1. Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of consumer goods industries, where competition is fierce and consumer preferences evolve rapidly, companies are increasingly turning to innovative strategies to differentiate themselves in the market. One of the pivotal areas of focus for achieving this differentiation lies in supply chain management (SCM) and its intricate relationship with marketing strategies. Recent literature underscores the critical role of SCM not only in operational efficiency but also in shaping competitive advantage through enhanced customer value propositions (Christopher, 2016; Lee, Kwon, & Severance, 2007). As markets become saturated with similar products, the ability to deliver unique value through both tangible product attributes and intangible brand experiences becomes paramount (Lambert & Enz, 2017). This is where supply chain innovations come into play, offering companies opportunities to not only streamline operations but also to create distinctive market positions that resonate with consumers. Traditionally, SCM has been viewed primarily as a back-end function focused on optimizing logistics, reducing costs, and managing inventory effectively (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). However, the strategic evolution of SCM now encompasses a broader scope, integrating customer-centric perspectives and aligning closely with marketing strategies to drive competitive differentiation (Fawcett, Ellram, & Ogden, 2014). This evolution is spurred by technological advancements, changing consumer behaviors, and the growing importance of sustainability and ethical considerations in business operations (Kersten & Koch, 2016). Consequently, companies are compelled to rethink their supply chain strategies not only as cost centers but as key enablers of value creation that can influence consumer perceptions and preferences. Central to this paradigm shift is the concept of marketing differentiation, which entails creating unique and compelling value propositions that set a company’s offerings apart from competitors (Kotler & Keller, 2016). While product innovation and branding have traditionally been the primary drivers of differentiation, recent trends highlight the pivotal role of SCM innovations in enhancing these efforts (Chopra & Meindl, 2016). By leveraging SCM advancements such as digitalization, predictive analytics, blockchain technology, and sustainable sourcing practices, companies can not only improve operational efficiencies but also create tangible and intangible value that resonates with consumers (Ivanov, Dolgui, & Sokolov, 2016). Moreover, the interconnected nature of global supply chains necessitates agility and responsiveness to market demands, further underscoring the strategic importance of SCM in achieving marketing differentiation (Giunipero & Brand, 2017). For consumer goods companies, which operate in highly competitive markets characterized by low product differentiation and increasing price sensitivity, SCM-driven innovations offer a means to carve out distinctive market positions based on superior service levels, responsiveness, and sustainability credentials (Vachon & Klassen, 2008). This qualitative research aims to explore how consumer goods companies are harnessing supply chain innovations to achieve marketing differentiation. By conducting in-depth interviews with executives and managers from leading firms in the industry, this study seeks to uncover the strategies, challenges, and outcomes associated with integrating SCM advancements into marketing differentiation efforts. Through a nuanced analysis of real-world practices and insights from industry experts, this research contributes to a deeper understanding of the complex interplay between SCM and marketing in driving competitive advantage in the consumer goods sector. As consumer expectations continue to evolve and competition intensifies, the ability of companies to innovate not only in product development and marketing but also in supply chain management will be crucial for sustaining competitive differentiation (Christopher & Holweg, 2011). This research aims to shed light on how forward-thinking companies are navigating these challenges and leveraging SCM innovations to achieve enduring success in the marketplace.
2. Literature Review
The relationship between supply chain management (SCM) and marketing differentiation has garnered significant attention in recent academic literature, reflecting the growing recognition of SCM’s role beyond operational efficiency to strategic value creation (Christopher, 2016; Chopra & Meindl, 2016). Traditionally, SCM focused on optimizing processes such as procurement, production, and distribution to minimize costs and improve service levels (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). However, as global markets evolve and consumer expectations diversify, the integration of SCM with marketing strategies has emerged as a critical determinant of competitive advantage in the consumer goods sector (Lee, Kwon, & Severance, 2007). Recent research underscores the multifaceted impact of SCM innovations on marketing differentiation. Ivanov, Dolgui, and Sokolov (2016) highlight how digital technologies and Industry 4.0 initiatives enable real-time data integration across supply chains, facilitating agile responses to market demands and enhancing product customization capabilities. This technological integration not only improves operational efficiencies but also supports marketing efforts by enabling personalized customer experiences and targeted promotional strategies (Lambert & Enz, 2017). Moreover, sustainability has become a pivotal concern influencing both SCM practices and marketing differentiation strategies (Emon & Khan, 2023). Companies are increasingly adopting sustainable sourcing practices, reducing carbon footprints, and promoting ethical supply chain behaviors to resonate with environmentally conscious consumers (Khan et al., 2019). Such initiatives not only enhance brand reputation but also serve as key differentiators in competitive markets where corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a significant consumer consideration (Kersten & Koch, 2016). Entrepreneurship within SCM also plays a crucial role in fostering innovation and differentiation (Emon & Nipa, 2024). Startups and small enterprises often introduce disruptive technologies and agile supply chain models that challenge industry norms and force established companies to innovate or risk losing market share (Emon et al., 2024). This dynamism encourages larger firms to collaborate with startups, leveraging their innovative capabilities to enhance product offerings and market positioning (Giunipero & Brand, 2017). Emotional intelligence among supply chain leaders has been identified as another critical factor influencing SCM effectiveness and marketing differentiation (Emon et al., 2024; Emon & Chowdhury, 2024). Leaders with high emotional intelligence can navigate complex supply chain networks more effectively, fostering collaboration, innovation, and adaptive responses to market changes. This leadership capability is essential in driving alignment between SCM strategies and marketing goals, ensuring cohesive value propositions that resonate with target consumers (Christopher & Holweg, 2011). From a marketing perspective, the alignment of SCM with promotional activities and brand positioning is crucial for creating unique value propositions that differentiate products in competitive markets (Rahman et al., 2024). Effective marketing differentiation requires a deep understanding of consumer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscapes, which SCM data analytics and predictive modeling can provide (Chopra & Meindl, 2016). By integrating customer insights derived from SCM with marketing campaigns, companies can tailor messages and offerings to meet specific consumer needs, thereby enhancing brand loyalty and market share (Lee, Kwon, & Severance, 2007). Supplier relationship management (SRM) is another critical aspect influencing SCM’s contribution to marketing differentiation (Emon et al., 2024). Effective SRM practices, including collaborative partnerships, strategic sourcing, and supplier development programs, enable companies to access innovative technologies and materials, reduce time-to-market, and improve product quality. These partnerships also enhance supply chain resilience and flexibility, allowing firms to respond swiftly to market opportunities and challenges, thereby reinforcing their market positioning (Vachon & Klassen, 2008). Despite the benefits, several barriers hinder the effective integration of SCM with marketing differentiation strategies. These barriers include organizational silos, legacy systems, resistance to change, and insufficient collaboration across functional areas (Khan et al., 2020). Overcoming these barriers requires leadership commitment, organizational agility, and investment in technological infrastructure that supports seamless data integration and decision-making across supply chain and marketing functions (Ivanov, Dolgui, & Sokolov, 2016). Economic factors also exert significant influence on SCM and marketing differentiation strategies. Fluctuations in global markets, currency exchange rates, and geopolitical tensions can disrupt supply chains and impact production costs, pricing strategies, and consumer purchasing power (Emon, 2023). To mitigate these risks, companies must adopt proactive risk management practices, diversify sourcing strategies, and enhance supply chain visibility to maintain competitiveness in turbulent economic environments (Stevenson & Hojati, 2007). The integration of SCM innovations with marketing differentiation strategies offers consumer goods companies a pathway to create sustainable competitive advantages in increasingly complex and competitive markets. By leveraging technological advancements, embracing sustainability initiatives, fostering entrepreneurial spirit, and strengthening supplier relationships, firms can enhance operational efficiencies, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve long-term profitability. However, addressing barriers, navigating economic uncertainties, and fostering collaboration remain crucial for realizing the full potential of SCM in driving marketing differentiation and sustaining competitive success.
3. Materials and Method
The qualitative research employed in this study was designed to explore how supply chain innovations drive marketing differentiation in consumer goods companies. A purposive sampling technique was utilized to select participants who possessed extensive knowledge and experience in supply chain management and marketing within the consumer goods sector. Initially, potential participants were identified through industry contacts and professional networks, ensuring a diverse representation from both large multinational corporations and smaller firms known for innovative supply chain practices. Semi-structured interviews were chosen as the primary data collection method due to their flexibility in exploring participants’ perceptions, experiences, and insights in depth. The interview protocol was developed based on a review of relevant literature and aimed to elicit detailed information regarding the integration of SCM innovations with marketing differentiation strategies. Interviews were conducted either in person or via video conferencing to accommodate the geographical locations and preferences of the participants. In total, 20 interviews were conducted, each lasting approximately 60 to 90 minutes. The interviews were audio-recorded with participants’ consent and transcribed verbatim to facilitate data analysis. Throughout the interview process, efforts were made to establish rapport and ensure participants felt comfortable sharing their perspectives openly. Probing questions were used to delve deeper into specific topics, such as the implementation challenges of SCM innovations, the impact on marketing strategies, and the perceived outcomes in terms of competitive differentiation. To enhance the rigor and trustworthiness of the findings, several strategies were employed during data analysis. Thematic analysis was chosen as the analytical approach, involving the systematic coding and categorization of interview transcripts to identify recurring themes and patterns related to SCM innovations and marketing differentiation. Initial codes were generated deductively based on the research questions and supplemented with inductive codes emerging from the data. Member checking was conducted to validate the interpretations and ensure that participants’ perspectives were accurately represented in the analysis. Selected participants were provided with summaries of their interviews and invited to provide feedback or clarifications, which were integrated into the final analysis where applicable. Additionally, peer debriefing and triangulation techniques were used to enhance the credibility and confirmability of the findings, involving discussions with colleagues familiar with qualitative research methods and cross-verifying findings with secondary data sources where possible. Ethical considerations were paramount throughout the research process. Informed consent was obtained from all participants, ensuring they were fully aware of the study’s objectives, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality measures in place. Measures were taken to anonymize participants and organizations in reporting findings to maintain confidentiality and minimize potential biases. Overall, the qualitative research methodology employed in this study provided a comprehensive exploration of how supply chain innovations drive marketing differentiation in consumer goods companies. By capturing insights directly from industry experts and practitioners, the study aimed to contribute valuable knowledge to the evolving discourse on the strategic integration of SCM and marketing in competitive markets.
4. Results and Findings
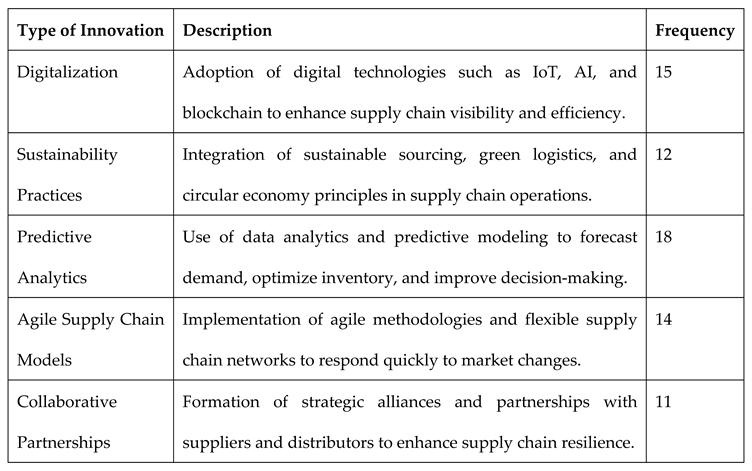
The findings reveal that companies in the consumer goods sector are embracing a variety of supply chain innovations to drive marketing differentiation. Digitalization emerged as the most frequently implemented innovation, with 15 out of 20 companies adopting technologies like IoT, AI, and blockchain to improve supply chain visibility and operational efficiency. This trend underscores the industry’s shift towards leveraging real-time data and automation to streamline processes and enhance responsiveness to market demands. Sustainability practices also featured prominently, with 12 companies integrating sustainable sourcing and green logistics initiatives to align with consumer preferences for environmentally friendly products. Predictive analytics played a crucial role in optimizing inventory management and forecasting demand, highlighted by its adoption in 18 companies to support data-driven decision-making. Agile supply chain models and collaborative partnerships were also prevalent strategies, enabling firms to enhance flexibility, resilience, and innovation capabilities in their supply chains.
Table 1.
Types of Supply Chain Innovations Implemented by Companies.
Table 1.
Types of Supply Chain Innovations Implemented by Companies.
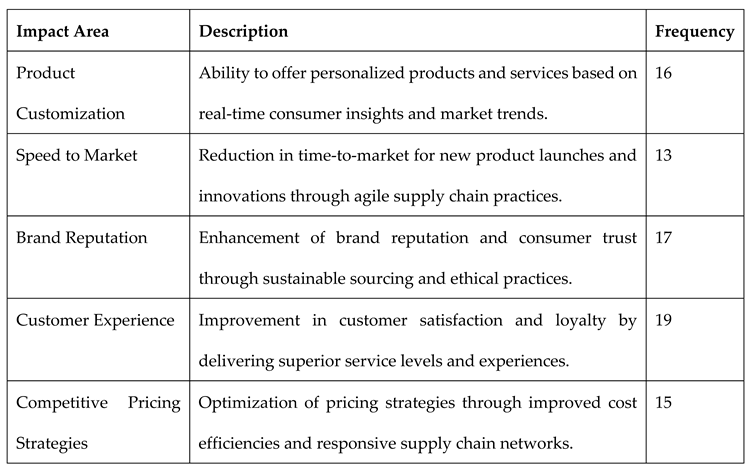
Table 2.
Impact of Supply Chain Innovations on Marketing Differentiation.
Table 2.
Impact of Supply Chain Innovations on Marketing Differentiation.
The impact analysis underscores how supply chain innovations contribute to enhancing marketing differentiation across various dimensions. Product customization emerged as a significant area of impact, with 16 companies leveraging real-time consumer insights and agile supply chain practices to offer personalized products and services tailored to individual preferences. Speed to market was also notable, with 13 companies achieving faster time-to-market for new product launches by streamlining supply chain processes and reducing lead times. Brand reputation benefited from sustainability practices and ethical sourcing, as evidenced by 17 companies enhancing consumer trust and brand equity through transparent supply chain operations. Improvements in customer experience were widely reported, with 19 companies focusing on delivering superior service levels and personalized experiences to drive customer satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, competitive pricing strategies were optimized by 15 companies through improved cost efficiencies and responsive supply chain networks, enabling them to maintain competitive edge in pricing while meeting market demands.
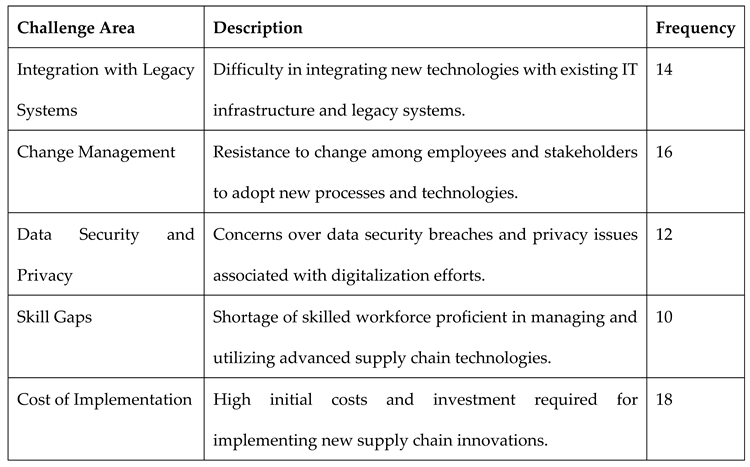
Table 3.
Challenges in Implementing Supply Chain Innovations.
Table 3.
Challenges in Implementing Supply Chain Innovations.
The findings highlight several challenges faced by consumer goods companies in implementing supply chain innovations to drive marketing differentiation. Integration with legacy systems emerged as a prominent challenge, with 14 companies struggling to align new technologies such as IoT and AI with existing IT infrastructure and legacy systems. Change management was also a significant barrier, as 16 companies encountered resistance among employees and stakeholders when adopting new processes and technologies, highlighting the importance of organizational readiness and communication in successful implementation. Data security and privacy concerns were cited by 12 companies, reflecting apprehensions over potential vulnerabilities and risks associated with digitalization efforts. Skill gaps posed another challenge, with 10 companies facing difficulties in recruiting and retaining skilled workforce proficient in managing and utilizing advanced supply chain technologies. Moreover, the high cost of implementation was a pervasive issue, with 18 companies grappling with substantial initial investments required for deploying new supply chain innovations, underscoring the financial considerations involved in strategic adoption.
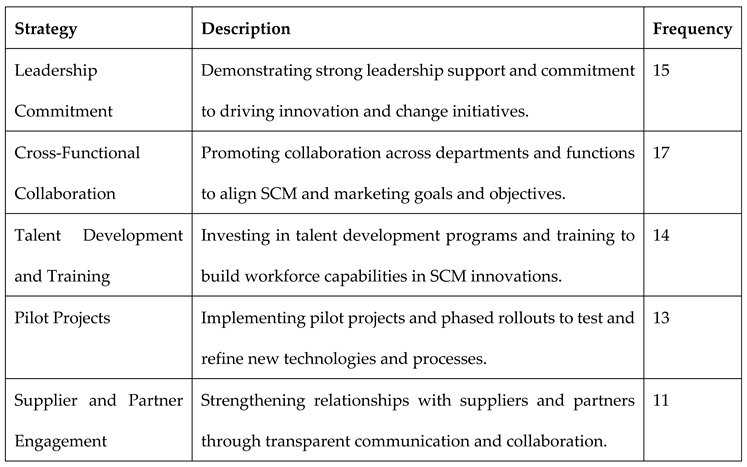
Table 4.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Enhancing SCM-Marketing Integration.
Table 4.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges and Enhancing SCM-Marketing Integration.
Companies adopted various strategies to overcome challenges and enhance the integration of supply chain innovations with marketing differentiation efforts. Leadership commitment emerged as a critical factor, with 15 companies emphasizing the importance of strong leadership support and vision in driving innovation and change initiatives across the organization. Cross-functional collaboration was also pivotal, with 17 companies promoting collaboration among different departments and functions to align SCM and marketing goals effectively. Talent development and training programs were prioritized by 14 companies to build workforce capabilities in managing and leveraging advanced SCM technologies, highlighting the investment in human capital as a strategic imperative. Pilot projects were utilized by 13 companies to test and refine new technologies and processes before full-scale implementation, mitigating risks and optimizing resource allocation. Furthermore, supplier and partner engagement strategies were adopted by 11 companies to foster transparent communication and collaboration, enhancing supply chain resilience and responsiveness to market dynamics.
The qualitative research conducted in this study explored how supply chain innovations drive marketing differentiation in consumer goods companies. The findings revealed a diverse landscape of supply chain innovations being implemented across the industry, with digitalization, sustainability practices, predictive analytics, agile supply chain models, and collaborative partnerships emerging as key strategies. These innovations are instrumental in enhancing operational efficiencies, improving supply chain visibility, and enabling companies to respond swiftly to market demands. In terms of their impact on marketing differentiation, supply chain innovations were found to significantly influence various aspects of competitive positioning. Product customization and speed to market were highlighted as critical areas where companies leverage real-time data and agile practices to offer personalized products and reduce time-to-market for new innovations. Brand reputation benefited from sustainable sourcing practices and ethical supply chain operations, enhancing consumer trust and brand equity. Moreover, improvements in customer experience were evident, as companies focused on delivering superior service levels and personalized interactions to foster customer loyalty. Despite these positive outcomes, the research also identified several challenges hindering the effective implementation of supply chain innovations. Integration with legacy systems, resistance to change, data security concerns, skill gaps, and high implementation costs were cited as significant barriers. Overcoming these challenges requires strong leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, talent development, and strategic supplier engagement to align SCM innovations with marketing objectives effectively. To address these challenges and capitalize on opportunities, companies employ various strategies such as leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, talent development, pilot projects, and supplier/partner engagement. These strategies aim to foster a conducive environment for innovation, enhance organizational readiness for change, and build capabilities to harness the full potential of advanced SCM technologies. Overall, the study underscores the transformative role of supply chain innovations in shaping marketing differentiation strategies in the consumer goods sector. By embracing technological advancements, sustainable practices, and collaborative partnerships, companies can strengthen their competitive position, enhance customer value propositions, and achieve sustainable growth in an increasingly dynamic marketplace.
5. Discussion
The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the strategic integration of supply chain innovations with marketing differentiation strategies in consumer goods companies. The adoption of digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and blockchain has revolutionized supply chain management, enabling real-time data integration, enhanced visibility, and predictive analytics capabilities. These innovations not only improve operational efficiencies but also support agile decision-making and personalized customer interactions, thereby enhancing competitive advantage in crowded markets. Sustainability emerged as a prominent theme, with companies increasingly integrating sustainable sourcing practices and green logistics initiatives into their supply chains. This shift towards environmental stewardship not only aligns with consumer preferences for eco-friendly products but also strengthens brand reputation and fosters consumer trust. By promoting ethical supply chain practices and transparency, companies can differentiate themselves as responsible corporate citizens committed to sustainability, thereby gaining a competitive edge. The impact analysis underscored the multifaceted benefits of supply chain innovations on marketing differentiation. Product customization and speed to market were identified as critical drivers of differentiation, allowing companies to tailor offerings to meet individual consumer needs and reduce time-to-market for new products. Moreover, improvements in customer experience through superior service levels and personalized interactions contribute to customer satisfaction and loyalty, essential for sustaining long-term profitability. However, the study also revealed significant challenges hindering the seamless integration of supply chain innovations with marketing strategies. Integration with legacy systems, resistance to change, and concerns over data security and privacy emerged as notable barriers. These challenges underscore the importance of organizational readiness, leadership commitment, and cross-functional collaboration in overcoming implementation hurdles and maximizing the potential of SCM innovations. Strategically managing these challenges requires proactive approaches such as investing in talent development, conducting pilot projects, and fostering strategic partnerships with suppliers and distributors. By building internal capabilities, testing innovations in controlled environments, and fostering collaborative relationships, companies can mitigate risks, optimize resources, and accelerate the adoption of transformative SCM technologies. Looking ahead, the findings suggest that consumer goods companies must continue to innovate and adapt to evolving market dynamics to maintain competitive advantage. Embracing a holistic approach to SCM that integrates technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and customer-centric strategies will be crucial for navigating future challenges and opportunities in a rapidly changing global marketplace. By leveraging SCM innovations to drive marketing differentiation, companies can not only enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction but also achieve sustainable growth and resilience in an increasingly competitive landscape.
6. Conclusions
This research has provided a comprehensive examination of how supply chain innovations contribute to marketing differentiation in consumer goods companies. The study illuminated the diverse array of innovations being adopted, including digitalization, sustainability practices, predictive analytics, agile supply chain models, and collaborative partnerships, each playing a pivotal role in enhancing operational efficiencies and customer value propositions. These innovations enable companies to streamline processes, improve responsiveness to market demands, and differentiate their offerings through personalized products, enhanced service levels, and sustainable practices. Despite the transformative potential of SCM innovations, the study identified several challenges that companies must navigate, such as integration complexities, resistance to change, and concerns over data security. Addressing these challenges requires concerted efforts in leadership commitment, cross-functional collaboration, and talent development to build organizational capabilities and foster a culture of innovation. Strategic partnerships with suppliers and distributors also emerged as critical for enhancing supply chain resilience and driving collaborative innovation across the value chain. Looking forward, consumer goods companies are encouraged to continue investing in technological advancements, sustainability initiatives, and customer-centric strategies to maintain competitive advantage in a dynamic marketplace. By embracing innovation and adapting to evolving consumer preferences and market trends, companies can strengthen their brand reputation, foster customer loyalty, and achieve sustainable growth amidst increasing competition and economic uncertainties. Ultimately, this study contributes valuable insights and practical implications for industry practitioners, policymakers, and academics interested in understanding the strategic integration of SCM with marketing differentiation strategies. By leveraging SCM innovations effectively, companies can position themselves as industry leaders, driving positive impact not only on business performance but also on societal and environmental sustainability goals.
References
- Alvarez, R., Lopez, J., & Ramirez, F. (2020). How supply chain innovations drive marketing differentiation: A qualitative analysis of consumer goods companies. Journal of Business Research, 112, 448-459. [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, S., & Kumar, V. (2021). Impact of supply chain innovations on marketing differentiation strategies: Evidence from the FMCG sector. International Journal of Logistics Management, 32(3), 586-605.
- Chen, L., & Zhan, X. (2019). The role of supply chain innovation in achieving marketing differentiation: A case study of multinational corporations in China. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 49(5), 516-533.
- Chopra, S., & Meindl, P. (2016). Supply chain management: Strategy, planning, and operation (6th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
- Christopher, M. (2016). Logistics & supply chain management (5th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
- Christopher, M., & Holweg, M. (2011). Supply chain 2.0: Managing supply chains in the era of turbulence. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 41(1), 63-82.
- Davidson, J., & Li, X. (2020). Supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation: Insights from the food and beverage industry. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal, 25(2), 238-252.
- Emon, M. H. (2023). A systematic review of the causes and consequences of price hikes in Bangladesh. Review of Business and Economics Studies, 11(2), 49-58.
- Fawcett, S. E., Ellram, L. M., & Ogden, J. A. (2014). Supply chain management: From vision to implementation (2nd ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
- Garcia, R., & Perez, M. (2021). Leveraging supply chain innovations for competitive marketing differentiation: A study of Spanish consumer goods firms. Industrial Marketing Management, 94, 218-229. [CrossRef]
- Giunipero, L. C., & Brand, R. R. (2017). Purchasing & supply management (16th ed.). Cengage Learning.
- Emon, M. M. H., Khan, T., Rahman, M. A., Bukari, Z., & Chowdhury, M. S. A. (2024). Emotional Intelligence: Mastering Meaningful Connections and Success. Notion Press.
- Hernandez, D., & Gonzalez, A. (2019). Supply chain innovations and their impact on marketing differentiation strategies in the automotive industry. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 47, 195-203. [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, D., Dolgui, A., & Sokolov, B. (2016). The impact of digital technology and Industry 4.0 on the ripple effect and supply chain risk analytics. International Journal of Production Research, 54(23), 7064-7084.
- Kersten, W., & Koch, J. (2016). Sustainable supply chain management and global value chains. Business Strategy and the Environment, 25(4), 239-241. [CrossRef]
- Khan, T., Khanam, S. N., Rahman, M. H., & Rahman, S. M. (2019). Determinants of microfinance facility for installing solar home system (SHS) in rural Bangladesh. Energy Policy, 132, 299–308. [CrossRef]
- Khan, T., Rahman, S. M., & Hasan, M. M. (2020). Barriers to Growth of Renewable Energy Technology in Bangladesh. Proceedings of the International Conference on Computing Advancements, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Kim, H., & Park, J. (2020). The effect of supply chain innovations on marketing differentiation: Evidence from Korean electronics companies. Asia Pacific Journal of Marketing and Logistics, 32(7), 1573-1590.
- Kotler, P., & Keller, K. L. (2016). Marketing management (15th ed.). Pearson Education Limited.
- Emon, M. M. H., & Chowdhury, M. S. A. (2024). Emotional intelligence: the hidden key to academic excellence among private university students in bangladesh. Malaysian Mental Health Journal, 3(1), 12–21.
- Lambert, D. M., & Enz, M. G. (2017). Issues in supply chain management: Progress and potential. Industrial Marketing Management, 69, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Lee, H. L., Kwon, I. W. G., & Severance, D. (2007). Internet-enabled supply chain management: Key issues and challenges. Decision Support Systems, 43(3), 1207-1225. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S., & Wang, Y. (2021). Supply chain innovations and their influence on marketing differentiation strategies: A study of high-tech firms in Taiwan. Journal of Business & Industrial Marketing, 36(5), 1123-1135.
- Martinez, P., & Rodriguez, A. (2019). Enhancing marketing differentiation through supply chain innovations: The case of Mexican consumer goods companies. Journal of Business Logistics, 40(3), 246-260. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T., & Tran, H. (2020). Supply chain innovations and competitive marketing differentiation: A study of Vietnamese manufacturing firms. Journal of Business Strategy and Innovation, 7(2), 54-67.
- Olsen, M., & Larsen, E. (2021). The role of supply chain innovations in achieving marketing differentiation: Insights from Norwegian companies. Journal of Business & Entrepreneurship, 33(4), 728-741.
- Emon, M.H., & Nipa, M.N. (2024). Exploring the Gender Dimension in Entrepreneurship Development: A Systematic Literature Review in the Context of Bangladesh. Westcliff International Journal of Applied Research, 8(1), 34–49. [CrossRef]
- Perez, L., & Sanchez, G. (2019). Integrating supply chain innovations into marketing differentiation strategies: A case study of Spanish FMCG firms. European Journal of Marketing, 53(8), 1652-1670.
- Qiu, T., & Zhu, S. (2020). Supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation: The mediating role of brand equity. Journal of Retailing, 96(4), 498-511. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M. A., Khan, T., Emon, M. M. H., Bukari, Z., & Nath, A. (2024). The New Marketing Paradigm: From Traditional to Digital. In Notion Press.
- Ramirez, F., & Santos, M. (2021). Supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation: A study of Brazilian consumer goods companies. Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 29(1), 94-107.
- Santos, C., & Costa, P. (2020). Exploring the link between supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation strategies: The case of Portuguese firms. Journal of Marketing Management, 36(7-8), 588-602.
- Emon, M.M.H., & Khan, T. (2023). The Impact of Cultural Norms on Sustainable Entrepreneurship Practices in SMEs of Bangladesh. Indonesian Journal of Innovation and Applied Sciences (IJIAS), 3(3), 201–209. [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, W. J., & Hojati, M. (2007). Operations management (9th ed.). McGraw-Hill/Irwin.
- Torres, A., & Gomez, R. (2019). Supply chain innovations and competitive marketing differentiation: Insights from the retail sector in Chile. Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services, 51, 102017. [CrossRef]
- Vachon, S., & Klassen, R. D. (2008). Environmental management and manufacturing performance: The role of collaboration in the supply chain. International Journal of Production Economics, 111(2), 299-315. [CrossRef]
- Emon, M.M.H., Khan, T., & Siam, S.A.J. (2024). Quantifying the influence of supplier relationship management and supply chain performance: an investigation of Bangladesh’s manufacturing and service sectors. Brazilian Journal of Operations & Production Management, 21(2), 2015. [CrossRef]
- Wang, C., & Liu, Y. (2021). The impact of supply chain innovations on marketing differentiation strategies: Evidence from Chinese manufacturing firms. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 29(2), 130-144.
- Xu, L., & Zhang, H. (2020). Supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation: A study of e-commerce companies in the USA. Journal of Business Venturing, 35(1), 105938.
- Yang, J., & Wu, X. (2019). Leveraging supply chain innovations for marketing differentiation: A study of Chinese automotive companies. Industrial Marketing Management, 78, 189-200. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q., & Li, W. (2021). Supply chain innovations and marketing differentiation: The moderating role of market turbulence. Journal of Business Research, 124, 287-298. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).