Submitted:
19 June 2024
Posted:
20 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Chemicals
Cell Culture
1H-NMR Analysis
Protein Estimation
Cell Survival
Enzymatic Estimation of 3-Hydroxybutyrate Level
Statistical Analysis
Results
Discussion
Acknowledgement:
Data Availability
Cometing interests:
Funding
References
- Beard, E.; Lengacher, S.; Dias, S.; Magistretti, P.J.; Finsterwald, C. Astrocytes as Key Regulators of Brain Energy Metabolism: New Therapeutic Perspectives. Front Physiol 2022, 12, 825816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bélanger, M.; Allaman, I.; Magistretti, P.J. Brain Energy Metabolism: Focus on Astrocyte-Neuron Metabolic Cooperation. Cell Metabolism 2011, 14, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonvento, G.; Bolaños, J.P. Astrocyte-Neuron Metabolic Cooperation Shapes Brain Activity. Cell Metabolism 2021, 33, 1546–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamprecht, B.; Verleysdonk, S.; Wiesinger, H. Enzymes of Carbohydrate and Energy Metabolism. In Neuroglia; Kettenmann, H., Ransom, B.R., Eds.; Oxford University Press, 2004; p. 0 ISBN 978-0-19-515222-7.
- Verkhratsky, A.; Semyanov, A. The Great Astroglial Metabolic Revolution: Mitochondria Fuel Astrocyte Homeostatic Support and Neuroprotection. Cell Calcium 2022, 104, 102583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The Blood–Brain Barrier. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardridge, W.M. Brain Metabolism: A Perspective from the Blood-Brain Barrier. Physiol Rev 1983, 63, 1481–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.D.; Ye, M.; Levy, A.F.; Rothstein, J.D.; Bergles, D.E.; Searson, P.C. The Blood-Brain Barrier: An Engineering Perspective. Front. Neuroeng. 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, Q.R. Transport of Glutamate and Other Amino Acids at the Blood-Brain Barrier. The Journal of Nutrition 2000, 130, 1016S–1022S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaragozá, R. Transport of Amino Acids Across the Blood-Brain Barrier. Front Physiol 2020, 11, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yudkoff, M.; Daikhin, Y.; Nissim, I.; Horyn, O.; Luhovyy, B.; Lazarow, A.; Nissim, I. Brain Amino Acid Requirements and Toxicity: The Example of Leucine. The Journal of Nutrition 2005, 135, 1531S–1538S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, M.E.; Hutson, S.M. BCAA Metabolism and NH3 Homeostasis. In The Glutamate/GABA-Glutamine Cycle; Schousboe, A., Sonnewald, U., Eds.; Advances in Neurobiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-45094-0. [Google Scholar]
- Griffin, J.W.D.; Bradshaw, P.C. Amino Acid Catabolism in Alzheimer’s Disease Brain: Friend or Foe? Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2017, 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperringer, J.E.; Addington, A.; Hutson, S.M. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Metabolism. Neurochem Res 2017, 42, 1697–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Wu, G. Metabolism of Amino Acids in the Brain and Their Roles in Regulating Food Intake. In Amino Acids in Nutrition and Health; Wu, G., Ed.; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; ISBN 978-3-030-45327-5. [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo, C.; Andersen, J.V.; Vinten, K.T.; Pinborg, L.H.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; Freude, K.K.; Aldana, B.I. Functional Metabolic Mapping Reveals Highly Active Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism in Human Astrocytes, Which Is Impaired in iPSC-Derived Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2021, 13, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryawan, A.; Hawes, J.W.; Harris, R.A.; Shimomura, Y.; Jenkins, A.E.; Hutson, S.M. A Molecular Model of Human Branched-Chain Amino Acid Metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998, 68, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Branched-Chain Amino Acids and Brain Function. The Journal of Nutrition 2005, 135, 1539S–1546S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixel, M.G.; Engelmann, J.; Willker, W.; Hamprecht, B.; Leibfritz, D. Metabolism of [U-(13)C]Leucine in Cultured Astroglial Cells. Neurochem Res 2004, 29, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murín, R.; Mohammadi, G.; Leibfritz, D.; Hamprecht, B. Glial Metabolism of Isoleucine. Neurochemical Research 2009, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murín, R.; Mohammadi, G.; Leibfritz, D.; Hamprecht, B. Glial Metabolism of Valine. Neurochemical Research 2009, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixel, M.G.; Hamprecht, B. Generation of Ketone Bodies from Leucine by Cultured Astroglial Cells. J Neurochem 1995, 65, 2450–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixel, M.G.; Hamprecht, B. Immunocytochemical Localization of Beta-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase in Astroglial Cells and Neurons in Culture. J Neurochem 2000, 74, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murín, R.; Verleysdonk, S.; Rapp, M.; Hamprecht, B. Immunocytochemical Localization of 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase in Cultured Ependymal, Microglial and Oligodendroglial Cells. Journal of Neurochemistry 2006, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murín, R.; Schaer, A.; Kowtharapu, B.S.; Verleysdonk, S.; Hamprecht, B. Expression of 3-Hydroxyisobutyrate Dehydrogenase in Cultured Neural Cells. Journal of Neurochemistry 2008, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Serrano, A.M.; Duarte, J.M.N. Brain Metabolism Alterations in Type 2 Diabetes: What Did We Learn From Diet-Induced Diabetes Models? Front Neurosci 2020, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.J.; Jiang, L.; Hamza, M.; Rangel, E.S.; Dai, F.; Belfort-DeAguiar, R.; Parikh, L.; Koo, B.B.; Rothman, D.L.; Mason, G.; et al. Blunted Rise in Brain Glucose Levels during Hyperglycemia in Adults with Obesity and T2DM. JCI Insight 2017, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneville, R.; den Hertog, H.M.; Güiza, F.; Gunst, J.; Derese, I.; Wouters, P.J.; Brouland, J.-P.; Polito, A.; Gray, F.; Chrétien, F.; et al. Impact of Hyperglycemia on Neuropathological Alterations during Critical Illness. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism 2012, 97, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sickmann, H.M.; Waagepetersen, H.S. Effects of Diabetes on Brain Metabolism – Is Brain Glycogen a Significant Player? Metab Brain Dis 2015, 30, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Bai, M.; Xie, X.; Wang, J.; Weng, C.; Dai, H.; Chen, J.; Han, F.; Lin, W. Impaired Amino Acid Metabolism and Its Correlation with Diabetic Kidney Disease Progression in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Kráľová Trančíková, A.; Baranovičová, E.; Šofranko, J.; Hatok, J.; Kowtharapu, B.S.; Galanda, T.; Dobrota, D.; Kubatka, P.; Busselberg, D.; et al. Expression of 3-Methylcrotonyl-CoA Carboxylase in Brain Tumors and Capability to Catabolize Leucine by Human Neural Cancer Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondáš, E.; Kráľová Trančíková, A.; Šofranko, J.; Majerová, P.; Lučanský, V.; Dohál, M.; Kováč, A.; Murín, R. The Presence of Pyruvate Carboxylase in the Human Brain and Its Role in the Survival of Cultured Human Astrocytes. Physiol Res 2023, 72, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schousboe, A.; Westergaard, N.; Sonnewald, U.; Petersen, S.B.; Huang, R.; Peng, L.; Hertz, L. Glutamate and Glutamine Metabolism and Compartmentation in Astrocytes. Dev Neurosci 1993, 15, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.J. Neuron-Glia Metabolic Coupling and Plasticity. J Exp Biol 2006, 209, 2304–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Sorg, O.; Yu, N.; Martin, J.-L.; Pellerin, L. Neurotransmitters Regulate Energy Metabolism in Astrocytes: Implications for the Metabolic Trafficking between Neural Cells. Dev Neurosci 1993, 15, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magistretti, P.J.; Allaman, I. Lactate in the Brain: From Metabolic End-Product to Signalling Molecule. Nat Rev Neurosci 2018, 19, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, R.A.; Benington, J.H. Astrocyte Glucose Metabolism under Normal and Pathological Conditions in Vitro. Dev Neurosci 1996, 18, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesinger, H.; Hamprecht, B.; Dringen, R. Metabolic Pathways for Glucose in Astrocytes. Glia 1997, 21, 22–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walz, W.; Mukerji, S. Lactate Production and Release in Cultured Astrocytes. Neuroscience Letters 1988, 86, 296–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellerin, L.; Pellegri, G.; Bittar, P.G.; Charnay, Y.; Bouras, C.; Martin, J.-L.; Stella, N.; Magistretti, P.J. Evidence Supporting the Existence of an Activity-Dependent Astrocyte-Neuron Lactate Shuttle. Dev Neurosci 1998, 20, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvat, A.; Zorec, R.; Vardjan, N. Lactate as an Astroglial Signal Augmenting Aerobic Glycolysis and Lipid Metabolism. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 735532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schousboe, A.; Scafidi, S.; Bak, L.K.; Waagepetersen, H.S.; McKenna, M.C. Glutamate Metabolism in the Brain Focusing on Astrocytes. In Glutamate and ATP at the Interface of Metabolism and Signaling in the Brain; Parpura, V., Schousboe, A., Verkhratsky, A., Eds.; Advances in Neurobiology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2014; ISBN 978-3-319-08893-8. [Google Scholar]
- Rabah, Y.; Francés, R.; Minatchy, J.; Guédon, L.; Desnous, C.; Plaçais, P.-Y.; Preat, T. Glycolysis-Derived Alanine from Glia Fuels Neuronal Mitochondria for Memory in Drosophila. Nat Metab 2023, 5, 2002–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schousboe, A.; Sonnewald, U.; Waagepetersen, H.S. Differential Roles of Alanine in GABAergic and Glutamatergic Neurons. Neurochemistry International 2003, 43, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Bachhawat, A.K. Pyroglutamic Acid: Throwing Light on a Lightly Studied Metabolite. Current Science 2012, 102, 288–297. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, N.J.; Wodschow, H.Z.; Nilsson, M.; Rungby, J. Effects of Ketone Bodies on Brain Metabolism and Function in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Rodríguez, D.; Giménez-Cassina, A. Ketone Bodies in the Brain Beyond Fuel Metabolism: From Excitability to Gene Expression and Cell Signaling. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 732120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buser, D.P.; Ritz, M.-F.; Moes, S.; Tostado, C.; Frank, S.; Spiess, M.; Mariani, L.; Jenö, P.; Boulay, J.-L.; Hutter, G. Quantitative Proteomics Reveals Reduction of Endocytic Machinery Components in Gliomas. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavel, M.; Renna, M.; Park, S.J.; Menzies, F.M.; Ricketts, T.; Füllgrabe, J.; Ashkenazi, A.; Frake, R.A.; Lombarte, A.C.; Bento, C.F.; et al. Contact Inhibition Controls Cell Survival and Proliferation via YAP/TAZ-Autophagy Axis. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
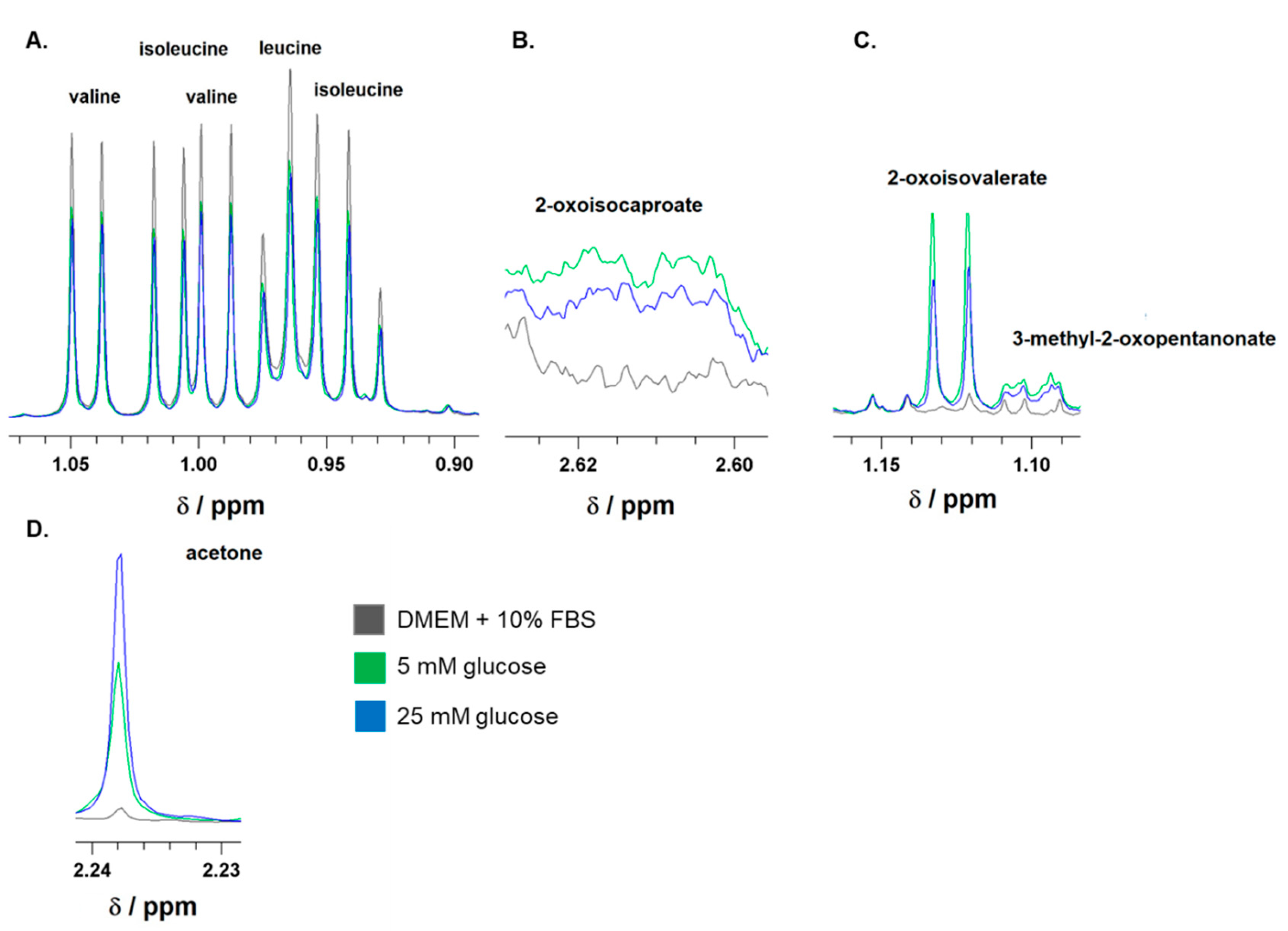
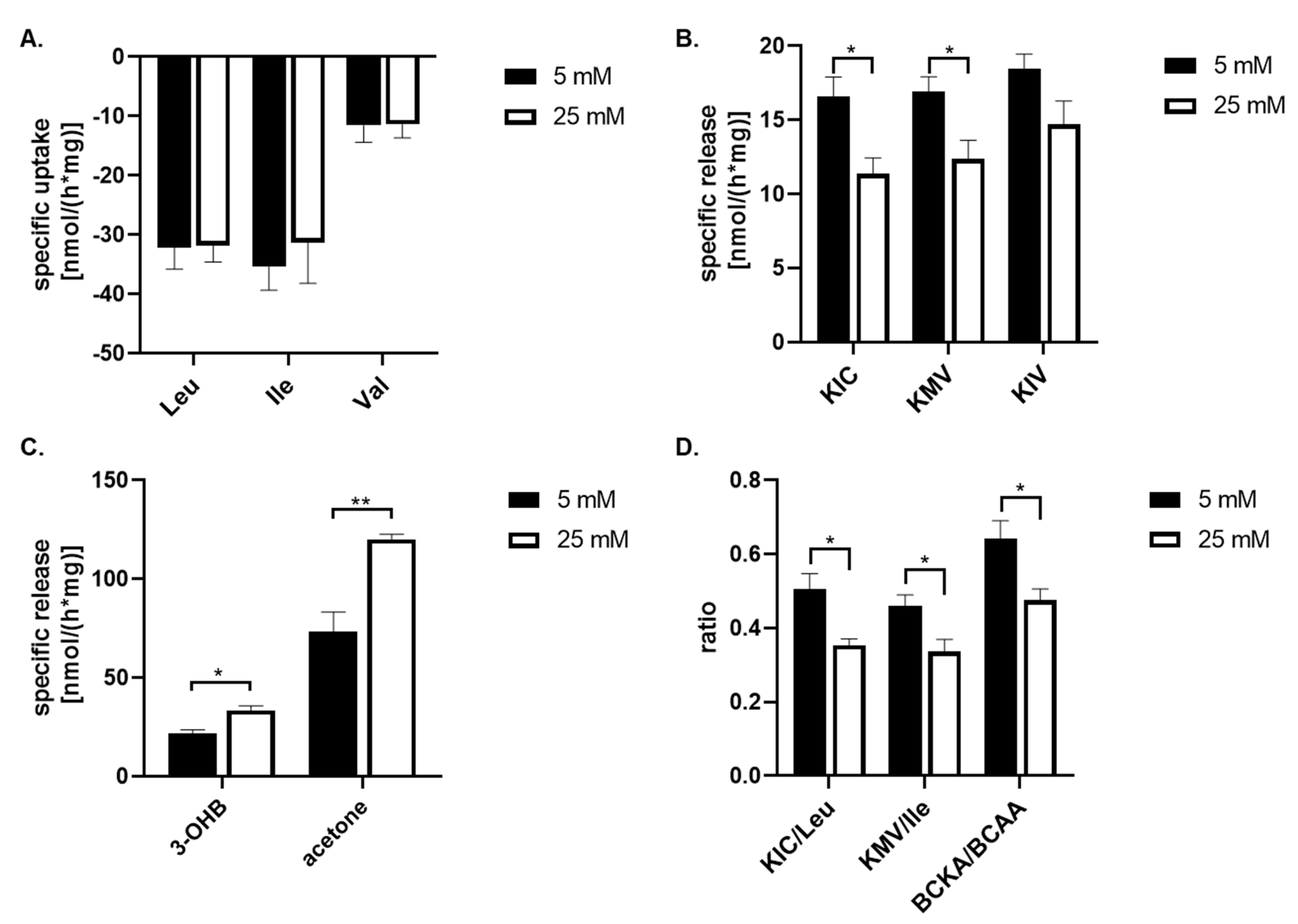
| Parameter (Unit) | Glucose | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 mM | 25 mM | ||
| Protein content (mg) | 0.11 ±0.03 | 0.09 ±0.03 | |
| Cell survival (%) | 70 ±5 | 67 ±6 | |
| as [LDH] (U/g) | 266 ±29 | 231 ±50 | |
| Concentration (µM) | Medium | Glucose | |
| 5 mM | 25 mM | ||
| lactate | 801 ±38 | 2195 ±176 ** | 1862 ±60 |
| pyruvate | 917 ±26 | 341 ±27 ** | 430 ±27 |
| citrate | 18.5 ±0.5 | 25 ±1 | 26 ±1 |
| acetate | 90 ±12 | 136 ±14 | 128 ±40 |
| acetone | 29 ±2 | 174 ±78 | 253 ±98 |
| 3-hydroxybutyrate | 0 | 56 ±2 | 62 ±5 |
| glutamine | 5045 ±180 | 3878 ±136 * | 3716 ±50 |
| leucine | 793 ±15 | 714 ±18 | 727 ±7 |
| α-ketoisocaproate | 22 ±4 | 61 ±5 ** | 45 ±3 |
| isoleucine | 751 ±19 | 663 ±24 | 674 ±12 |
| α-keto-methylvalerate | 14 ±2 | 53 ±4 *** | 39 ±2 |
| valine | 773 ±10 | 745 ±14 | 748 ±16 |
| α-ketoisovalerate | 7 ±1 | 48 ±4 ** | 35 ±2 |
| alanine | 148 ±2 | 206 ±6 ** | 190 ±3 |
| histidine | 464 ±8 | 467 ±12 | 465 ±11 |
| lysine | 867 ±40 | 1024 ±21 * | 980 ±68 |
| methionine | 209 ±3 | 222 ±5 ** | 210 ±2 |
| phenylalanine | 470 ±6 | 487 ±8 | 482 ±8 |
| threonine | 1016 ±34 | 1043 ±41 | 1014 ±41 |
| tryptophan | 21 ±1 | 23 ±2 | 23 ±1 |
| tyrosine | 367 ±6 | 381 ±7 * | 371 ±6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





