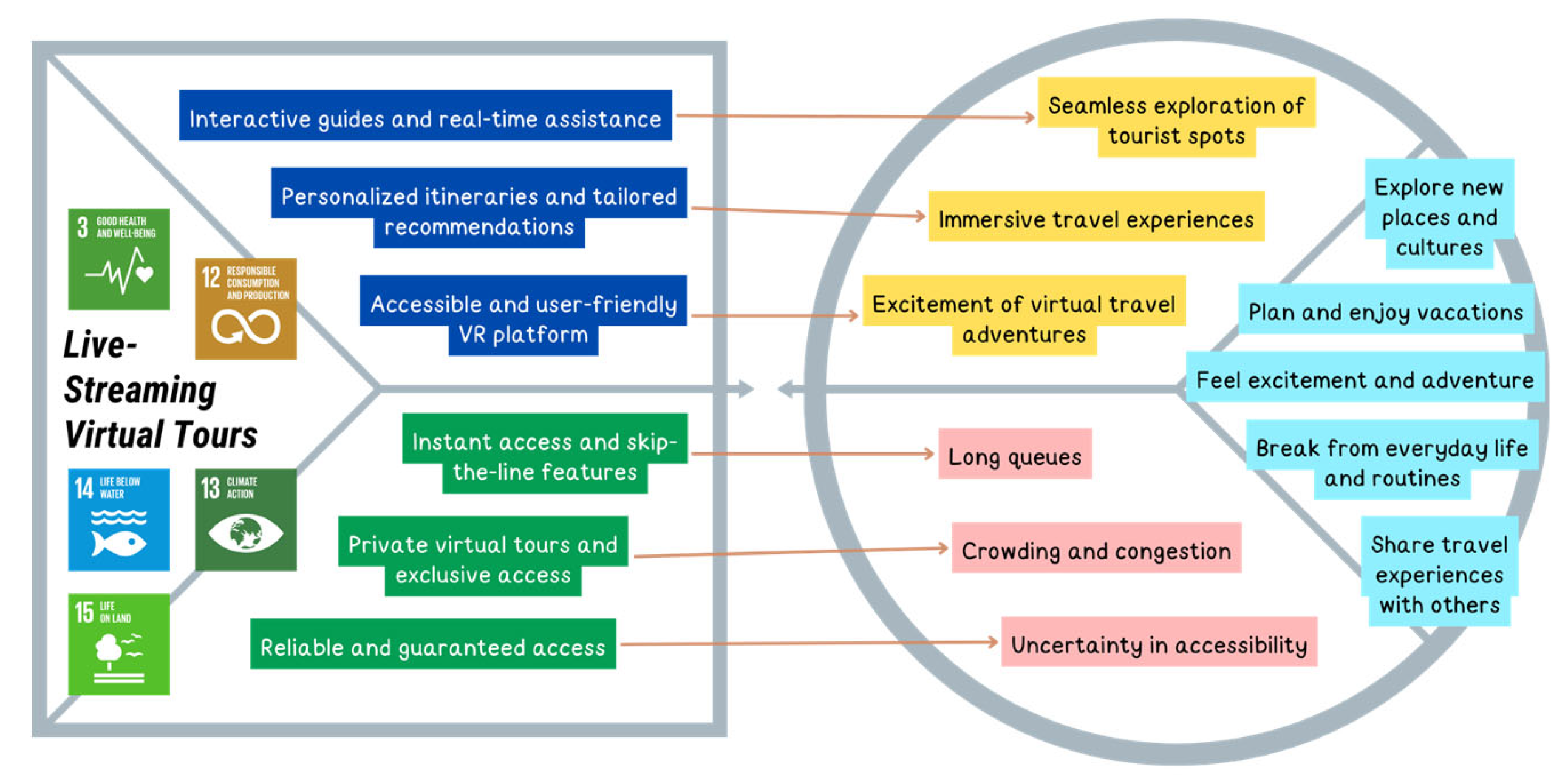
| U8 | Traveler, Surveyor | Reviewing tourist locations with a 360-degree panoramic view | Tourism | [73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80] | 3, 12, 13, 14 |
| Code | Needs | Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| U1J1 | Improve communication skills | Functional | U1 |
| U1J2 | Convey messages effectively | Functional | |
| U1J3 | Advance career prospects | Functional | |
| U1J4 | Build self-confidence | Emotional | |
| U1J5 | Reduce anxiety about speaking in front of an audience | Emotional | |
| U1J6 | Gain respect and recognition from peers | Social | |
| U1J7 | Enhance social standing | Social | |
| U2J1 | Experience live performances | Functional | U2 |
| U2J2 | Access exclusive events and entertainment | Functional | |
| U2J3 | Share memorable experiences with friends and community | Social | |
| U2J4 | Engage with fellow fans | Social | |
| U3J1 | Convenient access to a wide range of films | Functional | U3 |
| U3J2 | Enjoy high-quality entertainment | Functional | |
| U3J3 | Bond with family and friends | Social | |
| U3J4 | Create shared viewing experiences | Social | |
| U4J1 | Find suitable accommodation | Functional | U4 |
| U4J2 | Ensure comfort and convenience during travel | Functional | |
| U4J3 | Feel secure and satisfied with lodging choices | Emotional | |
| U4J4 | Reduce travel-related stress | Emotional | |
| U4J5 | Share travel plans and recommendations with others | Social | |
| U5J1 | Manage mental health issues effectively | Functional | U5 |
| U5J2 | Feel understood and supported | Emotional | |
| U5J3 | Reduce stigma associated with mental health | Emotional | |
| U5J4 | Maintain relationships and social connections | Social | |
| U5J5 | Receive support from loved ones | Social | |
| U6J1 | Find a comfortable space for relaxation or work | Functional | U6 |
| U6J2 | Experience a pleasant ambiance | Emotional | |
| U6J3 | Take a break from routine | Emotional | |
| U6J4 | Socialize and connect with friends or colleagues | Social | |
| U6J5 | Participate in social activities | Social | |
| U7J1 | Access a wide range of books and resources | Functional | U7 |
| U7J2 | Utilize study and work spaces | Functional | |
| U7J3 | Enjoy a quiet and focused environment | Emotional | |
| U7J4 | Experience the joy of learning and discovery | Emotional | |
| U7J5 | Engage with other readers and learners | Social | |
| U7J6 | Participate in community events and discussions | Social | |
| U8J1 | Explore new places and cultures | Functional | U8 |
| U8J2 | Plan and enjoy vacations | Functional | |
| U8J3 | Feel excitement and adventure | Emotional | |
| U8J4 | Break from everyday life and routines | Emotional | |
| U8J5 | Share travel experiences with others | Social |
| Issues | Code | Pains | Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Issues in Public Speaking | U1P1 | Lack of language proficiency | Functional | U1 |
| U1P2 | Limited access to public speaking practice venues [81] | Functional | ||
| U1P3 | Concerns about evaluation | Emotional | ||
| U1P4 | Lack of confidence due to unfamiliarity with the environment [81] | Emotional | ||
| Issues in Attending Concerts and Festivals | U2P1 | Location constraints | Functional | U2 |
| U2P2 | Ticket quota limitations | Functional | ||
| U2P3 | Crowd density | Social | ||
| Issues Related to Home Viewing Experience | U3P1 | Film selection limitations | Functional | U3 |
| U3P2 | Social limitations | Social | ||
| U3P3 | Screen limitations | Functional | ||
| U3P4 | Lack of special sensations | Functional | ||
| Issues in Hotel Reservations | U4P1 | Location and facility uncertainty | Functional | U4 |
| U4P2 | Mismatch with expectations | Functional | ||
| Issues Related to Mental Health Therapy | U5P1 | Fear of judgment or stigma | Emotional | U5 |
| U5P2 | Discomfort in discussing personal issues | Emotional | ||
| U5P3 | Inability to adjust to schedule or availability | Functional | ||
| Issues Related to Hanging Out at Cafes/Coffee Shops | U6P1 | Discomfort due to crowded and noisy cafes | Emotional | U6 |
| U6P2 | Time pressure to vacate tables | Emotional | ||
| U6P3 | Limited space for privacy | Emotional | ||
| Issues Related to Library Visits | U7P1 | Stiff and unappealing atmosphere | Emotional | U7 |
| U7P2 | Time or opening hours constraints | Functional | ||
| U7P3 | Visit quota limitations | Functional | ||
| U7P4 | Complex book arrangement and indexing systems | Functional | ||
| Issues Related to Visiting Tourist Locations | U8P1 | Long queues | Functional | U8 |
| U8P2 | Crowding and congestion | Social | ||
| U8P3 | Uncertainty in accessibility | Functional |
| Problems | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev. | Cronbach’s a | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1P1 | 2 | 7 | 6,24 | 0,83 | 0,84 | U1 |
| U1P2 | 3 | 7 | 5,96 | 1,03 | 0,84 | |
| U1P3 | 1 | 7 | 5,85 | 1,19 | 0,84 | |
| U1P4 | 1 | 7 | 5,81 | 1,1 | 0,84 | |
| U2P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,18 | 1,67 | 0,83 | U2 |
| U2P2 | 1 | 7 | 5,52 | 1,56 | 0,83 | |
| U2P3 | 1 | 7 | 5,44 | 1,59 | 0,83 | |
| U3P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,63 | 1,53 | 0,83 | U3 |
| U3P2 | 1 | 7 | 5 | 1,86 | 0,84 | |
| U3P3 | 1 | 7 | 4,93 | 1,91 | 0,83 | |
| U3P4 | 1 | 7 | 5,03 | 1,83 | 0,83 | |
| U4P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,9 | 1,28 | 0,83 | U4 |
| U4P2 | 1 | 7 | 6,06 | 1,19 | 0,84 | |
| U5P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,53 | 1,53 | 0,84 | U5 |
| U5P2 | 1 | 7 | 5,61 | 1,39 | 0,84 | |
| U5P3 | 1 | 7 | 5,44 | 1,48 | 0,83 | |
| U6P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,81 | 1,16 | 0,84 | U6 |
| U6P2 | 1 | 7 | 5,49 | 1,55 | 0,84 | |
| U6P3 | 1 | 7 | 5,49 | 1,51 | 0,84 | |
| U7P1 | 1 | 7 | 5,35 | 1,66 | 0,84 | U7 |
| U7P2 | 1 | 7 | 5,47 | 1,46 | 0,83 | |
| U7P3 | 1 | 7 | 5,38 | 1,38 | 0,83 | |
| U7P4 | 1 | 7 | 5,76 | 1,26 | 0,83 | |
| U8P1 | 4 | 7 | 6,09 | 0,81 | 0,84 | U8 |
| U8P2 | 1 | 7 | 6,13 | 0,99 | 0,84 | |
| U8P3 | 3 | 7 | 6,15 | 0,87 | 0,84 |
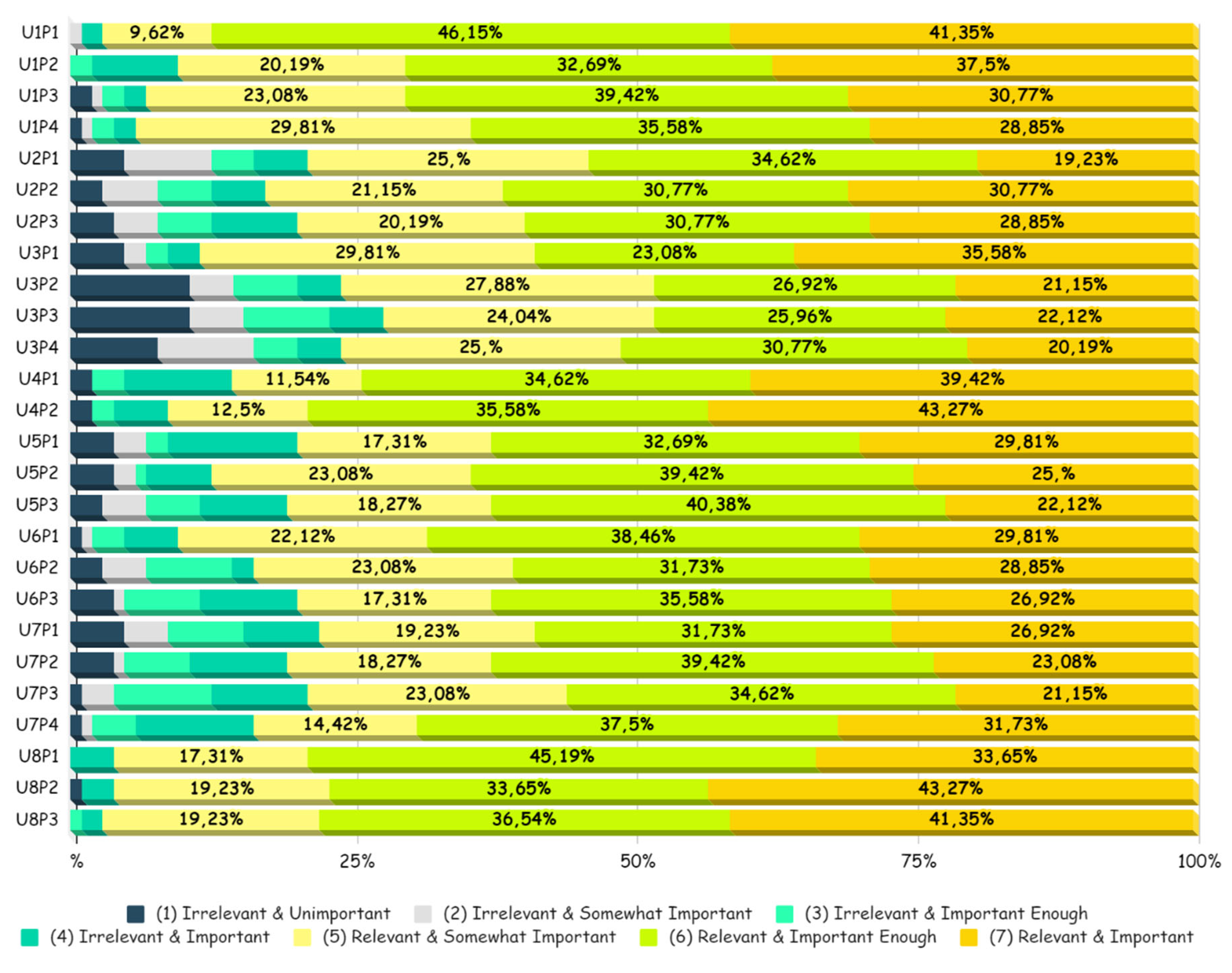
| Scores | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | Total Relevance | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Problems | |||||||||
| U1P1 | 0% | 0,96% | 0% | 1,92% | 9,62% | 46,15% | 41,35% | 97,12% | |
| U1P2 | 0% | 0% | 1,92% | 7,69% | 20,19% | 32,69% | 37,5% | 90,38% | |
| U1P3 | 1,92% | 0,96% | 1,92% | 1,92% | 23,08% | 39,42% | 30,77% | 93,27% | |
| U1P4 | 0,96% | 0,96% | 1,92% | 1,92% | 29,81% | 35,58% | 28,85% | 94,24% | |
| U2P1 | 4,81% | 7,69% | 3,85% | 4,81% | 25% | 34,62% | 19,23% | 78,85% | |
| U2P2 | 2,88% | 4,81% | 4,81% | 4,81% | 21,15% | 30,77% | 30,77% | 82,69% | |
| U2P3 | 3,85% | 3,85% | 4,81% | 7,69% | 20,19% | 30,77% | 28,85% | 79,81% | |
| U3P1 | 4,81% | 1,92% | 1,92% | 2,88% | 29,81% | 23,08% | 35,58% | 88,47% | |
| U3P2 | 10,58% | 3,85% | 5,77% | 3,85% | 27,88% | 26,92% | 21,15% | 75,95% | |
| U3P3 | 10,58% | 4,81% | 7,69% | 4,81% | 24,04% | 25,96% | 22,12% | 72,12% | |
| U3P4 | 7,69% | 8,65% | 3,85% | 3,85% | 25% | 30,77% | 20,19% | 75,96% | |
| U4P1 | 1,92% | 0% | 2,88% | 9,62% | 11,54% | 34,62% | 39,42% | 85,58% | |
| U4P2 | 1,92% | 0% | 1,92% | 4,81% | 12,5% | 35,58% | 43,27% | 91,35% | |
| U5P1 | 3,85% | 2,88% | 1,92% | 11,54% | 17,31% | 32,69% | 29,81% | 79,81% | |
| U5P2 | 3,85% | 1,92% | 0,96% | 5,77% | 23,08% | 39,42% | 25% | 87,50% | |
| U5P3 | 2,88% | 3,85% | 4,81% | 7,69% | 18,27% | 40,38% | 22,12% | 80,77% | |
| U6P1 | 0,96% | 0,96% | 2,88% | 4,81% | 22,12% | 38,46% | 29,81% | 90,39% | |
| U6P2 | 2,88% | 3,85% | 7,69% | 1,92% | 23,08% | 31,73% | 28,85% | 83,66% | |
| U6P3 | 3,85% | 0,96% | 6,73% | 8,65% | 17,31% | 35,58% | 26,92% | 79,81% | |
| U7P1 | 4,81% | 3,85% | 6,73% | 6,73% | 19,23% | 31,73% | 26,92% | 77,88% | |
| U7P2 | 3,85% | 0,96% | 5,77% | 8,65% | 18,27% | 39,42% | 23,08% | 80,77% | |
| U7P3 | 0,96% | 2,88% | 8,65% | 8,65% | 23,08% | 34,62% | 21,15% | 78,85% | |
| U7P4 | 0,96% | 0,96% | 3,85% | 10,58% | 14,42% | 37,5% | 31,73% | 83,65% | |
| U8P1 | 0% | 0% | 0% | 3,85% | 17,31% | 45,19% | 33,65% | 96,15% | |
| U8P2 | 0,96% | 0% | 0% | 2,88% | 19,23% | 33,65% | 43,27% | 96,15% | |
| U8P3 | 0% | 0% | 0,96% | 1,92% | 19,23% | 36,54% | 41,35% | 97,12% | |
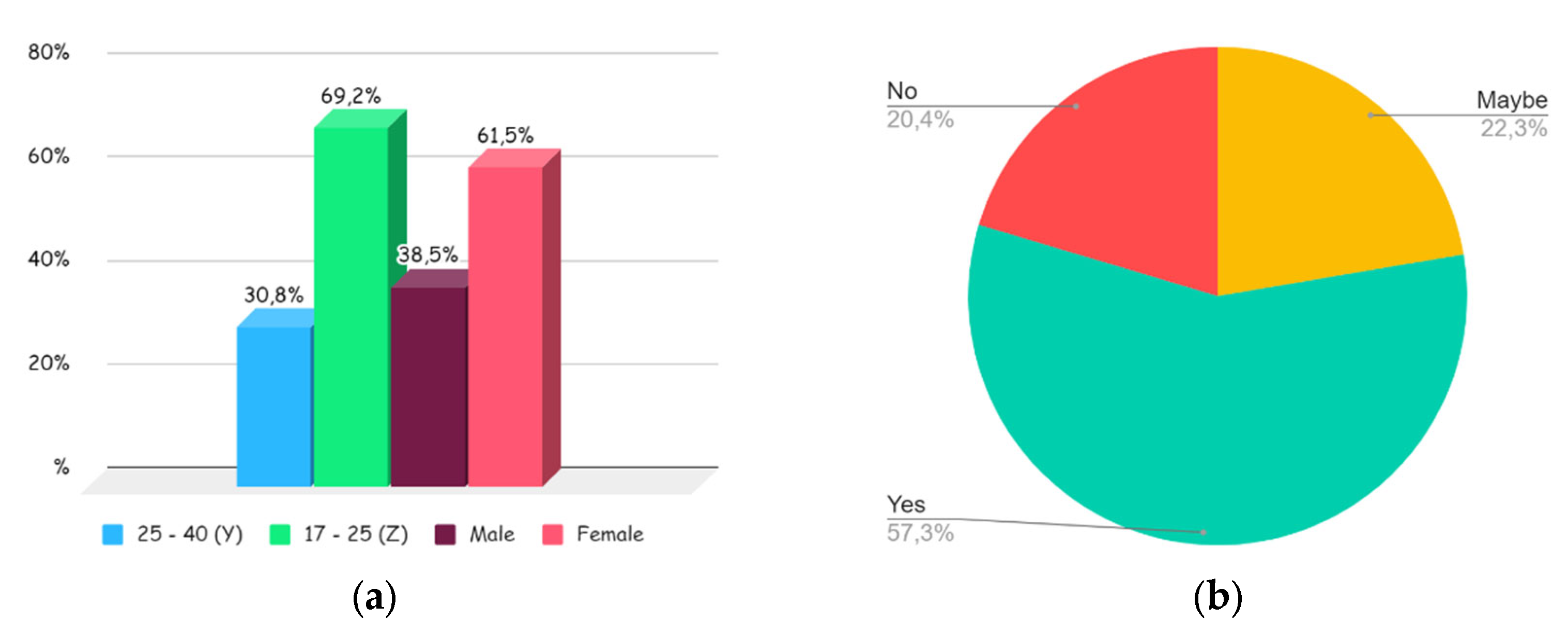
| Characteristic | Generation Z (17-25 years) | Generation Y (25-40 years) | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| Number of Respondents | 72 | 69.2 | 32 | 30.8 | 104 | 100 |
| Gender Distribution | ||||||
|
48 | 46.2 | 16 | 15.4 | 64 | 61.5 |
|
24 | 23.1 | 16 | 15.4 | 40 | 38.5 |
| Primary Activity | ||||||
|
65 | 90.3 | 5 | 15.6 | 70 | 67.3 |
|
3 | 4.2 | 22 | 68.8 | 25 | 24.0 |
|
4 | 5.6 | 5 | 15.6 | 9 | 8.7 |
| Familiarity with Technology | ||||||
|
54 | 75.0 | 24 | 75.0 | 78 | 75.0 |
|
18 | 75.0 | 8 | 25.0 | 26 | 25.0 |
|
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Need | Evidence | Average | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improve communication skills | 93.75% Young generation experience issues in public speaking | 97.12% acknowledge the inability to organize sentences properly and neatly in speaking, delivering messages effectively, and following the presentation flow well | U1P1 |
| Convey messages effectively | |||
| Advance career prospects | 90.38% acknowledge the lack of access to suitable places or facilities for practicing public speaking | U1P2 | |
| Build self-confidence | |||
| Reduce anxiety about speaking in front of an audience | 93.27% acknowledge concerns about how the audience will judge or fear criticism, thus disturbing focus and confidence when speaking in public | U1P3 | |
| Gain respect and recognition from peers | 94.24% acknowledge discomfort or anxiety due to unfamiliarity with the space, audience, or situation faced | U1P4 | |
| Enhance social standing | |||
| Experience live performances | 80.45% Experience issues in attending concerts and festivals | 78.85% acknowledge concerts and festivals only held in specific locations or far from home, thus posing barriers to attendance | U2P1 |
| Access exclusive events and entertainment | 82.69% acknowledge unfair ticket distribution, leaving few tickets available for purchase | U2P2 | |
| Share memorable experiences with friends and community | 79.81% acknowledge high crowd density at concerts and festivals making the experience uncomfortable | U2P3 | |
| Engage with fellow fans | |||
| Convenient access to a wide range of films | 78.13% Experience issues related to watching at home | 88.47% acknowledge some films not available on a streaming platform or only available at an additional cost | U3P1 |
| Enjoy high-quality entertainment | 75.95% acknowledge the experience of watching movies at home may not be as intense as watching with friends or family at the cinema | U3P2 | |
| Bond with family and friends | 72.12% acknowledge the size of the television screen at home is not as large as the cinema screen, reducing the intensity of the movie-watching experience | U3P3 | |
| Create shared viewing experiences | 75.96% acknowledge special effects like IMAX or 3D cannot be fully replicated when watching at home | U3P4 | |
| Find suitable accommodation | 88.47% Experience issues in hotel bookings | 85.58% acknowledge inadequate information about the location, facilities, or room conditions of hotels on booking sites | U4P1 |
| Ensure comfort and convenience during travel | 91.35% acknowledge photos, videos, and hotel descriptions not always reflecting reality, causing discrepancies with expectations | U4P2 | |
| Feel secure and satisfied with lodging choices | |||
| Reduce travel-related stress | |||
| Share travel plans and recommendations with others | |||
| Manage mental health issues effectively | 82.69% Experience issues related to mental health therapy | 79.81% acknowledge embarrassment or fear of rejection when seeking mental health therapy, hindering the pursuit or expression of such needs | U5P1 |
| Feel understood and supported | 87.50% acknowledge feeling uncomfortable or embarrassed about opening up about personal issues to therapists they have not known long | U5P2 | |
| Reduce stigma associated with mental health | 80.77% acknowledge busy or irregular schedules making it difficult to attend therapy sessions regularly | U5P3 | |
| Maintain relationships and social connections | |||
| Receive support from loved ones | |||
| Find a comfortable space for relaxation or work | 84.62% Experience issues in hanging out at cafes/coffee shops | 90.39% acknowledge noise and crowds in cafes making it difficult to enjoy leisure time or converse with friends | U6P1 |
| Experience a pleasant ambiance | 83.66% acknowledge some cafes impose time limits on table use, creating pressure to vacate seats quickly | U6P2 | |
| Take a break from routine | |||
| Socialize and connect with friends or colleagues | 79.81% acknowledge some cafes have spaces with less privacy, reducing comfort in speaking or behaving according to personality | U6P3 | |
| Participate in social activities | |||
| Access a wide range of books and resources | 80.29% Experience issues related to library visits | 77.88% acknowledge rigid and unappealing library atmospheres may reduce interest in visiting or using facilities | U7P1 |
| Utilize study and work spaces | 80.77% acknowledge limited or inconvenient library opening hours that make it difficult to visit | U7P2 | |
| Enjoy a quiet and focused environment | |||
| Experience the joy of learning and discovery | 78.85% acknowledge limited visit quotas or crowded visitors making it difficult to enter or use library facilities comfortably | U7P3 | |
| Engage with other readers and learners | |||
| Participate in community events and discussions | 83.65% acknowledge the complexity of book arrangement systems making it difficult to find or navigate in the library | U7P4 | |
| Explore new places and cultures | 96.47% Experience issues in visiting tourist locations | 96.15% acknowledge long queues to enter tourist locations wasting time and lowering visitor experience | U8P1 |
| Plan and enjoy vacations | |||
| Feel excitement and adventure | 96.15% acknowledge crowded visitors and uncomfortable physical conditions making it difficult to enjoy tourist locations optimally | U8P2 | |
| Break from everyday life and routines | |||
| Share travel experiences with others | 97.12% acknowledge difficult tourist location access for people with physical disabilities or disabilities, limiting accessibility | U8P3 |
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Development Instruments | A-Frame WebXR framework, Next.js, Sketchfab |
| Channel | Website |
| Operating system | Android, iOS |
| End User Devices | Mobile devices (Smartphones), VR Headsets - Virtual Reality 3D Glasses Smartphone Headsets (B*b* VR Z6) |
| Participants | 6 participants represented the Generation Y group, 6 participants represented the Generation Z group, a total of 12 participants |
| Findings | Description |
|---|---|
| Response Variation | Responses from participants varied, from impressive to critical. |
| Physical Endurance | On average, participants were able to use the VR headset for around 4 minutes without stopping. |
| Side Effects Nausea | Two participants experienced nausea, due to delays in graphical movement or differences in viewing angles. |
| No. | Occupation | VR Experience | Interest (1-5) | Comments | Assumption Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Student | Yes | 4 | Device rental costs may need consideration | Potential for U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, and U8 if device cost issues are addressed. |
| 2 | Student | No | 2 | Not interested in virtual concerts | Low interest in U2, focus on other aspects like U1, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, U8. |
| 3 | Employee | Yes | 3 | Likes the idea of virtual libraries | High potential for U7, also introduce to U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U8. |
| 4 | Student | No | 1 | Prefers watching movies in traditional cinemas | Very low interest in U3, focus on other aspects like U1, U2, U4, U5, U6, U7, U8. |
| 5 | Student | No | 2 | Not yet interested in online mental health consultations | Low interest in U5, focus on other aspects like U1, U2, U3, U4, U6, U7, U8. |
| 6 | Student | Yes | 4 | Needs more exclusive content | Potential for U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, and U8 if exclusive content is increased. |
| 7 | Employee | No | 3 | Subscription costs may need further consideration | High potential if subscription costs are addressed, especially for U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, U8. |
| 8 | Employee | No | 2 | Prefers exploring tourist locations in person | Low interest in U8, focus on other aspects like U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7. |
| 9 | Student | Yes | 3 | Likes the concept of virtual cafes | High potential for U6, also introduce to U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U7, U8. |
| 10 | Employee | No | 2 | Mental health consultations need higher privacy | Low interest in U5, focus on other aspects like U1, U2, U3, U4, U6, U7, U8. |
| 11 | Student | Yes | 4 | Open to new experiences | Potential for U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, and U8. |
| 12 | Employee | No | 3 | Needs improved image quality | High potential if image quality is improved, especially for U1, U2, U3, U4, U5, U6, U7, U8. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





